Design for Robustness: Bio-Inspired Perspectives in Structural Engineering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design for Robustness
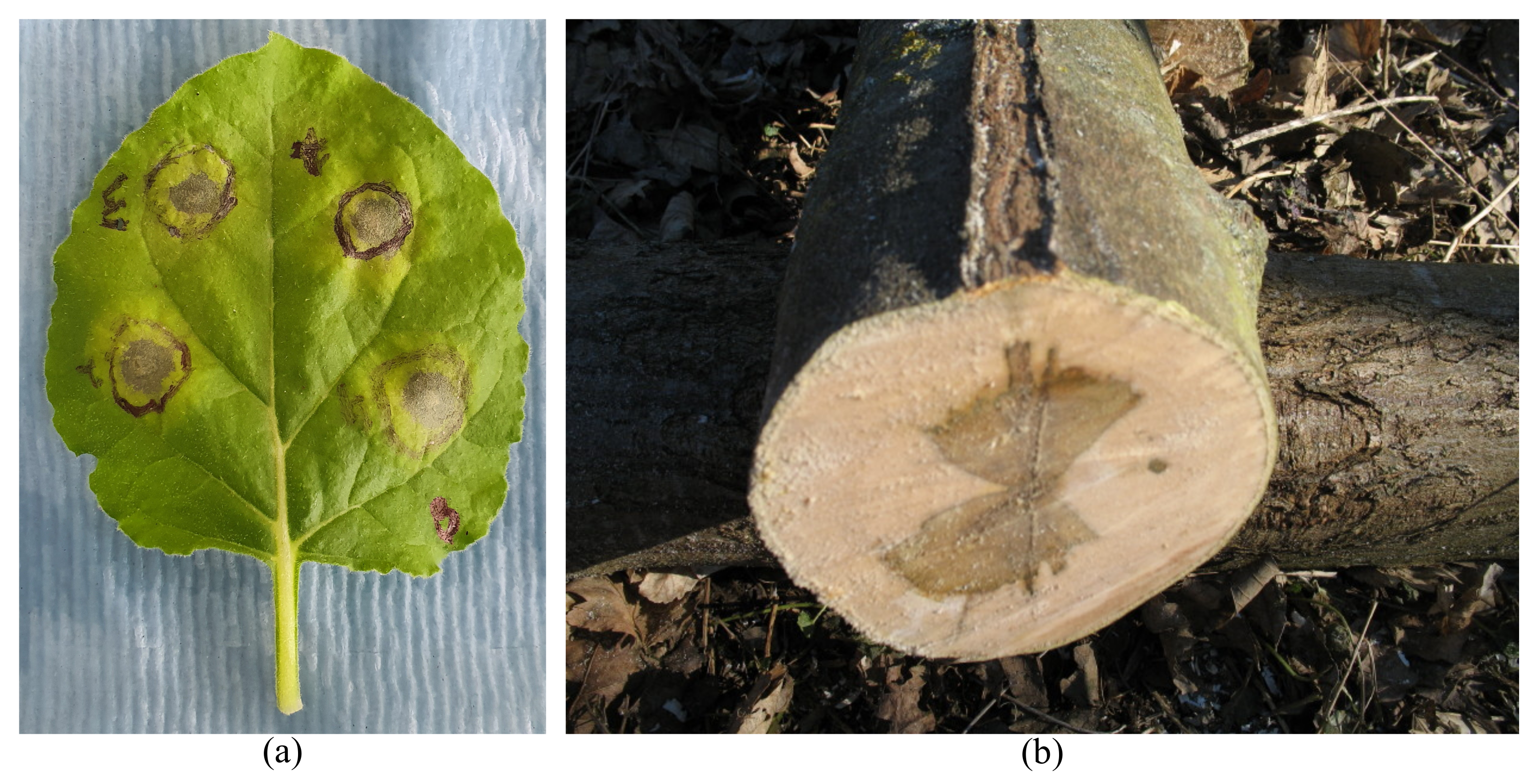
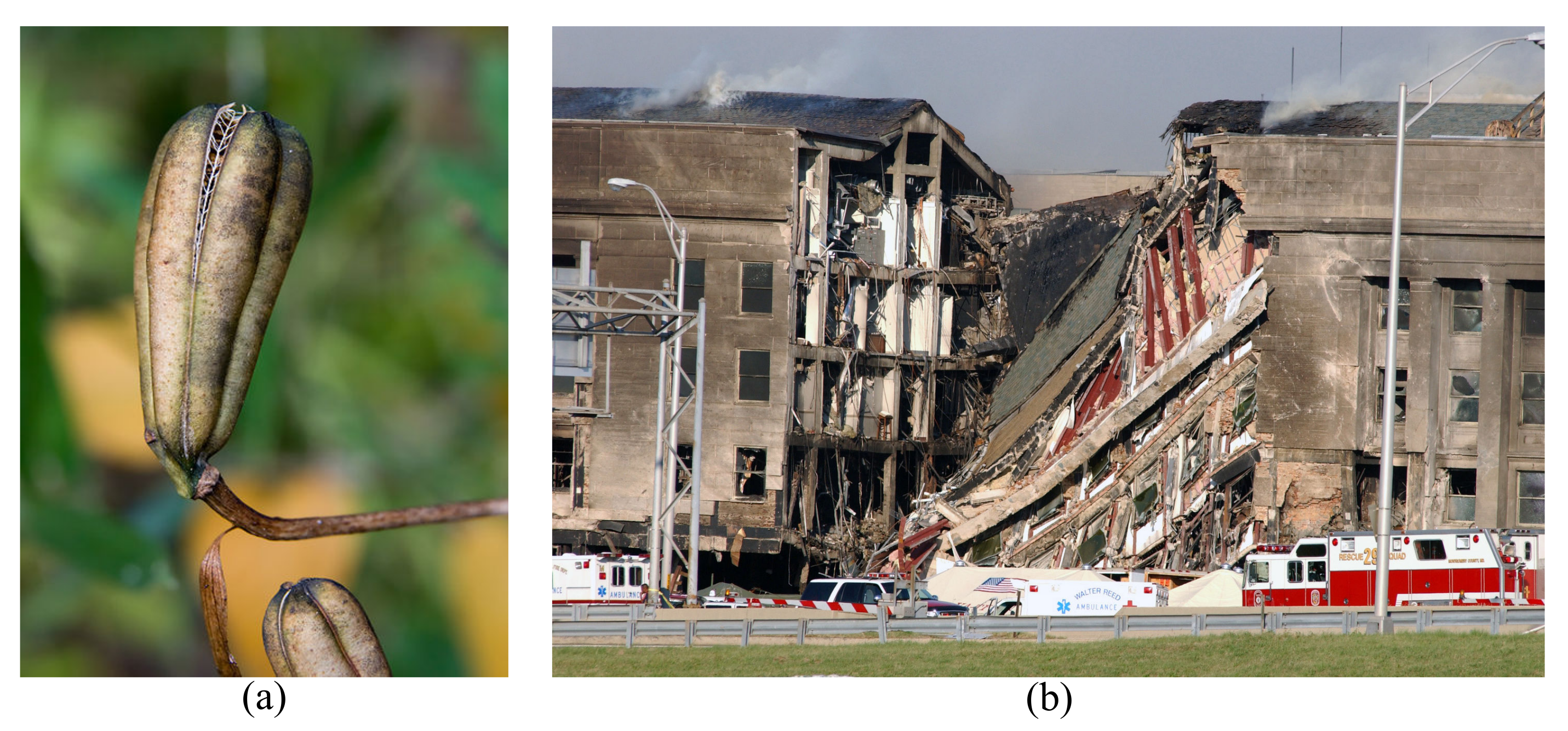
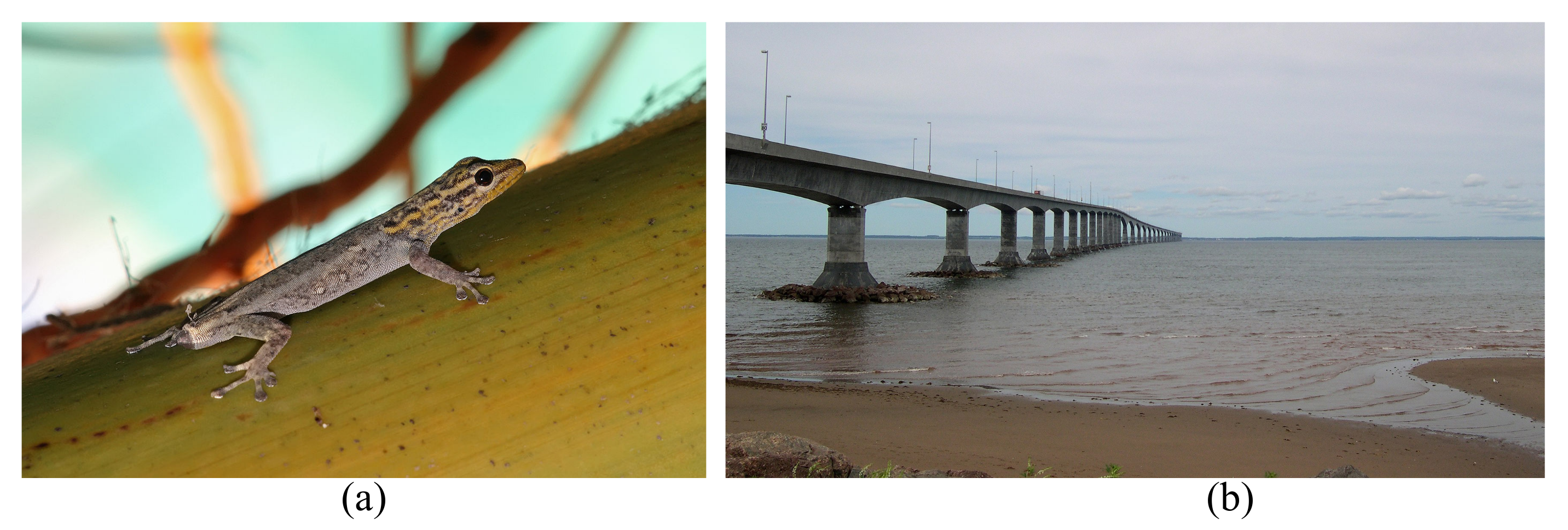
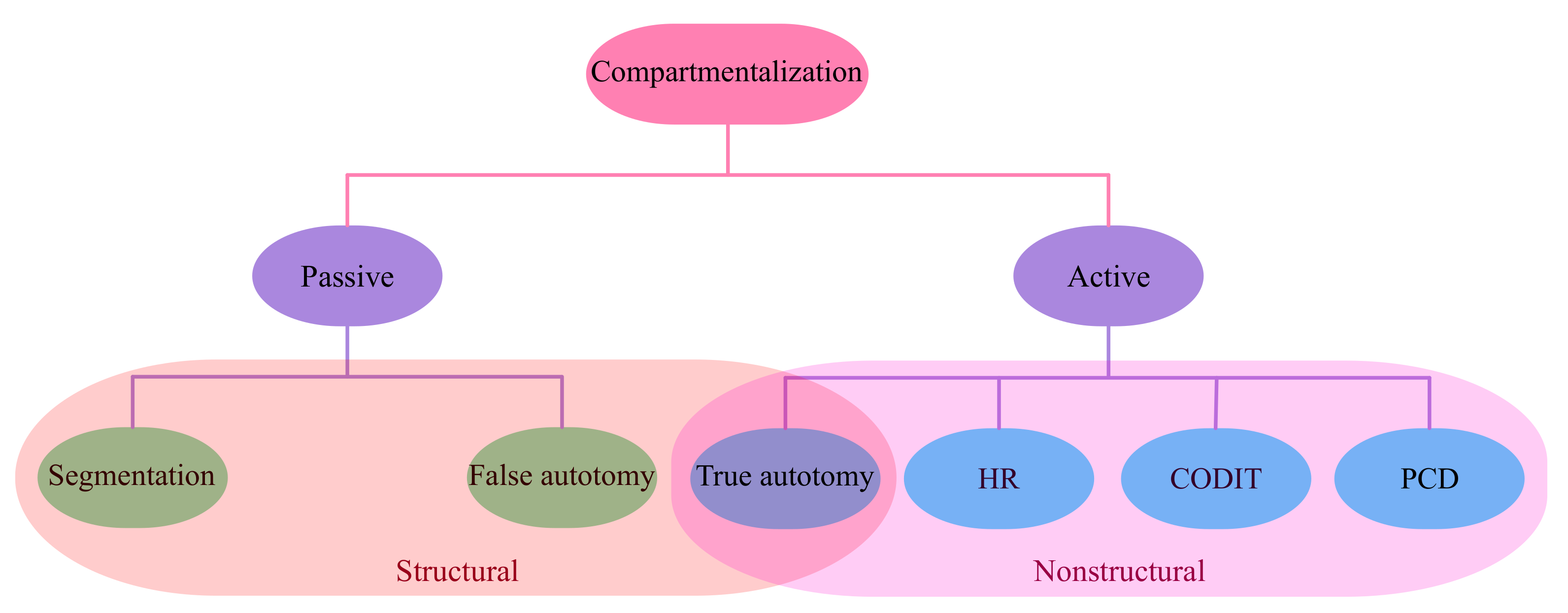
2.1. Compartmentalization
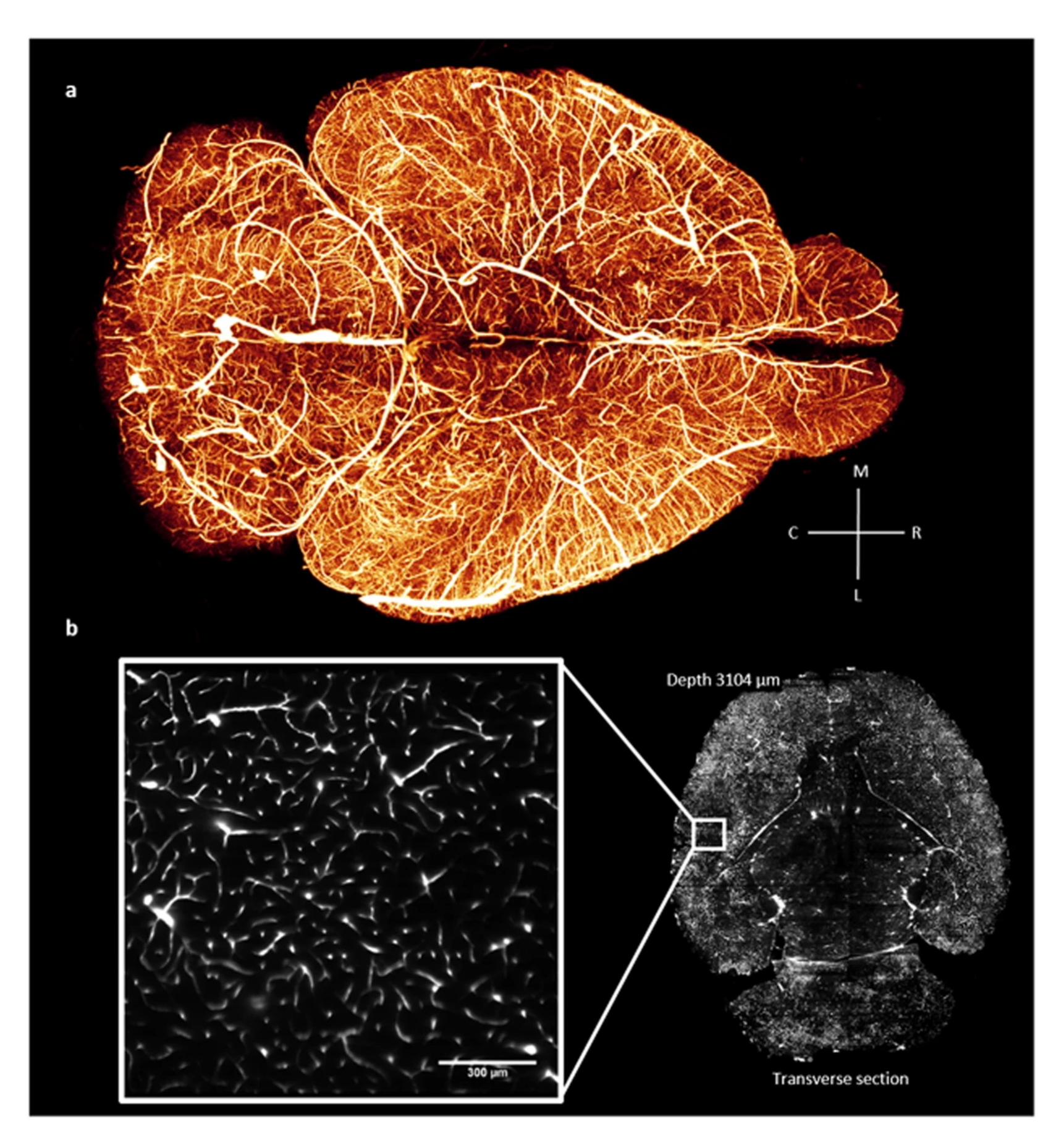
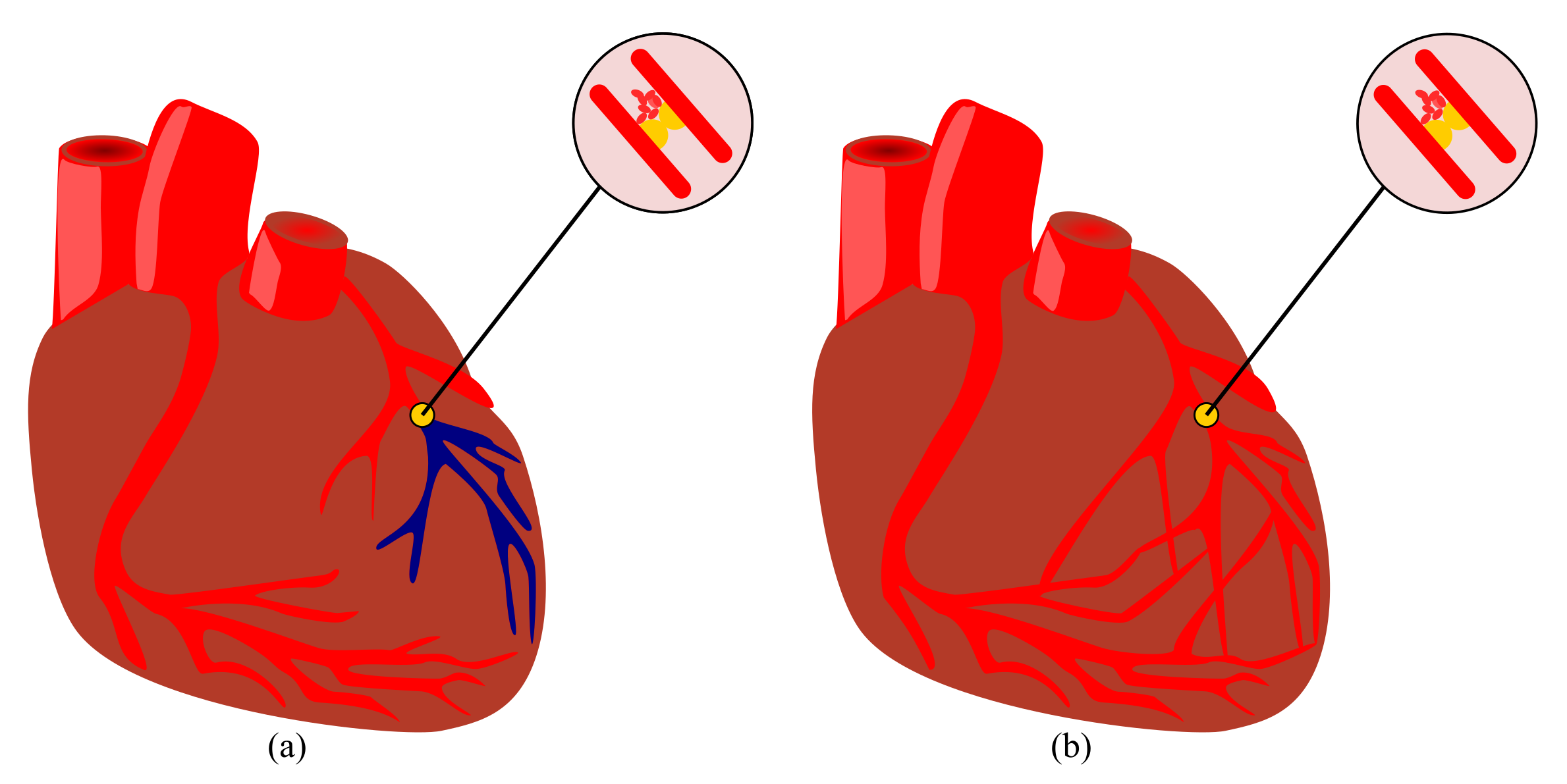
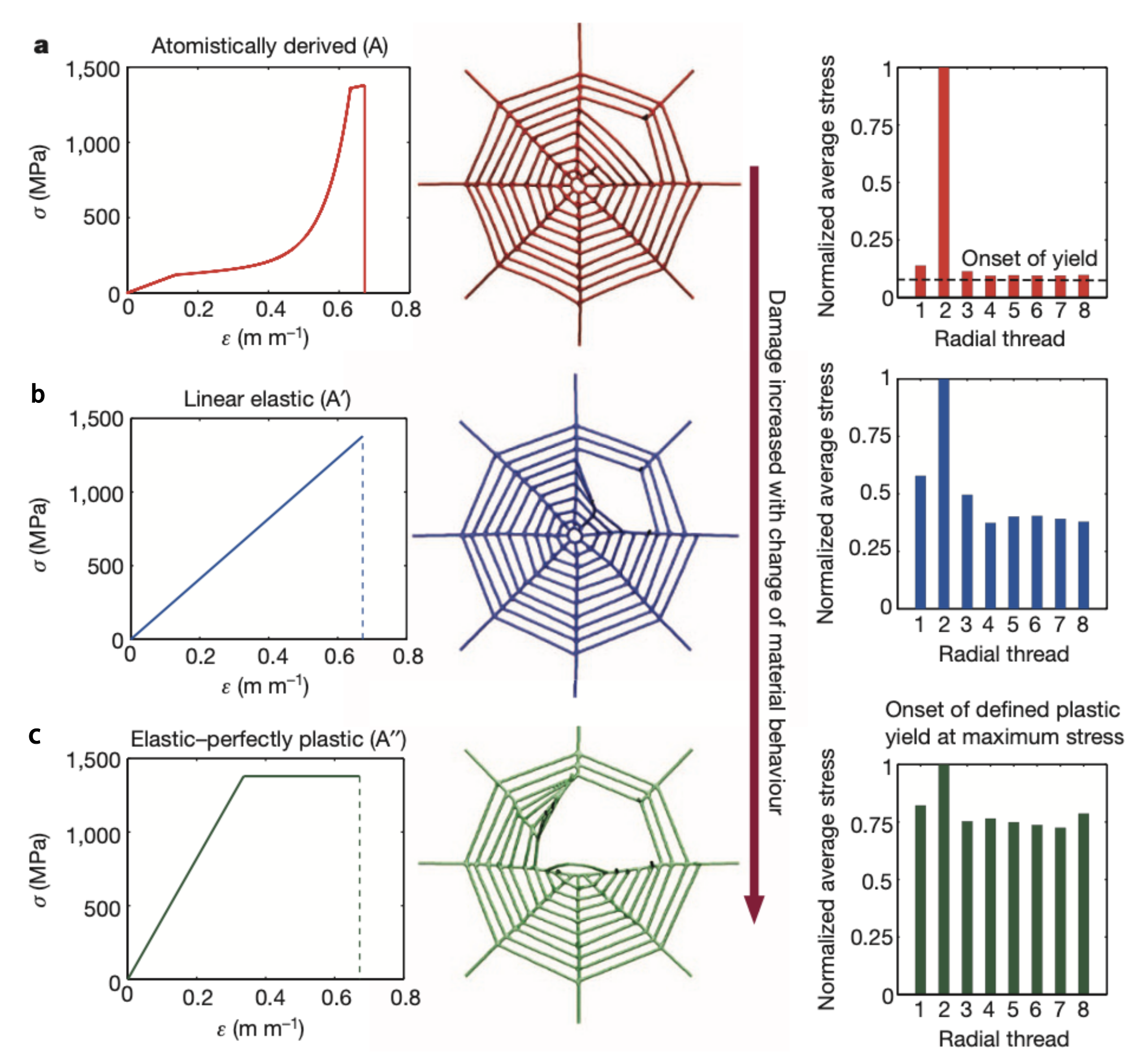
2.2. Complexity
3. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Badarnah, L.; Kadri, U. A methodology for the generation of biomimetic design concepts. Archit. Sci. Rev. 2015, 58, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zari, M.P. Biomimetic approaches to architectural design for increased sustainability. In Proceedings of the SB07 NZ Sustainable Building Conference, Auckland, New Zealand, 14–16 November 2007; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, G.; Zou, H.X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, L.C.; Wu, Z.Y.; Zhang, W.M. Bio-inspired vibration isolation: Methodology and design. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2021, 73, 020801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Ha, N.; Lu, G. A review of recent research on bio-inspired structures and materials for energy absorption applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 181, 107496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Han, Q.; Zhang, J.; Han, Z.; Niu, S.; Ren, L. Advanced bio-inspired structural materials: Local properties determine overall performance. Mater. Today 2020, 41, 177–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, J.; Yu, T. Dynamic behaviors of bio-inspired structures: Design, mechanisms, and models. Eng. Struct. 