Optimizing CT Abdomen–Pelvis Scan Radiation Dose: Examining the Role of Body Metrics (Waist Circumference, Hip Circumference, Abdominal Fat, and Body Mass Index) in Dose Efficiency
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Gaps in Current Research and Knowledge
1.2. Study Aim and Objectives
1.3. The Relevance and Significance of this Study
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Collection
2.2. CT Machine
2.3. Scan Protocol
2.4. Body Measurements (BMI, AC, HC, WC, APD, LD, and AF)
2.5. Radiation Dose (CTDIvol, DLP, and SSDE)
2.6. Data Analysis and Machine Learning
2.7. Ethical Approval
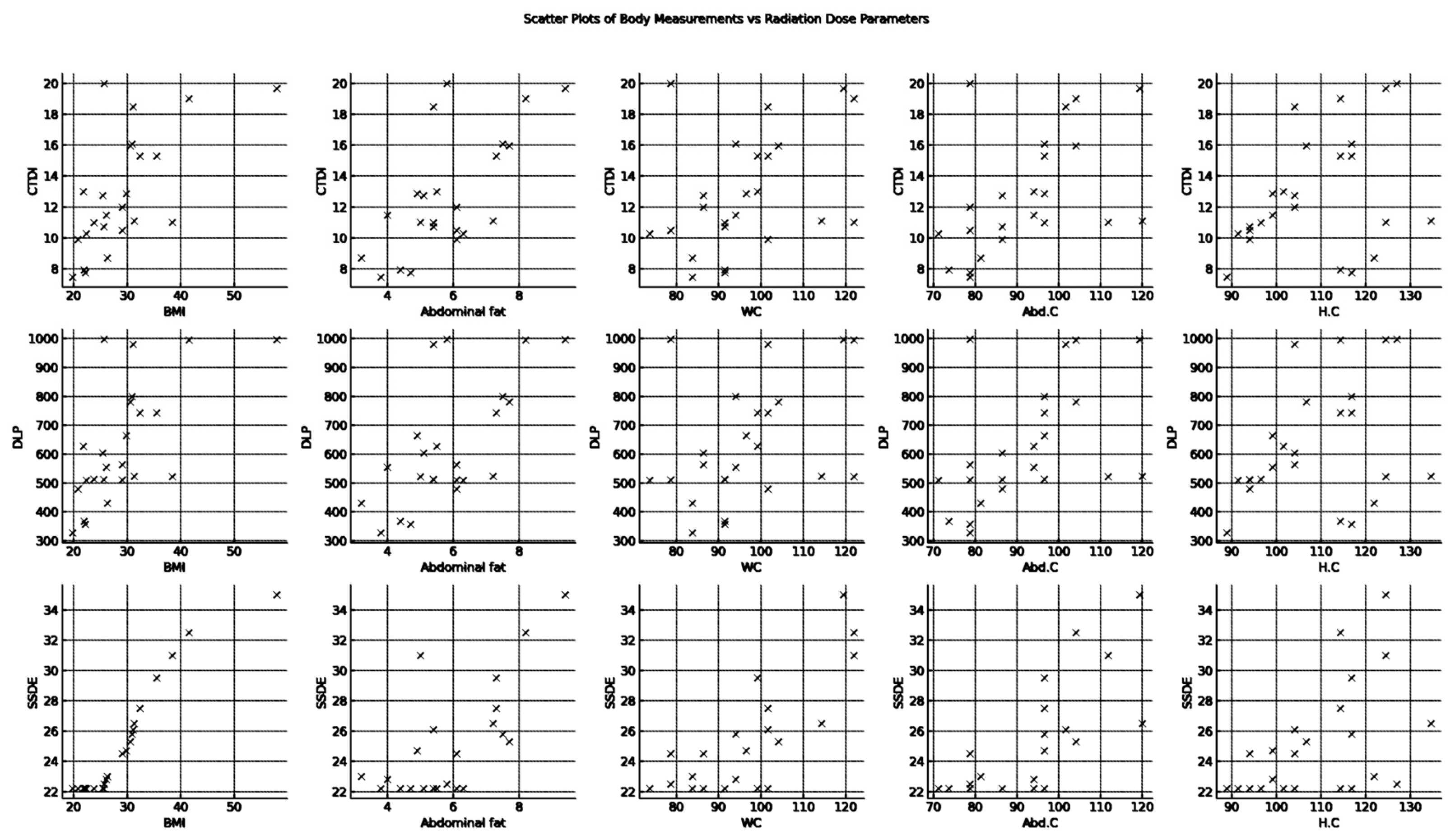
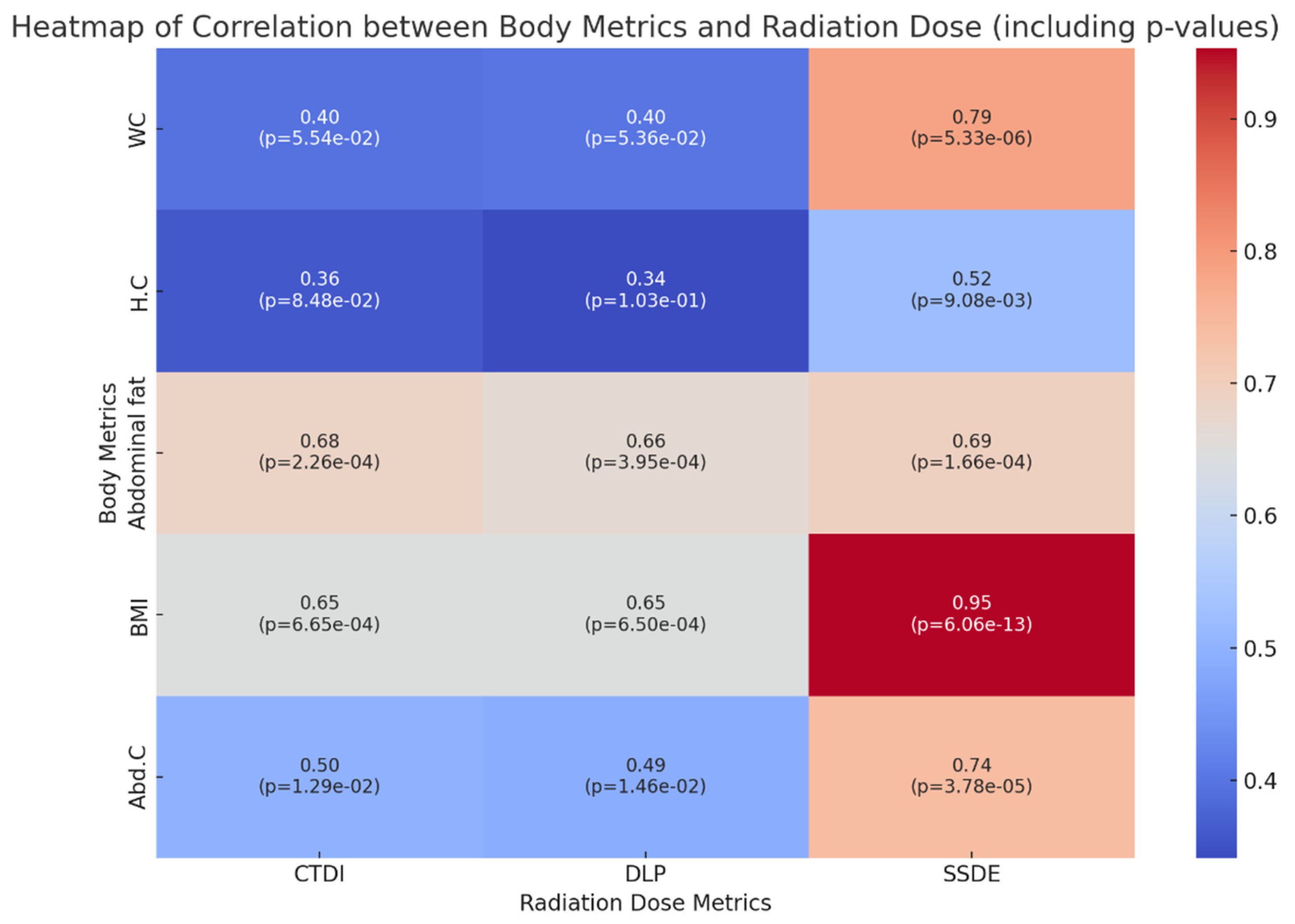
3. Results
Descriptive Analysis
- –
- CTDIvol (mGy): The average CTDIvol is approximately 12.8, with a standard deviation (SD) of 3.8, indicating some variability in the dose index across the sample. The values range from a minimum of 7.45 to a maximum of 20.
