Bioinspired Honeycomb Core Design: An Experimental Study of the Role of Corner Radius, Coping and Interface
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Corner Radius
1.2. Coping
1.3. Interface
2. Materials and Methods
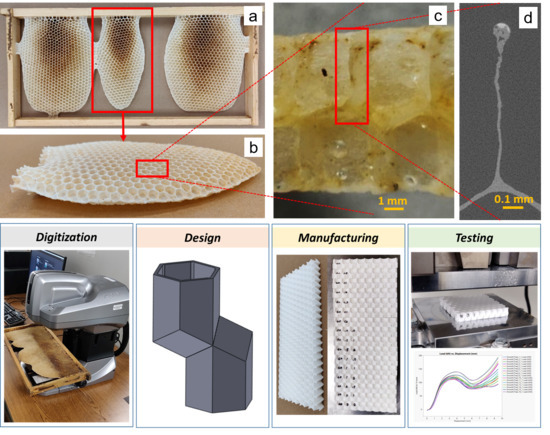
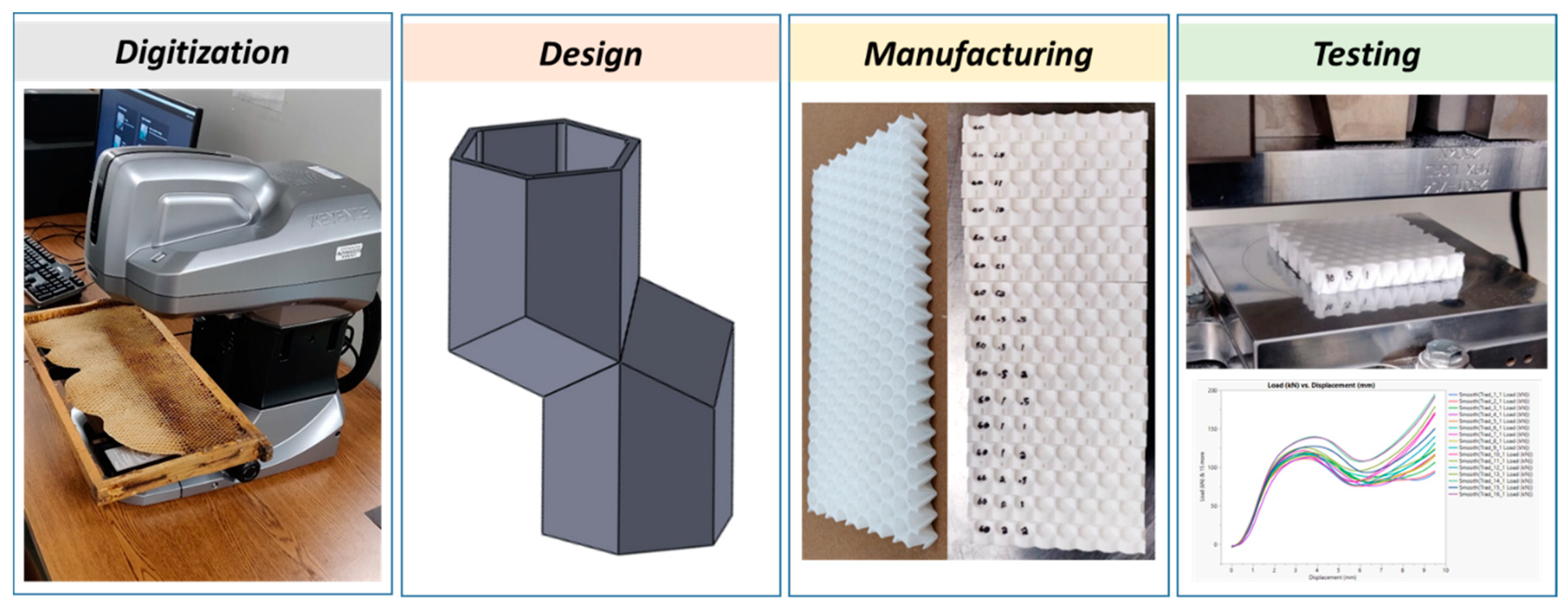
2.1. Overall Approach
2.2. Digitization
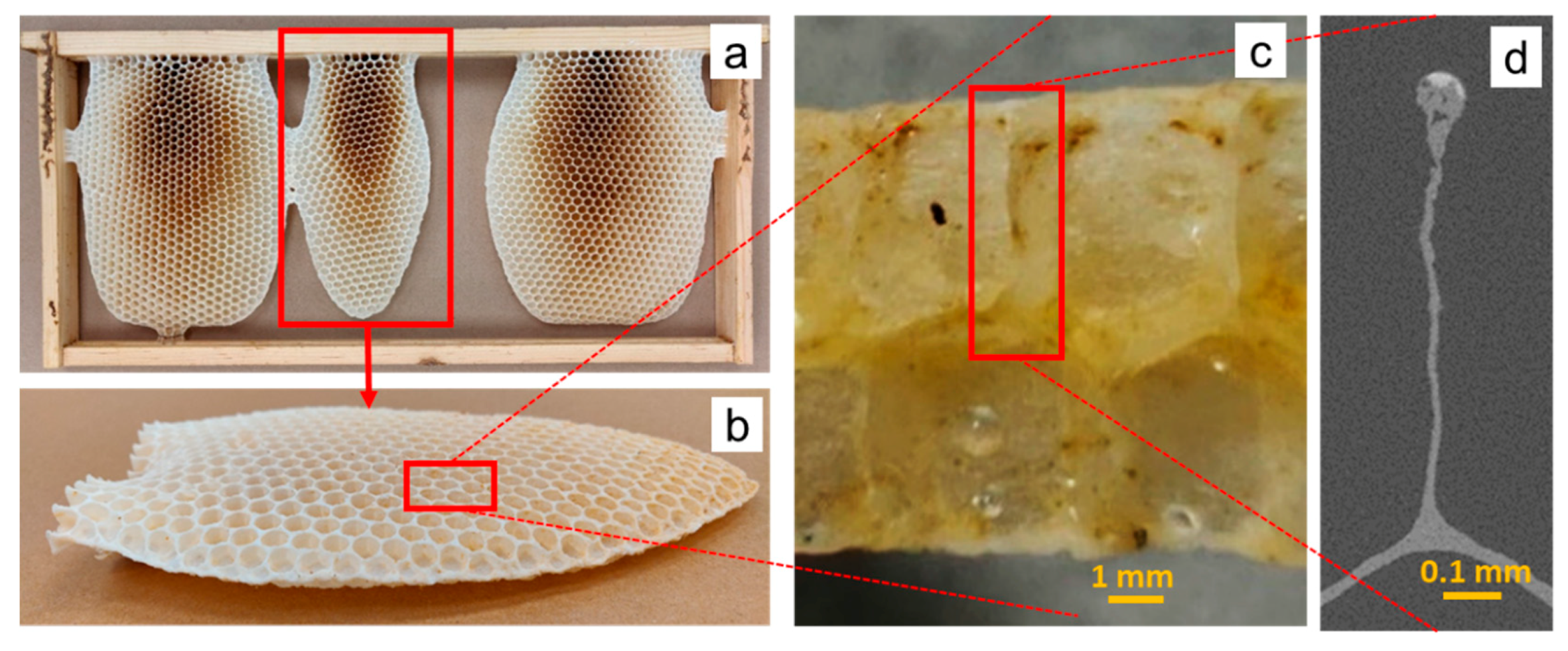
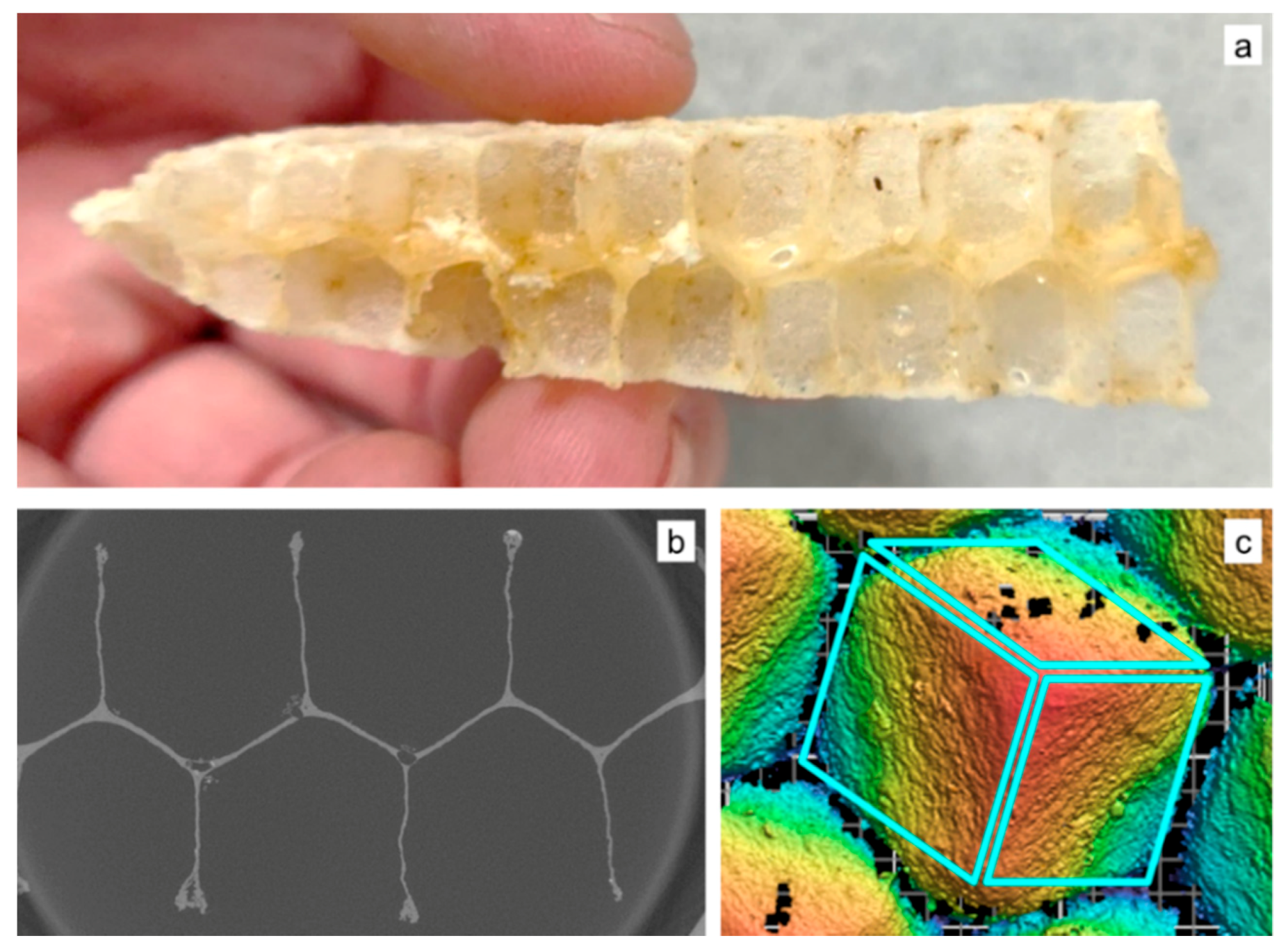
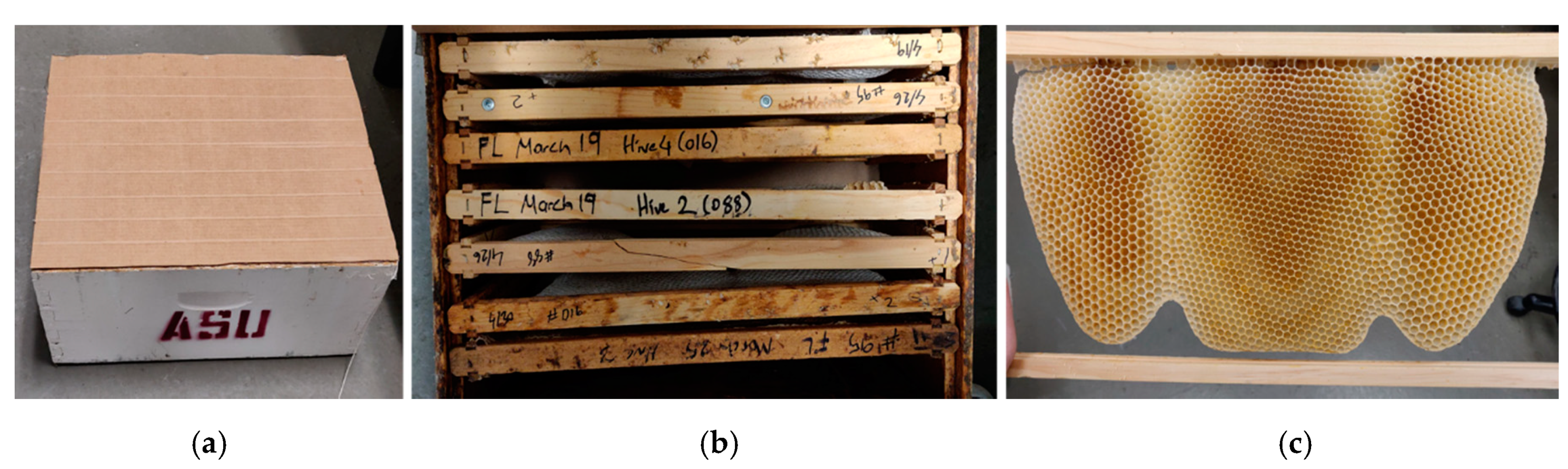
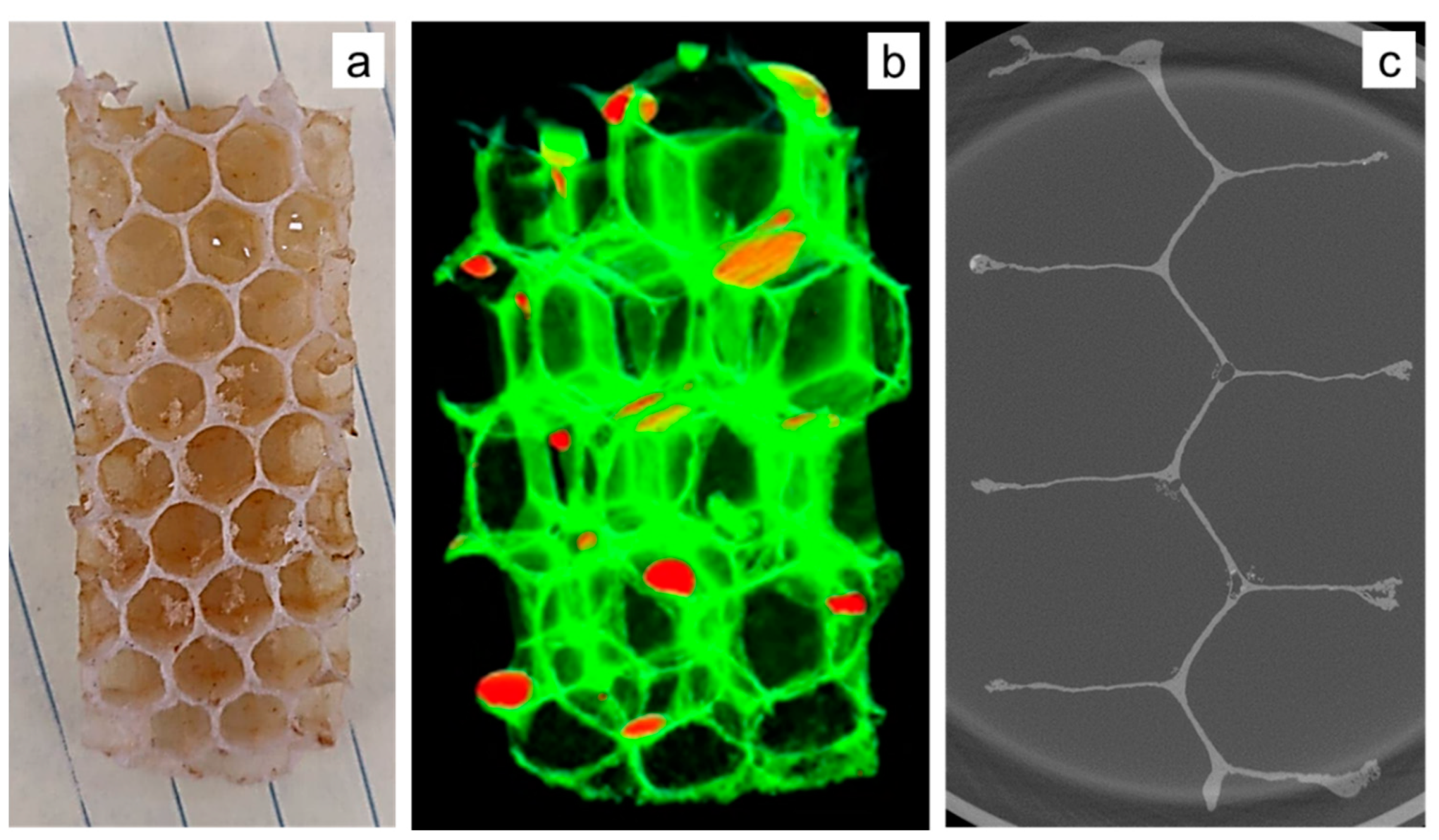
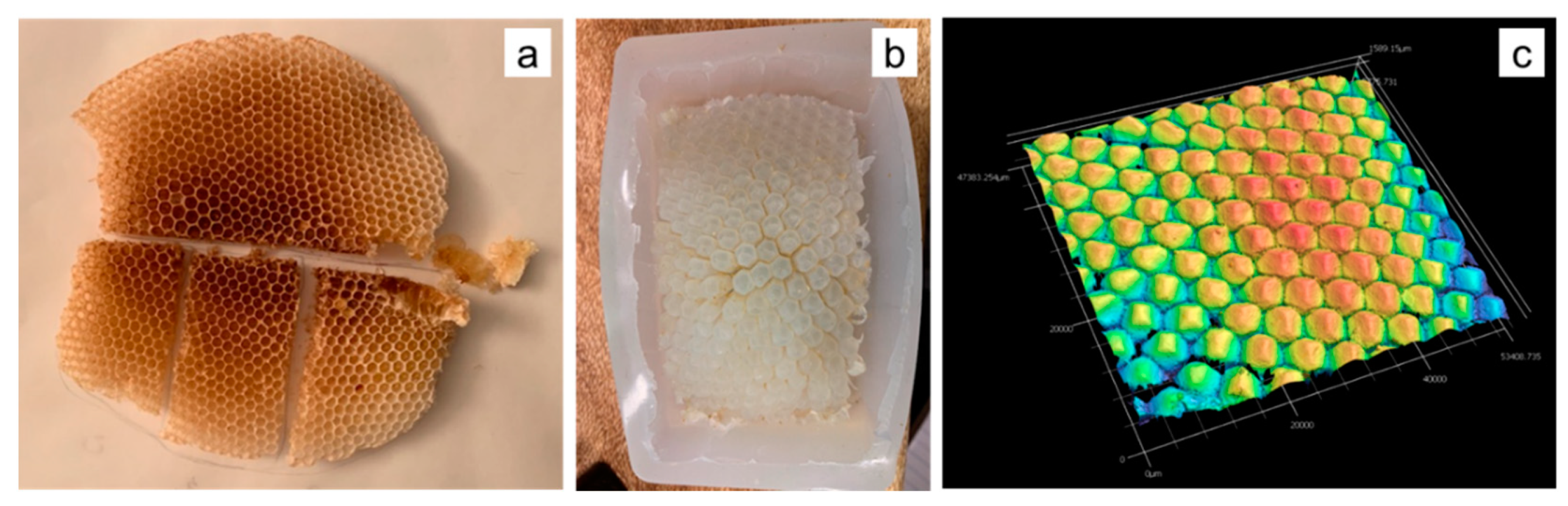
2.2.1. Honeybee Comb Specimens
