Bioinspired Design of Ergonomic Tool Handles Using 3D-Printed Cellular Metamaterials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
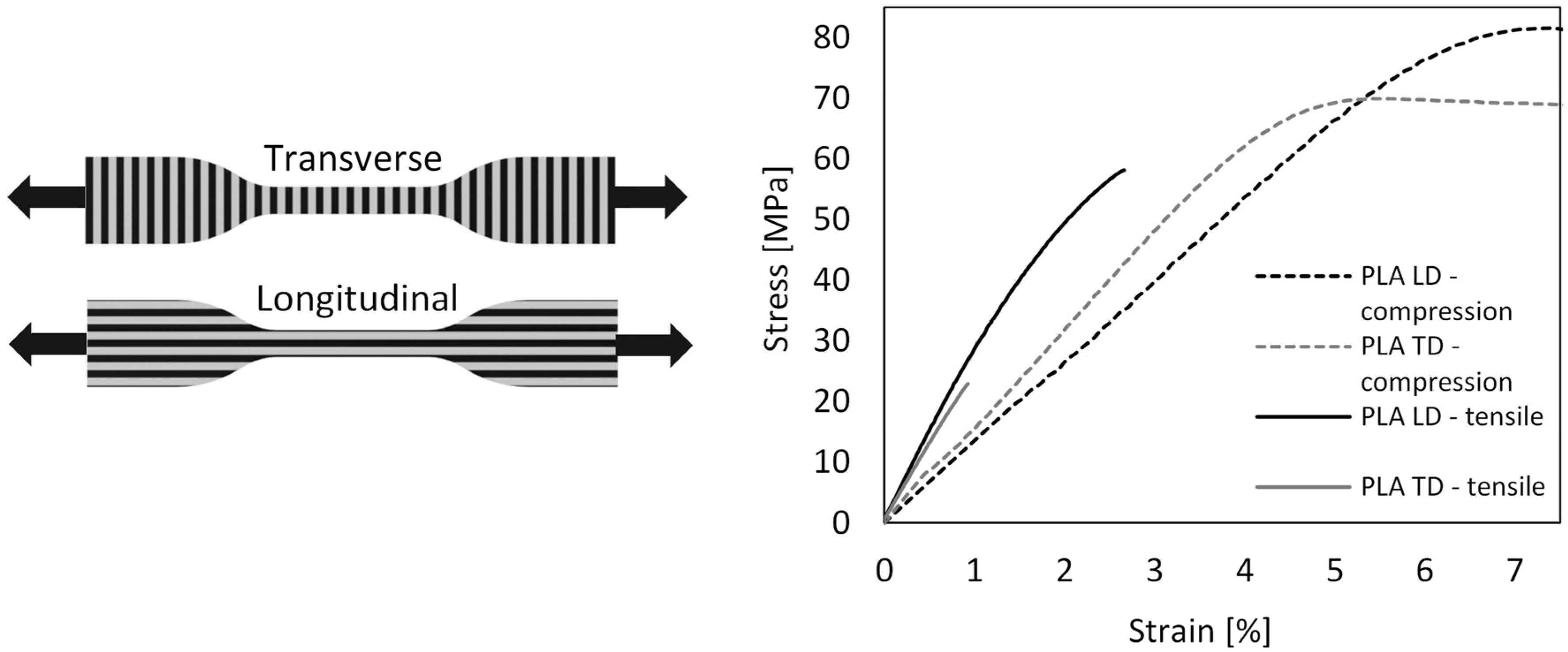
2.1. Handle Material Properties
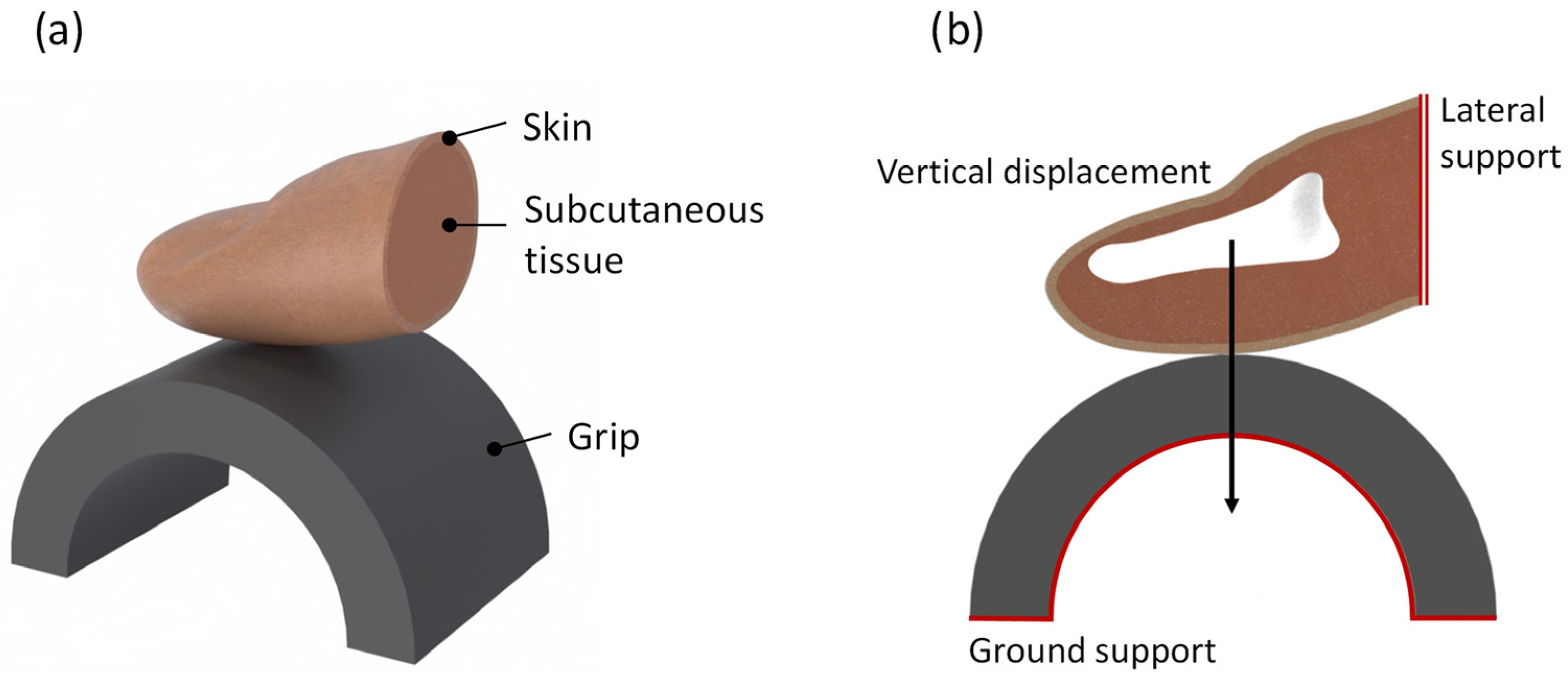
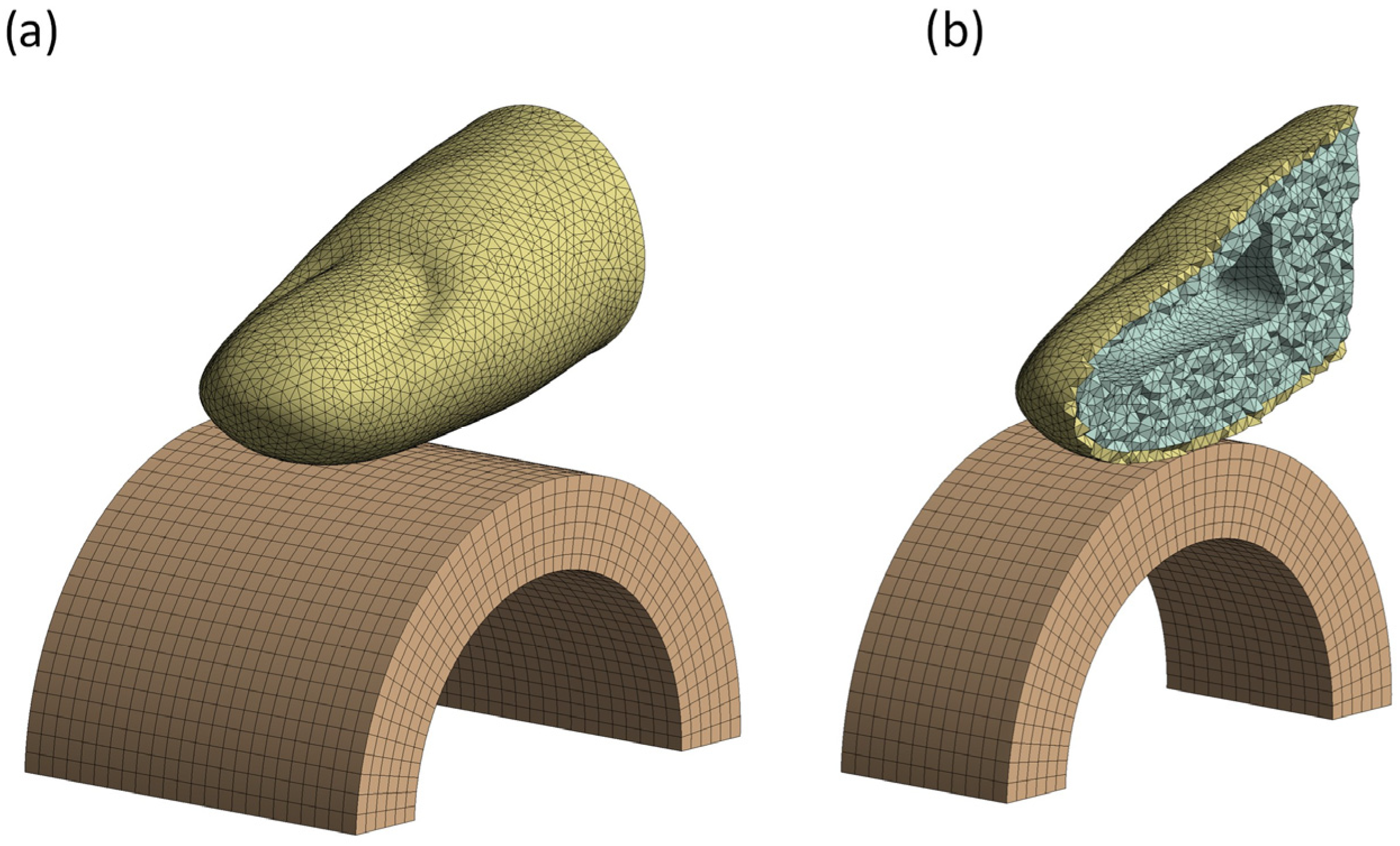
2.2. Biomechanical Finger–Handle Numerical Model
2.3. Task Definition and Subjective Comfort Questionnaire
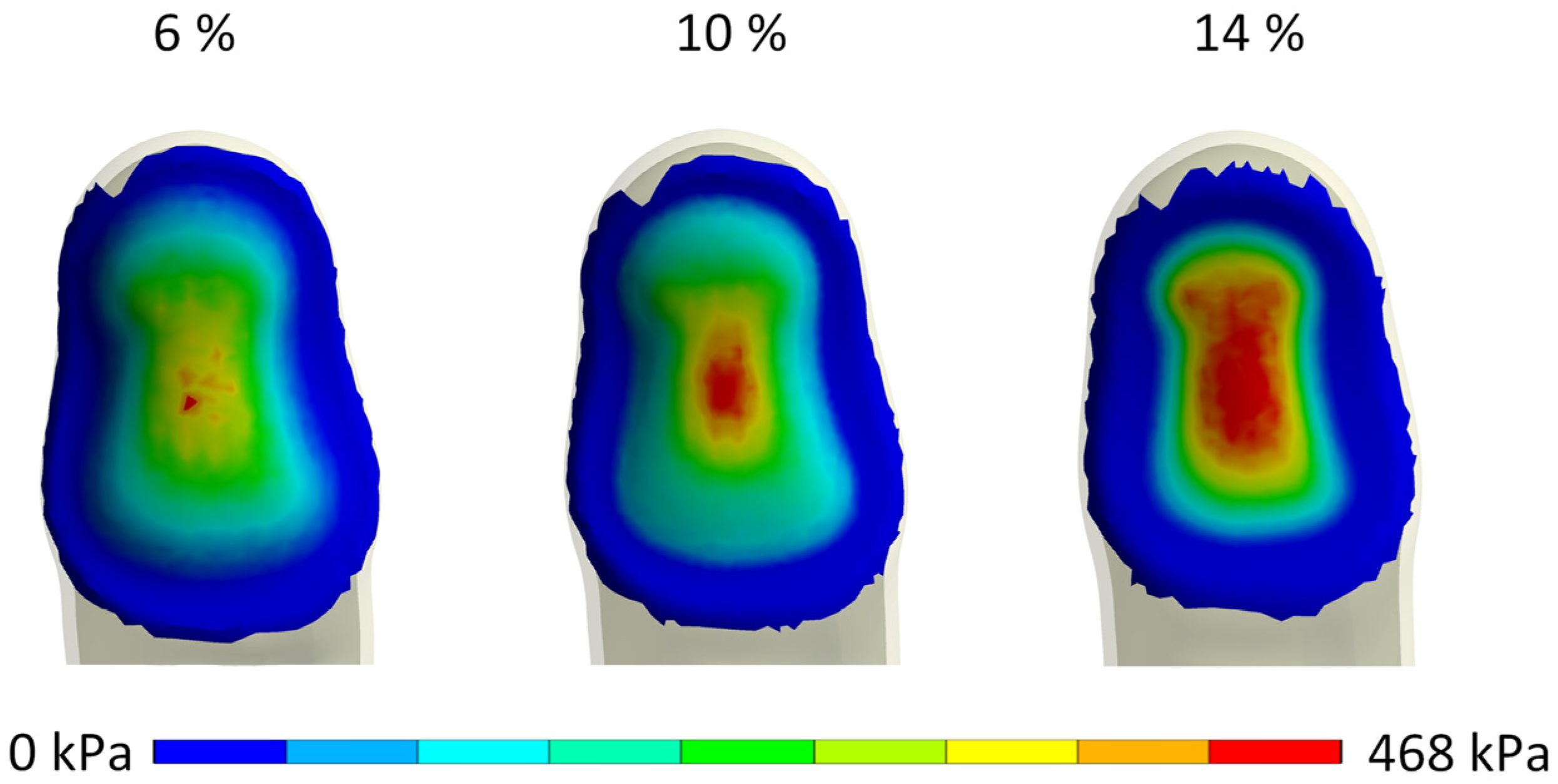
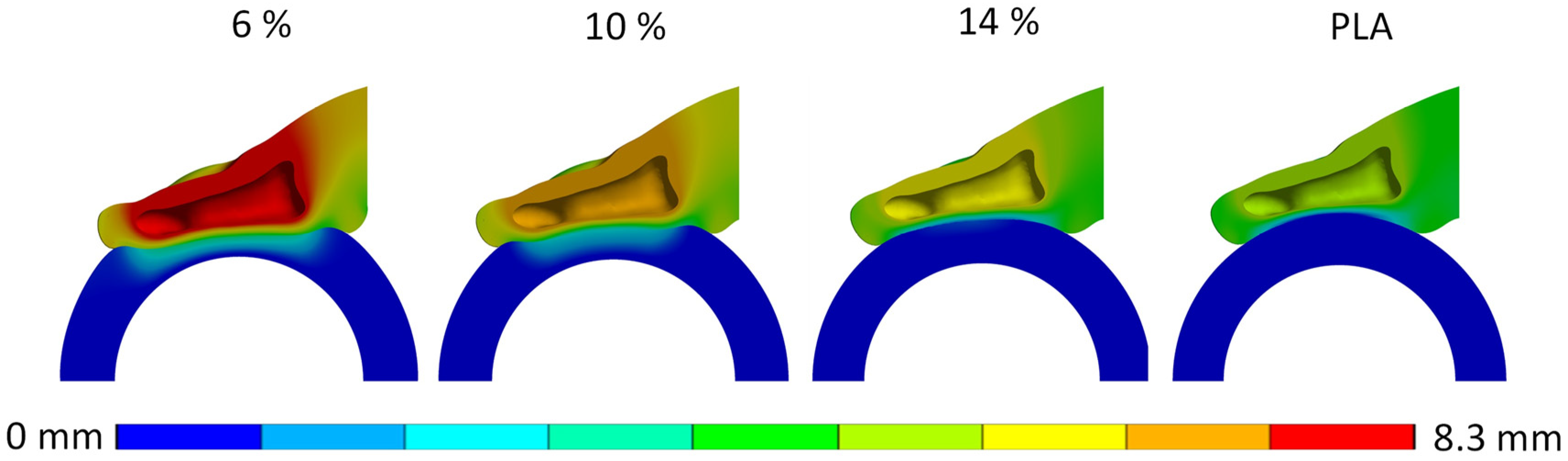
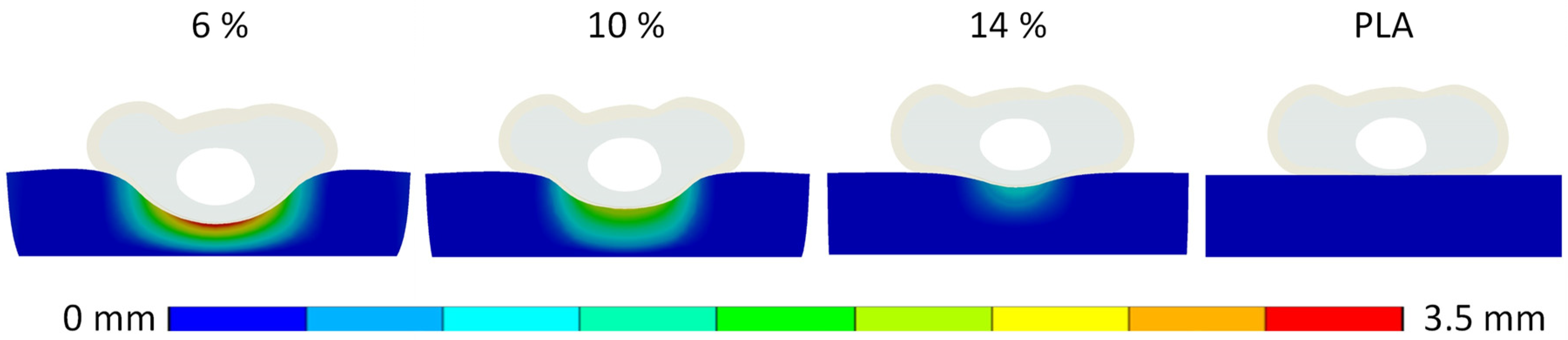
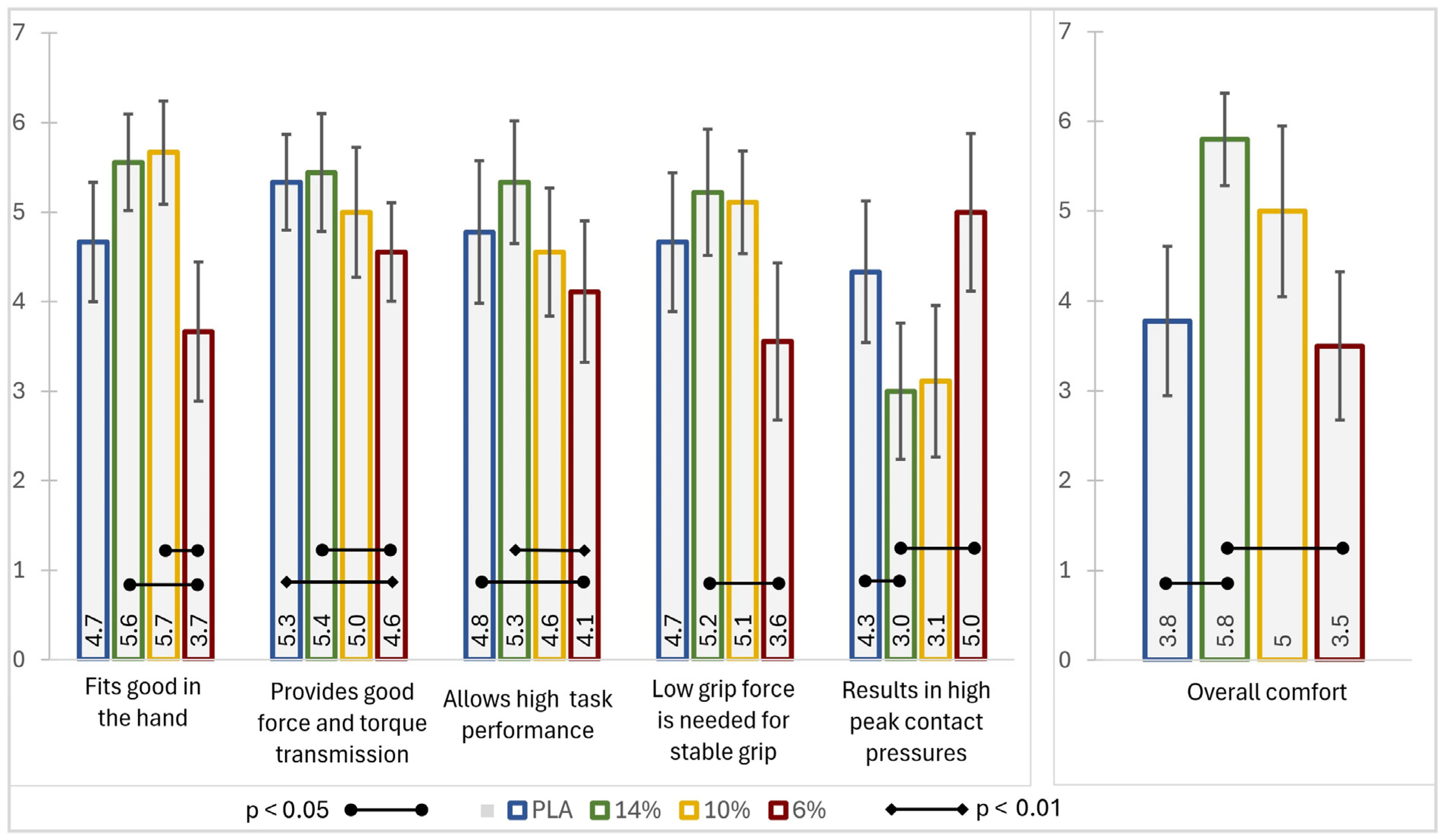
3. Results
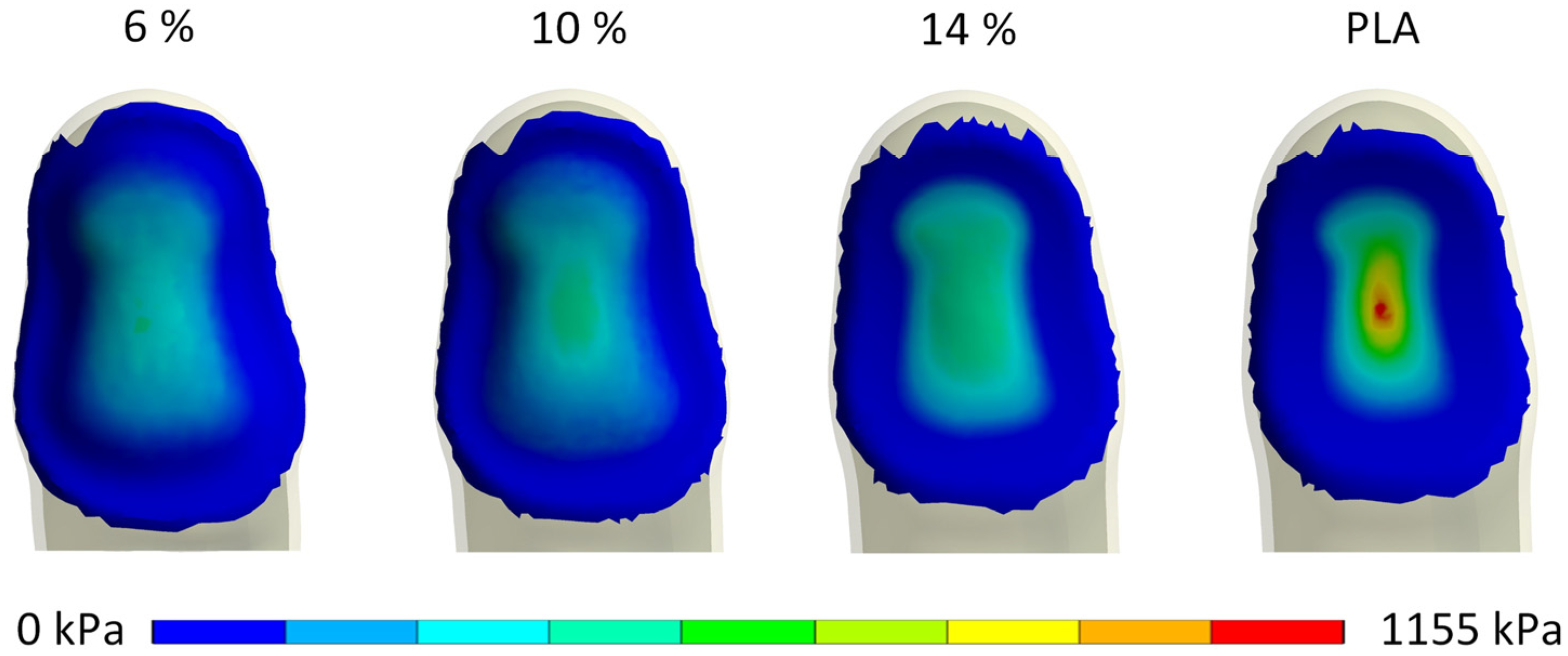
3.1. Biomechanical Finger–Handle Numerical Model
3.2. Subjective Comfort Rating
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Welcome, D.; Rakheja, S.; Dong, R.; Wu, J.Z.; Schopper, A.W. An investigation on the relationship between grip, push and contact forces applied to a tool handle. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2004, 34, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Lowe, B. Optimal cylindrical handle diameter for grip force tasks. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2005, 35, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuijt-Evers, L.F.M.; Vink, P.; de Looze, M.P. Comfort predictors for different kinds of hand tools: Differences and similarities. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2007, 37, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, N.J.; Armstrong, T.J. Investigation of Grip Force, Normal Force, Contact Area, Hand Size, and Handle Size for Cylindrical Handles. Hum. Factors 2008, 50, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garneau, C.J.; Parkinson, M.B. Optimization of product dimensions for discrete sizing applied to a tool handle. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2011, 42, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, N.J.; Armstrong, T.J. Effect of elliptic handle shape on grasping strategies, grip force distribution, and twisting ability. Ergonomics 2011, 54, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.C.; Gu, J.K.; Charles, L.E.; Andrew, M.E.; Dong, R.G.; Burchfiel, C.M. Work-related upper extremity musculoskeletal disorders in the United States: 2006, 2009, and 2014 National Health Interview Survey. Work 2018, 60, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.-K.; Kim, D.-M. The relationship between hand anthropometrics, total grip strength and individual finger force for various handle shapes. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2015, 21, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, J.; De Monsabert, B.G.; Berton, E.; Vigouroux, L. Handle shape affects the grip force distribution and the muscle loadings during power grip tasks. J. Appl. Biomech. 2015, 31, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Z.; Dong, R.G. Analysis of the contact interactions between fingertips and objects with different surface curvatures. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2005, 219, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Maeda, N.; Loh, P.Y. The effects of umbrella handle shape and grip type on muscle activation and postural variability under windy conditions. Appl. Ergon. 2024, 116, 104208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y. Plausible 3D Human Hand Modeling for Virtual Ergonomic Assessments of Handheld Product: Construction, Contact simulation and Variational Modeling. Ph.D. Thesis, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Peña-Pitarch, E.; Yang, J.; Abdel-Malek, K. Virtual Human Hand: Grasping and Simulation. In Digital Human Modeling; Duffy, V., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 5620, pp. 140–149. [Google Scholar]
- Merle, A.; Chandon, J.L.; Roux, E.; Alizon, F. Perceived value of the mass-customized product and mass customization experience for individual consumers. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2010, 19, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Goonetilleke, R.; Jiang, Z. Pressure thresholds of the human foot: Measurement reliability and effects of stimulus characteristics. Ergonomics 2011, 54, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuijt-Evers, L.F.; Bosch, T.; Huysmans, M.A.; De Looze, M.P.; Vink, P. Association between objective and subjective measurements of comfort and discomfort in hand tools. Appl. Ergon. 2007, 38, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldien, Y.; Welcome, D.; Rakheja, S.; Dong, R.; Boileau, P.E. Contact pressure distribution at hand–handle interface: Role of hand forces and handle size. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2005, 35, 267–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Johansson, L.; Kjellberg, A.; Kilbom, A.; Hagg, G.M. Perception of surface pressure applied to the hand. Ergonomics 1999, 42, 1274–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokari, K.; Pramudita, J.A.; Ito, M.; Noda, S.; Tanabe, Y. The relationships of gripping comfort to contact pressure and hand posture during gripping. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2019, 70, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joodaki, H.; Panzer, M.B. Skin mechanical properties and modeling: A review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2018, 232, 323–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duray, R. Mass customization origins: Mass or custom manufacturing? Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2002, 22, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellows, G.L.; Freivalds, A. Ergonomics evaluation of a foam rubber grip for tool handles. Appl. Ergon. 1991, 22, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harih, G.; Borovinšek, M.; Ren, Z.; Dolšak, B. Optimal product’s hand-handle interface parameter identification. Int. J. Simul. Model. 2015, 14, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Jahanian, O.; Slavens, B.A.; Hsiao-Wecksler, E.T. Biomechanical Evaluation of Pneumatic Sleeve Orthosis for Lofstrand Crutches. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2023, 31, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Jahanian, O.; Schnorenberg, A.; Slavens, B.; Hsiao-Wecksler, E. Design and biomechanical evaluation methodology of pneumatic ergonomic crutch. In Proceedings of the 2017 Design of Medical Devices Conference, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 10–13 April 2017; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nottelmann, K.; Woods, F.; Pittsley, M.; Beasley, J.; Ashby, B.; Anderson, K. How Can Joint Protection Apply to Grocery Shopping?; An Evaluation to Determine the Optimal Handle Diameter of Shopping Carts. J. Hand Ther. 2016, 29, 370–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germann, R.; Schröder, N.; Matthiesen, S. The contact length parameter as a geometric factor for user-centered design of pistol grip geometries of power tools. Appl. Ergon. 2022, 99, 103636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokari, K.; Arimoto, R.; Pramudita, J.A.; Ito, M.; Noda, S.; Tanabe, Y. Palmar Contact Pressure Distribution During Grasping a Cylindrical Object: Parameter Study Using Hand Finite Element Model. Adv. Exp. Mech. 2019, 4, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.; Yick, K.L.; Ng, S.P.; Yip, J.; Chan, Y.F. Numerical simulation of pressure therapy glove by using finite element method. Burns 2016, 42, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamoret, D.; Bodo, M.; Roth, S. A first step in finite-element simulation of a grasping task. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2016, 21 (Suppl. 