Effect of Segment Types on Characterization of Soft Sensing Textile Actuators for Soft Wearable Robots
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
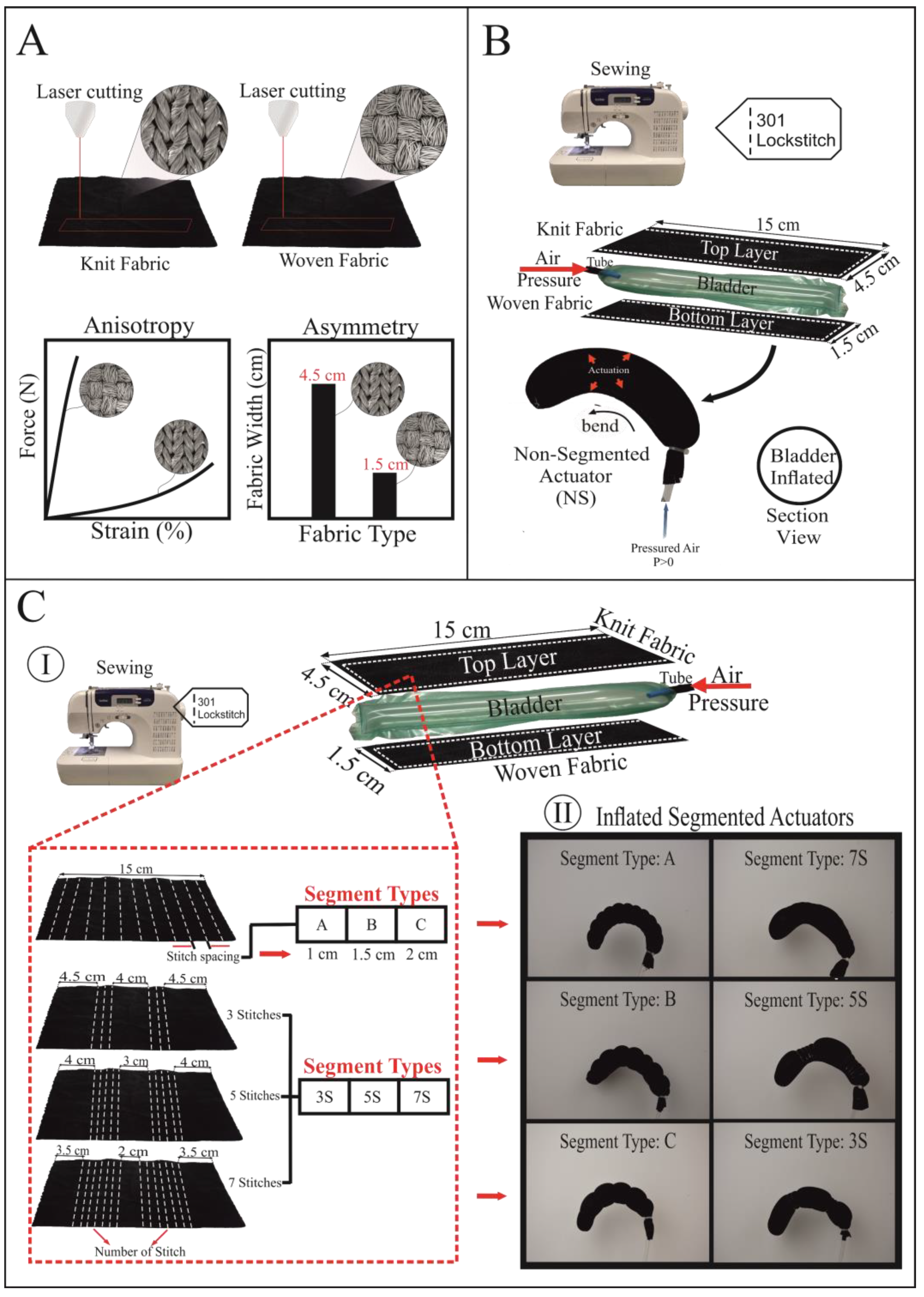
2.1. Fabric Materials
2.2. Fabrication of Soft Fabric Actuator
2.3. Fabrication of Thermoplastic Air Bladder
2.4. Sensor Integration to Actuator
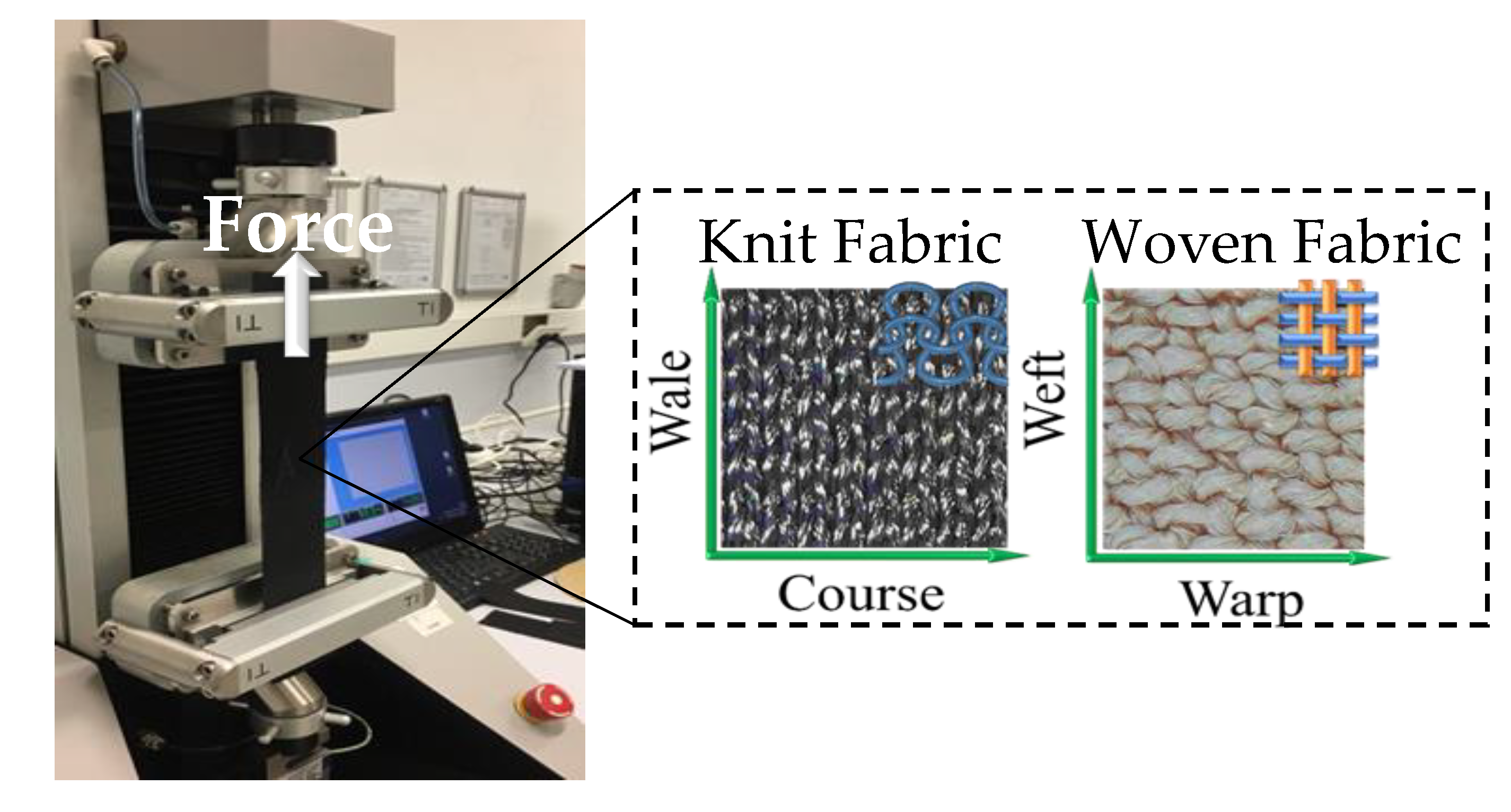
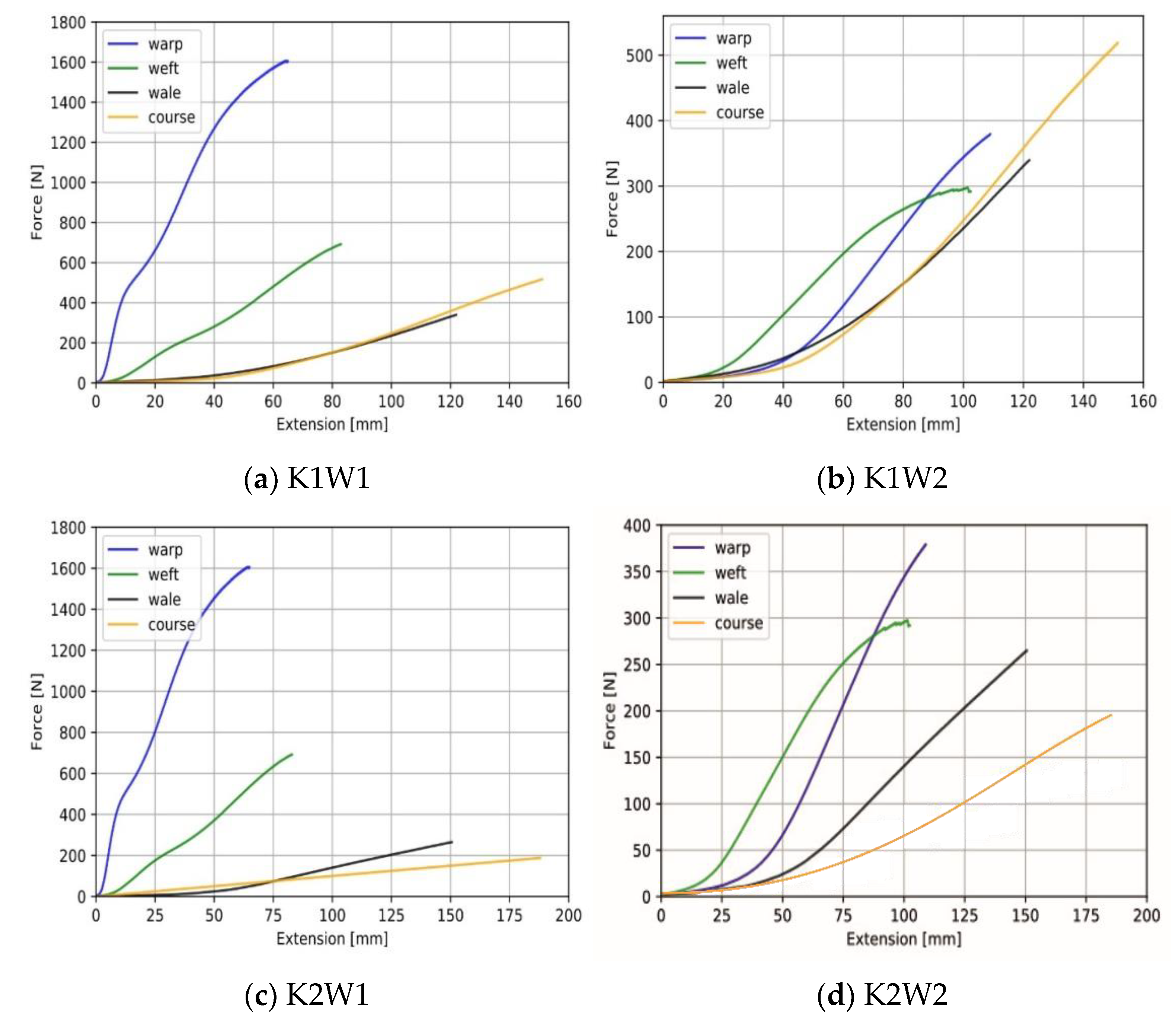
2.5. Tensile Test
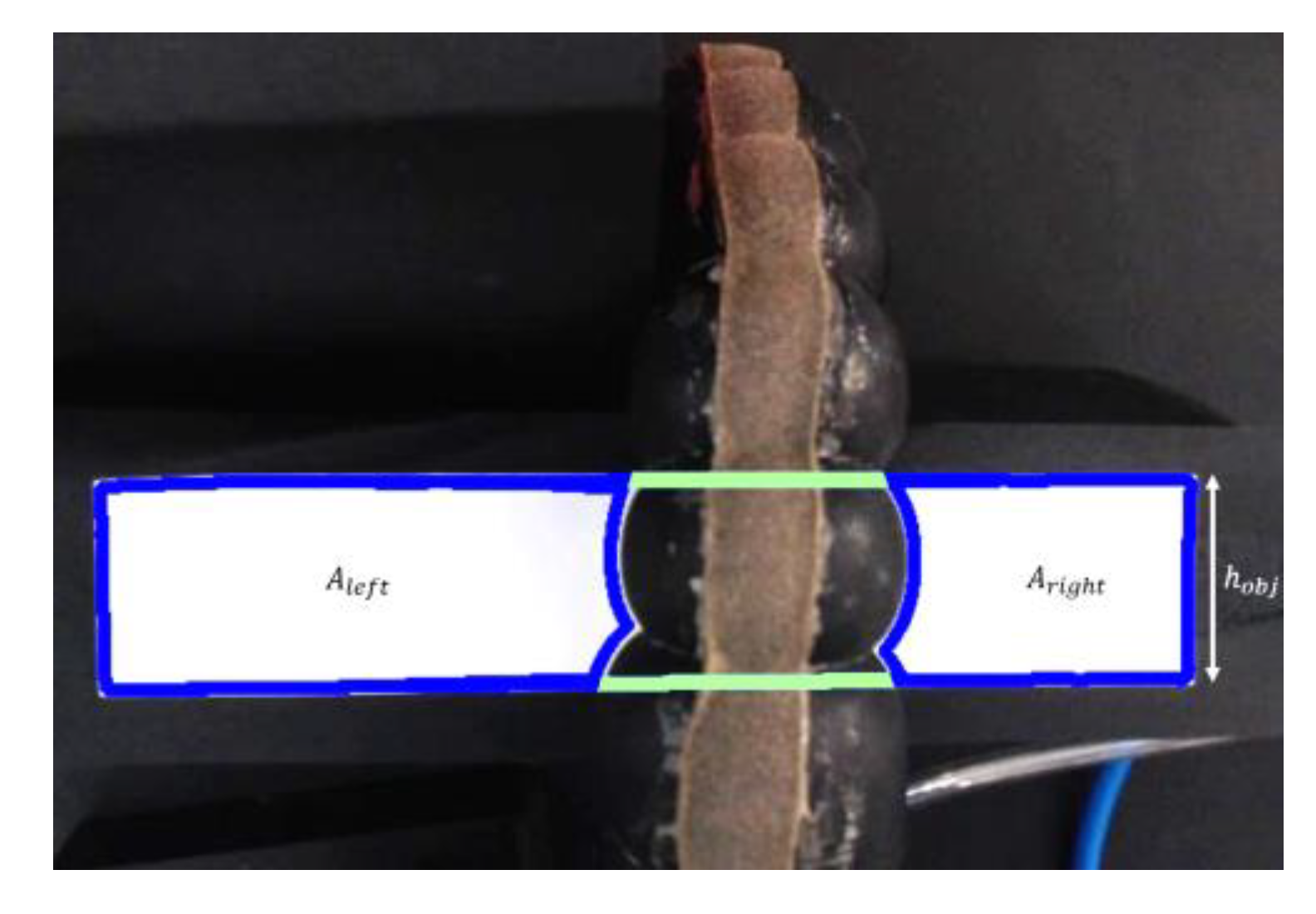
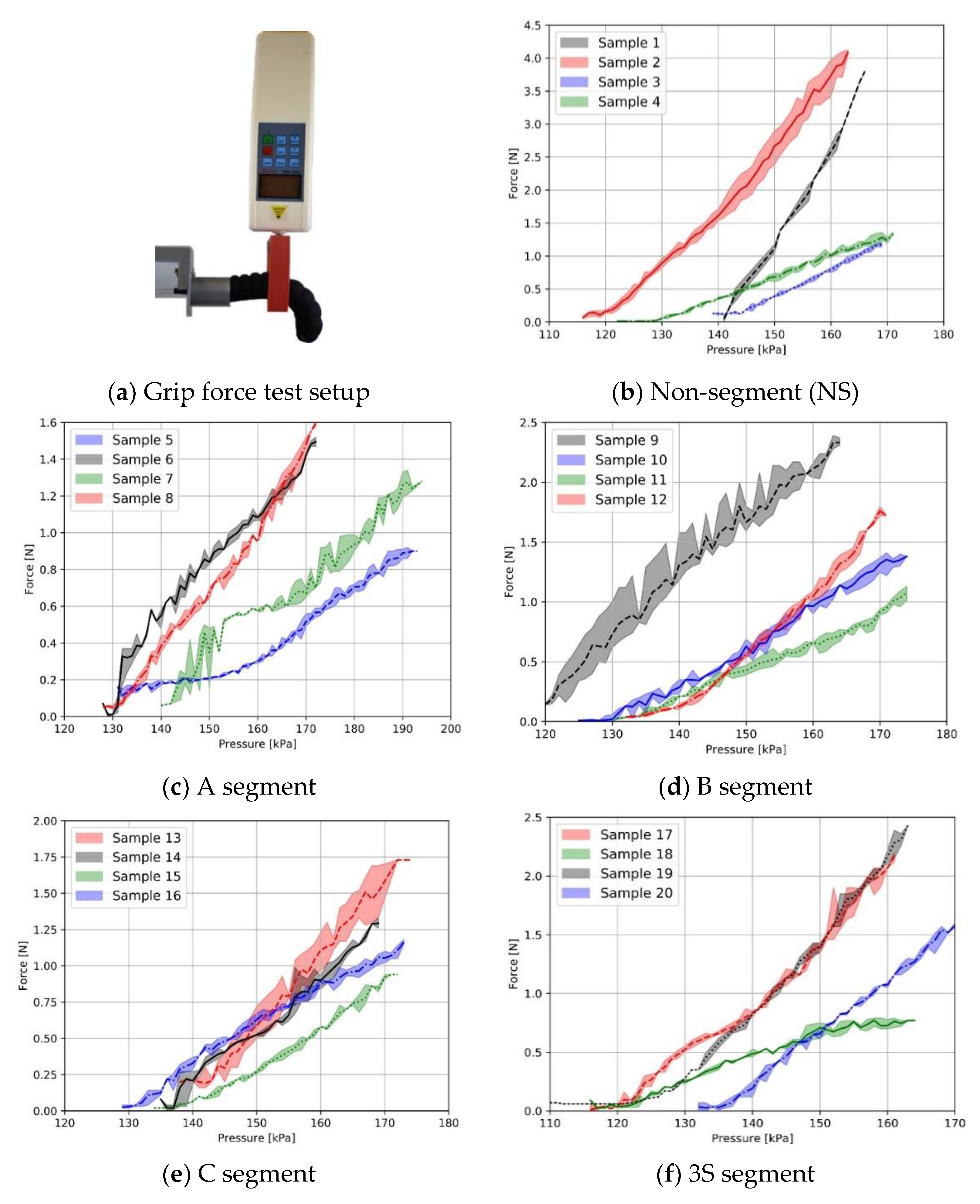
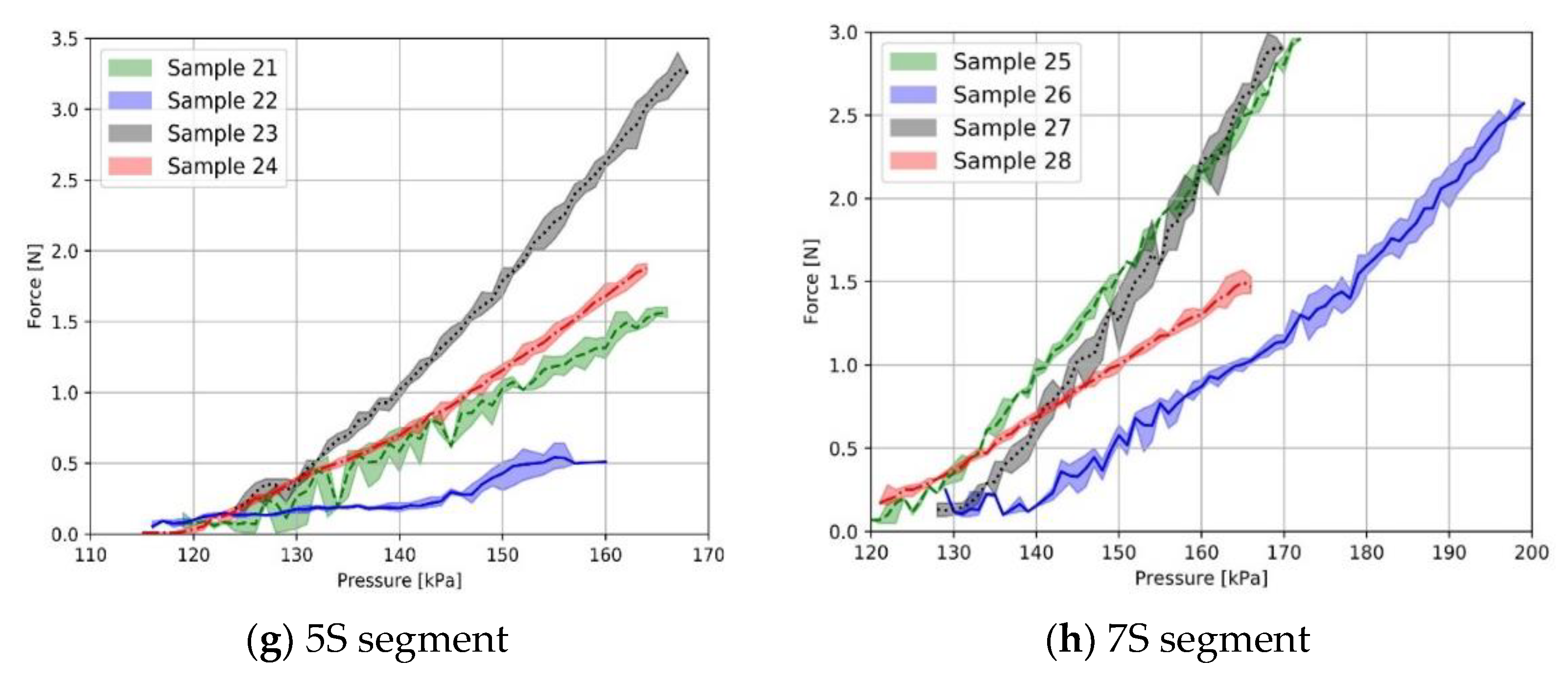
2.6. Grip Force–Pressure Test
2.7. Bending Angle–Pressure Test
2.8. Torque–Pressure Test
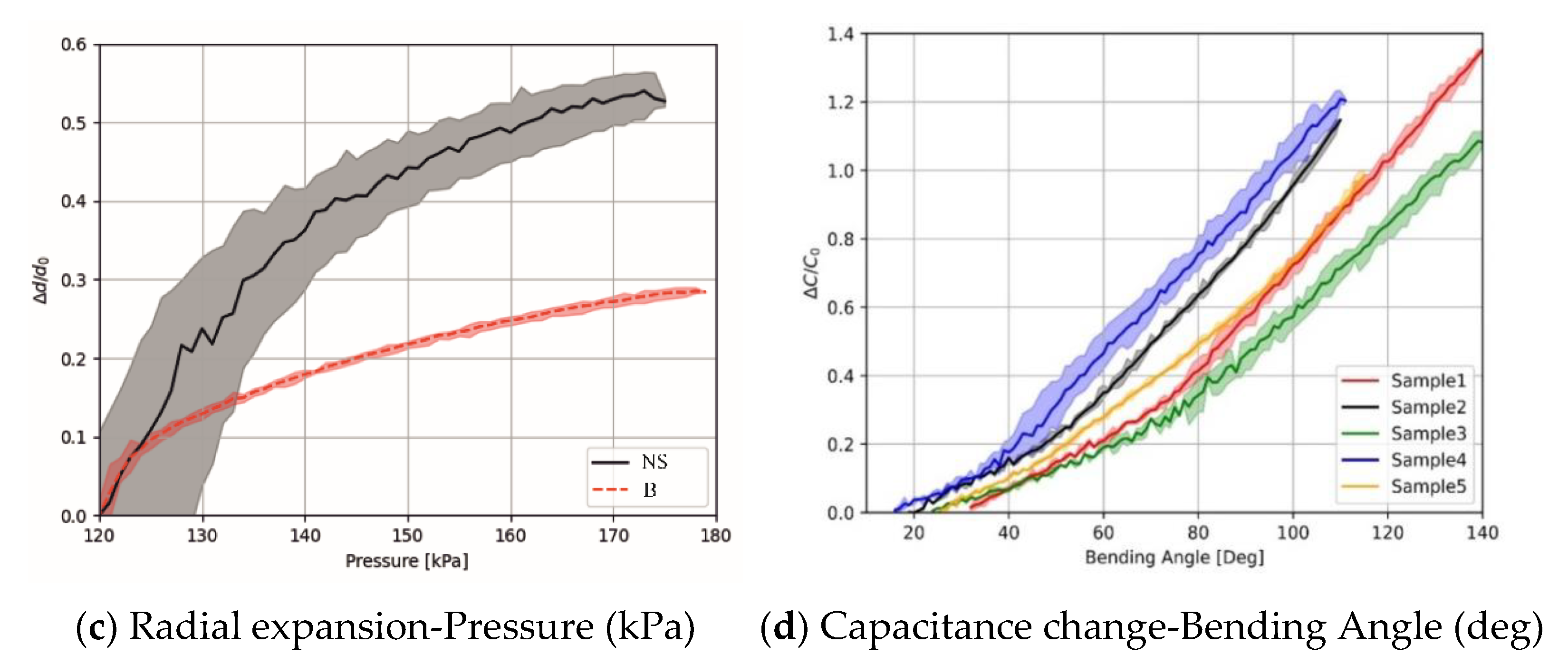
2.9. Radial Expansion Test
2.10. Capacitance Measurement
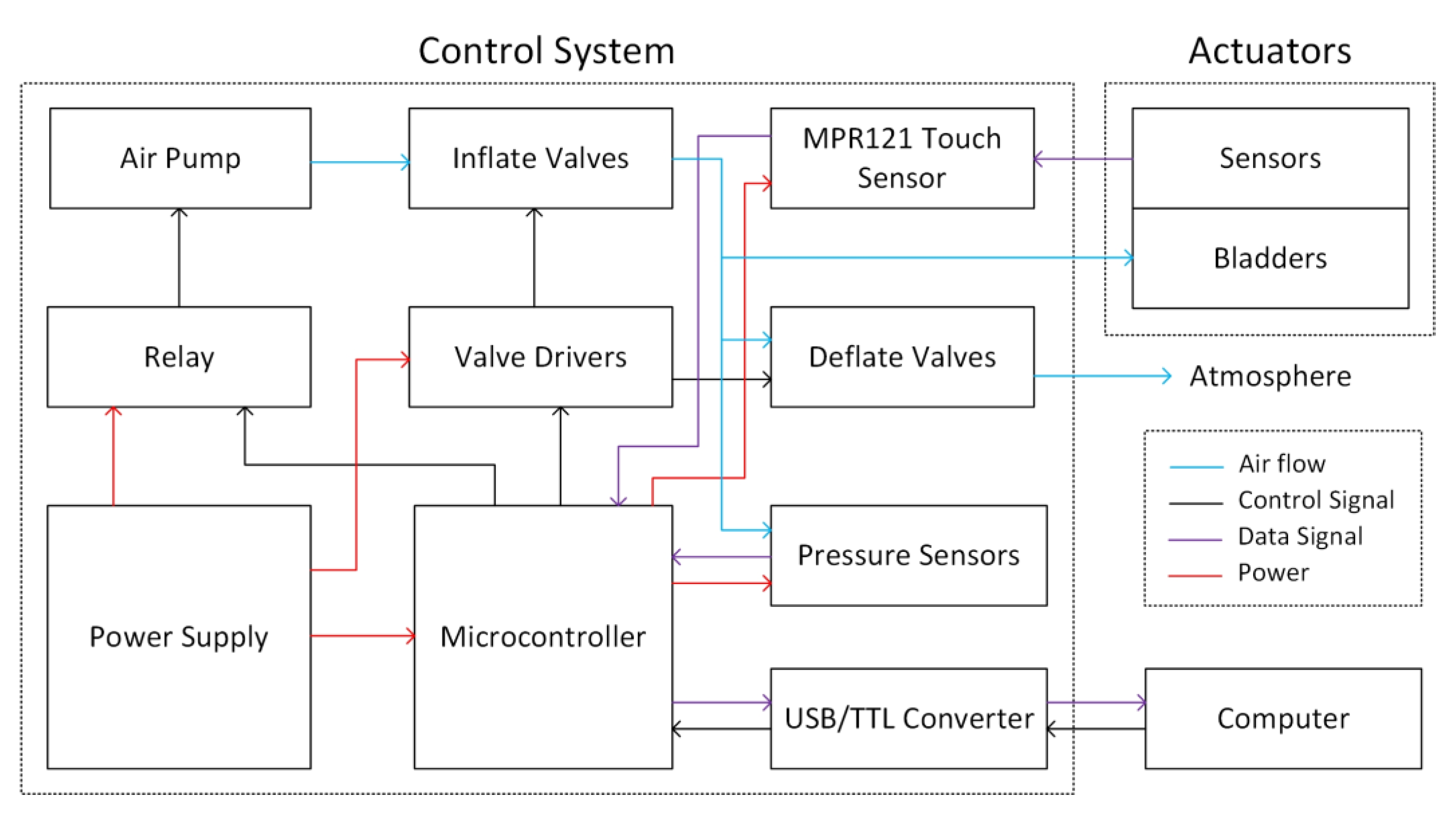
2.11. Control Strategy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Uniaxial Tensile Characteristic of Woven and Knit Fabrics
3.2. Characterization of Fabric-Based Actuators
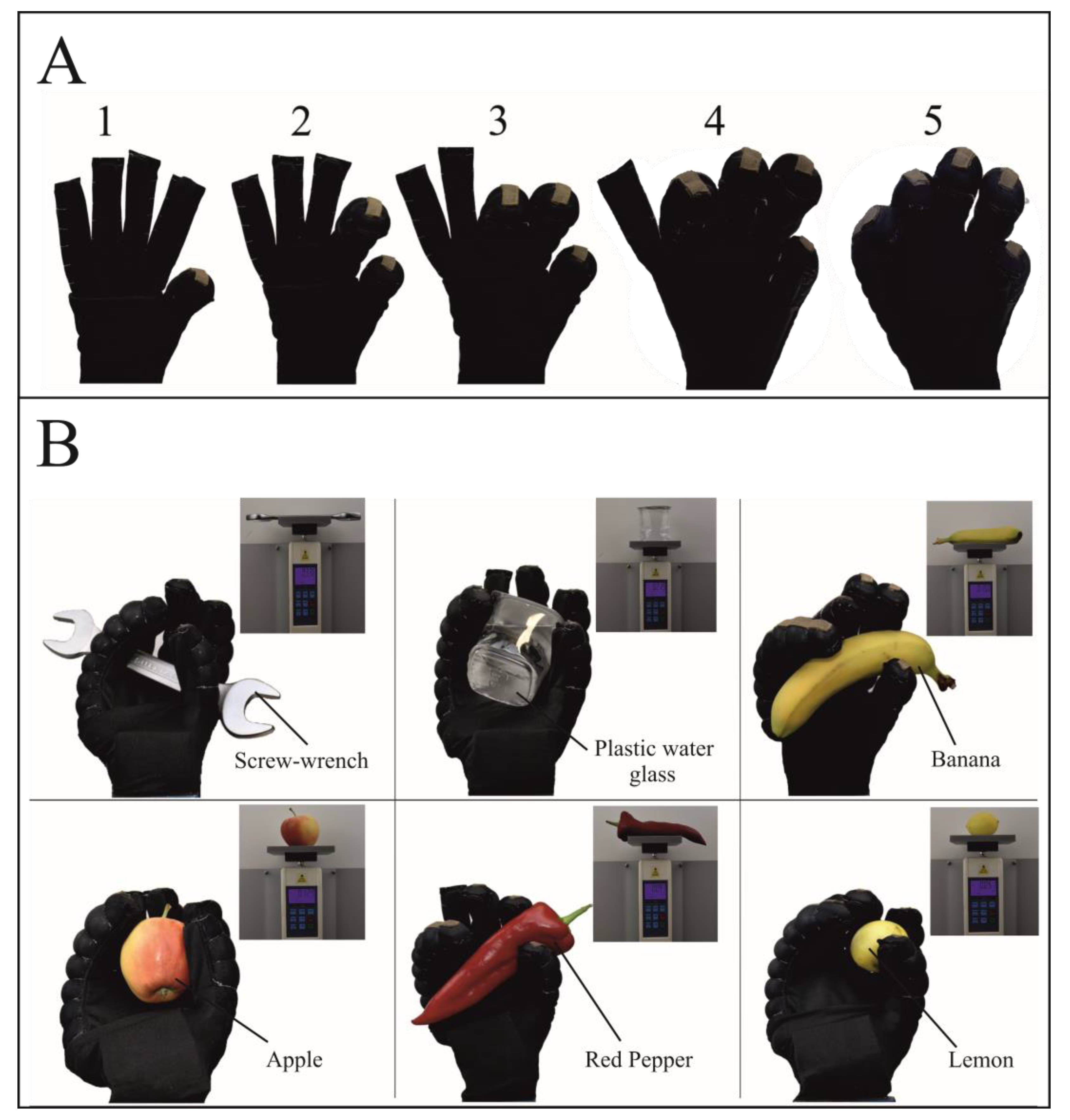
3.3. Application
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Atab, N.; Mishra, R.B.; Al-Modaf, F.; Joharji, L.; Alsharif, A.A.; Alamoudi, H.; Diaz, M.; Qaiser, N.; Hussain, M.M. Soft Actuators for Soft Robotic Applications: A Review. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 2000128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Totaro, M.; Beccai, L. Toward perceptive soft robots: Progress and challenges. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1800541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, V.; Walsh, C.J.; Wood, R.J. Textile Technology for Soft Robotic and Autonomous Garments. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2008278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Chen, J.; Lee, P.S. Functional Fibers and Fabrics for Soft Robotics, Wearables, and Human-Robot Interface. Adv. Mater. 2020, 33, e2002640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, F.; Wagner, D.A.; Walsh, C.; Bertoldi, K. Sew-Free Anisotropic Textile Composites for Rapid Design and Manufacturing of Soft Wearable Robots. EML 2019, 27, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, D.; Gaponov, I.; Ryu, J.-H. Portable Exoskeleton Glove with Soft Structure for Hand Assistance in Activities of Daily Living. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2016, 22, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, G.; Heimgartner, R.; Arumukhom Revi, D.; Karavas, N.; Nathanson, D.; Galiana, I.; Eckert-Erdheim, A.; Murphy, P.; Perry, D.; et al. Reducing the Metabolic Rate of Walking and Running with a Versatile, Portable Exosuit. Science 2019, 365, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiloyannis, M.; Annese, E.; Canesi, M.; Kodiyan, A.; Bicchi, A.; Micera, S.; Ajoudani, A.; Masia, L. Design and Validation of a Modular One-To-Many Actuator for a Soft Wearable Exosuit. Front. Neurorobot. 2019, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In, H.; Kang, B.B.; Sin, M.; Cho, K.-J. Exo-Glove: A Wearable Robot for the Hand with a Soft Tendon Routing System. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2015, 22, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, L.N.; Bae, K.J.; O’Donnell, S.; Rossi, M.D.; Hendron, K.; Sloot, L.H.; Kudzia, P.; Allen, S.; Holt, K.G.; Ellis, T.D.; et al. A Soft Robotic Exosuit Improves Walking in Patients after Stroke. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaai9084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.T.; Ryu, J.W.; Park, S.-H.; Lee, Y.B.; Koo, S.H.; Park, Y.-L.; Lee, G. An Active Compression Sleeve with Variable Pressure Levels Using a Wire-Fabric Mechanism and a Soft Sensor. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 114002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.; Duarte, J.E.; Grimmer, M.; Sancho-Puchades, A.; Wei, H.; Easthope, C.S.; Riener, R. The Myosuit: Bi-Articular Anti-Gravity Exosuit that Reduces Hip Extensor Activity in Sitting Transfers. Front. Neurorobot. 2017, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, C.T.; Proietti, T.; Nuckols, K.; Clarke, M.E.; Hohimer, C.J.; Cloutier, A.; Lin, D.J.; Walsh, C.J. Infatable Soft Wearable Robot for Reducing Therapist Fatigue during Upper Extremity Rehabilitation in Severe Stroke. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 3899–3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, M.; Meller, M.A.; Garcia, E. Variable Recruitment Fluidic Articial Muscles: Modeling and Experiments. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 074009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naclerio, N.D.; Hawkes, E.W. Simple, Low-Hysteresis, Foldable, Fabric Pneumatic Articial Muscle. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 3406–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappello, L.; Galloway, K.C.; Sanan, S.; Wagner, D.A.; Granberry, R.; Engelhardt, S.; Haufe, F.L.; Peisner, J.D.; Walsh, C.J. Exploiting Textile Mechanical Anisotropy for Fabric-Based Pneumatic Actuators. Soft Robot. 2018, 5, 30024312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmoughni, H.M.; Yilmaz, A.F.; Ozlem, K.; Khalilbayli, F.; Cappello, L.; Tuncay Atalay, A.; Ince, G.; Atalay, O. Machine-Knitted Seamless Pneumatic Actuators for Soft Robotics: Design, Fabrication, and Characterization. Actuators 2021, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polygerinos, P.; Lyne, S.; Wang, Z.; Nicolini, L.F.; Mosadegh, B.; Whitesides, G.M.; Walsh, C.J. Towards a Soft Pneumatic Glove for Hand Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the IROS 2013: New Horizon, Conference Digest—2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 1512–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Chen, F.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Han, D.; Wang, T.; Gu, G. Design, Modeling, and Evaluation of Fabric-Based Pneumatic Actuators for Soft Wearable Assistive Gloves. Soft Robot. 2020, 7, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Do, T.N.; Hawkes, E.; Visell, Y. Fluidic Fabric Muscle Sheets for Wearable and Soft Robotics. Soft Robot. 