Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensors for SARS-CoV-2: Where Are We Now?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers
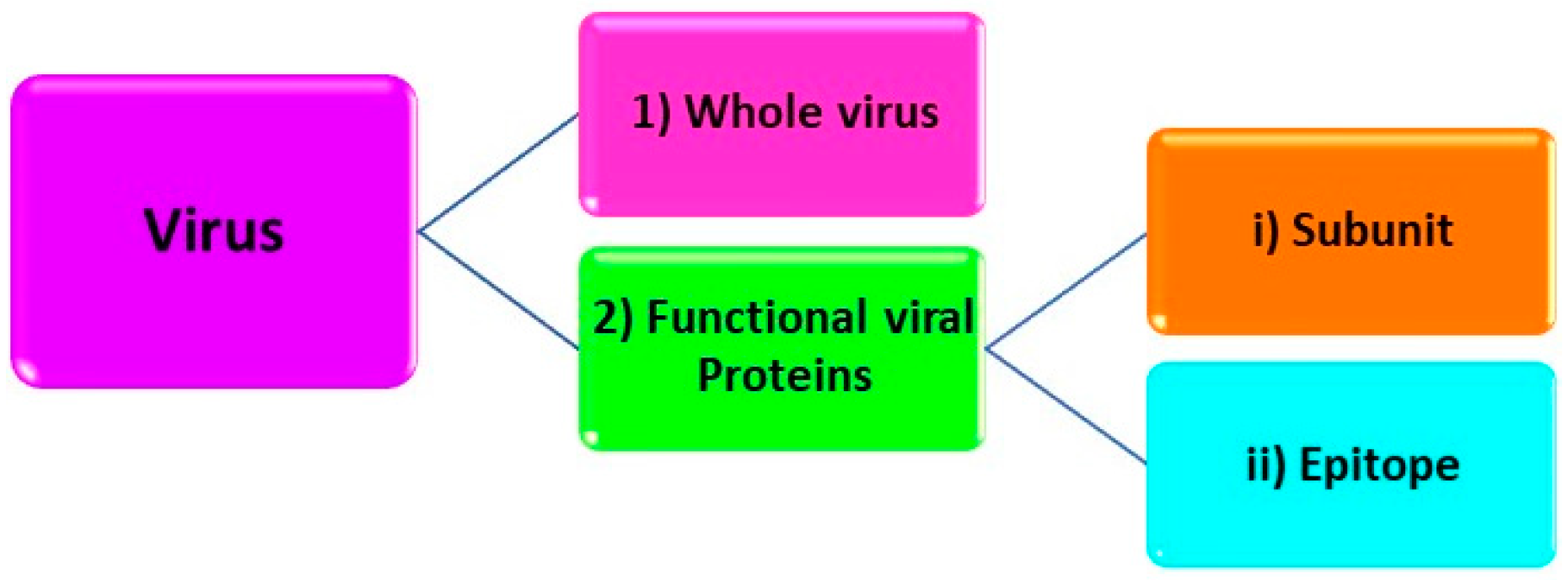
2.1. Structural Levels Target Analytes
2.2. Steps of MIP Preparation
3. MIP-Based Biomimetic Sensors for SARS-CoV-2 Detection
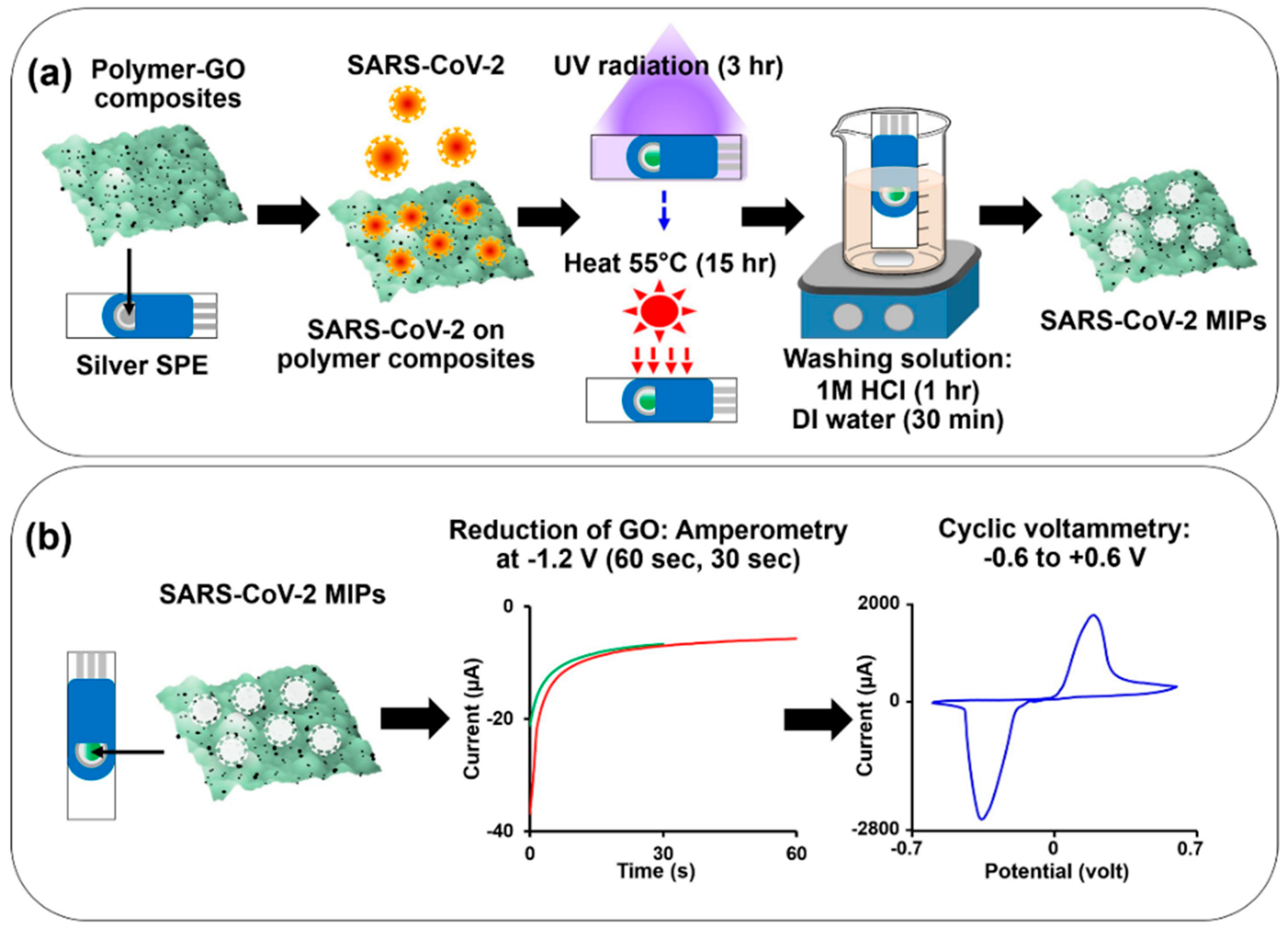
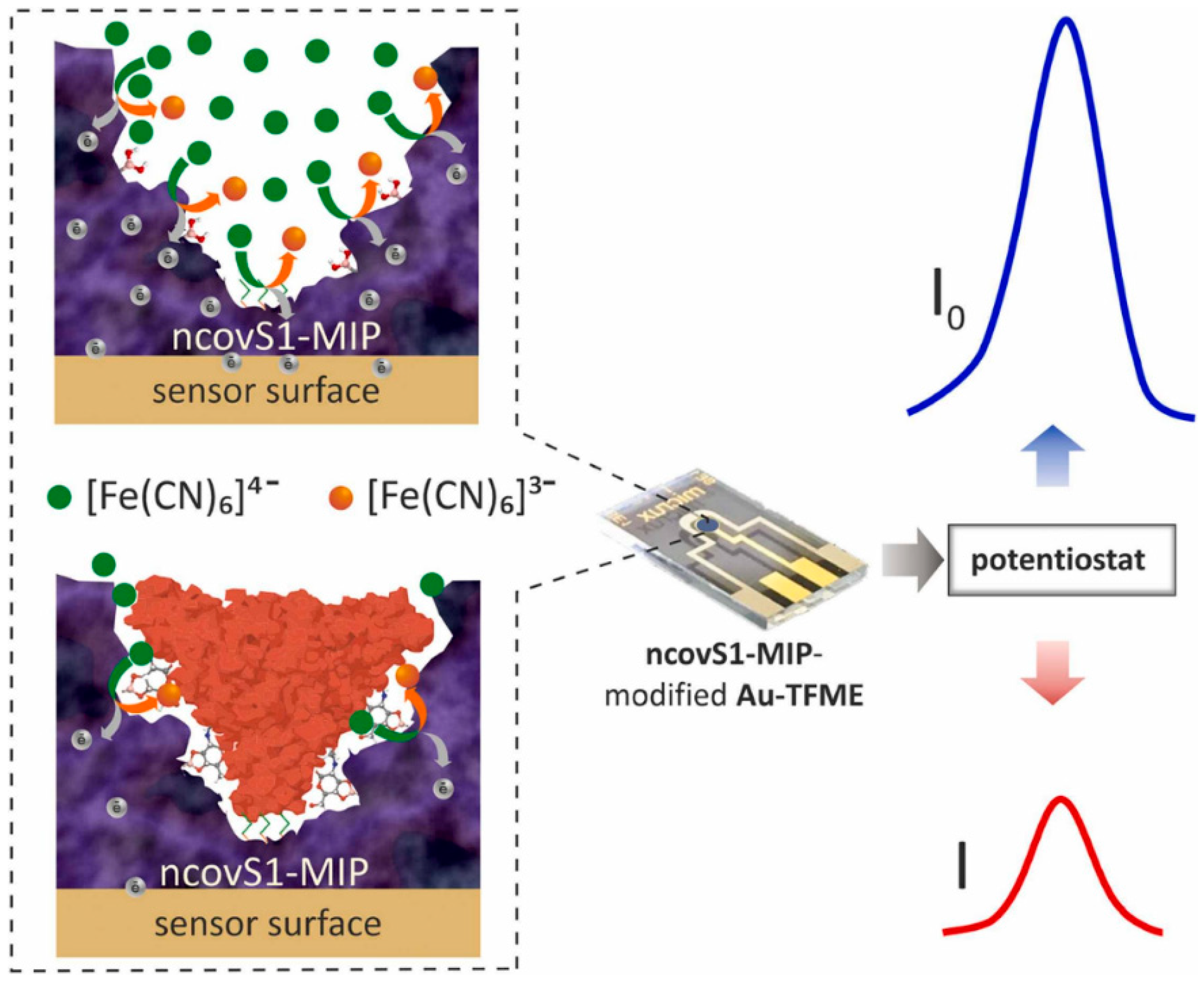
3.1. Electrochemical Detection of SARS-CoV-2
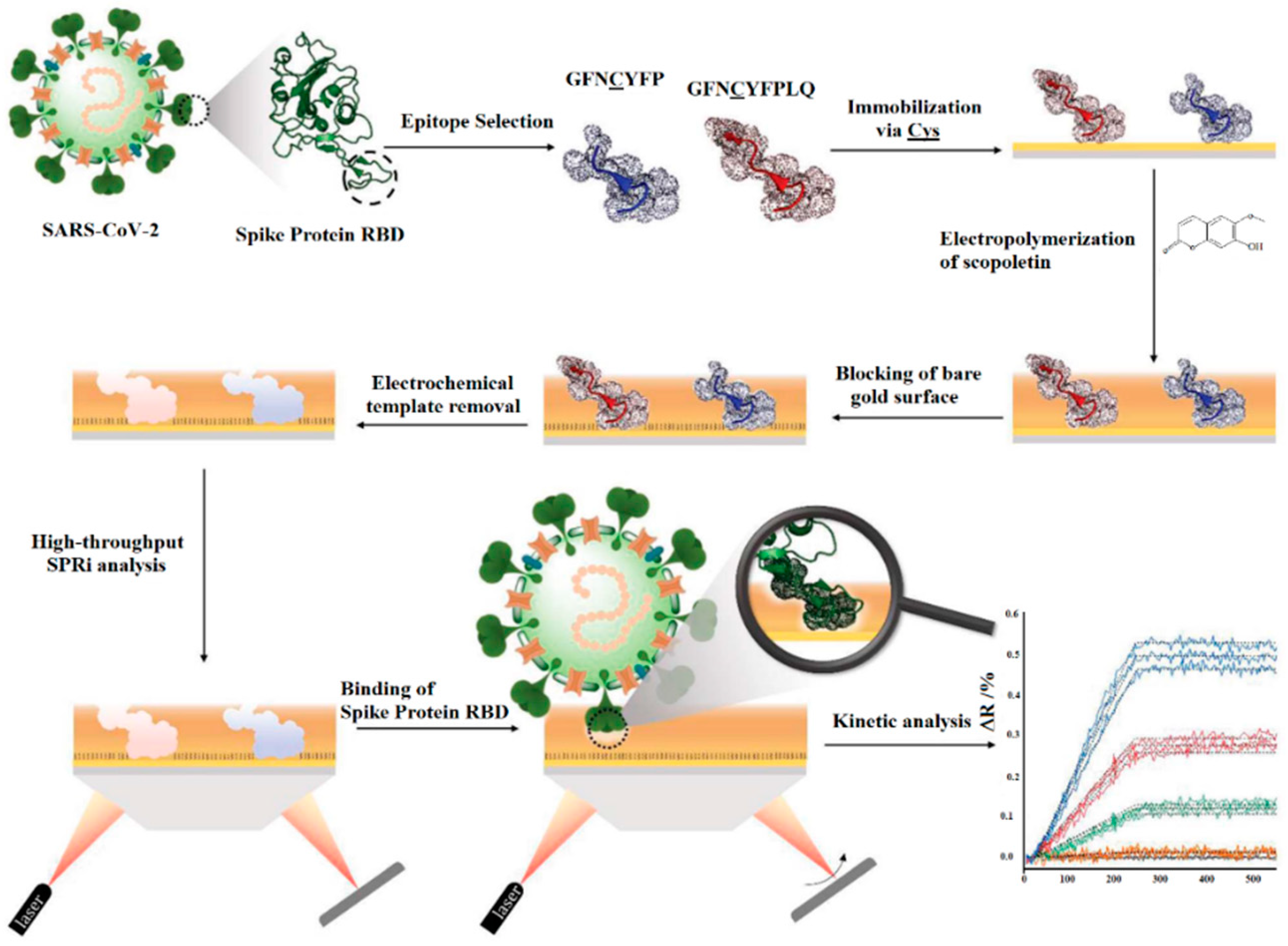
3.2. Optical Detection of SARS-CoV-2
3.3. Commercial MIP for SARS-CoV-2
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taleghani, N.; Taghipour, F. Diagnosis of COVID-19 for controlling the pandemic: A review of the state-of-the-art. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 174, 112830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalla, M.S.; Altintas, Z.; Forster, R.J.; Chemistry, B.; Industries, B.P.; St, R.H.; Abageyah, A.; Governorate, C. Current Trends of SARS-CoV-2 and Its New Variants Diagnostics in Different Body Fluids: Surface Antigen, Antibody, Nucleic Acid, and RNA Sequencing Detection Techniques. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4016299 (accessed on 9 April 2022).
- Huang, Y.; Yang, C.; Xu, X.; Xu, W.; Liu, S. Structural and functional properties of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: Potential antivirus drug development for COVID-19. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Z.; Cao, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, J. The SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein and Its Role in Viral Structure, Biological Functions, and a Potential Target for Drug or Vaccine Mitigation. Viruses 2021, 13, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kevadiya, B.D.; Machhi, J.; Herskovitz, J.; Oleynikov, M.D.; Blomberg, W.R.; Bajwa, N.; Soni, D.; Das, S.; Hasan, M.; Patel, M.; et al. Diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2 infections. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobysh, M.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Viter, R.; Ramanavicius, A. Affinity Sensors for the Diagnosis of COVID-19. Micromachines 2021, 12, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.A.; Hassan, R.Y.A.; Chino, M.; Febbraio, F. Point-of-care diagnostics of COVID-19: From current work to future perspectives. Sensors 2020, 20, 4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, S.A.; Ahmed Muneer, A.; Al-Kadmy, I.M.S.; Sattar, A.A.; Beshbishy, A.M.; Batiha, G.E.S.; Hetta, H.F. Biosensors as a future diagnostic approach for COVID-19. Life Sci. 2021, 273, 119117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Wu, X.; Wan, Z.; Li, Y.; Zuo, L.; Qin, J.; Jin, X.; Zhang, C. Development of a Novel Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Method for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Virol. Sin. 2020, 35, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pfefferle, S.; Reucher, S.; Nörz, D.; Lütgehetmann, M. Evaluation of a quantitative RT-PCR assay for the detection of the emerging coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 using a high throughput system. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holenya, P.; Lange, P.J.; Reimer, U.; Woltersdorf, W.; Panterodt, T.; Glas, M.; Wasner, M.; Eckey, M.; Drosch, M.; Hollidt, J.; et al. Peptide microarray-based analysis of antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 identifies unique epitopes with potential for diagnostic test development. Eur. J. Immunol. 2021, 51, 1839–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMullan, M.A.; Ibrayeva, A.; Trettner, K.; Deming, L.; Das, S.; Tran, F.; Moreno, J.R.; Casian, J.G.; Chellamuthu, P.; Kraft, J.; et al. ELISA detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in saliva. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Choi, M.; Jung, Y.; Lee, S.K.; Lee, C.S.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, N.H.; Kim, B.T.; Kim, H.G. A novel rapid detection for SARS-CoV-2 spike 1 antigens using human angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 171, 112715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Warmt, C.; Henkel, J.; Schrick, L.; Nitsche, A.; Bier, F.F. Lateral flow–based nucleic acid detection of SARS-CoV-2 using enzymatic incorporation of biotin-labeled dUTP for POCT use. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 3177–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broughton, J.P.; Deng, X.; Yu, G.; Fasching, C.L.; Servellita, V.; Singh, J.; Miao, X.; Streithorst, J.A.; Granados, A.; Sotomayor-Gonzalez, A.; et al. CRISPR–Cas12-based detection of SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drobysh, M.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Viter, R.; Chen, C.F.; Samukaite-Bubniene, U.; Ratautaite, V.; Ramanavicius, A. Biosensors for the Determination of SARS-CoV-2 Virus and Diagnosis of COVID-19 Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanavicius, S.; Jagminas, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Advances in molecularly imprinted polymers based affinity sensors (review). Polymers 2021, 13, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menger, M.; Yarman, A.; Erdossy, J.; Yildiz, H.B.; Gyurcsányi, R.E.; Scheller, F.W. MIPs and aptamers for recognition of proteins in biomimetic sensing. Biosensors 2016, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarman, A.; Scheller, F.W. How reliable is the electrochemical readout of MIP sensors? Sensors 2020, 20, 2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarman, A.; Kurbanoglu, S.; Zebger, I.; Scheller, F.W. Simple and robust: The claims of protein sensing by molecularly imprinted polymers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 330, 129369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakov, M.V. Adsorption properties and structure of silica gel. Zhur Fiz Khim 1931, 2, 709–805. [Google Scholar]
