Abstract
Although this is an era of pandemics and many devastating diseases, this is also a time when bionanotechnology flourishes, illuminating a multidisciplinary field where vaccines are quickly becoming a balsam and a prevention against insidious plagues. In this work, we tried to gain and also give a deeper understanding on nanovaccines and their way of acting to prevent or cure cancer, infectious diseases, and diseases caused by parasites. Major nanoadjuvants and nanovaccines are temptatively exemplified trying to contextualize our own work and its relative importance to the field. The main properties for novel adjuvants seem to be the nanosize, the cationic character, and the biocompatibility, even if it is achieved in a low dose-dependent manner.
1. The Importance of Nanoadjuvants for Vaccines
In this pandemics era, the exponential growth of nanobiotechnology certainly benefits the development of nanovaccines, displaying resourceful alternatives for controlling and hopefully eradicating infectious diseases [1,2,3,4,5,6]. The early models for vaccination using attenuated pathogens offered the antigens and the pathogen molecular patterns (PMPs) able to properly activate the antigen presenting cells (APCs), however, many modern vaccines carry purified antigens so that adjuvants and stimulators become essential to trigger activation of APCs. Against many diseases such as cancer, tuberculosis, mycosis, malaria, and parasites infestation, vaccines have to enhance both antibody production and cellular immunity [7].
Most commercially available vaccines promote antibody and Th2 response and are able to fight invading microorganisms that do not enter the host cells. However, against intracellular infections and cancers, both cellular and humoral immune responses are essential [8]. The CD8+ T-cells respond to infection or transformation of nucleated cells expressing major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and, upon differentiation into cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CTLs), kill target cells directly; in addition, CD8+ T-cells release chemokines and cytokines that call more effector cells, such as the neutrophils and the macrophages [8].
Because most antigens are negatively charged, electrostatics guarantees that cationic nanoadjuvants properly adsorb antigens, yielding nanometric sizes for the adjuvant/antigen assemblies that are not retained at the site of injection, avoid physiological barriers, and are rapidly drained to the lymph nodes rich in dendritic cells [3,9,10,11,12,13]. Nanoadjuvants can be obtained from a variety of lipids, polymers, or lipids, and polymers mostly as bilayer vesicles [14,15], open bilayer disks [16,17,18,19,20], lipid nanoparticles [21], or hybrid nanoparticles [4,5,22,23,24,25,26]. For example, the molecular geometry of dioctadecyldimethylammonium bromide (DODAB), a cationic and synthetic double-chained amphiphile, favors its self-assembly in water solution as bilayers either closed (large vesicles) or open (bilayer fragments or disks) [15,27]. The latter, from now on called DODAB BF, displays nanometric sizes (<100 nm), have hydrophobic defects and fuse upon salt-induced screening of their surface potential [28]. DODAB bilayers are very versatile, adsorbing several biomolecules: proteins [14,17,29,30], peptides [25,31,32], oligonucleotides [18,33], mononucleotides [34,35], and nucleic acids [36,37], and also enhancing cellular immune responses to antigens, though yielding poor humoral responses [14,17,18,22]. DODAB assemblies also interact with negatively charged particles such as polystyrene sulfate latexes [22,25,38,39,40] or silica [41,42,43,44]. Optimal bilayer deposition led to the description of supported DODAB bilayers on polystyrene sulfate (PSS) nanoparticles [22,25,40] or silica for presentation of adsorbed antigens [43,44]. The good miscibility of DODAB with the biocompatible polymer poly (methylmethacrylate) (PMMA) [23,45] led to the synthesis of polymeric PMMA nanoparticles by emulsion polymerization of methylmethacrylate (MMA) in the presence of DODAB BF, which produced the hybrid, cationic, nanometric and biocompatible PMMA/DODAB NPs [26]. These NPs combined well with oppositely charged ovalbumin (OVA) and induced a mixed Th1-Th2 immune response [46].
For use in humans, there are few adjuvants [47]. Commercially available vaccines largely promote antibody and Th2 responses [48]. In the US, there are aluminum salts (alum) added of monophosphoryl lipid A, a toll-like receptor 4 agonist [48], whereas, in Europe, there are the virosomes, the virus-like particles (VLPs), and the oil-in-water emulsions [49]. A good example of vaccine with VLPs as adjuvants is a prophylactic vaccine against infections by the human papilloma virus (HPV) that is able to prevent cervical cancer [50].
Strong Th1 response in animals has been provided by viral constructs [51,52], DNA- [53,54,55], and mRNA-based vaccines [54,56,57]. These vectors promote the process of cross-presentation in APCs, meaning that vaccine-encoded peptide fragments are released in the cytosol and presented by MHC-I in APCs [6,58,59]. DNA- and mRNA-based vaccines have success for veterinary use [60]. However, efficacy, safety, and tolerability remains to be established for humans, despite of the use of these technologies in coronavirus vaccination [61,62].
Bacterial toxins, particulates, plant derivatives, and pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PMPs) are some examples of adjuvants [63,64]. Adjuvants belong to two groups: they are immunopotentiators or they are delivery systems according to their mechanism of action [48,65]. Delivery systems prevent antigen degradation and promote uptake of antigens by APCs [65], whereas immunopotentiators act as agonists of pathogen recognition receptors (PRRs) [48]. Efficient adjuvants may result from combinations of delivery systems and immunopotentiators [66,67].
In this review, supramolecular assemblies yielding nanostructured materials able to combine well with antigens to potentiate the immune response are overviewed. Nanoparticles, vesicles, liposomes, bilayer disks, niosomes, and hydrogels are evaluated from the perspective of efficient antigen presentation in novel nanovaccines.
2. Molecular and Supramolecular Assemblies for Vaccines and Beyond
Molecular assemblies based on non-covalent, physical intermolecular interactions have been extensively explored in drug and vaccine delivery [16,67,68,69,70,71]. For example, amphiphiles such as lipids and surfactants self-assemble in water solution to yield a variety of useful nano- or micro-structures such as micelles, bilayer membranes, inverted phases, vesicles, nanodisks, etc.; type of assembly can be predicted from theory and molecular geometry [72,73]. Intermolecular interactions can be attractive and/or repulsive depending not only on the chemical structure of molecules involved but also on composition of the intervening medium [45,74,75]. Adsorption of counter-ions onto a cationic bilayer can modify the type of bilayer assembly. NaCl added to DODAB BF promoted fusion and appearance of large and closed bilayer vesicles in the dispersion and appearance of hydrophobic defects in the bilayer. Monovalent salt at a moderate concentration was reported to fuse cationic bilayer fragments [15,28,76,77], with induction of hydrophobic defects in the bilayer [78]. When the electrostatic repulsion is high, as in pure water or at low salt concentrations, interdigitation can take place, allowing some relaxation of the electrostatic repulsion between adjacent DODAB molecules in the bilayer. Adhesion between the cationic bilayers may occur due to interdigitation [79]. Computer simulations along time for the DODAB self-assembly in water dispersions [80], differential scanning calorimetry and scattering of X-rays in the subgel phase [81] evidenced consistently the intra-bilayer tilting and the occurrence of hydrophobic defects. Figure 1 illustrates molecular dynamics simulations for the self-assembly of the cationic lipid DODAB.
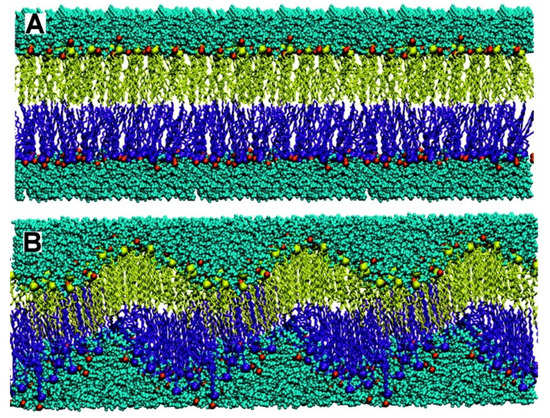
Figure 1.
The dynamics of the self-assembly process simulated in the computer for dioctadecyldimethylammonium bromide at 25 °C at times zero (A) and 90 ns (B). Reprinted with permission from [80]. Copyright 2010 American Chemical Society.
The importance of intermolecular interactions in determining structure and function of supramolecular assemblies made by men or found in nature is paramount. For example, biological supramolecular assemblies such as complexes of nucleic acids and histones occur in the chromatin of eukaryotic cells [82,83]. Surface electrostatic potential and less predictable hydrophobic contacts drive the DNA–protein interactions. The recognition of specific DNA sequences by proteins depends on the formation of hydrogen bonds with specific bases, primarily in the major groove, and on sequence-dependent deformations of the DNA helix. From analysis of the three-dimensional structures of protein–DNA assemblies, arginine residues attached to narrow minor grooves was often the mode for protein–DNA recognition; narrow minor grooves increase locally the DNA negative electrostatic potential thereby attracting positively charged regions on proteins [82].
After crystallites of nucleosomes, the core particles of chromatin, were obtained, X-ray diffraction revealed their crystal structure at 2.8 angstroms resolution, a major achievement in 1997 [84]. Figure 2 shows the organization in the nucleosome particle; 146 base pairs of DNA helix surround the histones, representing a way of compacting long DNA chains of the chromatin in eukaryotes; linear DNA compaction thereby occurs by a factor of 30–40 [84]. The nucleosomes further associate into higher-order assemblies linked by the linker histone H1 so that DNA bends and forms high ordered helixes shaped by the histones [85]. The nucleosome is responsible for packaging DNA within the nucleus, largely determining DNA accessibility.
