Bioinspired Swimming Robots with 3D Biomimetic Shark Denticle Structures for Controlled Marangoni Propulsion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication of 3D-Printed Self-Propelled Swimmer
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Propulsion Performance Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
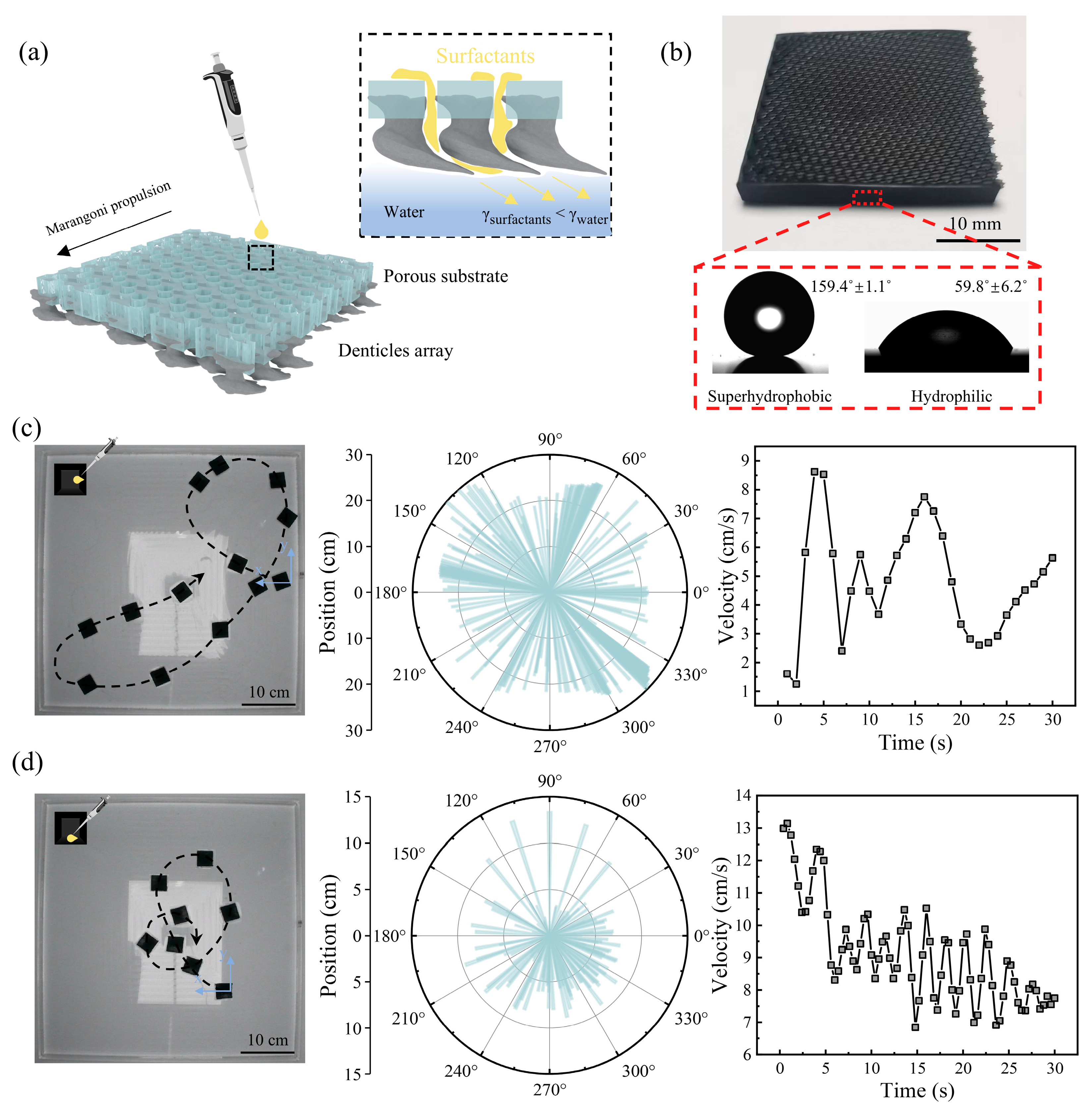
3.1. Concept and Design Approach
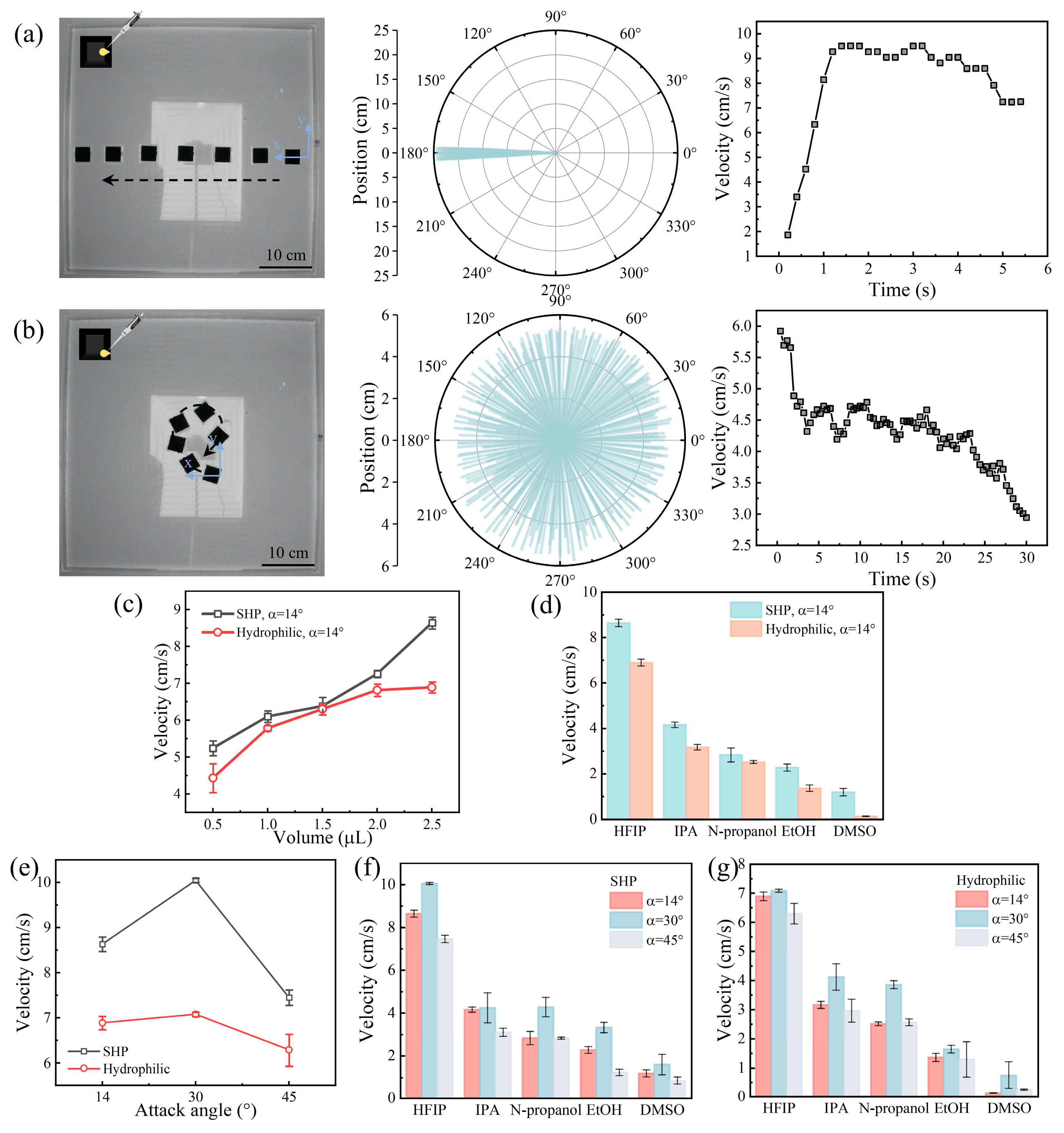
3.2. Design and Hydrodynamics Locomotion of Self-Propelled Swimmers
3.3. Design and Aerodynamics Locomotion of the Swimmers
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ze, Q.; Wu, S.; Nishikawa, J.; Dai, J.; Sun, Y.; Leanza, S.; Zemelka, C.; Novelino, L.S.; Paulino, G.H.; Zhao, R.R. Soft robotic origami crawler. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabm7834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-L.; Ma, J.-N.; Liu, S.; Han, D.-D.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Chen, Z.-D.; Mao, J.-W.; Sun, H.-B. A “Yin”-“Yang” complementarity strategy for design and fabrication of dual-responsive bimorph actuators. Nano Energy 2020, 68, 104302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.W.; Han, D.D.; Zhou, H.; Sun, H.B.; Zhang, Y.L. Bioinspired Superhydrophobic Swimming Robots with Embedded Microfluidic Networks and Photothermal Switch for Controllable Marangoni Propulsion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 33, 2208677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Pinchin, N.P.; Lin, C.H.; Tejedor, I.H.; Scarfo, M.G.; Shahsavan, H.; Pena-Francesch, A. Self-Propelled Morphing Matter for Small-Scale Swimming Soft Robots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2413129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Croon, G.; Dupeyroux, J.J.G.; Fuller, S.B.; Marshall, J.A.R. Insect-inspired AI for autonomous robots. Sci. Robot. 2022, 7, eabl6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, V.; Najafi, A.; James, J.; Fuller, S.; Gollakota, S. Wireless steerable vision for live insects and insect-scale robots. Sci. Robot. 2020, 5, eabb0839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozuyuk, U.; Wrede, P.; Yildiz, E.; Sitti, M. Roadmap for Clinical Translation of Mobile Microrobotics. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2311462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Esteban-Fernandez de Avila, B.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J. Micro/Nanorobots for Biomedicine: Delivery, Surgery, Sensing, and Detoxification. Sci. Robot. 2017, 2, eaam6431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Cai, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Zhao, Y.-D.; Chen, W. Light-controlled spiky micromotors for efficient capture and transport of targets. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 358, 131523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, D.; Xiao, Y.; Pan, T.; Lu, D.; Zhu, G.; Xiong, J.; Li, B.; Xin, H. Light-Induced Cold Marangoni Flow for Microswarm Actuation: From Intelligent Behaviors to Collective Drug Delivery. Laser Photon. Rev. 2022, 16, 2200533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Urena Marcos, J.C.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Niu, R.; Zhao, Q.; Qu, J.; Liebchen, B. Self-Solidifying Active Droplets Showing Memory-Induced Chirality. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2300866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Li, Z.; Tan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jiao, Y. Near-Infrared Light-Steered Graphene Aerogel Micromotor with High Speed and Precise Navigation for Active Transport and Microassembly. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 23134–23144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Jiang, D.; Zhu, G.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Tian, P.; Wang, D.; Wang, E.; Ouyang, H.; Xiao, M.; et al. A Light-Powered Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on the Photothermal Marangoni Effect. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 22206–22215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, M.; Zhou, X.; Ming, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhu, L.; Yu, J.; Wang, Z.L.; Xiong, J. Self-Propelled Nanocellulose Aerogel Eco-Robots for Self-Powered Aquatic Environment Perception. ACS Energy Lett. 2024, 9, 4852–4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, J.W.M.; Hu, D.L. Walking on water: Biolocomotion at the Interface. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2006, 38, 339–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Jin, D.; Chan, K.F.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, K.; Zhang, L. Active generation and magnetic actuation of microrobotic swarms in bio-fluids. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Chan, K.F.; Schweizer, K.; Du, X.; Jin, D.; Yu, S.C.H.; Nelson, B.J.; Zhang, L. Ultrasound Doppler-guided real-time navigation of a magnetic microswarm for active endovascular delivery. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Mayorga-Martinez, C.C.; Pane, S.; Zhang, L.; Pumera, M. Magnetically Driven Micro and Nanorobots. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 4999–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Luo, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, L.; Guo, Z.; Liang, J.; Zhang, S.; Xue, H.; Gao, J. Superhydrophobic, mechanically durable coatings for controllable light and magnetism driven actuators. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 603, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Ji, F.; Zhu, J.; Ma, P.; Su, H.; Chen, P.; Feng, X.; Du, W.; Liu, B.