- Wulff, G.; Sarhan, A. Macromolecular Colloquium. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1972, 11, 334–342. [Google Scholar]
- Arshady, R.; Mosbach, K. Synthesis of Substrate-selective Polymers by Host-Guest Polymerizatioa. Die Makromol. Chem. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1981, 692, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieplak, M.; Kutner, W. Artificial Biosensors: How Can Molecular Imprinting Mimic Biorecognition? Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 922–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratautaite, V.; Janssens, S.D.; Haenen, K.; Nesládek, M.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Baleviciute, I.; Ramanavicius, A. Molecularly imprinted polypyrrole based impedimentric sensor for theophylline determination. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 130, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarman, A.; Scheller, F.W. Coupling biocatalysis with molecular imprinting in a biomimetic sensor. Angew. Chem.—Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 11521–11525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarman, A.; Scheller, F.W. The first electrochemical MIP sensor for tamoxifen. Sensors 2014, 14, 7647–7654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yarman, A.; Scheller, F.W. MIP-esterase/Tyrosinase Combinations for Paracetamol and Phenacetin. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 2222–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, L.; Şahin, Y. Determination of paracetamol based on electropolymerized-molecularly imprinted polypyrrole modified pencil graphite electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 127, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uygun, Z.O.; Dilgin, Y. A novel impedimetric sensor based on molecularly imprinted polypyrrole modified pencil graphite electrode for trace level determination of chlorpyrifos. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 188, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodsi, J.; Rafati, A.A. A novel molecularly imprinted sensor for imidacloprid pesticide based on poly(levodopa) electro-polymerized/TiO2 nanoparticles composite. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 7621–7633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, J.; Hu, L.; Feng, S. Epitope-imprinted mesoporous silica nanoparticles for specific recognition of tyrosine phosphorylation. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 9927–9930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahshid, S.S.; Flynn, S.E.; Mahshid, S. The potential application of electrochemical biosensors in the COVID-19 pandemic: A perspective on the rapid diagnostics of SARS-CoV-2. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 176, 112905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sari, E. Selective Recognition of Kanamycin via Molecularly Imprinted Nanosensor. Hittite J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgönüllü, S.; Yavuz, H.; Denizli, A. Development of gold nanoparticles decorated molecularly imprinted–based plasmonic sensor for the detection of aflatoxin M1 in milk samples. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, K.; Garcia Cruz, A.; Di Masi, S.; Voorhaar, A.; Ahmad, O.S.; Cowen, T.; Piletska, E.; Langford, N.; Coats, T.J.; Sims, M.R.; et al. Disposable paracetamol sensor based on electroactive molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for plasma monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 329, 129128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navakul, K.; Sangma, C.; Yenchitsomanus, P.-t.; Chunta, S.; Lieberzeit, P.A. Enhancing sensitivity of QCM for dengue type 1 virus detection using graphene-based polymer composites. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 6191–6198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, N.; Abu Bakar, N.K.; Muhammad Ekramul Mahmud, H.N.; Jamaludin, N.S. Molecularly imprinted polymers-based DNA biosensors. Anal. Biochem. 2021, 630, 114328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gast, M.; Sobek, H.; Mizaikoff, B. Advances in imprinting strategies for selective virus recognition a review. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 114, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, M.S.; Sales, M.G.F.; Frasco, M.F. Recent advances in virus imprinted polymers. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2022, 10, 100131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aurelio, R.; Tothill, I.E.; Salbini, M.; Calò, F.; Mazzotta, E.; Malitesta, C.; Chianella, I. A comparison of EIS and QCM NanoMIP-based sensors for morphine. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, A.; Corvaglia, S.; Pompa, P.P.; Malitesta, C. An innovative and simple all electrochemical approach to functionalize electrodes with a carbon nanotubes/polypyrrole molecularly imprinted nanocomposite and its application for sulfamethoxazole analysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 599, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hand, R.A.; Piletska, E.; Bassindale, T.; Morgan, G.; Turner, N. Application of molecularly imprinted polymers in the anti-doping field: Sample purification and compound analysis. Analyst 2020, 145, 4716–4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossi, A.M.; Maniglio, D. BioMIPs: Molecularly imprinted silk fibroin nanoparticles to recognize the iron regulating hormone hepcidin. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, O.I.; Dattilo, M.; Patitucci, F.; Malivindi, R.; Delbue, S.; Ferrante, P.; Parapini, S.; Galeazzi, R.; Cavarelli, M.; Cilurzo, F.; et al. Design and development of plastic antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 RBD based on molecularly imprinted polymers that inhibit in vitro virus infection. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 16885–16899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yarman, A.; Erdossy, J.; Katz, S.; Zebger, I.; Jetzschmann, K.J.; Altintas, Z.; Wollenberger, U.; Gyurcsányi, R.E.; Scheller, F.W. Electrosynthesized MIPs for transferrin: Plastibodies or nano-filters? Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 105, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovic, Z.; Erdőssy, J.; Keltai, K.; Scheller, F.W.; Gyurcsányi, R.E. Electrosynthesized molecularly imprinted polyscopoletin nanofilms for human serum albumin detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 977, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramanavicius, S.; Ramanavicius, A. Conducting polymers in the design of biosensors and biofuel cells. Polymers 2021, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesavento, M.; Marchetti, S.; De Maria, L.; Zeni, L.; Cennamo, N. Sensing by molecularly imprinted polymer: Evaluation of the binding properties with different techniques. Sensors 2019, 19, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kupai, J.; Razali, M.; Buyuktiryaki, S.; Kecili, R.; Szekely, G. Long-term stability and reusability of molecularly imprinted polymers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ertürk, G.; Uzun, L.; Tümer, M.A.; Say, R.; Denizli, A. Fab fragments imprinted SPR biosensor for real-time human immunoglobulin G detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 28, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetzschmann, K.J.; Yarman, A.; Rustam, L.; Kielb, P.; Urlacher, V.B.; Fischer, A.; Weidinger, I.M.; Wollenberger, U.; Scheller, F.W. Molecular LEGO by domain-imprinting of cytochrome P450 BM3. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 164, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caserta, G.; Zhang, X.; Yarman, A.; Supala, E.; Wollenberger, U.; Gyurcsányi, R.E.; Zebger, I.; Scheller, F.W. Insights in electrosynthesis, target binding, and stability of peptide-imprinted polymer nanofilms. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 381, 138236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickert, F.L.; Hayden, O.; Lieberzeit, P.; Haderspoeck, C.; Bindeus, R.; Palfinger, C.; Wirl, B. Nano- and micro-structuring of sensor materials—From molecule to cell detection. Synth. Met. 2003, 138, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, O.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Blaas, D.; Dickert, F.L. Artificial antibodies for bioanalyte detection—Sensing viruses and proteins. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klangprapan, S.; Choke-arpornchai, B.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Choowongkomon, K. Sensing the classical swine fever virus with molecularly imprinted polymer on quartz crystal microbalance. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altintas, Z.; Gittens, M.; Guerreiro, A.; Thompson, K.A.; Walker, J.; Piletsky, S.; Tothill, I.E. Detection of Waterborne Viruses Using High Affinity Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 6801–6807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altintas, Z. Advanced Imprinted Materials for Virus Monitoring. In Advanced Molecularly Imprinting Materials; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 389–411. [Google Scholar]
