Differential Assessment of Internal Jugular Vein Stenosis in Patients Undergoing CT and MRI with Contrast
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Scanning Protocols
2.3. Imaging Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IJVS | Internal Jugular Vein Stenosis |
| IJ | Internal Jugular |
Appendix A
| Scanner | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Property | 1.5 T Philips | 3 T Philips | 3 T GE |
| T2-STIR | |||
| TR (ms) | 6000 | 8500 | 7800 |
| TE (ms) | 90 | 80 | 83 |
| ST (mm) | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| SS (mm) | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| EN | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| DWI | |||
| B | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| TR (ms) | 4500 | 4125 | 8500 |
| TE (69) | 69 | 86 | 77 |
| ST (mm) | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| SS (mm) | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5 |
| EN | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| FLAIR | |||
| TR (ms) | 6000 | 8000 | 9800 |
| TE (69) | 100 | 135 | 141 |
| ST (mm) | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| SS (mm) | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| EN | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| SWI | |||
| TR (ms) | 52 | 31 | 53 |
| TE (69) | 0 | 0 | 23 |
| ST (mm) | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| SS (mm) | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| EN | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 3D-MPRAGE | |||
| TR (ms) | 8 | 8 | 10 |
| TE (69) | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| ST (mm) | 1.8 | 1 | 1 |
| SS (mm) | 0.9 | 1 | 0.5 |
| EN | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| T1 post | |||
| TR (ms) | 650 | 360 | 425 |
| TE (69) | 10 | 4 | 15 |
| ST (mm) | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| SS (mm) | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| EN | 1 | 1 | 1 |
References
- England, R.W.; Arun, A.; Vosler, P.S.; Lo, S.-F.L.; Gujar, S.K.; Tariq, N.; Weiss, C.R.; Luciano, M.G.; Hui, F.K. Catheter-directed venography for evaluating internal jugular vein pseudo-occlusion. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 98, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Chao, A.-C.; Chang, F.-C.; Chung, C.-P.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Sheng, W.-Y.; Wu, J.; Hu, H.-H. Obstruction of venous drainage linked to transient global amnesia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalkader, M.; Hui, F.; Amans, M.R.; Raz, E.; Hanning, U.; Ma, A.; Brinjikji, W.; Malek, A.M.; Oxley, T.J.; Nguyen, T.N. Cerebral venous disorders: Diagnosis and endovascular management. J. Neuroradiol. 