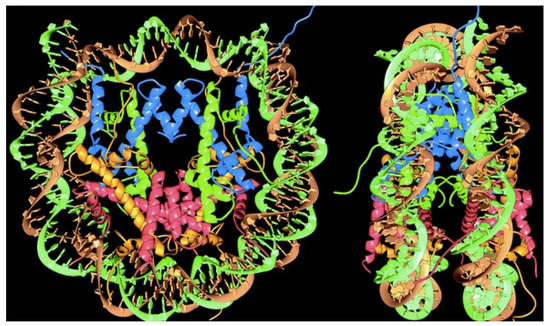
Figure 2.
Nucleosome particle showing the histones core surrounded by DNA. Reproduced with permission from reference [84].
Similarly to DODAB supramolecular assemblies, characteristics of nucleosomes also depend on physico-chemical properties of their environment such as ionic strength and divalent-ion concentration, and on histone or DNA-modification and/or DNA state [86]. For assemblies in vitro, variable nucleosome inter-spacing was related to variable electrostatic attraction between DNA and histones; if the salt concentration during the assembly process increased, the repeat distance between nucleosomes also increased [87,88]. The compacting effect of cationic NPs on long-chained bacteriophage DNA was reconstituted using supported cationic bilayers on polymeric nanoparticles; these nucleosome mimetic systems were available over a range of nanosizes for the primary polymeric particles surrounded by the supported cationic bilayer; this opened new possibilities for a variety of DNA- or mRNA-based nanovaccines [36]. Figure 3 shows images of supramolecular assemblies mimicking nucleosomes; they assembled from cationic nanoparticles and giant bacteriophages DNA under conditions of charge neutralization; in the same micrograph, some single nanoparticles and isolated DNA molecules could also be seen, although the majority of supramolecular assemblies corresponded to electrostatically driven associations between anionic DNA molecules and cationic PSS/DODAB NPs [36]. Another important feature was the compaction of the long DNA chains by the cationic NPs, imparting a truly nucleosome mimetic character for the assemblies.
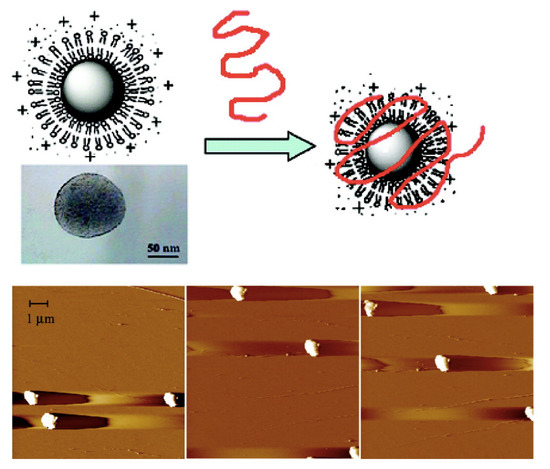
Figure 3.
Scheme and AFM micrographs for PSS/DODAB/T2-DNA dispersions at charge neutralization. They display nucleosome-mimetic micrometric assemblies. One should notice some isolated PSS/DODAB nanoparticles and the long T2 DNA chain on the top right corner of the AFM micrograph on the left. Reproduced with permission from reference [36]. Copyright 2008. American Chemical Society.
Cancer immunity evolves in two steps: the preparatory and the effector ones [89]. The preparatory step takes place in the LN with release and presentation of cancer antigens for priming and activating T cells. In the next step, T cells reach the tumor mass, trying to recognize and kill the cancer cells in the tumor. However, the tumor tissue and microenvironment can be immunosuppressive due to low immunogenicity of tumor cells, presence of immunosuppressive cytokines, and biological barriers hampering chemotherapeutic agents and immunotherapies to reach the tumor cells [90,91]. Therefore, nanotechnology is needed for surmounting these key biological barriers and effectively deliver chemo- and immune-therapeutic agents and vaccines to their sites of action; sensitive antigens easily degradable in the physiological medium can be protected using nanotechnologies able to increase their half-lives, minimize systemic toxicity, and promote their delivery to APCs in the LN [91]. Nanostructures such as NPs [5,17,43,92], bilayer fragments (BF) [4,12], or peptide supramolecular assemblies [93] become drained directly to the LNs, performing well in the preparatory step [89]. In the effector step, activated T cells should infiltrate the tumor, and stable, long-circulating, and targeted nanostructures could help T cells infiltration improving the outcomes of immunotherapies, which may give a low response rate due to the T-cell poor infiltration in the tumor tissue. Despite the approval of nanomedicines for cancer treatment, the low observed survival was possibly due to abnormal phenotypes of the tumor microenvironment (TME); nanostructures should incorporate anticancer drugs, drugs for improving tumor perfusion, and others to return TME to normality [94]. The extracellular matrix (ECM) produced by cancer associated fibroblasts (CAF) supports cancer cells expressing α-smooth muscle actin and fibroblast activation protein (FAP), both upregulating the expression of other functional cell surface proteins like platelet-derived growth factor receptor β and the insulin-like growth factor receptor II; activated fibroblasts could benefit from delivery of nanoparticles carrying drugs, especially in liver cancer to downregulate growth factors [95]. Figure 4 reproduced from reference [94] illustrates the tasks ahead for nanomedicines: they should also enable normalization of abnormal TME phenotypes, such as the one restricting penetration of cells for immunotherapy (in purple) and the one with inflammatory character (in red); the normal TME appears centralized in blue. The defective vasculature in cancer tissue can not only reduce oxygen supply, but also hampers the penetration of anti-cancer cellular immunity; drugs and normalizers of the vasculature and drugs to prevent the production of dense extracellular matrixes by cancer associated fibroblasts would possibly normalize the TME by improving perfusion, oxygen supply and drug delivery of cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory chemotherapeutics. Importantly, responses to immunotherapy increased when TME normalization approaches were applied [94].
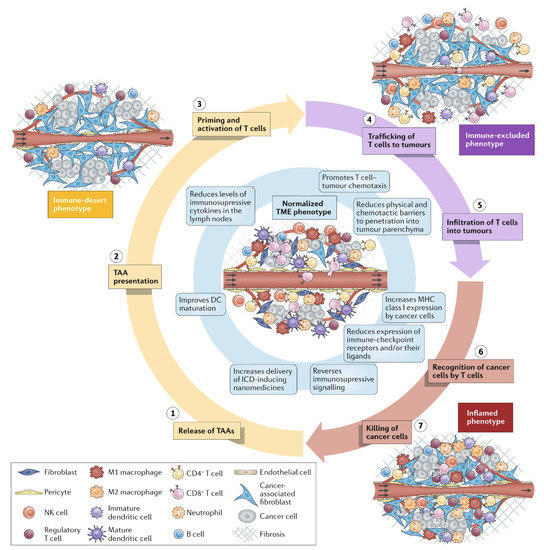
Figure 4.
Possible tumor microenvironment phenotypes (TME) in cancer as compared to the normalized one. Combined medicines in nanoformulations, such as normalizers of TME and anti-cancer drugs, can advantageously penetrate the tumor mass as compared to microformulations. Abbreviations are DC for dendritic cell; ICD for immunogenic cell death; NK for natural killer; TAA for tumor-associated antigen. Reprinted with permission from [94].
Having recognized the importance of formulating drugs and vaccines in nanostructures, here we present several instances of nano-vaccines delivery based on surfactants, lipids, polymers, biopolymers, proteins, etc. Self-assembled vehicles discussed are vesicles, liposomes, niosomes, bilayer fragments or disks, nanoparticles, and hydrogels.
3. Vesicles, Liposomes, Lipid Nanoparticles, Disks, and Niosomes
In this section, meaningful examples of vaccine delivery using self-assembled nanostructures are discussed and major research areas in need of vaccines are pointed out.
A HIV vaccine yielding long-lasting anti-HIV antibodies is not yet available. The immunodeficiency typical of HIV has its basis on the scarce numbers of trimmer spike proteins on the virus; this efficiently prevents IgG bivalent binding, meaning low elicitation of neutralizing antibodies; there are only 14 HIV spikes per virus [96]. Interesting combinations between antigen NPs and liposomes enhanced specific humoral responses against HIV. In a possible vaccine strategy, liposomes were employed to increase the density of exposed BG505 MD39, which is a gp140 envelope trimmer; covalently linked trimmers with good orientation were exposed by the liposomes at high densities; in this case, the nanoparticles attached to the liposomes were the trimmers; immunization with avid MD39-specific IgG antibodies in serum was thereby achieved [97]. Figure 5a illustrates the low density of trimmeric protein spikes on HIV and their implications in vaccine formulation, whereas Figure 5b shows the design of the liposomal formulation proposed to improve HIV antigen presentation at high densities [96,97]. Figure 5a evidenced the contrast between high-density and low density epitope display for papilloma virus (PV) and HIV, respectively, as reproduced from [96], whereas Figure 5b shows a liposomal formulation for displaying the gp140 trimer MD39; one should notice that the bar on the micrograph corresponds to 100 nm [97]. Liposomes in the electron microscopy micrograph eventually occur as concentric and closed multi-bilayers with a large variability in size, however there was a very regular distribution of the trimeric lipoprotein on the bilayers measured as the spacing between trimers on the bottom right portion of Figure 5b.