- Dickert, F.L.; Hayden, O.; Bindeus, R.; Mann, K.-J.; Blaas, D.; Waigmann, E. Bioimprinted QCM sensors for virus detection—Screening of plant sap. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 1929–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Gong, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, C. A virus resonance light scattering sensor based on mussel-inspired molecularly imprinted polymers for high sensitive and high selective detection of Hepatitis A Virus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanaviciene, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Molecularly imprinted polypyrrole-based synthetic receptor for direct detection of bovine leukemia virus glycoproteins. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 20, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratautaite, V.; Boguzaite, R.; Brazys, E.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Ciplys, E.; Juozapaitis, M.; Slibinskas, R.; Bechelany, M.; Ramanavicius, A. Molecularly imprinted polypyrrole based sensor for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 403, 139581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raziq, A.; Kidakova, A.; Boroznjak, R.; Reut, J.; Öpik, A.; Syritski, V. Development of a portable MIP-based electrochemical sensor for detection of SARS-CoV-2 antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 178, 113029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amouzadeh Tabrizi, M.; Fernández-Blázquez, J.P.; Medina, D.M.; Acedo, P. An ultrasensitive molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrochemical sensor for the determination of SARS-CoV-2-RBD by using macroporous gold screen-printed electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 196, 113729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayankojo, A.G.; Boroznjak, R.; Reut, J.; Öpik, A.; Syritski, V. Molecularly imprinted polymer based electrochemical sensor for quantitative detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 353, 131160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertürk, G.; Mattiasson, B. Molecular imprinting techniques used for the preparation of biosensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, M.; Gupta, N.; Raghuwanshi, R. Epitope Imprinting Approach to Monitor Diseases. J. Mol. Genet. Med. 2017, 11, 2–7. [Google Scholar]
- Iskierko, Z.; Sharma, P.S.; Noworyta, K.R.; Borowicz, P.; Cieplak, M.; Kutner, W.; Bossi, A.M. Selective PQQPFPQQ Gluten Epitope Chemical Sensor with a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Recognition Unit and an Extended-Gate Field-Effect Transistor Transduction Unit. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 4537–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquardini, L.; Bossi, A.M. Molecularly imprinted polymers by epitope imprinting: A journey from molecular interactions to the available bioinformatics resources to scout for epitope templates. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 6101–6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenci, L.; Guella, G.; Andreetto, E.; Ambrosi, E.; Anesi, A.; Bossi, A.M. Guided folding takes a start from the molecular imprinting of structured epitopes. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 15665–15670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, W.; Pei, J.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Epitope Imprinting Technology: Progress, Applications, and Perspectives toward Artificial Antibodies. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1902048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fresco-Cala, B.; Rajpal, S.; Rudolf, T.; Keitel, B.; Groß, R.; Münch, J.; Batista, A.D.; Mizaikoff, B. Development and characterization of magnetic SARS-CoV-2 peptide-imprinted polymers. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fresco-Cala, B.; Mizaikoff, B. Surrogate Imprinting Strategies: Molecular Imprints via Fragments and Dummies. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 3714–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, S.P.B.; Reis, R.L.; Peppas, N.A.; Gomes, M.E.; Domingues, R.M.A. Epitope-imprinted polymers: Design principles of synthetic binding partners for natural biomacromolecules. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabi9884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietl, S.; Sobek, H.; Mizaikoff, B. Epitope-imprinted polymers for biomacromolecules: Recent strategies, future challenges and selected applications. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 143, 116414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachkov, A.; Minoura, N. Towards molecularly imprinted polymers selective to peptides and proteins. The epitope approach. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 2001, 1544, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachkov, A.; Minoura, N. Recognition of oxytocin and oxytocin-related peptides in aqueous media using a molecularly imprinted polymer synthesized by the epitope approach. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 889, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, H.; Huang, C.S.; Shea, K.J. Selective protein capture by epitope imprinting. Angew. Chem.—Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 2393–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechtrirat, D.; Jetzschmann, K.J.; Stöcklein, W.F.M.; Scheller, F.W.; Gajovic-Eichelmann, N. Protein rebinding to a surface-confined imprint. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 5231–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, A.D.; Rajpal, S.; Keitel, B.; Dietl, S.; Fresco-Cala, B.; Dinc, M.; Groß, R.; Sobek, H.; Münch, J.; Mizaikoff, B. Plastic Antibodies Mimicking the ACE2 Receptor for Selective Binding of SARS-CoV-2 Spike. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2101925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinc, M.; Esen, C.; Mizaikoff, B. Recent advances on core–shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for biomacromolecules. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 114, 202–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bognár, Z.; Supala, E.; Yarman, A.; Zhang, X.; Bier, F.F.; Scheller, F.W.; Gyurcsányi, R.E. Peptide epitope-imprinted polymer microarrays for selective protein recognition. Application for SARS-CoV-2 RBD protein. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altintas, Z.; Takiden, A.; Utesch, T.; Mroginski, M.A.; Schmid, B.; Scheller, F.W.; Süssmuth, R.D. Integrated Approaches Toward High-Affinity Artificial Protein Binders Obtained via Computationally Simulated Epitopes for Protein Recognition. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1807332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Caserta, G.; Yarman, A.; Supala, E.; Waffo, A.F.T.; Wollenberger, U.; Gyurcsányi, R.E.; Zebger, I.; Scheller, F.W. “Out of Pocket” Protein Binding—A Dilemma of Epitope Imprinted Polymers Revealed for Human Hemoglobin. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, K.J.; Thompson, E. Template synthesis of macromolecules. Selective functionalization of an organic polymer. J. Org. Chem. 1978, 43, 4253–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, F.; Mizaikoff, B. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers as Artificial Receptors. In Artificial Receptors for Chemical Sensors; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2010; pp. 391–437. [Google Scholar]
- Yarman, A.; Turner, A.P.F.; Scheller, F.W. Electropolymers for (Nano-)Imprinted Biomimetic Biosensors; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Sawston, UK, 2014; ISBN 9780857096609. [Google Scholar]
- Whitcombe, M.J.; Rodriguez, M.E.; Villar, P.; Vulfson, E.N. A New Method for the Introduction of Recognition Site Functionality into Polymers Prepared by Molecular Imprinting: Synthesis and Characterization of Polymeric Receptors for Cholesterol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 7105–7111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viveiros, R.; Rebocho, S.; Casimiro, T. Green strategies for molecularly imprinted polymer development. Polymers 2018, 10, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirsky, V.M.; Hirsch, T.; Piletsky, S.A.; Wolfbeis, O.S. A spreader-bar approach to molecular architecture: Formation of stable artificial chemoreceptors. Angew. Chem.—Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 1108–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Du, X.; Huang, X.; Lv, Z. Creating protein-imprinted self-assembled monolayers with multiple binding sites and biocompatible imprinted cavities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 9248–9251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-I.; Subramanian, A.; Mueller, S.; Levon, K.; Nam, C.-Y.; Rafailovich, M.H. Potentiometric Biosensors Based on Molecular-Imprinted Self-Assembled Monolayer Films for Rapid Detection of Influenza A Virus and SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 5045–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunta, S.; Suedee, R.; Boonsriwong, W.; Lieberzeit, P.A. Biomimetic sensors targeting oxidized-low-density lipoprotein with molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1116, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basan, H.; Dinc, M.; Mizaikoff, B. Inhibitor-assisted synthesis of molecularly imprinted microbeads for protein recognition. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Song, H.; Wang, Y.; Tian, X.; Tang, Y.; Gao, R.; Zhang, C. Hydrophilic magnetic molecularly imprinted nanobeads for efficient enrichment and high performance liquid chromatographic detection of 17beta-estradiol in environmental water samples. Talanta 2020, 220, 121367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia Lopez, J.; Piletska, E.V.; Whitcombe, M.J.; Czulak, J.; Piletsky, S.A. Application of molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for degradation of the bacterial autoinducer: N-hexanoyl homoserine lactone. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 2664–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Zhou, X.; Luan, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, N.; Lu, Y.; Liu, T.; Xu, W. A sensitive electrochemical sensor modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes doped molecularly imprinted silica nanospheres for detecting chlorpyrifos. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, W.; Liu, S.; Yu, J.; Xing, X.; Li, J.; Cui, M.; Huang, J. Electrochemical sensor based on gold nanoparticles fabricated molecularly imprinted polymer film at chitosan-platinum nanoparticles/graphene-gold nanoparticles double nanocomposites modified electrode for detection of erythromycin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 38, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowdon, J.W.; Diliën, H.; Singla, P.; Peeters, M.; Cleij, T.J.; van Grinsven, B.; Eersels, K. MIPs for commercial application in low-cost sensors and assays—An overview of the current status quo. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 325, 128973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dronina, J.; Samukaite-Bubniene, U.; Ramanavicius, A. Advances and insights in the diagnosis of viral infections. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Cao, S.; Whitcombe, M.J.; Piletsky, S.A. Size matters: Challenges in imprinting macromolecules. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamalipour Soufi, G.; Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Molecularly imprinted polymers for the detection of viruses: Challenges and opportunities. Analyst 2021, 146, 3087–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sener, G.; Ozgur, E.; Rad, A.Y.; Uzun, L.; Say, R.; Denizli, A. Rapid real-time detection of procalcitonin using a microcontact imprinted surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Analyst 2013, 138, 6422–6428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saylan, Y.; Erdem, Ö.; Ünal, S.; Denizli, A. An alternative medical diagnosis method: Biosensors for virus detection. Biosensors 2019, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verheyen, E.; Schillemans, J.P.; Van Wijk, M.; Demeniex, M.A.; Hennink, W.E.; Van Nostrum, C.F. Challenges for the effective molecular imprinting of proteins. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3008–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, P.S.; Pietrzyk-Le, A.; D’Souza, F.; Kutner, W. Electrochemically synthesized polymers in molecular imprinting for chemical sensing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 3177–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Erdossy, J.; Horváth, V.; Yarman, A.; Scheller, F.W.; Gyurcsányi, R.E. Electrosynthesized molecularly imprinted polymers for protein recognition. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malitesta, C.; Mazzotta, E.; Picca, R.A.; Poma, A.; Chianella, I.; Piletsky, S.A. MIP sensors—The electrochemical approach. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 1827–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wangchareansak, T.; Thitithanyanont, A.; Chuakheaw, D.; Gleeson, M.P.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Sangma, C. Influenza A virus molecularly imprinted polymers and their application in virus sub-type classification. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2190–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertürk, G.; Hedström, M.; Mattiasson, B. A sensitive and real-time assay of trypsin by using molecular imprinting-based capacitive biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanavičius, S.; Morkvėnaitė-vilkončienė, I.; Samukaitė-bubnienė, U.; Ratautaitė, V.; Plikusienė, I.; Viter, R.; Ramanavičius, A. Electrochemically Deposited Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensors. Sensors 2022, 22, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giulio, T.; Mazzotta, E.; Malitesta, C. Molecularly imprinted polyscopoletin for the electrochemical detection of the chronic disease marker lysozyme. Biosensors 2021, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, C.D.; Whitesides, G.M. Modeling Organic Surfaces with Self-Assembled Monolayers. Angew. Chem. 1989, 101, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujahid, A.; Iqbal, N.; Afzal, A. Bioimprinting strategies: From soft lithography to biomimetic sensors and beyond. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 1435–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Whitesides, G.M. Soft Lithography Younan. Angew. Chem.—Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 550–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Xia, Y.; Whitesides, G.M. Soft lithography for micro- and nanoscale patterning. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whitesides, G.M.; Ostuni, E.; Takayama, S.; Jiang, X.; Ingber, D.E. Soft Lithography in Biology and Microbiology. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 3, 335–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dickert, F.L.; Lieberzeit, P.; Hayden, O. Sensor strategies for microorganism detection-from physical principles to imprinting procedures. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 377, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenik, M.; Schirhagl, R.; Schirk, C.; Hayden, O.; Lieberzeit, P.; Blaas, D.; Paul, G.; Dickert, F.L. Sensing picornaviruses using molecular imprinting techniques on a quartz crystal microbalance. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 5320–5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarman, A. Development of a molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrochemical sensor for tyrosinase. Turk. J. Chem. 2018, 42, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarman, A. Electrosynthesized Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Laccase Using the Inactivated Enzyme as the Target. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2018, 39, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozal-Palabiyik, B.; Erkmen, C.; Uslu, B. Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensors: Analytical and Pharmaceutical Applications Based on Ortho-Phenylenediamine Polymerization. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 16, 350–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozal-Palabiyik, B.; Lettieri, M.; Uslu, B.; Marrazza, G. Electrochemical Detection of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor by Molecularly Imprinted Polymer. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira Gonçalves, L. Electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymers: Perceptions based on recent literature for soon-to-be world-class scientists. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 25, 100640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.A. An overview of bio-inspired intelligent imprinted polymers for virus determination. Biosensors 2021, 11, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wankar, S.; Turner, N.W.; Krupadam, R.J. Polythiophene nanofilms for sensitive fluorescence detection of viruses in drinking water. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 82, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shumyantseva, V.V.; Bulko, T.V.; Sigolaeva, L.V.; Kuzikov, A.V.; Archakov, A.I. Electrosynthesis and binding properties of molecularly imprinted poly-o-phenylenediamine for selective recognition and direct electrochemical detection of myoglobin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, R.A.; Carro, A.M.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Concheiro, A. To remove or not to remove? The challenge of extracting the template to make the cavities available in molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 4327–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pirzada, M.; Altintas, Z. Template Removal in Molecular Imprinting: Principles, Strategies, and Challenges. In Molecular Imprinting for Nanosensors and Other Sensing Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 367–406. [Google Scholar]
- Lahcen, A.A.; Amine, A. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Sensors Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers and Nanomaterials. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcelikay, G.; Kurbanoglu, S.; Yarman, A.; Scheller, F.W.; Ozkan, S.A. Au-Pt nanoparticles based molecularly imprinted nanosensor for electrochemical detection of the lipopeptide antibiotic drug Daptomycin. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 320, 128285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarman, A.; Kurbanoglu, S.; Erkmen, C.; Uslu, B.; Scheller, F.W. Quantum Dot-Based Electrochemical Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Sensors: Potentials and Challenges. In Electroanalytical Applications of Quantum Dot-Based Biosensors; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 121–153. ISBN 9780128216705. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Xia, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zeng, B. Determination of patulin using dual-dummy templates imprinted electrochemical sensor with PtPd decorated N-doped porous carbon for amplification. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piloto, A.M.L.; Ribeiro, D.S.M.; Rodrigues, S.S.M.; Santos, J.L.M.; Ferreira Sales, M.G. Label-free quantum dot conjugates for human protein IL-2 based on molecularly imprinted polymers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 304, 127343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Couto, R.A.S.; Coelho, C.; Mounssef, B.; Morais, S.F.d.A.; Lima, C.D.; Dos Santos, W.T.P.; Carvalho, F.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Braga, A.A.C.; Gonçalves, L.M.; et al. 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) sensing based on electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymers on silver nanoparticles and carboxylated multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idil, N.; Bakhshpour, M.; Perçin, I.; Mattiasson, B.; Denizli, A. Molecular Imprinting-Based Sensing Platforms for Recognition of Microorganisms. In Molecular Imprinting for Nanosensors and Other Sensing Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 255–281. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, O.S.; Bedwell, T.S.; Esen, C.; Garcia-Cruz, A.; Piletsky, S.A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in Electrochemical and Optical Sensors. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crapnell, R.D.; Dempsey-Hibbert, N.C.; Peeters, M.; Tridente, A.; Banks, C.E. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based Electrochemical Biosensors: Overcoming the Challenges of Detecting Vital Biomarkers and Speeding up Diagnosis. Talanta Open 2020, 2, 100018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.A.; Kandeil, A.; Gomaa, M.; Mohamed El Nashar, R.; El-Sherbiny, I.M.; Hassan, R.Y.A. SARS-CoV-2-Impedimetric Biosensor: Virus-Imprinted Chips for Early and Rapid Diagnosis. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 4098–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EL Sharif, H.F.; Dennison, S.R.; Tully, M.; Crossley, S.; Mwangi, W.; Bailey, D.; Graham, S.P.; Reddy, S.M. Evaluation of electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymers (E-MIPs) on disposable electrodes for detection of SARS-CoV-2 in saliva. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1206, 339777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukjee, W.; Thitithanyanont, A.; Manopwisedjaroen, S.; Seetaha, S.; Thepparit, C.; Sangma, C. Virus MIP-composites for SARS-CoV-2 detection in the aquatic environment. Mater. Lett. 2022, 315, 131973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, S.A.; Bahrani, S.; Mousavi, S.M.; Omidifar, N.; Behbahan, N.G.G.; Arjmand, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Lankarani, K.B.; Moghadami, M.; Firoozsani, M. Graphene-Based Femtogram-Level Sensitive Molecularly Imprinted Polymer of SARS-CoV-2. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2101466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Y. Highly sensitive electrochemical determination of the SARS-CoV-2 antigen based on a gold/graphene imprinted poly-arginine sensor. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 5772–5776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cennamo, N.; Agostino, G.D.; Perri, C.; Arcadio, F.; Chiaretti, G.; Parisio, E.M.; Camarlinghi, G.; Vettori, C.; Di Marzo, F.; Cennamo, R.; et al. Proof of Concept for a Quick and Highly Sensitive On-Site Detection of SARS-CoV-2 by Plasmonic Optical Fibers and Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Sensors 2021, 21, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimi, Y.; Ohdaira, R.; Iiyama, C.; Sakai, K. ‘Gate effect’ of thin layer of molecularly-imprinted poly(methacrylic acid-co-ethyleneglycol dimethacrylate). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 73, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.S.; Garcia-Cruz, A.; Cieplak, M.; Noworyta, K.R.; Kutner, W. ‘Gate effect’ in molecularly imprinted polymers: The current state of understanding. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2019, 16, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalecki, J.; Iskierko, Z.; Cieplak, M.; Sharma, P.S. Oriented Immobilization of Protein Templates: A New Trend in Surface Imprinting. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 3710–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rump, A.; Risti, R.; Kristal, M.L.; Reut, J.; Syritski, V.; Lookene, A.; Ruutel Boudinot, S. Dual ELISA using SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein produced in E. coli and CHO cells reveals epitope masking by N-glycosylation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 534, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Cruz, A.; Haq, I.; Di Masi, S.; Trivedi, S.; Alanazi, K.; Piletska, E.; Mujahid, A.; Piletsky, S.A. Design and fabrication of a smart sensor using in silico epitope mapping and electro- responsive imprinted polymer nanoparticles for determination of insulin levels in human plasma. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 169, 112536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Cruz, A.; Ahmad, O.S.; Alanazi, K.; Piletska, E.; Piletsky, S.A. Generic sensor platform based on electro-responsive molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles (e-NanoMIPs). Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2020, 6, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Template | Monomer | Transducer | Detection Method | (Linear) Range and LOD | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SARS-CoV-2 whole virus | 3-AP | CNT/WO3-SPCE | EIS | LOD: 57 pg/mL | [139] |
| SARS-CoV-2 whole virus | NHMA MBAm (cross-linker) | SPE | EIS | 3–7 log10 pfu/mL LOD: 4.9 log10 pfu/mL | [140] |
| SARS-CoV-2 whole virus | AAM, MAA, MMA, and NVP; DHEBA (cross-linker) | GO integrated Ag-SPE | CV | 0.01 fM to 100 fM LOD: 0.1 fM | [141] |
| SARS-CoV-2 whole virus | Pyrrole; (graphene oxide) APBA (cross-linker); | GCE | DPV and amperometry | DPV: 0.74–9.03 fg mL–1 and LOD: 0.326 fg mL–1 Amperometry: 13.14–118.9 fg mL–1 and LOD: 11.32 fg mL–1 | [142] |
| SARS-CoV-2 nucleoprotein | m-PD | 4-ATP-modified Au-TFE | DPV | Up to 111 fM; LOD: 15 fM (in lysis buffer) | [63] |
| SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein | Arginine | Au/Gr-modified SPCE | DPV | 10.0–200.0 fM; LOD: 3 fM | [143] |
| SARS-CoV-2 spike protein | Pyrrole | Pt Electrode | CA | 0 μg/mL to 25 μg/mL | [62] |
| SARS-CoV-2 RBD | o-PD | MP-Au-SPE | EIS | 2.0 pg·mL−1–40 pg·mL−1 LOD: 0.7 pg·mL−1 | [64] |
| SARS-CoV-2 spike protein subunit S1 | APBA | 4-ATP-modified Au-TFME | SWV | LOD: 15 fM (in PBS) and 64 fM (patient’s nasopharyngeal samples) | [65] |
| SARS-CoV-2 spike protein subunit S1 | Aam, TBAm, and HEMA; BIS (cross-Linker) | POF-based SPR chip | SPR | LOD: 0.058 µM | [144] |
| SARS-CoV-2 spike protein RBD epitope (GFNCYFPLQ) | Scopoletin | Au- SPRi chips | SPR | NS | [82] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yarman, A.; Kurbanoglu, S. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensors for SARS-CoV-2: Where Are We Now? Biomimetics 2022, 7, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7020058
Yarman A, Kurbanoglu S. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensors for SARS-CoV-2: Where Are We Now? Biomimetics. 2022; 7(2):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7020058
Chicago/Turabian StyleYarman, Aysu, and Sevinc Kurbanoglu. 2022. "Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensors for SARS-CoV-2: Where Are We Now?" Biomimetics 7, no. 2: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7020058
APA StyleYarman, A., & Kurbanoglu, S. (2022). Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensors for SARS-CoV-2: Where Are We Now? Biomimetics, 7(2), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7020058







