Sliding Mode Repetitive Control Based on the Unknown Dynamics Estimator of a Two-Stage Supply Pressure Hydraulic Hexapod Robot
Abstract
1. Introduction
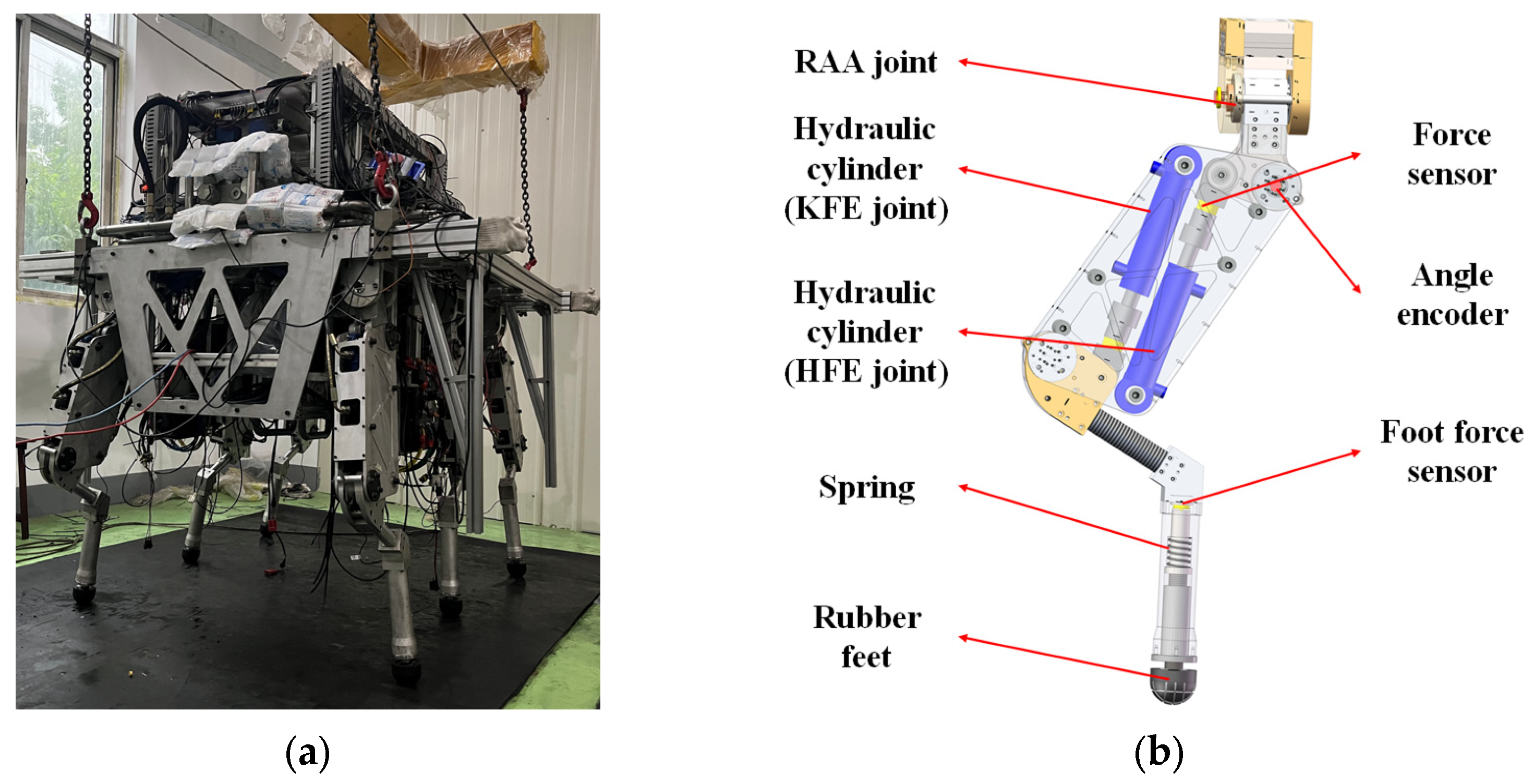
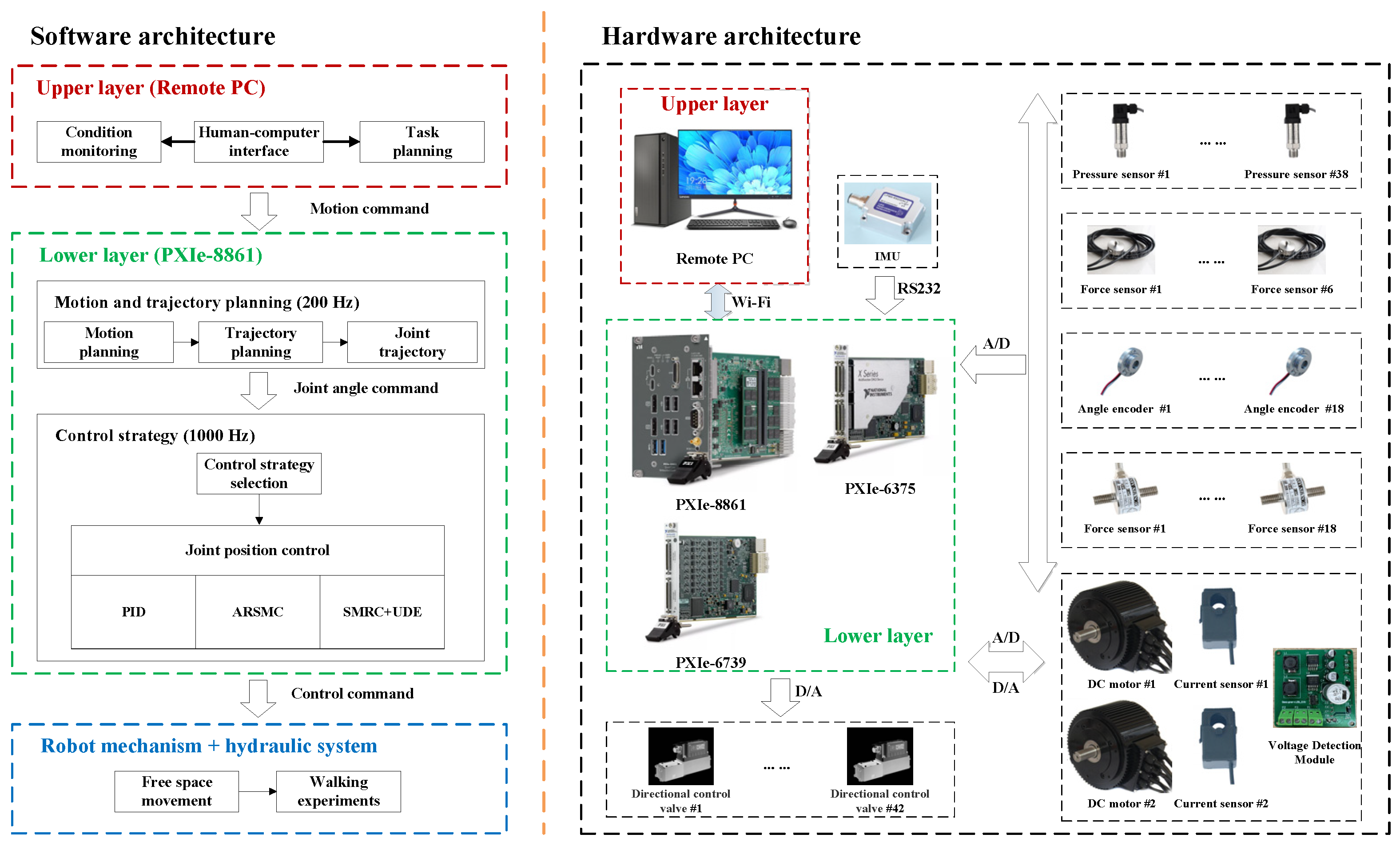
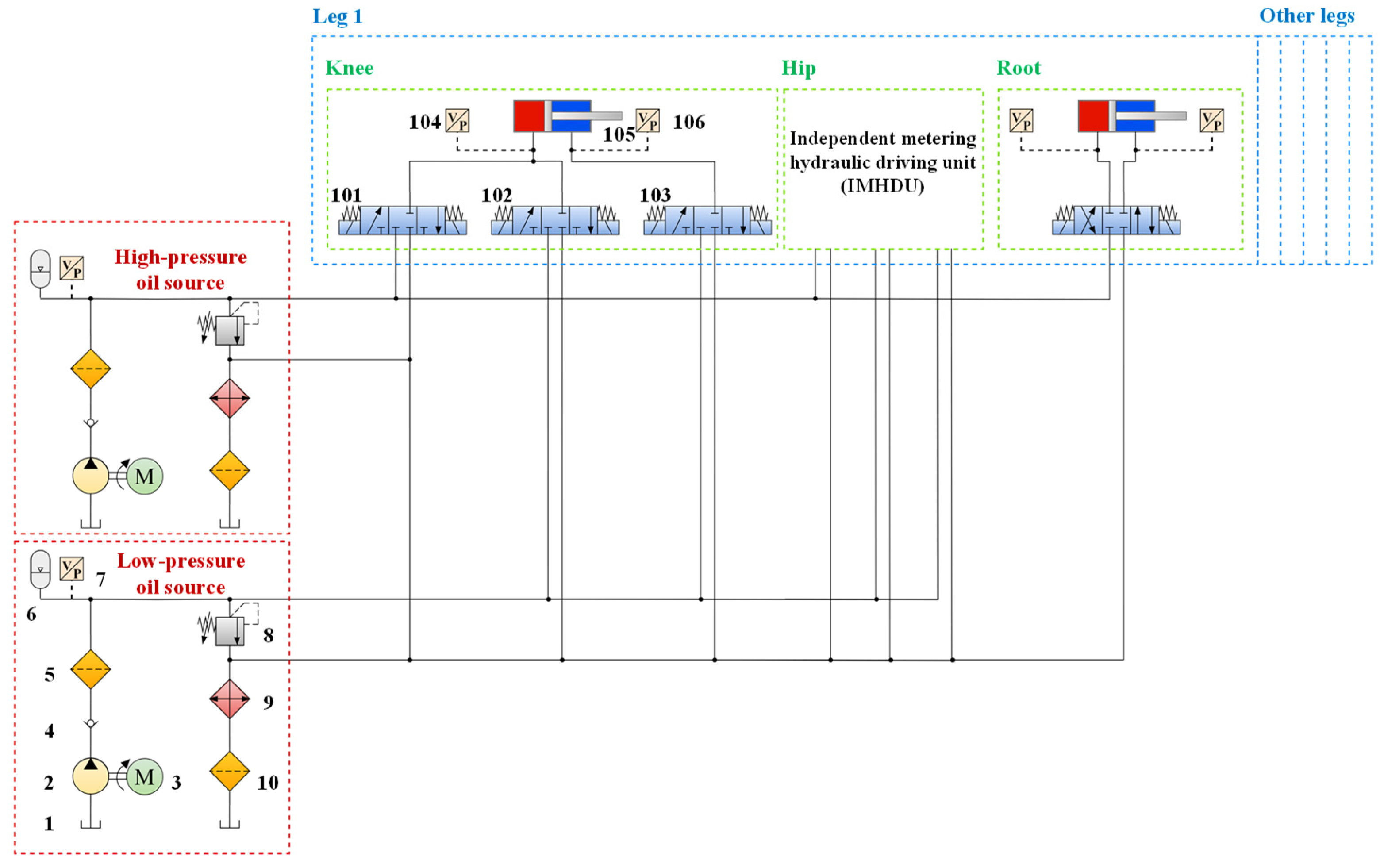
