Bionic Design of High-Performance Joints: Differences in Failure Mechanisms Caused by the Different Structures of Beetle Femur–Tibial Joints
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Handling and Sample Preparation
2.2. Mechanical Testing
2.3. Micro Computed Tomography
2.4. Digital Image Correlation Testing
2.5. Finite Element
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
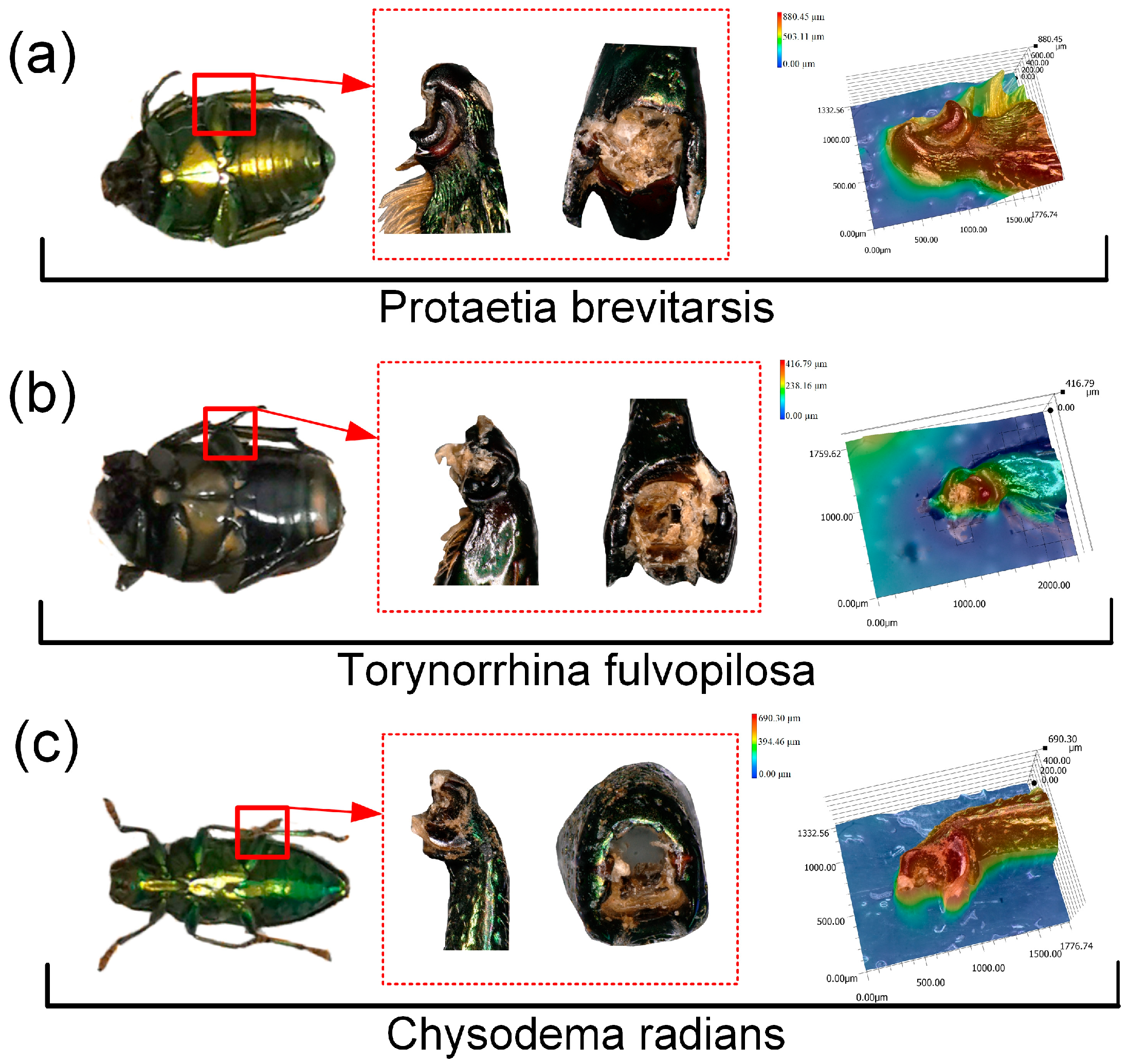
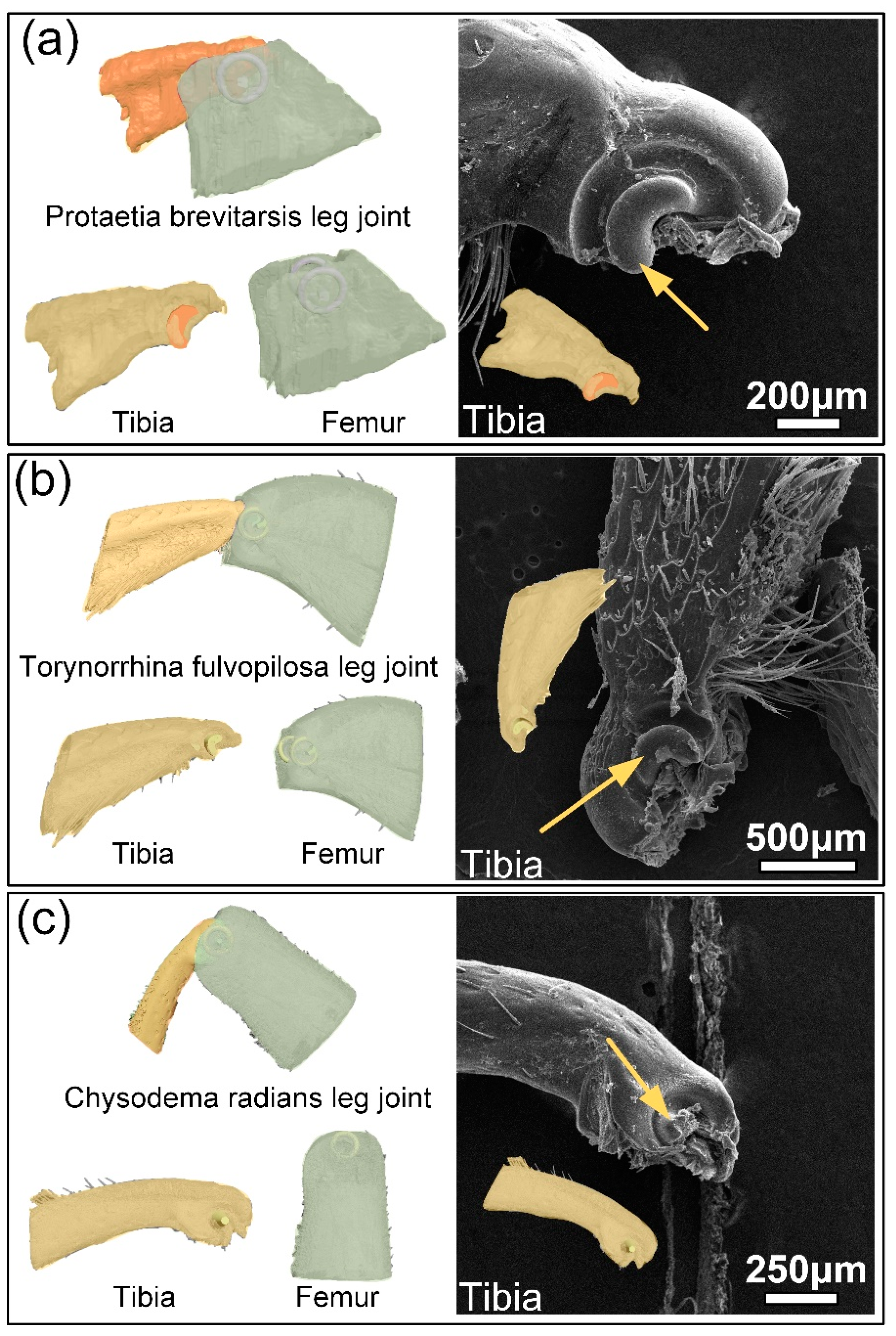
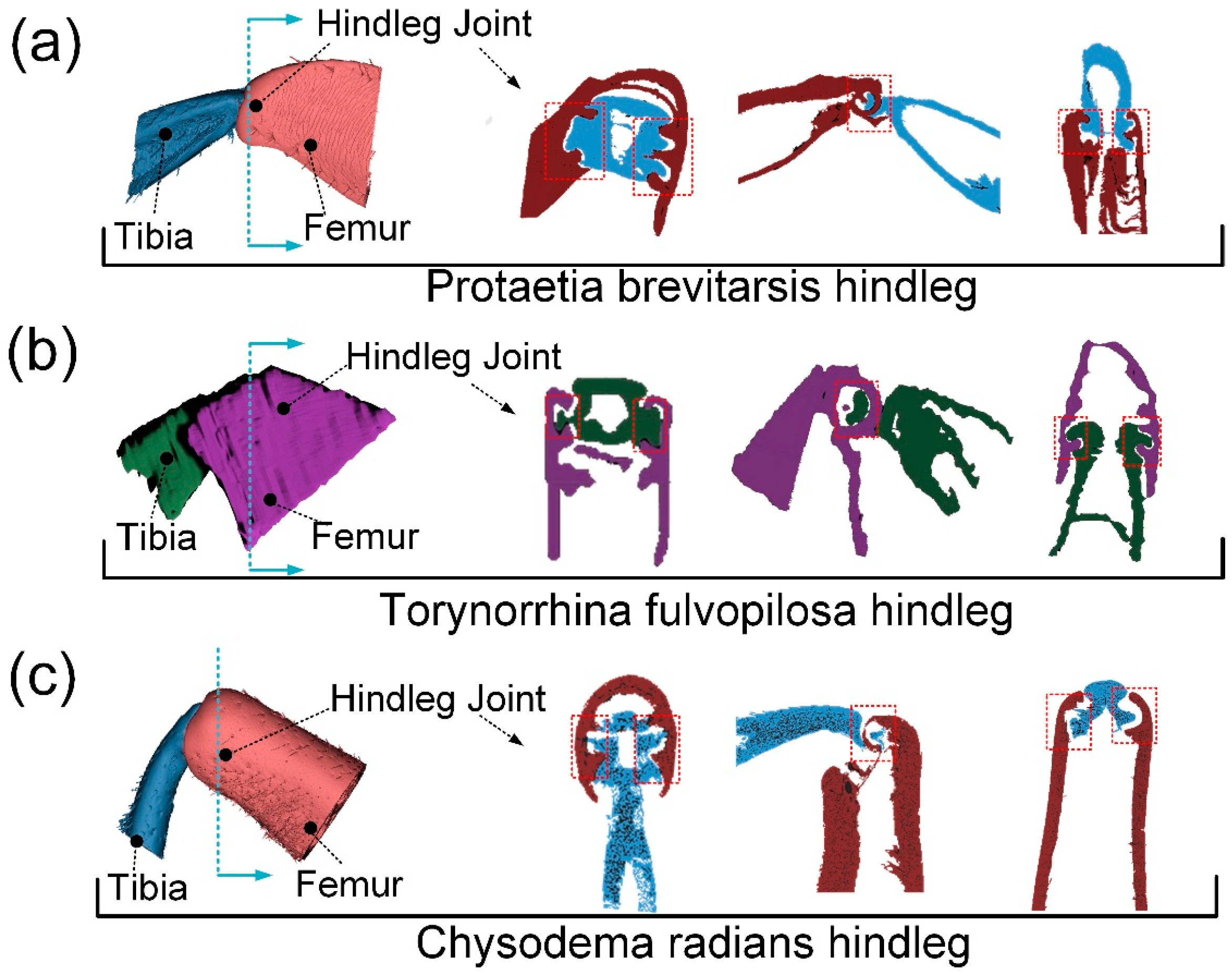
3.1. Structure of Leg Joints
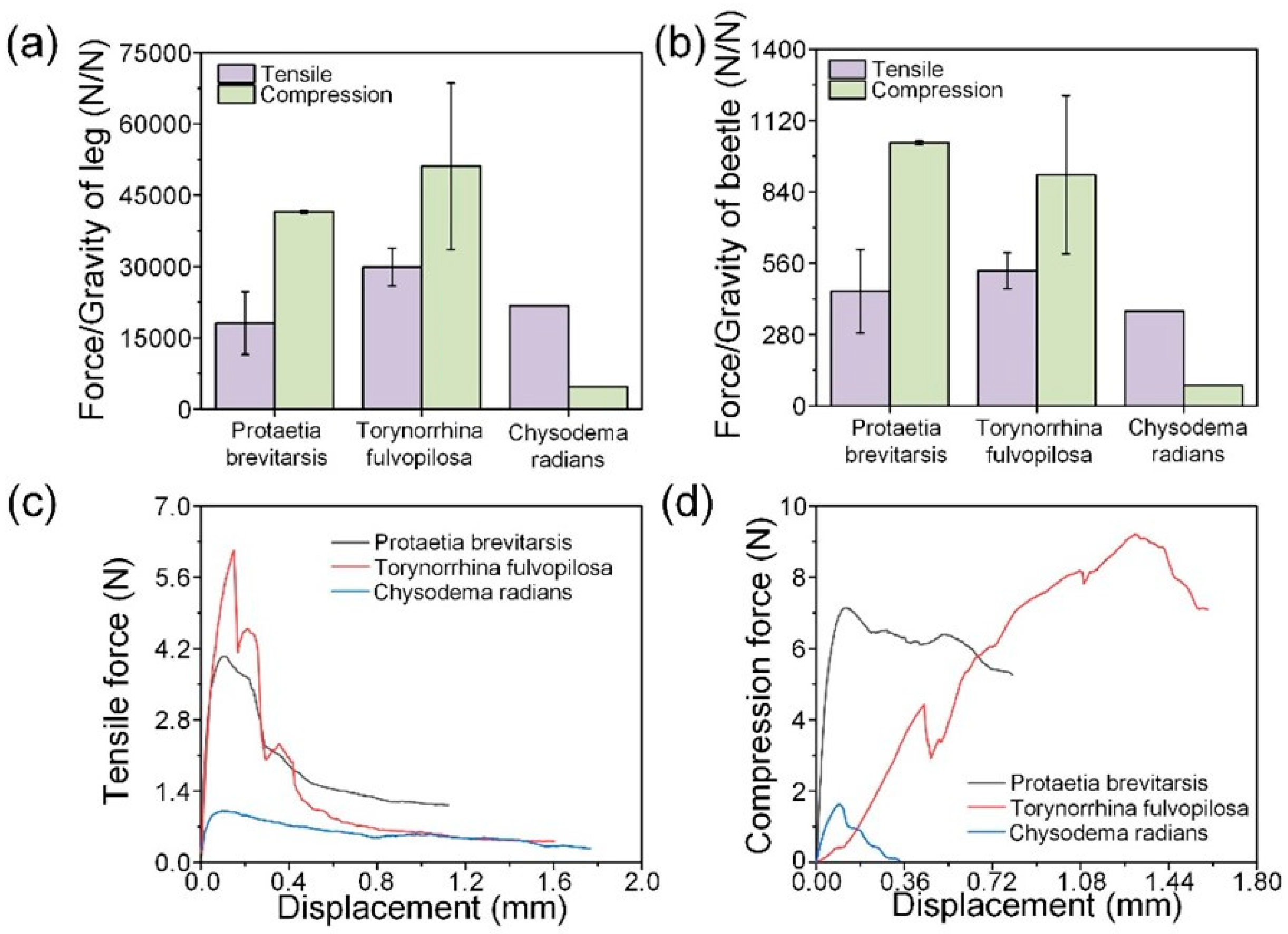
3.2. Mechanical Properties of Leg Joints
3.3. Bionic Model Design of Leg Joints
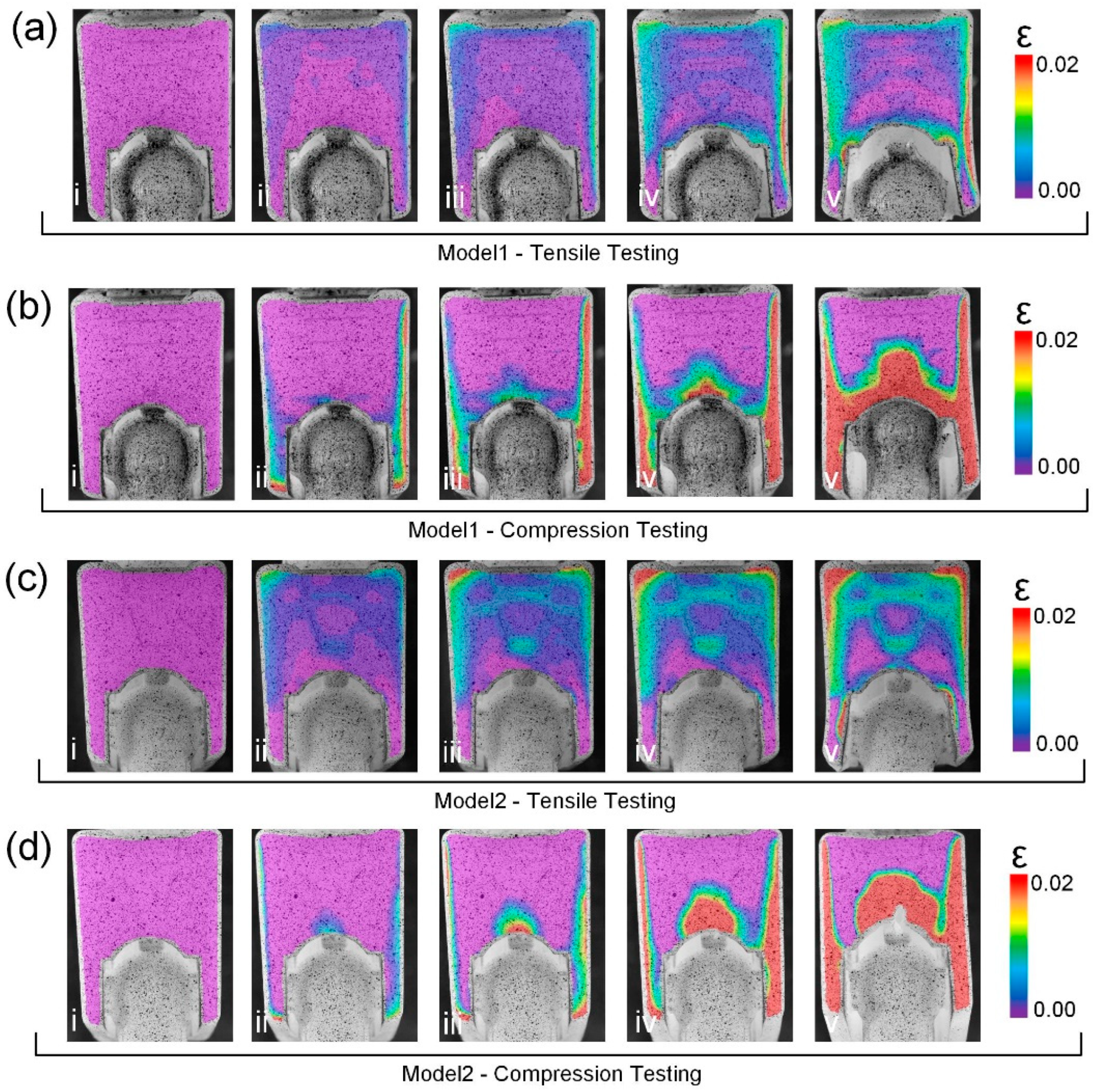
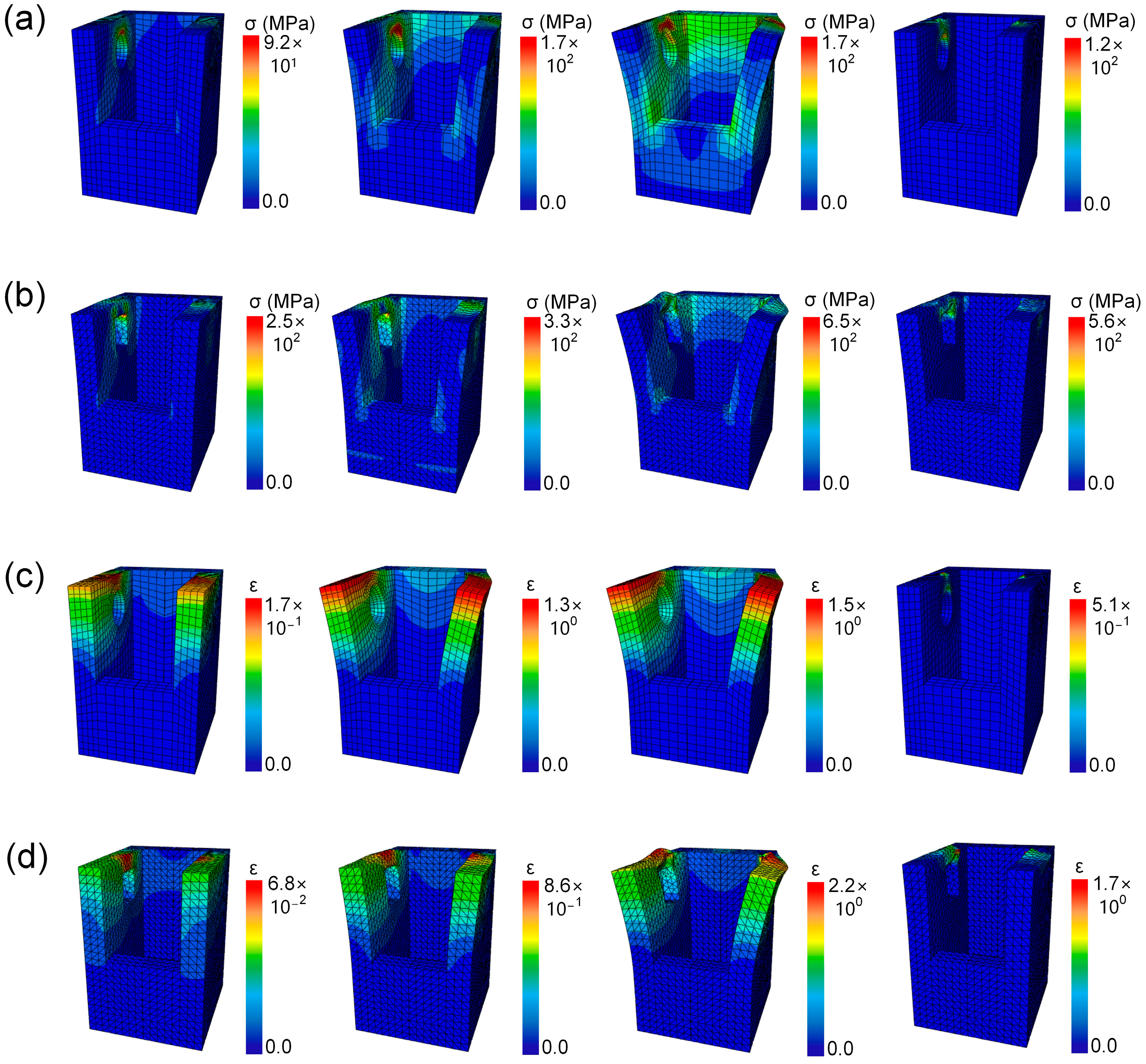
3.4. Failure Process of the Bionic Models
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Ren, L.; Ren, L. Bioinspired soft actuators with highly ordered skeletal muscle structures. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2022, 5, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Han, Z. Bionic structures and materials inspired by plant leaves: A comprehensive review for innovative problem-solving. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2023, 139, 101181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.C.; Zou, M.; Liu, G.M.; Song, J.F.; Wang, H.X. Experimental study on energy absorption of bionic tubes inspired by bamboo structures under axial crushing. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2018, 115, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lu, L.; Lu, X.; Liang, Z.; Tang, B.; Xie, Y. Laser-induced jigsaw-like graphene structure inspired by Oxalis corniculata Linn. leaf. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2022, 5, 700–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, Q.X.; Wang, W.; Peng, X. Structure bionic design method oriented to integration of biological advantages. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2021, 64, 1017–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtle, S.; Ang, S.F.; Schneider, G.A. On the mechanical properties of hierarchically structured biological materials. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 6378–6385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Zaheri, A.; Gao, W.; Hayashi, C.; Espinosa, H.D. AFM identification of beetle exocuticle: Bouligand structure and nanofiber anisotropic elastic properties. Adv. Funct. 2017, 27, 1603993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yin, Q.; Pan, F.; Cui, C.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, B. Advances in mechanics of hierarchical composite materials. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 214, 108970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegst, U.G.; Bai, H.; Saiz, E.; Tomsia, A.P.; Ritchie, R.O. Bioinspired structural materials. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Shishehbor, M.; Guarín-Zapata, N.; Kirchhofer, N.D.; Li, J.; Cruz, L.; Wang, T.; Bhowmick, S.; Stauffer, D.; Manimunda, P.; et al. A natural impact-resistant bicontinuous composite nanoparticle coating. Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunenfelder, L.K.; Milliron, G.; Herrera, S.; Gallana, I.; Yaraghi, N.; Hughes, N.; Evans-Lutterodt, K.; Zavattieri, P.; Kisailus, D. Ecologically driven ultrastructural and hydrodynamic designs in stomatopod cuticles. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, J.; Murata, S.; Hosseini, M.S.; Trikanad, A.A.; James, R.; Pickle, A.; Yaraghi, N.; Matsumoto, N.; Yang, W.; Parkinson, D.Y.; et al. Structural design variations in beetle elytra. Adv. Funct. 2021, 31, 2106468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, J.; Hosseini, M.S.; Restrepo, D.; Murata, S.; Vasile, D.; Parkinson, D.Y.; Barnard, H.S.; Arakaki, A.; Zavattieri, P.; Kisailus, D. Toughening mechanisms of the elytra of the diabolical ironclad beetle. Nature 2020, 586, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Bhushan, B. Structure and mechanical properties of beetle wings: A review. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 12606–12623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalet, J.M.; Sprouse, P.A.; Schroeder, J.D.; Dittmer, N.; Kramer, K.J.; Kanost, M.R.; Gehrke, S.H. Temporal changes in the physical and mechanical properties of beetle elytra during maturation. Acta Biomater. 2022, 151, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomakin, J.; Huber, P.A.; Eichler, C.; Arakane, Y.; Kramer, K.J.; Beeman, R.W.; Kanost, M.R.; Gehrke, S.H. Mechanical properties of the beetle elytron, a biological composite material. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Yang, Z. Macro-/micro-structures of elytra, mechanical properties of the biomaterial and the coupling strength between elytra in beetles. J. Bionic Eng. 2010, 7, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuo, Z.; Yang, K.; Ma, S.; Cui, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liang, Y.; Liu, C.; Lin, Z.; Han, Z.; et al. Multi-Level Structural Enhancement Mechanism of the Excellent Mechanical Properties of Dung Beetle Femur-tibial joint. Small 2024, 20, 2311588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shima, D.; Gan, J.H.; Umezu, S.; Sato, H. Smooth and slipless walking mechanism inspired by the open–close cycle of a beetle claw. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2020, 16, 016011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadein, K.; Gorb, S. Smart joints: Auto-cleaning mechanism in the legs of beetles. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linz, D.M.; Hu, Y.; Moczek, A.P. The origins of novelty from within the confines of homology: The developmental evolution of the digging tibia of dung beetles. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 286, 20182427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadein, K.; Kovalev, A.; Gorb, S.N. Jumping mechanism in the marsh beetles (Coleoptera: Scirtidae). Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran-Ngoc, P.T.; Lim, L.Z.; Gan, J.H.; Wang, H.; Vo-Doan, T.T.; Sato, H. A robotic leg inspired from an insect leg. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2022, 17, 056008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.; Zhang, C.; He, J.; Yue, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiao, D. Observation and analysis of diving beetle movements while swimming. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, C.; Bhushan, B. A review of beetle hindwings: Structure, mechanical properties, mechanism and bioinspiration. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. 2019, 94, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, J.; Valdez, J.W. Locomotion with a twist: Aquatic beetle walks upside down on the underside of the water’s surface. Ethology 2021, 127, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribera, I.; Foster, G.N.; Holt, W.V. Functional types of diving beetle (Coleoptera: Hygrobiidae and Dytiscidae), as identified by comparative swimming behaviour. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1997, 61, 537–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadein, K.; Betz, O. Jumping mechanisms and performance in beetles. II. Weevils (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Rhamphini). Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2018, 47, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadein, K.; Betz, O. Jumping mechanisms and performance in beetles. I. Flea beetles (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae: Alticini). J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219, 2015–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadein, K.; Kovalev, A.; Gorb, S. Tribological properties of the beetle leg joints. Friction 2024, 12, 2791–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadein, K.; Gorb, S. Abrasive wear in the leg joints of insects. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 11, 2300743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadein, K.; Kovalev, A.; Thøgersen, J.; Weidner, T.; Gorb, S. Insects use lubricants to minimize friction and wear in leg joints. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2021, 288, 20211065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadein, K.; Gorb, S. Lubrication in the joints of insects (Arthropoda: Insecta). J. Zool. 2022, 316, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippov, A.E.; Nadein, K.; Gorb, S.N.; Kovalev, A. Solid lubricant in the insect leg joints: Numerical simulation of tribological properties. Adv. Theor. Simul. 2024, 7, 2400348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippov, A.E.; Nadein, K.; Gorb, S.N.; Kovalev, A. Bio-bearings: Numerical model of the solid lubricant in the leg joints of insects. Tribol. Lett. 2024, 72, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippov, A.E.; Nadein, K.; Gorb, S.N.; Kovalev, A. Large-scale numerical simulation of the solid lubricant behaviour in the leg joints of insects. Adv. Theor. Simul. 