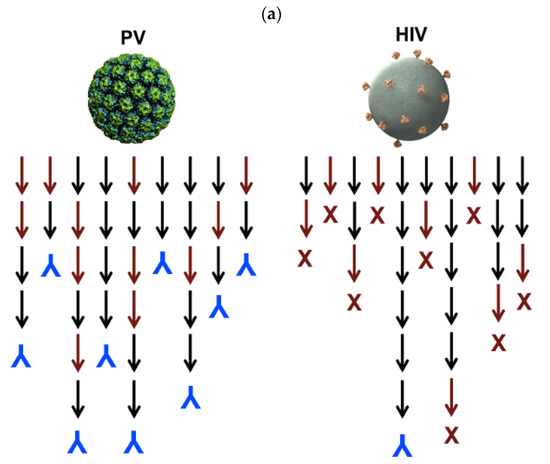
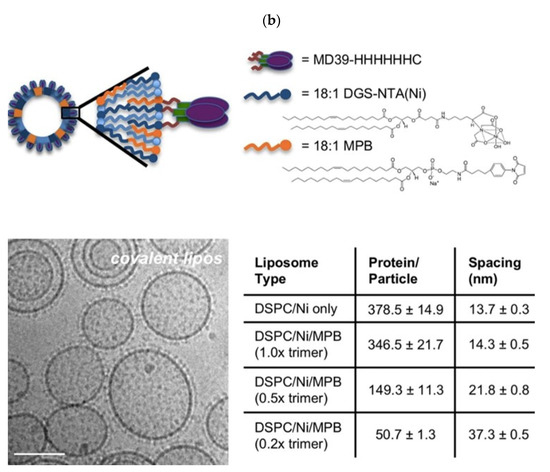
Figure 5.
(a) Compared densities of spike proteins in papilloma virus (PV) and HIV able to elicit neutralizing antibodies (in blue). Reproduced from [96]. (b) Increasing the density of HIV antigens on liposomes. The HIV antigens were the MD39 trimmer covalently linked to the liposomes. On the cryo-electron microscopy micrograph, liposomes display the trimmers in a regular manner (bar corresponds to 100 nm); on the table, trimmer densities and spacing in between them depends on coupling strategy and trimmer concentration used for coupling [97].
The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 is the first point of virus contact with the cell to be invaded; for invasion, this viral protein binds to a host receptor. In order to prevent virus entrance in the host cell, it is possible to raise neutralizing antibodies able to attach to the receptor-binding domain of the viral spike protein; it is even possible to make a selection of the best antibodies, such as those recently found and named S2H97 and S2E12 [98]. The S2H97 antibody was able to neutralize several viruses belonging to the coronavirus family as well as coronavirus mutants; in vivo, hamsters treated with this antibody, and then infected with the virus two days after treatment, showed a serum decrease in viral RNA concentrations of more than ten thousand times as compared to the untreated hamsters [98]. S2H97 displayed a large breadth and resistance to escape, possibly encompassing neutralization of future mutants due to its broad capability to treat infections by several viruses belonging to the coronavirus family; patients recovered from coronavirus infection did not have antibodies able to compete with S2H97 for neutralizing the virus, meaning low probability of occurring mutants with changes in the epitope where S2H97 binds [98,99]. The S2E12 neutralizing ability was not as broad as the one of the S2H97, but its potency was also considerable; virus mutants escaping neutralization by S2E12 were not able to bind to the receptor of the host cell and therefore could not replicate, making their outbreaks unlikely [98]. S2E12 displayed a modest breadth against the virus of the coronavirus family and could not be ruled out, eventually becoming applicable to neutralize infections by coronavirus mutants or other members of the coronavirus family [98]. Importantly, in sub-Saharan Africa, the cross-reactivity in serum against the coronavirus was recently determined and associated to reduced figures of infections and deaths [100].
Despite the challenging requirement of messenger–RNA protection in vivo due to possible degradation by lytic enzymes, mRNA vaccines have been successfully formulated with nanoparticles made of lipids (LNPs); using several administration routes, these vaccines yielded high antigen production from images in vivo [101]. For example, LNPs safely and efficiently carried BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine developed and funded by Pfizer [62]. Although several formulations are available, these LNPs made of an amino lipid, phospholipid, cholesterol, and a poly (ethylene glycol)-lipid conjugate have been considered the most advanced ones [102]. LNPs were nanostructures with 70 to 100 nm in diameter and similar to those used for formulating small interference RNA [103]. The principles for designing an optimal mRNA lipid nanoparticle vaccine and major types of LNPs were recently reviewed [104,105]. Recently, the need for an additional improvement in m-RNA vaccines was pointed out: the optimization of the vaccines’ stability at low temperature [106].
Instead of using complicated compositions and expensive lipids, an unexplored though promising strategy is formulating the antigen with bilayer disks made of DODAB; they are positively charged, chemically stable, display colloidal stability in water due to the electrostatic repulsion, and readily adsorb oppositely charged nucleic acids or protein antigens [16,17,19,79,107,108]. Furthermore, DODAB as immunoadjuvant elicits a potent cellular immune response so often required against several pathogens and cancer, despite DODAB dose-dependent toxicity [3,4,12,46]. Figure 6 shows some LNP disks made from cationic lipid DODAB [20] (Figure 6a), anionic lipid dihexadecylphosphate DHP [109] (Figure 6b), or from a neutral composition of several lipids including PEGylated-lipids [110] (Figure 6c).
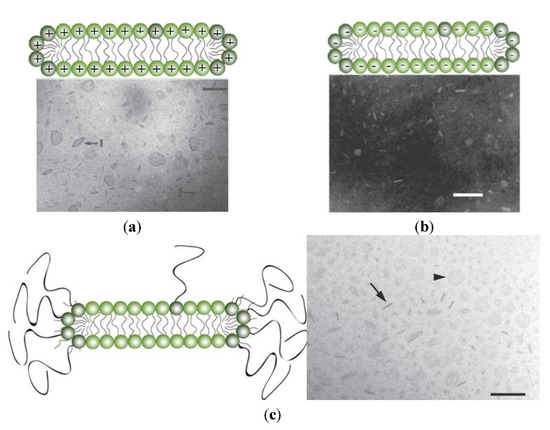
Figure 6.
Schemes for cross sections of lipid bilayer fragments or disks and their respective micrographs. On (a), dioctadecyldimethylammonium bromide bilayer fragments or disks seen edge on 1 or face on 2 from cryo-transmission electron microscopy; bar is 100 nm. Adapted with permission from [20]. Copyright 1995 American Chemical Society. On (b), sodium dihexadecylphosphate bilayer fragments or disks seen after negative staining by transmission electron microscopy: scale bar is 100 nm. Adapted with permission from [109]. Copyright 1991 American Chemical Society. On (c), composition of phospholipid, cholesterol, and ceramide conjugated to poly (ethylene glycol) (35:40:25 mol%) seen edge on (arrow) or face on (arrow head) by cryo-TEM; scale bar is 100 nm. Reprinted from [110] with permission from Elsevier, Copyright 2011.
Niosomes are non-ionic surfactant vesicles consisting of one or more than one closed bilayer delimiting inner water compartment(s) [111,112]. First described by Uchegbu and Florence as similar to liposomes, they could be obtained when surfactants were added to water [113] and their utility for antigen presentation and vaccines delivered by the oral route revealed their potential as mucosal adjuvants able to carry not only protein antigens, but also genetic material [114,115]. Compared to phospholipids/cholesterol liposomes, niosomes were chemically more stable and only slightly more leaky than the liposomes tested for determining permeability of the fluorescent compound calcein; permeability of niosomes towards KCl was also higher than the one displayed by the liposomes, thus niosomes were more leaky self-assembled bilayers [111].
Aiming at an oral vaccination against tetanus, the stability of niosomes carrying the tetanus toxoid was improved by adding O-palmitoyl pullulan to the composition; the polysaccharide moiety imparted stability to the formulation in a liquid that had a pH of about 1.5 and was similar to the gastric juice. These loaded niosomes, delivered orally, yielded a higher humoral response than the controls and high mucosal IgA titers, showing their suitability for oral vaccine delivery [112].
4. Nanoparticles
In a major, highly recommended review article, Irvine and coworkers considered that biotechnology combined with the nanomaterials science could bring about safer and more efficient vaccine formulations with major roles for the nanoparticles (NPs) [116]. In a fast moving field encompassing cancer nanotechnology [50,89,90,95,117], vaccinology against pathogenic viruses [61,62,96,97,98,99,100,106,118], and microbes such as bacteria [19,108,112,119,120], fungi [119], and parasites [22,120,121,122,123,124], elegant nanomaterials that are difficult to scale up for commercialization cannot become useful in clinics [116,125].
Synthetic nanoparticles for cancer vaccines have to fulfill several tasks: tumor antigens and stimulators have to be delivered to APCs in LN so that inside the APC, antigen escape from the lysosomes to the cytosol defines antigen cross-presentation via major histocompatibility complex I (MHC-I), promoting the cellular immunity represented by the cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) [117]. Figure 7, taken from references [8,126], illustrates the sequence of events for T-cell activation, namely, Ag delivery to DC in the LN, Ag intracellular traffic in DCs to their cytosol, and cross-presentation by MHC-I; secretion of stimulatory molecules and cytokines; type-I interferons stimulate the differentiation of naïve CD4 + T cells into Th1 subtype, whereas IL-4 leads to Th2 subtype. Against cancer and intracellular infections such as in malaria [121] and tuberculosis [126,127,128,129], cellular immune responses are essential.