2. Overview of Hydraulic Hexapod Robot
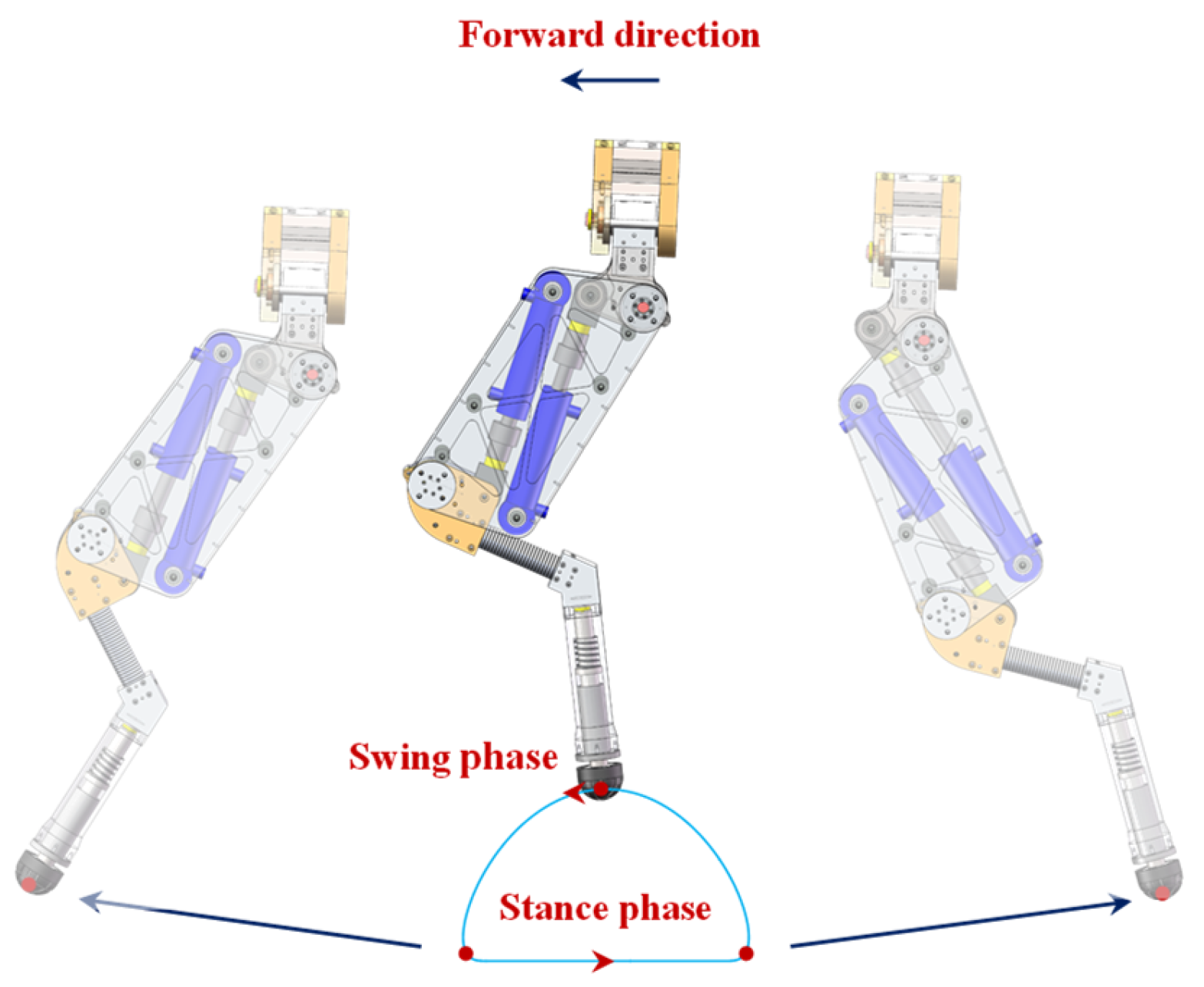
2.1. Mechanical Structure
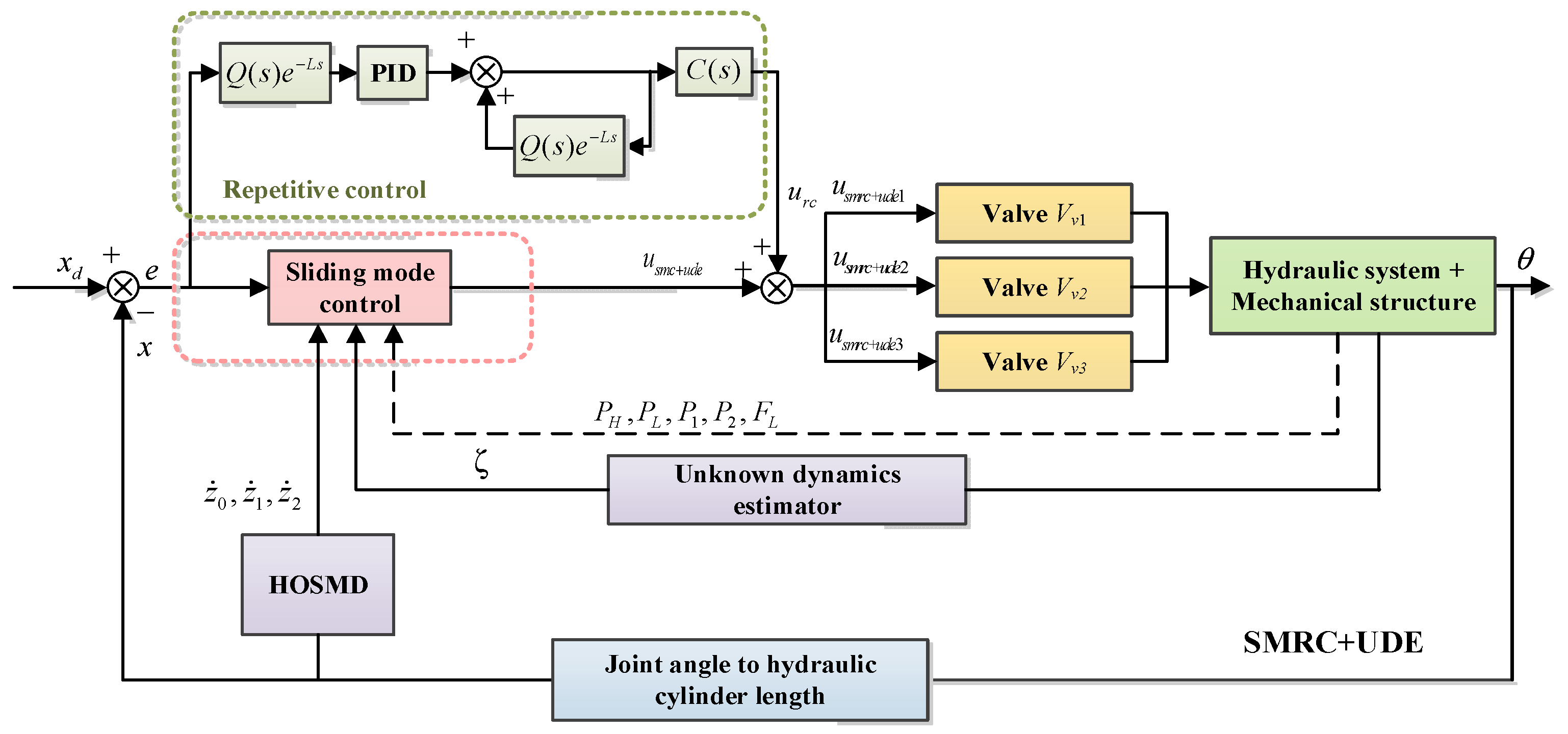
2.2. Control System Architecture
2.3. Onboard Hydraulic System
3. HHR System Modeling
3.1. Kinematic Modeling
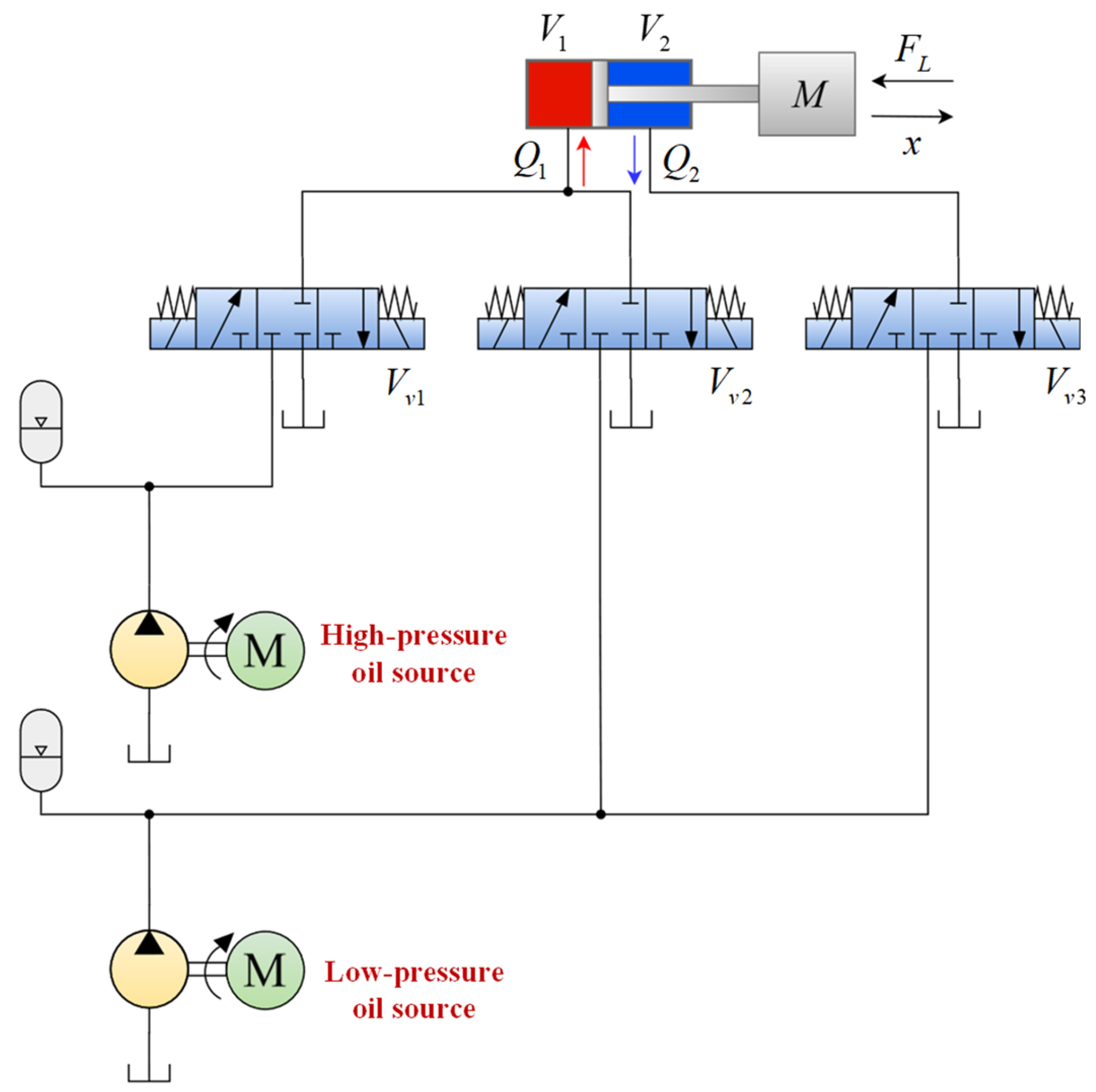