2023, 50, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalkader, M.; Nguyen, T.N.; Norbash, A.M.; Raz, E.; Shapiro, M.; Lenck, S.; Brinjikji, W.; Weber, P.; Sakai, O. State of the art: Venous causes of pulsatile tinnitus and diagnostic considerations guiding endovascular therapy. Radiology 2021, 300, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Yang, Y.H.; Chen, C.H.; Lin, R.T.; Lin, W.C. Successful treatment of cerebral venous thrombosis associated with bilateral internal jugular vein stenosis using direct thrombolysis and stenting: A case report. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2005, 21, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, A.; Mattox, D.; Fountain, A.; Hudgins, P. CT arteriography and venography in pulsatile tinnitus: Preliminary results. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2006, 27, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, M.K.; Hamieh, T.; Larkin, B.; Mcmillan, W. Cerebral hemorrhage due to internal jugular vein stenosis in a hemodialysis patient. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2012, 16, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Ding, J.; Asmaro, K.; Pan, L.; Ya, J.; Yang, Q.; Fan, C.; Ding, Y.; Ji, X.; Meng, R. Clinical characteristics and neuroimaging findings in internal jugular venous outflow disturbance. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 119, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Meng, R.; Zhang, X.; Guo, L.; Li, S.; Wu, W.; Duan, J.; Song, H.; Ding, Y.; Ji, X. Intracranial hypertension induced by internal jugular vein stenosis can be resolved by stenting. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, 365.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, M.; Boxerman, J.; Davis, L.; Haas, R.; Rogg, J. Incidence of extrinsic compression of the internal jugular vein in unselected patients undergoing CT angiography. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wu, X.; Lan, D.; Zhou, D.; Ding, Y.; Ji, X.; Meng, R. Differentiation between anatomical slenderness and acquired stenosis of the internal jugular veins. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2022, 28, 1849–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buch, K.; Groller, R.; Nadgir, R.N.; Fujita, A.; Qureshi, M.M.; Sakai, O. Variability in the cross-sectional area and narrowing of the internal jugular vein in patients without multiple sclerosis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2016, 206, 1082–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, A.; Kurmann, C.; Pospieszny, K.; Meinel, T.R.; Shahin, M.; Heldner, M.R.; Umarova, R.; Jung, S.; Arnold, M.; El-Koussy, M. Diagnostic