Tribological Effects of Surface Biomimetic Micro–Nano Textures on Metal Cutting Tools: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
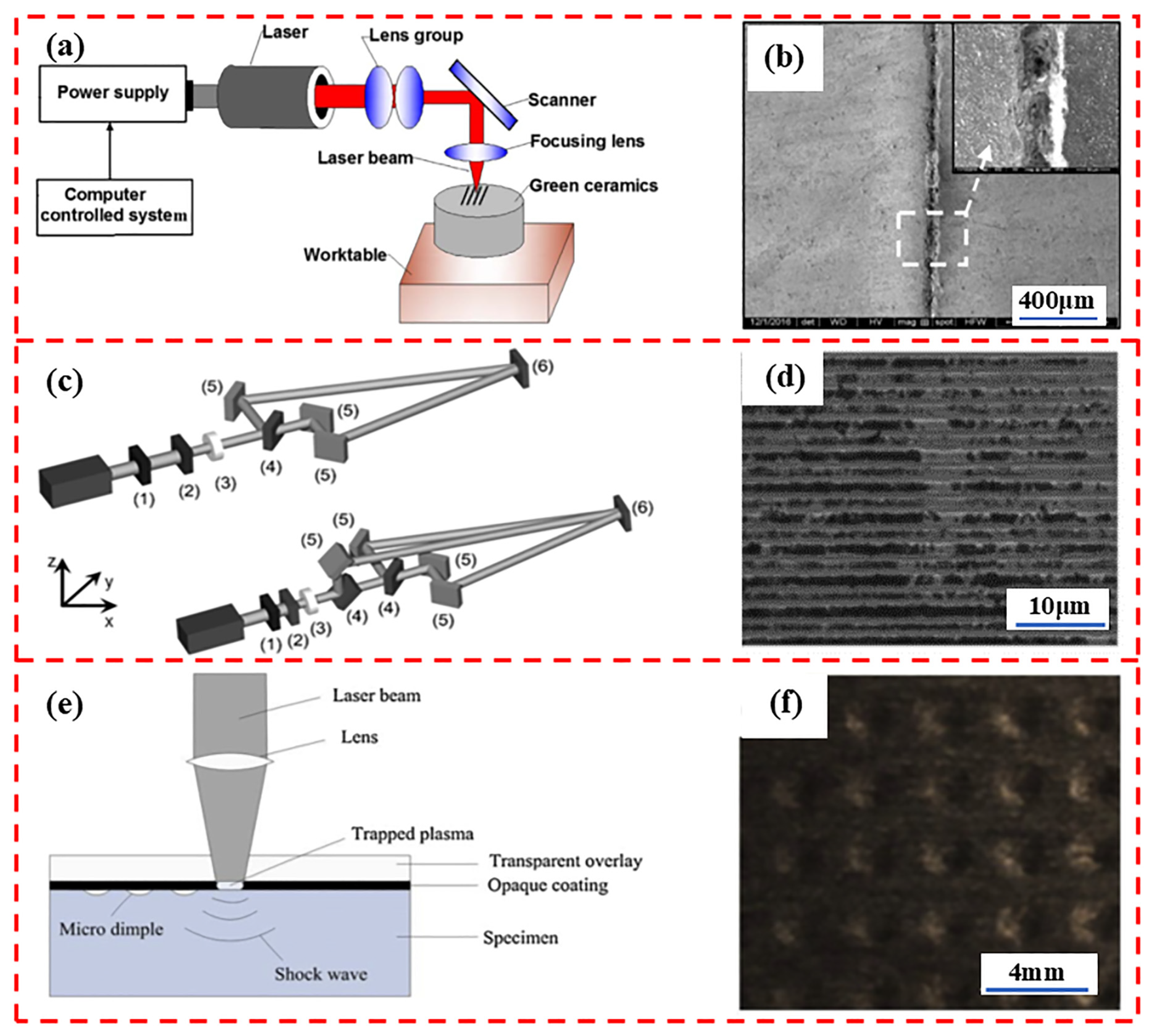
2. Common Preparation Methods for Biomimetic Micro–Nano Textures
2.1. Laser Processing Technology
2.2. Reactive Ion Etching
2.3. Soft Lithography
2.4. 3D Printing
2.5. Discussion
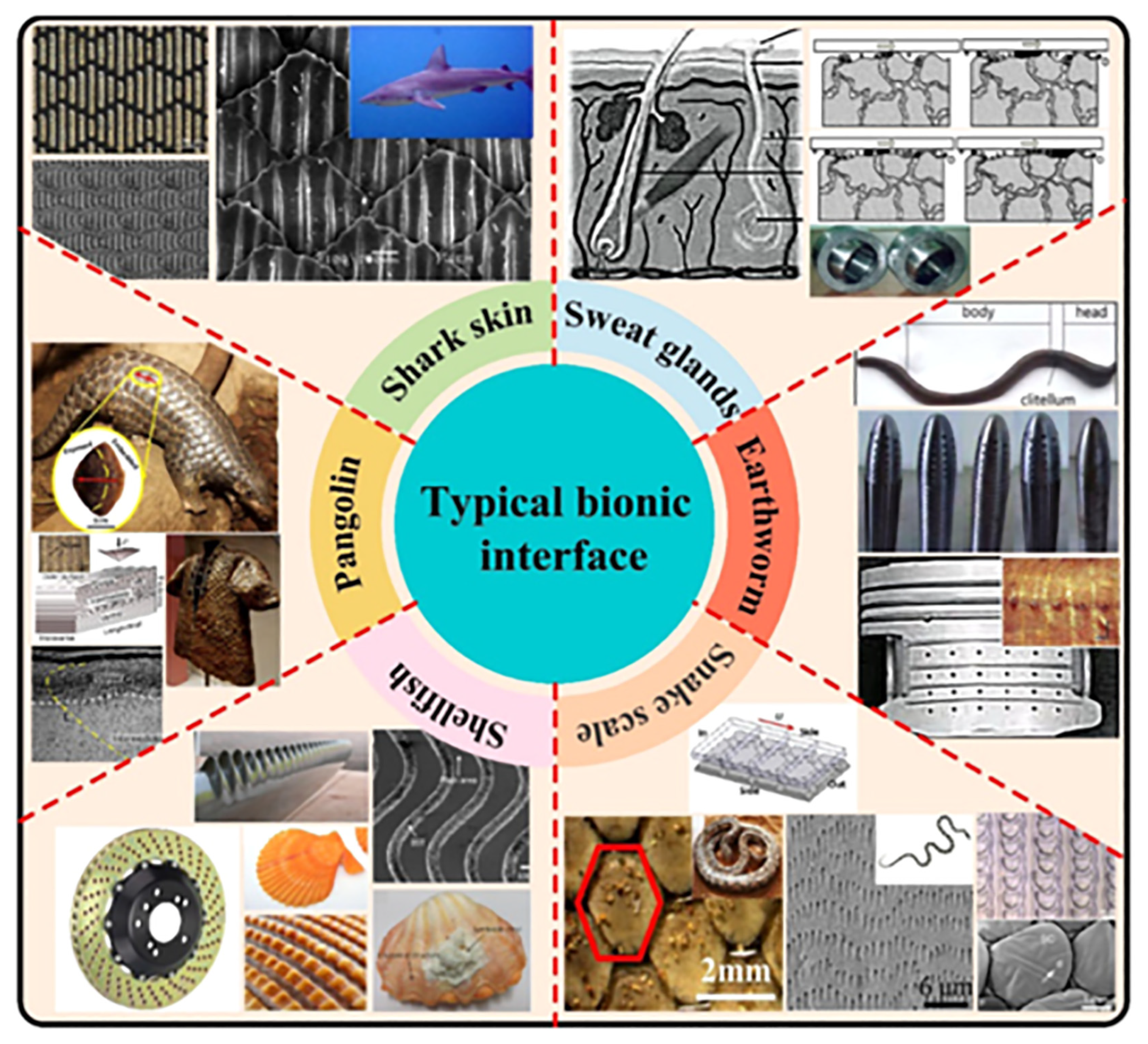
3. Common Biological Surface Textures and Their Mechanisms
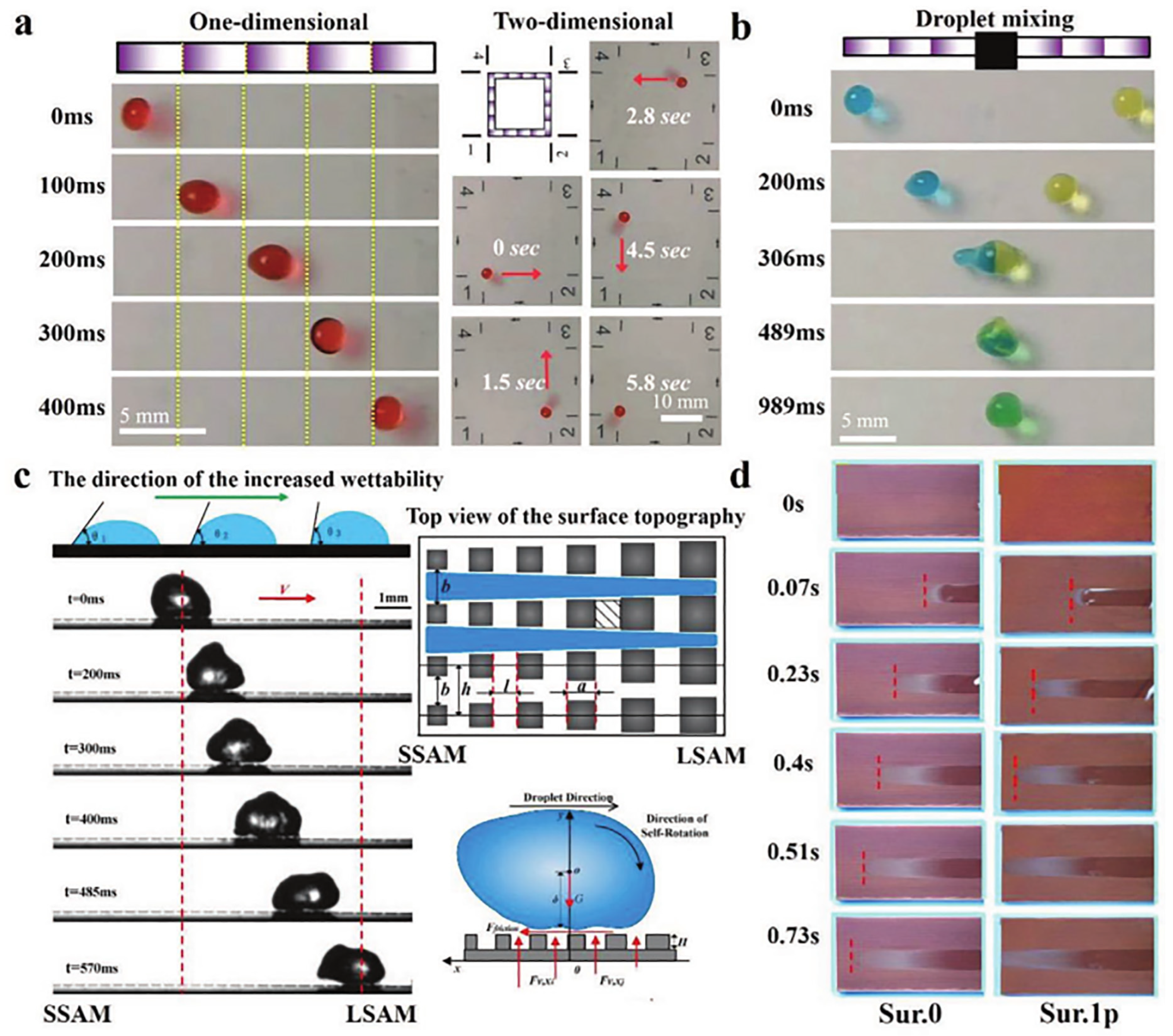
3.1. Snakes and Other Reptiles

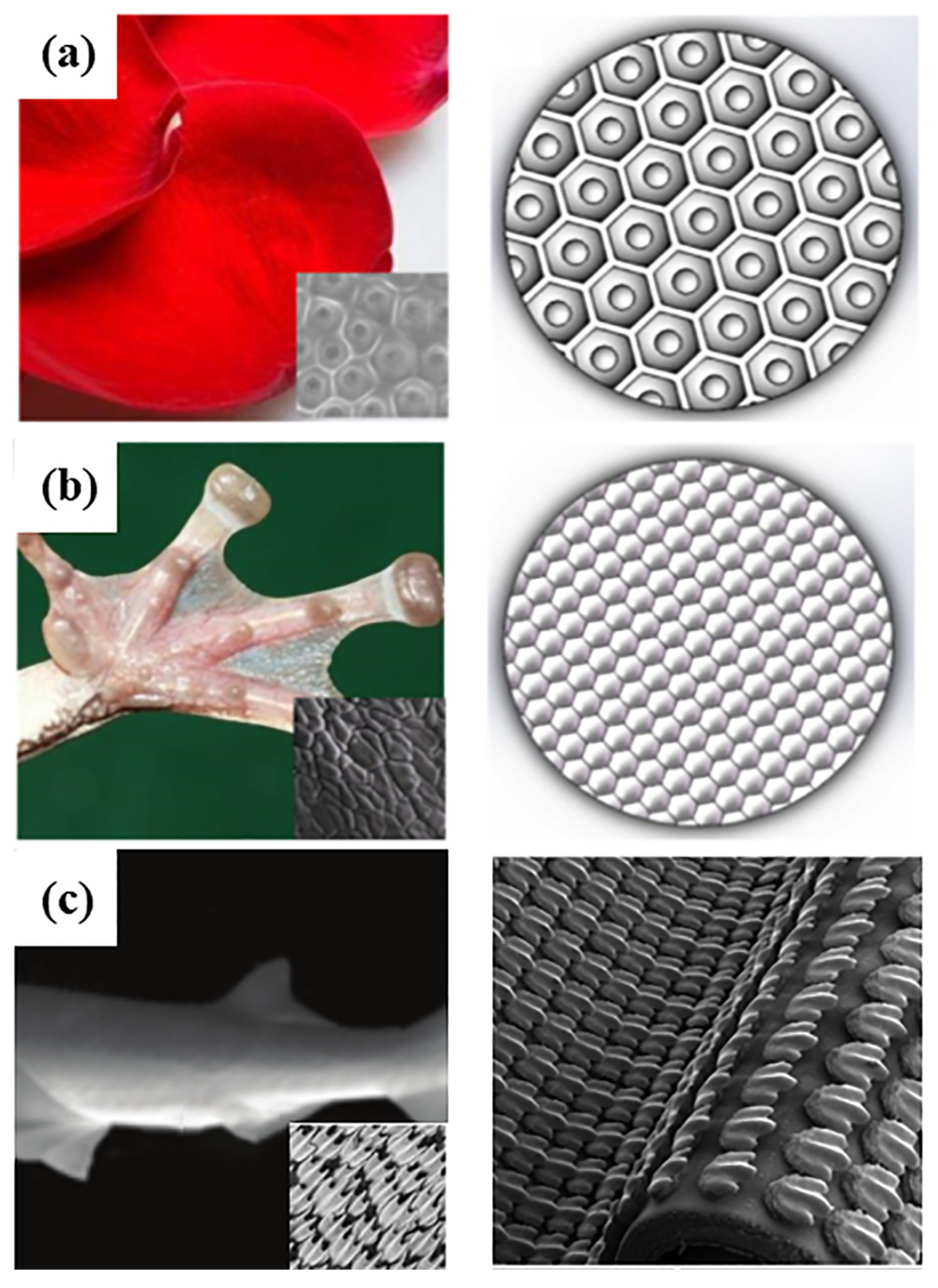
3.2. Sharks and Aquatic Organisms
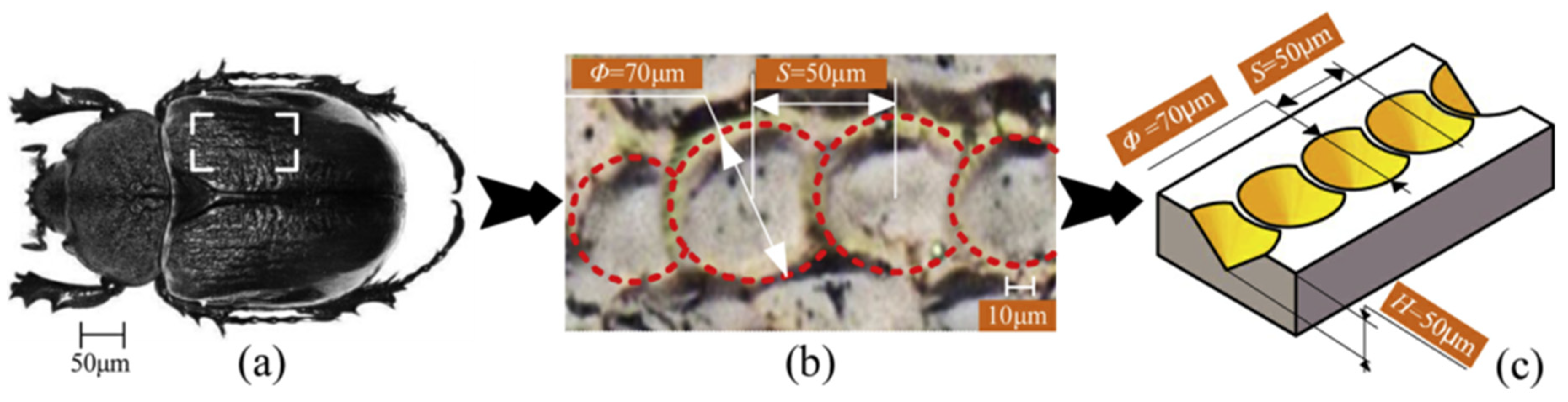
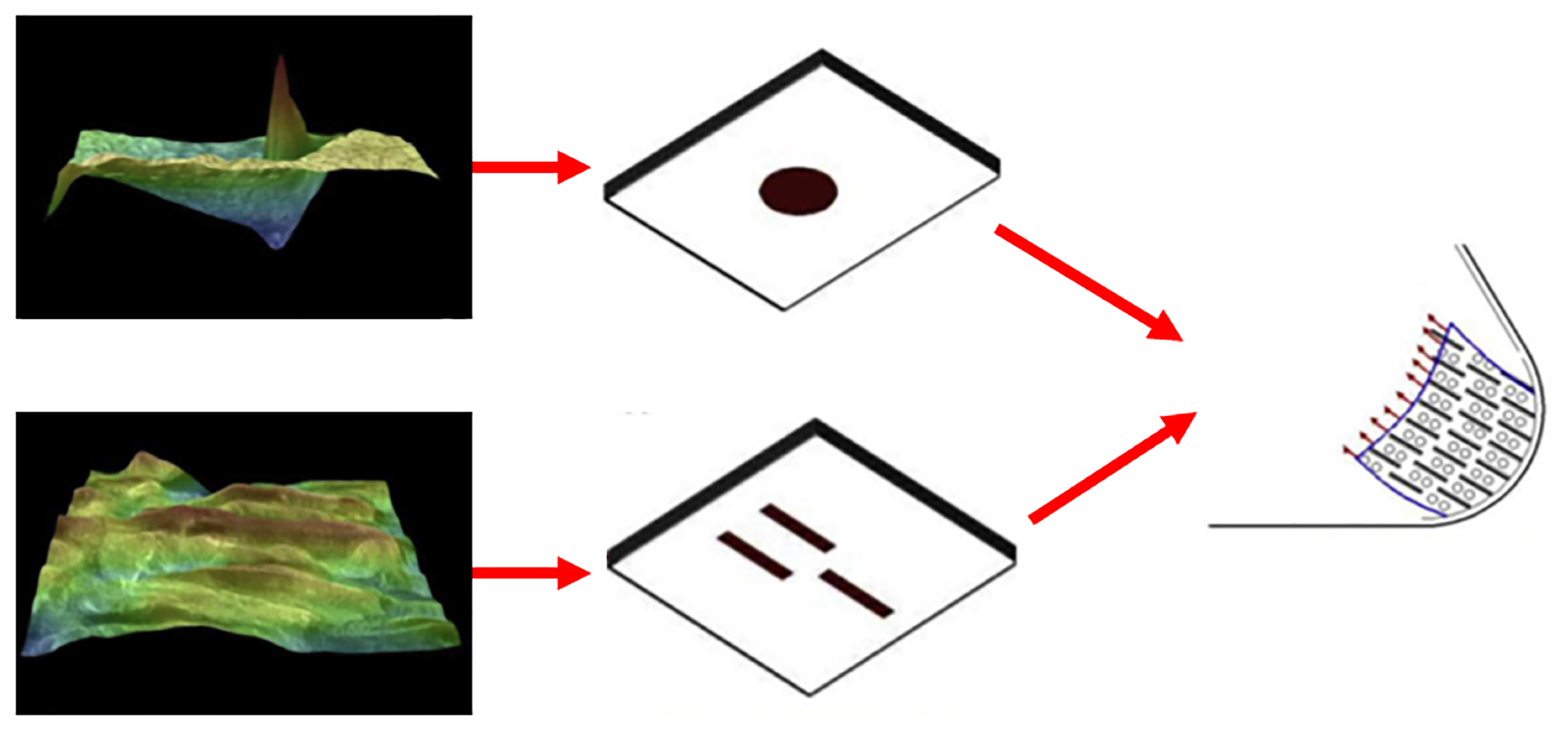
3.3. Dung Beetles and Insect-like Organisms
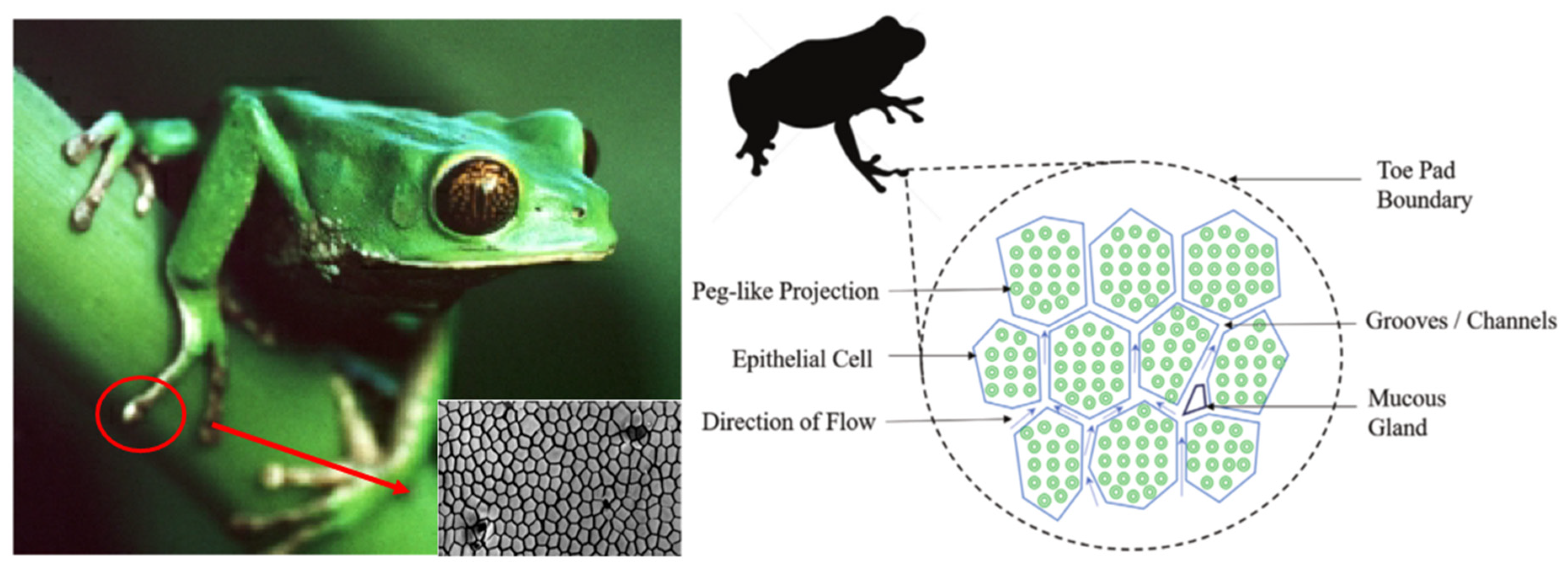
3.4. Tree Frogs and Geckos
3.5. Shellfish
3.6. Plants
4. Effect of Texture Morphology and Parameters on Their Tribological Properties
5. Biomimetic Textures on Metal Cutting Tools
6. Prospects for Biomimetic Texturing on Metal Cutting Tools
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, K.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Lv, G.; Gao, Y. Research progress of improving surface friction properties by surface texture technology. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 116, 2797–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, S. Evaluation and analysis of abrasive wear resistance of hybrid roller bearings under lubricant contamination. Wear 2024, 558, 205570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, Z.; Jiao, X.; Guo, Z.; Fu, F. Bioinspired lubricant-infused porous surfaces: A review on principle, fabrication, and applications. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 53, 105037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasegi, N.; Sugimori, H.; Morimoto, H.; Morita, N.; Hori, I. Development of cutting tools with microscale and nanoscale textures to improve frictional behavior. Precis. Eng. 2009, 33, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etsion, I. State of the art in laser surface texturing. J. Trib. 2005, 127, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzone, A.; Costa, H.; Lonardo, P.; Lucca, D. Advances in engineered surfaces for functional performance. CIRP Ann. 2008, 57, 750–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, N.; Tian, H.; Suh, N.P. Boundary lubrication of undulated metal surfaces at elevated temperatures. Tribol. Trans. 1989, 32, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kato, K.; Adachi, K. The lubrication effect of micro-pits on parallel sliding faces of SiC in water. Tribol. Trans. 2002, 45, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawelski, O.; Rasp, W.; Zwick, W.; Nettelbeck, H.-J.; Steinhoff, K. The influence of different work-roll texturing systems on the development of surface structure in the temper rolling process of steel sheet used in the automotive industry. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1994, 45, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspinwall, D.; Wise, M.; Stout, K.; Goh, T.; Zhao, F.; El-Menshawy, M. Electrical discharge texturing. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 1992, 32, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etsion, I.; Sher, E. Improving fuel efficiency with laser surface textured piston rings. Tribol. Int. 2009, 42, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryk, G.; Etsion, I. Testing piston rings with partial laser surface texturing for friction reduction. Wear 2006, 261, 792–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etsion, I.; Halperin, G.; Becker, E. The effect of various surface treatments on piston pin scuffing resistance. Wear 2006, 261, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kligerman, Y.; Etsion, I.; Shinkarenko, A. Improving tribological performance of piston rings by partial surface texturing. J. Trib. 2005, 127, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryk, G.; Kligerman, Y.; Etsion, I. Experimental investigation of laser surface texturing for reciprocating automotive components. Tribol. Trans. 2002, 45, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronen, A.; Etsion, I.; Kligerman, Y. Friction-reducing surface-texturing in reciprocating automotive components. Tribol. Trans. 2001, 44, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryk, G.; Kligerman, Y.; Etsion, I.; Shinkarenko, A. Experimental investigation of partial laser surface texturing for piston-ring friction reduction. Tribol. Trans. 2005, 48, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Masjuki, H.; Varman, M.; Kalam, M.; Habibullah, M.; Al Mahmud, K. An overview of geometrical parameters of surface texturing for piston/cylinder assembly and mechanical seals. Meccanica 2016, 51, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quazi, M.; Fazal, M.; Haseeb, A.; Yusof, F.; Masjuki, H.H.; Arslan, A. Laser-based surface modifications of aluminum and its alloys. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2016, 41, 106–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quazi, M.; Fazal, M.; Haseeb, A.; Yusof, F.; Masjuki, H.; Arslan, A. A review to the laser cladding of self-lubricating composite coatings. Lasers Manuf. Mater. Process. 2016, 3, 67–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Xiong, D.-S. The effect of laser surface texturing on frictional performance of face seal. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 197, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etsion, I.; Halperin, G. A laser surface textured hydrostatic mechanical seal. Tribol. Trans. 2002, 45, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kato, K. Improving the anti-seizure ability of SiC seal in water with RIE texturing. Tribol. Lett. 2003, 14, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kato, K.; Adachi, K.; Aizawa, K. Loads carrying capacity map for the surface texture design of SiC thrust bearing sliding in water. Tribol. Int. 2003, 36, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Adachi, K.; Otsuka, K.; Kato, K. Optimization of the surface texture for silicon carbide sliding in water. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 253, 1282–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Huang, W.