1), 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallard, J.; Merlhiot, X.; Duprey, S.; Wang, X.; Micaelli, A. Fingertip finite element modelling–on choosing the right material property. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 17, 30–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, H.; Tada, M.; Mochimaru, M. A study of frictional property of the human fingertip using three-dimensional finite element analysis. Mol. Cell. Biomech. 2011, 8, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.Z.; Dong, R.G.; Welcome, D.E.; Xu, X.Y.S. A method for analyzing vibration power absorption density in human fingertip. J. Sound Vib. 2010, 329, 5600–5614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouliquen, M.; Duriez, C.; Andriot, C.; Bernard, A.; Chodorge, L.; Gosselin, F. Real-time finite element finger pinch grasp simulation. In Proceedings of the Eurohaptics Conference and Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems, Fontenay-aux-Roses, France, 18–20 March 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Harih, G.; Plesec, V. Can a Numerical Digital Human Finger Model Predict Subjective Comfort Rating of Handheld Products? In Proceedings of the International Conference on Digital Human Modeling, Antwerpen, Belgium, 4–6 September 2023; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Novak, N.; Plesec, V.; Harih, G.; Cupar, A.; Kaljun, J.; Vesenjak, M. Development, fabrication and mechanical characterisation of auxetic bicycle handlebar grip. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dianat, I.; Nedaei, M.; Mostashar Nezami, M.A. The effects of tool handle shape on hand performance, usability and discomfort using masons’ trowels. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2015, 45, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plesec, V.; Harih, G. Bioinspired Design of 3D-Printed Cellular Metamaterial Prosthetic Liners for Enhanced Comfort and Stability. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harih, G. Development of a Tendon Driven Finger Joint Model Using Finite Element Method. In Proceedings of the AHFE 2018 International Conferences on Human Factors and Simulation and Digital Human Modeling and Applied Optimization, Orlando, FL, USA, 21–25 July 2018; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fruhstorfer, H.; Abel, U.; Garthe, C.; Knüttel, A. Thickness of stratum corneum of the volar fingertips. Clin. Anat. 2000, 13, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.K.; Kim, D.M.; Lee, K.S.; Jung, M.C. Comparison of comfort, discomfort, and continuum ratings of force levels and hand regions during gripping exertions. Appl. Ergon. 2012, 43, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goonetilleke, R.S.; Eng, T.J. Contact Area Effects on Discomfort. Proc. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. Annu. Meet. 1994, 38, 688–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Component | Material Model | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Subcutaneous tissue | Ogden 3rd-Order | μ1 = −0.04895 MPa |
| μ2 = 0.00989 MPa | ||
| μ3 = 0.03964 MPa | ||
| A1 = 5.511 | ||
| A2 = 6.571 | ||
| A3 = 5.262 | ||
| D1 = −4.2267 MPa−1 | ||
| D2 = 20.92 MPa−1 | ||
| D3 = 5.2194 MPa−1 | ||
| Skin | Ogden 3rd-Order | μ1 = −0.07594 MPa |
| μ2 = 0.01138 MPa | ||
| μ3 = 0.06572 MPa | ||
| A1 = 4.941 | ||
| A2 = 6.425 | ||
| A3 = 4.712 | ||
| D1 = −2.7245 MPa−1 | ||
| D2 = 18.181 MPa−1 | ||
| D3 = 3.1482 MPa−1 | ||
| Distal phalanx | Rigid structure | (-) |
| Handle—PLA | Linear–elastic | E = 2952.8 MPa |
| ν = 0.33 | ||
| Handle—custom gyroid | Multilinear elastic | Defined by σ and ε points from experiment (Figure 1). |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harih, G.; Plesec, V. Bioinspired Design of Ergonomic Tool Handles Using 3D-Printed Cellular Metamaterials. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10080519
Harih G, Plesec V. Bioinspired Design of Ergonomic Tool Handles Using 3D-Printed Cellular Metamaterials. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(8):519. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10080519
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarih, Gregor, and Vasja Plesec. 2025. "Bioinspired Design of Ergonomic Tool Handles Using 3D-Printed Cellular Metamaterials" Biomimetics 10, no. 8: 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10080519
APA StyleHarih, G., & Plesec, V. (2025). Bioinspired Design of Ergonomic Tool Handles Using 3D-Printed Cellular Metamaterials. Biomimetics, 10(8), 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10080519







