A Novel Artificial Coronary Plaque to Model Coronary Heart Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Plaque Components
1.2. State of the Art—Artificial Plaque Compositions
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Plaque Model Fabrication
2.2. Plaque Casting Mold
2.3. Donor Plaques
2.4. Oscillatory Rheology
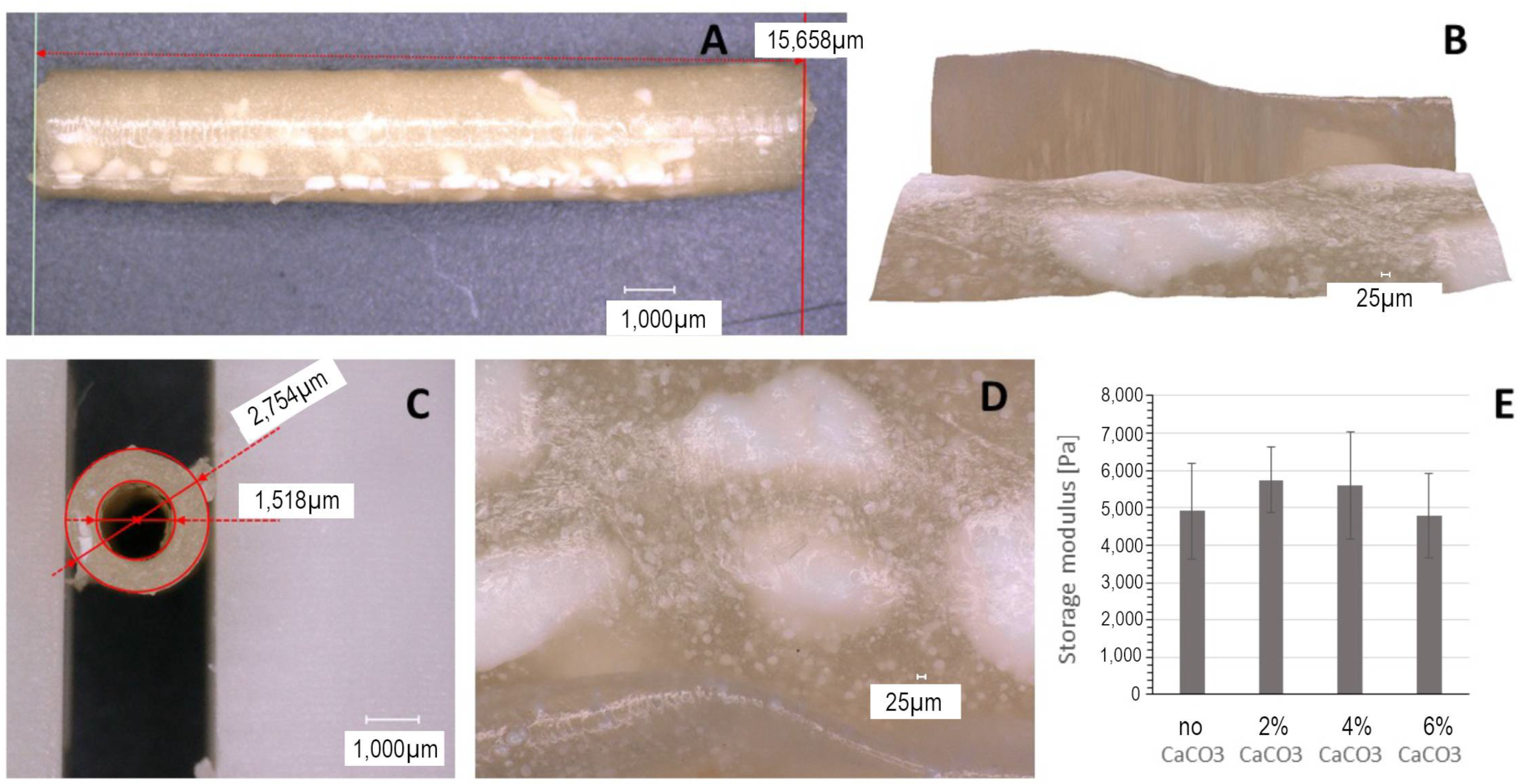
2.5. Microscopic Imaging and Stability Measurements
2.6. Neutralization of Excess GA
2.7. Cytotoxicity Test: MTT Assay Protocol for Determining the Cytotoxicity of Plaques
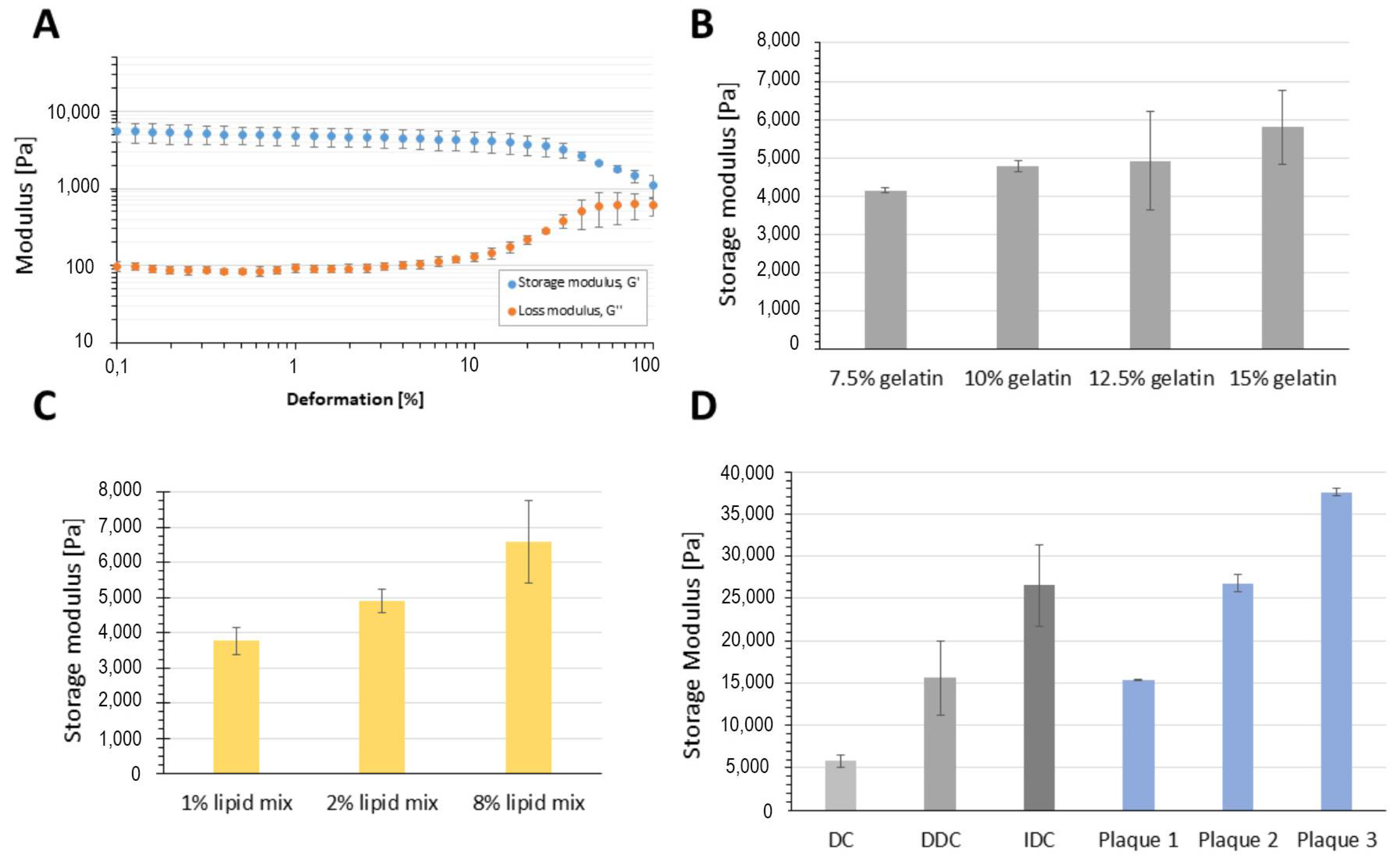
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Composition on Plaque Material Properties and Appearance
3.2. Effect of Incubation on Plaque Stability
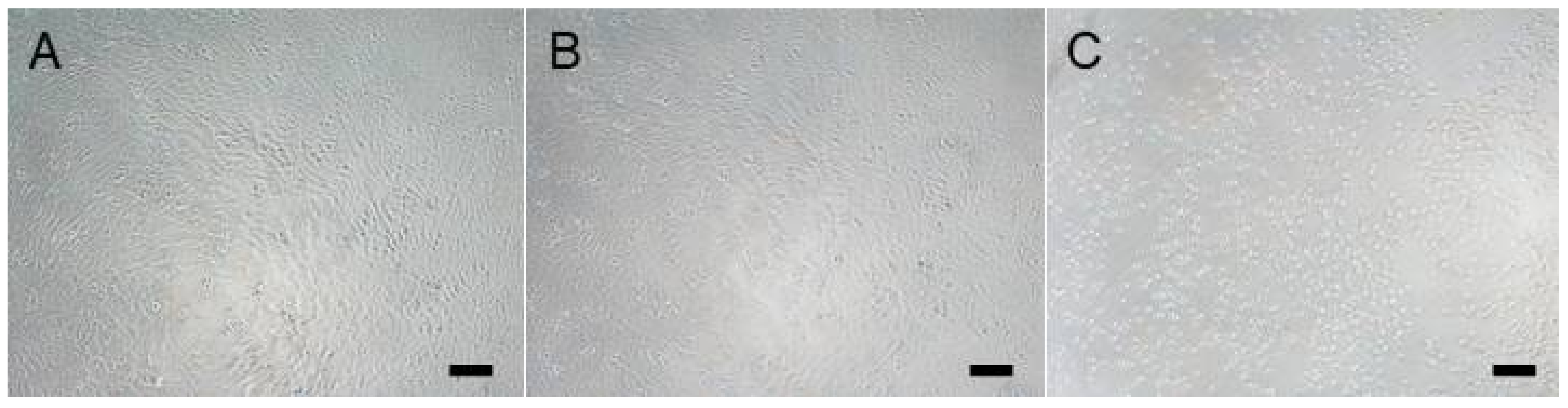
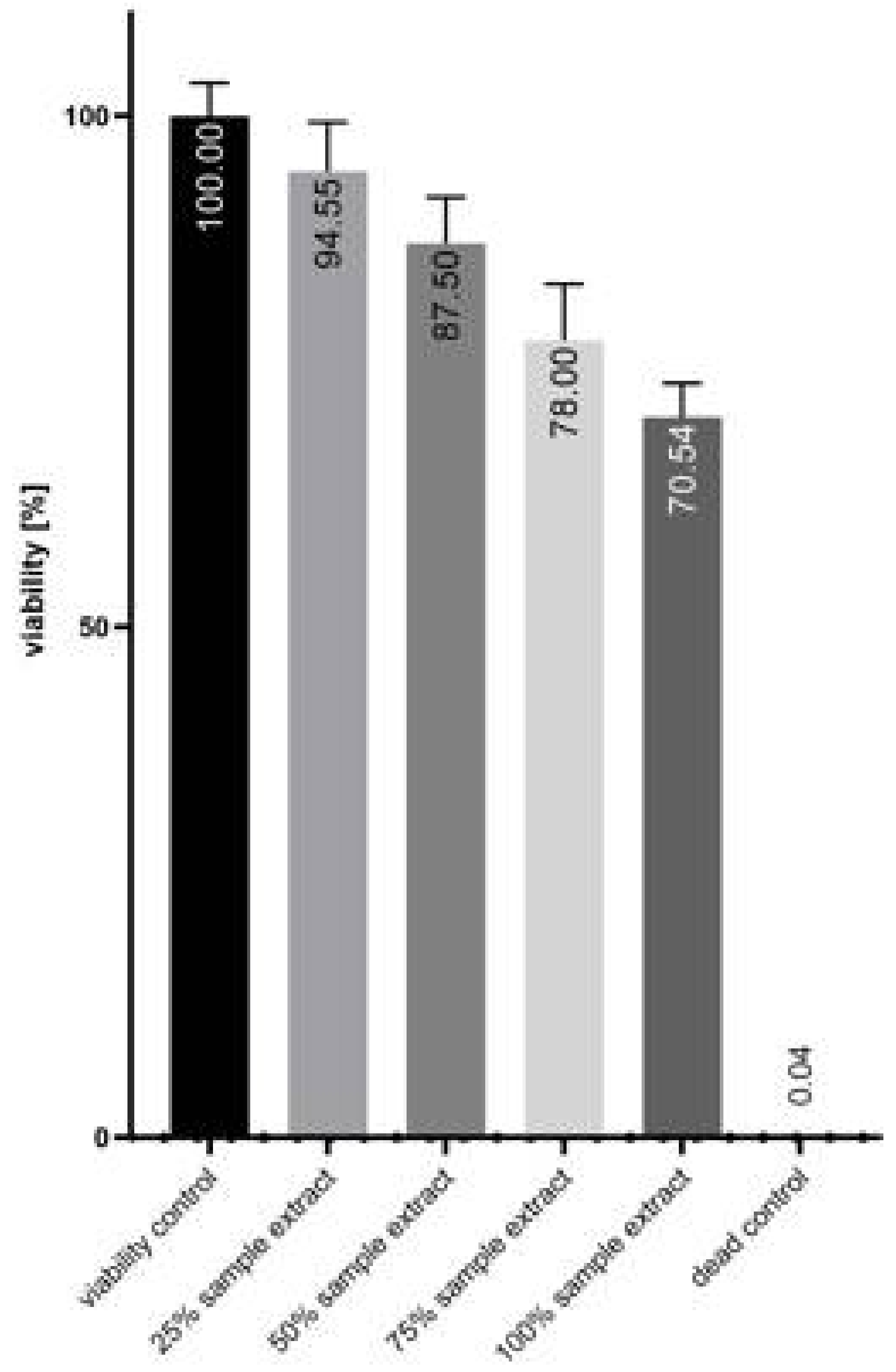
3.3. Cytotoxicity
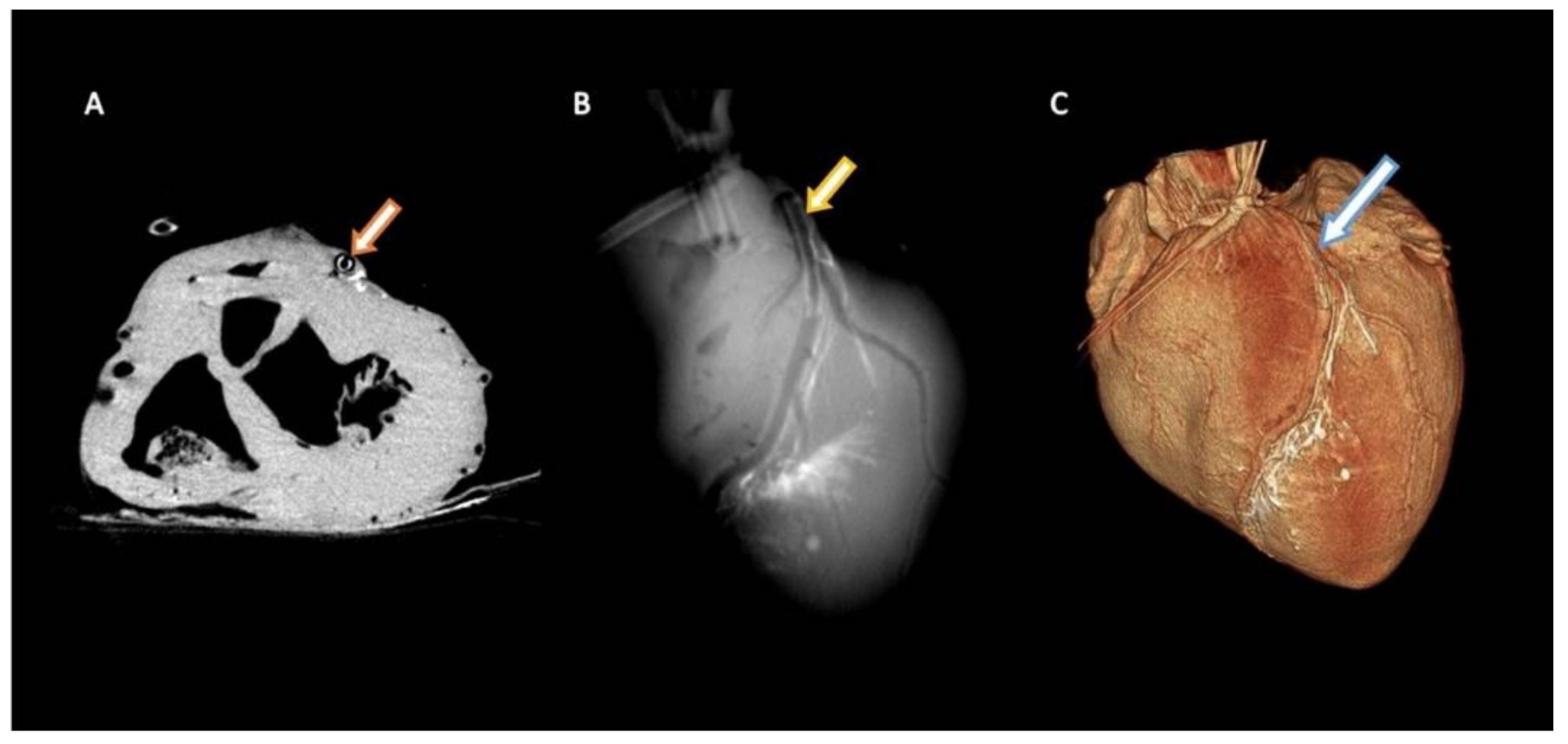
3.4. Implantability in Porcine Coronary Artery
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAP | artificial atherosclerotic plaque |
| CaCO3 | calcium carbonate |
| CHD | coronary heart disease |
| DC | direct crosslinking |
| DDC | double direct crosslinking |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| GA | glutaraldehyde |
| HA | hydroxyapatite |
| IDC | indirect crosslinking procedure |
| LAD | left anterior descending artery |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| PVA | polyvinyl alcohol |
| SMCs | smooth muscle cells |
References
- Falk, E. Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Xian, X.; Wang, Z.; Bi, Y.; Bi, Y.; Chen, Q.; Han, X.; Tang, D.; Chen, R. Research progress on the relationship between atherosclerosis and inflammation. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milutinović, A.; Šuput, D.; Zorc-Pleskovič, R. Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis in the tunica intima, media, and adventitia of coronary arteries: An updated review. Bosn. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2020, 20, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Munter, E.; Alonso, A.; Bittercourt, S.A.