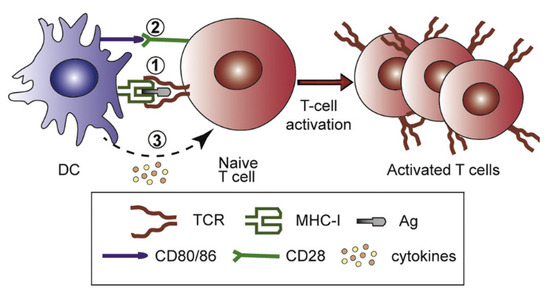
Figure 7.
Events for T-cell activation. Reprinted from [8,126]. Reprinted from [126] with permission from Elsevier, Copyright 2017.
The problem of delivering Ag to DCs involves its transport to DC-rich areas such as the LN, its binding to DCs and its internalization by DCs for Ag processing and presentation [130]. Clearance of NPs smaller than 5 nm from the blood is very fast so that they bypass the LN. The effect of particle size on the delivery route for NPs to LN was described: NPs larger than 200 nm mean diameter largely depended on dendritic cells transportation and entered the LNs after 18 h; NPs with diameters smaller than 200 nm entered LN within 2–3 h and were drained by the lymphatic vessels directly to the LN, independently of DC-transportation [9]. As the second route is much faster, nanovaccines have been developed using NPs with diameters smaller than 200 nm and larger than 5 nm.
Synthetic nanoparticles that mimic viruses are not only safe and efficient, but also advantageous from the point of view of strengthening the immune response [131]; virus-mimetics can benefit vaccine design and was recently reviewed [132]. Viruses are regular biological nanoparticles, all of the same size, often displaying several copies of antigenic spike proteins in a regular manner surrounding its nanoparticle structure, these properties common to several viruses should be copied in virus-mimetic vaccinology.
DNA synthesis for encoding several antigens of bacteria allowed the expression of all the antigens for attachment to a lipid core peptide adjuvant and self-assembly based on the lipid core; 40 nm diameter NPs spontaneously formed upon addition of the lipoproteins to the buffer, thereby antibodies against all antigens could be produced in mice without any further need of adjuvants [133].
The antimicrobial peptides that occur in nature [134] motivated a whole new area of peptidomimetics that is heavily based on chemical synthesis and library screening for selecting optimal antimicrobial activity [135]; for example, the LptD is a β-barrel protein in bacteria essential for bacteria outer membrane synthesis; the peptidomimetic assemblies mimicking LptD at nanomolar concentrations blocked outer membrane synthesis of P. aeruginosa [136].
The design of supramolecular synthetic vaccines has also been using robust chemical synthesis to mimic antigen epitopes [137]. Synthetic nanoparticles similar to viruses or synthetic virus-like particles (SVLPs) prepared using supramolecular chemistry can display B- and T-cell epitopes and ligands for pattern recognition receptors; this would achieve the optimal surface properties for efficient dendritic cell-mediated delivery of B-cell and T-cell epitopes, and also agonists for pattern recognition receptors, into lymph nodes. In addition, the multiple presentation of the epitope mimetics on the surface of the nanoparticle was highly immunogenic, triggering strong epitope-specific humoral immune responses that target the pathogen causing the infection. Figure 8 shows some hybrid lipid–peptide covalent constructions achieved by chemical conjugation with applications against pathogenic bacteria or in vaccine design. Chemical conjugation strategies for the development of protein-based nanovaccines have been reviewed [126].
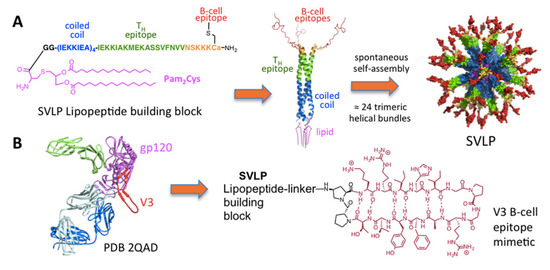
Figure 8.
(A) Chemical structure and self-assembly of lipopeptides with epitopes to stimulate B cells (orange) and T cells (green) yielding synthetic virus like particles (SVLP). (B) SVLP aiming at eliciting antibodies against HIV. Reproduced from reference [137] with permission from American Chemical Society Copyright 2017.
Nanotechnologies impact the vaccine field. Through decoration of immunogens as multiple copies on nanoparticles, improved humoral immunity can be achieved, however scaling-up production of these nanovaccines is still a major draw-back for their use in clinics. Trying to circumvent this issue, an interesting approach was the delivery of synthetic DNA by electroporation to obtain in vivo the synthesis of the multivalent nanoparticles; the self-assembly of multiple HIV antigens to yield a nanoparticle took place in vivo, inducing higher antibody titers than the monomers and also eliciting cellular immunity in contrast to the recombinant protein nanovaccine; similar results were obtained using hemagglutinin DNA nanovaccine, where the nanovaccine with multiple copies of the epitopes of interest was produced in vivo yielding protection against influenza in mice [138]. Recently, a similar approach using DNA-launched vaccines was applied for suppression of melanoma tumors: multiple copies of Gp100 and Trp2 epitopes in nanoparticles assembled in vivo induced stronger immune response and CD8+ T cells immunity than the corresponding DNA monomeric copies, or vaccines with CpG as an additional stimulator [139].
Another interesting, and much needed, area of research regards the development of vaccines against malaria, a significant neglected disease in many regions of the planet. This research area has also been using synthetic nanoparticles to build vaccines able to moderately protect against murine malaria in the blood [120]. Against malaria, adjuvants have to induce both antibodies and helper T cells; non-inflammatory polystyrene nanoparticles (PS NPs) as adjuvants and a protein conserved across several Plasmodium species named MSP4/5 as antigen, Th1 and Th2 immune responses was obtained; there was 50–80% protection against blood-stage malaria linked to interferon–gamma production [120]. Currently, no efficient vaccine against malaria in clinics is available; efforts to develop malaria vaccines have been reviewed [121,122,123]. Both discovery of better immunostimulatory formulations and adjuvants are needed. In addition, Toll-like receptors ligands that can increase immunity have also been considered important to be added as stimulators both in malaria [122,123] and cancer vaccines [140].
In our group we have been developing biomimetic nanoparticles for drug and vaccine delivery over the last 30 years [15,38,68,141,142,143,144,145]. Some review articles discussed the major role of novel cationic nanostructures based on polymers, lipids, and/or surfactants on efficient delivery of antigens to the immune system [3,4,12,69,146]. More recently, cationic nanoparticles based on biocompatible polymer PMMA [5,23,24,26,46,147] have also been developed besides the lipid nanodisks [16,17,18] and the supported bilayers [22,43,44]. In order to compare the immune responses elicited by the different cationic nanostructures first described in our laboratory while carrying ovalbumin (OVA), we recently made a scheme relating the nanostructure with the obtained immune response [46]. Figure 9 schematically shows a cross section of a DODAB bilayer fragment (DODAB BF) carrying OVA and inducing Th-1 response in mice [18], NPs of PDDA/OVA eliciting a Th-2 response (the hydrophilic PDDA cationic polymer combined with oppositely charged OVA yielding NPs) [92], NPs of PMMA/DODAB/PDDA/OVA eliciting a Th-1/Th-2 dual immune response [5], and NPs of PMMA/DODAB/OVA also yielding a dual Th-1/Th2 immune response [46]. The comparison between DODAB BF/OVA (Th-I inducer) and PDDA/OVA (Th-2 inducer) suggested that the interaction between DODAB BF and OVA inside the APC was weak and OVA readily desorbed from DODAB BF, reached the cytosol and was presented by MHC-I, whereas the interaction between PDDA and OVA in the APC was much stronger so that OVA could not so easily reach the APC cytosol remaining inside the endosome and being processed for presentation by MHC-II for enhancement of humoral immunity. OVA endosomal escape for Th-1 improved response was also obtained for two other cationic and biocompatible nanoparticles especially designed and synthesized from methylmethacrylate in the presence of DODAB or DODAB and PDDA to impart the cationic character to them; these NPs were mostly constituted of the biocompatible polymer PMMA and were named PMMA/DODAB/PDDA [5,147,148] and PMMA/DODAB NPs [23,26,46]. They could embed DODAB well mixed and distributed in the PMMA polymeric matrix [45] and displayed a core-shell structure when PDDA was also added to their synthesis: PMMA and DODAB in the core and PDDA as shell of PMMA/DODAB/PDDA NPs [5,24,147]. Importantly, macrophages and fibroblasts viability remained unaffected by DODAB and PDDA at the concentrations used in the NPs for testing their adjuvanticity in vivo [5,24,148]. Combined with OVA, NPs/OVA enhanced Th-1 and Th-2 responses [5,46]. Figure 9 displays some schematic cross-sections of four cationic adjuvants tested by our group along some decades; the type of response they induced is also quoted.
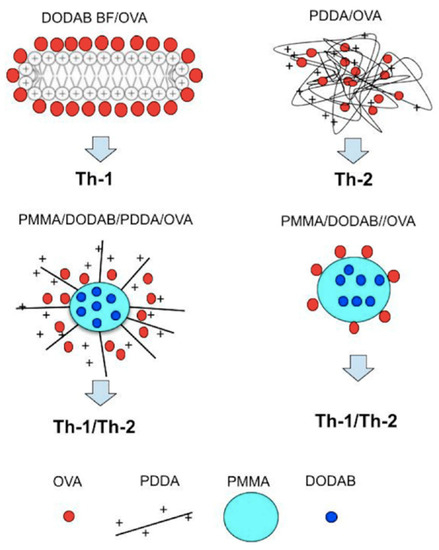
Figure 9.