2022, 265, 114490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.; Sagaseta, J.; Cormie, D.; Jones, A. Historical review of prescriptive design rules for robustness after the collapse of Ronan Point. Structures 2019, 20, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiakojouri, F.; Sheidaii, M.R.; De Biagi, V.; Chiaia, B. Progressive collapse of structures: A discussion on annotated nomenclature. Structures 2021, 29, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiakojouri, F.; De Biagi, V.; Chiaia, B.; Sheidaii, M.R. Progressive collapse of framed building structures: Current knowledge and future prospects. Eng. Struct. 2020, 206, 110061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiakojouri, F.; De Biagi, V.; Chiaia, B.; Sheidaii, M.R. Strengthening and retrofitting techniques to mitigate progressive collapse: A critical review and future research agenda. Eng. Struct. 2022, 262, 114274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starossek, U. Progressive Collapse of Structures, 2nd ed.; ICE Publishing: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Ma, L.; Broyd, T.; Chen, K. Digital twin and its implementations in the civil engineering sector. Autom. Constr. 2021, 130, 103838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bado, M.F.; Tonelli, D.; Poli, F.; Zonta, D.; Casas, J.R. Digital Twin for Civil Engineering Systems: An Exploratory Review for Distributed Sensing Updating. Sensors 2022, 22, 3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, L.; Chen, W.; Ye, J.; Li, G.Q. Review on quantitative measures of robustness for building structures against disproportionate collapse. Int. J. High-Rise Build. 2020, 9, 127–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozza, A.; Asprone, D.; Parisi, F.; Manfredi, G. Alternative resilience indices for city ecosystems subjected to natural hazards. Comput.-Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2017, 32, 527–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, H. Towards a Theory of Biological Robustness. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2007, 3, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesne, A. Robustness: Confronting lessons from physics and biology. Biol. Rev. 2008, 83, 509–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jen, E. Robust Design: A Repertoire of Biological, Ecological, and Engineering Case Studies; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tavakoli, H.; Kiakojouri, F. Progressive collapse of framed structures: Suggestions for robustness assessment. Sci. Iran. 2014, 21, 329–338. [Google Scholar]
- Parisi, F.; Balestrieri, C.; Asprone, D. Blast resistance of tuff stone masonry walls. Eng. Struct. 2016, 113, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Biagi, V.; Parisi, F.; Asprone, D.; Chiaia, B.; Manfredi, G. Collapse resistance assessment through the implementation of progressive damage in finite element codes. Eng. Struct. 2017, 136, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, F.; Scalvenzi, M. Progressive collapse assessment of gravity-load designed European RC buildings under multi-column loss scenarios. Eng. Struct. 2020, 209, 110001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T. Concrete for lunar base construction. In Proceedings of the Lunar Bases and Space Activities of the 21st Century; Lunar and Planetary Institute: Houston, TX, USA, 1985; pp. 381–390. [Google Scholar]
- Pandolfi, C.; Izzo, D. Biomimetics on seed dispersal: Survey and insights for space exploration. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2013, 8, 025003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilium Auratum. 2022. Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Lilium_auratum_01.jpg (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- The Pentagon. 2022. Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:DN-SD-03-11451.JPEG (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- Parry, D. Spider leg-muscles and the autotomy mechanism. J. Cell Sci. 1957, 3, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorana, V.C. Tail autotomy, functional conflicts and their resolution by a salamander. Nature 1977, 265, 533–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkie, I. Arm autotomy in brittlestars (Echinodermata: Ophiuroidea). J. Zool. 1978, 186, 311–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, A.W.; Kiama, S.G.; Seifert, M.G.; Goheen, J.R.; Palmer, T.M.; Maden, M. Skin shedding and tissue regeneration in African spiny mice (Acomys). Nature 2012, 489, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shtein, I.; Koyfman, A.; Eshel, A.; Bar-On, B. Autotomy in plants: Organ sacrifice in Oxalis leaves. J. R. Soc. Interface 2019, 16, 20180737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrall, M.; DeJong, J.T.; Martinez, A.; Wilson, D.W. Vertical pullout tests of orchard trees for bio-inspired engineering of anchorage and foundation systems. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2020, 16, 016009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autotomy. 2022. Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:White-headed_dwarf_gecko.jpg (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- Confederation Bridge. 2022. Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Bridge_to_PEI.jpg (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- Bateman, P.; Fleming, P. To cut a long tail short: A review of lizard caudal autotomy studies carried out over the last 20 years. J. Zool. 2009, 277, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baban, N.S.; Orozaliev, A.; Stubbs, C.J.; Song, Y.A. Biomimicking interfacial fracture behavior of lizard tail autotomy with soft microinterlocking structures. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2022, 17, 036002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisner, T.; Camazine, S. Spider leg autotomy induced by prey venom injection: An adaptive response to “pain”? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 3382–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tell, S.; Andersson, A.; Najafi, A.; Spencer Jr, B.F.; Karoumi, R. Real-time hybrid testing for efficiency assessment of magnetorheological dampers to mitigate train-induced vibrations in bridges. Int. J. Rail Transp. 2021, 10, 436–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.L.; Xu, Z.D.; Wang, C. Wind vibration control of stay cables using magnetorheological dampers under optimal equivalent control algorithm. J. Sound Vib. 2019, 443, 732–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigo, A.L. Compartmentalization: A conceptual framework for understanding how trees grow and defend themselves. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1984, 22, 189–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.T. Compartmentalization, resource allocation, and wood quality. Curr. For. Rep. 2015, 1, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.H.; Savina, M.; Du, J.; Devendran, A.; Ramakanth, K.K.; Tian, X.; Sim, W.S.; Mironova, V.V.; Xu, J. A sacrifice-for-survival mechanism protects root stem cell niche from chilling stress. Cell 2017, 170, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bursch, W.; Ellinger, A.; Gerner, C.; Fröhwein, U.; Schulte-Hermann, R. Programmed cell death (PCD): Apoptosis, autophagic PCD, or others? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 926, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenabeele, P.; Galluzzi, L.; Berghe, T.V.; Kroemer, G. Molecular mechanisms of necroptosis: An ordered cellular explosion. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 700–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, P.; Lu, M.; Petersen, S.; Ashkenazi, A. Apoptosis initiation through the cell-extrinsic pathway. Methods Enzymol. 2014, 544, 99–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hypersensitive Response. 2022. Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Plant_hypersensitive_response_lesions.jpg (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- Compartmentalization of Decay in Trees. 