Application Value of a Novel Micro-Coil in High-Resolution Imaging of Experimental Mice Based on 3.0 T Clinical MR
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
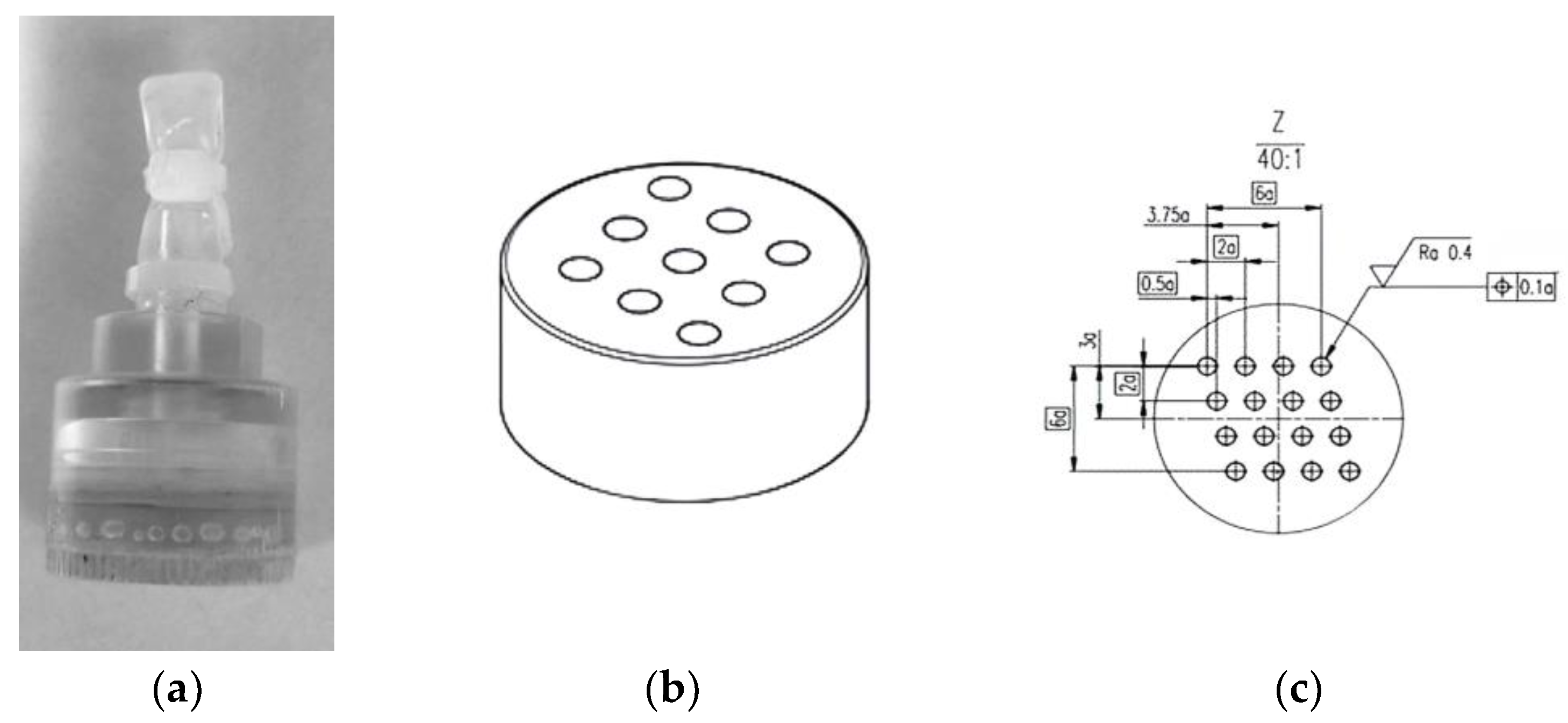
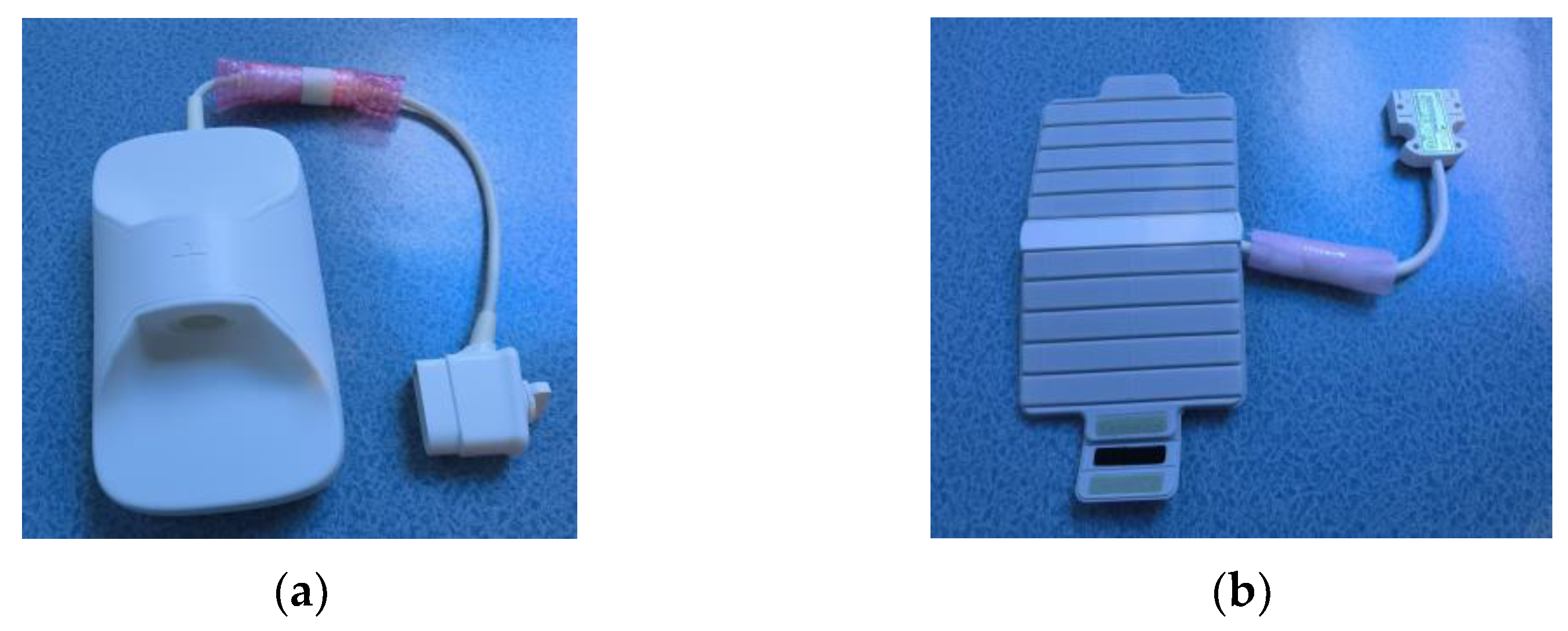
2.1. Materials
2.2. Magnetic Resonance Scanning Method and Parameter Settings
2.3. Subjective Evaluation of Images
2.4. Objective Evaluation of the Images
2.5. Statistical Methods
3. Results
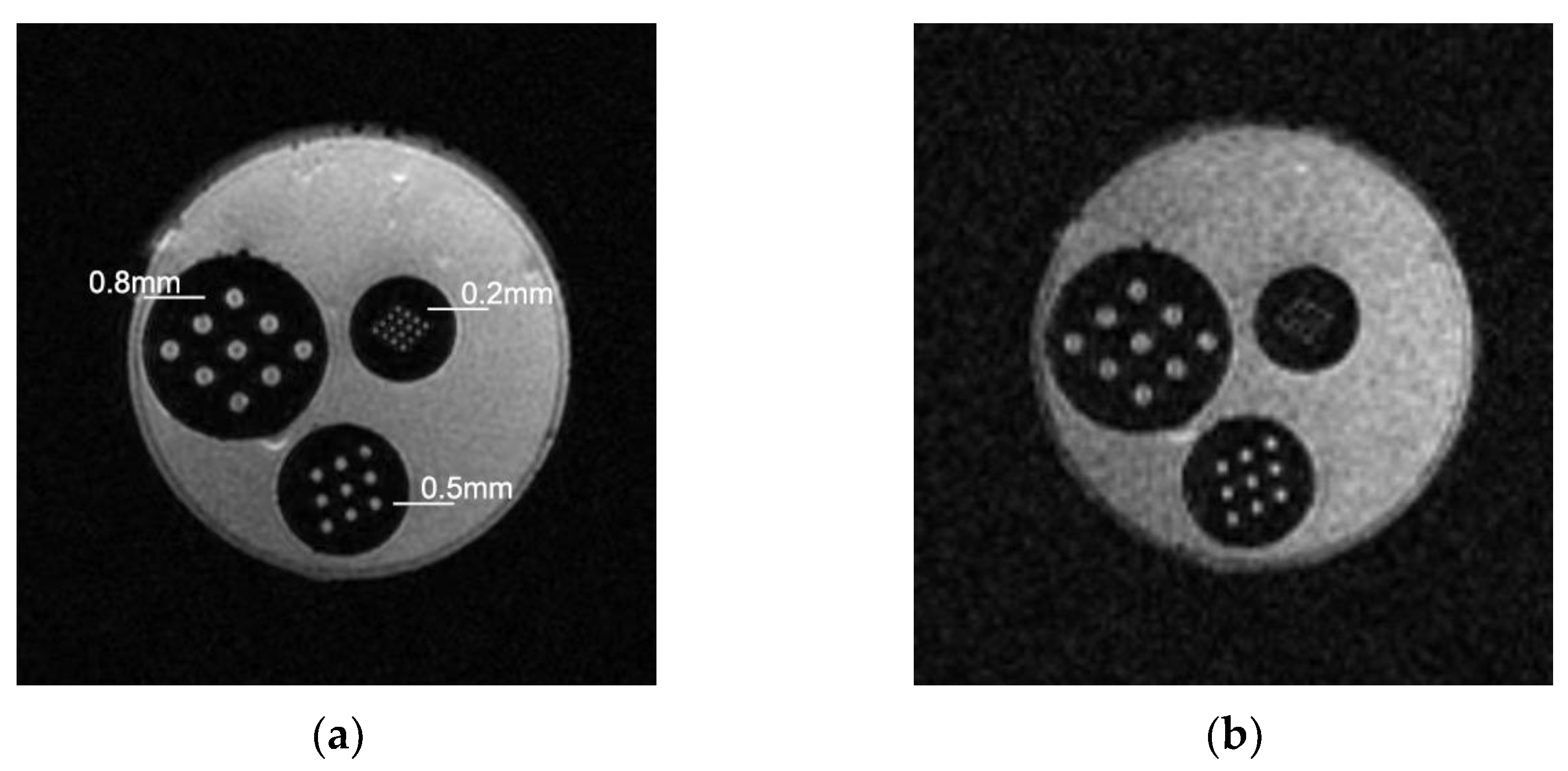
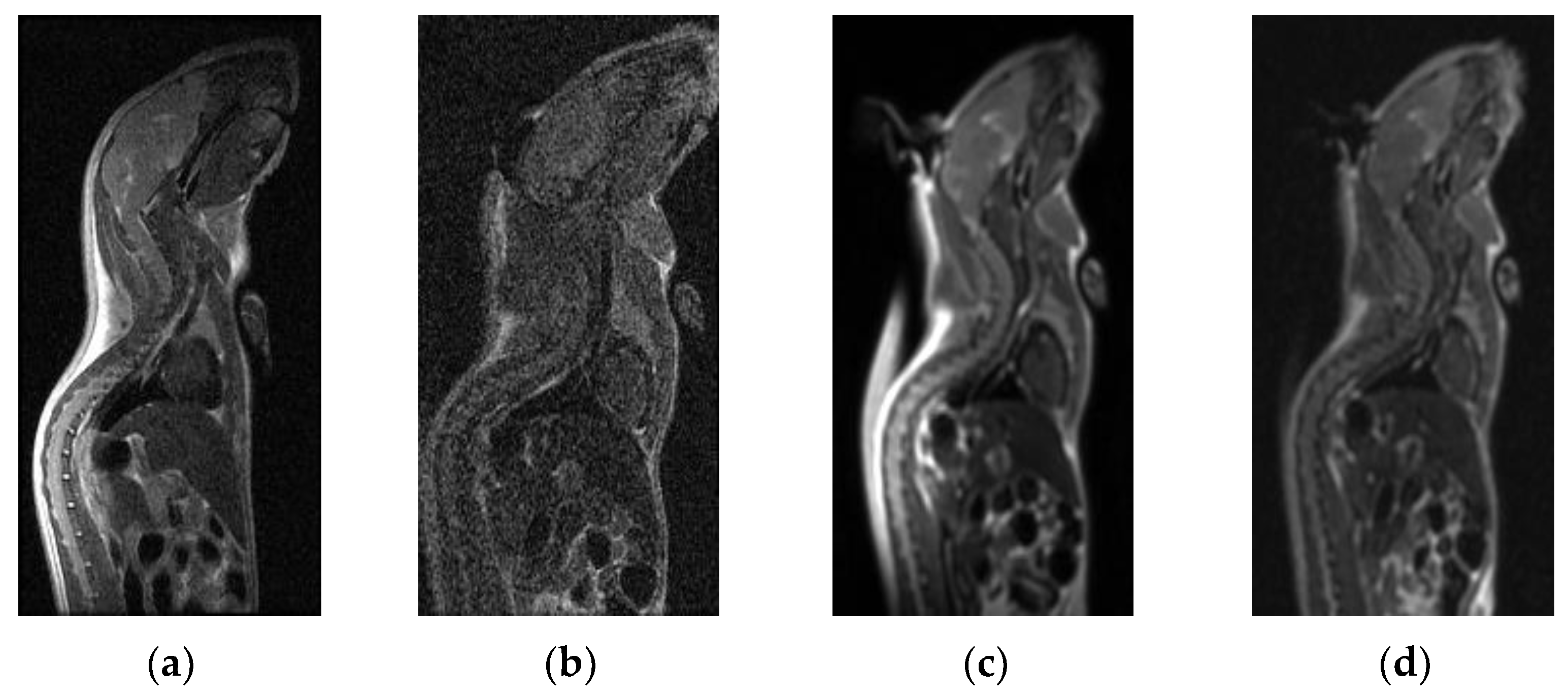
3.1. Maximum Spatial Resolution
3.2. Subjective Ratings of Two Types of Coils’ Scanning Images
3.3. SNR and CNR Values of Two Types of Coils’ Scanning Images
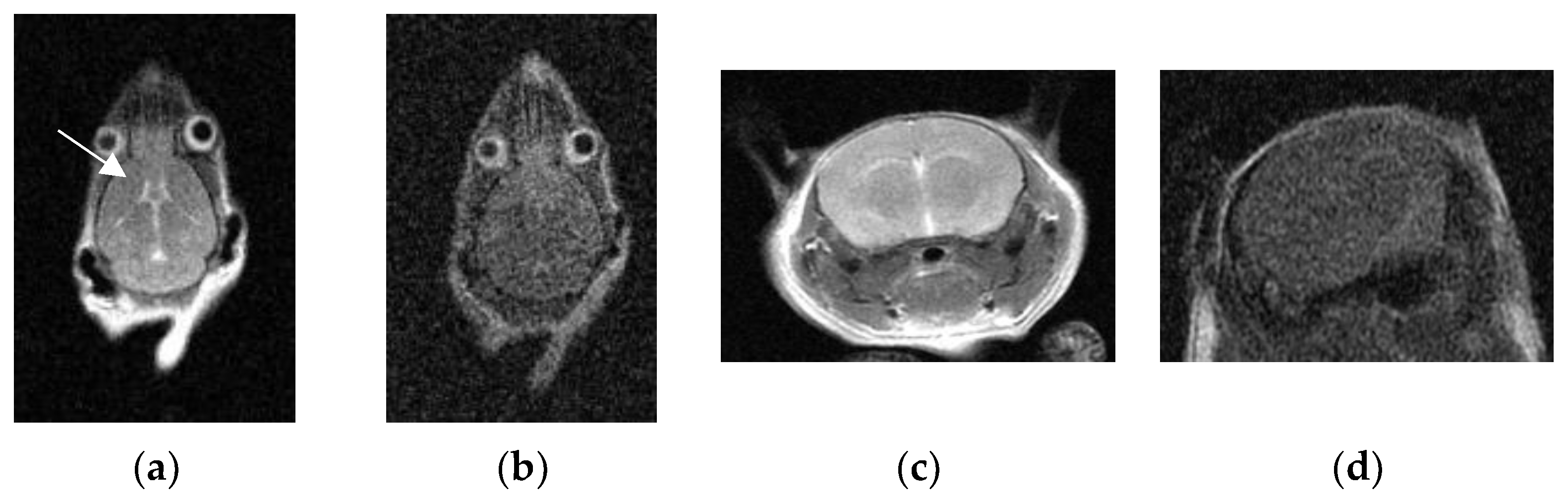
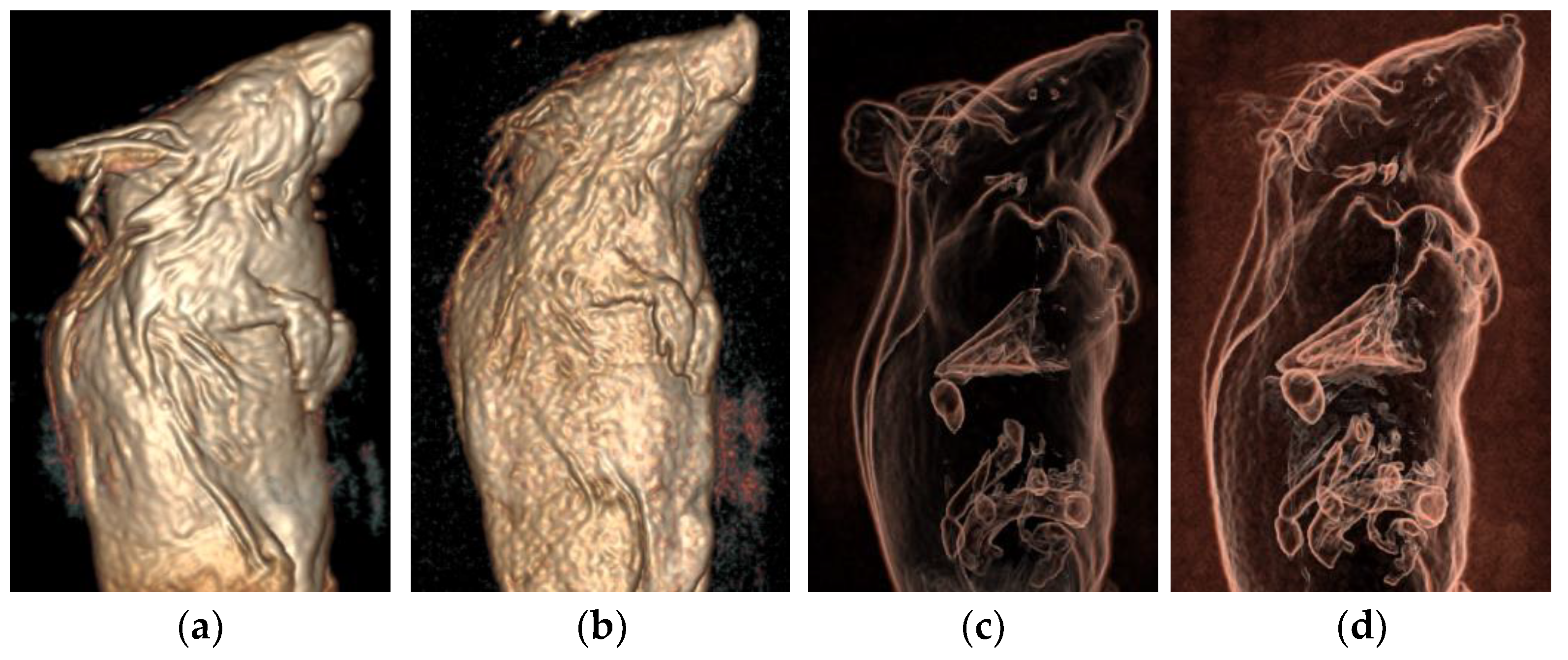
3.4. VR Three-Dimensional Images
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brockhurst, J.K.; Villano, J.S. The role of animal research in pandemic responses. Comp. Med. 2021, 71, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shochet, L.; Kitching, A.R. Animal models of vasculitis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2022, 34, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xu, T.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Wu, D. Hypertriglyceridemia acute pancreatitis: Animal experiment research. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2022, 67, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boerma, M.; Sridharan, V.; Krager, K.J.; Pawar, S.A. Small animal models of localized heart irradiation. Methods Cell Biol. 2022, 168, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Diianni, T.; Morrison, K.P.; Yu, B.; Murphy, K.R.; de Lecea, L.; Airan, R.D. High-throughput ultrasound neuromodulation in awake and freely behaving rats. Brain Stimul. 