Nanoparticles (NPs) from cationic lipid and ovalbumin; cationic polymer and ovalbumin; biocompatible polymer, cationic lipid, cationic polymer, and ovalbumin; biocompatible polymer, cationic lipid, and ovalbumin. Reproduced from [46].
5. Hydrogels
Hydrogels made of synthetic and natural materials can also contain vaccines with the ability to modulate the immune response [149,150]. They impart a desirable sustained releasing property for the antigen/adjuvant able to enhance the humoral response [151].
Some interesting examples of hydrogels are those formed on the basis of the hydrophobic effect from polymerization of hydrophobic and hydrophilic monomers such as stearyl methacrylamide and acrylamide, respectively, in aqueous sodium dodecylsulphate dispersion; adding NaCl led to micelles growth; in another example, interactions that kept the hydrogel network were the hydrogen bridges between poly (vinyl alcohol) and the amino moiety of melamine; interestingly, in both hydrogels, deformations underwent self-healing, taking place by freezing and thawing the hydrogel under strain [151]. In a third example, a dodecyl-modified hydroxypropylmethylcellulose hydrogel interacted with poly (ethylene glycol)–b-poly(lactic acid) nanoparticles carrying OVA and poly(I:C) so that noncovalent interactions determined the cross-linking inside the polymeric hydrogel matrix; after injection of this hydrogel vaccine subcutaneously in mice, APC infiltrating the hydrogel became active and migrated to the LN; the result was sustained enhancement of OVA-specific humoral immune response; noncovalent interactions between the polymer and NPs were multiple physical cross-links within the hydrogel structure [150]. Figure 10 adapted from reference [150] illustrates the concept behind the sustained release behavior of vaccines formulated in hydrogels.
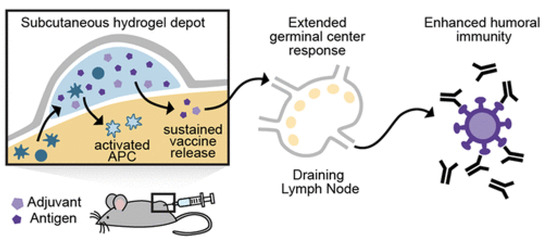
Figure 10.
The concept of subcutaneous hydrogel depot for carrying vaccines. Adapted from [150].
In an insightful work, considering that inflammation promotes cancer growth and suppresses immune responses against the cancer cells, peptides modified with anti-inflammatory moieties were used to obtain hydrogel carriers in the design of cancer vaccines; the incorporation of OVA in the hydrogel by vortexing hydrogel and OVA increased IgG and IgG2a production besides stimulating the secretion of IFN-γ and IL-6 cytokines in accordance with an enhanced dual immune responses of the humoral and cellular types [152]. In this respect, indomethacin is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug of hydrophobic nature, but bears a carboxylate in its chemical structure that could be well formulated with DODAB in aqueous dispersion to yield nanoparticles surrounded by an outermost layer of carboxymethyl cellulose, an hydrophilic biopolymer prone to be used in hydrogels [153].
Hydrogels can also respond to changes in temperature. Some of them are liquid at room temperature and change their state to gel at body temperature; they could be applied locally in tumors for cancer due to their sustained in situ delivery of therapeutic drugs, a very useful property for such thermo-responsive gels [154].
Additionally applicable as therapy for cancer, some interesting nanogels shaped as nanoparticles were obtained from polymerization induced by ultra-violet light of [2-(methacryloyloxy)-ethyl] trimethylammonium chloride and dextran methacrylate in an oil-in-water emulsion; after loading these nanogels with appropriate peptides with or without cysteine moieties, there was an electrostatically driven adsorption or covalent binding of the peptides or cys-peptides to the nanogels, respectively; because the peptides had been synthesized with epitopes that induced maturation of dendritic cells, enhanced responses in terms of cellular immunity and cytokines secretion were also obtained; this was more so when the stimulator of Toll-like receptor poly(I:C) was also added to the formulation [155]. Figure 11 illustrates the cationic nanogels with applications for cancer nanovaccines in action [155].
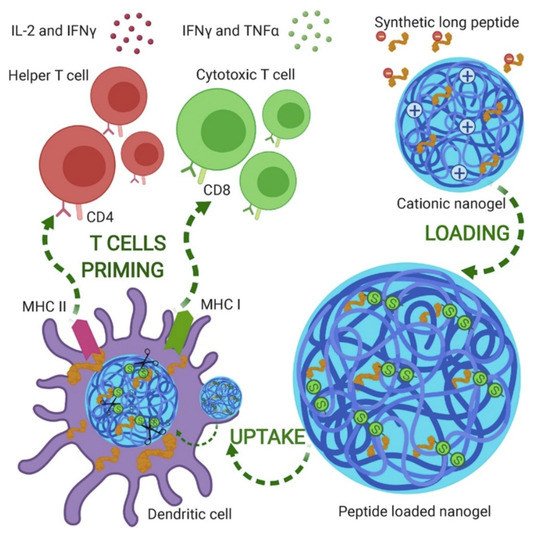
Figure 11.
Positively charged gels developed as nanoparticles (sizes around 200 nm) used to carry peptides with epitopes for activating humoral and cellular immunity. Reproduced from [155].
6. Conclusions
This review is an overview on promising old and new biomimetic adjuvants for nanovaccines considering the requirements of nanometric size and biocompatibility. Nano systems such as bilayers fragments, disks or lipid nanoparticles, vesicles, liposomes, niosomes, nanoparticles, or hydrogels have been revealing their potential as adjuvants for decades, and indeed enhance immunity against important diseases affecting mankind.
Funding
This research was funded by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), grants 302758/2019-4 and 302352/2014-7, and by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP), grant 2019/17685-2.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Seyfoori, A.; Shokrollahi Barough, M.; Mokarram, P.; Ahmadi, M.; Mehrbod, P.; Sheidary, A.; Madrakian, T.; Kiumarsi, M.; Walsh, T.; McAlinden, K.D.; et al. Emerging Advances of Nanotechnology in Drug and Vaccine Delivery against Viral Associated Respiratory Infectious Diseases (VARID). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrie, Y.; Mohammed, A.R.; Kirby, D.J.; McNeil, S.E.; Bramwell, V.W. Vaccine Adjuvant Systems: Enhancing the Efficacy of Sub-Unit Protein Antigens. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 364, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Nanomaterials Based on Lipids for Vaccine Development. In Micro and Nanotechnology in Vaccine Development; Skwarczynski, M., Toth, I., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 241–257. ISBN 978-0-323-39981-4. [Google Scholar]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; Pérez-Betancourt, Y. Cationic Nanostructures for Vaccines Design. Biomimetics 2020, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Betancourt, Y.; Távora, B.D.C.L.F.; Faquim-Mauro, E.L.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Biocompatible Lipid Polymer Cationic Nanoparticles for Antigen Presentation. Polymers 2021, 13, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foged, C.; Hansen, J.; Agger, E.M. License to Kill: Formulation Requirements for Optimal Priming of CD8(+) CTL Responses with Particulate Vaccine Delivery Systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. Off. J. Eur. Fed. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 45, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffman, R.L.; Sher, A.; Seder, R.A. Vaccine Adjuvants: Putting Innate Immunity to Work. Immunity 2010, 33, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.K.; Lichtman, A.H.; Pillai, S. Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 9th ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018; ISBN 9780323479783. [Google Scholar]
- Manolova, V.; Flace, A.; Bauer, M.; Schwarz, K.; Saudan, P.; Bachmann, M.F. Nanoparticles Target Distinct Dendritic Cell Populations According to Their Size. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 1404–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fifis, T.; Gamvrellis, A.; Crimeen-Irwin, B.; Pietersz, G.A.; Li, J.; Mottram, P.L.; McKenzie, I.F.C.; Plebanski, M. Size-Dependent Immunogenicity: Therapeutic and Protective Properties of Nano-Vaccines against Tumors. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 3148–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.D.; Scholzen, A.; Minigo, G.; David, C.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Mottram, P.L.; Plebanski, M. Pathogen Recognition and Development of Particulate Vaccines: Does Size Matter? Methods 2006, 40, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Cationic nanostructures for vaccines. In Immune Response Activation; Duc, G.H.T., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2014; pp. 1–45. ISBN 978-953-51-1374-4. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C. Design and Application of Nanoparticles as Vaccine Adjuvants against Human Corona Virus Infection. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2021, 219, 111454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuruta, L.R.; Quintilio, W.; Costa, M.H.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Interactions between Cationic Liposomes and an Antigenic Protein: The Physical Chemistry of the Immunoadjuvant Action. J. Lipid Res. 1997, 38, 2003–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Synthetic Amphiphile Vesicles. Chem Soc. Rev. 1992, 21, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Lipid Bilayer Fragments and Disks in Drug Delivery. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 1359–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lincopan, N.; Espíndola, N.M.; Vaz, A.J.; da Costa, M.H.B.; Faquim-Mauro, E.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Novel Immunoadjuvants Based on Cationic Lipid: Preparation, Characterization and Activity in Vivo. Vaccine 2009, 27, 5760–5771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozenfeld, J.H.K.; Silva, S.R.; Raneia, P.A.; Faquim-Mauro, E.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Stable Assemblies of Cationic Bilayer Fragments and CpG Oligonucleotide with Enhanced Immunoadjuvant Activity in Vivo. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2012, 160, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, A.F.; De Gaspari, E. Dioctadecyldimethylammonium Bromide (DODAB-BF) as a New Adjuvant for Maternal-Fetal Immunization in Mice against Neisseria Meningitidis: Evaluation of Humoral Response. Pathog. Dis. 2018, 76, ftx128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, M.; Hammarstroem, L.; Edwards, K. Effect of Bilayer Phase Transitions on Vesicle Structure, and Its Influence on the Kinetics of Viologen Reduction. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 14531–14538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the MRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincopan, N.; Espindola, N.M.; Vaz, A.J.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Cationic Supported Lipid Bilayers for Antigen Presentation. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 340, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naves, A.F.; Palombo, R.R.; Carrasco, L.D.M.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Antimicrobial Particles from Emulsion Polymerization of Methyl Methacrylate in the Presence of Quaternary Ammonium Surfactants. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2013, 29, 9677–9684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches, L.M.; Petri, D.F.S.; de Melo Carrasco, L.D.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. The Antimicrobial Activity of Free and Immobilized Poly (Diallyldimethylammonium) Chloride in Nanoparticles of Poly (Methylmethacrylate). J. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, G.R.S.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Cationic Biomimetic Particles of Polystyrene/Cationic Bilayer/Gramicidin for Optimal Bactericidal Activity. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathiazzi, B.I.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Hybrid Nanoparticles of Poly (Methyl Methacrylate) and Antimicrobial Quaternary Ammonium Surfactants. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.M.; Chaimovich, H. Preparation and Characterization of Large Dioctadecyldimethylammonium Chloride Liposomes and Comparison with Small Sonicated Vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1983, 733, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; Chaimovich, H. Salt-Induced Aggregation and Fusion of Dioctadecyldimethylammonium Chloride and Sodium Dihexadecylphosphate Vesicles. Biophys. J. 1986, 50, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.A.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Interactions between Cationic Vesicles and Serum Proteins. Langmuir 1998, 14, 6077–6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincopan, N.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Protein Assembly onto Cationic Supported Bilayers. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2009, 9, 3578–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, C.A.; Olivares-Ortega, C.; Soto-Arriaza, M.A.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Interaction of Gramicidin with DPPC/DODAB Bilayer Fragments. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 3064–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragioto, D.A.M.T.; Carrasco, L.D.M.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Novel Gramicidin Formulations in Cationic Lipid as Broad-Spectrum Microbicidal Agents. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 3183–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenfeld, J.H.K.; Oliveira, T.R.; Lamy, M.T.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Interaction of Cationic Bilayer Fragments with a Model Oligonucleotide. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1808, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, I.S.; Viviani, W.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Nucleotide Insertion in Cationic Bilayers. J. Phys. Chem. A 1999, 103, 8050–8055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nantes, I.L.; Correia, F.M.; Faljoni-Alario, A.; Kawanami, A.E.; Ishiki, H.M.; Amaral, A.T.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Nucleotide Conformational Change Induced by Cationic Bilayers. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 416, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, H.; Petri, D.F.S.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Interactions between Bacteriophage DNA and Cationic Biomimetic Particles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 16422–16430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, I.S.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Interactions between DNA and Synthetic Cationic Liposomes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 2829–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; Midmore, B.R. Synthetic Bilayer Adsorption onto Polystyrene Microspheres. Langmuir 1992, 8, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; de Moraes Lessa, M. Interactions between Bilayer Membranes and Latex. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1999, 153, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.M.A.; Vieira, D.B.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Cationic Bilayers on Polymeric Particles: Effect of Low NaCl Concentration on Surface Coverage. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 11490–11495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapuano, R.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Supported Bilayers on Silica. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 226, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, S.P.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Cationic Bilayer Fragments on Silica at Low Ionic Strength: Competitive Adsorption and Colloid Stability. Langmuir 2003, 19, 6664–6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincopan, N.; Santana, M.R.; Faquim-Mauro, E.; da Costa, M.H.B.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Silica-Based Cationic Bilayers as Immunoadjuvants. BMC Biotechnol. 2009, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, R.T.; Braga, V.H.A.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Biomimetic Cationic Nanoparticles Based on Silica: Optimizing Bilayer Deposition from Lipid Films. Biomimetics 2017, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, E.M.A.; Kosaka, P.M.; Rosa, H.; Vieira, D.B.; Kawano, Y.; Petri, D.F.S.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Hybrid Materials from Intermolecular Associations between Cationic Lipid and Polymers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 9301–9310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Betancourt, Y.; Araujo, P.M.; Távora, B.D.C.L.F.; Pereira, D.R.; Faquim-Mauro, E.L.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Cationic and Biocompatible Polymer/Lipid Nanoparticles as Immunoadjuvants. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbow, M.L.; De Gregorio, E.; Valiante, N.M.; Rappuoli, R. New Adjuvants for Human Vaccines. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2010, 22, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giudice, G.D.; Rappuoli, R.; Didierlaurent, A.M. Correlates of Adjuvanticity: A Review on Adjuvants in Licensed Vaccines. Semin. Immunol. 2018, 39, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux-Roels, G. Unmet Needs in Modern Vaccinology: Adjuvants to Improve the Immune Response. Vaccine 2010, 28 (Suppl. 3), C25–C36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, L.L. HPV Prophylactic Vaccination: The First Years and What to Expect from Now. Cancer Lett. 2011, 305, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupovic, J.; Ring, S.S.; Onder, L.; Colston, J.M.; Lütge, M.; Cheng, H.-W.; De Martin, A.; Provine, N.M.; Flatz, L.; Oxenius, A.; et al. Adenovirus Vector Vaccination Reprograms Pulmonary Fibroblastic Niches to Support Protective Inflating Memory CD8+ T Cells. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Médico Zajac, M.P.; Molinari, P.; Gravisaco, M.J.; Maizon, D.O.; Morón, G.; Gherardi, M.M.; Calamante, G. MVAΔ008 Viral Vector Encoding the Model Protein OVA Induces Improved Immune Response against the Heterologous Antigen and Equal Levels of Protection in a Mice Tumor Model than the Conventional MVA. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 139, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, P.B.A.; Assis, M.L.; Vallochi, A.L.; Pacheco, A.R.; Lima, L.M.; Quaresma, K.R.L.; Pereira, B.A.S.; Costa, S.M.; Alves, A.M.B. T Cell Responses Induced by DNA Vaccines Based on the DENV2 E and NS1 Proteins in Mice: Importance in Protection and Immunodominant Epitope Identification. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.A. A Comparison of Plasmid DNA and MRNA as Vaccine Technologies. Vaccines 2019, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobernik, D.; Bros, M. DNA Vaccines—How Far From Clinical Use? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Yang, K.; Li, R.; Zhang, L. MRNA Vaccine Era-Mechanisms, Drug Platform and Clinical Prospection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardi, N.; Hogan, M.J.; Porter, F.W.; Weissman, D. MRNA Vaccines—A New Era in Vaccinology. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Xue, C.; Gao, Q.; Mao, H.-Q.; Leong, K.W.; Chen, Y. Potency of a Scalable Nanoparticulate Subunit Vaccine. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 3007–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.L.; Soema, P.C.; Slütter, B.; Ossendorp, F.; Jiskoot, W. PLGA Particulate Delivery Systems for Subunit Vaccines: Linking Particle Properties to Immunogenicity. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2016, 12, 1056–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, M.J. Recent Advances in Vaccine Technologies. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2018, 48, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, M.M.; Moreira, G.M.S.G.; Mendonça, M. DNA Vaccines against COVID-19: Perspectives and Challenges. Life Sci. 2021, 267, 118919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 MRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulendran, B.; Arunachalam, P.S.; O’Hagan, D.T. Emerging Concepts in the Science of Vaccine Adjuvants. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 454–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, S.G.; Orr, M.T.; Fox, C.B. Key Roles of Adjuvants in Modern Vaccines. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1597–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastola, R.; Noh, G.; Keum, T.; Bashyal, S.; Seo, J.-E.; Choi, J.; Oh, Y.; Cho, Y.; Lee, S. Vaccine Adjuvants: Smart Components to Boost the Immune System. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2017, 40, 1238–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutwiri, G.; Gerdts, V.; van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk, S.; Auray, G.; Eng, N.; Garlapati, S.; Babiuk, L.A.; Potter, A. Combination Adjuvants: The next Generation of Adjuvants? Expert Rev. Vaccines 2011, 10, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Biomimetic Nanomaterials from the Assembly of Polymers, Lipids, and Surfactants. In Surfactants and Detergents; Dutta, A.K., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2019; pp. 1–16. ISBN 978-1-78984-661-4. [Google Scholar]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Biomimetic Nanoparticles: Preparation, Characterization and Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2010, 5, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Biomimetic Lipid Polymer Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. In Nanoparticles in Biology and Medicine: Methods and Protocols; Ferrari, E., Soloviev, M., Eds.