A Simplified Murine Model to Imitate Flexor Tendon Adhesion Formation without Suture
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Processing of Longitudinal Incision Model
2.2. Histological Analysis
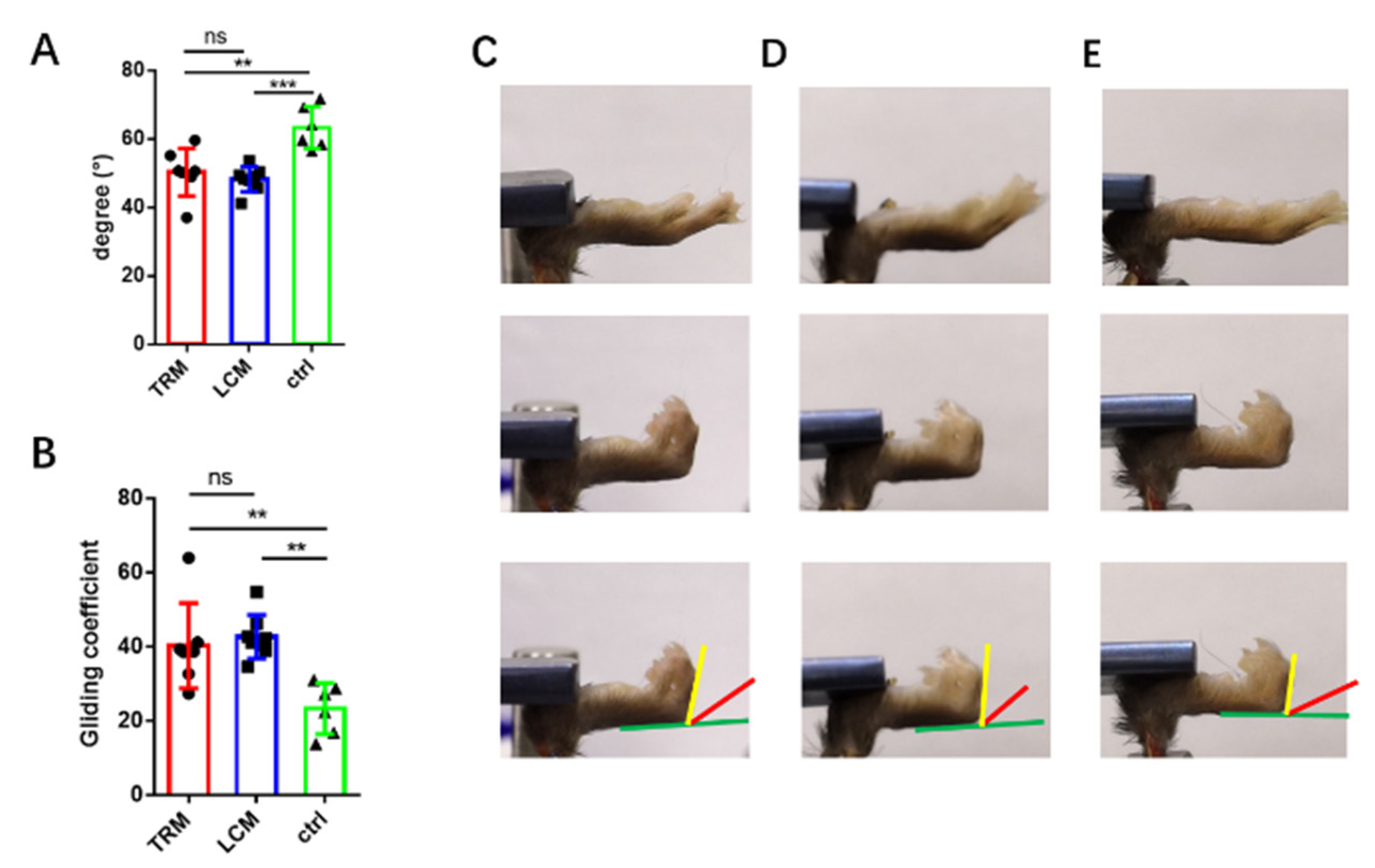
2.3. The Range of Motion and Gliding Coefficient
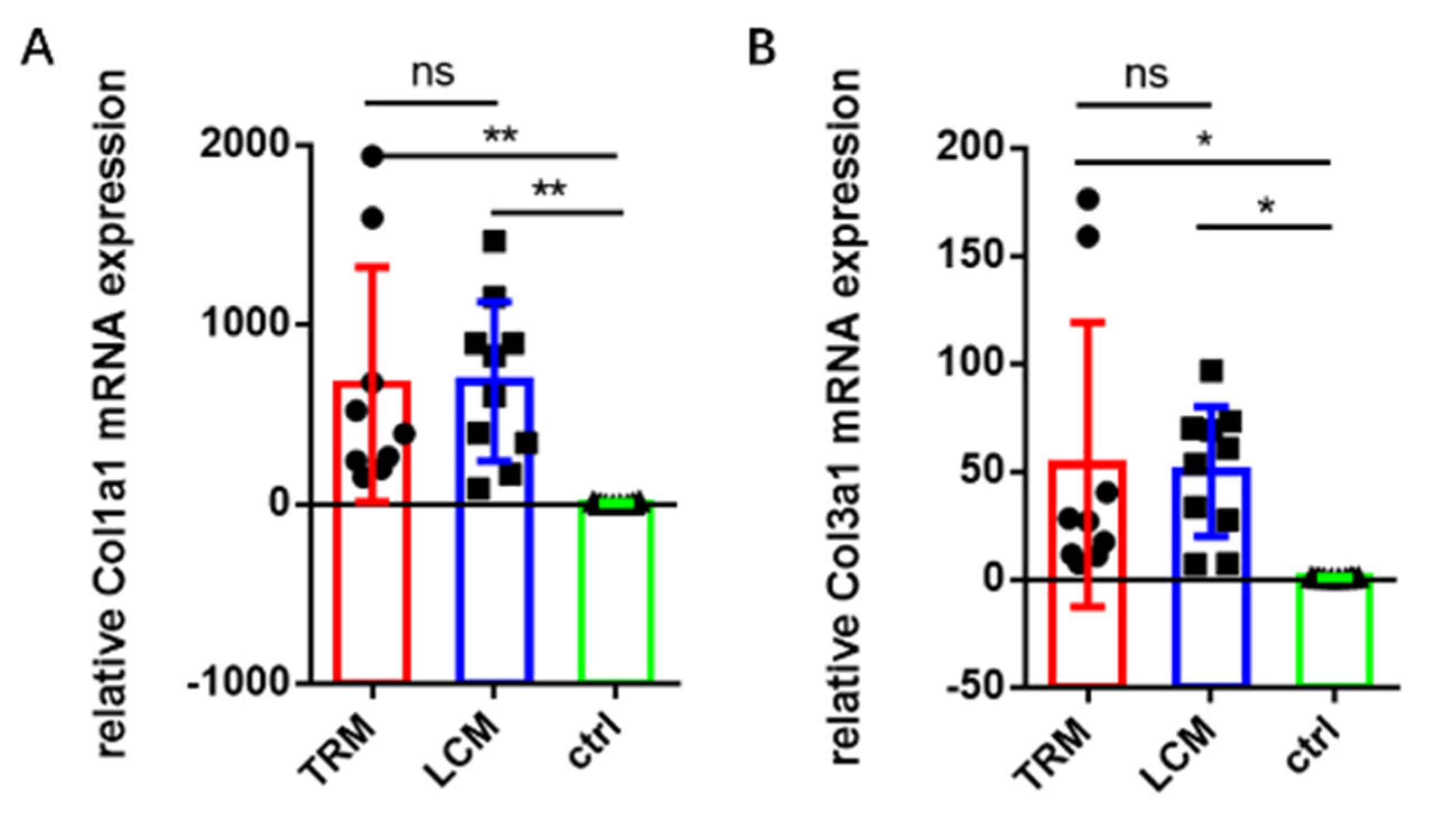
2.4. Gene Expression Using Real-Time PCR
2.5. Biomechanical Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Histological Analysis of Longitudinal Incision Model
3.2. ROM of Longitudinal Incision Models
3.3. Gene Expression in Longitudinal Incision Model
3.4. Biomechanics of Longitudinal Incision Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A




| Species | Official Full Name | Product Length | Primer Sequence | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mouse | Col1a1 | 117 | 5′ TGA CTG GAA GAG CGG AGA GTA 3′ 5′ TGA CTG GAA GAG CGG AGA GTA 3′ | BioTNT |
| mouse | Col3a1 | 89 | 5′ CCT GGA GCC CCT GGA CTA ATA 3′ 5′ CCT GGA GCC CCT GGA CTA ATA 3′ | BioTNT |
| mouse | Gapdh | 115 | 5′ AAA TGG TGA AGG TCG GTG TG 3′ 5′AAA TGG TGA AGG TCG GTG TG 3′ | BioTNT |
References
- Hasslund, S.; O’Keefe, R.J.; Awad, H.A. A Mouse Model of Flexor Tendon Repair. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1130, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottagisio, M.; Lovati, A.B. A review on animal models and treatments for the reconstruction of Achilles and flexor tendons. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2017, 28, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasslund, S.; Jacobson, J.A.; Dadali, T.; Basile, P.; Ulrich-Vinther, M.; Søballe, K.; Schwarz, E.M.; O’Keefe, R.J.; Mitten, D.J.; Awad, H.A. Adhesions in a murine flexor tendon graft model: Autograft versus allograft reconstruction. J. Orthop. Res. 2008, 26, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loiselle, A.E.; Frisch, B.J.; Wolenski, M.; Jacobson, J.A.; Calvi, L.M.; Schwarz, E.M.; Awad, H.A.; O’Keefe, R.J. Bone Marrow-Derived Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Is Associated with Fibrous Adhesion Formation after Murine Flexor Tendon Injury. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Lü, H.; Yang, H. Chitosan prevents adhesion during rabbit flexor tendon repair via the sirtuin 1 signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 4598–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, S.H.; Al-Youha, S.; Van Agtmael, T.; Lu, Y.; Wong, J.; McGrouther, D.A.; Kadler, K.E. Tendon Is Covered by a Basement Membrane Epithelium That Is Required for Cell Retention and the Prevention of Adhesion Formation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ackerman, J.E.; Best, K.T.; O’Keefe, R.J.; Loiselle, A.E. Deletion of EP4 in S100a4-lineage cells reduces scar tissue formation during early but not later stages of tendon healing. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsubone, T.; Moran, S.L.; Subramaniam, M.; Amadio, P.; Spelsberg, T.; An, K. Effect of TGF-β inducible early gene deficiency on flexor tendon healing. J. Orthop. Res. 2006, 24, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, E.; Hayashi, K. Mechanical Properties of Collagen Fascicles from the Rabbit Patellar Tendon. J. Biomech. Eng. 1999, 121, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabak, T.K.; Sertkaya, O.; Acar, N.; Donmez, B.O.; Ustunel, I. The Effect of Phospholipids (Surfactant) on Adhesion and Biomechanical Properties of Tendon: A Rat Achilles Tendon Repair Model. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 689314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper; Treuting, M.; Suzanne; Dintzis, M.; Kathleen, S. Montine Comparative Anatomy and Histology: A Mouse, Rat and Human Atlas; Elsevier Press: London, UK, 2018; p. 85. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Amadio, P.C.; Momose, T.; Zobitz, M.E.; Couvreur, P.; An, K.-N. Remodeling of the gliding surface after flexor tendon repair in a canine model in vivo. J. Orthop. Res. 2002, 20, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, M.; Sun, Y.-L.; Zhao, C.; Zobitz, M.E.; Cha, C.-J.; Jay, G.D.; An, K.-N.; Amadio, P.C. Lubricin Surface Modification Improves Extrasynovial Tendon Gliding in a Canine Model in Vitro. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2008, 90, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.R.; Smith, R.K.; David, F.; Lam, R.; Hughes, G.; De Godoy, R.; Carr, A.J.; Goodship, A.E.; Dudhia, J. Evaluation of the Effects of Synovial Multipotent Cells on Deep Digital Flexor Tendon Repair in a Large Animal Model of Intra-Synovial Tendinopathy. J. Orthop. Res. 2020, 38, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, R.H.; Zhao, C.; Zobitz, M.E.; Amadio, P.C.; An, K.-N. Mechanical properties of intrasynovial and extrasynovial tendon fascicles. Clin. Biomech. 