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y. Experimental study of two-phase mechanical face seals with laser surface texturing. Tribol. Int. 2014, 72, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Deng, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Yue, H.; Duan, R.; Ge, D. Effect of surface textures and electrohydrodynamically atomized WS2 films on the friction and wear properties of ZrO2 coatings. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 1020–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Deng, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Sun, J.; Ge, D.; Liu, Y.; Duan, R. Tribological properties of WS2 coatings deposited on textured surfaces by electrohydrodynamic atomization. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 352, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Deng, J.; Chai, Y.; Fan, W. Surface textures on cemented carbide cutting tools by micro EDM assisted with high-frequency vibration. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 82, 2157–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugihara, T.; Enomoto, T. Crater and flank wear resistance of cutting tools having micro textured surfaces. Precis. Eng. 2013, 37, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouathiya, A.; Meziani, S.; Sahli, M.; Barriere, T. Experimental investigation of microtextured cutting tool performance in titanium alloy via turning. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 69, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajrani, K.K.; Sankar, M.R.; Dixit, U.S. Environmentally friendly machining with MoS2-filled mechanically microtextured cutting tools. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2018, 32, 3797–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Bao, H.; Liu, L.; Xing, Y.; Huang, P.; Zhao, G. Numerical investigation of the performance of micro-textured cutting tools in cutting of Ti-6Al-4V alloys. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 108, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Qiu, X.; Yu, Z.; Li, S.; Li, P.; Niu, Q.; Kurniawan, R.; Ko, T.J. Novel environmentally friendly manufacturing method for micro-textured cutting tools. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2021, 8, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaraj, S.; Malkapuram, R.; Singaravel, B. Performance analysis of micro textured cutting insert design parameters on machining of Al-MMC in turning process. Int. J. Lightweight Mater. Manuf. 2021, 4, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajrani, K.K.; Suresh, S.; Sankar, M.R. Environmental friendly hard machining performance of uncoated and MoS2 coated mechanical micro-textured tungsten carbide cutting tools. Tribol. Int. 2018, 125, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Tian, Y. Performances of micro-textured WC-10Ni3Al cemented carbides cutting tool in turning of Ti6Al4V. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2019, 84, 104987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajrani, K.K.; Sankar, M.R.; Dixit, U.S. Tribological performance of MoS2-filled microtextured cutting tools during dry sliding test. J. Tribol. 2018, 140, 021301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajrani, K.K.; Pavan Kumar Reddy, R.; Ravi Sankar, M. Tribo-mechanical and surface morphological comparison of untextured, mechanical micro-textured (MμT), and coated-MμT cutting tools during machining. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2019, 233, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajrani, K.K.; Sankar, M.R. Sustainable machining with self-lubricating coated mechanical micro-textured cutting tools. In Reference Module in Materials Science and Materials Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson, U.; Jacobson, S. Textured surfaces for improved lubrication at high pressure and low sliding speed of roller/piston in hydraulic motors. Tribol. Int. 2007, 40, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiang, J.; Fu, Q.; Wood, R.J.; Wang, S. Study on the friction performance of textured surface on water hydraulic motor piston pair. Tribol. Trans. 2022, 65, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gu, L.; Li, L. Experimental studies on the overall efficiency performance of axial piston motor with a laser surface textured valve plate. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2013, 227, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sharma, S.C. Influence of dimple geometry and micro-roughness orientation on performance of textured hybrid thrust pad bearing. Meccanica 2018, 53, 3579–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Guo, S.; Wei, Y.; Yuan, G.; Geng, H. Optimization research on the lubrication characteristics for friction pairs surface of journal bearings with micro texture. Meccanica 2019, 54, 1135–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Bailey, B.N.; Stoll, R.; Raeymaekers, B. The accuracy of the compressible Reynolds equation for predicting the local pressure in gas-lubricated textured parallel slider bearings. Tribol. Int. 2014, 72, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, M.; Minson, B.R.; Raeymaekers, B. The effect of texture shape on the friction coefficient and stiffness of gas-lubricated parallel slider bearings. Tribol. Int. 2013, 67, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, V.G.; Gabriel, D.; Knoll, G.; Filippone, S. Theoretical and experimental analysis of a laser textured thrust bearing. Tribol. Lett. 2011, 44, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, R.; Mirzaee, I.; Shirvani, A.; Shirvani, H. An analytical approach for analysis and optimisation of slider bearings with infinite width parallel textures. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 1551–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, M.; Weikert, T.; Tremmel, S. On friction reduction by surface modifications in the TEHL cam/tappet-contact-experimental and numerical studies. Coatings 2019, 9, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhang, K.; Huang, Q.; Guo, X.; Wang, C. A study on tribological properties of textured Co-Cr-Mo alloy for artificial hip joints. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2021, 95, 105463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratap, T.; Patra, K. Mechanical micro-texturing of Ti-6Al-4V surfaces for improved wettability and bio-tribological performances. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 349, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratap, T.; Patra, K. Tribological performances of symmetrically micro-textured Ti-6Al-4V alloy for hip joint. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 182, 105736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capitanu, L.; Badita, L.-L.; Tiganesteanu, C.; Florescu, V.; Isvoranu, L.F. Increasing the wear resistance of hip prosthesis by laser surface microtexturing of the femoral head. Acta Electroteh. 2019, 60, 43–57. [Google Scholar]