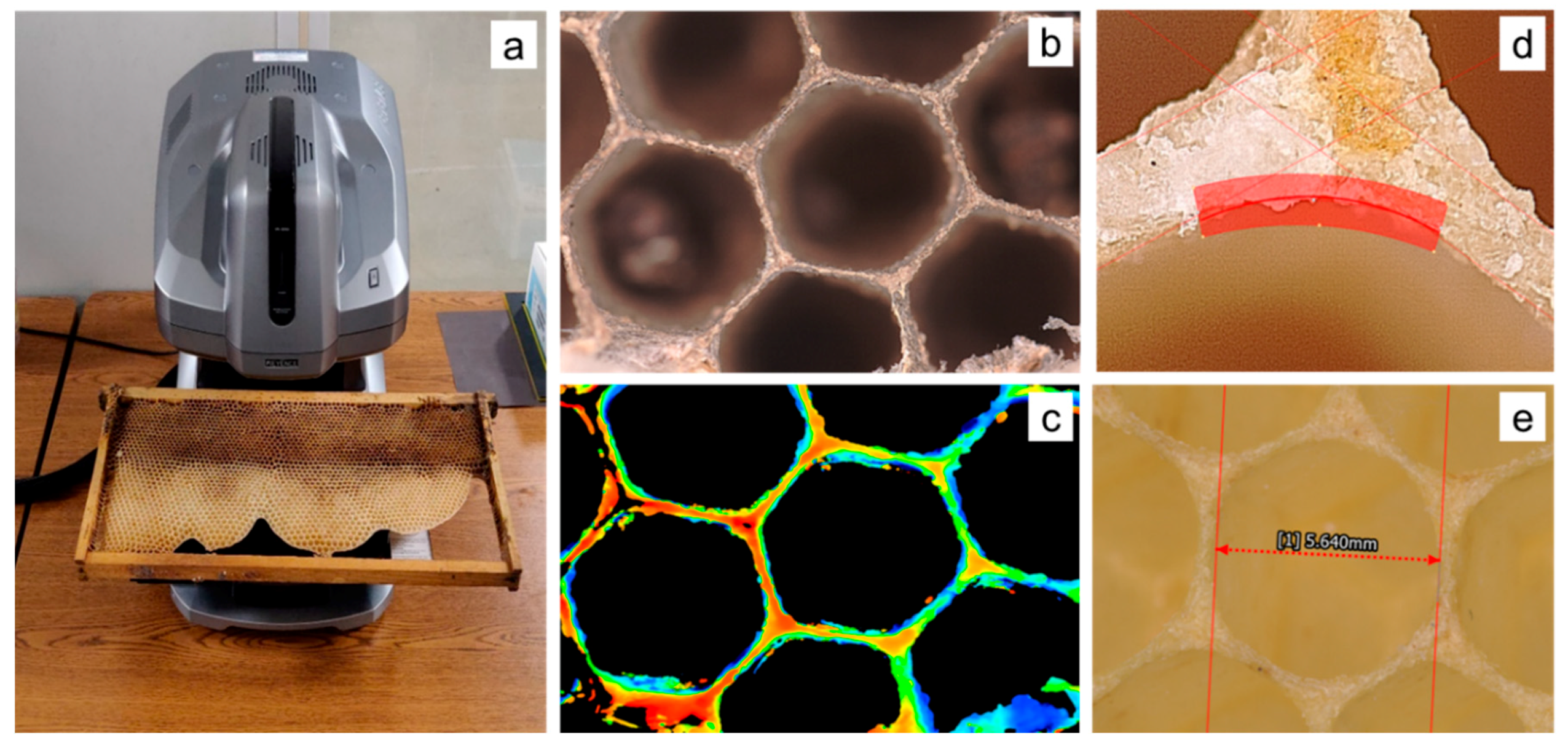
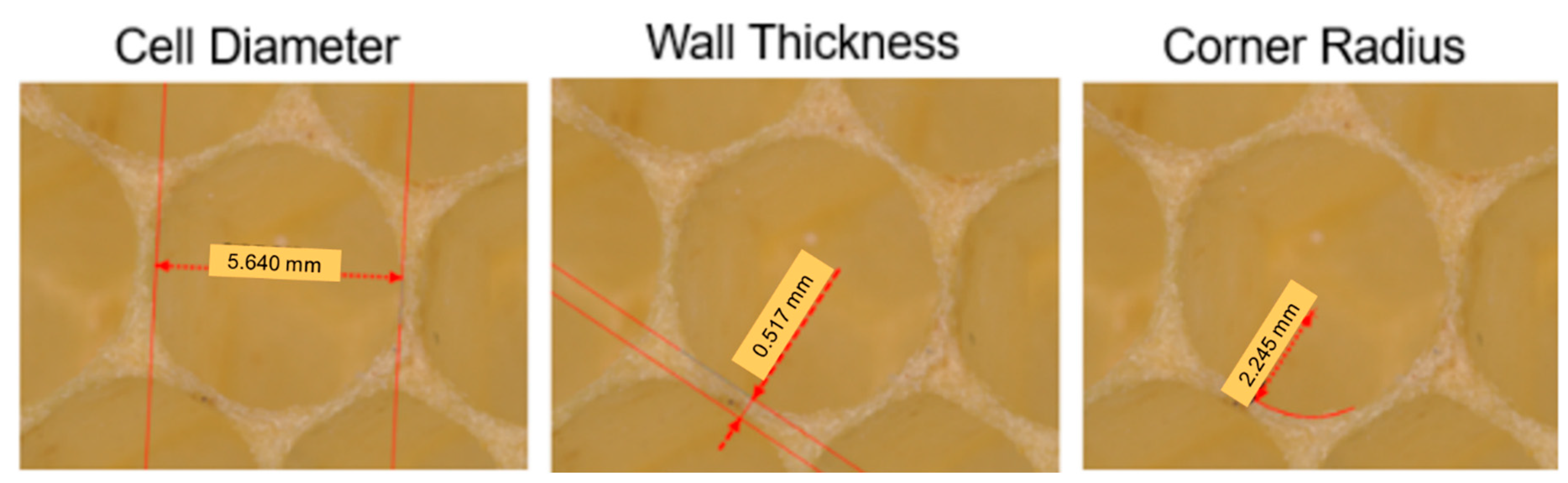
2.2.2. Structured White Light Microscopy
2.2.3. X-ray Tomography
2.2.4. Silicone Molding
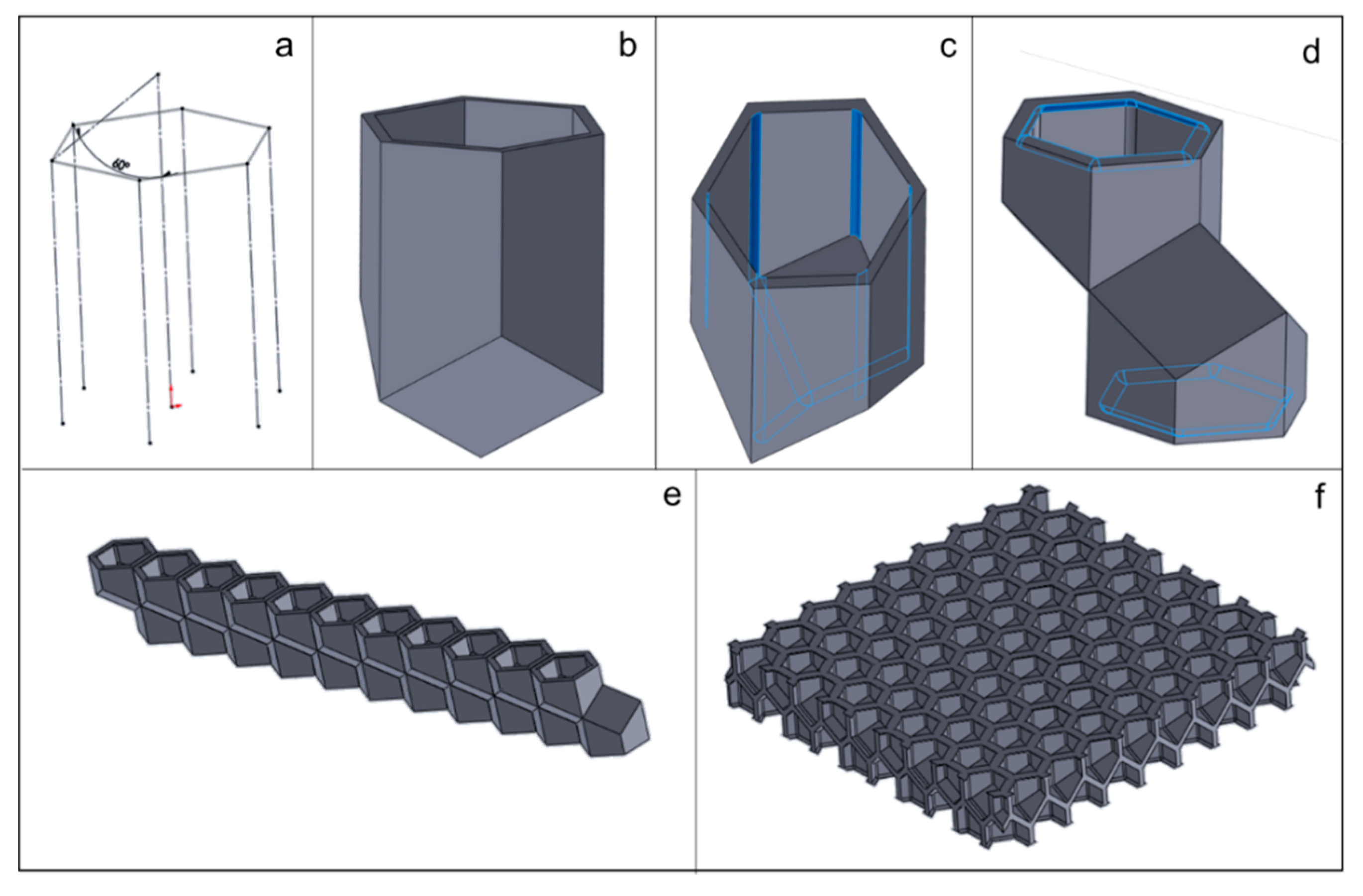
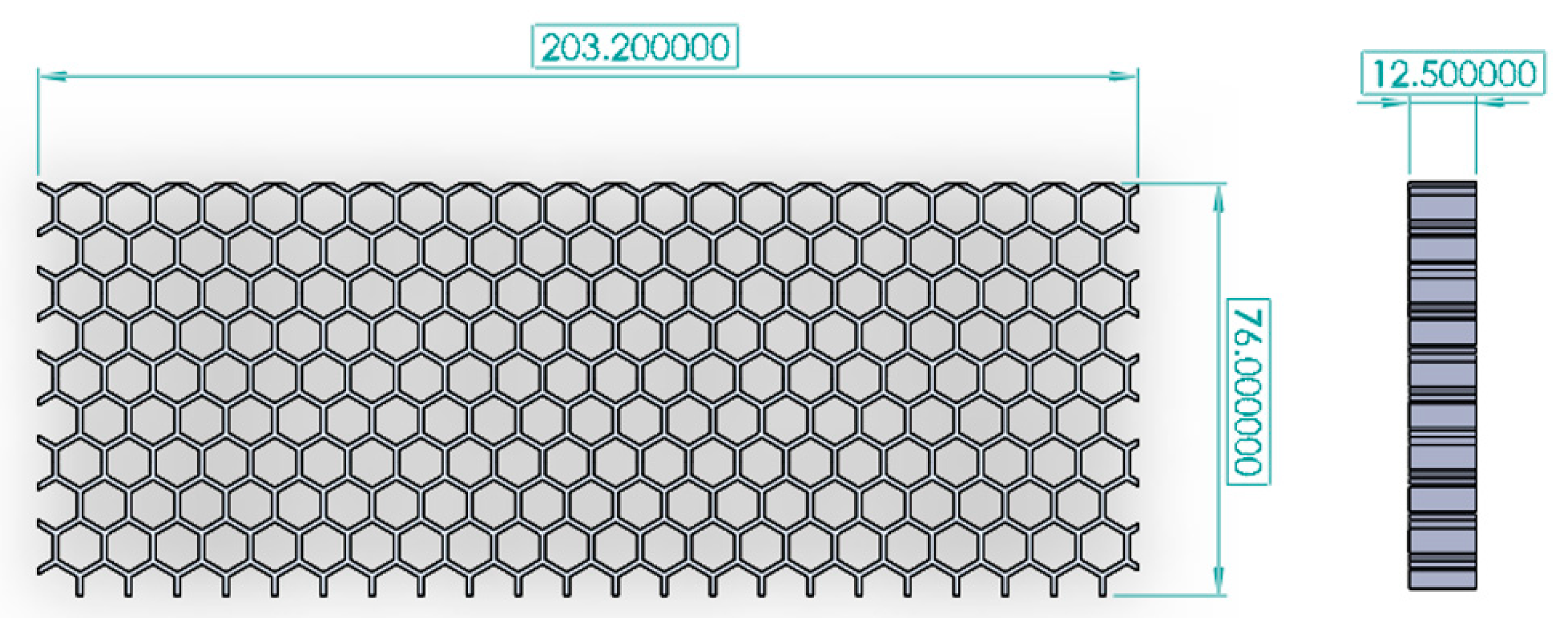
2.3. Honeycomb Panel Design