2020, 7, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granberry, R.; Eschen, K.; Holschuh, B.; Abel, J. Functionally Graded Knitted Actuators with Niti-Based Shape Memory Alloys for Topographically Self-Fitting Wearables. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1900548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Kim, U.; Park, C.H. A Novel Fabric Muscle Based on Shape Memory Alloy Springs. Soft Robot. 2020, 7, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Hawkes, E.; Choy, K.; Joldaz, M.; Foleyz, J.; Wood, R. Micro Artificial Muscle Fiber Using Niti Spring for Soft Robotics. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, St. Louis, MO, USA, 11–15 October 2009; pp. 2228–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Yuan, C.; Liang, X.; Dong, T.; Liu, T.; Zhang, J.; Zou, J.; Yang, H.; Bowen, C. Soft Actuators and Robotic Devices for Rehabilitation and Assistance. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2021, 4, 2100140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappello, L.; Meyer, J.T.; Galloway, K.C.; Peisner, J.D.; Granberry, R.; Wagner, D.; Engelhardt, S.; Paganoni, S.; Walsh, C.J. Assisting Hand Function after Spinal Cord Injury with a Fabric-Based Soft Robotic Glove. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2018, 15, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, M.; Yang, D.; Gu, G. High-Force Fabric-Based Pneumatic Actuators with Asymmetric Chambers and Interference-Reinforced Structure for Soft Wearable Assistive Gloves. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 3105–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Ruan, Q.; Man, Y.; Xie, Z.; Yue, H.; Li, B.; Liu, R. Design and Optimize of a Novel Segmented Soft Pneumatic Actuator. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 122304–122313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosadegh, B.; Polygerinos, P.; Keplinger, C.; Wennstedt, S.; Shepherd, R.F.; Gupta, U.; Shim, J.; Bertoldi, K.; Walsh, C.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Pneumatic networks for soft robotics that actuate rapidly. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2163–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, K.C.; Becker, K.P.; Phillips, B.; Kirby, J.; Licht, S.; Tchernov, D.; Wood, R.J.; Gruber, D.F. Soft Robotic Grippers for Biological Sampling on Deep Reefs. Soft Robot. 2016, 3, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fei, Y.; Pang, W. Design, Modeling, and Testing of a Soft Pneumatic Glove with Segmented Pneunets Bending Actuators. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2019, 24, 990–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalay, A.; Sanchez, V.; Atalay, O.; Vogt, D.M.; Haufe, F.; Wood, R.J.; Walsh, C.J. Batch Fabrication of Customizable Silicone-Textile Composite Capacitive Strain Sensors for Human Motion Tracking. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2017, 2, 1700136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, H.W. Electromagnetic Compatibility Engineering; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mpr121: Proximity Capacitive Touch Sensor Controller Archived. Available online: https://www.nxp.com/products/no-longer-manufactured/proximity-capacitive-touch-sensor-controller:MPR121 (accessed on 29 July 2021).
- Ozlem, K.; Atalay, O.; Atalay, A.; Ince, G. Textile Based Sensing System for Lower Limb Motion Monitoring. In Converging Clinical and Engineering Research on Neurorehabilitation III; Masia, L., Micera, S., Akay, M., Pons, J.L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 395–399. [Google Scholar]



| Properties of Fabrics | Knit Fabric 1 (K1) | Knit Fabric 2 (K2) |
|---|---|---|
| GSM (g/m2) | 180 | 235 |
| Course per cm | 41 | 50 |
| Wale per cm | 35 | 26 |
| Thickness (mm) | 0.58 | 0.48 |
| Fiber Type | Polyester/Elastane | Polyamide/Elastane |
| Knit Structure | Single Jersey | Single Jersey |
| Properties of Fabrics | Woven Fabric 1 (W1) | Woven Fabric 2 (W2) |
|---|---|---|
| GSM (g/m2) | 195 | 165 |
| Warp density (ends/cm) | 52 | 34 |
| Weft density (picks/cm) | 35 | 24 |
| Thickness (mm) | 0.45 | 0.41 |
| Fiber Type | Polyester | Polyester |
| Weave Structure | Coated Plain Weave | Plain Weave |
| Segment Types | Sample | Fabric Combinations |
|---|---|---|
| Non-Segmented (NS) | 1 | K1W1 |
| 2 | K2W1 | |
| 3 | K1W2 | |
| 4 | K2W2 | |
| A | 5 | K1W2 |
| 6 | K1W1 | |
| 7 | K2W2 | |
| 8 | K2W1 | |
| B | 9 | K1W1 |
| 10 | K1W2 | |
| 11 | K2W2 | |
| 12 | K2W1 | |
| C | 13 | K2W1 |