- Etsion, I. Improving tribological performance of mechanical components by laser surface texturing. Tribol. Lett. 2004, 17, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, A.; Masjuki, H.; Varman, M.; Kalam, M.; Quazi, M.; Al Mahmud, K.; Gulzar, M.; Habibullah, M. Effects of texture diameter and depth on the tribological performance of DLC coating under lubricated sliding condition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 356, 1135–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, A.; Masjuki, H.; Varman, M.; Kalam, A.; Mufti, R.; Gulzar, M.; Quazi, M. Effect of surface texture on the tribological performance of DLC coating. In Proceedings of the Malaysian International Tribology Conference, Penang, Malaysia, 16–17 November 2015; Malaysian Tribology Society: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sugihara, T.; Enomoto, T. Improving anti-adhesion in aluminum alloy cutting by micro stripe texture. Precis. Eng. 2012, 36, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Duong, N.H.; Lei, S. 3D numerical investigation of the performance of microgroove textured cutting tool in dry machining of Ti-6Al-4V. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 79, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugihara, T.; Enomoto, T. Development of a cutting tool with a nano/micro-textured surface—Improvement of anti-adhesive effect by considering the texture patterns. Precis. Eng. 2009, 33, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Guo, Z.; Xie, X.; Yuan, C. Effect of spherical-convex surface texture on tribological performance of water-lubricated bearing. Tribol. Int. 2019, 134, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.; Braun, D.; Greiner, C. Laser textured surfaces for mixed lubrication: Influence of aspect ratio, textured area and dimple arrangement. Lubricants 2017, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Lin, N.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Wu, Y. Correlation between surface textural parameter and tribological behaviour of four metal materials with laser surface texturing (LST). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 583, 152410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Khonsari, M. Texture shape optimization for seal-like parallel surfaces: Theory and experiment. Tribol. Trans. 2016, 59, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.M.; Jing, Y.; Zhao, F. Self-adaptive surface texture design for friction reduction across the lubrication regimes. Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop. 2015, 4, 014004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.a.; Liu, Z.; Chen, D.; Xie, Z.; Song, J. Influence of different surface texture parameters on the contact performance of piston ring-sleeve friction pair of hydraulic cylinders. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5495995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgornik, B.; Sedlacek, M. Performance, characterization and design of textured surfaces. J. Tribol. 2012, 134, 041701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.; Ibatan, T.; Shankar, S. Influence of surface texture shape, geometry and orientation on hydrodynamic lubrication performance of plane-to-plane slider surfaces. Lubr. Sci. 2017, 29, 153–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Wood, R.J.; Gee, M.G.; Wang, L.; Pfleging, W. A novel surface texture shape for directional friction control. Tribol. Lett. 2018, 66, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikam, M.D.; Shimpi, D.; Bhole, K.; Mastud, S.A. Design and development of surface texture for tribological application. Key Eng. Mater. 2019, 803, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Yang, X.; Cheng, J.; Wang, S.; Duan, D.; Xiao, J.; Li, W. Optimization of performance parameters and mechanism of bionic texture on friction surface. Coatings 2020, 10, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Yuanpei, D. Study on secondary cutting phenomenon of micro-textured self-lubricating ceramic cutting tools with different morphology parameters formed via in situ forming of Al2O3-TiC. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 104, 3821–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Meng, X.; Wang, S.; Ding, X. Study on the mutual influence of surface roughness and texture features of rough-textured surfaces on the tribological properties. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2021, 235, 256–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yi, P.; Jia, H.-Y.; Yang, X.-S.; Shi, Y.-J.; Liu, Y.; Hao, M. Effects of morphology parameters of sinusoidal texture on tribological properties under dry friction. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2022, 74, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, A.; Masjuki, H.; Kalam, M.; Varman, M.; Mufti, R.; Mosarof, M.; Khuong, L.; Quazi, M. Surface texture manufacturing techniques and tribological effect of surface texturing on cutting tool performance: A review. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2016, 41, 447–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maani, N.; Rayz, V.S.; Nosonovsky, M. Biomimetic approaches for green tribology: From the lotus effect to blood flow control. Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop. 2015, 3, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Chen, G.; Chen, Z.; Yu, Z.; Huang, J. Progress on bionic textured cutting tools: A review and prospects. J. Bionic Eng. 2024, 21, 19–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Deng, J.; Cao, S.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, X. In-situ forming textured cutting tools based on electrohydrodynamic atomization and laser micro-cladding technology. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 684, 161856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, Z.; Huang, Q.; Yuan, C. Application of Bionic Tribology in Water-Lubricated Bearing: A Review. J. Bionic Eng. 2022, 19, 902–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kou, B.; Liu, G.; Fan, W.; Liu, L. Resistance reduction by bionic coupling of the earthworm lubrication function. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2010, 53, 2989–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Su, S.; Zhang, J. Tribological study on new therapeutic bionic lubricants. Tribol. Lett. 2007, 28, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, K.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L. Effects of bionic units in different scales on the wear behavior of bionic impregnated diamond bits. J. Bionic Eng. 2016, 13, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Gong, W.; Zheng, J. Bionic design perspectives based on the formation mechanism of dental anti-wear function. Biosurface Biotribol. 2017, 3, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Luo, C.; Wan, Y.; Huang, P.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, K. Formation of bionic surface textures composed by micro-channels using nanosecond laser on Si3N4-based ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 12768–12779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Shi, X.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, K.; Gao, Y.; Wu, C. Synergetic effects of biomimetic microtexture with multi-solid lubricants to improve tribological properties of AISI 4140 steel. Tribol. Int. 2022, 167, 107395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaduri, D.; Batal, A.; Dimov, S.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, H.; Fallqvist, M.; M’saoubi, R. On design and tribological behaviour of laser textured surfaces. Procedia Cirp 2017, 60, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mücklich, F.; Lasagni, A.; Daniel, C. Laser interference metallurgy—Periodic surface patterning and formation of intermetallics. Intermetallics 2005, 13, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, B.; Liao, Y.; Li, B. Gradient twinning microstructure generated by laser shock peening in an AZ31B magnesium alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 457, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Deng, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Sun, Q.; Wu, J. Tribological properties of Bi2S3/MoS2 composite coatings deposited on biomimetic leaf vein textured surfaces. Tribol. Lett. 2023, 71, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Deng, J.; Meng, R.; Zou, X.; Wu, F. Fabrication of micro-scale textured grooves on green ZrO2 ceramics by pulsed laser ablation. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 6519–6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Morales, A.I.; Alamri, S.; Lasagni, A.F. Micro-fabrication of high aspect ratio periodic structures on stainless steel by picosecond direct laser interference patterning. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 252, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieda, M.; Schmädicke, C.; Roch, T.; Lasagni, A. Ultra-low friction on 100cr6-steel surfaces after direct laser interference patterning. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2015, 17, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Chung, M.-H.; Dong, K.-Y.; Park, E.-M.; Ham, D.-J.; Park, Y.; Song, I.S.; Pak, J.J.; Ju, B.-K. Investigation on fabrication of nanoscale patterns using laser interference lithography. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Yao, Z.; Hu, Y.; Gu, W. Friction and wear performance of laser peen textured surface under starved lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2014, 77, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakimets, I.; Richard, C.; Béranger, G.; Peyre, P. Laser peening processing effect on mechanical and tribological properties of rolling steel 100Cr6. Wear 2004, 256, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Kim, P.; Jeong, H.; Jeong, S. Enhancement of abrasion and corrosion resistance of duplex stainless steel by laser shock peening. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2012, 212, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, B.; Siddaiah, A.; Liao, Y.; Menezes, P.L. Laser surface texturing and related techniques for enhancing tribological performance of engineering materials: A review. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 53, 153–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.; Guo, C. Femtosecond laser structuring of titanium implants. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 7272–7280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, J. Laser beam machining (LBM), state of the art and new opportunities. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 149, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semerok, A.; Chaléard, C.; Detalle, V.; Lacour, J.-L.; Mauchien, P.; Meynadier, P.; Nouvellon, C.; Sallé, B.; Palianov, P.; Perdrix, M. Experimental investigations of laser ablation efficiency of pure metals with femto, pico and nanosecond pulses. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1999, 138, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xi, F.; Wei, K.; Tong, Z.; Li, S.; Ding, Z.; Ma, W. Bridging efficiency and scalability: A systematic evaluation of diamond wire sawn silicon wafer texturing technologies for high-performance photovoltaics. Appl. Energy 2025, 386, 125591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzel, F.D.; Pitchford, W.H.; Kaur, J. Controlled gradual and local thinning of free-standing nanometer thick Si3N4 films using reactive ion etch. Microsyst. Technol. 2020, 26, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Qian, G.; Yang, L. Precise control of surface texture on carbon film by ion etching through filter: Optimization of texture size for improving tribological behavior. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 362, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, M.C.; Mohanta, D. Exceptional anisotropic superhydrophobicity of sword-lily striated leaf surface and soft lithographic biomimicking using polystyrene replica. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 105996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, S.R.; Chandrasekhar, A. Biomimicking hydrophobic leaf structure using soft lithography for fog harvesting, triboelectric nanogenerators as a self-powered rain sensor. iScience 2024, 27, 108878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.M.; Chi, Y.