2.4. Additive Manufacturing
2.5. Mechanical Testing
2.5.1. Out-of-Plane Compression
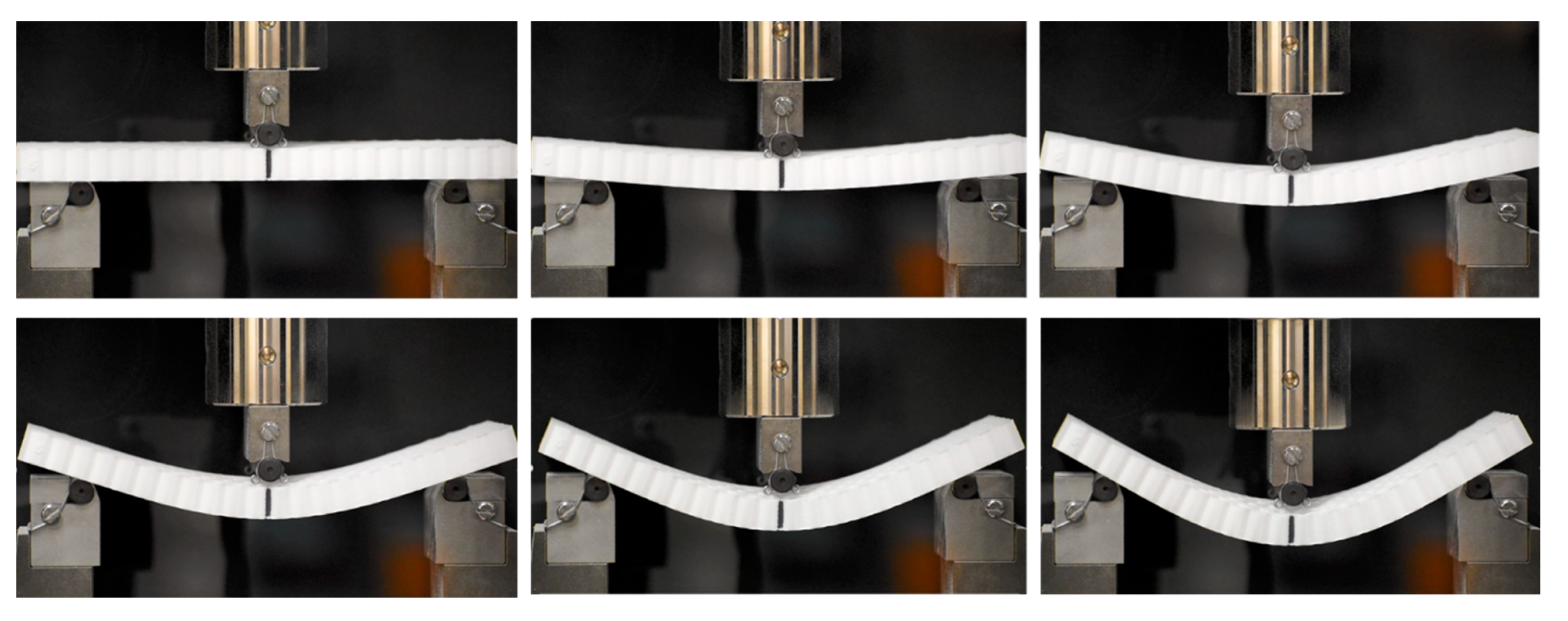
2.5.2. Three-Point Bending
3. Results
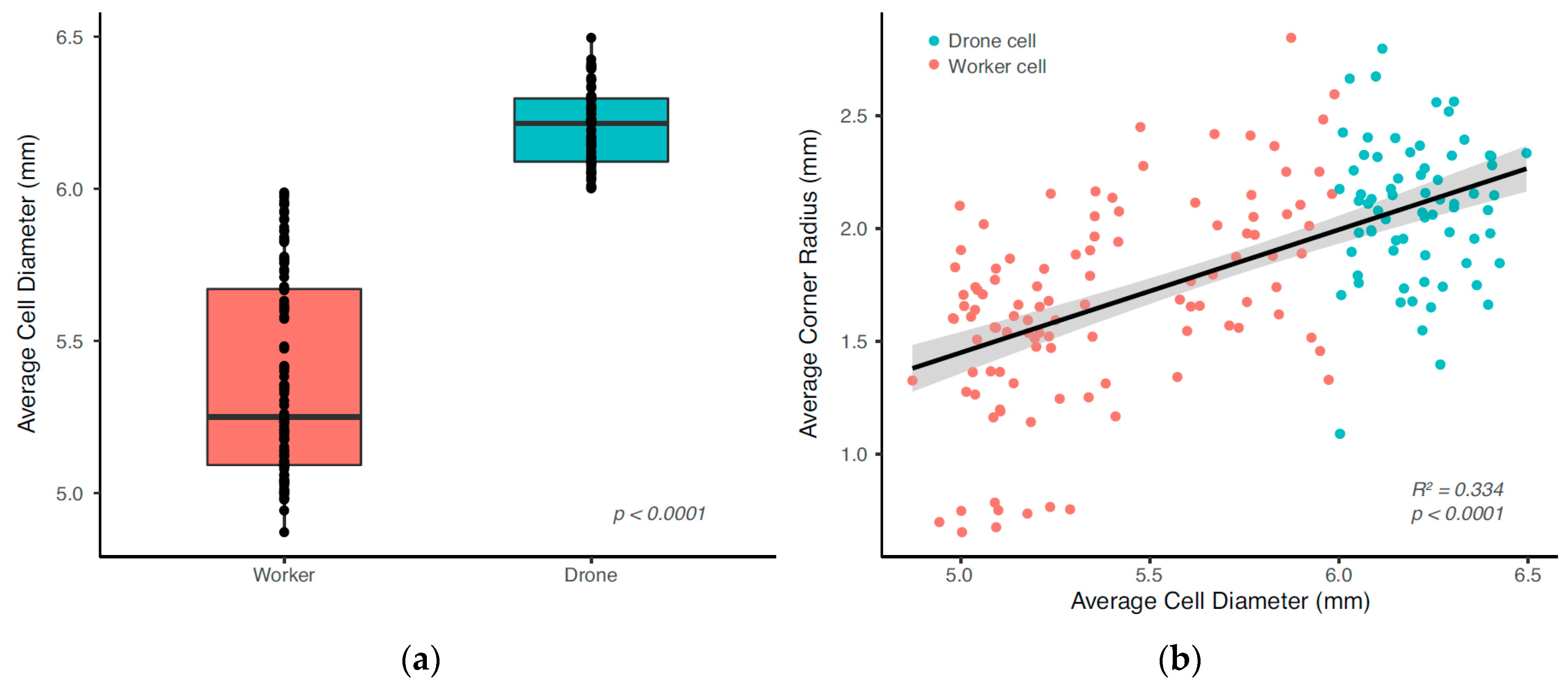
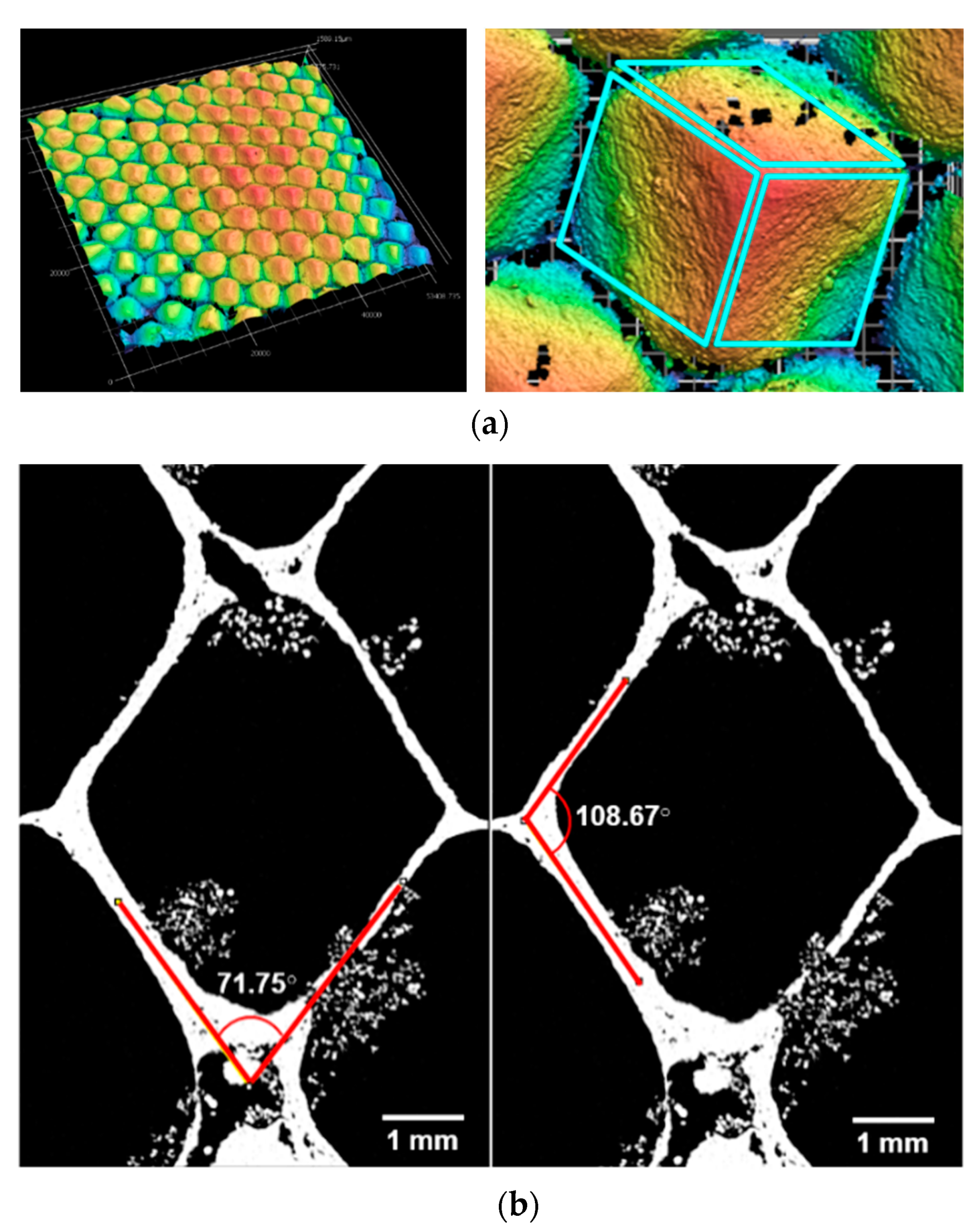
3.1. Honeybee Comb Features