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 45–60. ISBN 978-1-07-160319-2. [Google Scholar]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; Barbassa, L.; de Melo, L.D. Antimicrobial Biomimetics. In Biomimetic Based Applications; Cavrak, M., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 227–284. ISBN 978-953-307-195-4. [Google Scholar]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Self-Assembled Antimicrobial Nanomaterials. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israelachvili, J.N.; Mitchell, D.J.; Ninham, B.W. Theory of Self-Assembly of Lipid Bilayers and Vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Biomembr. 1977, 470, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelachvili, J.N. Intermolecular and Surface Forces; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-0-08-092363-5. [Google Scholar]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Biomimetic Systems in Nanomedicine. In Handbook of Nanobiomedical Research: Fundamentals, Applications and Recent Developments; Torchilin, W., Ed.; World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd.: Singapore, 2014; Volume 4, pp. 401–456. ISBN 978-981-4520-64-5. [Google Scholar]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. The versatile dioctadecyldimethylammonium bromide. In Application and Characterization of Surfactants; Najjar, R., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; pp. 157–182. ISBN 978-953-51-3326-1. [Google Scholar]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; Yoshida, L.S.; Chaimovich, H. Salt Effects on the Stability of Dioctadecyldimethylammonium Chloride and Sodium Dihexadecyl Phosphate Vesicles. J. Phys. Chem. 1985, 89, 2928–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claesson, P.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; Kurihara, K. Dihexadecyl Phosphate Monolayers: Intralayer and Interlayer Interactions. J. Phys. Chem. 1989, 93, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Interactions between Charged Spheric Vesicles. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 11843–11846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuruta, L.R.; Lessa, M.M.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Interactions between Dioctadecyldimethylammonium Chloride or Bromide Bilayers in Water. Langmuir 1995, 11, 2938–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamróz, D.; Kepczynski, M.; Nowakowska, M. Molecular Structure of the Dioctadecyldimethylammonium Bromide (DODAB) Bilayer. Langmuir 2010, 26, 15076–15079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitosa, E.; Adati, R.D.; Hansson, P.; Malmsten, M. Thermal and Structural Behavior of Dioctadecyldimethylammonium Bromide Dispersions Studied by Differential Scanning Calorimetry and X-Ray Scattering. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohs, R.; West, S.M.; Sosinsky, A.; Liu, P.; Mann, R.S.; Honig, B. The Role of DNA Shape in Protein–DNA Recognition. Nature 2009, 461, 1248–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, T.M.; Morrison, E.A.; Musselman, C.A. Reading More than Histones: The Prevalence of Nucleic Acid Binding among Reader Domains. Molecules 2018, 23, 2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luger, K.; Mäder, A.W.; Richmond, R.K.; Sargent, D.F.; Richmond, T.J. Crystal Structure of the Nucleosome Core Particle at 2.8 Å Resolution. Nature 1997, 389, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widom, J. Toward a Unified Model of Chromatin Folding. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 1989, 18, 365–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Holde, K.; Zlatanova, J. Scanning Chromatin: A New Paradigm? J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 12197–12200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, T.A.; Becker, P.B. The Effect of Nucleosome Phasing Sequences and DNA Topology on Nucleosome Spacing. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 260, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, T.A.; Becker, P.B. Electrostatic Mechanism of Nucleosome Spacing. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 252, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, S.; Song, J.; Zhang, J.; He, Z.; Sun, B.; Sun, J. Nano-Immunotherapy for Each Stage of Cancer Cellular Immunity: Which, Why, and What? Theranostics 2021, 11, 7471–7487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasan, N.; Baselga, J.; Hyman, D.M. A View on Drug Resistance in Cancer. Nature 2019, 575, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Huang, D.; Peppas, N.A. Advanced Engineered Nanoparticulate Platforms to Address Key Biological Barriers for Delivering Chemotherapeutic Agents to Target Sites. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 167, 170–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Betancourt, Y.; Távora, B.D.C.L.F.; Colombini, M.; Faquim-Mauro, E.L.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Simple Nanoparticles from the Assembly of Cationic Polymer and Antigen as Immunoadjuvants. Vaccines 2020, 8, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalash, A.O.; Hussein, W.M.; Skwarczynski, M.; Toth, I. Key Considerations for the Development of Safe and Effective SARS-CoV-2 Subunit Vaccine: A Peptide-Based Vaccine Alternative. Adv. Sci. Weinh. Baden-Wurtt. Ger. 2021, 8, e2100985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.D.; Cabral, H.; Stylianopoulos, T.; Jain, R.K. Improving Cancer Immunotherapy Using Nanomedicines: Progress, Opportunities and Challenges. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaps, L.; Schuppan, D. Targeting Cancer Associated Fibroblasts in Liver Fibrosis and Liver Cancer Using Nanocarriers. Cells 2020, 9, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, J.; Chackerian, B. Why HIV Virions Have Low Numbers of Envelope Spikes: Implications for Vaccine Development. PLOS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokatlian, T.; Kulp, D.W.; Mutafyan, A.A.; Jones, C.A.; Menis, S.; Georgeson, E.; Kubitz, M.; Zhang, M.H.; Melo, M.B.; Silva, M.; et al. Enhancing Humoral Responses Against HIV Envelope Trimers via Nanoparticle Delivery with Stabilized Synthetic Liposomes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, T.N.; Czudnochowski, N.; Liu, Z.; Zatta, F.; Park, Y.-J.; Addetia, A.; Pinto, D.; Beltramello, M.; Hernandez, P.; Greaney, A.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 RBD Antibodies That Maximize Breadth and Resistance to Escape. Nature 2021, 597, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cully, M. Broadly Neutralizing Anti-Coronavirus Antibodies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tso, F.Y.; Lidenge, S.J.; Peña, P.B.; Clegg, A.A.; Ngowi, J.R.; Mwaiselage, J.; Ngalamika, O.; Julius, P.; West, J.T.; Wood, C. High Prevalence of Pre-Existing Serological Cross-Reactivity against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) in Sub-Saharan Africa. Int. J. Infect. Dis. IJID Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Infect. Dis. 2021, 102, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardi, N.; Tuyishime, S.; Muramatsu, H.; Kariko, K.; Mui, B.L.; Tam, Y.K.; Madden, T.D.; Hope, M.J.; Weissman, D. Expression Kinetics of Nucleoside-Modified MRNA Delivered in Lipid Nanoparticles to Mice by Various Routes. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2015, 217, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaraman, M.; Ansell, S.M.; Mui, B.L.; Tam, Y.K.; Chen, J.; Du, X.; Butler, D.; Eltepu, L.; Matsuda, S.; Narayanannair, J.K.; et al. Maximizing the Potency of SiRNA Lipid Nanoparticles for Hepatic Gene Silencing in Vivo. Angew. Chem. 2012, 51, 8529–8533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, M.A.; Jayaraman, M.; Matsuda, S.; Liu, J.; Barros, S.; Querbes, W.; Tam, Y.K.; Ansell, S.M.; Kumar, V.; Qin, J.; et al. Biodegradable Lipids Enabling Rapidly Eliminated Lipid Nanoparticles for Systemic Delivery of RNAi Therapeutics. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2013, 21, 1570–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kon, E.; Elia, U.; Peer, D. Principles for Designing an Optimal MRNA Lipid Nanoparticle Vaccine. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 73, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenchov, R.; Bird, R.; Curtze, A.E.; Zhou, Q. Lipid Nanoparticles─From Liposomes to MRNA Vaccine Delivery, a Landscape of Research Diversity and Advancement. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 16982–17015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenmaker, L.; Witzigmann, D.; Kulkarni, J.A.; Verbeke, R.; Kersten, G.; Jiskoot, W.; Crommelin, D.J.A. MRNA-Lipid Nanoparticle COVID-19 Vaccines: Structure and Stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 601, 120586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgers, L.A.; Snippe, H. DDA as an Immunological Adjuvant. Res. Immunol. 1992, 143, 494–503; discussion 574-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gaspari, E.N. The Use of Monoclonal Antibodies to Neisseria Lactamica in an Antigen Selection to Neisseria Meningitides B Vaccine. Hybridoma 2008, 27, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; Castuma, C.E.; Sesso, A.; Schreier, S. Bilayer Structure and Stability in Dihexadecyl Phosphate Dispersions. J. Phys. Chem. 1991, 95, 5361–5366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zetterberg, M.M.; Reijmar, K.; Pränting, M.; Engström, Å.; Andersson, D.I.; Edwards, K. PEG-Stabilized Lipid Disks as Carriers for Amphiphilic Antimicrobial Peptides. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2011, 156, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartelds, R.; Nematollahi, M.H.; Pols, T.; Stuart, M.C.A.; Pardakhty, A.; Asadikaram, G.; Poolman, B. Niosomes, an Alternative for Liposomal Delivery. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katare, R.; Gupta, P.N.; Mahor, S.; Rawat, A.; Khatri, K.; Katare, Y.; Panda, A.K.; Vyas, S.P. Development of Polysaccharide-Capped Niosomes for Oral Immunization of Tetanus Toxoid. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2006, 16, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchegbu, I.F.; Florence, A.T. Non-Ionic Surfactant Vesicles (Niosomes): Physical and Pharmaceutical Chemistry. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1995, 58, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Singh, P.; Mishra, V.; Vyas, S.P. Mannosylated Niosomes as Adjuvant-Carrier System for Oral Genetic Immunization against Hepatitis B. Immunol. Lett. 2005, 101, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Vyas, S.P. Mannosylated Niosomes as Adjuvant-Carrier System for Oral Mucosal Immunization. J. Liposome Res. 2006, 16, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, D.J.; Hanson, M.C.; Rakhra, K.; Tokatlian, T. Synthetic Nanoparticles for Vaccines and Immunotherapy. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11109–11146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Song, T.; Hu, Y.; Ma, G. Synthetic Particles for Cancer Vaccines: Connecting the Inherent Supply Chain. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 2068–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Davies, J.E.; Felgner, J.; Strohmeier, S.; Pone, E.J.; Jain, A.; Jan, S.; Nakajima, R.; Jasinskas, A.; Strahsburger, E.; Krammer, F.; et al. Administration of Multivalent Influenza Virus Recombinant Hemagglutinin Vaccine in Combination-Adjuvant Elicits Broad Reactivity Beyond the Vaccine Components. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 692151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, L.D.S.; Silva, L.B.R.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Taborda, C.P. Neutrophil Cells Are Essential for The Efficacy of a Therapeutic Vaccine against Paracoccidioidomycosis. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.L.; Pouniotis, D.; Hanley, J.; Xiang, S.D.; Ma, C.; Coppel, R.L.; Plebanski, M. A Synthetic Nanoparticle Based Vaccine Approach Targeting MSP4/5 Is Immunogenic and Induces Moderate Protection Against Murine Blood-Stage Malaria. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, K.L.; Flanagan, K.L.; Prakash, M.D.; Plebanski, M. Malaria Vaccines in the Eradication Era: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2019, 18, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, A.; Kannan, D.; Mehta, S.K.; Singh, S.; Salunke, D.B. Synthetic Toll-like Receptor Agonists for the Development of Powerful Malaria Vaccines: A Patent Review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2018, 28, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, P.E.; Patrick Gorres, J. Malaria Vaccines since 2000: Progress, Priorities, Products. NPJ Vaccines 2020, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.C.S.; Sauter, I.P.; Borda-Samper, L.; Bentivoglio, E.; DaMata, J.P.; Taniwaki, N.N.; Orrego, P.R.; Araya, J.E.; Lincopan, N.; Cortez, M. Effect of DODAB Nano-Sized Cationic Bilayer Fragments against Leishmania Amazonensis. Molecules 2020, 25, 5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.D.; Shukla, S.; Chung, Y.H.; Beiss, V.; Chan, S.K.; Ortega-Rivera, O.A.; Wirth, D.M.; Chen, A.; Sack, M.; Pokorski, J.K.; et al. COVID-19 Vaccine Development and a Potential Nanomaterial Path Forward. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Samandi, L.Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.J.; Gao, J. Synthetic Nanovaccines for Immunotherapy. J. Controlled Release 2017, 263, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agger, E.M.; Rosenkrands, I.; Hansen, J.; Brahimi, K.; Vandahl, B.S.; Aagaard, C.; Werninghaus, K.; Kirschning, C.; Lang, R.; Christensen, D.; et al. Cationic Liposomes Formulated with Synthetic Mycobacterial Cordfactor (CAF01): A Versatile Adjuvant for Vaccines with Different Immunological Requirements. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwahab, W.M.; Riffey, A.; Buhl, C.; Johnson, C.; Ryter, K.; Evans, J.T.; Burkhart, D.J. Co-Adsorption of Synthetic Mincle Agonists and Antigen to Silica Nanoparticles for Enhanced Vaccine Activity: A Formulation Approach to Co-Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 593, 120119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidsen, J.; Rosenkrands, I.; Christensen, D.; Vangala, A.; Kirby, D.; Perrie, Y.; Agger, E.M.; Andersen, P. Characterization of Cationic Liposomes Based on Dimethyldioctadecylammonium and Synthetic Cord Factor from M. Tuberculosis (Trehalose 6,6′-Dibehenate)-a Novel Adjuvant Inducing Both Strong CMI and Antibody Responses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1718, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.T.; Swartz, M.A.; Hubbell, J.A. Targeting Dendritic Cells with Biomaterials: Developing the next Generation of Vaccines. Trends Immunol. 2006, 27, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Chen, J.-Y.; Chen, H.-W.; Hu, C.-M.J. Nanoparticle Vaccines Adopting Virus-like Features for Enhanced Immune Potentiation. Nanotheranostics 2017, 1, 244–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Halifa, S.; Gauthier, L.; Arpin, D.; Bourgault, S.; Archambault, D. Nanoparticle-Based Vaccines Against Respiratory Viruses. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyle, P.M.; Hartas, J.; Henningham, A.; Batzloff, M.R.; Good, M.F.; Toth, I. An Efficient, Chemically-Defined Semisynthetic Lipid-Adjuvanted Nanoparticulate Vaccine Development System. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2013, 9, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; De Melo Carrasco, L.D. Novel Formulations for Antimicrobial Peptides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 18040–18083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skwarczynski, M.; Toth, I. Recent Advances in Peptide-Based Subunit Nanovaccines. Nanomedicine 2014, 9, 2657–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.A. Folded Synthetic Peptides and Other Molecules Targeting Outer Membrane Protein Complexes in Gram-Negative Bacteria. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerbe, K.; Moehle, K.; Robinson, J.A. Protein Epitope Mimetics: From New Antibiotics to Supramolecular Synthetic Vaccines. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Wise, M.C.; Chokkalingam, N.; Walker, S.; Tello-Ruiz, E.; Elliott, S.T.C.; Perales-Puchalt, A.; Xiao, P.; Zhu, X.; Pumroy, R.A.; et al. In Vivo Assembly of Nanoparticles Achieved through Synergy of Structure-Based Protein Engineering and Synthetic DNA Generates Enhanced Adaptive Immunity. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1902802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chokkalingam, N.; Tello-Ruiz, E.; Wise, M.C.; Bah, M.A.; Walker, S.; Tursi, N.J.; Fisher, P.D.; Schultheis, K.; Broderick, K.E.; et al. A DNA-Launched Nanoparticle Vaccine Elicits CD8+ T-Cell Immunity to Promote in Vivo Tumor Control. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Noh, Y.-W.; Kang, T.H.; Kim, J.-E.; Kim, S.; Um, S.H.; Oh, D.-B.; Park, Y.-M.; Lim, Y.T. Synthetic Vaccine Nanoparticles Target to Lymph Node Triggering Enhanced Innate and Adaptive Antitumor Immunity. Biomaterials 2017, 130, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; Herrington, T.M. Phospholipid Adsorption onto Polystyrene Microspheres. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1993, 156, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Bilayer Vesicles and Liposomes as Interface Agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2001, 30, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, L.D.; Mamizuka, E.M.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Antimicrobial Particles from Cationic Lipid and Polyelectrolytes. Langmuir 2010, 26, 12300–12306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, D.B.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Synthetic Bilayer Fragments for Solubilization of Amphotericin B. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 244, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, D.B.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Cationic Nanoparticles for Delivery of Amphotericin B: Preparation, Characterization and Activity in Vitro. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2008, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Interactions between Cationic Liposomes and Drugs or Biomolecules. An. Acad. Bras. Ciênc. 2000, 72, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ribeiro, R.T.; Galvão, C.N.; Betancourt, Y.P.; Mathiazzi, B.I.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Microbicidal Dispersions and Coatings from Hybrid Nanoparticles of Poly (Methyl Methacrylate), Poly (Diallyl Dimethyl Ammonium) Chloride, Lipids, and Surfactants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvão, C.N.; Sanches, L.M.; Mathiazzi, B.I.; Ribeiro, R.T.; Petri, D.F.S.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Antimicrobial Coatings from Hybrid Nanoparticles of Biocompatible and Antimicrobial Polymers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Peppas, N.A. Hydrogels and Scaffolds for Immunomodulation. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6530–6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, G.A.; Gale, E.C.; Alcántara-Hernández, M.; Luo, W.; Axpe, E.; Verma, R.; Yin, Q.; Yu, A.C.; Lopez Hernandez, H.; Maikawa, C.L.; et al. Injectable Hydrogels for Sustained Codelivery of Subunit Vaccines Enhance Humoral Immunity. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 1800–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Gangwar, A.; Jyoti, K.; Sainaga Jyothi, V.G.S.; Sodhi, R.K.; Mehra, N.K.; Singh, S.B.; Madan, J. Self Healing Hydrogels: A New Paradigm Immunoadjuvant for Delivering Peptide Vaccine. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 194, 111171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liang, C.; Shi, F.; He, T.; Gong, C.; Wang, L.; Yang, Z. Cancer Vaccines Using Supramolecular Hydrogels of NSAID-Modified Peptides as Adjuvants Abolish Tumorigenesis. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 14058–14064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E.G.; Gomes, L.R.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Stable Indomethacin Dispersions in Water from Drug, Ethanol, Cationic Lipid and Carboxymethyl-Cellulose. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2016, 4, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafael, D.; Melendres, M.M.R.; Andrade, F.; Montero, S.; Martinez-Trucharte, F.; Vilar-Hernandez, M.; Durán-Lara, E.F.; Schwartz, S., Jr.; Abasolo, I. Thermo-Responsive Hydrogels for Cancer Local Therapy: Challenges and State-of-Art. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 606, 120954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordalivand, N.; Tondini, E.; Lau, C.Y.J.; Vermonden, T.; Mastrobattista, E.; Hennink, W.E.; Ossendorp, F.; van Nostrum, C.F. Cationic Synthetic Long Peptides-Loaded Nanogels: An Efficient Therapeutic Vaccine Formulation for Induction of T-Cell Responses. J. Control. Release 2019, 315, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).