-T.; Hung, Y.-H.; Reyes, L.M.C.; Yeh, J.-M. UV-cured electroactive polyurethane acrylate coatings with superhydrophobic surface structure of biomimetic peacock feather for anticorrosion application. Prog. Org. Coat. 2022, 165, 106679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Ding, J.; Yuan, N. Fabrication and tribological properties of superhydrophobic nickel films with positive and negative biomimetic microtextures. Friction 2014, 2, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, B.-H.; Kim, D.-E. Development of highly durable and low friction micro-structured PDMS coating based on bio-inspired surface design. CIRP Ann. 2015, 64, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddaiah, A.; Menezes, P.L. Advances in bio-inspired tribology for engineering applications. J. Bio- Tribo-Corros. 2016, 2, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.-i.; Kim, P.K.; Ha, T.-g. Fabricating transparent nanomesh-structured hydrophobic films by nanoimprinting UV-curable fluorinated polyurethane acrylates. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2020, 30, 095006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Hwang, I.; Kim, M.; Jung, H.; Bae, H.; Lee, Y. Simple, Fast, and Scalable Reverse-Offset Printing of Micropatterned Copper Nanowire Electrodes with Sub-10 μm Resolution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 5807–5814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelin, A.; Bog, U.; Kumar, R.; Niemeyer, C.M.; Hirtz, M. Writing Behavior of Phospholipids in Polymer Pen Lithography (PPL) for Bioactive Micropatterns. Polymers 2019, 11, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasturk, O.; Sivas, A.; Karasozen, B.; Demirci, U.; Hasirci, N.; Hasirci, V. Quantification of Type, Timing, and Extent of Cell Body and Nucleus Deformations Caused by the Dimensions and Hydrophilicity of Square Prism Micropillars. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 2972–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourya, V.; Bhore, S.P.; Wandale, P.G. Multiobjective optimization of tribological characteristics of 3D printed texture surfaces for ABS and PLA Polymers. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2024, 37, 772–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Zhang, P.; Lee, K.-H.; Lee, C.-H. Friction and wear of textured surfaces produced by 3D printing. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2017, 60, 1400–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, A.; Tan, K.T. Dynamic friction performance of hierarchical biomimetic surface pattern inspired by frog toe-pad. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 2000987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, Y.; Mei, H.; Kong, Z.; Mao, M.; Cheng, L. Excellent lubrication properties of 3D printed ceramic bionic structures. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 23463–23470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Mei, H.; Chang, P.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, L. High-strength printed ceramic structures for higher temperature lubrication. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 221, 109013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Weaver, J.C.; Lauder, G.V. Biomimetic shark skin: Design, fabrication and hydrodynamic function. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 217, 1656–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Deng, J.; Cao, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, Y. High temperature wear performance of in-situ forming textured Ni60/WC/h-BN composite coatings based on laser micro-cladding. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 3470–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Jiang, P.; Jia, X.; Wang, X. 3D printing of bioinspired textured surfaces with superamphiphobicity. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 2924–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coblas, D.G.; Fatu, A.; Maoui, A.; Hajjam, M. Manufacturing textured surfaces: State of art and recent developments. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2015, 229, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsilani Kouediatouka, A.; Ma, Q.; Liu, Q.; Mawignon, F.J.; Rafique, F.; Dong, G. Design methodology and application of surface texture: A review. Coatings 2022, 12, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, M.J.; Kovalev, A.E.; Gorb, S.N. Anisotropic frictional properties in snakes. In Bioinspiration, Biomimetics, and Bioreplication; SPIE: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2012; pp. 256–261. [Google Scholar]
- Hisham, A. On surface structure and friction regulation in reptilian limbless locomotion. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 22, 115–135. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Aal, H.; Vargiolu, R.; Zahouani, H.; El Mansori, M. A study on the frictional response of reptilian shed skin. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2011, 311, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Huang, H.; Li, X.; Ren, L. Fabrication and analysis of the multi-coupling bionic wear-resistant material. J. Bionic Eng. 2010, 7, S24–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskins, J.K.; Zou, M. Designing a Bioinspired Surface for Improved Wear Resistance and Friction Reduction. J. Tribol. 2021, 143, 051107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Shi, X.; Ma, J. Tribological behavior of surface bionic rhombic-textured M50 steel containing SnAgCu and MXene-Nb2C under dry sliding conditions. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 9390–9402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Lü, T.B.; Ma, Y.H.; Wang, H.K.; Ren, L.Q.; Arnell, R.D. Two-body abrasive wear of the surfaces of pangolin scales. J. Bionic Eng. 2007, 4, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Shan, H.; Zhou, H.; Chen, D.; Li, X.; Xia, W.; Ren, L. Friction and wear behaviors of compacted graphite iron with different biomimetic units fabricated by laser cladding. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 7699–7706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Shi, Z. Biomimetic anti-adhesive surface microstructures on electrosurgical blade fabricated by long-pulse laser inspired by pangolin scales. Micromachines 2019, 10, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Deng, J.; Wang, R.; Sun, Q.; Meng, Y.; Wu, J. Tribological properties of TiO2-MoS2 soft-hard alternate films deposited by electrohydrodynamic atomization with a bionic mask. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 647, 128971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Yu, X.; Cui, X.; Chen, D.; Shen, T.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Chen, H.; Fang, R.; Dong, Z. Surface Modification of 3D Biomimetic Shark Denticle Structures for Drag Reduction. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2417337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Hua, M.; Liu, Z. The biomimetic shark skin optimization design method for improving lubrication effect of engineering surface. J. Tribol. 2014, 136, 031703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Deng, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, J.; Wu, F. Tribological behavior of ZrO2/WS2 coating surfaces with biomimetic shark-skin structure. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 21759–21767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauder, G.V.; Wainwright, D.K.; Domel, A.G.; Weaver, J.C.; Wen, L.; Bertoldi, K. Structure, biomimetics, and fluid dynamics of fish skin surfaces. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2016, 1, 060502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wei, X.; Meng, K.; Zhong, L.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X. Bio-Tribology Properties of Bionic Carp Scale Morphology on Ti6A14V Surface. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 281, 012060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Yuan, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Feng, S.; Xie, Y.; Leng, D.; Tian, X. A brief review of bio-inspired surface technology and application toward underwater drag reduction. Ocean. Eng. 2020, 199, 106962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, B.; Gorb, S.; Manoonpong, P. Nature’s All-in-One: Multitasking Robots Inspired by Dung Beetles. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2408080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, C.; Zhao, G.; Chu, X.; Zhou, W.; Long, Y.; Lian, Y. Design, preparation and cutting performance of bionic cutting tools based on head microstructures of dung beetle. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 58, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Lv, J.; Meng, Z.; Feng, K.; Cai, J. Load-reduction mechanism of microstructure broach inspired by dung beetle surface. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 64, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, H.; Li, H.; Sui, Q. Effect of the orientation of laser stripes on the abrasion resistance of biomimetic laser textured surfaces. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 107, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Zhou, T.; Sui, Q.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.H. Study on the relationship between intervals among laser stripes and the abrasion resistance of biomimetic laser textured surfaces. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 104, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badler, D.; Kasem, H. Synergetic effect of the simultaneous use of different biomimetic adhesive micro-structures on tribological performances. Biotribology 2020, 22, 100124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.K.; Behmer, S.T.; Marquess, R.; Yegin, C.; Scholar, E.A.; Akbulut, M. Structural, tribological, and mechanical properties of the hind leg joint of a jumping insect: Using katydids to inform bioinspired lubrication systems. Acta Biomater. 2017, 62, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atahan, M.G.; Maskery, I.; Ashcroft, I.; Apalak, M.K.; Pappas, A. Effect of bio-mimicked surface texturing on the shear strength of additively manufactured metal single-lap joints: An innovative approach. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2025, 174, 109460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Sun, Y.; Bi, B.; Wang, T.; Shi, L.; Wang, X. Bio-and bioinspired textures for enhancing friction forces. Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop. 2025, 13, 013003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, S.B.; Diehl, D. Toe pad morphology and mechanisms of sticking in frogs. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1980, 13, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federle, W.; Barnes, W.; Baumgartner, W.; Drechsler, P.; Smith, J. Wet but not slippery: Boundary friction in tree frog adhesive toe pads. J. R. Soc. Interface 2006, 3, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsipenyuk, A.; Varenberg, M. Use of biomimetic hexagonal surface texture in friction against lubricated skin. J. R. Soc. Interface 2014, 11, 20140113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Ji, W.; Zhou, Z. Investigation of reciprocating friction characteristics between different bionic surfaces of prosthesis materials and skin. Biosurface Biotribol. 2019, 5, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, X. Biomimetic design of elastomer surface pattern for friction control under wet conditions. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2013, 8, 046001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, A.; Haq, M.I.U.; Raina, A.; Vohra, K.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, S.M. Natural systems and tribology-analogies and lessons. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 5228–5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Shi, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Huang, Q. Response Surface Optimization Design of G20CrMo Composite Surface Cylinder Texture Parameters and Analysis of Tribological Performance. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2024, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Peng, Z.; Shi, X.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, K.; Huang, Q. Optimization of textured parameters to improve the tribological behavior of TC4-based bionic coating using RSM. Tribol. Trans. 2022, 65, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Yi, P.