Mussel-Inspired Hydrogel Applied to Wound Healing: A Review and Future Prospects
Abstract
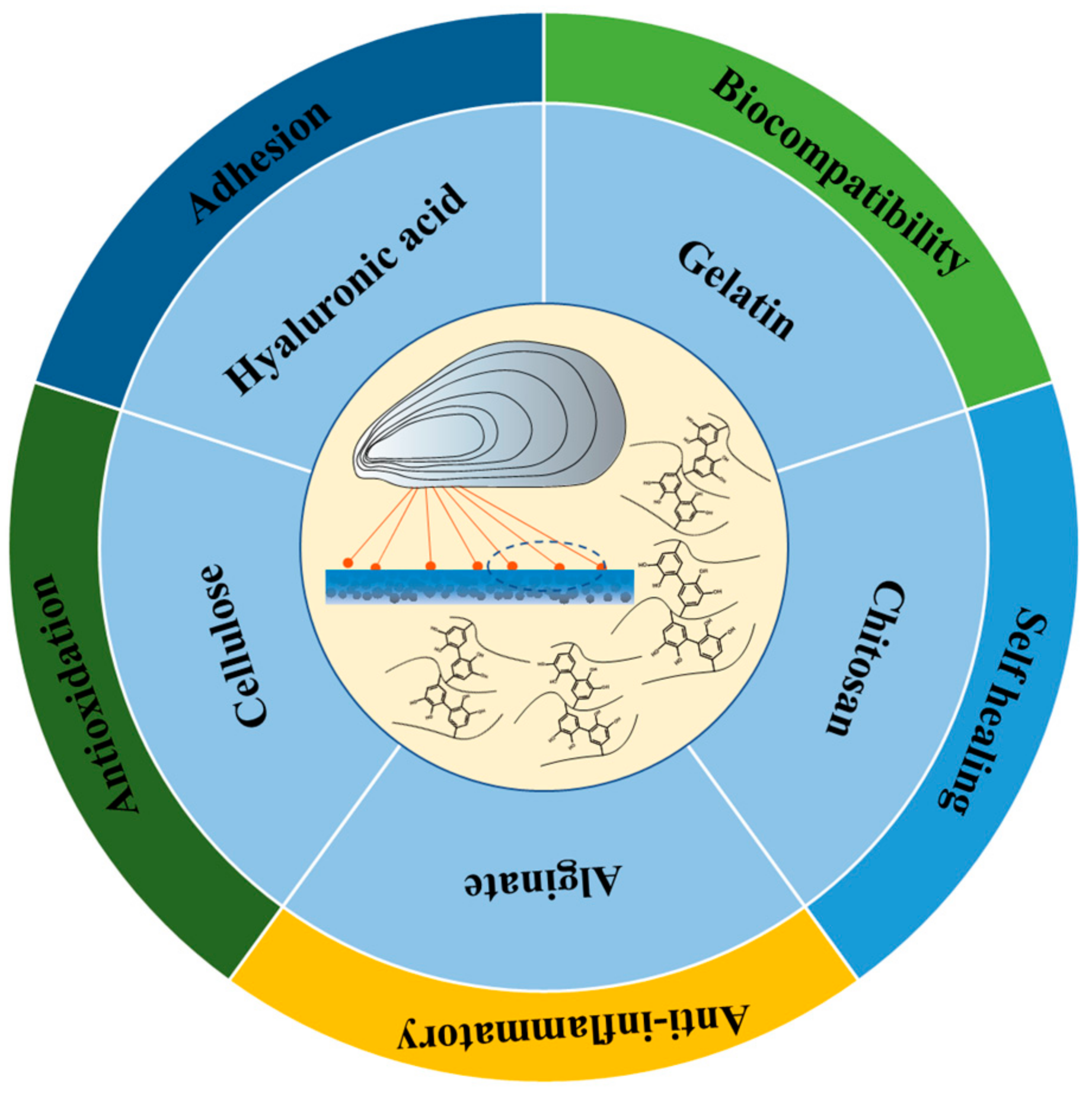
1. Introduction
2. Mussel-Inspired Hydrogel in Wound Repair
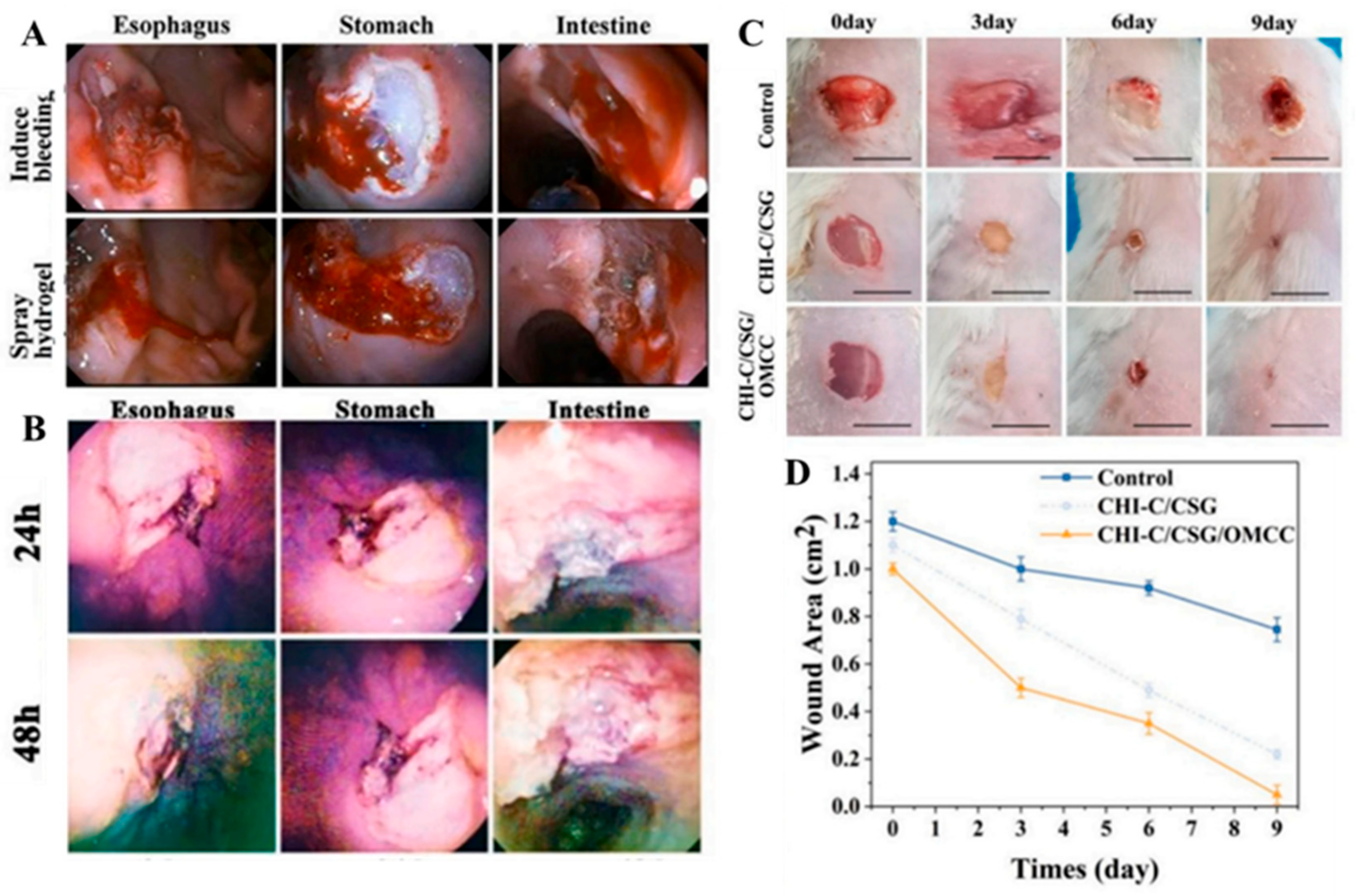
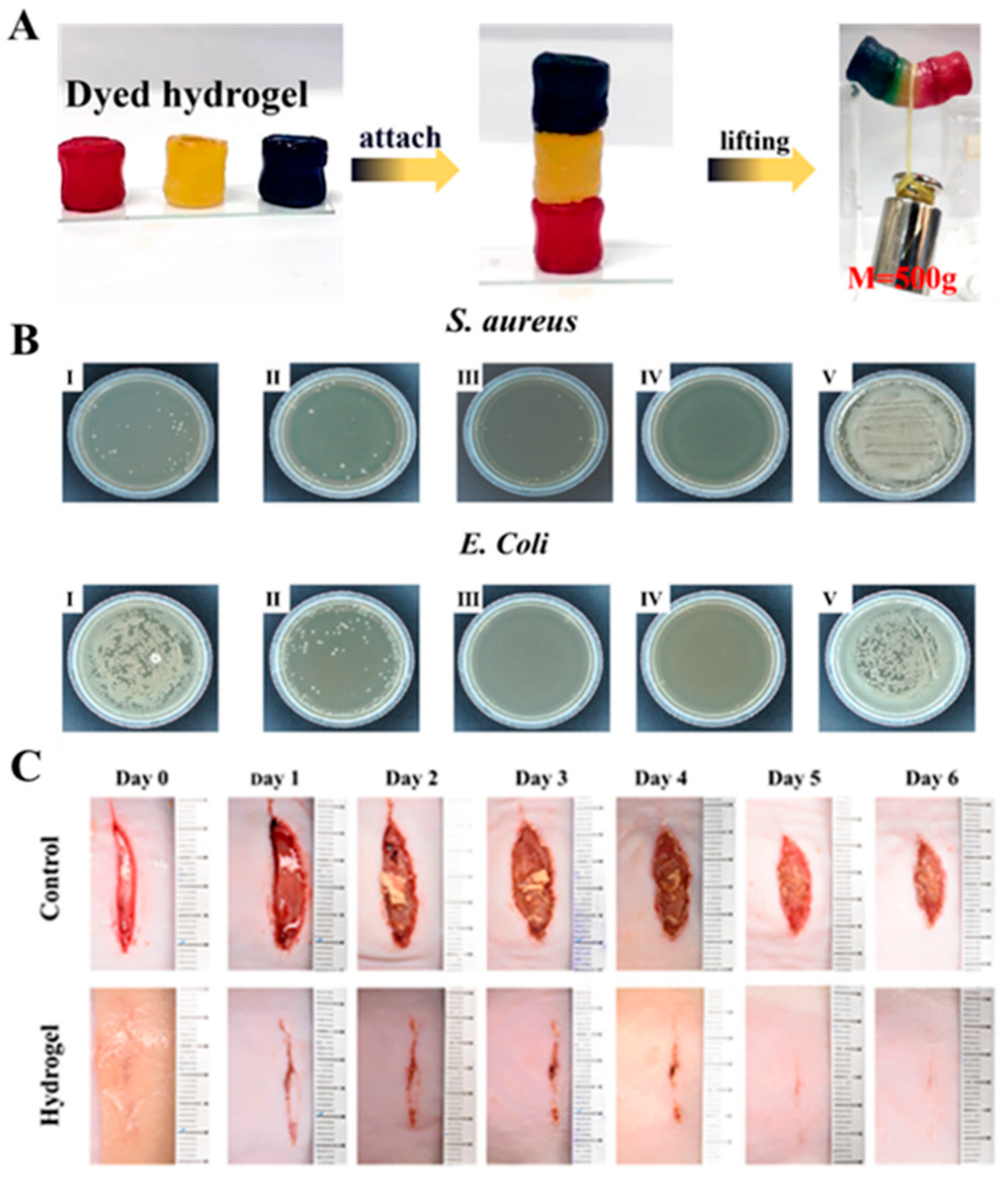
2.1. Chitosan Based Mussel-Inspired Hydrogel
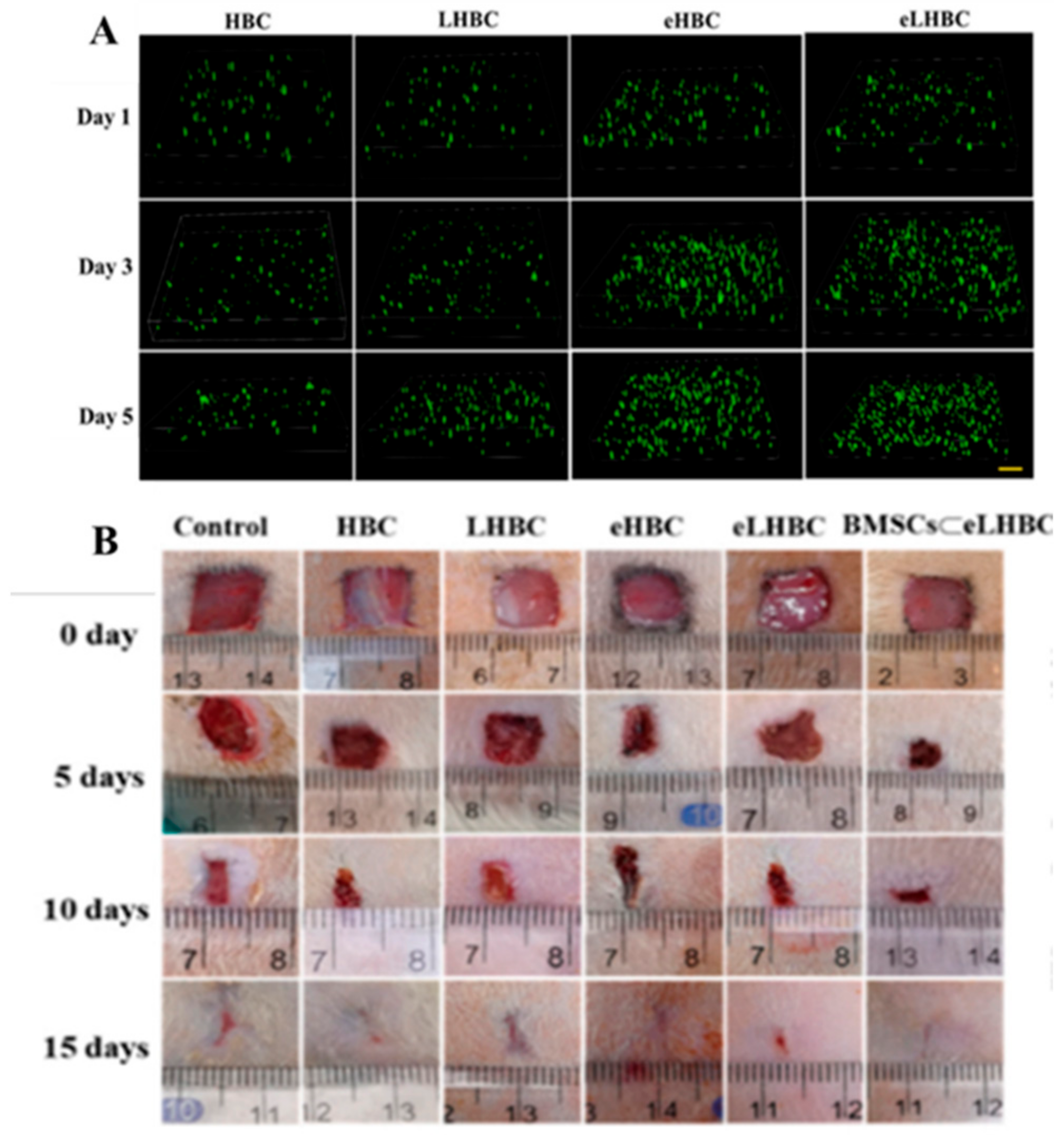
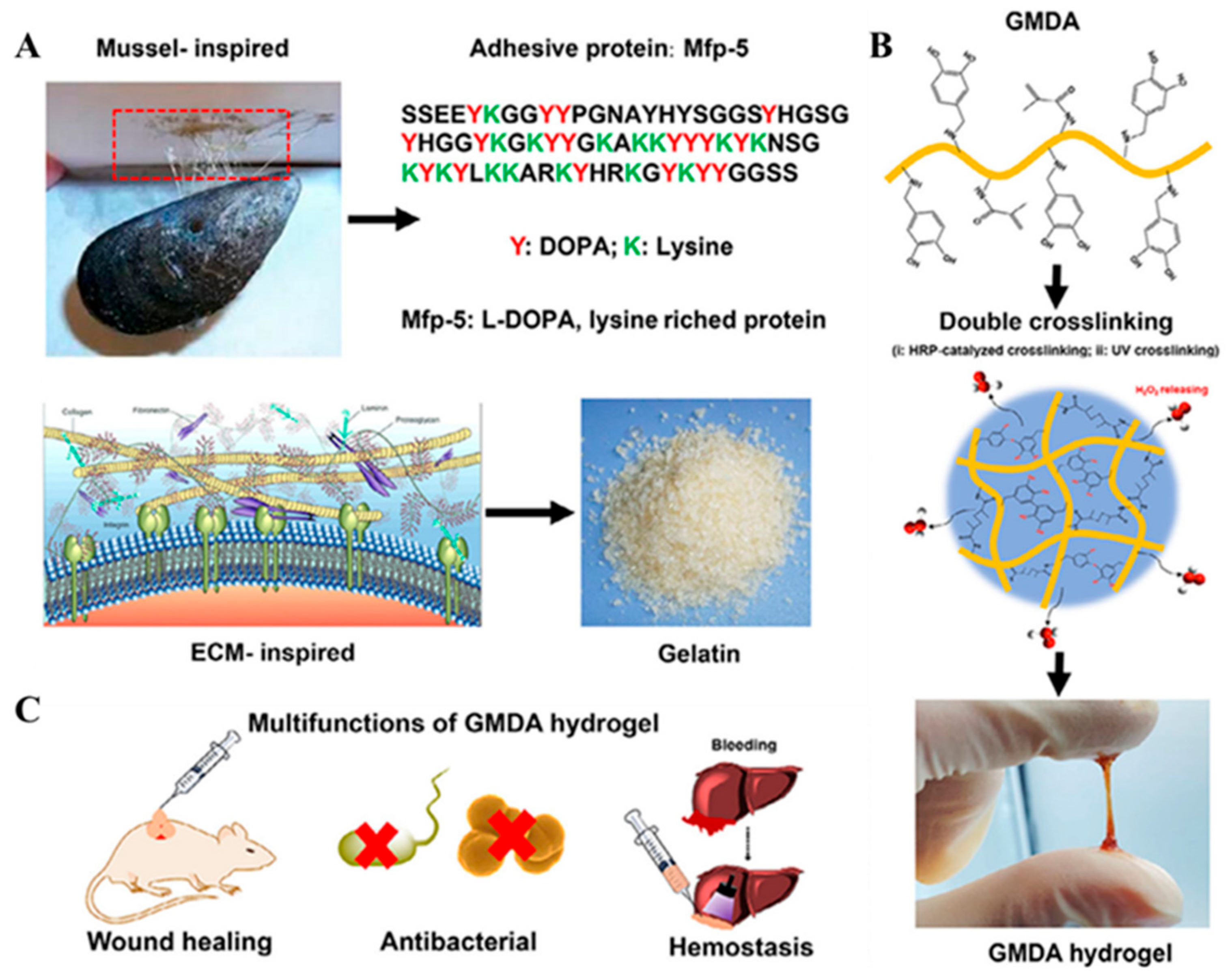
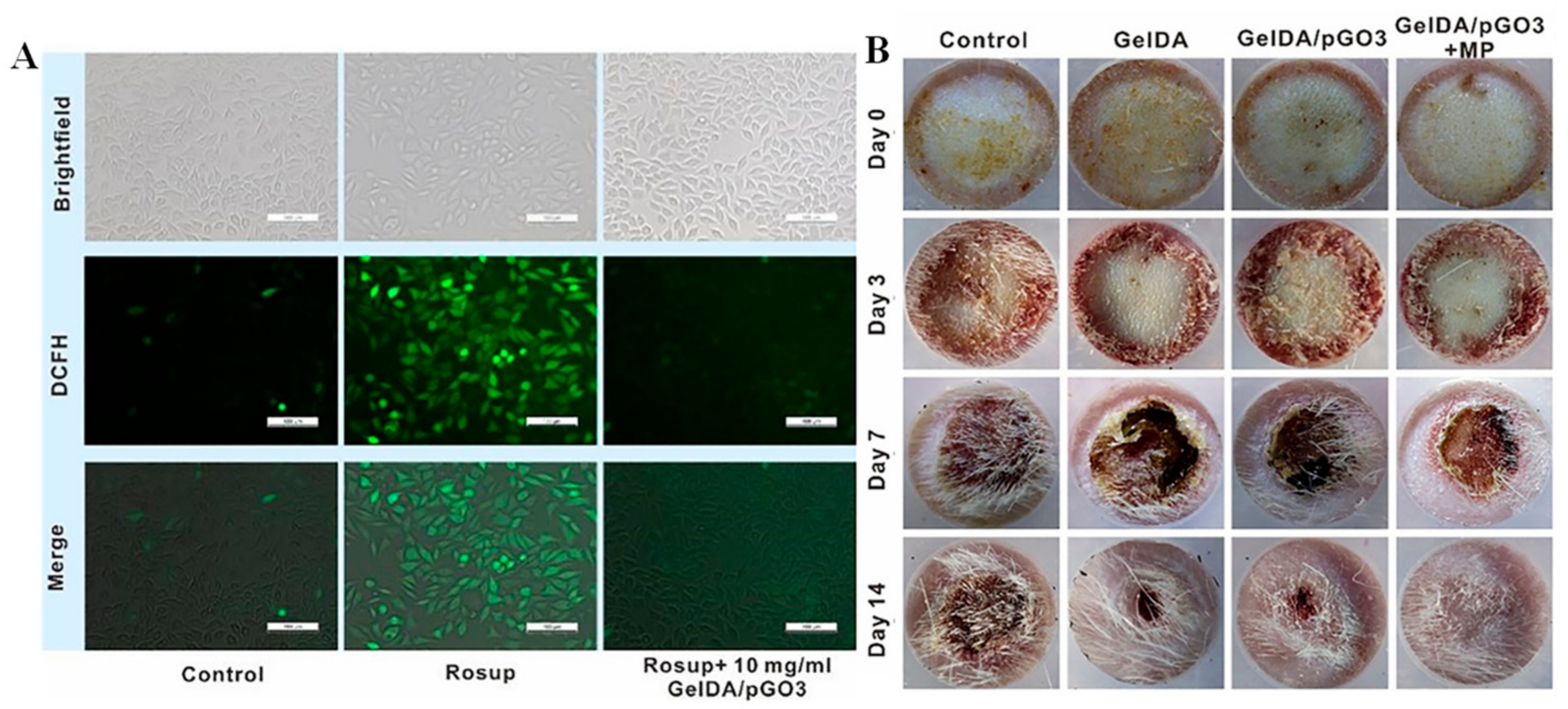
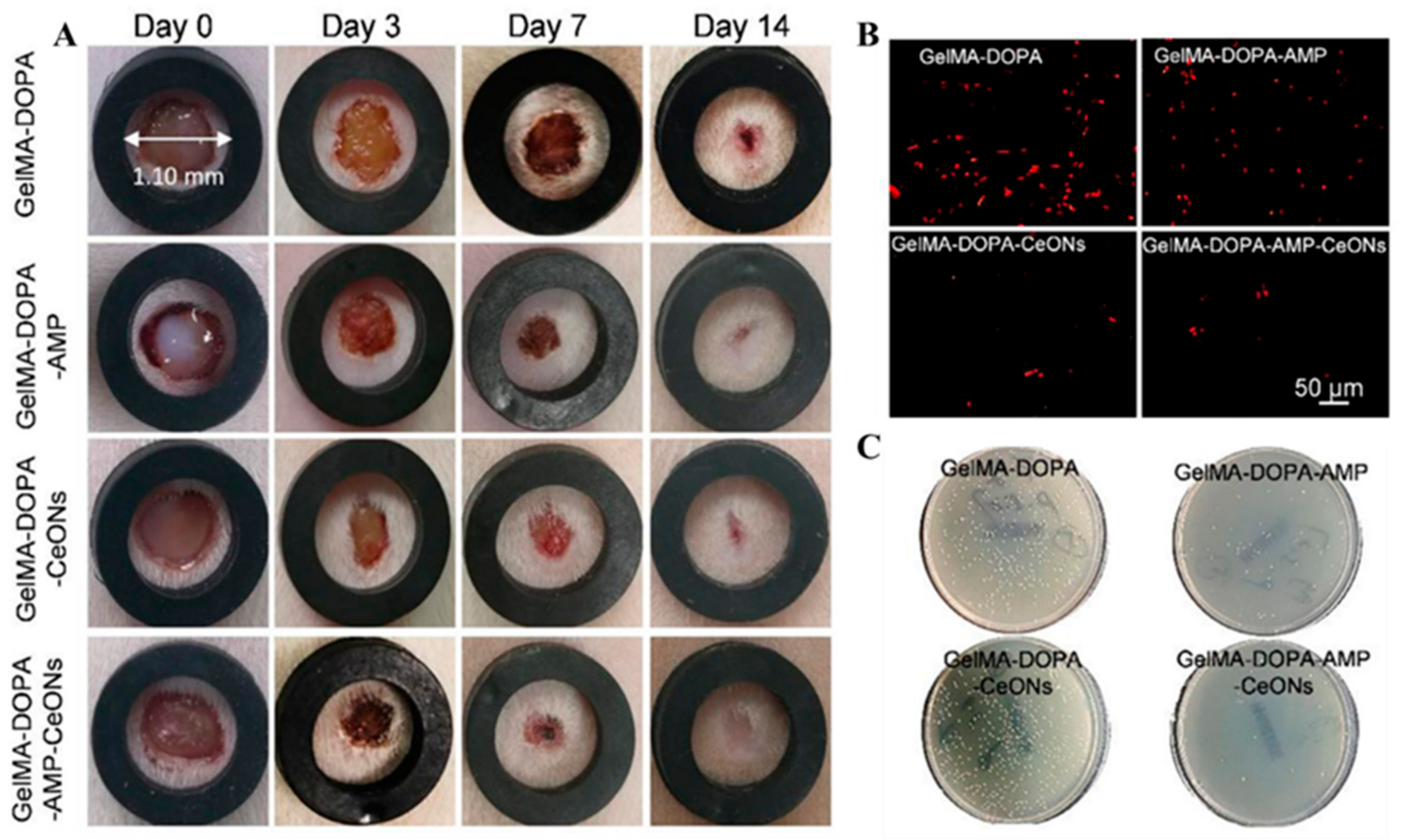
2.2. Gelatin Based Mussel-Inspired Hydrogel
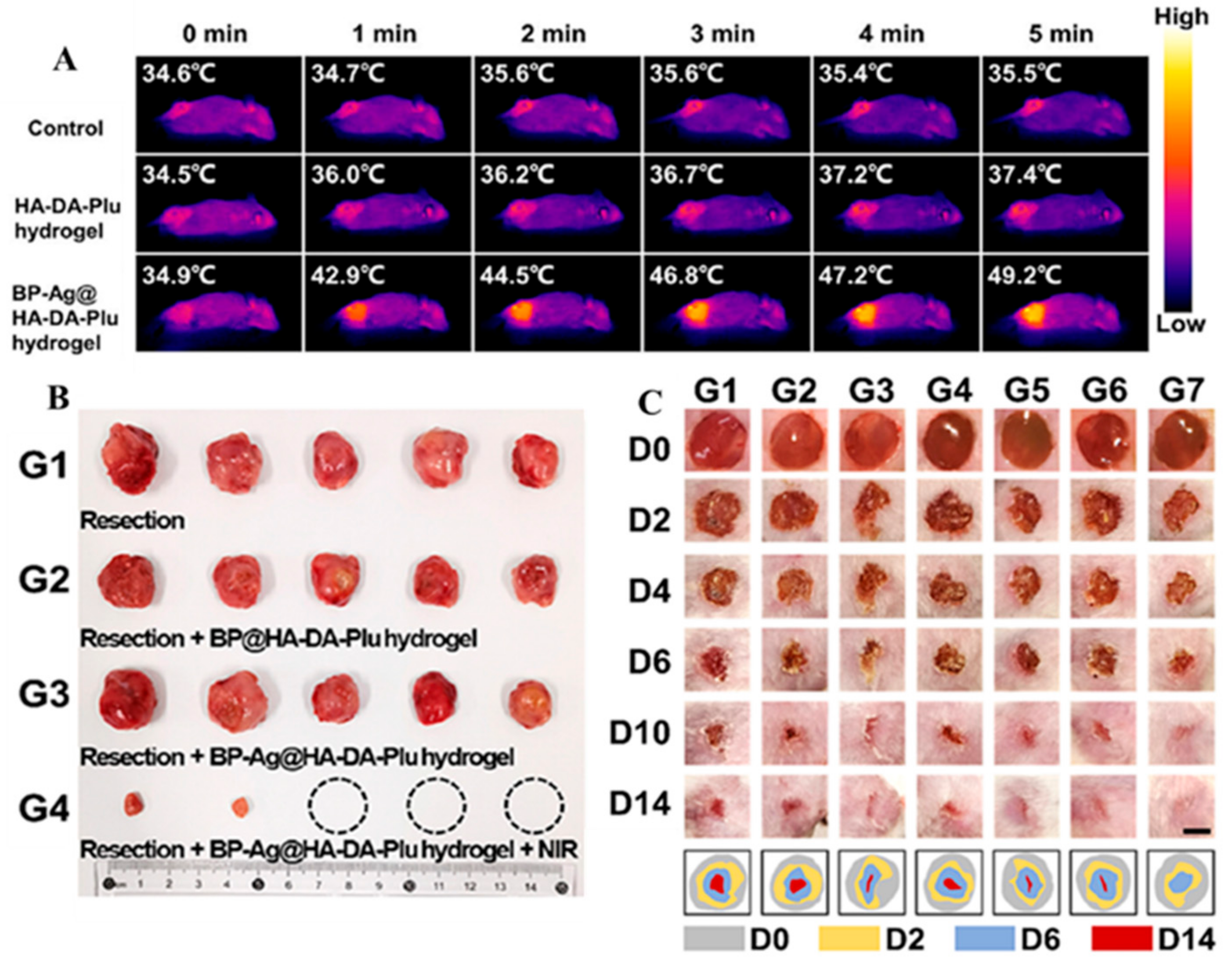
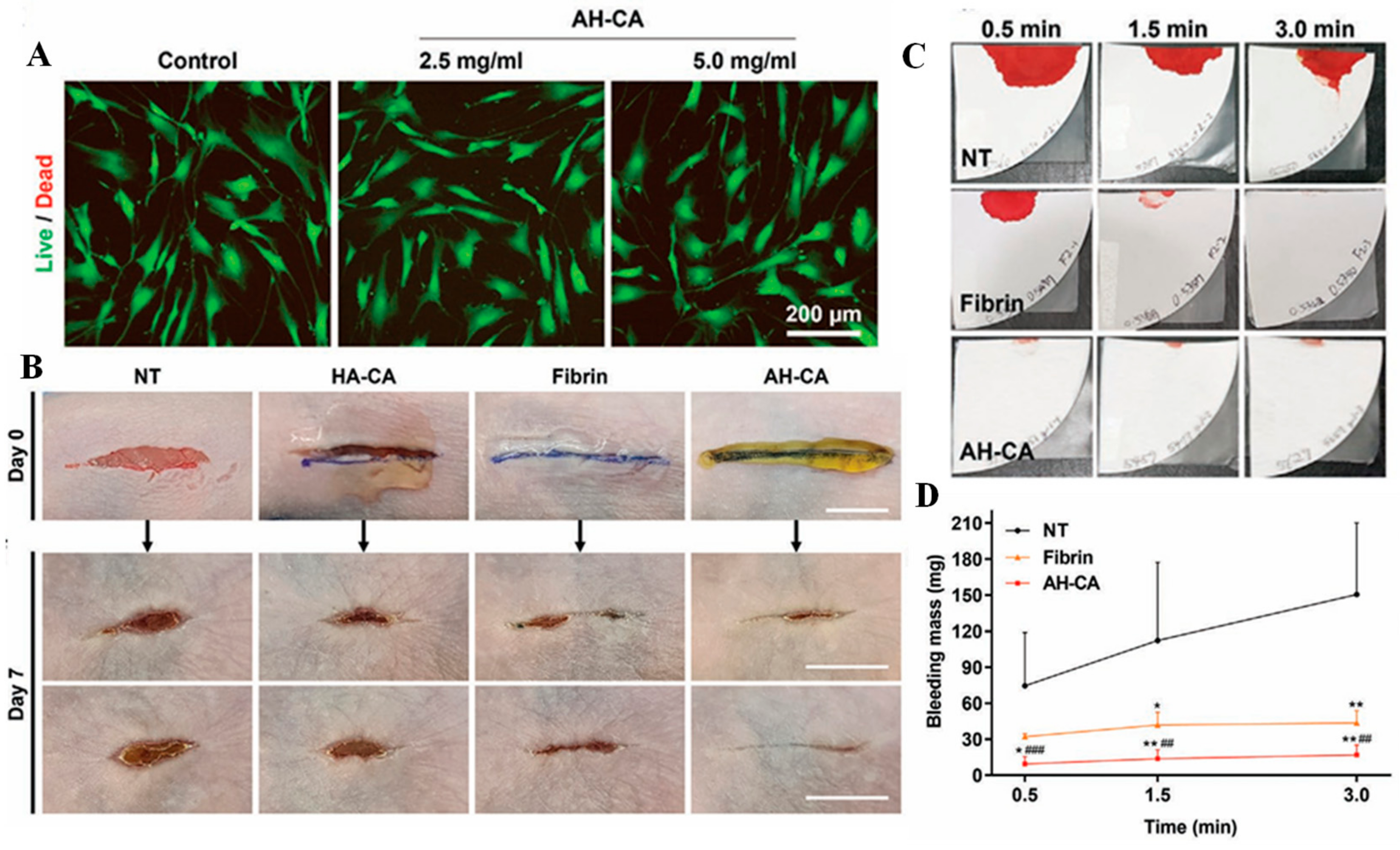
2.3. Hyaluronic Acid-Based Mussel-Inspired Hydrogel
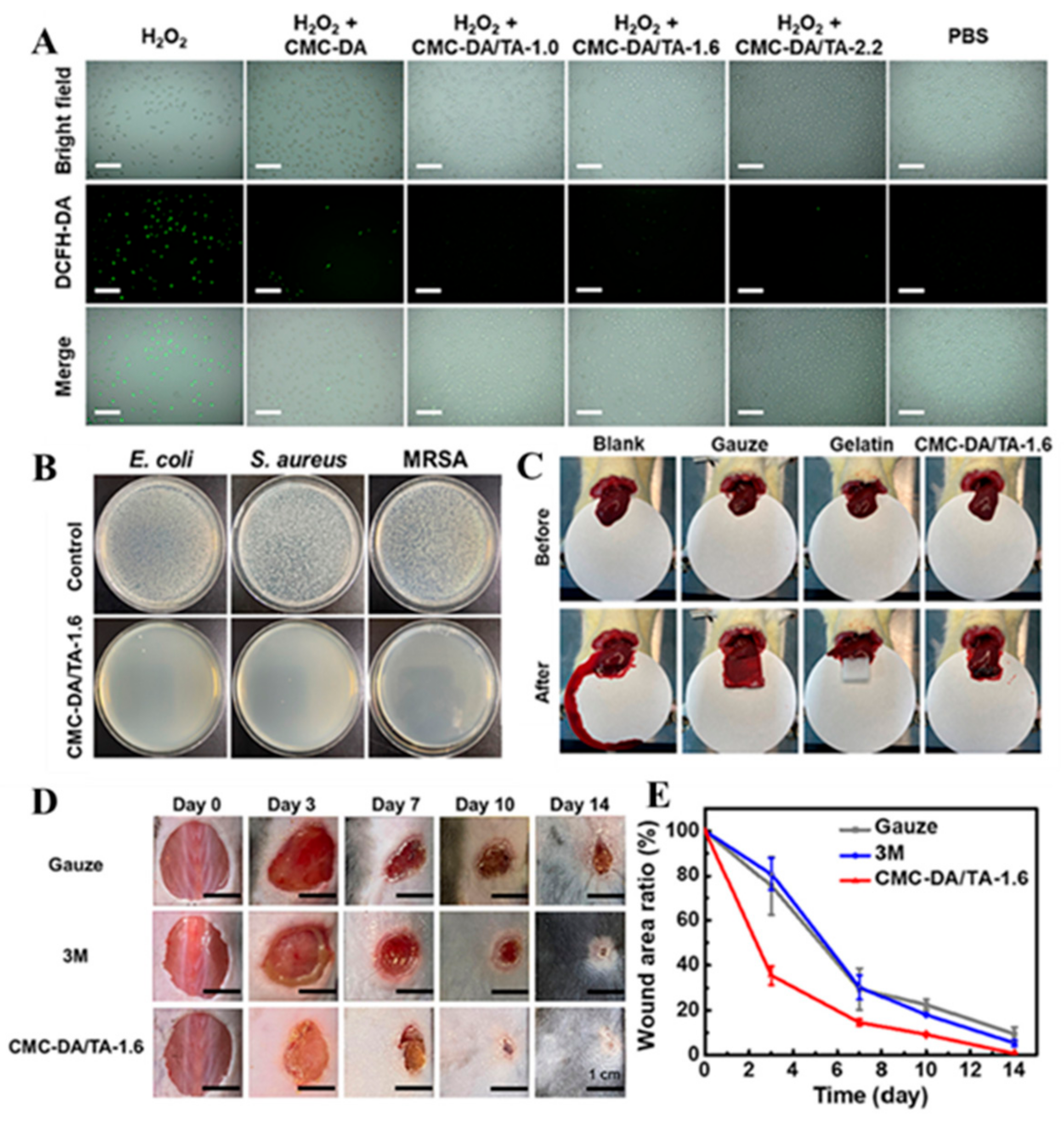
2.4. Cellulose-Based Mussel-Inspired Hydrogel
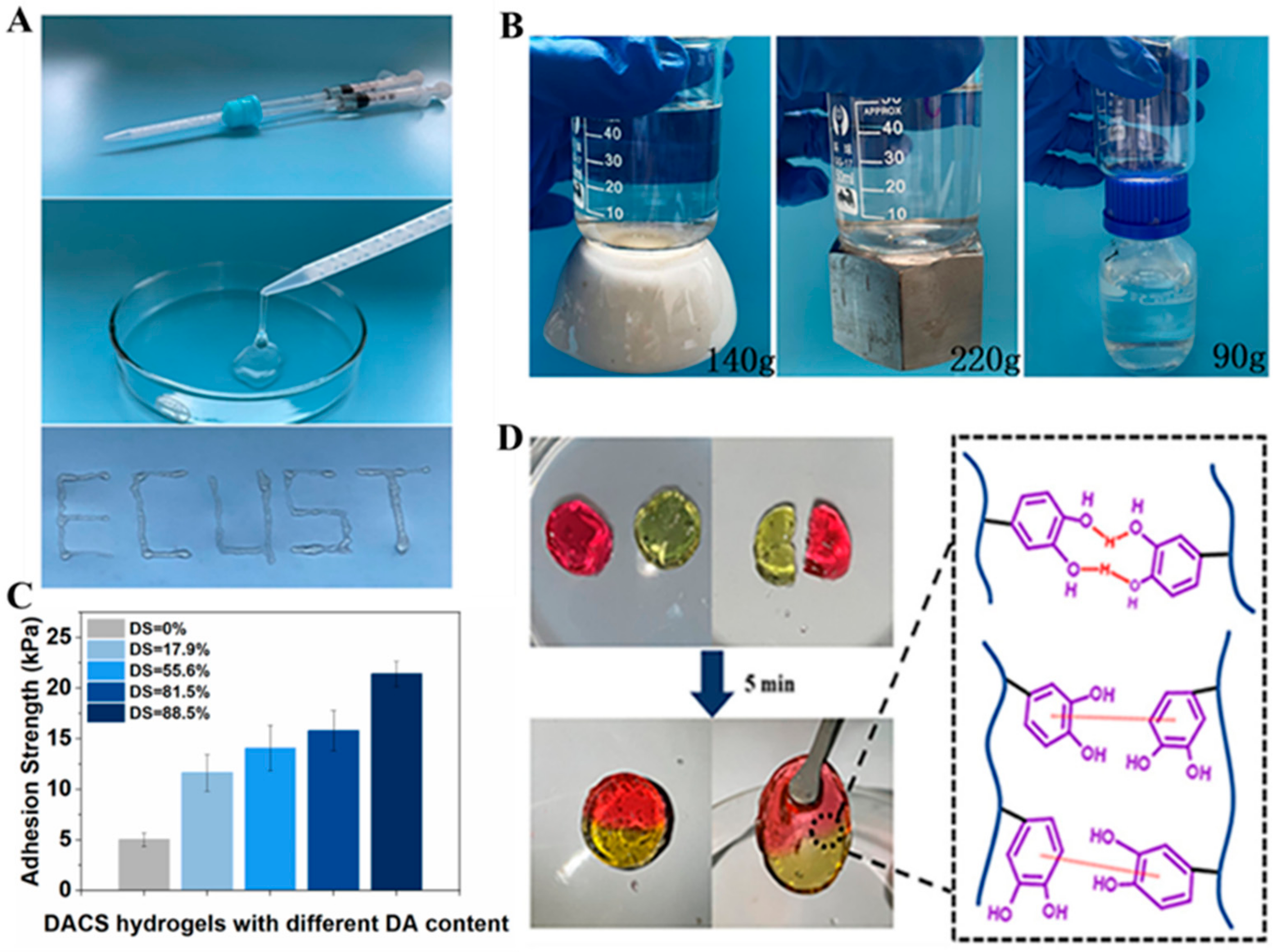
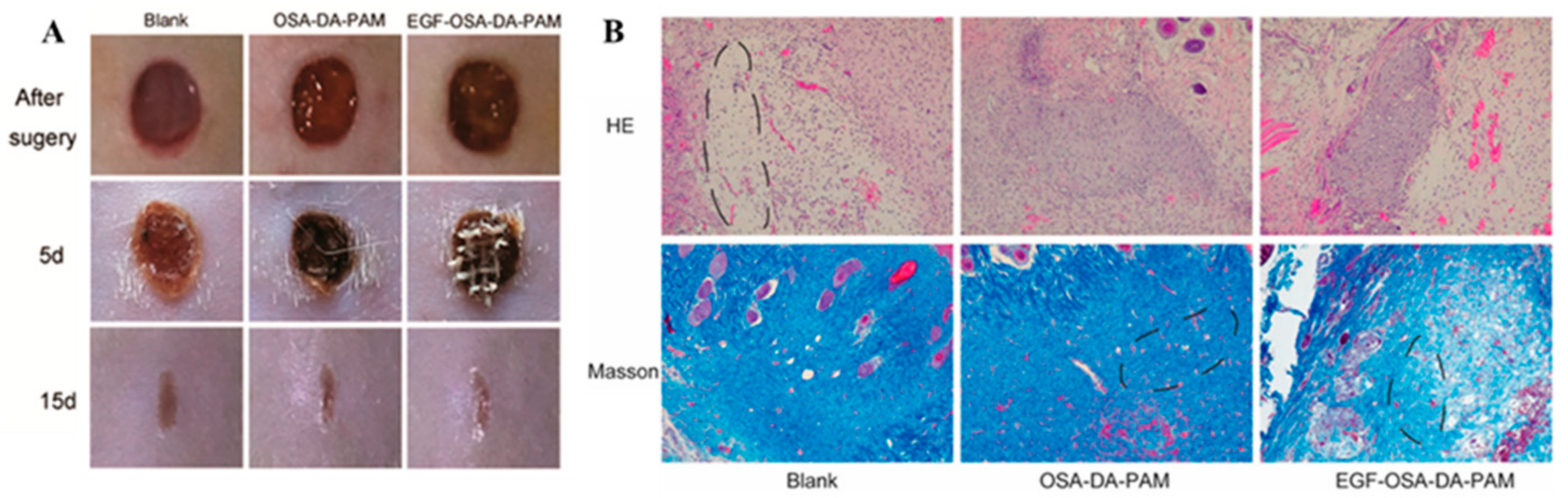
2.5. Alginate-Based Mussel-Inspired Hydrogel
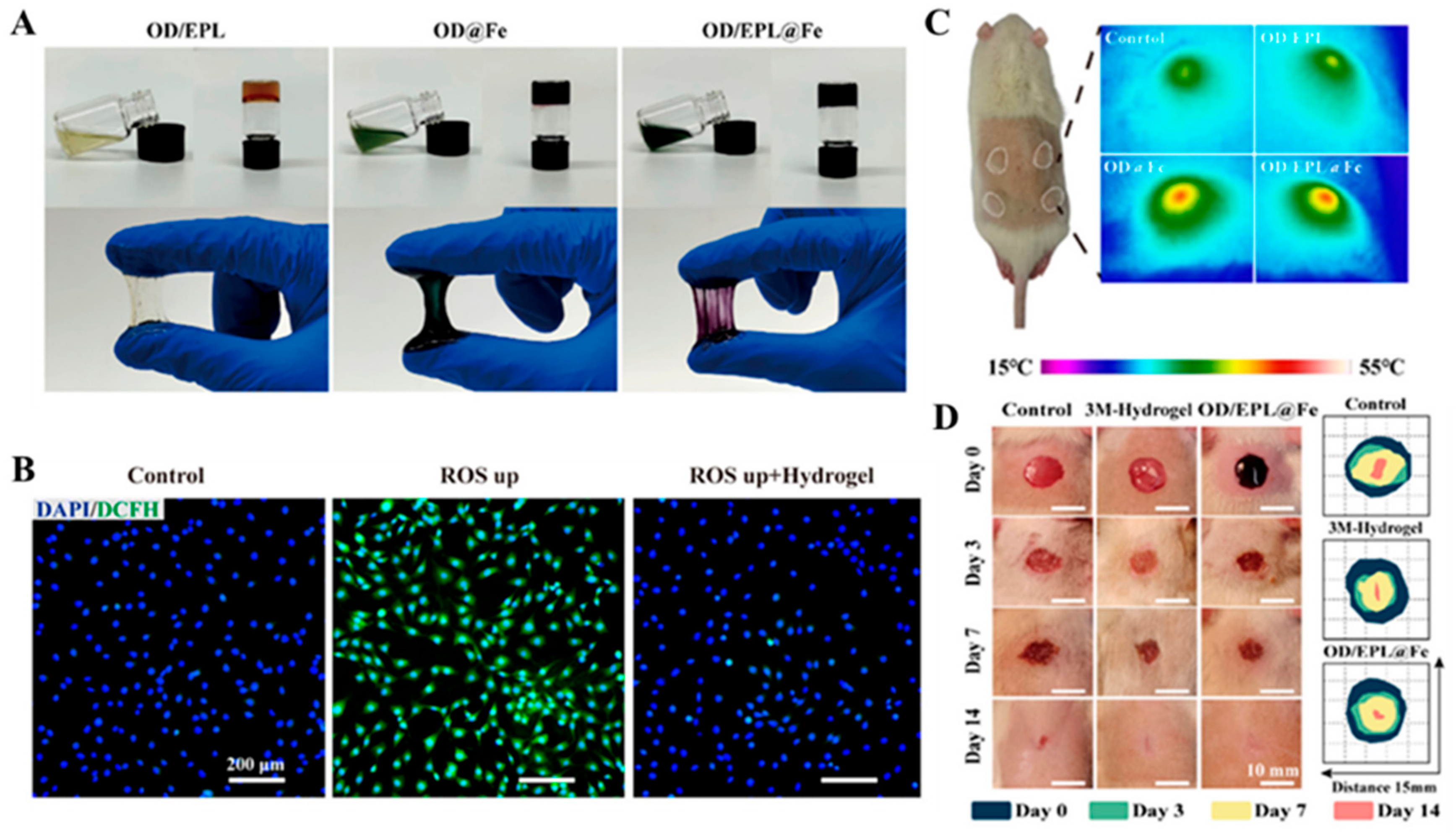
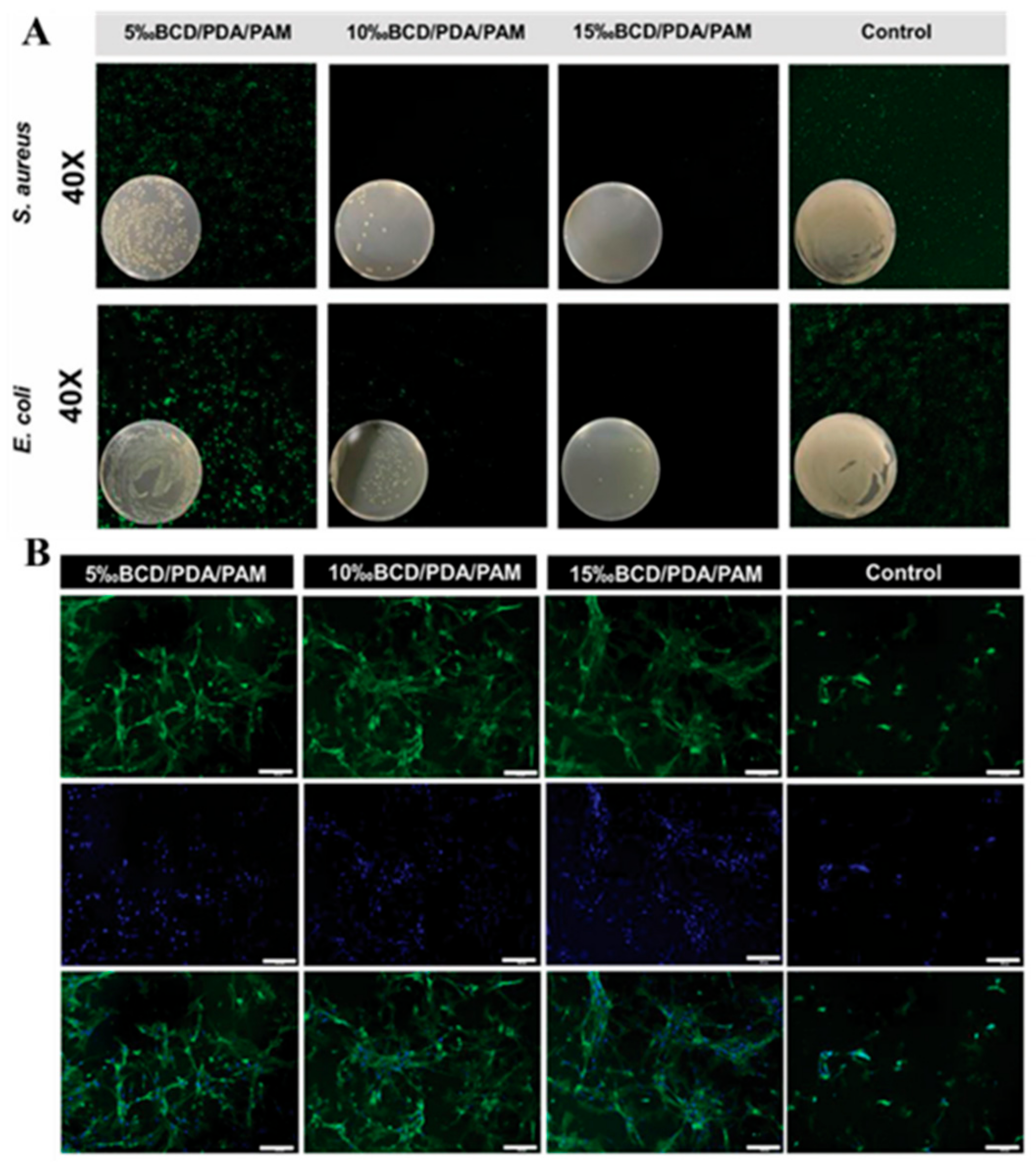
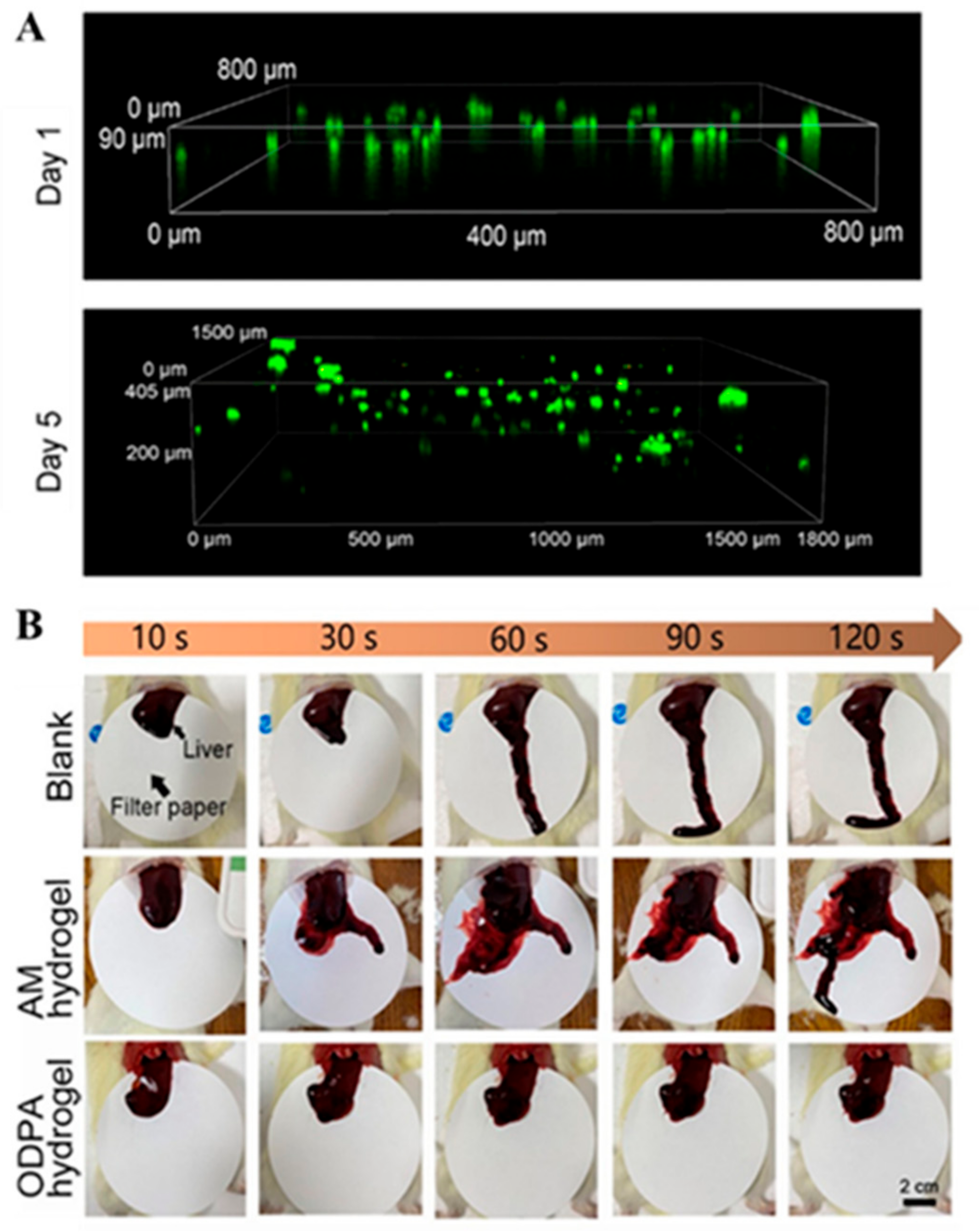
2.6. Other Mussel-Inspired Hydrogels
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.W.; Song, K.I.; Lee, J.; Park, S.; Huh, H.; Choi, G.; Shin, H.H.; Cha, H.J. A Customizable Proteinic Bioadhesive Patch with Water-Switchable Underwater Adhesiveness, Adjustable Biodegradability, and Modifiable Stretchability for Healing Diverse Internal Wounds. Adv. Mater. 2023, 36, 2310338. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, J.; Xu, H.; Zhong, Y.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Z. Surface modification of patterned electrospun nanofibrous films via the adhesion of DOPA-bFGF and DOPA-ponericin G1 for skin wound healing. Mater. Des. 2020, 188, 108432. [Google Scholar]
- Göksel, Y.; Akdogan, Y. Increasing spontaneous wet adhesion of DOPA with gelation characterized by EPR spectroscopy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 228, 124–130. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, J.; Woo, H.T.; Lee, S.; Cha, H.J. Visible light-induced simultaneous bioactive amorphous calcium phosphate mineralization and in situ crosslinking of coacervate-based injectable underwater adhesive hydrogels for enhanced bone regeneration. Biomaterials 2025, 315, 122948. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, L.; Yang, C.; Sun, X.; Yue, D.; Wang, W.; Chen, H.; Yang, H.; Yang, L. Antifreeze proteins and surface-modified cellulose nanocrystals for designing anti-freezing conductive hydrogel sensors. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 350, 123056. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, D.; Shuai, T.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z.; Ren, F.; Fang, L.; Wang, K.; Xie, C.; Lu, X. Mussel-Inspired Redox-Active and Hydrophilic Conductive Polymer Nanoparticles for Adhesive Hydrogel Bioelectronics. Nano-Micro Lett. 2020, 1, 169. [Google Scholar]