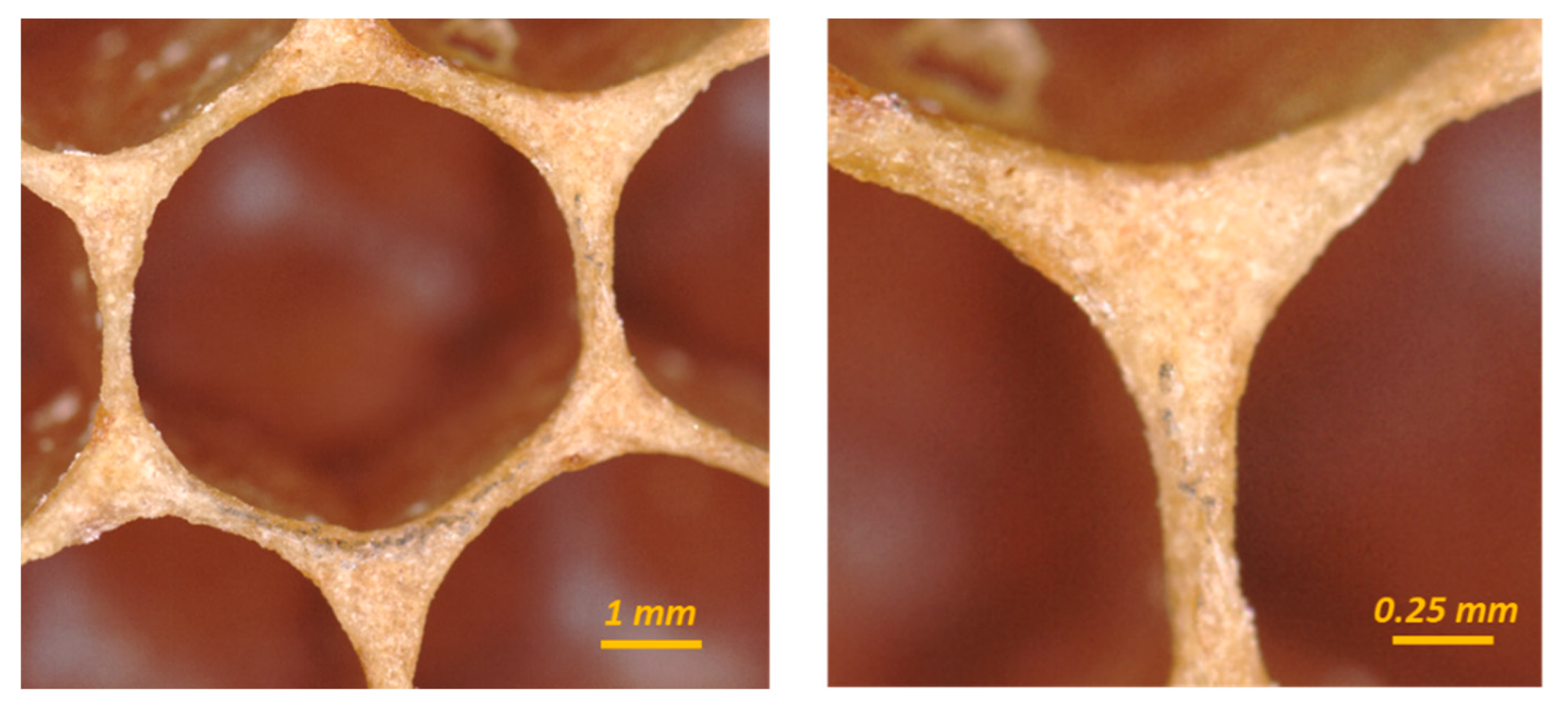
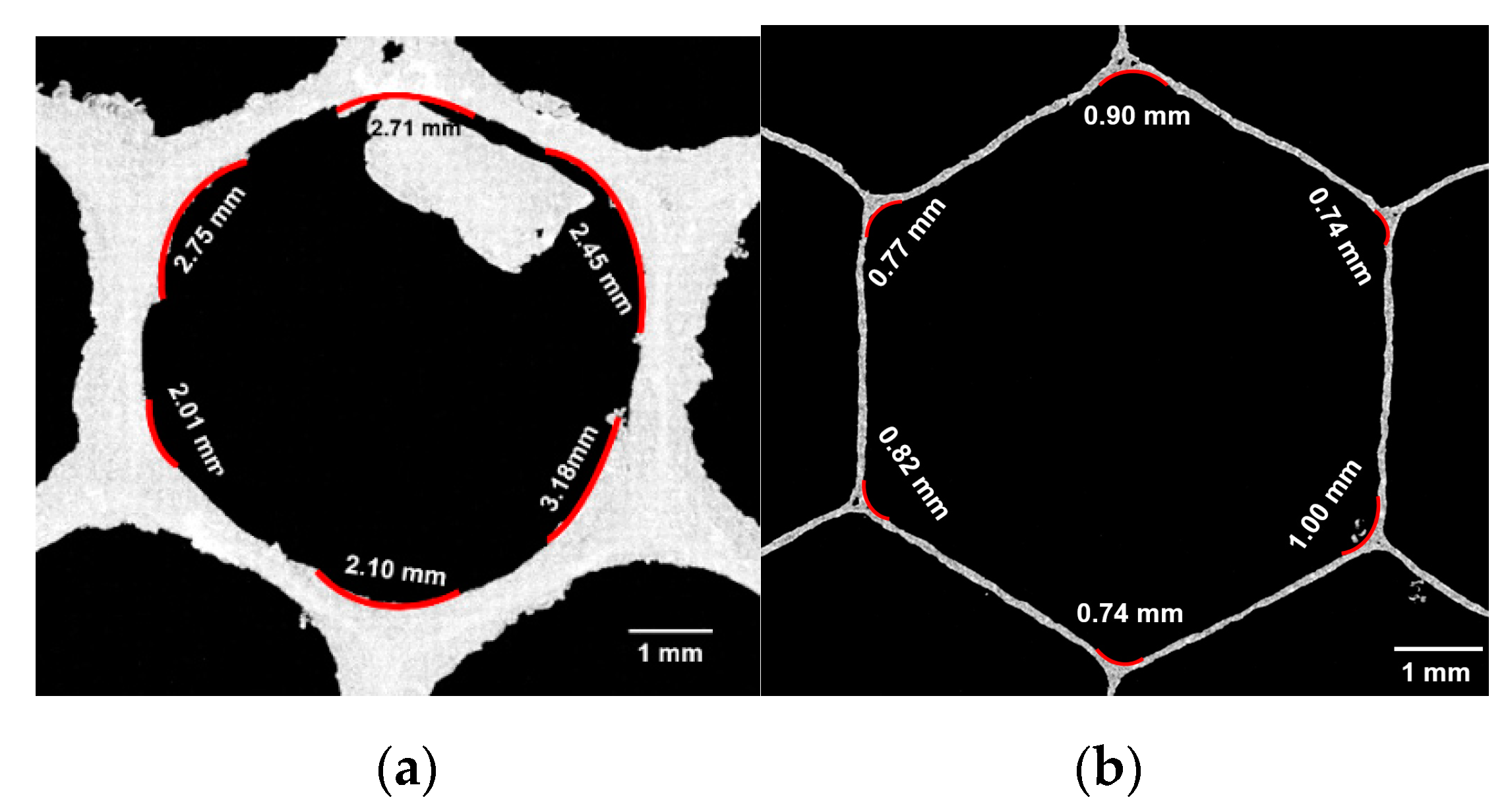
3.1.1. Corner Radius
3.1.2. Coping
3.1.3. Interface
3.2. Mechanical Testing
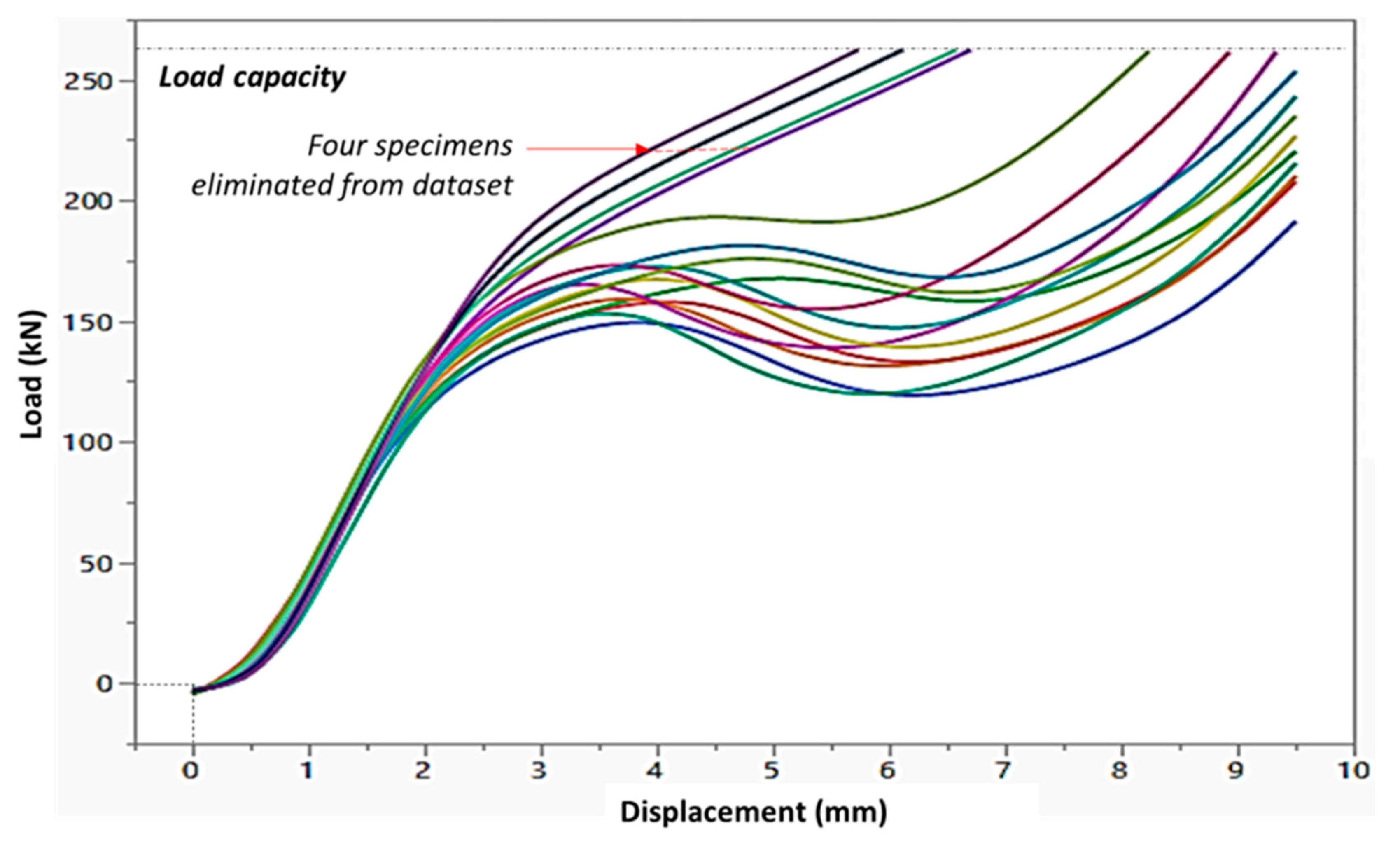
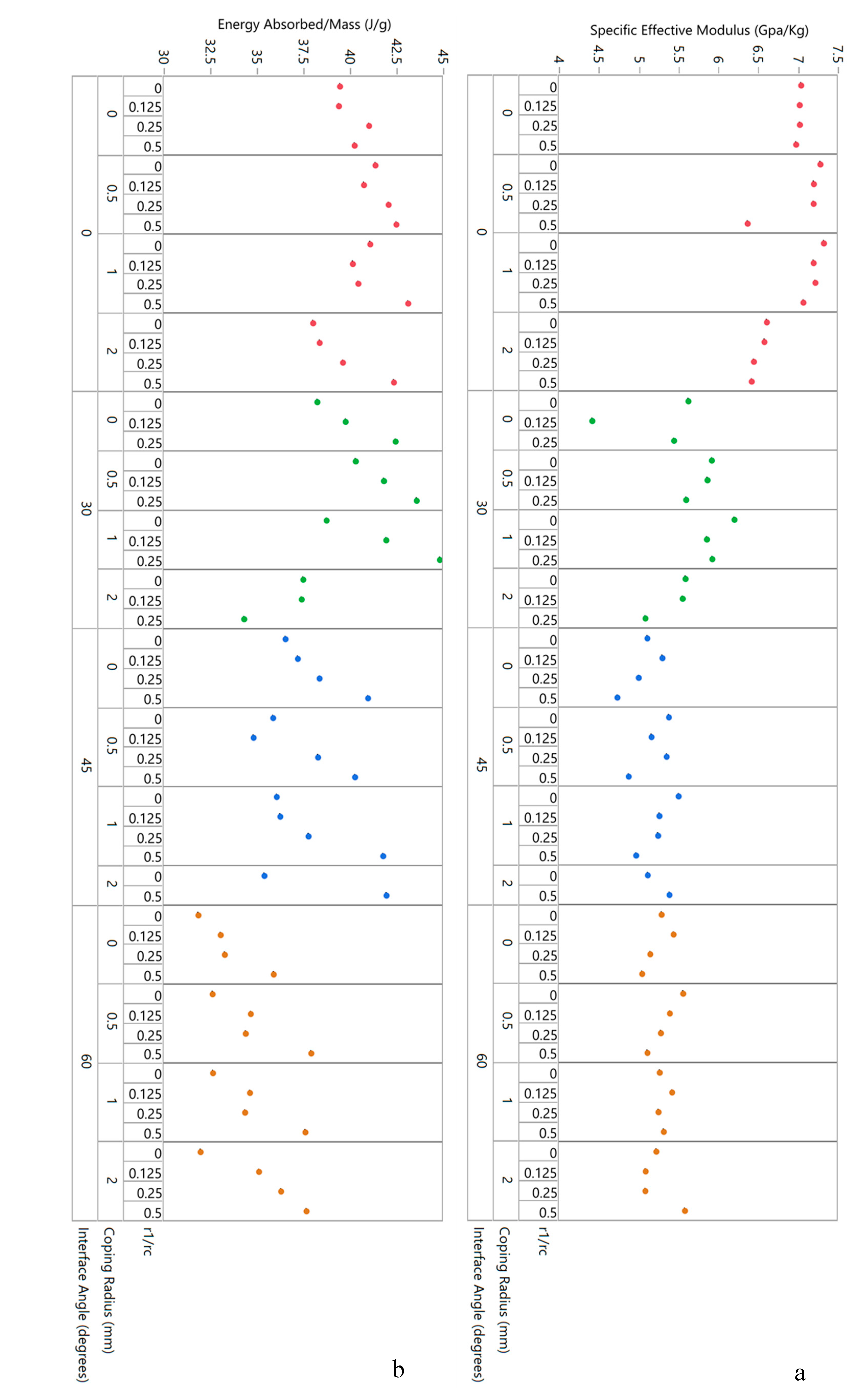
3.2.1. Out-of-Plane Compression
3.2.2. Three-Point Bending