2023, 16, 1743–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyodo, F.; Eto, H.; Naganuma, T.; Koyasu, N.; Elhelaly, A.E.; Noda, Y.; Kato, H.; Murata, M.; Akahoshi, T.; Hashizume, M.; et al. In vivo dynamic nuclear polarization magnetic resonance imaging for the evaluation of redox-related diseases and theranostics. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2022, 36, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Niu, Q.; Gao, C.; Du, F. Celecoxib treatment alleviates cerebral injury in a rat model of post-traumatic epilepsy. PeerJ 2023, 11, e16555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Nie, B.; An, L.; Wan, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Cai, G.; Wu, S. Progress in magnetic resonance imaging of autism model mice brain. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Cogn. Sci. 2022, 13, e1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, C.; Li, Y.; Deng, H.; Luo, X.; Xiao, R.; Zhang, C.; Yang, H. Asymmetry of brain development in adolescent rats studied by 3.0 T magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroreport 2023, 34, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rad, A.M.; Gao, X.; Deeb, D.; Gautam, S.C.; Arbab, A.S. Imaging Mouse Prostate Gland by 3 Tesla Clinical MRI System. Open Magn. Reson. Rev. 2008, 1, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehl, O.C.; Foster, P.J. The sensitivity of magnetic particle imaging and fluorine-19 magnetic resonance imaging for cell tracking. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ypsilantis, P.; Souftas, V.; Vyza, V.; Vraila, M.; Chatzaki, M.; Ypsilantou, I.; Pitiakoudis, M. Magnetic resonance imaging for early pregnancy diagnosis in the laboratory rat. Lab. Anim. 2021, 55, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, D.R.; Dittmar, M.S.; Baldaranov, D.; Heidemann, R.M.; Henning, E.C.; Schuierer, G.; Bogdahn, U.; Schlachetzki, F. Cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats—A 3 T MRI study on biphasic blood-brain barrier opening and the dynamics of edema formation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2009, 29, 1846–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.G.; Huang, B.T.; Huang, L.; Zhang, X.; He, P.P.; Chen, J.B. Prediction of extracapsular extension in prostate cancer using the Likert scale combined with clinical and pathological parameters. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1229552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AAsfuroğlu, U.; Asfuroğlu, B.B.; Özer, H.; Gönül, İ.I.; Tokgöz, N.; İnan, M.A.; Uçar, M. Which one is better for predicting extraprostatic extension on multiparametric MRI: ESUR score, Likert scale, tumor contact length, or EPE grade? Eur. J. Radiol. 2022, 149, 110228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khairi, M.; Zakaria, F.; Supar, R.; Mohd, Z. Comparison study of the MRI shoulder PROPELLER technique with differential image quality by variation of shoulder coils. Med. J. Malays. 