3.2. Independent Metering Hydraulic Driving Unit Modeling
3.3. Straight Gait Planning
3.4. Foot Trajectory Planning
4. Highly Accurate Joint Position Controller Design
4.1. Problem Statement
4.2. PID Controller
4.3. Adaptive Robust Sliding Mode Controller
4.4. Sliding Mode Repetitive Controller Based on Unknown Dynamics Estimator
5. Simulation and Experiment
- The maximum value of the absolute error (MAXE).
- 2.
- The root mean square error (RMSE).
5.1. MATLAB Simulink and ADAMS Co-Simulation
5.2. Prototype Experiment
5.2.1. Single-Leg Joint Control Experiment
- Experiment E1
- 2.
- Experiment E2
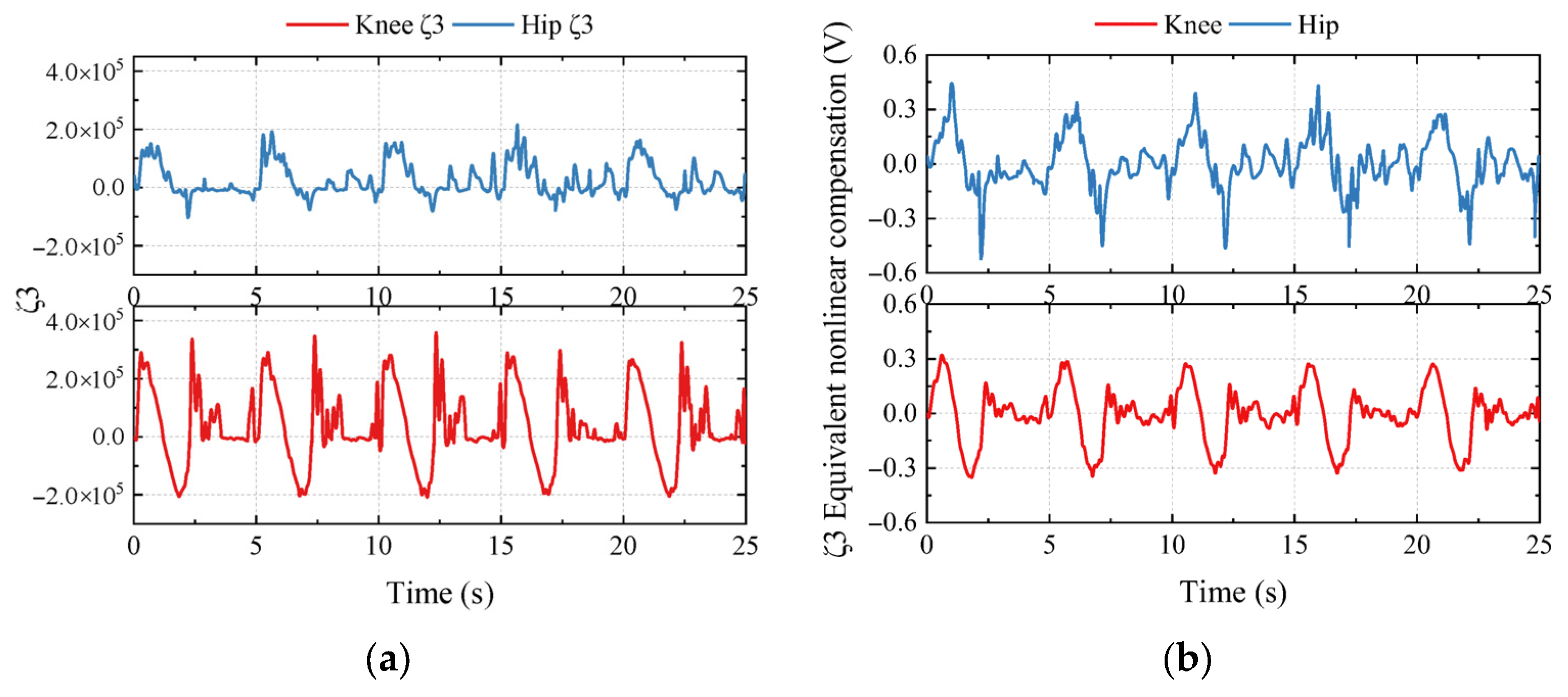
5.2.2. Dilemma Between Control Performance and Efficiency
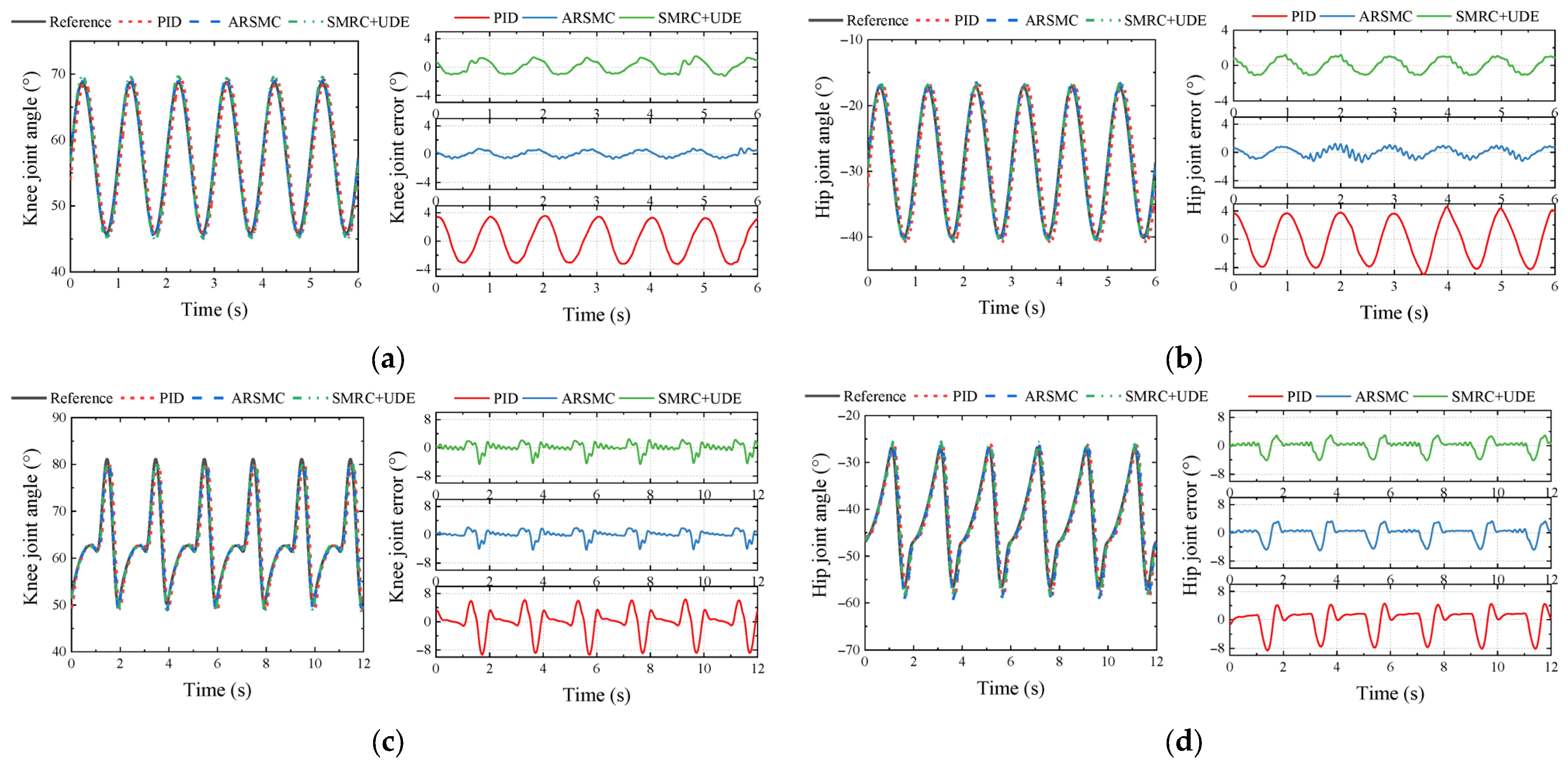
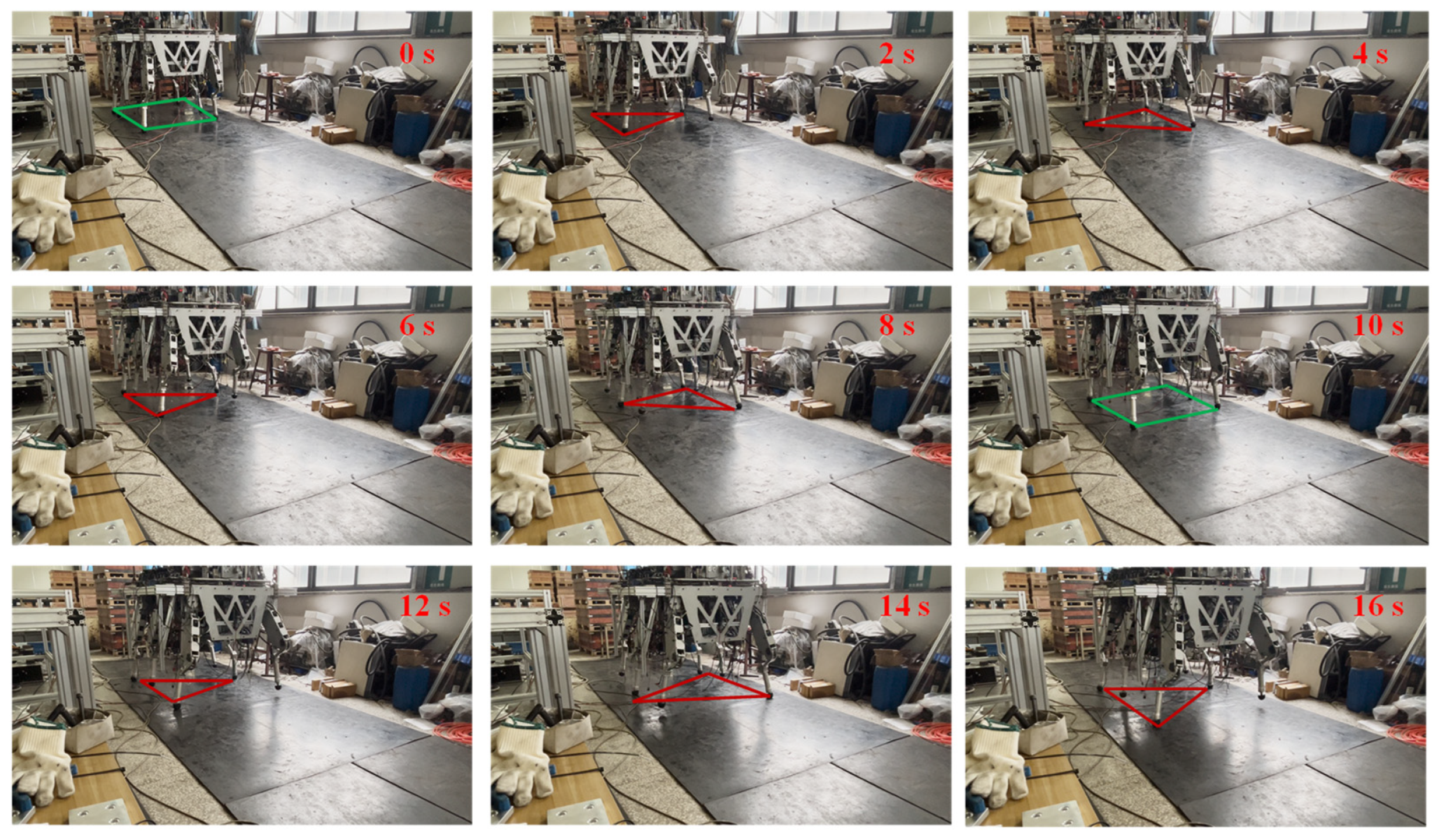
5.2.3. Walking Experiment
- Experiment E3
- 2.