4. Discussion
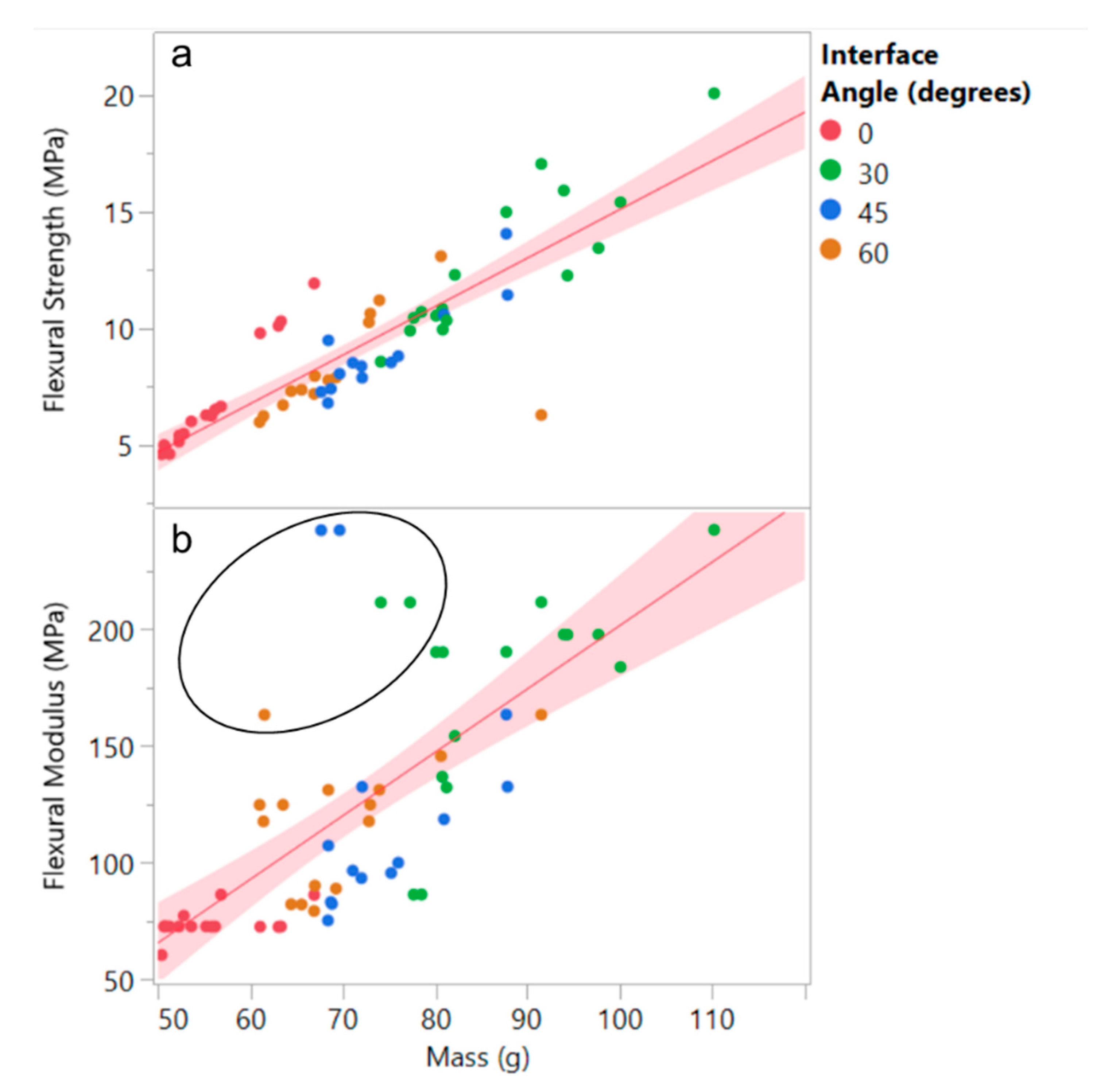
4.1. Material Allocation
- The addition of an interface increases specific flexural modulus (i.e., stiffness under bending) but has little benefit in out-of-plane compression.
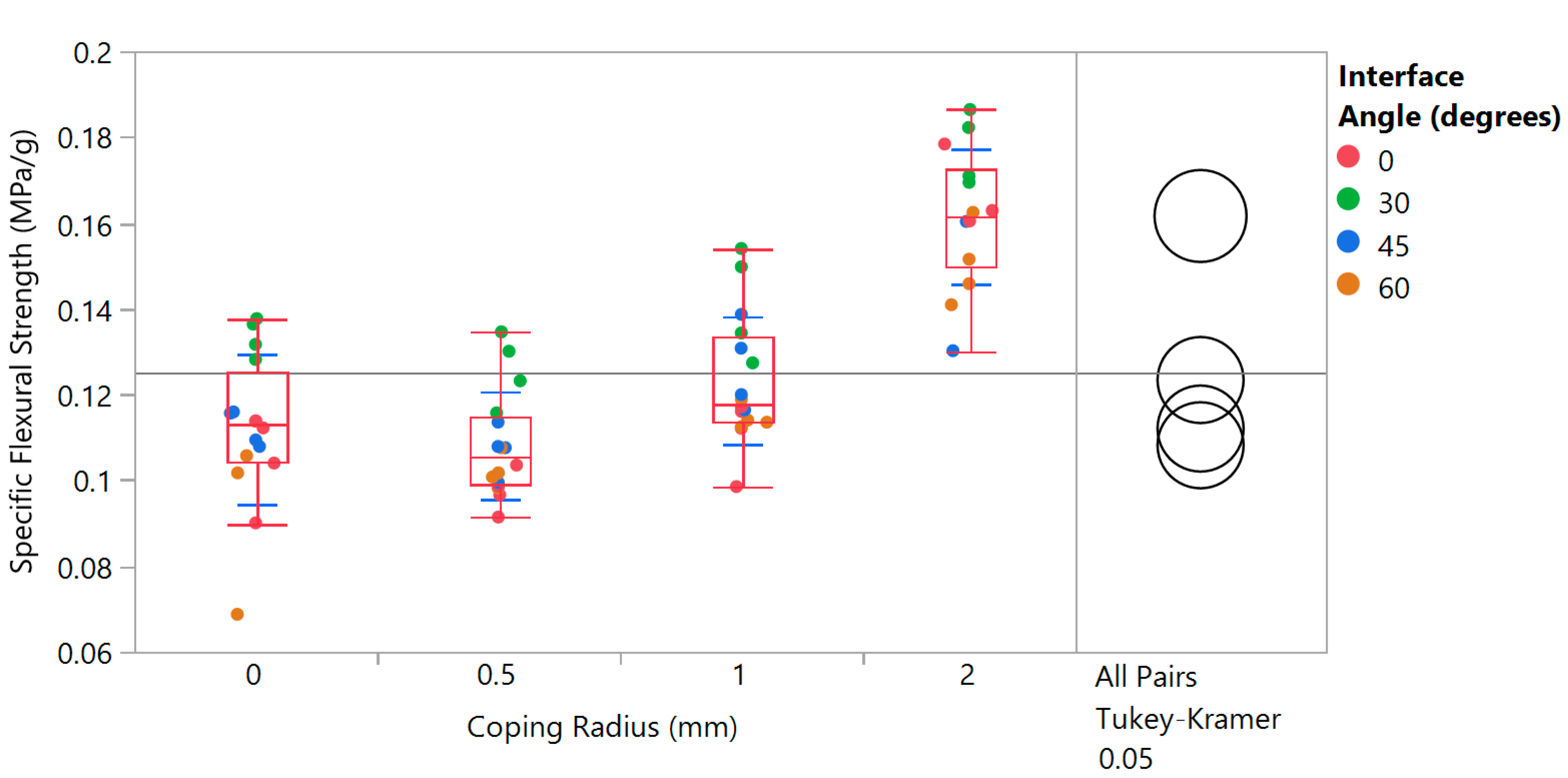
- The coping radius strongly influences specific flexural strength—this is perhaps the most remarkable and significant result from the experimental data.
- The corner radius has no significant effect in bending and, actually, is slightly detrimental for out-of-plane compression testing.