- Efremenko, E.; Aslanli, A.; Stepanov, N.; Senko, O.; Maslova, O. Various Biomimetics, Including Peptides as Antifungals. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanieck, K.; Hamann, L.; Bartz, M.; Uttich, E.; Hollermann, M.; Drack, M.; Beismann, H. Biomimetics Linked to Classical Product Development: An Interdisciplinary Endeavor to Develop a Technical Standard. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yan, B.; Zhang, L.; Tian, Y.; Zeng, H. Mussel-inspired antifouling coatings bearing polymer loops. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 15780–15783. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Jin, D.; Van der Bruggen, B. Modification of an anion exchange membrane based on rapid mussel-inspired deposition for improved antifouling performance. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 61, 126267. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhong, S.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Cui, X. Development and applications of mussel-inspired composite hydrogels for flexible bioelectronics. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 47, 145891. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Cheng, X.F.; Qian, W.H.; Zhou, J.; Sun, W.J.; Hou, X.; He, J.H.; Li, H.; Xu, Q.F.; Li, N.J.; et al. Mussel-Inspired Polydopamine Coating for Flexible Ternary Resistive Memory. Chem.—Asian J. 2018, 13, 1744–1750. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, G.; Guo, X.; Su, P.; Zhang, T.; Guan, J.; Wang, C. Mussel-inspired nanoparticle composite hydrogels for hemostasis and wound healing. Front. Chem. 2023, 1, 1154788. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, G.-S.; Kim, S.H.; Seo, H.I.; Ryu, J.H.; Yun, S.P.; Koh, M.-Y.; Lee, M.S.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.H. A multicenter, prospective, randomized clinical trial of marine mussel-inspired adhesive hemostatic materials, InnoSEAL Plus. Ann. Surg. Treat. Res. 2021, 10, 299–305. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, D.G.; Bushnell, G.G.; Messersmith, P.B. Mechanically Robust, Negative-Swelling, Mussel-Inspired Tissue Adhesives. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2012, 2, 745–775. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Wang, R.; Xu, T.; Ma, X.; Yao, Z.; Chi, B.; Xu, H. A mussel-inspired poly(γ-glutamic acid) tissue adhesive with high wet strength for wound closure. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 5668–5678. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Luo, J.; Sun, Z.; Xia, L.; Shi, M.; Liu, M.; Chang, J.; Wu, C. 3D printing of biomaterials with mussel-inspired nanostructures for tumor therapy and tissue regeneration. Biomaterials 2016, 111, 138–148. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, D.; Wang, Z.; Xie, C.; Wang, X.; Xing, W.; Ge, X.; Yuan, H.; Wang, K.; Tan, H.; Lu, X. Mussel-Inspired Tough Hydrogel with In Situ Nanohydroxyapatite Mineralization for Osteochondral Defect Repair. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1901103. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, X.; Liu, Y.; Shi, F.; Zhang, G.; Weng, J.; Qu, S. Enhanced Adhesion of Mussel-inspired Adhesive through Manipulating Contents of Dopamine Methacrylamide and Molecular Weight of Polymer. J. Bionic Eng. 2018, 15, 461–470. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Liu, K.; Wang, M.; Wang, K.; Fang, L.; Chen, H.; Zhou, J.; Lu, X. Mussel-Inspired Adhesive and Conductive Hydrogel with Long-Lasting Moisture and Extreme Temperature Tolerance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 28, 1704195. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Liu, J.-w.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.-z.; Jin, X.; Dai, C.-l. Mussel-inspired hydrogel particles with selective adhesion characteristics for applications in reservoir fracture control. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 361, 119598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Cheng, Q.; Chen, R.; Liu, C.; Qin, J.; Jiang, Q. Mussel-Mimetic Hydrogel Coating with Anticoagulant and Antiinflammatory Properties on a Poly(lactic acid) Vascular Stent. Biomacromolecules 2024, 25, 