2022. Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:CODIT_example_4_-_Auró.JPG (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- Johnson, S. Emergence: The Connected Lives of Ants, Brains, Cities, and Software; Simon and Schuster: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- De Biagi, V.; Chiaia, B. Complexity and robustness of frame structures. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2013, 50, 3723–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, W. Science and complexity. In Facets of Systems Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991; pp. 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabási, A.L.; Albert, R. Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science 1999, 286, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Biagi, V.; Chiaia, B. Scaling in structural complexity. Complexity 2014, 20, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Biagi, V.; Chiaia, B.M. Damage tolerance in parallel systems. Int. J. Damage Mech. 2016, 25, 1040–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalvenzi, M.; Ravasini, S.; Brunesi, E.; Parisi, F. Progressive collapse fragility of substandard and earthquake-resistant precast RC buildings. Eng. Struct. 2023, 275, 115242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, H. Biological robustness. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 826–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, J.M.; Doyle, J. Complexity and robustness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 2538–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giovanna, A.P.; Tibo, A.; Silvestri, L.; Müllenbroich, M.C.; Costantini, I.; Allegra Mascaro, A.L.; Sacconi, L.; Frasconi, P.; Pavone, F.S. Whole-brain vasculature reconstruction at the single capillary level. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marder, E. Variability, compensation, and modulation in neurons and circuits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 15542–15548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, D.S.; Wymbs, N.F.; Rombach, M.P.; Porter, M.A.; Mucha, P.J.; Grafton, S.T. Task-based core-periphery organization of human brain dynamics. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2013, 9, e1003171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizusaki, B.E.; O’Donnell, C. Neural circuit function redundancy in brain disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2021, 70, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbell, S.P. Neutral theory in community ecology and the hypothesis of functional equivalence. Funct. Ecol. 2005, 19, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüthgen, N.; Klein, A.M. Functional complementarity and specialisation: The role of biodiversity in plant–pollinator interactions. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2011, 12, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, R.S.; Guevara, R.; Ribeiro, M.C.; Culot, L.; Bufalo, F.S.; Galetti, M. Functional redundancy and complementarities of seed dispersal by the last neotropical megafrugivores. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaper, W.; Schaper, J. Collateral Circulation: Heart, Brain, Kidney, Limbs; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traupe, T.; Gloekler, S.; de Marchi, S.F.; Werner, G.S.; Seiler, C. Assessment of the human coronary collateral circulation. Circulation 2010, 122, 1210–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Biagi, V. Structural behavior of a metallic truss under progressive damage. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2016, 82, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Biagi, V. Complexity and Robustness of Structures against Extreme Events. Ph.D. Thesis, Politecnico di Torino, Torino, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Wahab, M.; Jenkins, C. Mechanics in naturally compliant structures. Mech. Mater. 