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Das, S.R.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 139, e56–e528. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lusis, A.J. Atherosclerosis. Nature 2000, 407, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruchart, J.C.; Duriez, P. Fundamental data on atherosclerosis. Ann. Endocrinol. 2001, 62, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, M.T.; Cunnane, E.M.; Mulvihill, J.J.; Akyildiz, A.C.; Gijen, F.J.H.; Holzapfel, G.A. Uniaxial tensile testing approaches for characterisation of atherosclerotic plaques. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.J. Prevention and Treatment of Atherosclerosis: A Practitioner’s Guide for 2008. Am. J. Med. 2009, 122, S38–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naghavi, M.; Libby, P.; Falk, E.; Casscells, S.W.; Litovsky, S.; Rumberger, J.; Badimon, J.J.; Stefandanis, C.; Moreno, P.; Pasterkamp, G.; et al. From vulnerable plaque to vulnerable patient: A call for new definitions and risk assessment strategies: Part, I. Circulation 2003, 108, 1664–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.; Kuban, B.D.; Tuzcu, E.M.; Schoenhangen, P.; Nissen, S.E.; Vince, G.D. Coronary plaque classification with intravascular ultrasound radiofrequency data analysis. Circulation 2002, 106, 2200–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Weert, T.T.; Ouhlpus, M.; Zondervan, P.E.; Hendriks, J.M.; Dippel, D.W.J.; van Sambeek, M.R.H.M.; van der Lugt, A. In vitro characterization of atherosclerotic carotid plaque with multidetector computed tomography and histopathological correlation. Eur. Radiol. 2005, 15, 1906–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vavuranakis, M.; Papaioannou, T.G.; Katsarou, O.A.; Vrachtis, D.A.; Sandias, E.A.; Siasos, G.; Kalogerar, K.I.; Schiaz, D.; Stefanadis, C.I.; Toustulis, D. Impact of atherosclerotic plaque components and their distribution on stent deployment: An intravascular-ultrasound virtual histology observational study. Minerva Cardioangiol. 2016, 64, 507–516. [Google Scholar]