3098–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, P.; Li, X.; Zhao, H.; Qu, S.; Jiang, Z.; Lei, X.; Wu, C.; Liu, L. Recent advances of silk-fibroin-based hydrogel in the field of antibacterial application. Polym. Int. 2024, 74, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, P.; Ni, Z.; Xue, Y.; Liu, J. Hydrogel Fibers-Based Biointerfacing. Adv. Mater. 2024, 37, e2413476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Gao, F.; Yang, D.; Lin, L.; Yu, W.; Tang, J.; Yang, R.; Jin, M.; Gu, Y.; Wang, P.; et al. ECM-mimicking composite hydrogel for accelerated vascularized bone regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 42, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Yu, X.; You, T.; Zhao, B.; Dong, L.; Huang, C.; Zhou, X.; Xing, M.; Qian, W.; Luo, G. 3D Printing-Based Hydrogel Dressings for Wound Healing. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2404580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, Y.; Xu, H.; Mao, Z. Hydrogel Fiber Actuators Prepared by Shell–Core Structure for High-Performance Water/Light Dual Response. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2024, 6, 1887–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Long, L.; Hu, C.; Kong, Q.; Wang, Y. A spatiotemporal release platform based on pH/ROS stimuli-responsive hydrogel in wound repairing. J. Control. Release 2022, 341, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ren, K.; Xiao, C. On-demand