2024, 79 (Suppl. 1), 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Ohno, N.; Miyati, T.; Oyabu, H.; Gabata, T.; Kobayashi, S. Combined maximum b-value and echo time: A practical method for determining the signal-to-noise ratio for magnetic resonance images. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2022, 23, e13497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullrich, T.; Kohli, M.D.; Ohliger, M.A.; Magudia, K.; Arora, S.S.; Barrett, T.; Bittencourt, L.K.; Margolis, D.J.; Schimmöller, L.; Turkbey, B.; et al. Quality Comparison of 3 Tesla multiparametric MRI of the prostate using a flexible surface receiver coil versus conventional surface coil plus endorectal coil setup. Abdom. Radiol. 2020, 45, 4260–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collick, B.D.; Behzadnezhad, B.; Hurley, S.A.; Mathew, N.K.; Behdad, N.; Lindsay, S.A.; Robb, F.; Stormont, R.S.; McMillan, A.B. Rapid development of application-specific flexible MRI receive coils. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 19NT01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohoe, D.L.; Dennert, K.; Kumar, R.; Freudinger, B.P.; Sherman, A.J. Design and 3D-printing of MRI-compatible cradle for imaging mouse tumors. 3D Print. Med. 2021, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Jiang, R.; Zou, C.; Tie, C.; Wen, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Zheng, H. A flexible 9-channel coil array for fast 3D MR thermometry in MR-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) studies on rabbits at 3T. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 65, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockmann, M.A.; Kemmling, A.; Groden, C. Current issues and perspectives in small rodent magnetic resonance imaging using clinical MRI scanners. Methods 2007, 43, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abel, F.; Tan, E.T.; Lunenburg, M.; van Leeuwen, C.; van Hooren, T.; van Uden, M.; Arteaga, C.; Vincent, J.; Robb, F.; Sneag, D.B. Flexible array coil for cervical and extraspinal (FACE) MRI at 3.0 Tesla. Phys. Med. Biol. 2023, 68, 215011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, D.R.; Heidemann, R.M.; Kumar, P.; Shanbhag, N.; Lanz, T.; Dittmar, M.S.; Sandner, B.; Beier, C.P.; Weidner, N.; Greenlee, M.W.; et al. Comprehensive small animal imaging strategies on a clinical 3 T dedicated head MR-scanner; adapted methods and sequence protocols in CNS pathologies. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Y.; Wilson, C.B.; Tycko, R. Enhanced spatial resolution in magnetic resonance imaging by dynamic nuclear polarization at 5 K. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2201644119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, B.; Luo, N.; Bian, J. Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-Weighted Imaging for Evaluation of the Cell Density and Angiogenesis of Cirrhosis-Related Nodules in an Experimental Rat Model: Comparison and Correlation With Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 51, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepelytskyi, Y.; Li, T.; Grynko, V.; Newman, C.; Hane, F.T.; Albert, M.S. Evaluation of fluorine-19 magnetic resonance imaging of the lungs using octafluorocyclobutane in a rat model. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 85, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wu, T.; Zang, X.; Li, M.; Li, J. 3D Cube FLAIR plus HyperSense compressed sensing is superior to 2D T2WI FLAIR scanning regarding image quality, spatial resolution, detection rate for cortical microinfarcts. Medicine 2022, 101, e28659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Shan, C.; Lan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, X.; Ji, H.; Li, M.; Cong, M. Combined high-resolution 3D CUBE T1-weighted imaging and non-contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance venography for evaluation of vein stenosis in May-Thurner syndrome. Phlebology 2022, 37, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.M.; Pan, S.N.; Wang, E.B.; Zheng, L.Q.; Guo, W.L.; Fu, X.H. Magnetic Resonance Three-dimensional Cube Technique in the Measurement of Piglet Femoral Anteversion. Chin. Med. J. 2016, 129, 1584–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Liu, Z.J.; Xu, J.B.; Li, F.Q.; Li, W.L.; Cao, W.T.; Zhou, Z.Y. Baseline and early 3D-CUBE volume reconstruction of locally advanced rectal cancer to predict tumor response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J. X-ray Sci. Technol. 2020, 28, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Wang, Q.; Peng, C.; Luo, B.; Zhang, J. Combined application of isotropic three-dimensional fast spin echo (3D-FSE-Cube) with 2-point Dixon fat/water separation (FLEX) and 3D-FSE-cube in MR dacryocystography. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20180157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter Category | 2D-FSE T2WI | 3D-CUBE |
|---|---|---|
| Repeat Time (ms) | 2500 | 2500 |
| Echo Time (ms) | 80 | 90 |
| Slice Thickness (mm) | 0.9 | 0.4 |
| Matrix | 256 × 256 | 192 × 192 |
| Field of View (mm) | 50 × 50 | 80 × 80 |
| Number of Excitation | 4 | 1 |
| Scanning Time (min:s) | 3:43 | 5:06 |
| Novel Micro-Coil | Flexible Coil | Z Value | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2D-FSE T2WI tra brain | 4.29 ± 0.45 | 2.63 ± 0.48 | −3.095 | 0.002 |
| 2D-FSE T2WI cor brain | 4.29 ± 0.45 | 2.63 ± 0.48 | −3.095 | 0.002 |
| 2D-FSE T2WI sag body | 4.75 ± 0.45 | 2.92 ± 0.29 | −3.169 | 0.002 |
| The 3D-CUBE sag body | 4.46 ± 0.50 | 3.17 ± 0.39 | −2.859 | 0.004 |
| VR 3D images body | 4.17 ± 0.39 | 3.08 ± 0.29 | −3.127 | 0.002 |
| Sequence and Location | Novel Micro-Coil | Flexible Coil | T Value | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNR | 2D-FSE T2WI tra brain | 18.92 ± 1.14 | 7.24 ± 0.57 | 27.868 | <0.001 |
| 2D-FSE T2WI cor brain | 21.52 ± 1.59 | 7.90 ± 0.83 | 24.448 | <0.001 | |
| 2D-FSE T2WI Sag spinal cord | 35.87 ± 2.35 | 6.23 ± 0.57 | 42.564 | <0.001 | |
| 2D-FSE T2WI Sag liver | 8.61 ± 0.60 | 6.09 ± 0.65 | 9.604 | <0.001 | |
| 3D-CUBE Sag spinal cord | 272.55 ± 55.86 | 50.75 ± 6.37 | 14.117 | <0.001 | |
