Interaction Between Chitosan and Mucin: Fundamentals and Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
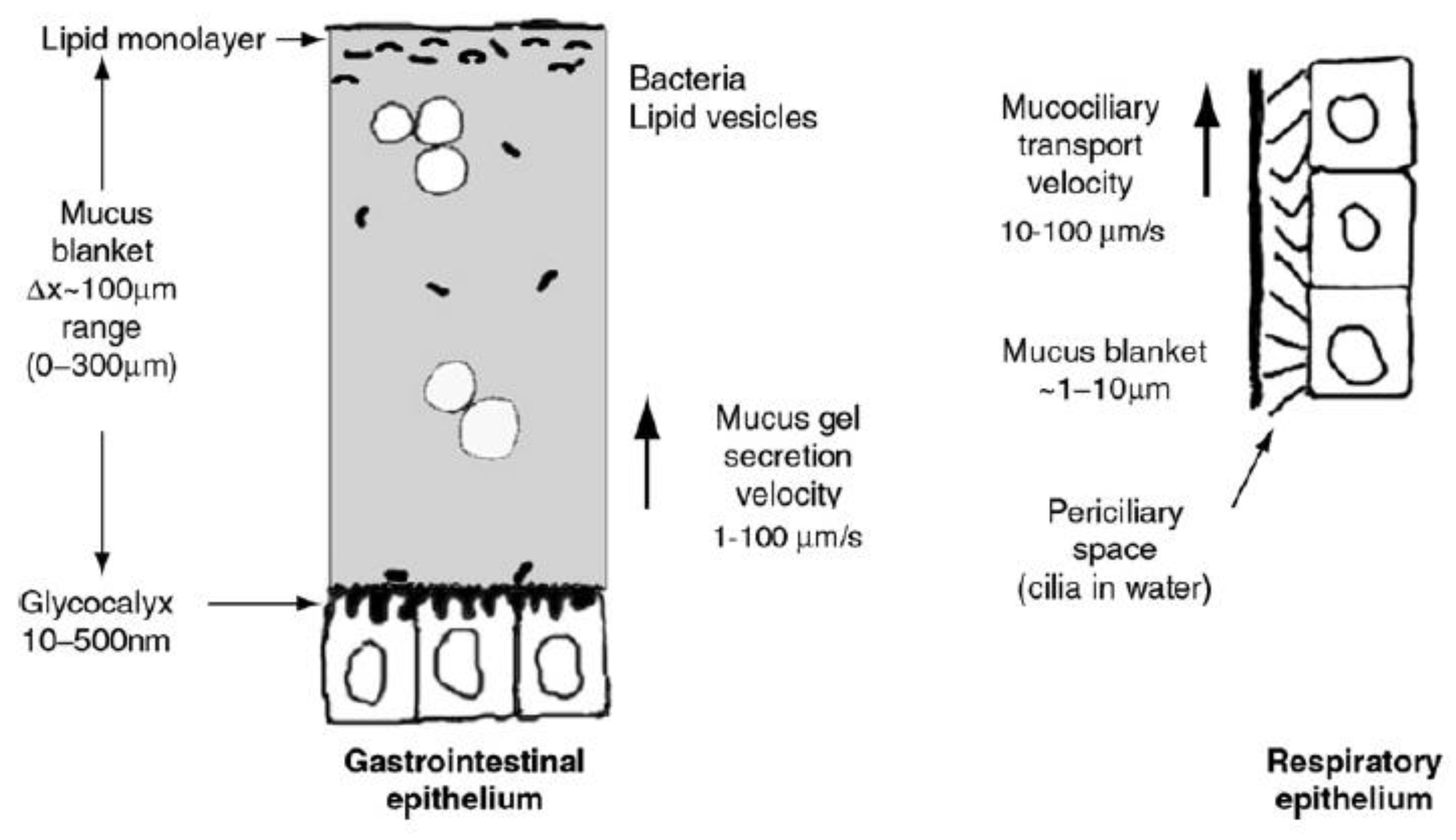
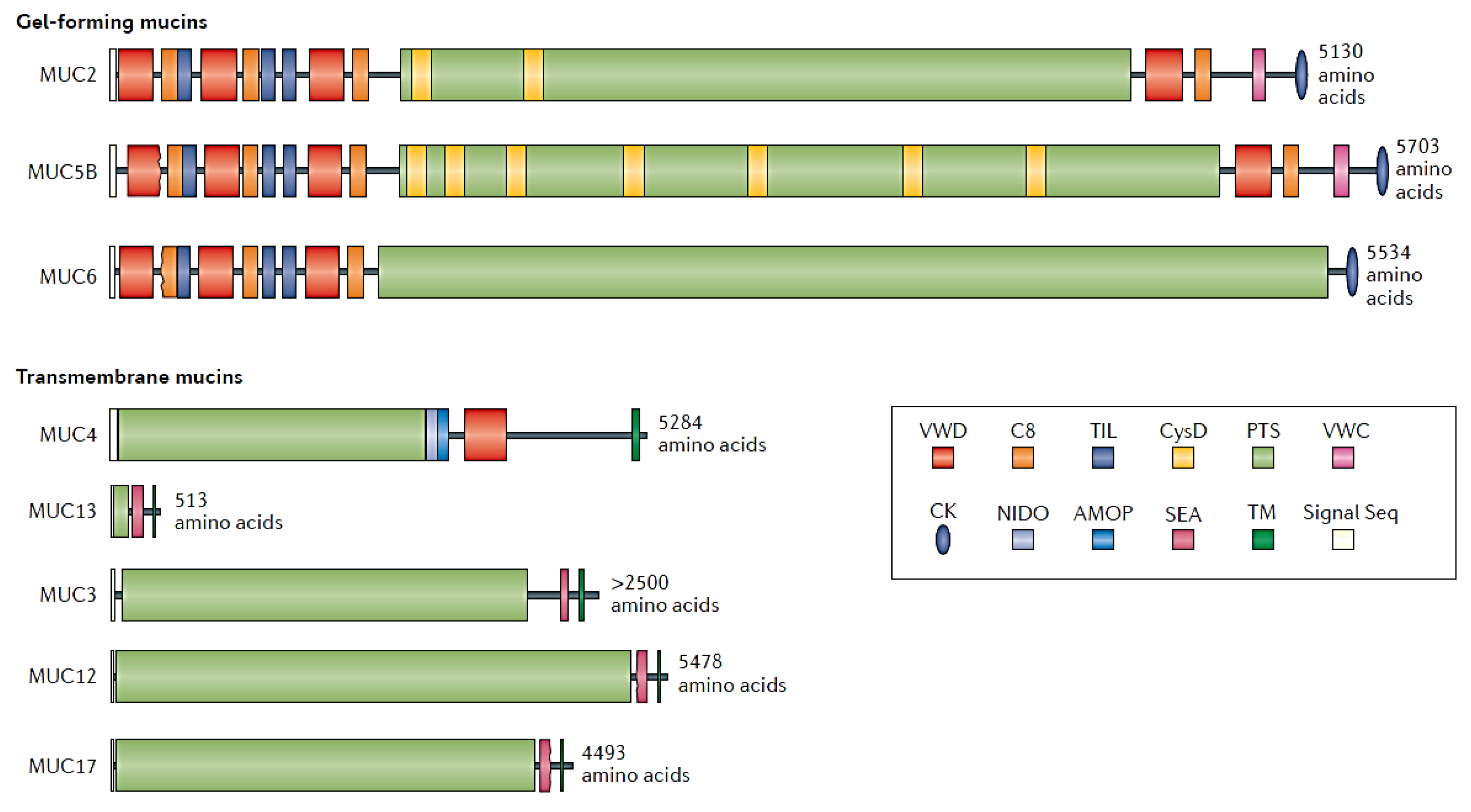
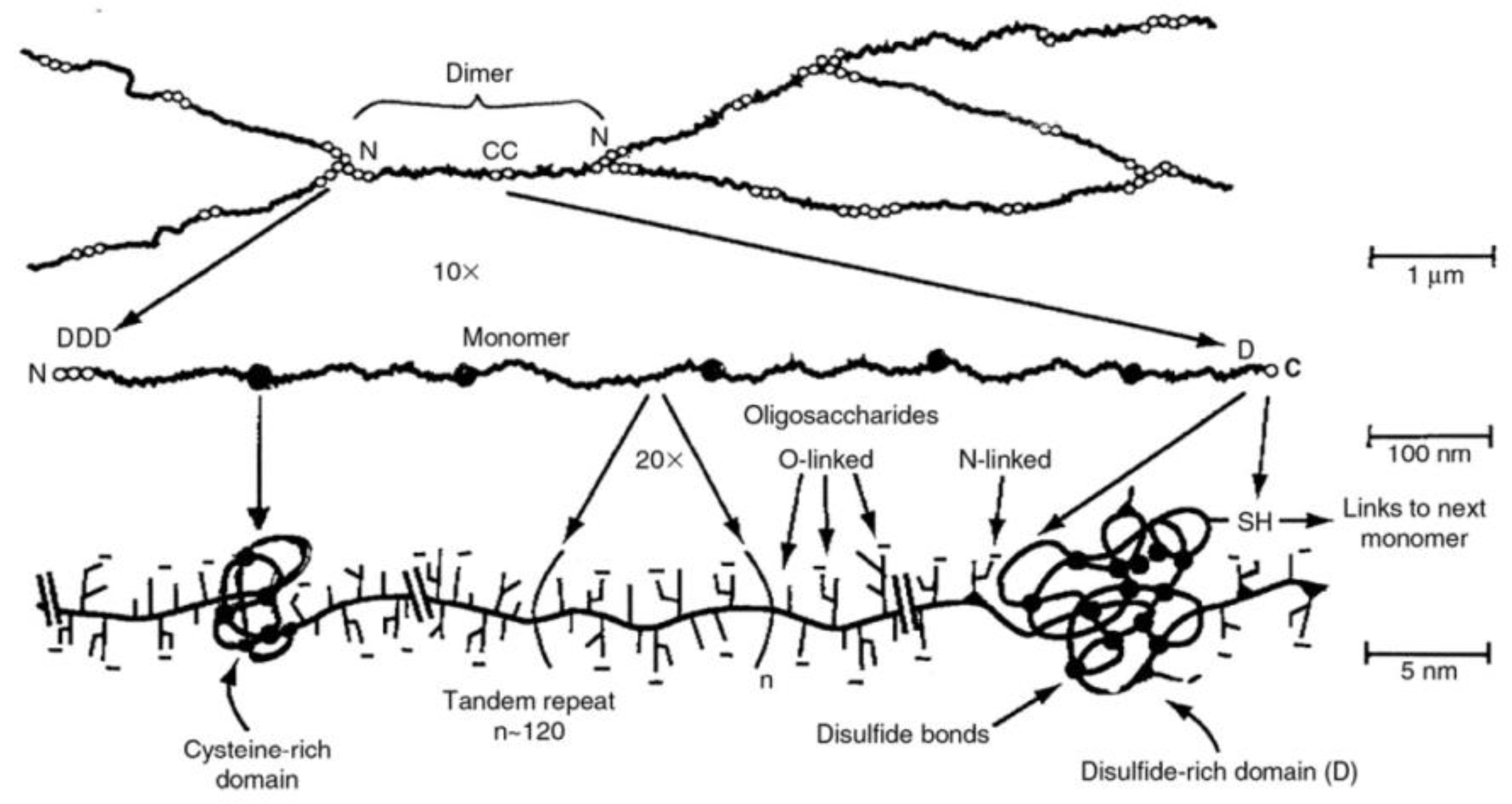
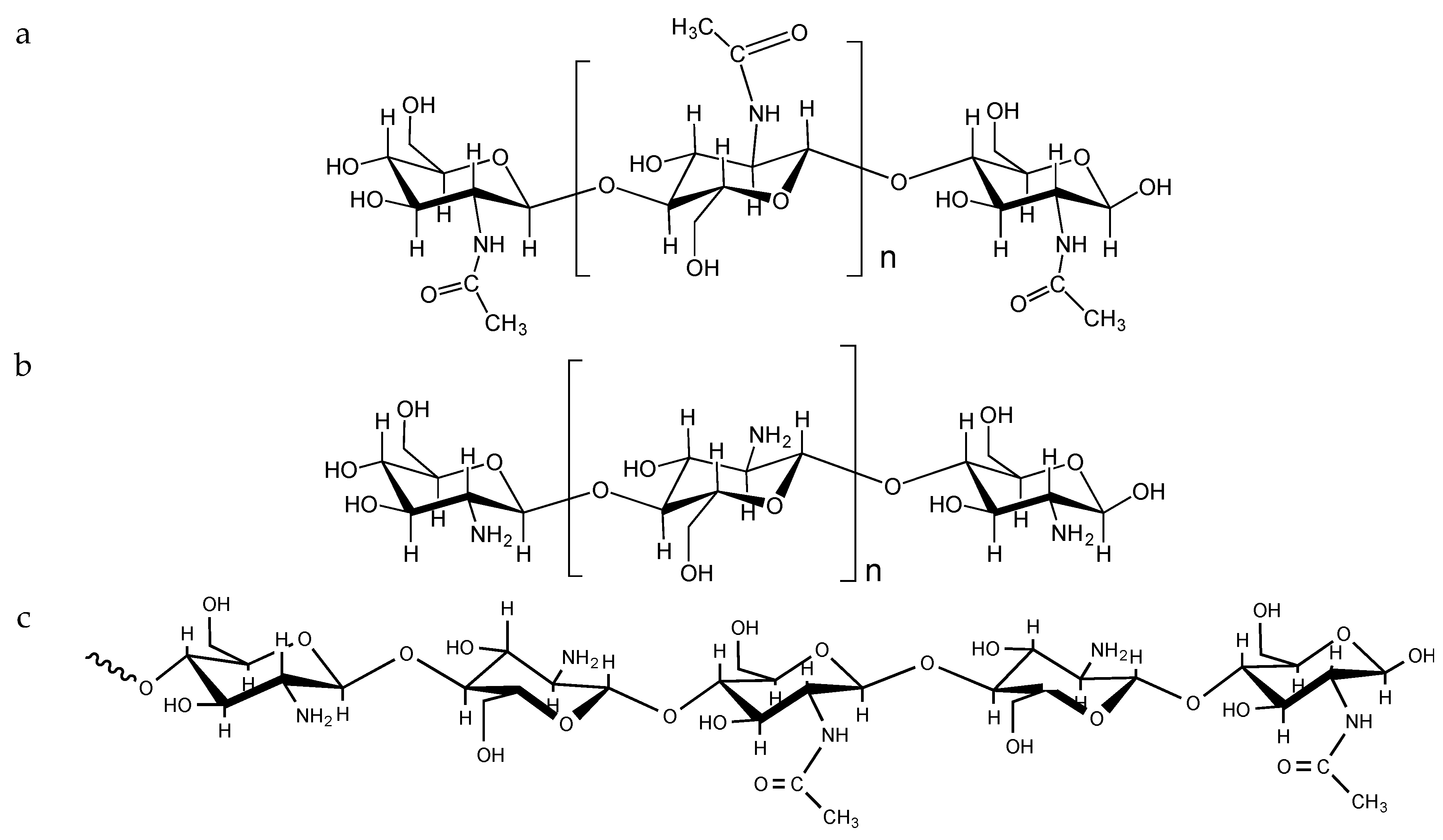
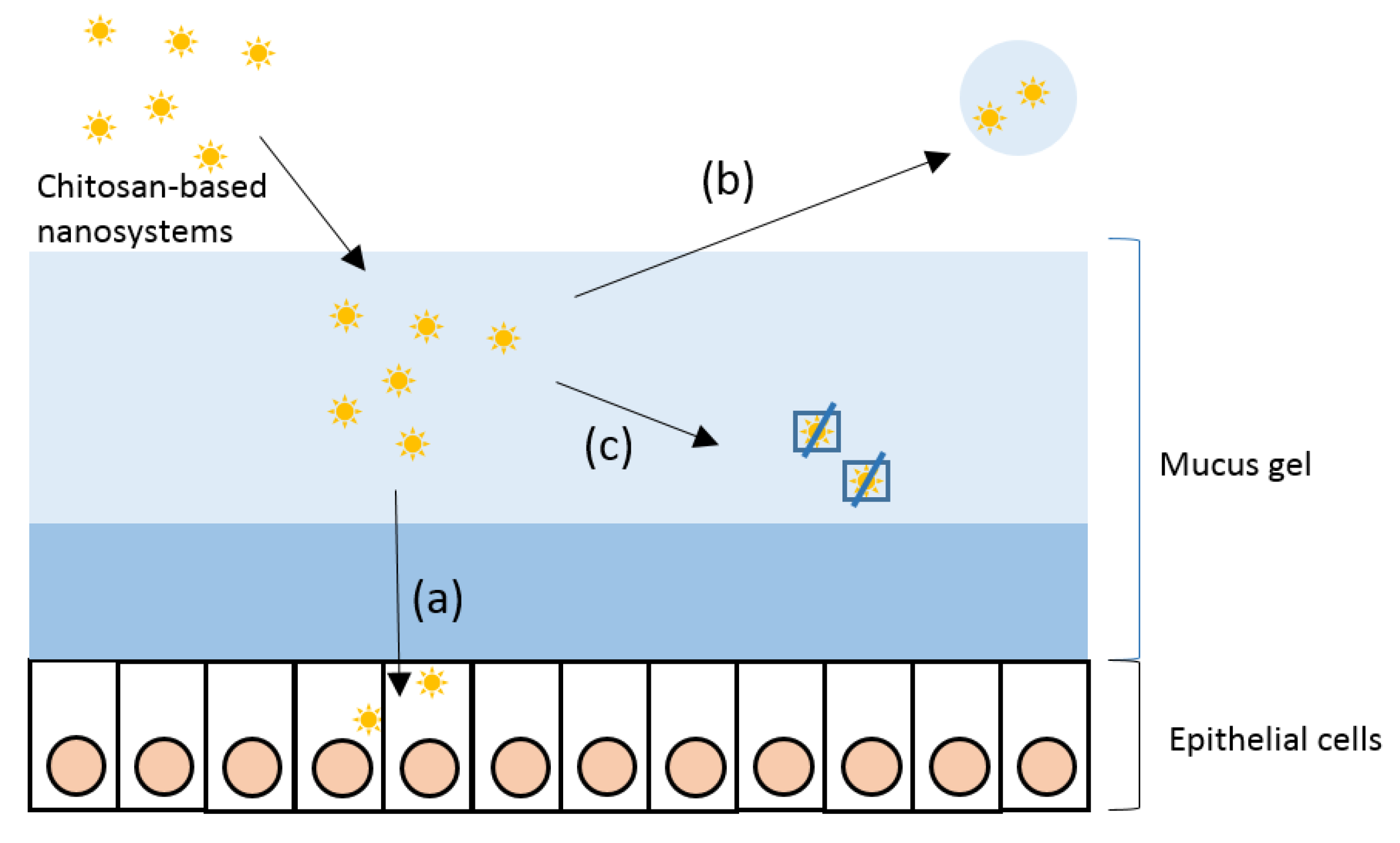
2. The Mucus Layer
3. Mucoadhesive Properties of Chitosan
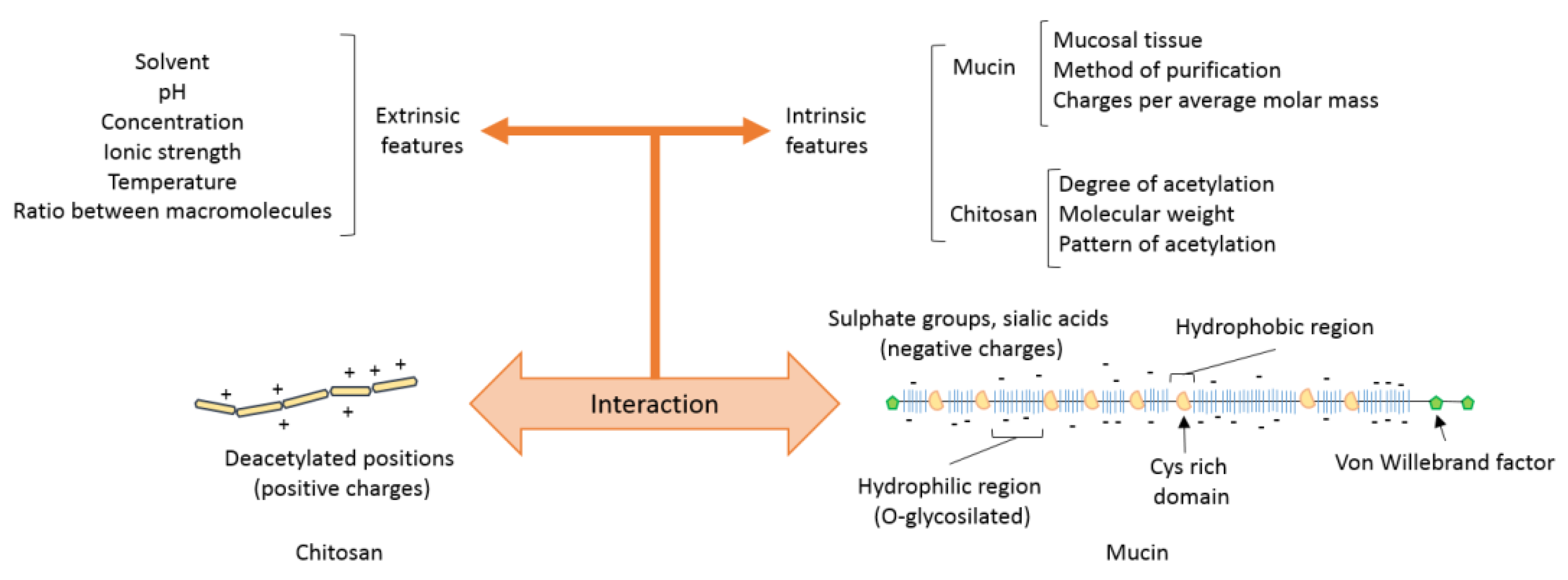
4. Main Forces Behind the Interaction Between Chitosan and Mucin
5. Chitosan-Mucin Complexes: Characterisation and Mucoadhesion
6. Mucoadhesion of Chitosan-Mucin Complexes
7. Chitosan Cross-linked Structures
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cone, R.A. Barrier properties of mucus. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, M.E.; Hansson, G.C. Immunological aspects of intestinal mucus and mucins. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuckin, M.A.; Linden, S.K.; Sutton, P.; Florin, T.H. Mucin dynamics and enteric pathogens. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bansil, R.; Turner, B.S. The biology of mucus: Composition, synthesis and organization. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 124, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.E.; Larsson, J.M.; Hansson, G.C. The two mucus layers of colon are organized by the MUC2 mucin, whereas the outer layer is a legislator of host-microbial interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108 (Suppl. 1), 4659–4665. [Google Scholar]
- Forstner, J.F. Intestinal mucins in health and disease. Digestion 1978, 17, 234–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corfield, A.; Wagner, S.A.; Clamp, J.R.; Kriaris, M.; Hoskins, L.C. Mucin degradation in the human colon: Production of sialidase, sialate O-acetylesterase, N-acetylneuraminate lyase, arylesterase, and glycosulfatase activities by strains of fecal bacterial. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 3971–3978. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Müller, M.; Rezwan, K.; Spencer, N.D. Porcine gastric mucin (PGM) at the water/poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) interface: Influence of pH and ionic strength on its conformation, adsorption, and aqueous lubrication properties. Langmuir 2005, 21, 8344–8353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordman, H.; Davies, J.R.; Herrmann, A.; Karlsson, N.G.; Hansson, G.C. Mucus glycoproteins from pig gastric mucosa: Identification of different mucin populations from the surface epithelium. Biochem. J. 1997, 326, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celli, J.P.; Turner, B.S.; Afdhal, N.H.; Ewoldt, R.H.; McKinley, G.H.; Bansil, R.; Erramilli, S. Rheology of gastric mucin exhibits a pH-dependent sol-gel transition. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1580–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, C.A.; Nobre, T.M.; Pavinatto, F.J.; Oliveira, O.N., Jr. Interaction of chitosan and mucin in a biomembrane model environment. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 376, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derrien, M.; van Passel, M.W.; van de Bovenkamp, J.H.; Schipper, R.G.; de Vos, W.M.; Dekker, J. Mucin-bacterial interactions in the human oral cavity and digestive tract. Gut Microbes 2010, 1, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikogeorgos, N.; Efler, P.; Kayitmazer, A.B.; Lee, S. “Bio-glues” to enhance slipperiness of mucins: Improved lubricity and wear resistance of porcine gastric mucin (PGM) layers assisted by mucoadhesion with chitosan. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, H.; Geyer, R. Strategies for analysis of glycoprotein glycosylation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1764, 1853–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deplancke, B.; Gaskins, H.R. Microbial modulation of innate defense: Globet cells and the intestinal mucus layer. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 73, 1131S–1141S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, N.G.; Nordman, H.; Karlsson, H.; Carlstedt, I.; Hansson, G.C. Glycosilation differences between pig gastric mucin populations: A comparative study of the neutral oligosaccharides using mass spectrometry. Biochem. J. 1997, 326, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunning, A.P.; Kirby, A.R.; Fuell, C.; Pin, C.; Tailford, L.E.; Juge, N. Mining the “glycocode”–exploring the spatial distribution of glycans in gastrointestinal mucin using force spectroscopy. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2013, 27, 2342–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsson, K.A.; Karlsson, N.G.; Hansson, G.C. Liquid chromatography-electrospray mass spectrometry as a tool for the analysis of sulfated oligosaccharides from mucin glycoproteins. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 854, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, O.; Arnebrant, T. Mucin layers and multilayers—Physicochemical properties and applications. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 15, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.S.; Bhaskar, K.R.; Hadzopoulou-Cladaras, M.; LaMont, J.T. Cysteine-rich regions of pig gastric mucin contain von Wiellebrand factor and cystine knot domains at the carboxyl terminal. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1447, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakubov, G.E.; Papagiannopoulos, A.; Rat, E.; Easton, R.L.; Waigh, T.A. Molecular structure and rheological properties of short-side-chain heavily glycosylated porcine stomach mucin. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 3467–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menchicchi, B.; Fuenzalida, J.P.; Bobbili, K.B.; Hensel, A.; Swamy, M.J.; Goycoolea, F.M. Structure of chitosan determines its interactions with mucin. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 3550–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mushi, N.E.; Kochumalayil, J.; Cervin, N.T.; Zhou, Q.; Berglund, L.A. Nanostructurally Controlled Hydrogel Based on Small-Diameter Native Chitin Nanofibers: Preparation, Structure, and Properties. ChemSusChem 2016, 9, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, K. Chitin and chitosan: Functional biopolymers from marine crustaceans. Mar. Biotechnol. 2006, 8, 203–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaudo, M. Non-covalent interactions in polysaccharide systems. Macromol. Biosci. 2006, 6, 590–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.S.; Mano, J.F.; Reis, R.L. Ionic liquids in the processing and chemical modification of chitin and chitosan for biomedical applications. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 1208–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadokawa, J.-i. Dissolution, gelation, functionalization, and material preparation of chitin using ionic liquids. Pure Appl. Chem. 2016, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarque, G.; Chaussard, G.; Domard, A. Thermodynamic aspects of the heterogeneous deacetylation of β-chitin: Reaction mechanisms. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1942–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.-K.; Kong, B.-G.; Jeong, Y.-I.; Lee, C.H.; Nah, J.-W. Physicochemical characterization of α-chitin, β-chitin, and γ-chitin separated from natural resources. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2004, 42, 3423–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiva, A.; Bonardd, S.; Pino, M.; Saldías, C.; Kortaberria, G.; Radić, D. Improving the performance of chitosan in the synthesis and stabilization of gold nanoparticles. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 68, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, V.K.; Thakur, M.K. Recent Advances in Graft Copolymerization and Applications of Chitosan: A Review. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2637–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan: Properties and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 603–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Powers, K.; Baney, R. Physicochemical properties and blood compatibility of acylated chitosan nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 58, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippova, O.E.; Korchagina, E.V.; Volkov, E.V.; Smirnov, V.A.; Khokhlov, A.R.; Rinaudo, M. Aggregation of some water-soluble derivatives of chitin in aqueous solutions: Role of the degree of acetylation and effect of hydrogen bond breaker. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panos, I.; Acosta, N.; Heras, A. New Drug Delivery Systems Based on Chitosan. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2008, 5, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aranaz, I.; Mengíbar, M.; Harris, R.; Paños, I.; Miralles, B.; Acosta, N.; Galed, G.; Heras, A. Functional characterization of chitin and chitosan. Curr. Chem. Biol. 2009, 3, 203–230. [Google Scholar]