- Rognoni, A.; Cudnoch-Jedrezejewska, A. Pathophysiology of Atherosclerotic Plaque Development. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Agents Med. Chem. 2015, 13, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacic, J.C.; Moreno, P.; Nabel, E.G.; Hachinski, V.; Fuster, V. Cellular senescence, vascular disease, and aging: Part 2 of a 2-part review: Clinical vascular disease in the elderly. Circulation 2011, 123, 1900–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valgimigli, M.; Rodriguez-Granillo, G.A.; Garcia-Garcia, H.M.; Vaina, S.; De De Jaegere, D.; De Feyter, P.; Surrys, P.W. Plaque Composition in the Left Main Stem Mimics the Distal but Not the Proximal Tract of the Left Coronary Artery. Influence of Clinical Presentation, Length of the Left Main Trunk, Lipid Profile, and Systemic Levels of C-Reactive Protein. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, B. Chemical composition and physical state of lipid deposits in atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 1985, 56, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutcheson, J.D.; Goettesch, C.; Bertazzo, S.; Bertazzo, S.; Maldonado, N.; Ruiz, J.L.; Goh, W.; Yabusaki, K.; Faits, T.; Bouten, C.; et al. Genesis and growth of extracellular-vesicle-derived microcalcification in atherosclerotic plaques. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackshear, W.M. Hemodynamic stress in lateral saccular aneurysms: Liepsch DW, Steiger HJ, Poll A, Reulen H-J. Biorheology 1987;24:689–710. J. Vasc. Surg. 1989, 9, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigioni, M.; Daniele, A.; Amodeo, C.; D’Averio, G.; Formigiani, R.; Di Donato, R.M. Particle image velocimetry analysis of the flow field in the total cavopulmonary connection. Artif. Organs 2000, 24, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordás, R.; Seshadhri, S.; Janiga, G.; Skalej, M.; Thévenin, D. Experimental validation of numerical simulations on a cerebral aneurysm phantom model. Interv. Med. Appl. Sci. 2012, 4, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionita, C.N.; Mokin, M.; Varble, N.; Bednarek, D.R.; Xiang, J.; Snyder, K.V.