Engineering a 3D Vascularized Adipose Tissue Construct Using a Decellularized Lung Matrix
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Adipocyte Isolation
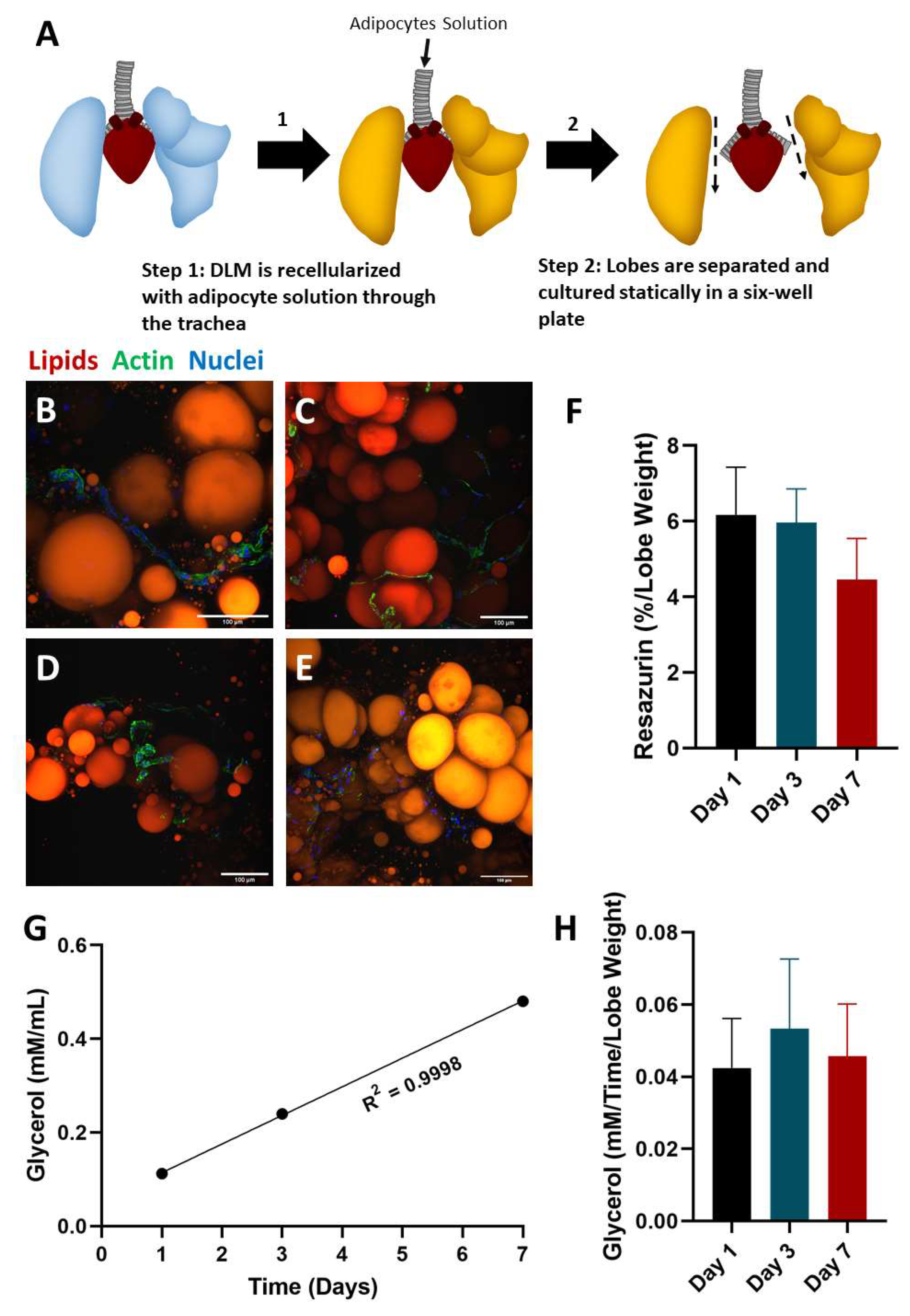
2.2. Static Culture of Whole Lobes
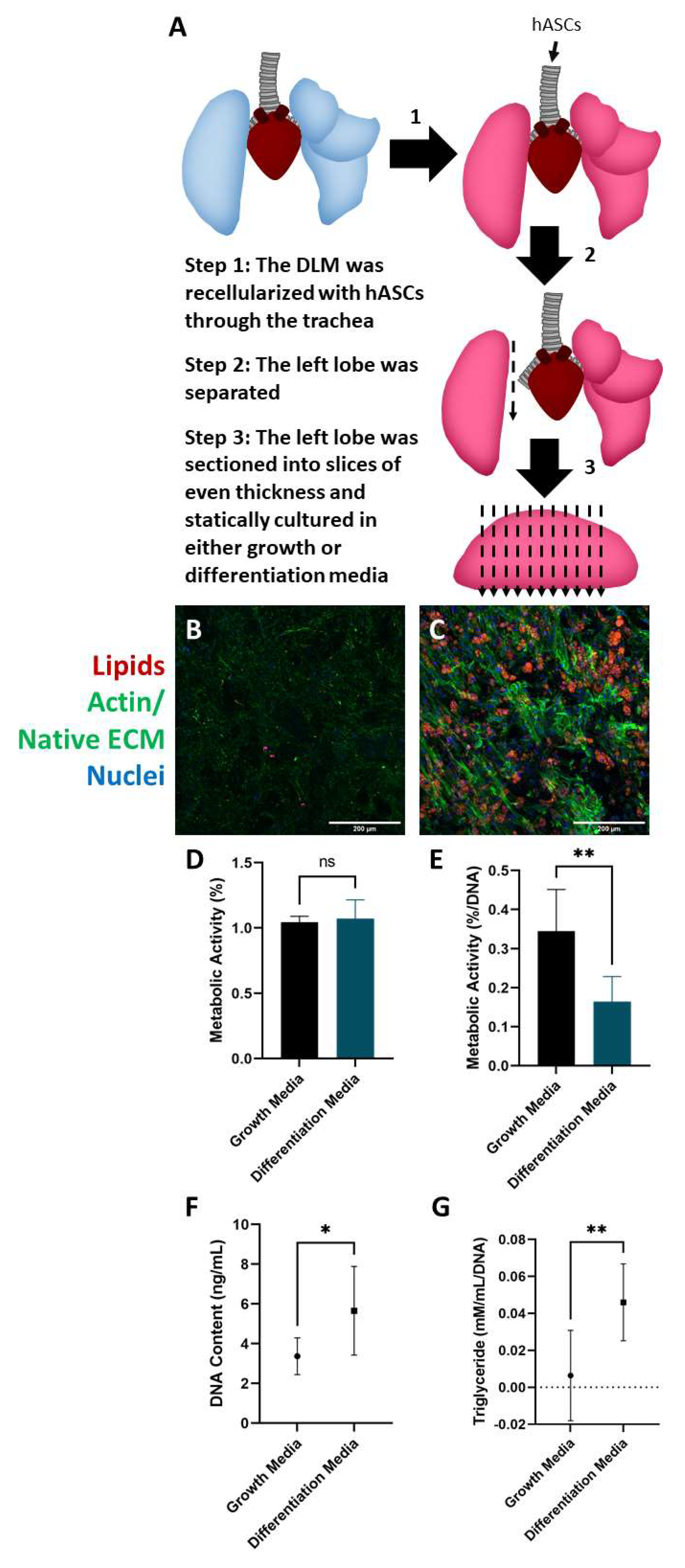
2.3. Culture and Differentiation of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells in the DLM
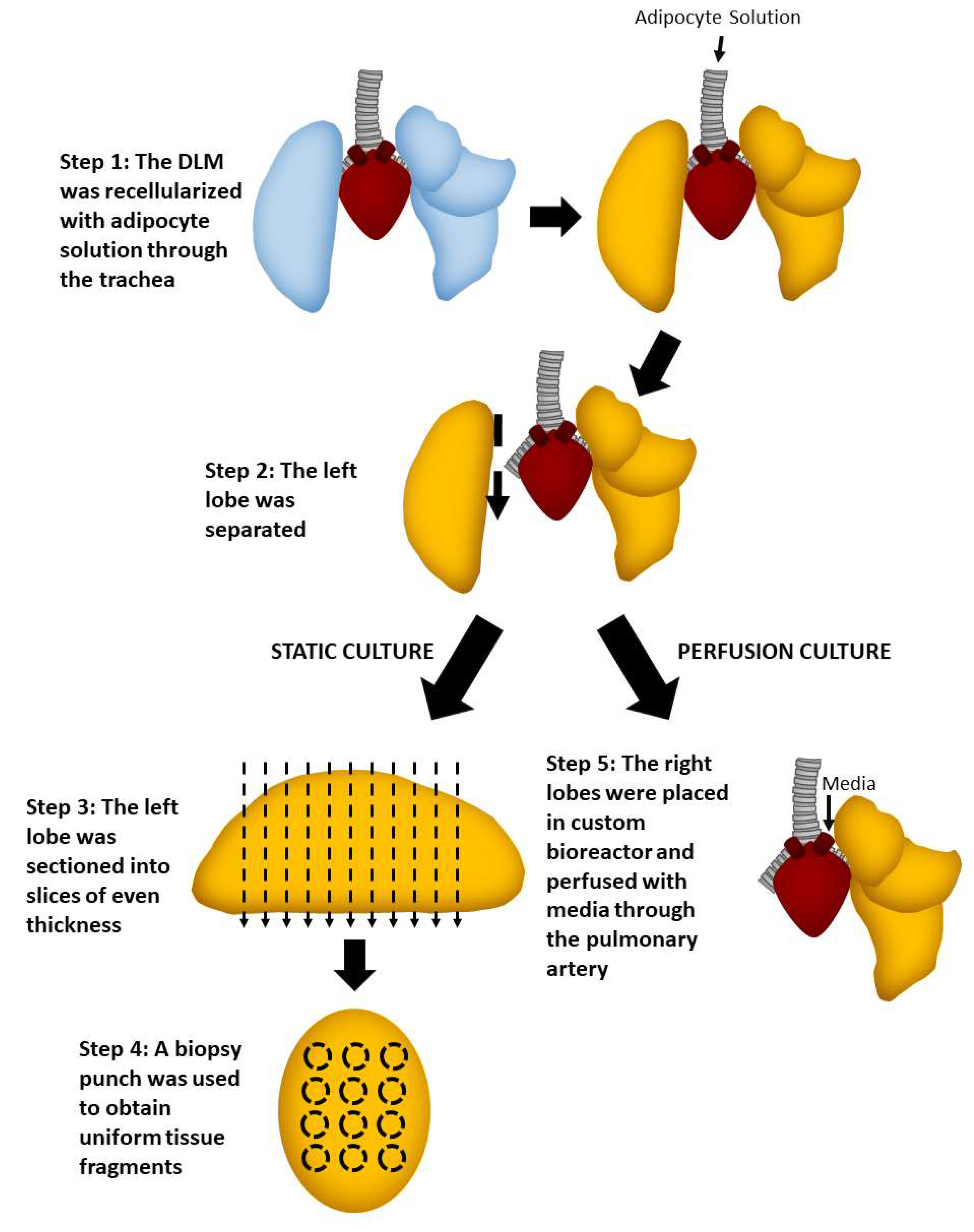
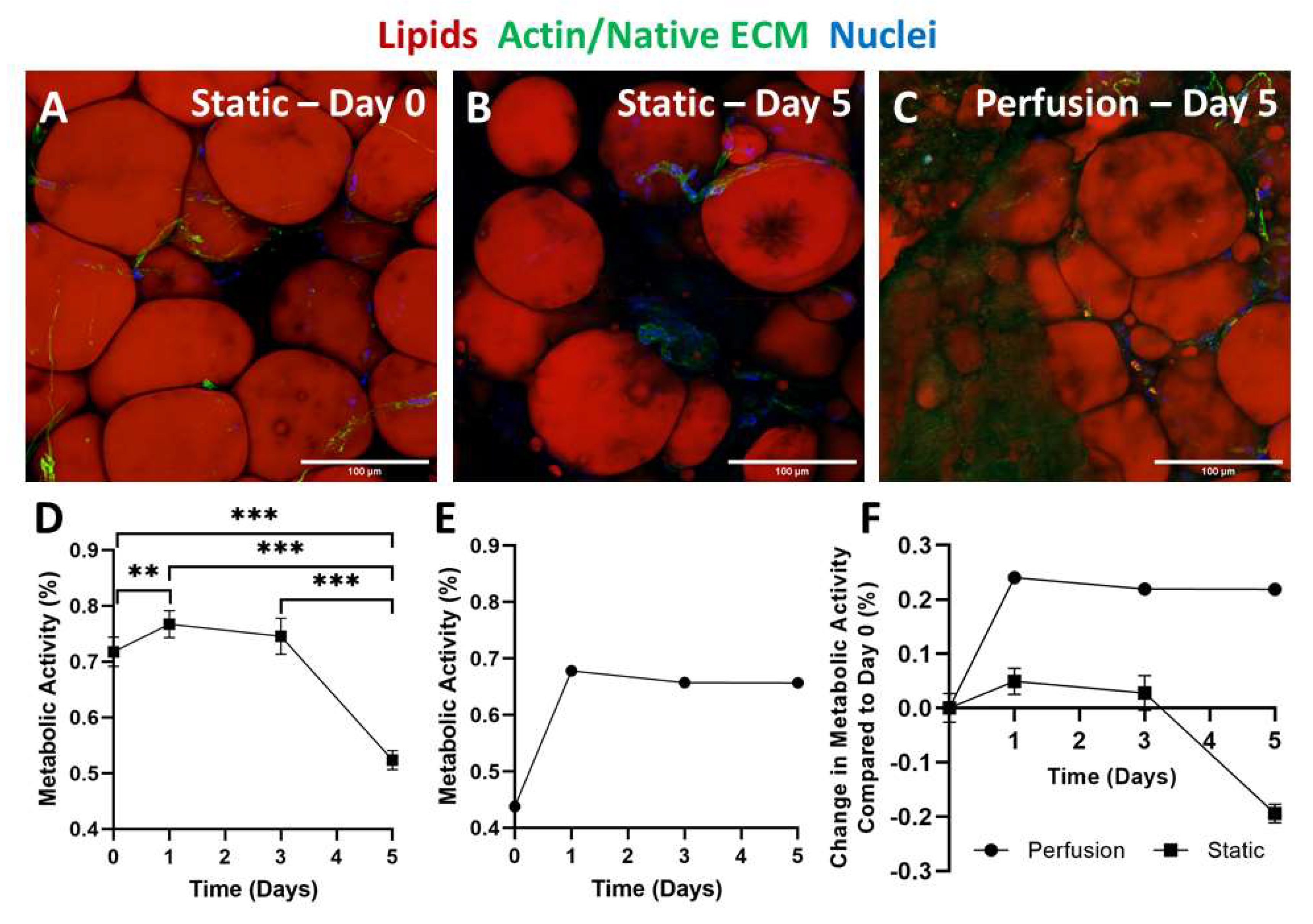
2.4. Static versus Perfusion Culture
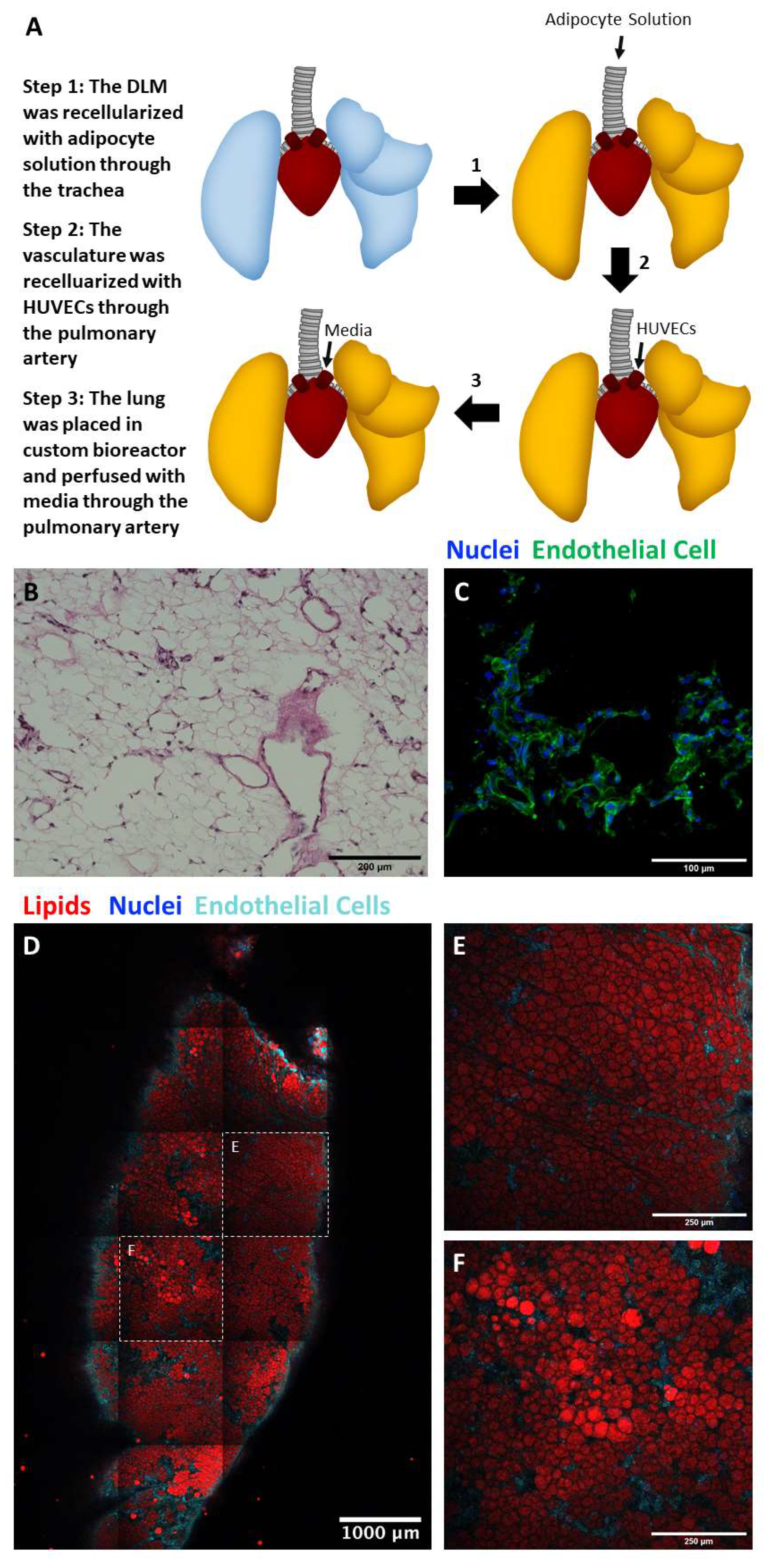
2.5. Perfusion Culture of Adipocyte and Endothelial Cell Seeded Lung Matrix
2.6. Limitations
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
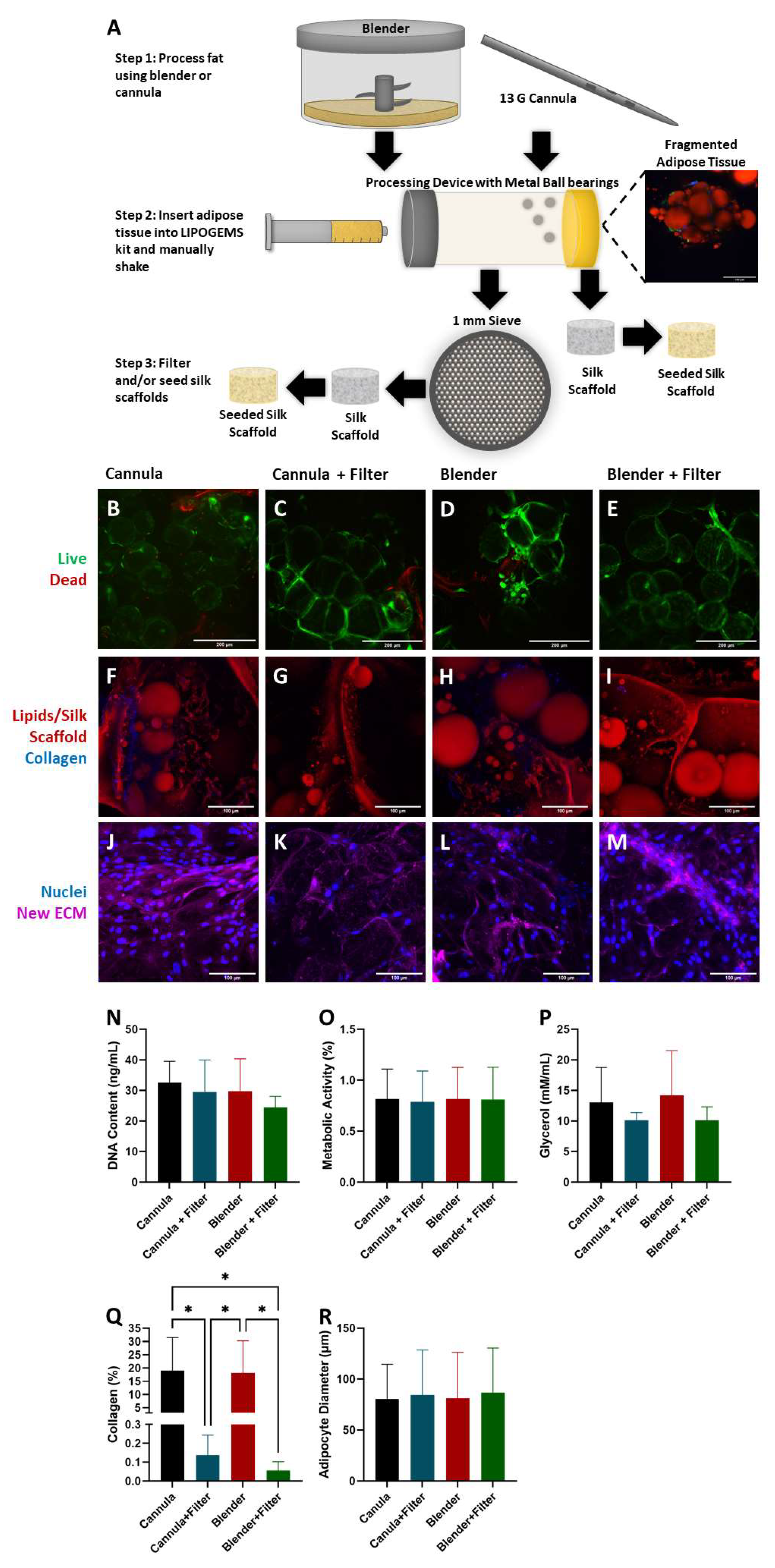
4.1. Adipose Tissue Culture on Silk Scaffolds
4.1.1. Preparation of Aqueous Silk Fibroin
4.1.2. Preparation of Silk Scaffolds
4.1.3. Adipose Tissue Processing
4.1.4. Seeding Scaffolds and Culture Conditions
4.1.5. Live/Dead Staining
4.1.6. Imaging
4.1.7. De Novo Protein Synthesis
4.1.8. Picogreen Assay
4.1.9. Metabolic Activity Assay
4.1.10. Glycerol Secretion
4.1.11. Statistics
4.2. Decellularizing the Lung
4.3. Whole Lobe Static Culture
4.3.1. Seeding the DLM
4.3.2. Imaging
4.3.3. Glycerol Secretion
4.3.4. Statistics
4.4. Static Culture of Sectioned DLM
4.4.1. Seeding DLM
4.4.2. Imaging
4.4.3. Metabolic Activity
4.4.4. Statistics
4.5. Perfusion Culture with Whole Adipose Tissue
4.5.1. Seeding DLM
4.5.2. Perfusion Culture
4.5.3. Imaging
4.5.4. Metabolic Activity
4.6. Static Stem Cell Seeded DLM Slices
4.6.1. Isolation of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (hASCs)
4.6.2. Seeding DLM
4.6.3. Imaging
4.6.4. Metabolic Activity
4.6.5. Picogreen Assay
4.6.6. Triglyceride Concentration
4.6.7. Statistics
4.7. Vascularized Whole Lobe Perfusion Culture
4.7.1. Adipose Tissue Processing
4.7.2. Endothelial Cell Culture
4.7.3. Seeding DLM
4.7.4. Histology
4.7.5. Imaging