- Rinaudo, M.; Pavlov, G.; Desbrieres, J. Influence of acetic acid concentration on the solubilization of chitosan. Polymers 1999, 40, 7029–7032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucard, N.; David, L.; Rochas, C.; Montembault, A.; Viton, C.; Domard, A. Polyelectrolyte microstructure in chitosan aqueous and alcohol solutions. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasaai, M.R. Calculation of Mark–Houwink–Sakurada (MHS) equation viscometric constants for chitosan in any solvent–temperature system using experimental reported viscometric constants data. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 68, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, C.; López, B.L. Medidas de la rigidez del quitosano en solución a través de la viscosidad intrínseca. Rev. Fac. Ing. Univ. Antioquía 2010, 53, 20–29. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, G.A.; Castile, J.; Smith, A.; Adams, G.G.; Harding, S.E. Macromolecular conformation of chitosan in dilute solution: A new global hydrodynamic approach. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 76, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Osuna, I.; Vauthier, C.; Chacun, H.; Ponchel, G. Specific permeability modulation of intestinal paracellular pathway by chitosan-poly(isobutylcyanoacrylate) core-shell nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. Off. J. Arb. Fur Pharm. Verfahr. E.V 2008, 69, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canali, M.M.; Pedrotti, L.P.; Balsinde, J.; Ibarra, C.; Correa, S.G. Chitosan enhances transcellular permeability in human and rat intestine epithelium. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 80, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattarai, N.; Gunn, J.; Zhang, M. Chitosan-based hydrogels for controlled, localized drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.W.; Lee, P.L.; Chen, C.T.; Mi, F.L.; Juang, J.H.; Hwang, S.M.; Ho, Y.C.; Sung, H.W. Elucidating the signaling mechanism of an epithelial tight-junction opening induced by chitosan. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6254–6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymanska, E.; Winnicka, K. Stability of chitosan—A challenge for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1819–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, F.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. A functional chitosan-based hydrogel as a wound dressing and drug delivery system in the treatment of wound healing. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 7533–7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menchicchi, B.; Fuenzalida, J.P.; Hensel, A.; Swamy, M.J.; David, L.; Rochas, C.; Goycoolea, F.M. Biophysical analysis of the molecular interactions between polysaccharides and mucin. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 924–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackie, A.R.; Goycoolea, F.M.; Menchicchi, B.; Caramella, C.M.; Saporito, F.; Lee, S.; Stephansen, K.; Chronakis, I.S.; Hiorth, M.; Adamczak, M.; et al. Innovative Methods and Applications in Mucoadhesion Research. Macromol. Biosci. 