Energy-Efficient Spiking Segmenter for Frame and Event-Based Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
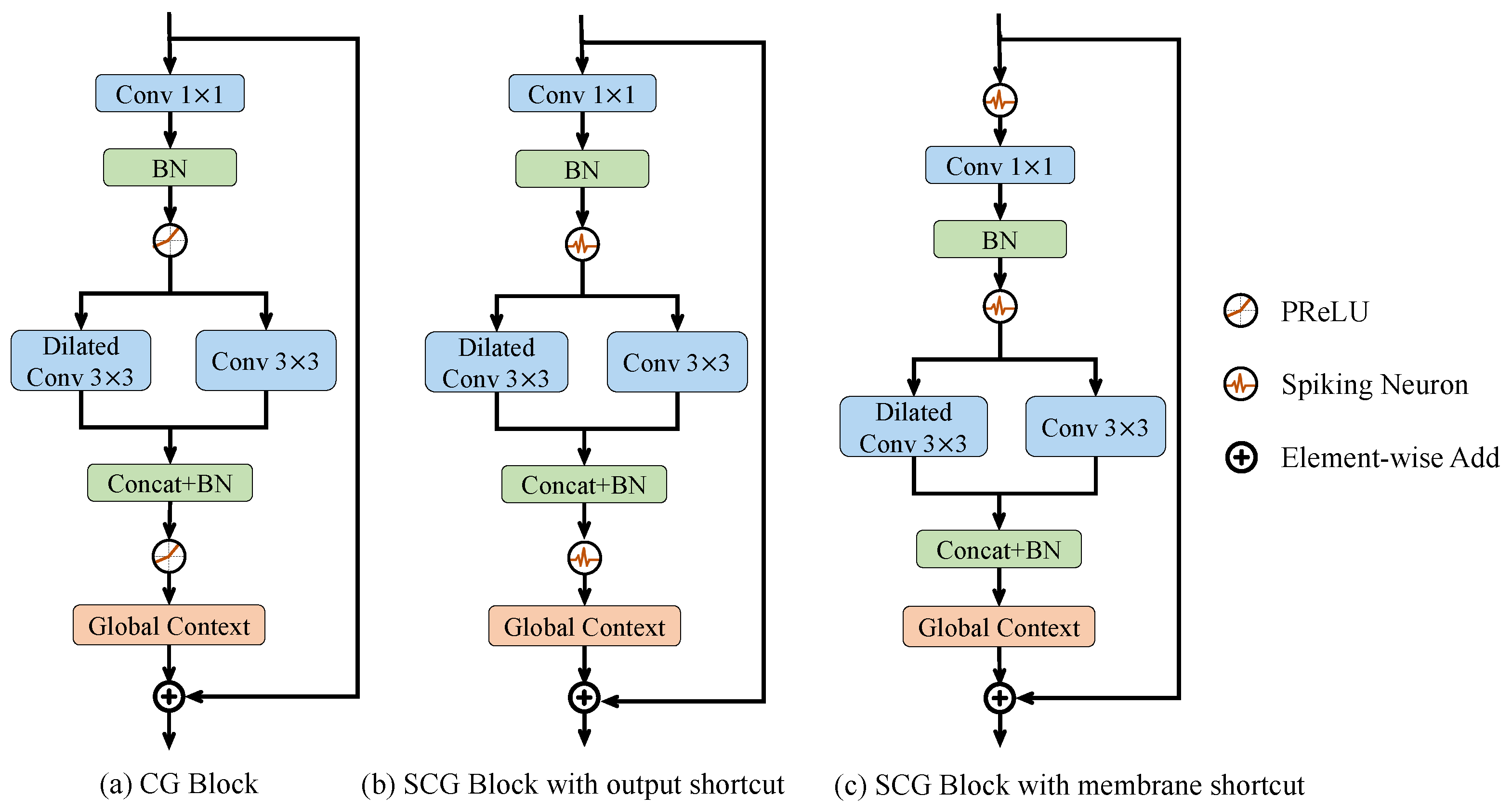
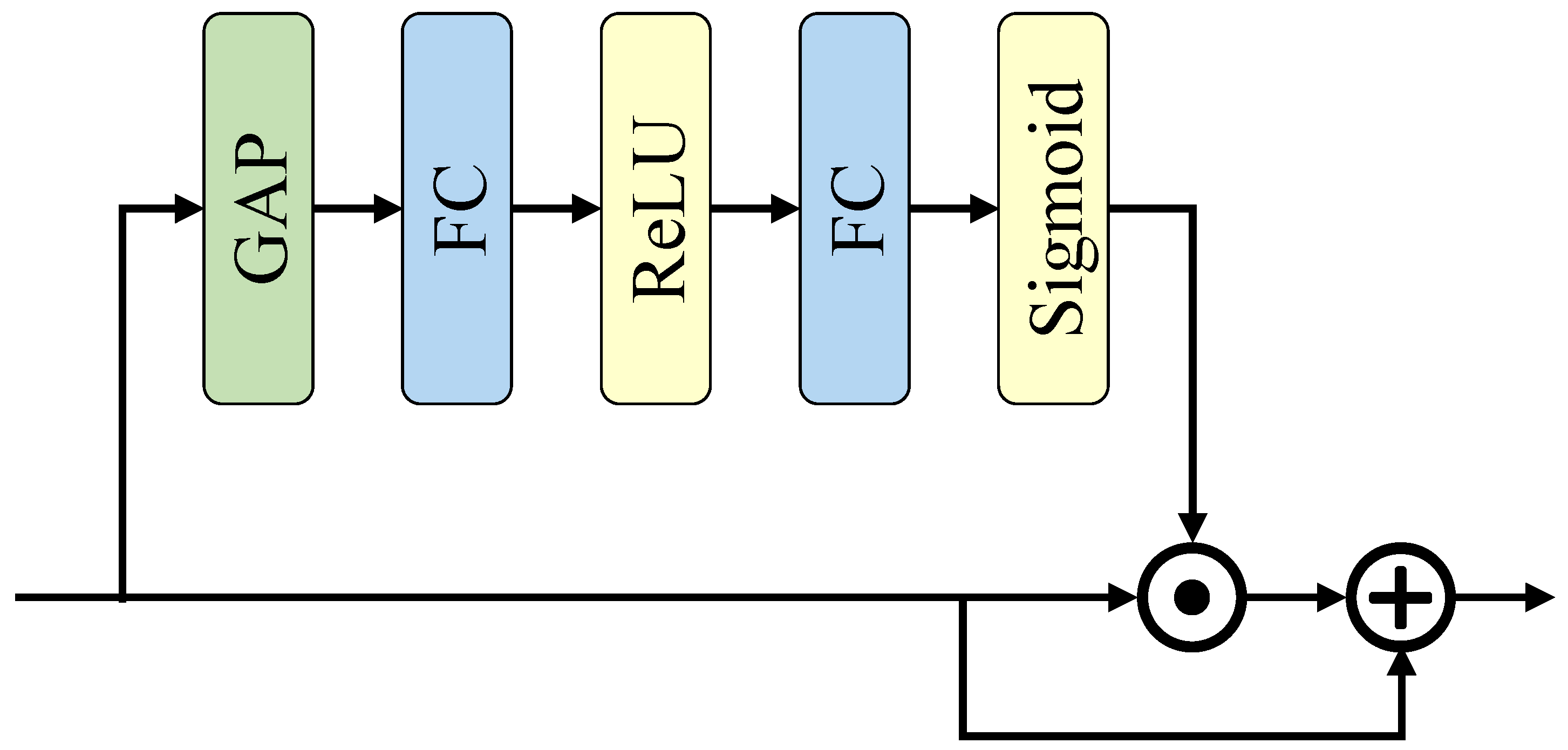
- This paper proposes a spiking context-guided block with spiking neurons and membrane shortcut connections to learn local feature and contextual information under the SNN computing paradigm. Furthermore, to learn global context better, the global context extractor is revised to refine the feature with minimal energy cost.