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Levy, E.I.; Meng, H.; Rudin, S. Challenges and limitations of patient-specific vascular phantom fabrication using 3D Polyjet printing. Med. Imaging 2014 Biomed. Appl. Mol. Struct. Funct. Imaging 2014, 9038, 90380M. [Google Scholar]
- Baldewsing, R.A.; de Korte, C.L.; Schaar, J.A.; Mastik, F.; van der Steen, A.F.W. A finite element model for performing intravascular ultrasound elastography of human atherosclerotic coronary arteries. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2004, 30, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Rajeswaran, T.; He, S.; Wilkinson, F.L.; Serracio-Inglott, F.; Azzwi, M.; Parikh, V.; Mirafabt, M.; Alexander, M.Y. Investigation of the composition of arterial plaques based on arterial waveforms and material properties. Proc. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. EMBS 2015, 2015, 993–996. [Google Scholar]
- Riel, L.; Dion, S.; Broutillette, M.; Berube, S.; Despartis, M.-A.; Bousser, E. Characterization of Calcified Plaques Retrieved from Occluded Arteries and Comparison with Potential Artificial Analogues. In Volume 3: Biomedical and Biotechnology Engineering; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.H.; Altreuter, D.H.; Gentile, F.T. Transport characterization of hydrogel matrices for cell encapsulation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1996, 50, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phromsopha, T.; Baimark, Y. Preparation of starch/gelatin blend microparticles by a water-in-oil emulsion method for controlled release drug delivery. Int. J. Biomater. 2014, 2014, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, E.; Creane, A.; Sultan, S.; Hynes, N.; Lally, C.; Kelly, D.J. Tensile and compressive properties of fresh human carotid atherosclerotic plaques. J. Biomech. 