2017, 17, 1600534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morariu, S.; Brunchi, C.-E.; Bercea, M. The Behavior of Chitosan in Solvents with Different Ionic Strengths. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 12959–12966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado-González, M.; Montalbán, M.G.; Peña-García, J.; Pérez-Sánchez, H.; Villora, G.; Díaz Baños, F.G. Chitosan as stabilizing agent for negatively charged nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 161, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.E.; Turner, B.S.; Rubinstein, M.; McKinley, G.H.; Ribbeck, K. A Rheological Study of the Association and Dynamics of MUC5AC Gels. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 3654–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng-Lund, E.; Muff-Westergaard, C.; Sander, C.; Madelung, P.; Jacobsen, J. A mechanistic based approach for enhancing buccal mucoadhesion of chitosan. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 461, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedinaite, A.; Lundin, M.; Macakova, L.; Auletta, T. Mucin-chitosan complexes at the solid-liquid interface: Multilayer formation and stability in surfactant solutions. Langmuir 2005, 21, 9502–9509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haugstad, K.E.; Hati, A.G.; Nordgard, C.T.; Adl, P.S.; Maurstad, G.; Sletmoen, M.; Draget, K.I.; Dias, R.S.; Stokke, B.T. Direct determination of chitosan-mucin interactions using a single-molecule strategy: Comparison to alginate-mucin interactions. Polymers 2015, 7, 161–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yamamoto, H.; Takeuchi, H.; Kawashima, Y. A novel method for modifying AFM probe to investigate the interaction between biomaterial polymers (chitosan-coated PLGA) and mucin film. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 75, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Li, J.; Kong, M.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, X.J.; Li, Y.; Park, H.J.; Chen, X.G. Surface charge effect on mucoadhesion of chitosan based nanogels for local anti-colorectal cancer drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 128, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Tam, M.; Samaei, S.; Lerouge, S.; Barralet, J.; Stevenson, M.M.; Cerruti, M. Mucoadhesive chitosan hydrogels as rectal drug delivery vessels to treat ulcerative colitis. Acta Biomater. 2017, 48, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, M.P.; McGurk, S.; Roberts, C.J.; Williams, P.M.; Tendler, S.J.B.; Davies, M.C.; Davis, S.S.; Harding, S.E. Atomic force microscopy of gastric mucin and chitosan mucoadhesive systems. Biochem. J. 2000, 348, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Ferrari, F.; Bonferroni, M.C.; Caramella, C. Characterization of chitosan hydrocloride-mucin interaction by means of viscosimetric and turbidimetric measurements. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 10, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Ferrari, F.; Bonferroni, M.C.; Caramella, C. Characterization of chitosan hydrochloride-mucin rheological interaction: Influence of polymer concentration and polymer:mucin weight ratio. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 12, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kootala, S.; Filho, L.; Srivastava, V.; Linderberg, V.; Moussa, A.; David, L.; Trombotto, S.; Crouzier, T. Reinforcing Mucus Barrier Properties with Low Molar Mass Chitosans. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymanska, E.; Winnicka, K.; Amelian, A.; Cwalina, U. Vaginal chitosan tablets with clotrimazole-design and evaluation of mucoadhesive properties using porcine vaginal mucosa, mucin and gelatine. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 62, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diop, M.; Auberval, N.; Viciglio, A.; Langlois, A.; Bietiger, W.; Mura, C.; Peronet, C.; Bekel, A.; Julien David, D.; Zhao, M.; et al. Design, characterisation, and bioefficiency of insulin-chitosan nanoparticles after stabilisation by freeze-drying or cross-linking. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 491, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dhawan, S.; Singla, A.K.; Sinha, V.R. Evaluation of mucoadhesive properties of chitosan microspheres prepared by different methods. AAPS PharmSciTech 2004, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cheng, H.; Dong, W.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Guan, J.; Wu, H.; Mao, S. Design and intestinal mucus penetration mechanism of core-shell nanocomplex. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2018, 272, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, H.; Tsujimoto, H.; Hase, K.; Ishihara, M. Characterization of a water-soluble chitosan derivative and its potential for submucosal injection in endoscopic techniques. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 175, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Chitosan | DA (%) | Mw (kDa) | C Chitosan (mg/mL) | Mucin | C Mucin (mg/mL) | Solvent | T (°C) | Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chitopharm L Chitopharm M Chitopharm S from Cognis SmbH | N/S | 500–5000 100–2000 50–1000 | 0.6 | Porcine gastric mucin type II with bound sialic acids 1% (Sigma-Aldrich) | 0.5 | 0.0125 M acetic acid at pH 5.2 or 0.016 M 2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid at pH 6.3 | 25 | Complex coacervation Isothermal titration calorimetry | [53] |
| Chitosan containing ≤1% insoluble matterfrom Fluka | 15.5 | 150 | 0.02 | Bovine submaxiliary mucins (BSMG) from Sigma | 0.025 | 20 mM NaNO3. The pH was 7.5 for mucin and 4 for chitosan | N/S | Surface force measurements Atomic force microscopy | [54] |
| Chitosanfrom Katakurachikkarin Co Ltd. | 15 | 150 | Attached to the cantilever | Mucin form stomach from Wako Chemical Inc. | Dry film | No solvent, the AFM worked in air conditions | 25 | Atomic force microscopy | [56] |