Accuracy of High-Resolution 3D T2-SPACE in Detecting Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2022, 43, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugler, J.P., III; Brookeman, J.R. Three-dimensional magnetization-prepared rapid gradient-echo imaging (3D MP RAGE). Magn. Reson. Med. 1990, 15, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; He, L.; Zheng, H.; Lu, Z.-L. Optimizing the magnetization-prepared rapid gradient-echo (MP-RAGE) sequence. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, L.; Mallarini, G. A comparison between NASCET and ECST methods in the study of carotids: Evaluation using Multi-Detector-Row CT angiography. Eur. J. Radiol. 2010, 76, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, M.L. Interrater reliability: The kappa statistic. Biochem. Medica 2012, 22, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettau, M.; Sartor, K.; Heiland, S.; Hähnel, S. 3T high-spatial-resolution contrast-enhanced MR angiography of the intracranial venous system with parallel imaging. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehman, R.L.; Felmlee, J.P. Flow artifact reduction in MRI: A review of the roles of gradient moment nulling and spatial presaturation. Magn. Reson. Med. 1990, 14, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiarz, L.; Romero, J.; Murphy, E.; Brobeck, B.; Schaefer, P.; González, R.; Lev, M. Contrast-enhanced MR angiography is not more accurate than unenhanced 2D time-of-flight MR angiography for determining ≥70% internal carotid artery stenosis. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randoux, B.; Marro, B.a.; Koskas, F.; Duyme, M.; Sahel, M.; Zouaoui, A.; Marsault, C. Carotid artery stenosis: Prospective comparison of CT, three-dimensional gadolinium-enhanced MR, and conventional angiography. Radiology 2001, 220, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babiarz, L.S.; Astor, B.; Mohamed, M.A.; Wasserman, B.A. Comparison of gadolinium-enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance angiography with high-resolution black blood cardiovascular magnetic resonance for assessing carotid artery stenosis. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2007, 9, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosottini, M.; Pingitore, A.; Puglioli, M.; Michelassi, M.C.; Lupi, G.; Abbruzzese, A.; Calabrese, R.; Lombardi, M.; Parenti, G.; Bartolozzi, C. Contrast-enhanced three-dimensional magnetic resonance angiography of atherosclerotic internal carotid stenosis as the noninvasive imaging modality in revascularization decision making. Stroke 2003, 34, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, G.; Absinta, M.; Reich, D.S. Optimized T1-MPRAGE sequence for better visualization of spinal cord multiple sclerosis lesions at 3T. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 2215–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Weert, T.T.; Ouhlous, M.; Meijering, E.; Zondervan, P.E.; Hendriks, J.M.; van Sambeek, M.R.; Dippel, D.W.; van der Lugt, A. In vivo characterization and quantification of atherosclerotic carotid plaque components with multidetector computed tomography and histopathological correlation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 2366–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba, L.; Caddeo, G.; Sanfilippo, R.; Montisci, R.; Mallarini, G. Efficacy and sensitivity of axial scans and different reconstruction methods in the study of the ulcerated carotid plaque using multidetector-row CT angiography: Comparison with surgical results. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2007, 28, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosugi, K.; Yamada, Y.; Yamada, M.; Yokoyama, Y.; Fujiwara, H.; Yoshida, K.; Yoshida, K.; Toda, M.; Jinzaki, M. Posture-induced changes in the vessels of the head and neck: Evaluation using conventional supine CT and upright CT. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eksioglu, A.S.; Yildiz, Y.T.; Senel, S. Normal sizes of internal jugular veins in children/adolescents aged birth to 18 years at rest and during the Valsalva maneuver. Eur. J. Radiol. 2014, 83, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josephson, S.; Bryant, S.; Mak, H.; Johnston, S.; Dillon, W.; Smith, W. Evaluation of carotid stenosis using CT angiography in the initial evaluation of stroke and TIA. Neurology 2004, 63, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokop, M.; Waaijer, A.; Kreuzer, S. CT angiography ofthe carotid arteries. JBR-BTR Organe Soc. R. Belg. Radiol. 2004, 87, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Lev, M.H.; Romero, J.M.; Goodman, D.N.; Bagga, R.; Kim, H.Y.K.; Clerk, N.A.; Ackerman, R.H.; Gonzalez, R.G. Total occlusion versus hairline residual lumen of the internal carotid arteries: Accuracy of single section helical CT angiography. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2003, 24, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Herzig, R.; Buřval, S.; Křupka, B.; Vlachová, I.; Urbánek, K.; Mareš, J. Comparison of ultrasonography, CT angiography, and digital subtraction angiography in severe carotid stenoses. Eur. J. Neurol. 2004, 11, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
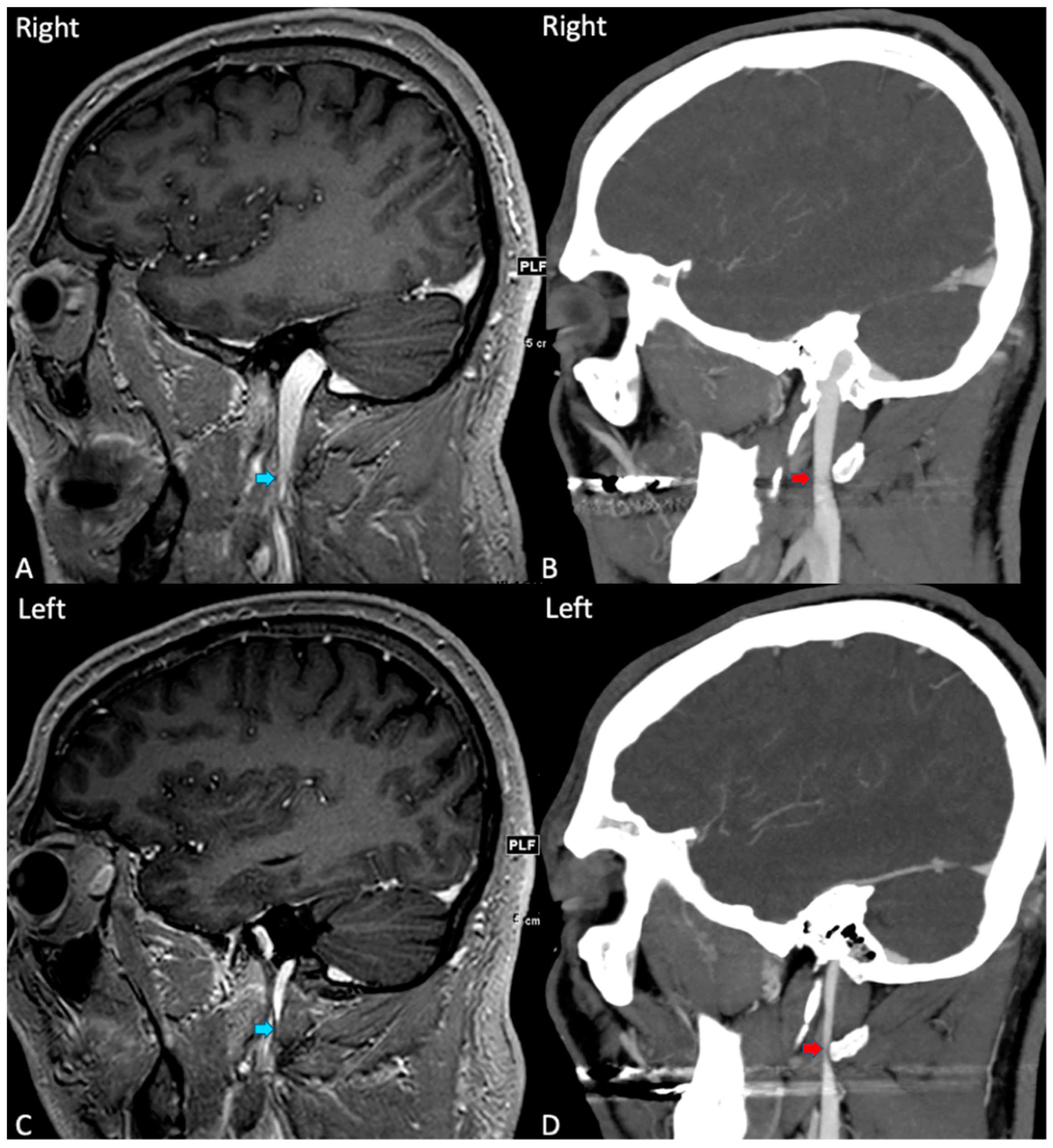
| Characteristic. | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Female | 24 (68.6) |
| Age (median, IQR) | 45.0 (37–62.5) |