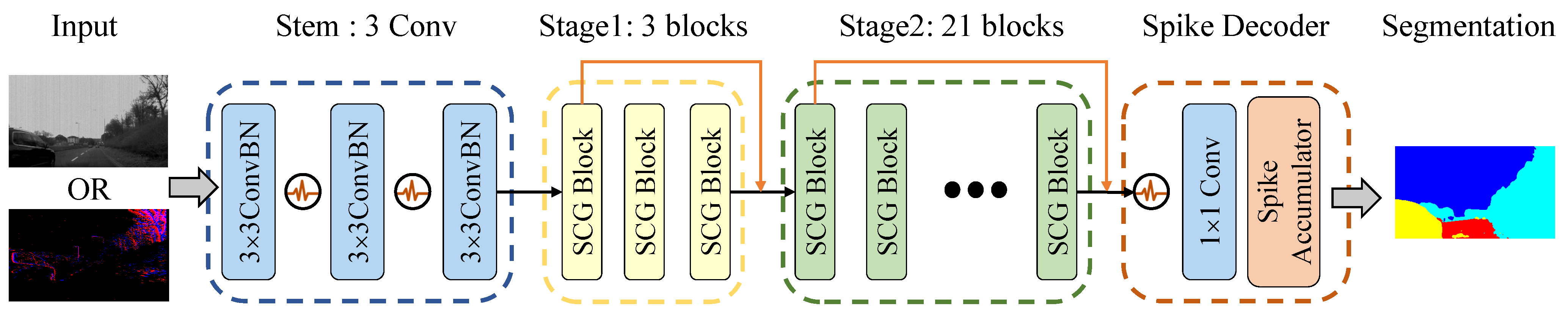
- This paper designs appropriate input representations and encoding layers for both frame and event-based images, respectively. On this basis, the direct-training Spiking CGNet is established with several modifications from ANN CGNet, including the stem network, multi-scale membrane connection, and the spike decoder.
- This paper validates the performance of Spiking CGNet by comparing it to the ANN and SNN segmenters in the literature on the frame-based Cityscapes dataset and event-based DAVIS driving dataset 2017 (DDD17).
2. Related Works
2.1. Semantic Segmentation
2.2. Spiking Neural Networks
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Spiking Neuron Model
3.2. Input Representation
3.3. Spiking Context Guided Block
3.3.1. SCG Block with Output and Membrane Shortcut
3.3.2. Global Context Extractor
3.4. Spiking Context Guided Network
3.5. Overall Training Algorithm
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Experimentall Settings
4.1.1. Cityscapes Dataset
4.1.2. DDD17 Dataset
4.1.3. Implementation Details
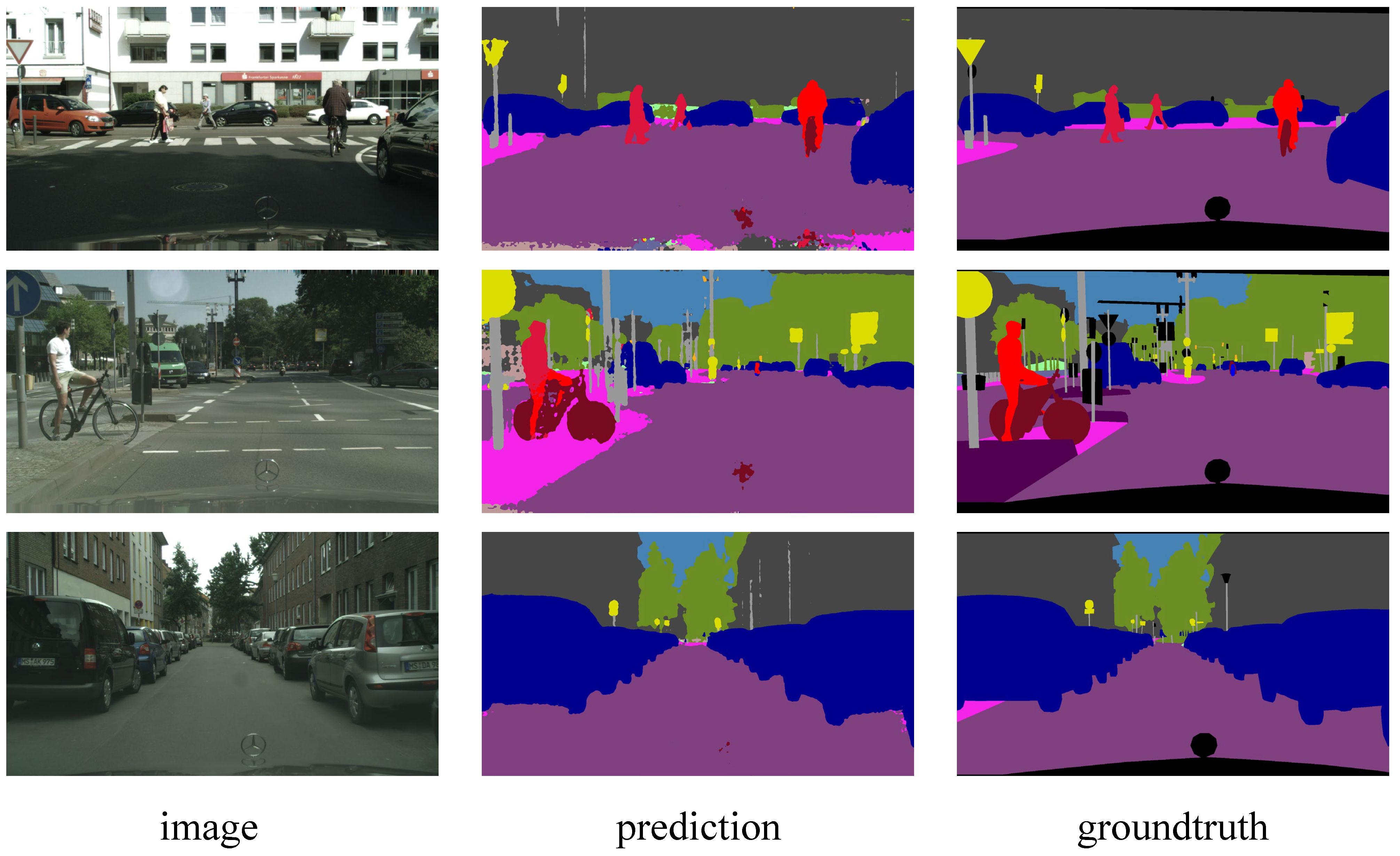
4.2. Comparisons on Cityscapes
4.3. Comparisons on DDD17
4.4. Ablation Studies
4.4.1. Energy Analysis
4.4.2. Effect of Global Context Extractor
5. Conclusions and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANN | Artificial neural network |
| SNN | Spiking neural network |
| Spiking CGNet | Spiking context-guided network |
| CGNet | Context-guided network |
| DVS | Dynamic vision sensors |
| PReLU | Parametric rectified linear unit |
| IF | Integrate-and-fire |
| LIF | Leaky integrate-and-fire |
| PLIF | Parametric leaky integrate-and-fire |
| GCE | Global context extractor |
| mIoU | Mean intersection over union |
| MAC | Multiply-and-accumulate |
| AC | Accumulate |
References
- Wu, T.; Tang, S.; Zhang, R.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y. Cgnet: A light-weight context guided network for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 30, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, E.; Wang, W.; Yu, Z.; Anandkumar, A.; Alvarez, J.M.; Luo, P. SegFormer: Simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 12077–12090. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; He, B.; Zhang, Y. Isomorphic model-based initialization for convolutional neural networks. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2022, 89, 103677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Binas, J.; Neil, D.; Liu, S.C.; Delbruck, T. DDD17: End-to-end DAVIS driving dataset. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.01458. [Google Scholar]