4.2. Structure–Function Relationships
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ball, P. Shapes, Nature’s Patterns; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hales, T.C. The honeycomb conjecture. Discret. Comput. Geom. 2001, 25, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, X.; Li, P.; Huang, G.; Feng, S.; Shen, C.; Han, B.; Zhang, X.; Jin, F.; Xu, F.; et al. Bioinspired engineering of honeycomb structure—Using nature to inspire human innovation. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 74, 332–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, S.; Gibson, L. Effective elastic properties of periodic hexagonal honeycombs. Mech. Mater. 2015, 91, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, L.; Ashby, M. Cellular Solids: Structure and Properties, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, C.; Huang, J. Elastic moduli and plastic collapse strength of hexagonal honeycombs with plateau borders. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2002, 44, 1827–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipperman, F.; Ryvkin, M.; Fuchs, M.B. Fracture toughness of two-dimensional cellular material with periodic microstructure. Int. J. Fract. 2007, 146, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, Q.M. Dynamic compressive behaviour of cellular materials: A review of phenomenon, mechanism and modelling. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2018, 112, 74–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.; Bhate, D.; Parsey, J.M.; Hsu, K.H. Determination of a Shape and Size Independent Material Modulus for Honeycomb Structures in Additive Manufacturing. Solid Free. Fabr. Symp. 2017, 2148–2169. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, Q.; Patil, D.; Le, T.; Eppley, T.; Salti, Z.; Goss, D.; Grishin, A.; Bhate, D. An examination of the low strain rate sensitivity of additively manufactured polymer, composite and metallic honeycomb structures. Materials 2019, 12, 3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhate, D. Four Questions in Cellular Material Design. Materials 2019, 12, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karihaloo, B.L.; Zhang, K.; Wang, J. Honeybee combs: How the circular cells transform into rounded hexagons. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20130299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Duan, H.; Karihaloo, B.L.; Wang, J. Hierarchical, multilayered cell walls reinforced by recycled silk cocoons enhance the structural integrity of honeybee combs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9502–9506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepburn, H.R.; Kurstjens, S.P. The combs of honeybees as composite materials. Apidologie 1988, 19, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepburn, H.R.; Muerrle, T.; Radloff, S.E. The cell bases of honeybee combs. Apidologie 2007, 38, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rasband, W.S.; Image, J. 1997. Available online: https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ (accessed on 31 August 2020).
- Systemes, D. Solidworks. 2019. Available online: https://www.solidworks.com/ (accessed on 31 August 2020).
- AMS STD 401. Sandwich Construction and Core Materials; General Test Methods; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, I.; Rosen, D.; Stucker, B. Additive Manufacturing Technologies, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D790-17. Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials. ASTM Stand. 2017, 12. [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Maechler, M. The lme4 Package, R Packag. Version 0.999375-22. 2007. Available online: http://cran.r-project.org (accessed on 14 September 2020).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 2018. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 14 September 2020).
- Von Frisch, K. Animal Architecture (English and German Edition), 1st ed.; Harcourt: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, P.C.; Winston, M.L. The effect of swarm size and date of issue on comb construction in newly founded colonies of honeybees (Apis mellifera L.). Can. J. Zool. 1985, 63, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.W. On Growth and Form, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1917. [Google Scholar]
- Schaedler, T.A.; Ro, C.J.; Sorensen, A.E.; Eckel, Z.; Yang, S.S.; Carter, W.B.; Jacobsen, A.J. Designing metallic microlattices for energy absorber applications. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2014, 16, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Schaedler, T.A.; Jacobsen, A.J.; Chen, X. Quasi-static energy absorption of hollow microlattice structures. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 67, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuhri, M.Y.M.; Guan, Z.W.; Cantwell, W.J. The mechanical properties of natural fibre based honeycomb core materials. Compos. Part B. 2014, 58, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, N.S.; Lu, G.; Xiang, X. Energy absorption of a bio-inspired honeycomb sandwich panel. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 6286–6300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivañez, I.; Fernandez-Cañadas, L.M.; Sanchez-Saez, S. Compressive deformation and energy-absorption capability of aluminium honeycomb core. Compos. Struct. 2017, 174, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepburn, H.R.; Pirk, C.W.W.; Duangphakdee, O. Honeybee Nests; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Plessis, A.D.; Broeckhoven, C.; Yadroitsava, I.; Yadroitsev, I.; Hands, C.H.; Kunju, R.; Bhate, D. Beautiful and Functional: A Review of Biomimetic Design in Additive Manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 27, 408–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.X. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids Size-dependent elastic properties of micro- and nano-honeycombs. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2010, 58, 696–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekoğlu, C.; Gibson, L.J.; Pardoen, T.; Onck, P.R. Size effects in foams: Experiments and modeling. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2011, 56, 109–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
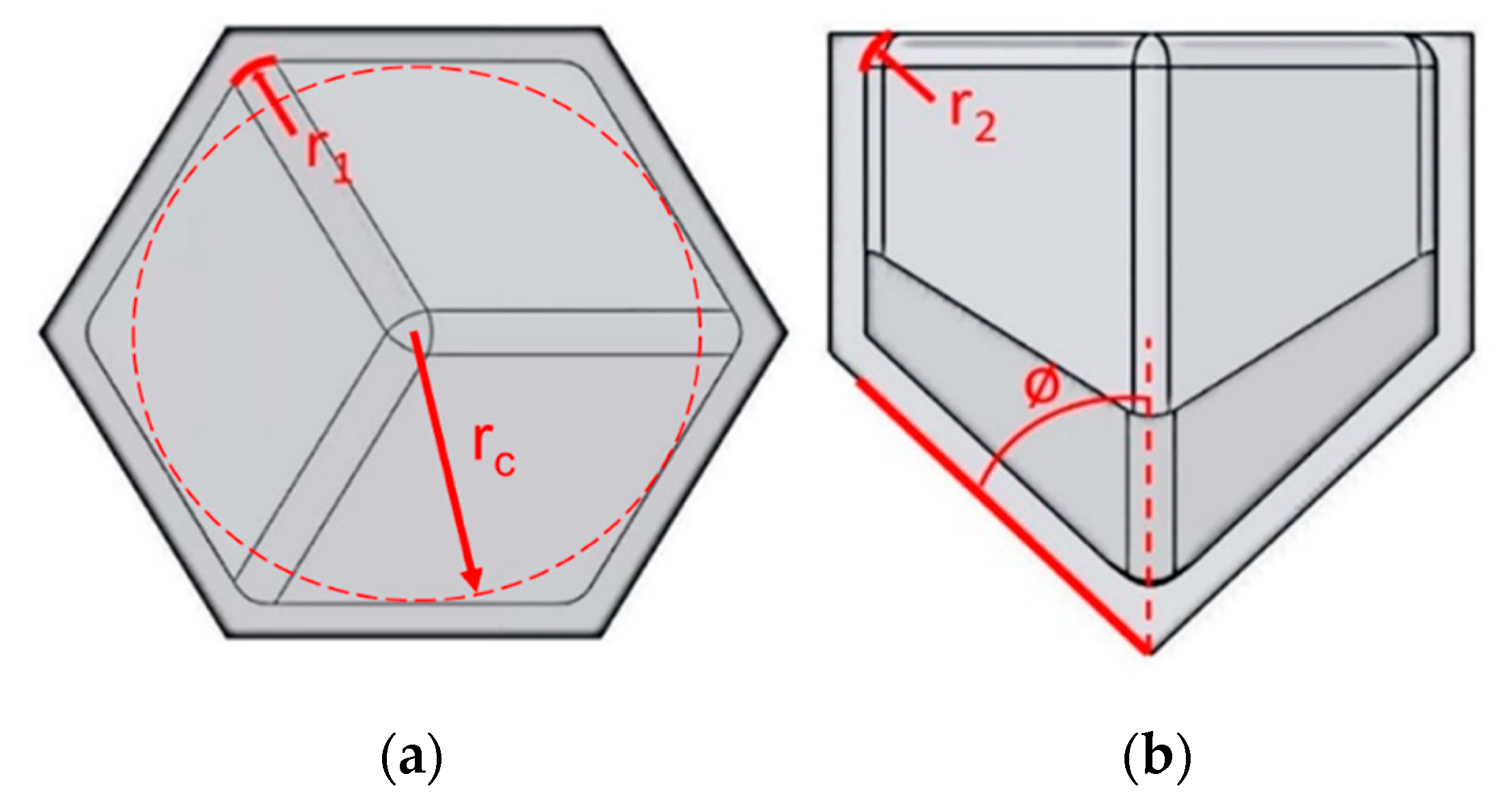









| Parameter | Baseline | Low | Middle | High |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corner/cell radius 1 (r1/rc) | 0 | 0.125 | 0.250 | 0.500 |
| Coping radius (mm) | 0 | 0.5 | 1 | 2 |
| Interface angle (deg.) | 0 (no interface) | 30 | 45 | 60 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goss, D.; Mistry, Y.; Niverty, S.; Noe, C.; Santhanam, B.; Ozturk, C.; Penick, C.A.; Lee, C.; Chawla, N.; Grishin, A.; et al. Bioinspired Honeycomb Core Design: An Experimental Study of the Role of Corner Radius, Coping and Interface. Biomimetics 2020, 5, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics5040059
Goss D, Mistry Y, Niverty S, Noe C, Santhanam B, Ozturk C, Penick CA, Lee C, Chawla N, Grishin A, et al. Bioinspired Honeycomb Core Design: An Experimental Study of the Role of Corner Radius, Coping and Interface. Biomimetics. 2020; 5(4):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics5040059
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoss, Derek, Yash Mistry, Sridhar Niverty, Cameron Noe, Bharath Santhanam, Cahit Ozturk, Clint A. Penick, Christine Lee, Nikhilesh Chawla, Alex Grishin, and et al. 2020. "Bioinspired Honeycomb Core Design: An Experimental Study of the Role of Corner Radius, Coping and Interface" Biomimetics 5, no. 4: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics5040059
APA StyleGoss, D., Mistry, Y., Niverty, S., Noe, C., Santhanam, B., Ozturk, C., Penick, C. A., Lee, C., Chawla, N., Grishin, A., Shyam, V., & Bhate, D. (2020). Bioinspired Honeycomb Core Design: An Experimental Study of the Role of Corner Radius, Coping and Interface. Biomimetics, 5(4), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics5040059