2024, 7, 2301236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, J.; Wang, Y.; Lin, S.; Tuo, Z.; Lin, Z.; Liang, Y.; Ren, L. Bionic Design of High-Performance Joints: Differences in Failure Mechanisms Caused by the Different Structures of Beetle Femur–Tibial Joints. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9100605
Cui J, Wang Y, Lin S, Tuo Z, Lin Z, Liang Y, Ren L. Bionic Design of High-Performance Joints: Differences in Failure Mechanisms Caused by the Different Structures of Beetle Femur–Tibial Joints. Biomimetics. 2024; 9(10):605. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9100605
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Jiandong, Yubo Wang, Sen Lin, Zhiwei Tuo, Zhaohua Lin, Yunhong Liang, and Luquan Ren. 2024. "Bionic Design of High-Performance Joints: Differences in Failure Mechanisms Caused by the Different Structures of Beetle Femur–Tibial Joints" Biomimetics 9, no. 10: 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9100605
APA StyleCui, J., Wang, Y., Lin, S., Tuo, Z., Lin, Z., Liang, Y., & Ren, L. (2024). Bionic Design of High-Performance Joints: Differences in Failure Mechanisms Caused by the Different Structures of Beetle Femur–Tibial Joints. Biomimetics, 9(10), 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9100605