- –
- DLP (mGy-cm): The DLP has an average of 629.2, with a higher SD of 207.4, suggesting a wider spread of values. The DLP spans from 327 to 998.
- –
- SSDE (mGy): The SSDE has a mean value of 25.04 and an SD of 3.67. Its values range from 22.2 to 35, showing moderate variability.
- –
- BMI: BMI averages 29.1, with a substantial SD of 8.2, reflecting the diverse body compositions of the patients. BMI values range broadly from 19.8 to 57.9.
- –
- Abdominal fat (AF) (cm): On average, abdominal fat measures 5.91 with a standard deviation of 1.50. The measurements vary from 3.2 to 9.4.
- –
- Waist circumference (WC) (cm): The average WC is 96.09 cm, and the standard deviation is 13.31 cm, indicating some variability in this measurement. The range is from 73.7 cm to 121.9 cm.
- –
- Abdomen circumference (Abd. C) (cm): The average (Abd. C) is 92.10 cm with a standard deviation of 13.65 cm, indicating a diverse set of measurements from 71.1 cm to 120 cm.
- –
- Hip circumference (H.C) (cm) has a mean of 108.48 cm and a standard deviation of 12.79 cm, ranging from 88.9 cm to 134.6 cm.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| WC | Waist Circumference |
| HC | Hip Circumference |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| AF | Abdomen Fat |
| AC | Abdomen Circumference |
| CTDIvol | Computed Tomography Dose Index |
| DLP | Dose–Length Product |
| SSDE | Size-Specific Dose Estimate |
| Eda | Exploratory Data Analysis |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| AAPM | American Association of Physicists in Medicine |
| UAE | United Arab Emirates |
| DRLs | Diagnostic Reference Levels |
| MOHAP | Ministry of Health and Prevention |
References
- Power, S.P.; Moloney, F.; Twomey, M.; James, K.; O’Connor, O.J.; Maher, M.M. Computed tomography and patient risk: Facts, perceptions and uncertainties. World J. Radiol. 2016, 8, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lell, M.M.; Wildberger, J.E.; Alkadhi, H.; Damilakis, J.; Kachelriess, M. Evolution in computed tomography: The battle for speed and dose. Investig. Radiol. 2015, 50, 629–644. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.T.; Law, M.W.M.; Huang, B.; Ng, S.; Li, Z.P.; Meng, Q.F.; Khong, P.L. Radiation dose and cancer risk from pediatric CT examinations on 64-slice CT: A phantom study. Eur. J. Radiol. 2010, 76, e19–e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhorayef, M.; Sulieman, A.; Alonazi, B.; Al-Nuaimi, M.; Alduaij, M.; Bradley, D. Estimation of radiation-induced cataract and cancer risks during routine CT head procedures. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2018, 155, 65–68. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0969806X17308228 (accessed on 15 January 2024). [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Samei, E.; Segars, W.P.; Sturgeon, G.M.; Colsher, J.G.; Toncheva, G.; Yoshizumi, T.T.; Frush, D.P. Patient-specific radiation dose cancer risk estimation in CT: Part, II. Application to patients. Med. Phys. 2011, 38, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brat, H.; Zanca, F.; Montandon, S.; Racine, D.; Rizk, B.; Meicher, E.; Yoshizumi, T.T.; Frush, D.P. Local clinical diagnostic reference levels for chest and abdomen CT examinations in adults as a function of body mass index and clinical indication: A prospective multicenter study. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 6794–6804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, D.; Rowan, M.; Cournane, S.; O’Connor, U.; Costello, D.; O’Hare, N. National DRLs for adult body CT scans based on body width. Phys. Med. 2014, 30, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, M.H.; Deevband, M.R.; Javad, M.; Birgani, T.; Yadollahpour, A.; Tahmasebi, M. A New Method for Estimating of Patient Effective Dose in Computed Tomography Based on Body Mass Index: Performance of the Method in Abdomen-Pelvic Examination. Curr. Trends Clin. Med. Imaging 2018, 15, 123. [Google Scholar]