2007, 39, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansell, M.; Hansell, M.H. Animal Architecture; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Aoyanagi, Y.; Okumura, K. Simple model for the mechanics of spider webs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 038102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranford, S.W.; Tarakanova, A.; Pugno, N.M.; Buehler, M.J. Nonlinear material behaviour of spider silk yields robust webs. Nature 2012, 482, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Nature Solution | Structural Engineering Solution |
|---|---|
| Segmentation | Construction joints |
| False autotomy | Structural segmentation/compartmentalization |
| True autotomy/HR/ PCD | Possible use in next generation active robustness techniques |
| CODIT | Possible use in next generation self-compartmentalizing concrete-corrosion in steel |
| Collateral circulation | ALP method |
| HOT | Structural complexity |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kiakojouri, F.; De Biagi, V.; Abbracciavento, L. Design for Robustness: Bio-Inspired Perspectives in Structural Engineering. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8010095
Kiakojouri F, De Biagi V, Abbracciavento L. Design for Robustness: Bio-Inspired Perspectives in Structural Engineering. Biomimetics. 2023; 8(1):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8010095
Chicago/Turabian StyleKiakojouri, Foad, Valerio De Biagi, and Lorenza Abbracciavento. 2023. "Design for Robustness: Bio-Inspired Perspectives in Structural Engineering" Biomimetics 8, no. 1: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8010095
APA StyleKiakojouri, F., De Biagi, V., & Abbracciavento, L. (2023). Design for Robustness: Bio-Inspired Perspectives in Structural Engineering. Biomimetics, 8(1), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8010095