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Dong, G.; Zhang, Y. Effects of texture spacing and bulges of bionic sinusoidal texture on the adhesion properties and fracture mechanism of plasma-sprayed coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 393, 125772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Lu, W.; Shi, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Chen, W. Effects of Ni3Al matrix bio-inspired shell-like composite surface structure on interfacial tribological behaviors. Tribol. Int. 2022, 170, 107522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Shi, X.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, K.; Huang, Q.; Wu, C.; Ma, J.; Shu, J. Coupling effects of bionic textures with composite solid lubricants to improve tribological properties of TC4 alloy. Tribol. Int. 2022, 173, 107691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B.; Nosonovsky, M.; Jung, Y.C. Lotus effect: Roughness-induced superhydrophobic surfaces. In Nanotribology and Nanomechanics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germnay, 2008; pp. 995–1072. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Wood, R.J.; Xue, Q. From natural lotus leaf to highly hard-flexible diamond-like carbon surface with superhydrophobic and good tribological performance. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 2258–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.A.; Yoon, E.-S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.; Jeong, H.E.; Suh, K.Y. Replication of surfaces of natural leaves for enhanced micro-scale tribological property. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2007, 27, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celia, E.; Darmanin, T.; de Givenchy, E.T.; Amigoni, S.; Guittard, F. Recent advances in designing superhydrophobic surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 402, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xi, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, N.; Xia, F.; Jiang, L. Petal effect: A superhydrophobic state with high adhesive force. Langmuir 2008, 24, 4114–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Sun, Y.; Gleichauf, K.; Lou, J.; Li, Q. Nanostructure on taro leaves resists fouling by colloids and bacteria under submerged conditions. Langmuir 2011, 27, 10035–10040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, R.; Bhandaru, N.; Mukherjee, R.; Chakraborty, S. Tunable hydrodynamic characteristics in microchannels with biomimetic superhydrophobic (lotus leaf replica) walls. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 3451–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.T.; Rodak, D.; Wong, C.; Hayden, C. Effects of micro-and nano-structures on the self-cleaning behaviour of lotus leaves. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, K.; Bhushan, B.; Jung, Y.C.; Barthlott, W. Fabrication of artificial Lotus leaves and significance of hierarchical structure for superhydrophobicity and low adhesion. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 1386–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Liu, W. Biomimic from the superhydrophobic plant leaves in nature: Binary structure and unitary structure. Plant Sci. 2007, 172, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, E.-S.; Singh, R.A.; Kong, H.; Kim, B.; Kim, D.-H.; Jeong, H.E.; Suh, K.Y. Tribological properties of bio-mimetic nano-patterned polymeric surfaces on silicon wafer. Tribol. Lett. 2006, 21, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yao, W.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Wan, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, L.; Tang, Y. A strongly hydrophobic and serum-repelling surface composed of CrN films deposited on laser-patterned microstructures that was optimized with an orthogonal experiment. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 391, 125708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Shi, X.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wu, C. Optimization of bionic textured parameter to improve the tribological performance of AISI 4140 self-lubricating composite through response surface methodology. Tribol. Int. 2021, 161, 107104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Huang, W.; Wang, X. Biomimetic surface design for ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene to improve the tribological properties. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2012, 226, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, G.; Wang, G.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, C.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, T. Electrochemical corrosion and anisotropic tribological properties of bioinspired hierarchical morphologies on Ti-6Al-4V fabricated by laser texturing. Tribol. Int. 2019, 134, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Y.a.; Zhang, W.; Bao, Y. Lubrication Performance of Compound Microtexture Friction Pairs. Mater. Perform. Charact. 2024, 13, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Deng, J.; Bao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J. Effect of composite microtextures on the tribological properties of triangular guide rails. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Deng, J.; Ma, K.; Wang, R.; Wu, J.; Lu, Y. Thick-film printing of TaS2 soft films on the textured surface to enhance wear life. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 476, 130231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Deng, J.; Cao, S.; Ma, K.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, Y. Laser micro-cladding in situ forming textured surface to improve the tribological performance. Wear 2024, 550, 205422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özel, T.; Biermann, D.; Enomoto, T.; Mativenga, P. Structured and textured cutting tool surfaces for machining applications. CIRP Ann. 2021, 70, 495–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yuan, P.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, X. Experimental investigation of different morphology textured ceramic tools by in-situ formed for the dry cutting. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2020, 17, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, M.; Liu, X.; Liu, K. Effect of conical micro-grooved texture on tool–chip friction property and cutting performance of WC-TiC/Co cemented carbide tools. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2019, 233, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Guo, Y.; Guo, J.; Ming, P. Performance analysis of laser-induced biomimetic ceramic tools in interrupted cutting. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 177, 105589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, J. Evaluation of the machinability of titanium alloy using a micro-textured ball end milling cutter. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 98, 2083–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, B.; Wang, S. Finite element simulation analysis of bionic ball-end milling cutter. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 103, 3151–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Xie, F.; Wu, F.; Yan, Q. Research on bionic design of cylindrical milling cutter based on the curvilinear configuration of the rake face of beaver teeth. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 130, 4905–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Chen, K.; Liu, X.; Zhang, K.; Ding, X. Research of bamboo rat tooth bionic bit structural design and cutting mechanism for CFRP drilling. Compos. Struct. 2024, 334, 117950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.; Chen, X.; Xie, C.; Long, Y.; Lin, F.; Zhou, W.; Chu, X. Cooling and crack suppression of bone material drilling based on microtextured bit modeled on dung beetle. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2023, 36, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Sun, K.; Ren, W.; Zhang, J.; Han, Z. Synergistic improvement of grinding fluid utilization and workpiece surface quality using combinatorial bionic structured grinding wheels. J. Manuf. Process 2024, 130, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Yan, K.; Guo, J. Bio-inspired fabrication, mechanical characterization and cutting performance evaluation of Al2O3/TiC micro-nano-composite ceramic with varying microscopic surfaces. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 8286–8299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Guo, J. Biomimetic fabrication, mechanical behavior and interrupted turning performance of the microscopic surface structures of Al2O3/TiC micro-nano-composite ceramic. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 811, 152012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.M.; Lee, I.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, B.H.; Park, H.W. Influence of a micropatterned insert on characteristics of the tool–workpiece interface in a hard turning process. J. Mater. Process. Technol 2016, 229, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alok, A.; Kumar, S.; Pandey, S.M.; Kumar, A. Review on the effect of surface textured tool in the field of machining. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 2024, 10, 814–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugihara, T.; Enomoto, T. Performance of cutting tools with dimple textured surfaces: A comparative study of different texture patterns. Precis. Eng. 2017, 49, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Lei, X.B. The Influence of Bionic Micro-Texture’s Surface on Tool’s Cutting Performance. Key Eng. Mater. 2016, 693, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yin, K.; Xiao, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Duan, J.A.; He, J. Laser fabrication of bioinspired gradient surfaces for wettability applications. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2001610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Jelagin, D.; Chen, F.; Gilabert, F.A.; Guarin, A. Effects of surface texture deterioration and wet surface conditions on asphalt runway skid resistance. Tribol. Int. 2021, 153, 106589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aal, H.A. Functional surfaces for tribological applications: Inspiration and design. Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop. 2016, 4, 043001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Texture Preparation Methods | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Laser ablation [123] | Fast processing speed, flexible operation and good controllability | The heating effect in both methods may lead to problems such as material degradation, and the heat-affected zone will affect the surface topography and mechanical properties of the machined area |
| Laser interference [87] | Creating textures in high resolution | |
| Laser impact processing [88] | Produces a surface hardening effect to enhance wear resistance | Need to manufacture microscopic features one by one, the process is less efficient |
| Reactive ion etching [8,101,102] | Fast etching process and high quality of the prepared textures | This technique results in more visible damage to the material surface, less precise control of the ion beam and harsh experimental environments and expensive equipment |
| Soft lithography [104,105] | Relatively low cost, easier set-up, higher efficiency and more accurate pattern resolution | Need to use other methods to create stamp masters, such as photolithography or electron beam lithography, and more difficult to create masters for animal body surface patterns |
| 3D printing [114] | Finer parts, patterns and moulds can be constructed and are faster, more flexible and cheaper than traditional techniques | The materials that can be used for 3D printing are very limited, and if the surface of the object to be manufactured is rounded, this can cause deviations in accuracy |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sheng, Z.; Zhu, H.; He, Y.; Shao, B.; Sheng, Z.; Wang, S. Tribological Effects of Surface Biomimetic Micro–Nano Textures on Metal Cutting Tools: A Review. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10050283
Sheng Z, Zhu H, He Y, Shao B, Sheng Z, Wang S. Tribological Effects of Surface Biomimetic Micro–Nano Textures on Metal Cutting Tools: A Review. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(5):283. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10050283
Chicago/Turabian StyleSheng, Zhenwen, Hui Zhu, Yu He, Bo Shao, Zhi Sheng, and Suqin Wang. 2025. "Tribological Effects of Surface Biomimetic Micro–Nano Textures on Metal Cutting Tools: A Review" Biomimetics 10, no. 5: 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10050283
APA StyleSheng, Z., Zhu, H., He, Y., Shao, B., Sheng, Z., & Wang, S. (2025). Tribological Effects of Surface Biomimetic Micro–Nano Textures on Metal Cutting Tools: A Review. Biomimetics, 10(5), 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10050283