| Two pharmaceutical grade CS HMC 15 HMC 30 from Heppe Medical Chitosan (HMC) GmbH | 14.8 32.4 | 27.5 17 | 10 | Porcine gastric mucin type III (Sigma-Aldrich) | 5 | 20 mM acetate buffer, pH 4.5 | 25 | Microviscosimetry Isothermal titration calorimetry | [22] |
| Four biomedical grade HDP 1 HDP 11 HDP 27 HDP 56 from Mathani chitosan Put. Ptd. | 1.6 11 27.5 56 | 124 122 143 266 | HMCs: 3–4 HDPs: 0.3–0.9 | 8 | MilliQ water and 0.1 M NaCl, both of them at pH 4.5 | 37 | Vicosity measurements | [48] | |
| Two types of chitosan | 1 49 | 162 250 | Cantilever modified with chitosan | Mucin samples from cardia and fundus of pigs | Film, mucin linked to a mica surface | 25 mM Hepes buffer, 150 mM NaCl, pH 6.9 and 25 mM acetate buffer, 150 mM NaCl, pH 5.5 | 25 | Atomic force microscopy | [55] |
| Chitosan | DA (%) | Mw (kDa) | C Chitosan (mg/mL) | Mucin | C Mucin (mg/mL) | Solvent | T (°C) | Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glutamate salt of chitosan from Pronova Ltd. Drammen, | 11 | N/S | N/S | Porcine gastric mucin (PGM) isolated by them | N/S | 0.1 M sodium acetate buffer, pH 4.5, 0.1 M NaCl. The ionic strength was increased up to 0.2 and 0.3 M | N/S | Complexes attached to mica surfaces and analised by atomic force microscopy performed in air | [59] |
| Chitosan HCl, high viscosity grade. Seacure® CL 313 Pronova Biopolymers a.s. | 84 | N/S | 0.02–0.08 in H2O, pH 4.6 0.2–0.8 in 0.1 M HCl, pH 1 | Purified mucin from bovine submaxillary glands (type I) BSMG and Partially purified mucin Pig stomach type III (sigma) | BSMG: 0.1–0.6 in H2O, pH 6.8 or 0.4–1.6 in 0.1 M HCl, pH 1 PGM: 0.4–1.6 in H2O (pH 4.7–5.1) or 0.1 M HCl (pH 1) | 0.1 M HCl or distilled water | N/S | Viscosity measurements | [60] |
| Chitosan HCl (high viscosity grade) (HCS) Seacure® CL 313. Pronova Biopolymer | N/S | N/S | 5–40 in H2O and 15–50 in 0.1 M HCl | Partially purified mucin from pig stomach (Sigma) | 7.5–400 in H2O and 10–500 in 0.1 M HCl | 0.1 M HCl or distilled water | N/S | Viscosity measurements and tensile stress test | [61] |
| Chitosan from Galena Farmacêutica | 19 | 113 | 0.1 | Porcine gastric mucin type II with bound sialic acids 1% (average Mw 29 MDa) | 0.1 | Langmuir monolayer | N/S | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) | [11] |
| Chitosan MMW with a viscosity near 1% solution in 1% acetic acid equals to 200 cP from Sigma Aldrich | 15–25 | N/S | Tablets containing chitosan | Porcine vaginal mucosa from large white pigs weighing ~200 kg | Porcine vaginal mucosa or 10% mucin gel was absorbed on a cellulose fiber | 0.08 M acetic buffer, pH 4.5 | 37 | Measurement of detachment force and work of adhesion by using texture analyser | [63] |
| Two pharmaceutical grade CS HMC 15 HMC 30 from Heppe Medical Chitosan (HMC) GmbH | 14.8 32.4 | 27.5 17 | 10 | Porcine gastric mucin type III (Sigma) | 5 | 20 mM acetate buffer, pH 4.5 | 25 | Microviscosimetry Isothermal titration calorimetry | [22] |
| Four biomedical grade HDP 1 HDP 11 HDP 27 HDP 56 from Mathani Chitosan Put. Ptd | 1.6 11 27.5 56 | 124 122 143 266 | |||||||