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saely, C.H.; Geiger, K.; Drexel, H. Brown versus white adipose tissue: A mini-review. Gerontology 2012, 58, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, C.W., Jr. Tissue engineering strategies for adipose tissue repair. Anat. Rec. 2001, 263, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Gimble, J.M.; Lee, K.; Marra, K.G.; Rubin, J.P.; Yoo, J.J.; Vunjak-Novakovic, G.; Kaplan, D.L. Adipose tissue engineering for soft tissue regeneration. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2010, 16, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shasti, M.; Jauregui, J.J.; Malik, A.; Slobogean, G.; Eglseder, W.A.; Pensy, R.A. Magnitude of Soft-Tissue Defect as a Predictor of Free Flap Failures: Does Size Matter? J. Orthop. Trauma 2017, 31, e412–e417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Kumer, S.; Kaplan, B. Novel immunosuppressive strategies for composite tissue allografts. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2014, 19, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novosel, E.C.; Kleinhans, C.; Kluger, P.J. Vascularization is the key challenge in tissue engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auger, F.A.; Gibot, L.; Lacroix, D. The Pivotal Role of Vascularization in Tissue Engineering. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 15, 177–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baiguera, S.; Ribatti, D. Endothelialization approaches for viable engineered tissues. Angiogenesis 2013, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, L.Q.; Niklason, L.E. Vascular tissue engineering: Building perfusable vasculature for implantation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2014, 3, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Yang, C.W. The pathogenesis and treatment of chronic allograft nephropathy. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2009, 5, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, J.B. Comparative physiology of the pulmonary blood-gas barrier: The unique avian solution. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2009, 297, R1625–R1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petersen, T.H.; Calle, E.A.; Zhao, L.; Lee, E.J.; Gui, L.; Raredon, M.B.; Gavrilov, K.; Yi, T.; Zhuang, Z.W.; Breuer, C.; et al. Tissue-engineered lungs for in vivo implantation. Science 2010, 329, 538–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Neill, J.D.; Anfang, R.; Anandappa, A.; Costa, J.; Javidfar, J.; Wobma, H.M.; Singh, G.; Freytes, D.O.; Bacchetta, M.D.; Sonett, J.R.; et al. Decellularization of human and porcine lung tissues for pulmonary tissue engineering. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2013, 96, 1046–1055, discussion 1055-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ren, X.; Moser, P.T.; Gilpin, S.E.; Okamoto, T.; Wu, T.; Tapias, L.F.; Mercier, F.E.; Xiong, L.; Ghawi, R.; Scadden, D.T.; et al. Engineering pulmonary vasculature in decellularized rat and human lungs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 1097–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daya, S.; Loughlin, A.J.; Macqueen, H.A. Culture and differentiation of preadipocytes in two-dimensional and three-dimensional in vitro systems. Differ. Res. Biol. Divers. 2007, 75, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.M.; Sousa, K.M.; Jennings, C.; MacDougald, O.A.; Kennedy, R.T. Continuous-flow enzyme assay on a microfluidic chip for monitoring glycerol secretion from cultured adipocytes. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 2350–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petersen, T.H.; Calle, E.A.; Colehour, M.B.; Niklason, L.E. Matrix Composition and Mechanics of Decellularized Lung Scaffolds. Cells Tissues Organs 2012, 195, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ballermann, B.J.; Dardik, A.; Eng, E.; Liu, A.L. Shear stress and the endothelium. Kidney Int. 1998, 54, S100–S108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, L.; Chen, F.; Bao, J.; Li, W. Decellularization of porcine whole lung to obtain a clinical-scale bioengineered scaffold. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part. A 2021, 109, 1623–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, E.C.; Bonvillain, R.W.; Skillen, C.D.; Burger, B.L.; Hara, H.; Lee, W.; Trygg, C.B.; Didier, P.J.; Grasperge, B.F.; Pashos, N.C.; et al. Evaluation of the host immune response to decellularized lung scaffolds derived from α-Gal knockout pigs in a non-human primate model. Biomaterials 2018, 187, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Tsuchiya, T.; Doi, R.; Matsumoto, K.; Higami, Y.; Kobayashi, E.; Nagayasu, T. Alteration of the extracellular matrix and alpha-gal antigens in the rat lung scaffold reseeded using human vascular and adipogenic stromal cells. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2019, 13, 2067–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilpin, S.E.; Guyette, J.P.; Gonzalez, G.; Ren, X.; Asara, J.M.; Mathisen, D.J.; Vacanti, J.P.; Ott, H.C. Perfusion decellularization of human and porcine lungs: Bringing the matrix to clinical scale. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2013, 33, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Kitano, K.; Ren, X.; Rajab, T.K.; Wu, M.; Gilpin, S.E.; Wu, T.; Baugh, L.; Black, L.D.; Mathisen, D.J.; et al. Bioengineering Human Lung Grafts on Porcine Matrix. Ann. Surg. 2018, 267, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, R.D.; Borowsky, F.E.; Alonzo, C.A.; Zieba, A.; Georgakoudi, I.; Kaplan, D.L. Variability in responses observed in human white adipose tissue models. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 12, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, R.D.; Kimmerling, E.P.; Cairns, D.M.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk as a Biomaterial to Support Long-Term Three-Dimensional Tissue Cultures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 21861–21868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, R.D.; Raja, W.K.; Wang, R.Y.; Stinson, J.A.; Glettig, D.L.; Burke, K.A.; Kaplan, D.L. Long term perfusion system supporting adipogenesis. Methods 2015, 84, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abbott, R.D.; Wang, R.Y.; Reagan, M.R.; Chen, Y.; Borowsky, F.E.; Zieba, A.; Marra, K.G.; Rubin, J.P.; Ghobrial, I.M.; Kaplan, D.L. The Use of Silk as a Scaffold for Mature, Sustainable Unilocular Adipose 3D Tissue Engineered Systems. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 1667–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tremolada, C.; Colombo, V.; Ventura, C. Adipose Tissue and Mesenchymal Stem Cells: State of the Art and Lipogems(R) Technology Development. Curr. Stem. Cell Rep. 2016, 2, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mauney, J.R.; Nguyen, T.; Gillen, K.; Kirker-Head, C.; Gimble, J.M.; Kaplan, D.L. Engineering adipose-like tissue in vitro and in vivo utilizing human bone marrow and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells with silk fibroin 3D scaffolds. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 5280–5290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ward, A.; Quinn, K.P.; Bellas, E.; Georgakoudi, I.; Kaplan, D.L. Noninvasive Metabolic Imaging of Engineered 3D Human Adipose Tissue in a Perfusion Bioreactor. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H.; Gimble, J.M.; Kaplan, D.L. In vitro 3D model for human vascularized adipose tissue. Tissue Eng. Part A 2009, 15, 2227–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, J.H.; Bellas, E.; Vunjak-Novakovic, G.; Kaplan, D.L. Adipogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells on 3D silk scaffolds. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 702, 319–330. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.H.; Gimble, J.M.; Vunjak-Novakovic, G.; Kaplan, D.L. Effects of hyperinsulinemia on lipolytic function of three-dimensional adipocyte/endothelial co-cultures. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2010, 16, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellas, E.; Marra, K.; Kaplan, D.L.P. Sustainable 3D tissue model of human adipose tissue. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2013, 19, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosen, E.D.