- Experiment E4
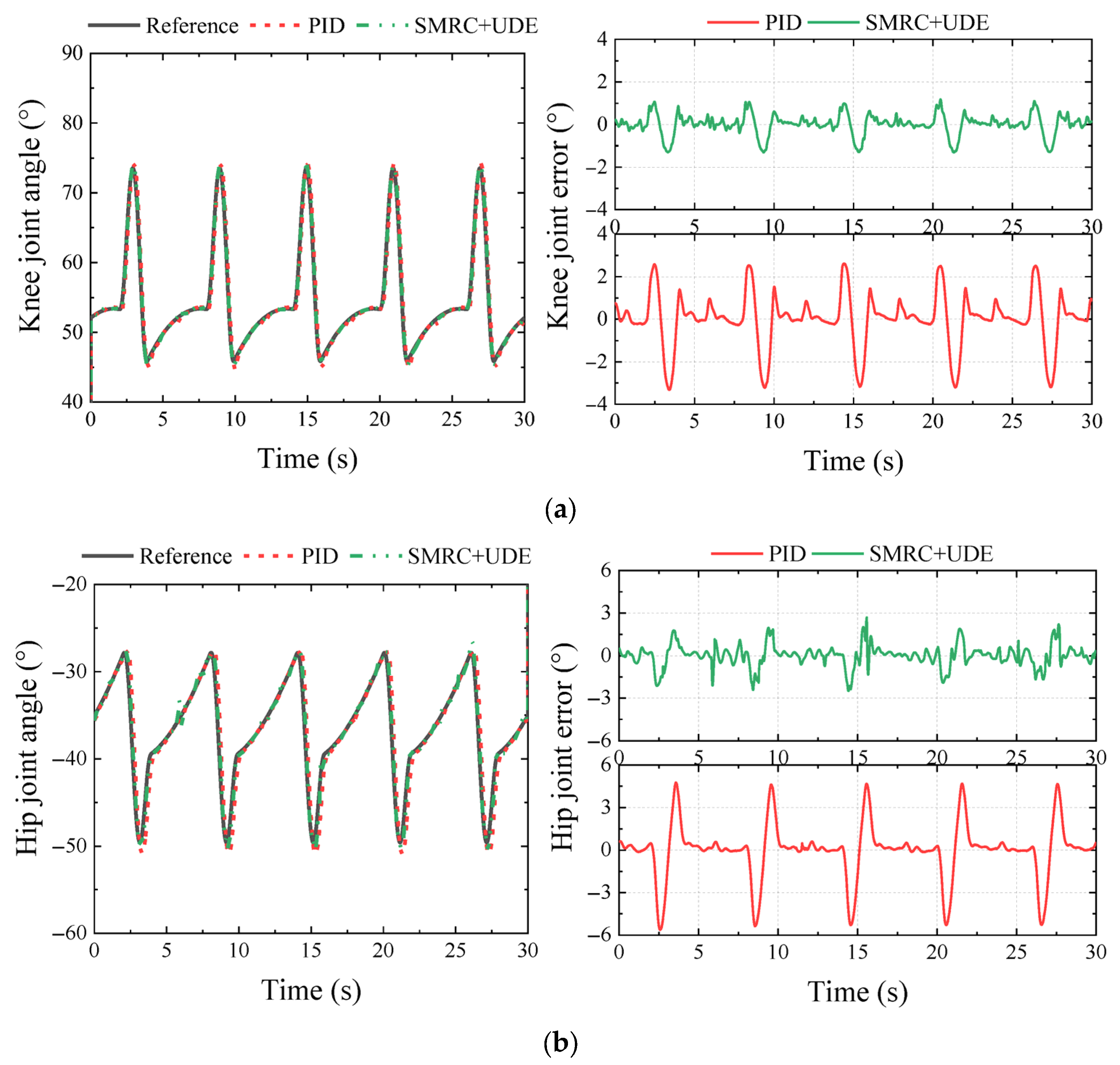
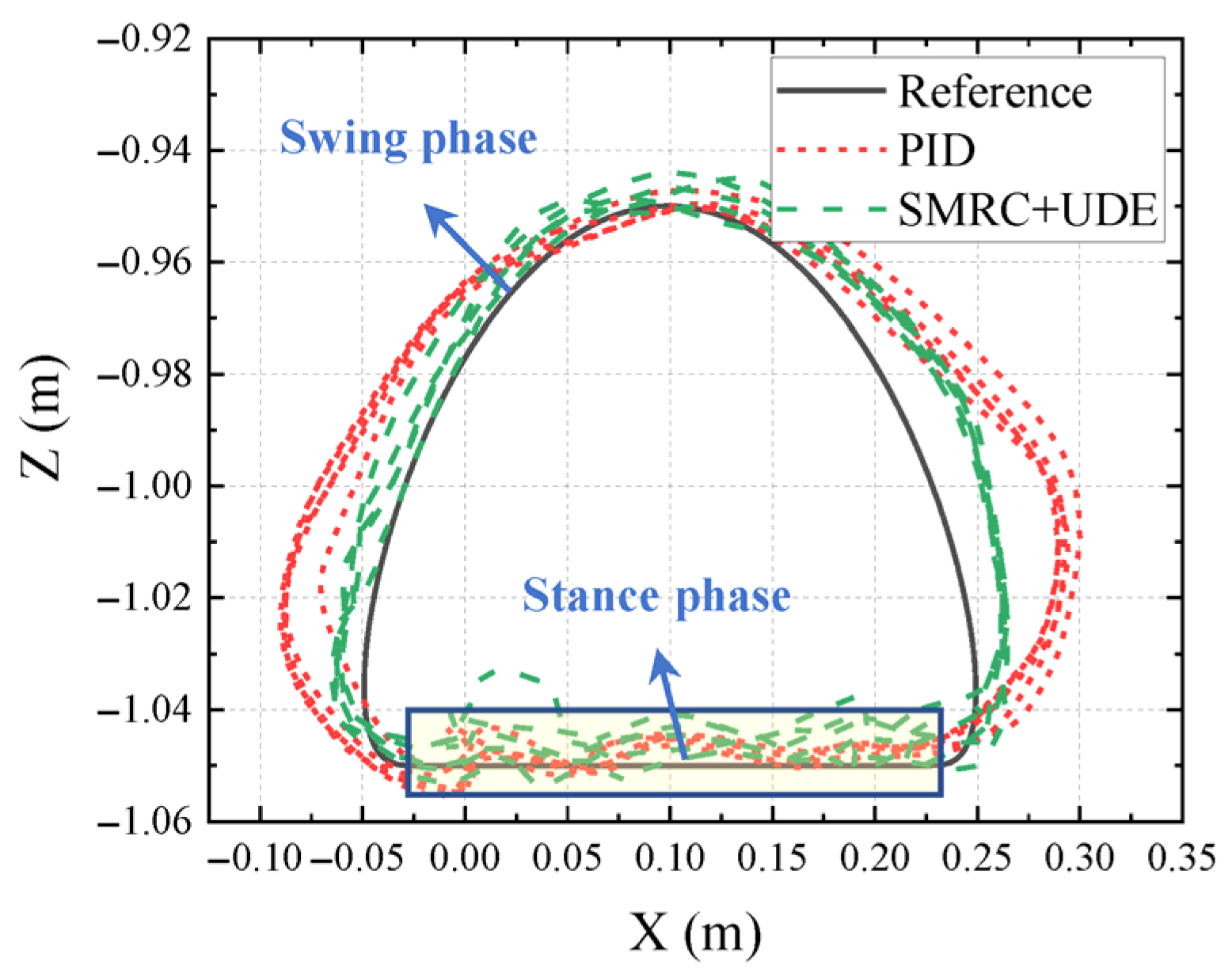
5.2.4. Data Analysis
6. Conclusions
- PID and ARSMC were used for comparison with the proposed method. In the single-leg joint control experiment, ARSMC and SMRC + UDE could significantly improve the control accuracy, while ARSMC exhibited the highest control accuracy among the three.