-F. Patterning candle soot for light-driven actuator via Marangoni effect. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 347, 130613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, Y.Q.; Liu, Y.; Han, B.; Wang, H.; Han, D.D.; Wang, J.N.; Zhang, Y.L.; Sun, H.B. Direct Laser Writing of Superhydrophobic PDMS Elastomers for Controllable Manipulation via Marangoni Effect. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1702946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tang, S.Y.; Li, S.; Ge, D.a.; Yang, J.; Zhou, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, W.; Sun, L. A Robot Boat Powered by Liquid Metal Engines. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 6, 2000840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Jin, H.; Shu, J.; Xie, J.; Wang, E.; Ge, D.A.; Tang, S.Y.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, S. Light-controlled versatile manipulation of liquid metal droplets: A gateway to future liquid robots. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 3063–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhu, Z.; Sun, M.; Li, S.; Gan, M.; Tang, S.Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, S.; Sun, L.; et al. 3D actuation of foam-core liquid metal droplets. Soft Matter 2023, 19, 1293–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Guan, X.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, K.; Huang, Y.; Zhong, J. Bio-inspired and programmable Marangoni motor for highly maneuverable and adaptable S-aquabots. eScience 2024, 5, 100335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Kinane, C.; Zhang, Z.; Pena-Francesch, A. Functional Chemical Motor Coatings for Modular Powering of Self-Propelled Particles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 39332–39342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Park, C.; Lee, A.C.; Bae, J.; Kim, H.; Choi, H.; Song, S.W.; Jeong, Y.; Choi, J.; Lee, H.; et al. Photopatterned microswimmers with programmable motion without external stimuli. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Guo, F.; Cui, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zhai, Y.; Du, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, N.; Zhao, Y. Controllable and Continuous Hollow Fiber Swimmers Based on the Marangoni Effect. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 53503–53509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Hou, Z.; Xia, X.; Chen, H.; Zou, B.; Zhang, Y. Marangoni Effect Enabling Autonomously Miniatured Swimmers: Mechanisms, Design Strategy, and Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2424235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.J.; Lauder, G.V.; Wainwright, D.K. Slippery and Smooth Shark Skin: How Mucus Transforms Surface Texture. J. Morphol. 