| Indication | |
| Stroke | 20 (57.1) |
| ICH | 3 (8.6) |
| Trauma | 3 (8.6) |
| AMS | 2 (5.7) |
| Other | 7 (20.0) |
| MR Scanner | |
| 1.5 T Philips | 18 (51.4) |
| 3 T Philips | 15 (42.8) |
| 3 T GE | 2 (5.7) |
| IJVS Grade | Right | Left | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| CT | |||
| Grade 0 N (%) | 17 (48.6) | 16 (45.7) | 33 (47.1) |
| Grade I N (%) | 2 (5.7) | 4 (11.4) | 6 (8.6) |
| Grade II N (%) | 9 (25.7) | 5 (14.3) | 14 (20.0) |
| Grade III N (%) | 5 (14.3) | 5 (14.3) | 10 (14.3) |
| Grade IV N (%) | 2 (5.7) | 5 (14.3) | 7 (10.0) |
| Total | 35 | 35 | 70 |
| MRI | |||
| Grade 0 N (%) | 12 (34.3) | 11 (31.4) | 23 (32.9) |
| Grade I N (%) | 3 (8.6) | 1 (2.9) | 4 (5.7) |
| Grade II N (%) | 1 (2.9) | 2 (5.7) | 3 (4.3) |
| Grade III N (%) | 2 (5.7) | 7 (20.0) | 9 (12.9) |
| Grade IV N (%) | 17 (48.6) | 14 (40.0) | 31 (44.3) |
| Total | 35 | 35 | 70 |
| Variable | CT | MR | p |
|---|---|---|---|
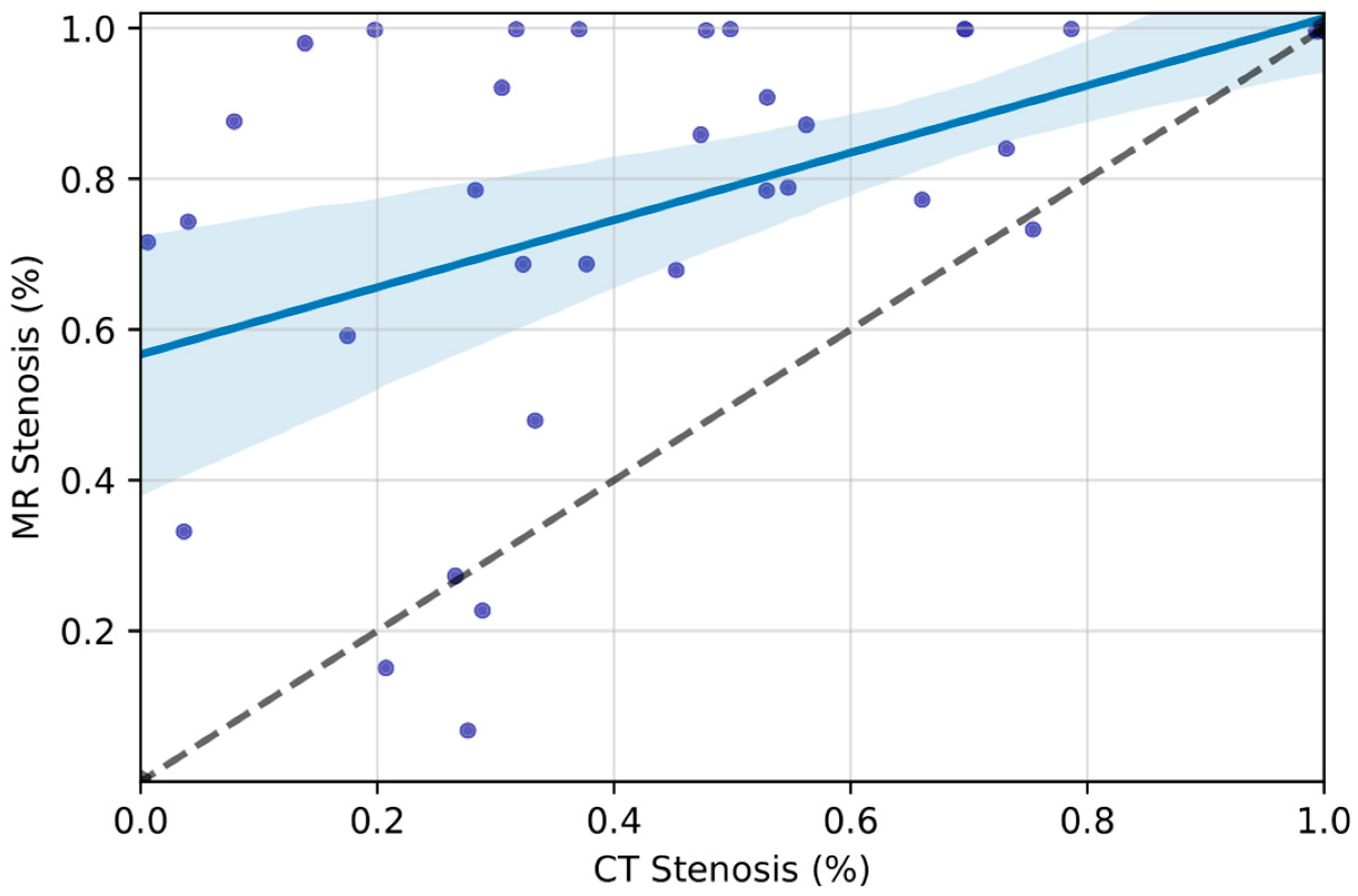
| IJs with Stenosis N (%) | 37 (52.9) | 47 (67.1) | 0.28 |
| IJVS Degree (%, 95% CI) | 45.6 (35.9–55.2) | 77.0 (67.8–86.1) | <0.001 |
| Minimum Surface Area (mm2) | 29.7 (23.1, 35.9) | 11.5 (7.08, 15.8) | <0.001 |
| Jugular Bulb Diameter (mm2, 95% CI) | 55.8 (48.0, 62.2) | 59.5 (52.6, 66.0) | 0.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdalkader, M.; Miller, M.I.; Klein, P.; Hui, F.K.; Siracuse, J.J.; Mian, A.Z.; Sakai, O.; Nguyen, T.N.; Setty, B.N. Differential Assessment of Internal Jugular Vein Stenosis in Patients Undergoing CT and MRI with Contrast. Tomography 2024, 10, 266-276. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10020021
Abdalkader M, Miller MI, Klein P, Hui FK, Siracuse JJ, Mian AZ, Sakai O, Nguyen TN, Setty BN. Differential Assessment of Internal Jugular Vein Stenosis in Patients Undergoing CT and MRI with Contrast. Tomography. 2024; 10(2):266-276. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10020021
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdalkader, Mohamad, Matthew I. Miller, Piers Klein, Ferdinand K. Hui, Jeffrey J. Siracuse, Asim Z. Mian, Osamu Sakai, Thanh N. Nguyen, and Bindu N. Setty. 2024. "Differential Assessment of Internal Jugular Vein Stenosis in Patients Undergoing CT and MRI with Contrast" Tomography 10, no. 2: 266-276. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10020021
APA StyleAbdalkader, M., Miller, M. I., Klein, P., Hui, F. K., Siracuse, J. J., Mian, A. Z., Sakai, O., Nguyen, T. N., & Setty, B. N. (2024). Differential Assessment of Internal Jugular Vein Stenosis in Patients Undergoing CT and MRI with Contrast. Tomography, 10(2), 266-276. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10020021