- Considering the performance of the control system hardware and the multiple IMHDUs (a total of 36 valves) of the hydraulic system, although ARSMC demonstrated superior control behavior, the dilemma between control performance and efficiency made it difficult to apply to our HHR. Thus, the proposed SMRC + UDE may be more suitable for achieving joint position control with high accuracy for the HHR, using only the directional control valves with lower cost.
- In the walking experiments, compared with PID, the MAXE of the knee and hip joints using SMRC + UDE in a quadrangular gait could reach 1.10° and 1.79°, with error reductions of 62.1% and 64.2%, respectively. In a tripod gait, the MAXE could reach 1.10° and 1.79°, with error reductions of 62.1% and 64.2%, respectively. Based on the characteristics of the repetitive control, the proposed SMRC + UDE demonstrated an excellent control performance when tracking the periodic gait (tripod and quadrangular gait).
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
| Controller | Gain | Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Root | Hip | Knee | ||
| PID | 50 | 200 | 200 | |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| ARSMC | - | 500 | 1000 | |
| - | 0.5 | 1 | ||
| - | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | ||
| - | 1 | 1 | ||
| - | 1000 | 1000 | ||
| - | ||||
| SMRC + UDE | - | 500 | 1000 | |
| - | 0.5 | 1 | ||
| - | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | ||
| - | 0.01 | 0.01 | ||
| - | 1 | 1 | ||
| - | 1000 | 1000 | ||
| - | 0.001 | 0.001 | ||
| - | 0.95 | 0.95 | ||
References
- Jin, Y.; Liu, X.; Shao, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, W. High-speed quadrupedal locomotion by imitation-relaxation reinforcement learning. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2022, 4, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arm, P.; Waibel, G.; Preisig, J.; Tuna, T.; Zhou, R.; Bickel, V.; Ligeza, G.; Miki, T.; Kehl, F.; Kolvenbach, H. Scientific exploration of challenging planetary analog environments with a team of legged robots. Sci. Robot. 2023, 8, eade9548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Um, Y.; Park, J.; Park, H.-W. Agile and versatile climbing on ferromagnetic surfaces with a quadrupedal robot. Sci. Robot. 2022, 7, eadd1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Chai, H.; Song, R.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, P.; Liu, J.; Yang, Z. Contact force/motion hybrid control for a hydraulic legged mobile manipulator via a force-controlled floating base. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2023, 29, 2316–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raibert, M.; Blankespoor, K.; Nelson, G.; Playter, R. Bigdog, the rough-terrain quadruped robot. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2008, 41, 10822–10825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefera, Y.; Sarakoglou, I.; Deore, S.; Kim, Y.; Barasuol, V.; Villa, M.; Anastasi, S.; Caldwell, D.; Tsagarakis, N.; Semini, C. Robot teleoperativo: Collaborative cybernetic systems for immersive remote teleoperation. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Conference on Telepresence, Pasadena, CA, USA, 16–17 November 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; He, X.; Zou, W.; Yu, B.; Yuan, L.; Li, M.; Pan, G.; Ba, K. Multi-objective optimal torque control with simultaneous motion and force tracking for hydraulic quadruped robots. Machines 2022, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonami, K.; Barai, R.K.; Irawan, A.; Daud, M.R.; Nonami, K.; Barai, R.K.; Irawan, A.; Daud, M.R. Design and optimization of hydraulically actuated hexapod robot comet-iv. In Hydraulically Actuated Hexapod Robots: Design, Implementation and Control; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 41–84. [Google Scholar]
- Rekleitis, G.; Vidakis, M.; Papadopoulos, E. Optimal leg sequencing for a hexapod subject to external forces and slopes. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Co nference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 6302–6308. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Yu, H.; Huang, Z.; He, X.; Ba, K.; Shi, Y.; Kong, X. Review of hydraulic driven key technologies for legged robots. J. Mech. Eng. 2023, 59, 81–110. [Google Scholar]
- Havoutis, I.; Semini, C.; Caldwell, D.G. Virtual model control for quadrupedal trunk stabilization. In Proceedings of the Dynamic Walking, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 10–13 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Villarreal, O.; Barasuol, V.; Wensing, P.M.; Caldwell, D.G.; Semini, C. Mpc-based controller with terrain insight for dynamic legged locomotion. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 2436–2442. [Google Scholar]
- Fahmi, S.; Mastalli, C.; Focchi, M.; Semini, C. Passive whole-body control for quadruped robots: Experimental validation over challenging terrain. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 2553–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Jin, B. Position-posture trajectory tracking of a six-legged walking robot. Int. J. Robot. Autom. 2019, 34, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, T.B.; Semini, C.; Guglielmino, E.; De Negri, V.J.; Yang, Y.; Caldwell, D.G. Gain scheduling control for the hydraulic actuation of the hyq robot leg. In Proceedings of the COBEM, Gramado, Brazil, 15–20 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J. From pid to active disturbance rejection control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 900–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focchi, M.; Guglielmino, E.; Semini, C.; Boaventura, T.; Yang, Y.; Caldwell, D.G. Control of a hydraulically-actuated quadruped robot leg. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Anchorage, AK, USA, 3–7 May 2010; pp. 4182–4188. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.; Liu, S.; Wu, H. Sliding mode observer-based fractional-order proportional–integral–derivative sliding mode control for electro-hydraulic servo systems. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2020, 234, 1887–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikdel, N.; Badamchizadeh, M.; Azimirad, V.; Nazari, M.A. Fractional-order adaptive backstepping control of robotic manipulators in the presence of model uncertainties and external disturbances. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 6249–6256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barai, R.K.; Nonami, K. Locomotion control of a hydraulically actuated hexapod robot by robust adaptive fuzzy control with self-tuned adaptation gain and dead zone fuzzy pre-compensation. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2008, 53, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Sun, C. Robust adaptive dynamic surface control for hydraulic quadruped robot hip joint. Trans. Beijing Inst. Technol. 2016, 36, 599–604. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B.; Han, W. Neural network model reference decoupling control for single leg joint of hydraulic quadruped robot. Assem. Autom. 2018, 38, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, F.; Yao, B. Observer based coordinated adaptive robust control of robot manipulators driven by single-rod hydraulic actuators. In Proceedings of the 2000 ICRA. Millennium Conference. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Symposia Proceedings (Cat. No. 00CH37065), San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–28 April 2000; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 3034–3039. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Shao, J.; Sun, G.; Shao, X. Active disturbance rejection control design using the optimization algorithm for a hydraulic quadruped robot. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2021, 2021, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Fan, Y.; Shao, J.; Sun, G. Improved active disturbance rejection control with the optimization algorithm for the leg joint control of a hydraulic quadruped robot. Meas. Control 2023, 56, 1359–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, H.; Yang, Z.; Yu, X.; Zhang, J.; Ai, J.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, F.; Su, Q.; Xu, B. Active disturbance rejection control of hydraulic quadruped robots rotary joints for improved impact resistance. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2024, 37, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Dong, R.; Jiang, C.; Song, J. Sliding mode robust control of hydraulic drive unit of hydraulic quadruped robot. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2022, 20, 1336–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Helian, B.; Chen, Z.; Yao, B. Adaptive robust constrained motion control of an independent metering electro-hydraulic system considering kinematic and dynamic constraints. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2025, 21, 5943–5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, S.; Wang, A.; Chuah, M.Y.; Hyun, D.J.; Lee, J.; Otten, D.M.; Lang, J.H.; Kim, S. Design principles for energy-efficient legged locomotion and implementation on the mit cheetah robot. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 20, 1117–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jin, B.; Dong, J.; Zhai, S.; Tang, X. Design and control of a hydraulic hexapod robot with a two-stage supply pressure hydraulic system. Machines 2022, 10, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Jin, B.; Liu, Z.; Chen, L. Energy-efficient hydraulic system for hexapod robot based on two-level pressure system for oil supply. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Rong, X.; Zhou, L.; Li, Y. Modeling and analysis on energy consumption of hydraulic quadruped robot for optimal trot motion control. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.S.; Pratihar, D.K. Effects of turning gait parameters on energy consumption and stability of a six-legged walking robot. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2012, 60, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B. High performance adaptive robust control of nonlinear systems: A general framework and new schemes. In Proceedings of the 36th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, San Diego, CA, USA, 10–12 December 1997; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1997; pp. 2489–2494. [Google Scholar]

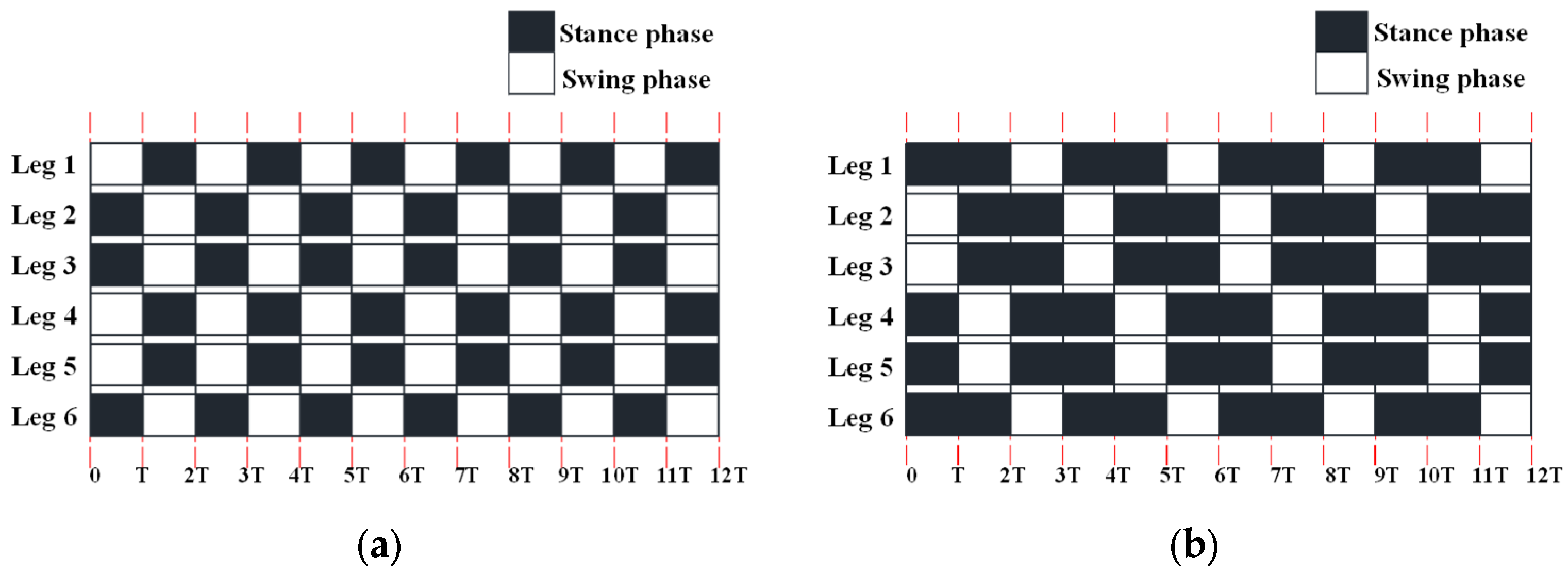






| Phase | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stance phase | On | Off | On | |
| Swing phase | Off | On | On |
| Control Algorithm | MAXE (°) | RMSE (°) | Runtime (ms) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PID | 8.71 | 9.57 | 3.64 | 3.67 | 0.25 |
| ARSMC | 5.83 | 4.34 | 2.18 | 1.62 | 2.04 |
| SMRC + UDE | 6.02 | 4.78 | 2.27 | 1.78 | 0.90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Jin, B.; Dong, J.; Yao, Q.; Jin, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, B. Sliding Mode Repetitive Control Based on the Unknown Dynamics Estimator of a Two-Stage Supply Pressure Hydraulic Hexapod Robot. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10070472
Liu Z, Jin B, Dong J, Yao Q, Jin Y, Liu T, Wang B. Sliding Mode Repetitive Control Based on the Unknown Dynamics Estimator of a Two-Stage Supply Pressure Hydraulic Hexapod Robot. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(7):472. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10070472
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ziqi, Bo Jin, Junkui Dong, Qingyun Yao, Yinglian Jin, Tao Liu, and Binrui Wang. 2025. "Sliding Mode Repetitive Control Based on the Unknown Dynamics Estimator of a Two-Stage Supply Pressure Hydraulic Hexapod Robot" Biomimetics 10, no. 7: 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10070472
APA StyleLiu, Z., Jin, B., Dong, J., Yao, Q., Jin, Y., Liu, T., & Wang, B. (2025). Sliding Mode Repetitive Control Based on the Unknown Dynamics Estimator of a Two-Stage Supply Pressure Hydraulic Hexapod Robot. Biomimetics, 10(7), 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10070472