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adipocytes as regulators of energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Nature 2006, 444, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeBari, M.K.; Abbott, R.D. Adipose Tissue Fibrosis: Mechanisms, Models, and Importance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, N.A.; Muir, L.A.; Washabaugh, A.R.; Neeley, C.K.; Chen, S.Y.; Flesher, C.G.; Vorwald, J.; Finks, J.F.; Ghaferi, A.A.; Mulholland, M.W.; et al. Diabetes-Specific Regulation of Adipocyte Metabolism by the Adipose Tissue Extracellular Matrix. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 1032–1043. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosmark, O.; Ahrman, E.; Muller, C.; Elowsson Rendin, L.; Eriksson, L.; Malmstrom, A.; Hallgren, O.; Larsson-Callerfelt, A.K.; Westergren-Thorsson, G.; Malmstrom, J. Quantifying extracellular matrix turnover in human lung scaffold cultures. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burgstaller, G.; Oehrle, B.; Gerckens, M.; White, E.S.; Schiller, H.B.; Eickelberg, O. The instructive extracellular matrix of the lung: Basic composition and alterations in chronic lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1601805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Citro, A.; Moser, P.T.; Dugnani, E.; Rajab, T.K.; Ren, X.; Evangelista-Leite, D.; Charest, J.M.; Peloso, A.; Podesser, B.K.; Manenti, F.; et al. Biofabrication of a vascularized islet organ for type 1 diabetes. Biomaterials 2019, 199, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariman, E.C.; Wang, P. Adipocyte extracellular matrix composition, dynamics and role in obesity. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 1277–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshimura, K.; Eto, H.; Kato, H.; Doi, K.; Aoi, N. In vivo manipulation of stem cells for adipose tissue repair/reconstruction. Regen. Med. 2011, 6, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, K.; Kusminski, C.M.; Scherer, P.E. Adipose tissue remodeling and obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2094–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Onal, G.; Kutlu, O.; Gozuacik, D.; Dokmeci Emre, S. Lipid Droplets in Health and Disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, D.; Li, N.; Zhang, G. Spontaneous adipogenic differentiation potential of adipose-derived stem cells decreased with increasing cell passages. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 6109–6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knight, D.M.; Chapman, A.B.; Navre, M.; Drinkwater, L.; Bruno, J.J.; Ringold, G.M. Requirements for triggering of adipocyte differentiation by glucocorticoids and indomethacin. Mol. Endocrinol. 1987, 1, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBeath, R.; Pirone, D.M.; Nelson, C.M.; Bhadriraju, K.; Chen, C.S. Cell shape, cytoskeletal tension, and RhoA regulate stem cell lineage commitment. Dev. Cell 2004, 6, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verseijden, F.; Jahr, H.; Posthumus-van Sluijs, S.J.; Ten Hagen, T.L.; Hovius, S.E.; Seynhaeve, A.L.; van Neck, J.W.; van Osch, G.J.; Hofer, S.O. Angiogenic capacity of human adipose-derived stromal cells during adipogenic differentiation: An in vitro study. Tissue Eng. Part A 2009, 15, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyllonen, L.; Haimi, S.; Mannerstrom, B.; Huhtala, H.; Rajala, K.M.; Skottman, H.; Sandor, G.K.; Miettinen, S. Effects of different serum conditions on osteogenic differentiation of human adipose stem cells in vitro. Stem Cell Res. 2013, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neuhuber, B.; Swanger, S.A.; Howard, L.; Mackay, A.; Fischer, I. Effects of plating density and culture time on bone marrow stromal cell characteristics. Exp. Hematol. 2008, 36, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, H.; Guo, L.; Wozniak, M.J.; Kawazoe, N.; Tateishi, T.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G. Effect of cell density on adipogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 381, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnaert, M.; Papantoniou, I.; Luyten, F.P.; Schrooten, J.I. Quantitative Validation of the Presto Blue Metabolic Assay for Online Monitoring of Cell Proliferation in a 3D Perfusion Bioreactor System. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2015, 21, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platz, J.; Bonenfant, N.R.; Uhl, F.E.; Coffey, A.L.; McKnight, T.; Parsons, C.; Sokocevic, D.; Borg, Z.D.; Lam, Y.W.; Deng, B.; et al. Comparative Decellularization and Recellularization of Wild-Type and Alpha 1,3 Galactosyltransferase Knockout Pig Lungs: A Model for Ex Vivo Xenogeneic Lung Bioengineering and Transplantation. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2016, 22, 725–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rockwood, D.N.; Preda, R.C.; Yücel, T.; Wang, X.; Lovett, M.L.; Kaplan, D.L. Materials fabrication from Bombyx mori silk fibroin. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1612–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Xing, Y.; Jacome, E.R.; Fok, S.W.; Ren, X. Bioorthogonal Labeling and Chemoselective Functionalization of Lung Extracellular Matrix. Bio Protoc. 2021, 11, e3922. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
DeBari, M.K.; Ng, W.H.; Griffin, M.D.; Kokai, L.E.; Marra, K.G.; Rubin, J.P.; Ren, X.; Abbott, R.D. Engineering a 3D Vascularized Adipose Tissue Construct Using a Decellularized Lung Matrix. Biomimetics 2021, 6, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics6030052
DeBari MK, Ng WH, Griffin MD, Kokai LE, Marra KG, Rubin JP, Ren X, Abbott RD. Engineering a 3D Vascularized Adipose Tissue Construct Using a Decellularized Lung Matrix. Biomimetics. 2021; 6(3):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics6030052
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeBari, Megan K., Wai Hoe Ng, Mallory D. Griffin, Lauren E. Kokai, Kacey G. Marra, J. Peter Rubin, Xi Ren, and Rosalyn D. Abbott. 2021. "Engineering a 3D Vascularized Adipose Tissue Construct Using a Decellularized Lung Matrix" Biomimetics 6, no. 3: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics6030052
APA StyleDeBari, M. K., Ng, W. H., Griffin, M. D., Kokai, L. E., Marra, K. G., Rubin, J. P., Ren, X., & Abbott, R. D. (2021). Engineering a 3D Vascularized Adipose Tissue Construct Using a Decellularized Lung Matrix. Biomimetics, 6(3), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics6030052