2025, 286, e70046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechert, D.; Reif, W. On the Drag Reduction of the Shark Skin. In Proceedings of the 23rd ASM, Reno, NV, USA, 14–17 January 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Motta, P.; Habegger, M.L.; Lang, A.; Hueter, R.; Davis, J. Scale morphology and flexibility in the shortfin mako Isurus oxyrinchus and the blacktip shark Carcharhinus limbatus. J. Morphol. 2012, 273, 1096–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechert, D.W.; Bartenwerfer, M. The viscous flow on surfaces with longitudinal ribs. J. Fluid Mech. 2006, 206, 105–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechert, D.W.; Bartenwerfer, M.; Hoppe, G.; Reif, W.-E. Drag reduction mechanisms derived from shark skin. In Proceedings of the 15th ICAS Congress, London, UK, 7–12 September 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Bechert, D.W.; Bruse, M.; Hage, W. Experiments with three-dimensional riblets as an idealized model of shark skin. Exp. Fluids 2000, 28, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechert, D.W.; Bruse, M.; Hage, W.; Van Der Hoeven, J.G.T.; Hoppe, G. Experiments on drag-reducing surfaces and their optimization with an adjustable geometry. J. Fluid Mech. 1997, 338, 59–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechert, D.W.; Hage, W. Drag reduction with riblets in nature and engineering. In Flow Phenomena in Nature Volume 2; Liebe, R.J., Ed.; WIT: Southampton, UK, 2006; Volume 4, pp. 457–504. [Google Scholar]
- WALSH, M. Turbulent boundary layer drag reduction using riblets. In Proceedings of the 20th ASM, Orlando, FL, USA, 11–14 January 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, M.; Lindemann, A. Optimization and application of riblets for turbulent drag reduction. In Proceedings of the 22nd ASM, Reno, NV, USA, 9–12 January 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, L.; Weaver, J.C.; Lauder, G.V. Biomimetic shark skin: Design, fabrication and hydrodynamic function. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 217, 1656–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domel, A.G.; Domel, G.; Weaver, J.C.; Saadat, M.; Bertoldi, K.; Lauder, G.V. Hydrodynamic properties of biomimetic shark skin: Effect of denticle size and swimming speed. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2018, 13, 056014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, L.M.; Lang, A.; Wahidi, R.; Bonacci, A.; Gautam, S.; Devey, S.; Parsons, J. Passive separation control of shortfin mako shark skin in a turbulent boundary layer. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2021, 128, 110433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauder, G.V.; Wainwright, D.K.; Domel, A.G.; Weaver, J.C.; Wen, L.; Bertoldi, K. Structure, biomimetics, and fluid dynamics of fish skin surfaces. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2016, 1, 060502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feld, K.; Kolborg, A.N.; Nyborg, C.M.; Salewski, M.; Steffensen, J.F.; Berg-Sorensen, K. Dermal Denticles of Three Slowly Swimming Shark Species: Microscopy and Flow Visualization. Biomimetics 2019, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savino, B.S.; Wu, W. Thrust generation by shark denticles. J. Fluid Mech. 2024, 1000, A80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, C.B.; Orgeig, S.; Sullivan, L.C.; Ling, N.; Bennett, M.B.; Schurch, S.; Val, A.L.; Brauner, C.J. The origin and evolution of the surfactant system in fish: Insights into the evolution of lungs and swim bladders. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 2004, 77, 732–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shephard, K.L. The Influence of Mucus on the Diffusion of Water across Fish Epidermis. Physiol. Zool. 1981, 54, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shephard, K.L. Mucus on the epidermis of fish and its influence on drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1993, 11, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shephard, K.L. Functions for fish mucus. Rev. Fish. Biol. Fish. 1994, 4, 401–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Yu, X.; Cui, X.; Chen, D.; Shen, T.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Chen, H.; Fang, R.; Dong, Z.; et al. Surface Modification of 3D Biomimetic Shark Denticle Structures for Drag Reduction. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, e2417337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, K.; Wang, C.; Jiang, L.; Fang, R.; Dong, Z. Bioinspired Swimming Robots with 3D Biomimetic Shark Denticle Structures for Controlled Marangoni Propulsion. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10080479
Yang K, Wang C, Jiang L, Fang R, Dong Z. Bioinspired Swimming Robots with 3D Biomimetic Shark Denticle Structures for Controlled Marangoni Propulsion. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(8):479. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10080479
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Kang, Chengming Wang, Lei Jiang, Ruochen Fang, and Zhichao Dong. 2025. "Bioinspired Swimming Robots with 3D Biomimetic Shark Denticle Structures for Controlled Marangoni Propulsion" Biomimetics 10, no. 8: 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10080479
APA StyleYang, K., Wang, C., Jiang, L., Fang, R., & Dong, Z. (2025). Bioinspired Swimming Robots with 3D Biomimetic Shark Denticle Structures for Controlled Marangoni Propulsion. Biomimetics, 10(8), 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10080479