- Alshurbaji, M.; Haout, S.E.; Chanchal, A.; Dhou, S. Investigating the Effect of Patient-Related Factors on Computed Tomography Radiation Dose Using. Regression and Correlation Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, P.D.; Chawke, L.; Twomey, M.; Murphy, K.P.; O’Neill, S.B.; McWilliams, S.R.; James, K.; Kavanagh, R.G.; Sullivan, C.; Chan, F.E.; et al. Body composition determinants of radiation dose during abdominopelvic CT. Insights Imaging 2018, 9, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kim, K.W.; Kwon, H.J.; Lee, J.; Koo, K.; Song, G.W.; Lee, S.G. Relationship of body mass index and abdominal fat with radiation dose received during preoperative liver CT in potential living liver donors: A cross-sectional study. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2022, 12, 2206–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunney, P.E.; Zink, A.N.; Holm, A.A.; Billington, C.J.; Kotz, C.M. Use of Water Equivalent Diameter for Calculating Patient Size and Size-Specific Dose Estimates (SSDE) in CT. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 176, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, P.; Luo, K.; He, X. Size-Specific Dose Estimates of Radiation Based on Body Weight and Body Mass Index for Chest and Abdomen-Pelvic CTs. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 6046501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greffier, J.; Larbi, A.; Macri, F.; Beregi, J.P.; Pereira, F. Effect of patient size, anatomical location and modulation strength on dose delivered and image-quality on CT examination. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2017, 177, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Report of AAPM Task Group 204. Size-Specific Dose Esitmates (SSDE) in Pediatric and Adult Body CT Examinations; American Association of Physicists in Medicine: College Park, MD, USA, 2011.
- Zheng, X. Body size and tube voltage-dependent guiding equations for optimal selection of image acquisition parameters in clinical X-ray imaging. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2018, 11, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuzaid, M.M.; Elshami, W.; Tekin, H.O.; Ghonim, H.; Shawki, M.; Salama, D.H. Computed tomography radiation doses for common computed tomography examinations: A nationwide dose survey in United Arab Emirates. Insights Imaging 2020, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, Y.; Itoh, H.; Nagahara, K.; Hata, H.; Mitsui, K. Relationships of Radiation Dose Indices with Body Size Indices in Adult Body Computed Tomography. Tomography 2023, 9, 1381–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuzaid, M.M.; Elshami, W.; El Serafi, A.; Hussien, T.; McConnell, J.R.; Tekin, H.O. Toward national ct diagnostic reference levels in the united arab emirates: A multicenter review of CT dose index and dose area product. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2020, 190, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almohammed, H.I.; Elshami, W.; Hamd, Z.Y.; Abuzaid, M. Optimizing CT Abdomen–Pelvis Scan Radiation Dose: Examining the Role of Body Metrics (Waist Circumference, Hip Circumference, Abdominal Fat, and Body Mass Index) in Dose Efficiency. Tomography 2024, 10, 643-653. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10050049
Almohammed HI, Elshami W, Hamd ZY, Abuzaid M. Optimizing CT Abdomen–Pelvis Scan Radiation Dose: Examining the Role of Body Metrics (Waist Circumference, Hip Circumference, Abdominal Fat, and Body Mass Index) in Dose Efficiency. Tomography. 2024; 10(5):643-653. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10050049
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmohammed, Huda I., Wiam Elshami, Zuhal Y. Hamd, and Mohamed Abuzaid. 2024. "Optimizing CT Abdomen–Pelvis Scan Radiation Dose: Examining the Role of Body Metrics (Waist Circumference, Hip Circumference, Abdominal Fat, and Body Mass Index) in Dose Efficiency" Tomography 10, no. 5: 643-653. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10050049
APA StyleAlmohammed, H. I., Elshami, W., Hamd, Z. Y., & Abuzaid, M. (2024). Optimizing CT Abdomen–Pelvis Scan Radiation Dose: Examining the Role of Body Metrics (Waist Circumference, Hip Circumference, Abdominal Fat, and Body Mass Index) in Dose Efficiency. Tomography, 10(5), 643-653. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10050049