| Chitosan Batch 1001135895, from sigma | 80 | 250 | 0.1 | Porcine gastric mucin type III (Sigma) | 0.1 | 1:1 (v/v) 0.01 M phosphate buffer saline (pH 7.4) and 0.01 M HCl. The final pH was 3.2 | RT | ζ-potential, dynamic light scattering, optical waveguide light-mode spectroscopy, tribometry and tribopair | [13] |
| Three chitosans with DP 8 DP 52 DP 100 from Mahtani chitosan Ltd. India | <1% | 1.3 8.4 16.1 | 5 | Mucin purified from porcine stomachs. The mucins isolated were MUC5A and MUC5B Commercial bovine submaxillary mucins (BSM) from Sigma | Immobilized on a disc or in solution at 10 mg/mL | Acidified PBS, pH 5.5 | 25 | quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation (QCM-D) and microscopy | [62] |
| Ultra-pure chitosan chloride (CS protasan UP CL 113) from Nova Matrix | 10–25 | 70–150 | 1 | RevHT29MTX cell line Adenocarcinoma cell line Caco-2 from ATCC | In cell culture | Water and DMEM | 37 | Dynamic light scattering, ζ-potential, microscopy | [64] |
| Chitosan | DA (%) | Mw (kDa) | Method of Crosslinking | Mucin | C Mucin (mg/mL) | Solvent | T (°C) | Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chitosan with a viscosity at 1% in acetic acid 1% at 20 degrees equals to 400 mPa/s from Fluka | N/S | 600 | Thermal Glutaraldehyde Tripolyphosphate, Emulsification Ionotropic gelation | Mucin type III partially purified from porcine stomach, bound sialic acids ~1% (Sigma) | 0.025–0.5 | Milli-Q water | RT | Mucus glycoprotein assay | [65] |
| Chitosan from Jinan Hai debei marine bioengineering co. Ltd. | ≤15 | 150 | Ionotropic gelation | Mucus from jejune segments of porcine intestine | Mucus gel | Kreb’s-Ringer buffer | 37 | Multi particle tracking and confocal studies | [66] |
| CS from Biotech Co. | 11 | 10 | Ionic gelation plus crosslinking with tripolyphosphate or calcium | N/S | 0.5–2.5 | Oxygenated Kreb’s-Ringer buffer | 37 | Mucus glycoprotein assay | [57] |
| Carboxymethyl chitosan of 92% of substitution synthesized and characterized by authors | 19 | 12 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Collado-González, M.; González Espinosa, Y.; Goycoolea, F.M. Interaction Between Chitosan and Mucin: Fundamentals and Applications. Biomimetics 2019, 4, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics4020032
Collado-González M, González Espinosa Y, Goycoolea FM. Interaction Between Chitosan and Mucin: Fundamentals and Applications. Biomimetics. 2019; 4(2):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics4020032
Chicago/Turabian StyleCollado-González, Mar, Yadira González Espinosa, and Francisco M. Goycoolea. 2019. "Interaction Between Chitosan and Mucin: Fundamentals and Applications" Biomimetics 4, no. 2: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics4020032
APA StyleCollado-González, M., González Espinosa, Y., & Goycoolea, F. M. (2019). Interaction Between Chitosan and Mucin: Fundamentals and Applications. Biomimetics, 4(2), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics4020032