2008, 23, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, C.; Thoreson, A.R.; Zhao, C. The effects of lyophilization on flexural stiffness of extrasynovial and intrasynovial tendon. J. Biomech. 2018, 76, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogramaci, Y.; Kalac, A.; Atik, E.; Esen, E.; Altuğ, M.E.; Onel, E.; Koç, A.; Yanat, A. Effects of a Single Application of Extractum Cepae on the Peritendinous Adhesion. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2010, 64, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titan, A.L.; Foster, D.S.; Chang, J.; Longaker, M.T. Flexor Tendon: Development, Healing, Adhesion Formation, and Contributing Growth Factors. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 144, 639e–647e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasslund, S.; Dadali, T.; Ulrich-Vinther, M.; Søballe, K.; Schwarz, E.M.; Awad, H.A. Freeze-dried allograft-mediated gene or protein delivery of growth and differentiation factor 5 reduces reconstructed murine flexor tendon adhesions. J. Tissue Eng. 2014, 5, 2041731414528736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orner, C.A.; Geary, M.B.; Hammert, W.C.; O’Keefe, R.J.; Loiselle, A.E. Low-Dose and Short-Duration Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 Inhibition Does Not Affect Adhesion Formation during Murine Flexor Tendon Healing. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 137, 545e–553e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shalumon, K.; Sheu, C.; Chen, C.-H.; Chen, S.-H.; Jose, G.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Chen, J.-P. Multi-functional electrospun antibacterial core-shell nanofibrous membranes for prolonged prevention of post-surgical tendon adhesion and inflammation. Acta Biomater. 2018, 72, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Saravelos, S.H.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, X.; Xia, E.; Li, T.C. Prevention of postoperative adhesion reformation by intermittent intrauterine balloon therapy: A randomised controlled trial. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2019, 126, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Lu, H. Advances in the Development of Anti-Adhesive Biomaterials for Tendon Repair Treatment. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2021, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackerman, J.E.; Loiselle, A.E. Murine Flexor Tendon Injury and Repair Surgery. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, e54433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Jiang, S.; Liu, S.; Chen, S.; Lin, Z.Y.; Pan, G.; He, F.; Li, F.; Fan, C.; Cui, W. Optimization of intrinsic and extrinsic tendon healing through controllable water-soluble mitomycin-C release from electrospun fibers by mediating adhesion-related gene expression. Biomaterials 2015, 61, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakurum, G.; Buyukbebeci, O.; Kalender, M.; Gulec, A. Seprafilm® interposition for preventing adhesion formation after tenolysis: An experimental study on the chicken flexor tendons. J. Surg. Res. 2003, 113, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, F.; Gu, S.; Wu, T.; Chen, S.; Chen, S.; Wang, C.; Huang, G.; Jin, T.; Cui, W.; et al. Gene Silencing via PDA/ERK2-siRNA-Mediated Electrospun Fibers for Peritendinous Antiadhesion. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1801217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Qin, M.; Hu, C.; Wu, F.; Cui, W.; Jin, T.; Fan, C. Tendon healing and anti-adhesion properties of electrospun fibrous membranes containing bFGF loaded nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 4690–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Lu, M.; Chen, S.; Cai, C.; Yao, Z.; Cui, W.; Fan, C.; Liu, S. Beeswax-inspired superhydrophobic electrospun membranes for peritendinous anti-adhesion. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 116, 111166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Wen, S.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Z.; Deng, L.; Mao, H.-Q.; Cui, W.; Zhang, H. Ice-Inspired Superlubricated Electrospun Nanofibrous Membrane for Preventing Tissue Adhesion. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 6420–6428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Peng, S.; Ning, J.; Qian, Y.; Fan, C. MicroRNA-21-3p Engineered Umbilical Cord Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Inhibit Tendon Adhesion. J. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 13, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Jiang, S.; Zheng, W.; Tu, B.; Liu, S.; Ruan, H.; Fan, C. RelA/p65 inhibition prevents tendon adhesion by modulating inflammation, cell proliferation, and apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geary, M.B.; Orner, C.A.; Bawany, F.; Awad, H.A.; Hammert, W.C.; O’Keefe, R.J.; Loiselle, A.E. Systemic EP4 Inhibition Increases Adhesion Formation in a Murine Model of Flexor Tendon Repair. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.K.; Ahn, J.; Kim, S.A.; Go, E.J.; Lee, D.H.; Park, S.C.; Shetty, A.A.; Kim, S.J. Improved Healing of Rabbit Patellar Tendon Defects After an Atelocollagen Injection. Am. J. Sports Med. 2021, 49, 2924–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, M.; Zhao, C.; Thoreson, A.R.; Chikenji, T.; Jay, G.D.; An, K.-N.; Amadio, P.C. The Effect of Lubricin on the Gliding Resistance of Mouse Intrasynovial Tendon. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wichelhaus, D.A.; Beyersdoerfer, S.T.; Gierer, P.; Vollmar, B.; Mittlmeier, T. The effect of a collagen-elastin matrix on adhesion formation after flexor tendon repair in a rabbit model. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2016, 136, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyras, D.N.; Kazakos, K.; Georgiadis, G.; Mazis, G.; Middleton, R.; Richards, S.; O’Connor, D.; Agrogiannis, G. Does a Single Application of PRP Alter the Expression of IGF-I in the Early Phase of Tendon Healing? J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2011, 50, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukawa, T.; Yamaguchi, S.; Watanabe, A.; Sasho, T.; Akagi, R.; Muramatsu, Y.; Akatsu, Y.; Katsuragi, J.; Endo, J.; Osone, F.; et al. Quantitative Assessment of Tendon Healing by Using MR T2 Mapping in a Rabbit Achilles Tendon Transection Model Treated with Platelet-rich Plasma. Radiology 2015, 276, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bao, R.; Cheng, S.; Zhu, J.; Hai, F.; Mi, W.; Liu, S. A Simplified Murine Model to Imitate Flexor Tendon Adhesion Formation without Suture. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7030092
Bao R, Cheng S, Zhu J, Hai F, Mi W, Liu S. A Simplified Murine Model to Imitate Flexor Tendon Adhesion Formation without Suture. Biomimetics. 2022; 7(3):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7030092
Chicago/Turabian StyleBao, Rong, Shi Cheng, Jianyu Zhu, Feng Hai, Wenli Mi, and Shen Liu. 2022. "A Simplified Murine Model to Imitate Flexor Tendon Adhesion Formation without Suture" Biomimetics 7, no. 3: 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7030092
APA StyleBao, R., Cheng, S., Zhu, J., Hai, F., Mi, W., & Liu, S. (2022). A Simplified Murine Model to Imitate Flexor Tendon Adhesion Formation without Suture. Biomimetics, 7(3), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7030092