2009, 42, 2760–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, C.; Tseng, D.Y.; Squire, J.C.; Edelman, E.R. A Finite Element Analysis Approach to Pressure, Compliance, and Stent Design as Contributors to Vascular Injury. Circ. Res. 1999, 5, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliavacca, F.; Petrini, L.; Massarotti, P.; Schievano, S.; Auricchio, F.; Dubini, A. Stainless and shape memory alloy coronary stents: A computational study on the interaction with the vascular wall. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2004, 2, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lally, C.; Dolan, F.; Prendergast, P.J. Cardiovascular stent design and vessel stresses: A finite element analysis. J. Biomech. 2005, 38, 1574–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Early, M.; Lally, C.; Prendergast, P.J.; Kelly, D.J. Stresses in peripheral arteries following stent placement: A finite element analysis. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 12, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David Chua, S.N.; mac Donald, B.J.; Hashmi, M.S.J. Finite element simulation of stent and balloon interaction. J. Mater. Process Technol. 2003, 143–144, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auricchio, F.; di Loreto, M.; Sacco, E. Finite-element analysis of a stenotic artery revascularization through a stent insertion. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Engin 2001, 4, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedoya, J.; Meyer, C.A.; Timmins, L.H.; Moreno, M.R.; Moore, J.E. Effects of stent design parameters on normal artery wall mechanics. J. Biomech. Eng. 2006, 128, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gough, J.E.; Scotchford, C.A.; Downes, S. Cytotoxicity of glutaraldehyde crosslinked collagen/poly(vinyl alcohol) films is by the mechanism of apoptosis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 61, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, Y.J. High-concentration glutaraldehyde fixation of bovine pericardium in organic solvent and post-fixation glycine treatment: In vitro material assessment and in vivo anticalcification effect. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2011, 39, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glatt, H.; Turchi, G.S.; Heinritz, H.; Doehmer, J.; Oesch, F. Search for cell culture systems with diverse xenobiotic-metabolizing activities and their use in toxicological studies. Mol. Toxicol. 1987, 1, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Becker, A.; Epple, M.; Müller, K.M.; Schmitz, I. A comparative study of clinically well-characterized human atherosclerotic plaques with histological, chemical, and ultrastructural methods. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2004, 98, 2032–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentzon, J.F.; Otsuka, F.; Virmani, R.; Falk, E. Mechanisms of plaque formation and rupture. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 1852–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, A.; Juan, J.-M.; Kolodziejcky, E.; Acquistapace, S.; Donato-Capel, L.; Wooster, T.J. Impact of Protein Gel Porosity on the Digestion of Lipid Emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 8829–8837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Emulsion gels: The structuring of soft solids with protein-stabilized oil droplets. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 28, 224–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross-Murphy, S.B. Structure and rheology of gelatin gels. Imaging Sci. J. 1997, 45, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigi, A.; Cojazzi, G.; Panzavolta, S.; Rubini, K.; Roveri, N. Mechanical and thermal properties of gelatin films at different degrees of glutaraldehyde crosslinking. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olde Damink, L.H.H.; Dijkrista, P.J.; Van Lynn, M.J.A.; Van Wacher, P.B.; Nieuwenhuis, P.; Feijin, J. Glutaraldehyde as a crosslinking agent for collagen-based biomaterials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1995, 6, 460–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracqui, P.; Broisat, A.; Tockez, J.; Mesnier, N.; Ohayon, J.; Riou, L. Mapping elasticity moduli of atherosclerotic plaque in situ via atomic force microscopy. J. Struct. Biol. 2011, 174, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, C.K.; Ackyldiz, A.C.; Speelman, L.; Gijsen, F.J.H.; Oomens, C.W.J.; van Sambeek, M.R.H.M.; van der Lugt, A.; Baaijens, F.P.T. Local axial compressive mechanical properties of human carotid atherosclerotic plaques-characterisation by indentation test and inverse finite element analysis. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 1759–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.C.; Ko, C.C.; Douglas, W.H. Preparation of hydroxyapatite-gelatin nanocomposite. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 2853–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poznyak, A.V.; Silaeva, Y.Y.; Orekhov, A.N.; Deykin, A.V. Animal models of human atherosclerosis: Current progress. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2020, 53, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lindenhahn, P.; Richter, J.; Pepelanova, I.; Seeger, B.; Volk, H.A.; Hinkel, R.; Hiebl, B.; Scheper, T.; Hinrichs, J.B.; Becker, L.S.; et al. A Novel Artificial Coronary Plaque to Model Coronary Heart Disease. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9040197
Lindenhahn P, Richter J, Pepelanova I, Seeger B, Volk HA, Hinkel R, Hiebl B, Scheper T, Hinrichs JB, Becker LS, et al. A Novel Artificial Coronary Plaque to Model Coronary Heart Disease. Biomimetics. 2024; 9(4):197. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9040197
Chicago/Turabian StyleLindenhahn, Philipp, Jannik Richter, Iliyana Pepelanova, Bettina Seeger, Holger A. Volk, Rabea Hinkel, Bernhard Hiebl, Thomas Scheper, Jan B. Hinrichs, Lena S. Becker, and et al. 2024. "A Novel Artificial Coronary Plaque to Model Coronary Heart Disease" Biomimetics 9, no. 4: 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9040197
APA StyleLindenhahn, P., Richter, J., Pepelanova, I., Seeger, B., Volk, H. A., Hinkel, R., Hiebl, B., Scheper, T., Hinrichs, J. B., Becker, L. S., Haverich, A., & Kaufeld, T. (2024). A Novel Artificial Coronary Plaque to Model Coronary Heart Disease. Biomimetics, 9(4), 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9040197