- Merolla, P.A.; Arthur, J.V.; Alvarez-Icaza, R.; Cassidy, A.S.; Sawada, J.; Akopyan, F.; Jackson, B.L.; Imam, N.; Guo, C.; Nakamura, Y.; et al. A million spiking-neuron integrated circuit with a scalable communication network and interface. Science 2014, 345, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.; Srinivasa, N.; Lin, T.H.; Chinya, G.; Cao, Y.; Choday, S.H.; Dimou, G.; Joshi, P.; Imam, N.; Jain, S.; et al. Loihi: A neuromorphic manycore processor with on-chip learning. IEEE Micro 2018, 38, 82–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstner, W.; Kistler, W.M. Spiking Neuron Models: Single Neurons, Populations, Plasticity; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Rueckauer, B.; Lungu, I.A.; Hu, Y.; Pfeiffer, M. Theory and tools for the conversion of analog to spiking convolutional neural networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1612.04052. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, T.; Ding, J.; Yu, Z.; Huang, T. Optimized Potential Initialization for Low-latency Spiking Neural Networks. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.01440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Gu, S. Optimal conversion of conventional artificial neural networks to spiking neural networks. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.00476. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zeng, Y. Efficient and Accurate Conversion of Spiking Neural Network with Burst Spikes. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.13271. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Park, S.; Na, B.; Yoon, S. Spiking-yolo: Spiking neural network for energy-efficient object detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 11270–11277. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, S.B.; Orchard, G. Slayer: Spike layer error reassignment in time. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 3–8 December 2018; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Neftci, E.O.; Mostafa, H.; Zenke, F. Surrogate gradient learning in spiking neural networks: Bringing the power of gradient-based optimization to spiking neural networks. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2019, 36, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Yu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Huang, T.; Masquelier, T.; Tian, Y. Deep residual learning in spiking neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 21056–21069. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Deng, L.; Li, G. Advancing residual learning towards powerful deep spiking neural networks. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.08954. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.07122. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.; Milan, A.; Shen, C.; Reid, I. Refinenet: Multi-path refinement networks for high-resolution semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1925–1934. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015. Part III 18. pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Pohlen, T.; Hermans, A.; Mathias, M.; Leibe, B. Full-resolution residual networks for semantic segmentation in street scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4151–4160. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Wang, J.; Peng, C.; Gao, C.; Yu, G.; Sang, N. Bisenet: Bilateral segmentation network for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 325–341. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Gao, C.; Wang, J.; Yu, G.; Shen, C.; Sang, N. Bisenet v2: Bilateral network with guided aggregation for real-time semantic segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 3051–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Pan, H.; Sun, W.; Jia, Y. Deep dual-resolution networks for real-time and accurate semantic segmentation of road scenes. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.06085. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Xiong, Z.; Bhattacharyya, S.P. PIDNet: A Real-Time Semantic Segmentation Network Inspired by PID Controllers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 19529–19539. [Google Scholar]
- Kugele, A.; Pfeil, T.; Pfeiffer, M.; Chicca, E. Hybrid SNN-ANN: Energy-Efficient Classification and Object Detection for Event-Based Vision. In Proceedings of the DAGM German Conference on Pattern Recognition, Online, 28 September 28–1 October 2021; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2021; pp. 297–312. [Google Scholar]
- Kumaar, S.; Lyu, Y.; Nex, F.; Yang, M.Y. CABiNet: Efficient Context Aggregation Network for Low-Latency Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 13517–13524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Strudel, R.; Garcia, R.; Laptev, I.; Schmid, C. Segmenter: Transformer for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 7262–7272. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, B.; Misra, I.; Schwing, A.G.; Kirillov, A.; Girdhar, R. Masked-attention Mask Transformer for Universal Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhu, Y.; He, C.; Wang, Y.; Yan, S.; Tian, Y.; Yuan, L. Spikformer: When Spiking Neural Network Meets Transformer. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations, Kigali, Rwanda, 1–5 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, I.; Murillo, A.C. EV-SegNet: Semantic segmentation for event-based cameras. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1251–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Gehrig, D.; Gehrig, M.; Hidalgo-Carrió, J.; Scaramuzza, D. Video to events: Recycling video datasets for event cameras. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 3586–3595. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Chae, Y.; Yoon, K.J. Dual transfer learning for event-based end-task prediction via pluggable event to image translation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 2135–2145. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Messikommer, N.; Gehrig, D.; Scaramuzza, D. Ess: Learning event-based semantic segmentation from still images. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2022: 17th European Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2022. Part XXXIV. pp. 341–357. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, W.; Yu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Masquelier, T.; Huang, T.; Tian, Y. Incorporating learnable membrane time constant to enhance learning of spiking neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 2661–2671. [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta, A.; Ye, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, C.; Roy, K. Going deeper in spiking neural networks: VGG and residual architectures. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Bu, T.; Ding, J.; Huang, T.; Yu, Z. Reducing ANN-SNN Conversion Error through Residual Membrane Potential. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.02091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Deng, L.; Li, G.; Zhu, J.; Shi, L. Spatio-temporal backpropagation for training high-performance spiking neural networks. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Sarwar, S.S.; Panda, P.; Srinivasan, G.; Roy, K. Enabling spike-based backpropagation for training deep neural network architectures. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wu, Y.; Deng, L.; Hu, Y.; Li, G. Going deeper with directly-trained larger spiking neural networks. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 11062–11070. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Panda, P. Revisiting batch normalization for training low-latency deep spiking neural networks from scratch. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, M.; Gao, H.; Zhao, G.; Wang, D.; Lin, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, G. Temporal-wise attention spiking neural networks for event streams classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10221–10230. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, M.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Y.; Deng, L.; Tian, Y.; Xu, B.; Li, G. Attention spiking neural networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 9393–9410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miquel, J.R.; Tolu, S.; Schöller, F.E.; Galeazzi, R. Retinanet object detector based on analog-to-spiking neural network conversion. In Proceedings of the 2021 8th International Conference on Soft Computing & Machine Intelligence (ISCMI), Cario, Egypt, 26–27 November 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 201–205. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, B.; She, X.; Mukhopadhyay, S. A fully spiking hybrid neural network for energy-efficient object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 9014–9029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordone, L.; Miramond, B.; Thierion, P. Object Detection with Spiking Neural Networks on Automotive Event Data. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.04339. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.; Kosta, A.K.; Zhu, A.Z.; Chaney, K.; Daniilidis, K.; Roy, K. Spike-flownet: Event-based optical flow estimation with energy-efficient hybrid neural networks. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2020. Part XXIX 16. pp. 366–382. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Lv, H.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Liu, H.; Bi, G. Event-Based Optical Flow Estimation with Spatio-Temporal Backpropagation Trained Spiking Neural Network. Micromachines 2023, 14, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado, J.; Rançon, U.; Cottereau, B.; Barranco, F.; Masquelier, T. Optical flow estimation with event-based cameras and spiking neural networks. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.06492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Xu, M.; Yuan, C.; Cao, X.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, T.; Feng, Q. Siamsnn: Siamese spiking neural networks for energy-efficient object tracking. In Proceedings of the Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning—ICANN 2021: 30th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, Bratislava, Slovakia, 14–17 September 2021; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2021. Part V 30. pp. 182–194. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Otto, R.; Bing, Z.; Huang, K.; Knoll, A. Target Tracking Control of a Wheel-less Snake Robot Based on a Supervised Multi-layered SNN. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 October 2020–24 January 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 7124–7130. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Chough, J.; Panda, P. Beyond classification: Directly training spiking neural networks for semantic segmentation. Neuromorphic Comput. Eng. 2022, 2, 044015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A.; Chaurasia, A.; Kim, S.; Culurciello, E. Enet: A deep neural network architecture for real-time semantic segmentation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.02147. [Google Scholar]
- Cordts, M.; Omran, M.; Ramos, S.; Rehfeld, T.; Enzweiler, M.; Benenson, R.; Franke, U.; Roth, S.; Schiele, B. The Cityscapes Dataset for Semantic Urban Scene Understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, W.; Chen, Y.; Ding, J.; Chen, D.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Tian, Y. SpikingJelly. 2020. Available online: https://github.com/fangwei123456/spikingjelly (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romera, E.; Alvarez, J.M.; Bergasa, L.M.; Arroyo, R. Efficient convnet for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 11–14 June 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1789–1794. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, S.; Rastegari, M.; Caspi, A.; Shapiro, L.; Hajishirzi, H. Espnet: Efficient spatial pyramid of dilated convolutions for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 552–568. [Google Scholar]