| 14 | K1W1 | |
| 15 | K2W2 | |
| 16 | K1W2 | |
| 3S | 17 | K2W1 |
| 18 | K2W2 | |
| 19 | K1W1 | |
| 20 | K1W2 | |
| 5S | 21 | K2W2 |
| 22 | K1W2 | |
| 23 | K1W1 | |
| 24 | K2W1 | |
| 7S | 25 | K2W2 |
| 26 | K1W2 | |
| 27 | K1W1 | |
| 28 | K2W1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yilmaz, A.F.; Khalilbayli, F.; Ozlem, K.; Elmoughni, H.M.; Kalaoglu, F.; Atalay, A.T.; Ince, G.; Atalay, O. Effect of Segment Types on Characterization of Soft Sensing Textile Actuators for Soft Wearable Robots. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7040249
Yilmaz AF, Khalilbayli F, Ozlem K, Elmoughni HM, Kalaoglu F, Atalay AT, Ince G, Atalay O. Effect of Segment Types on Characterization of Soft Sensing Textile Actuators for Soft Wearable Robots. Biomimetics. 2022; 7(4):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7040249
Chicago/Turabian StyleYilmaz, Ayse Feyza, Fidan Khalilbayli, Kadir Ozlem, Hend M. Elmoughni, Fatma Kalaoglu, Asli Tuncay Atalay, Gökhan Ince, and Ozgur Atalay. 2022. "Effect of Segment Types on Characterization of Soft Sensing Textile Actuators for Soft Wearable Robots" Biomimetics 7, no. 4: 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7040249
APA StyleYilmaz, A. F., Khalilbayli, F., Ozlem, K., Elmoughni, H. M., Kalaoglu, F., Atalay, A. T., Ince, G., & Atalay, O. (2022). Effect of Segment Types on Characterization of Soft Sensing Textile Actuators for Soft Wearable Robots. Biomimetics, 7(4), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7040249