| 3D-CUBE Sag liver | 49.92 ± 9.89 | 22.92 ± 2.69 | 9.548 | <0.001 | |
| CNR | 2D-FSE T2WI tra brain | 16.61 ± 1.08 | 4.92 ± 0.45 | 31.355 | <0.001 |
| 2D-FSE T2WI cor brain | 19.51 ± 1.48 | 5.62 ± 0.63 | 28.814 | <0.001 | |
| 2D-FSE T2WI Sag spinal cord | 33.86 ± 2.23 | 3.96 ± 0.37 | 47.281 | <0.001 | |
| 2D-FSE T2WI Sag liver | 6.60 ± 0.50 | 3.82 ± 0.45 | 14.525 | <0.001 | |
| 3D-CUBE Sag spinal cord | 270.55 ± 55.67 | 48.71 ± 6.03 | 14.143 | <0.001 | |
| 3D-CUBE Sag liver | 47.92 ± 9.68 | 20.88 ± 2.39 | 9.769 | <0.001 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, X.; Liu, Y.; Lv, F. Application Value of a Novel Micro-Coil in High-Resolution Imaging of Experimental Mice Based on 3.0 T Clinical MR. Tomography 2024, 10, 839-847. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10060064
Qiu X, Liu Y, Lv F. Application Value of a Novel Micro-Coil in High-Resolution Imaging of Experimental Mice Based on 3.0 T Clinical MR. Tomography. 2024; 10(6):839-847. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10060064
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Xueke, Yang Liu, and Fajin Lv. 2024. "Application Value of a Novel Micro-Coil in High-Resolution Imaging of Experimental Mice Based on 3.0 T Clinical MR" Tomography 10, no. 6: 839-847. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10060064
APA StyleQiu, X., Liu, Y., & Lv, F. (2024). Application Value of a Novel Micro-Coil in High-Resolution Imaging of Experimental Mice Based on 3.0 T Clinical MR. Tomography, 10(6), 839-847. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10060064