- Nirkin, Y.; Wolf, L.; Hassner, T. HyperSeg: Patch-Wise Hypernetwork for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition—CVPR 2021, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 4061–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Pool, J.; Tran, J.; Dally, W. Learning both weights and connections for efficient neural network. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; Volume 28. [Google Scholar]
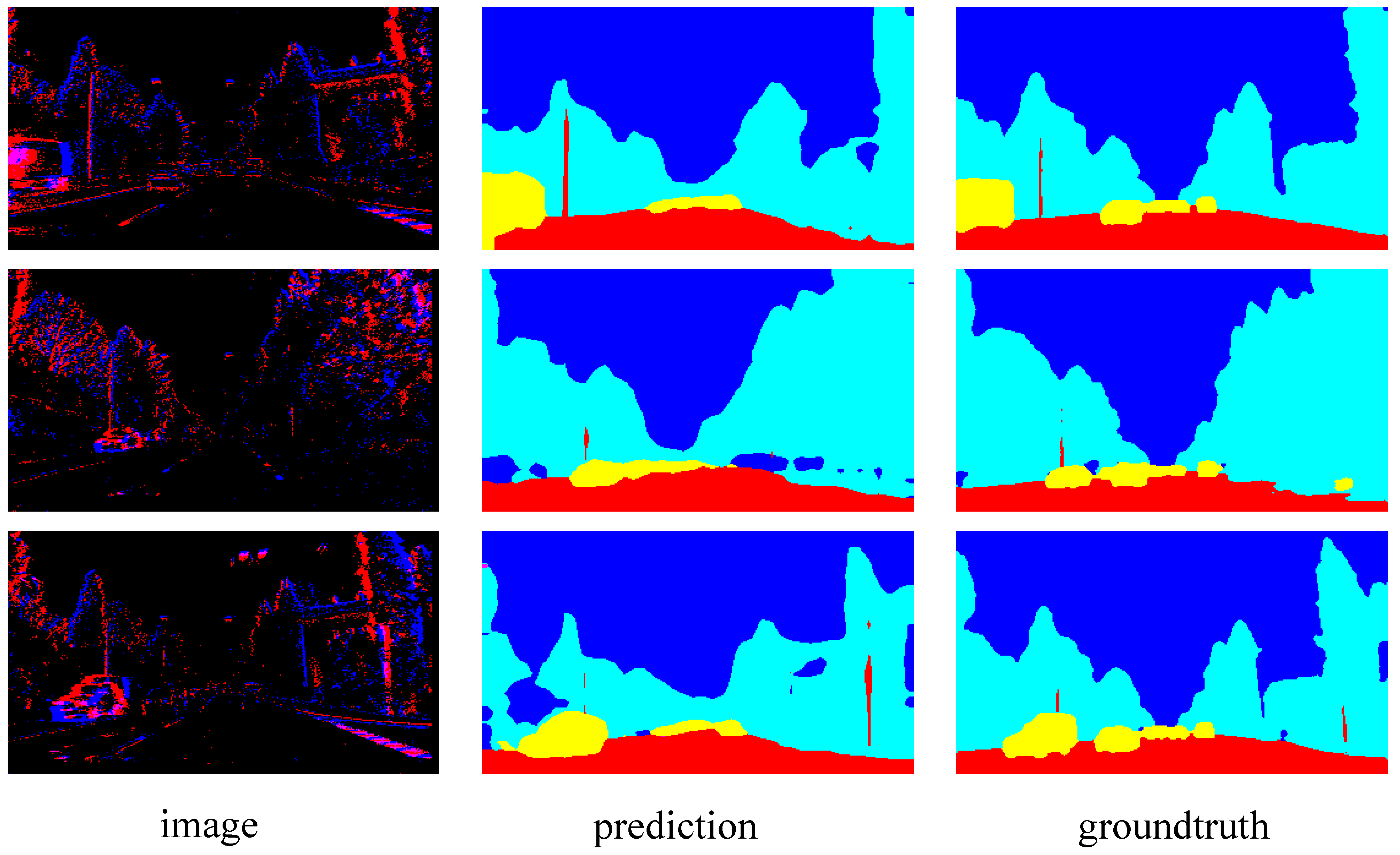
| Method | Network Type | Time Steps | Parameters (M) | FLOPS_MAC(G) | FLOPS_AC(G) | mIoU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SegNet [63] | ANN | - | 29.5 | 286.0 | 0 | 56.1 |
| ENet [60] | ANN | - | 0.4 | 3.8 | 0 | 58.3 |
| ERFNet [64] | ANN | - | 2.1 | 21.0 | 0 | 68.0 |
| ESPNet [65] | ANN | - | 0.4 | 4.0 | 0 | 60.3 |
| BiSeNet [25] | ANN | - | 5.8 | 5.2 | 0 | 68.4 |
| BiSeNetV2 [26] | ANN | - | - | 16.5 | 0 | 72.6 |
| CABiNet [30] | ANN | - | 2.6 | 2.3 | 0 | 75.9 |
| HyperSeg-S [66] | ANN | - | 10.2 | 5.9 | 0 | 78.1 |
| DDRNet-39 [27] | ANN | - | 32.3 | 54.9 | 0 | 80.4 |
| PIDNet-L [28] | ANN | - | 36.9 | 53.9 | 0 | 80.6 |
| CGNet [1] | ANN | - | 0.5 | 6.0 | 0 | 64.8 |
| SCGNet-S (ours) | SNN | 4 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 5.1 | 62.5 |
| SCGNet-L (ours) | SNN | 4 | 1.9 | 0.2 | 20.2 | 66.5 |
| Method | Time-Steps | mIoU (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Spiking DeepLab | 20 | 33.70 |
| Spiking FCN | 20 | 34.20 |
| SCGNet-S (ours) | 4 | 49.27 |
| SCGNet-L (ours) | 4 | 51.42 |
| Operation | Energy (pJ) |
|---|---|
| MULT | 3.7 |
| ADD | 0.9 |
| MAC (MULT + ADD) | 4.6 |
| AC (ADD) | 0.9 |
| 32bit-FP: MAC 4.6 pJ AC 0.9 pJ | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Network Type | Parameters | MACs | ACs | Energy | mIoU | |
| CGNet | ANN | 0.50 M | 6.87 G | 0 G | pJ | 1× (reference) | 64.80 |
| SCGNet-S (ours) | SNN | 0.49 M | 0.14 G | 6.50 G | pJ | 4.85× | 62.50 |
| SCGNet-L (ours) | SNN | 1.85 M | 0.28 G | 25.89 G | pJ | 1.29× | 66.55 |
| Network | With GCE | Energy | mIoU |
|---|---|---|---|
| SCGNet-S | ✗ | pJ | 61.06 |
| SCGNet-S | ✓ | pJ | 62.50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Fan, X.; Zhang, Y. Energy-Efficient Spiking Segmenter for Frame and Event-Based Images. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8040356
Zhang H, Fan X, Zhang Y. Energy-Efficient Spiking Segmenter for Frame and Event-Based Images. Biomimetics. 2023; 8(4):356. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8040356
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hong, Xiongfei Fan, and Yu Zhang. 2023. "Energy-Efficient Spiking Segmenter for Frame and Event-Based Images" Biomimetics 8, no. 4: 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8040356
APA StyleZhang, H., Fan, X., & Zhang, Y. (2023). Energy-Efficient Spiking Segmenter for Frame and Event-Based Images. Biomimetics, 8(4), 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8040356