dissolvable hydrogel dressings for promoting wound healing. J. Polym. Sci. 2024, 62, 2456–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Ju, Y.; Shen, N.; Zhu, S.; He, J.; Yang, L.; Lei, J.; He, X.; Shao, W.; Lei, L.; et al. Exos-Loaded Gox-Modified Smart-Response Self-Healing Hydrogel Improves the Microenvironment and Promotes Wound Healing in Diabetic Wounds. Adv. Heal. Mater. 2024, 14, e2403304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Jiang, H.; Wang, D.; Wang, S.; Song, W. Bio-Inspired Magnetic-Responsive Supramolecular-Covalent Semi-Convertible Hydrogel. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2401645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, G.; Pei, X.; Zhang, X. Advances of mussel-inspired hydrogels for Bone/Cartilage regeneration. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 487, 150560. [Google Scholar]
- Aranaz, I.; Alcántara, A.R.; Civera, M.C.; Arias, C.; Elorza, B.; Heras Caballero, A.; Acosta, N. Chitosan: An Overview of Its Properties and Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.; Peters, L.M.; Mucalo, M.R. Chitosan: A review of sources and preparation methods. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 169, 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Peers, S.; Montembault, A.; Ladavière, C. Chitosan hydrogels for sustained drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2020, 326, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Chen, J.; Duan, X.; Guo, B. Mussel-inspired adhesive antioxidant antibacterial hemostatic composite hydrogel wound dressing via photo-polymerization for infected skin wound healing. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 8, 341–354. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Tao, K.; Feng, Q.; Li, F.; Mu, X.; Du, C.; Zhao, R.; Wang, D.; Zhou, X.; et al. Blood-responsive mussel-inspired hydrogels for hemostasis, antibacterial action, and wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 135038. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, M.-P.; Zhang, A.-D.; Yao, Y.-X.; Chen, X.-G.; Liu, Y. Mussel-inspired adhesive and polypeptide-based antibacterial thermo-sensitive hydroxybutyl chitosan hydrogel as BMSCs 3D culture matrix for wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 261, 117878. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Long, L.; Cao, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y. Dual-crosslinked mussel-inspired smart hydrogels with enhanced antibacterial and angiogenic properties for chronic infected diabetic wound treatment via pH-responsive quick cargo release. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 411, 128564. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; You, L.; Zhang, R.; Meng, Q.; Zhong, S.; He, W.; Cui, X. Chitosan-based mussel-inspired hydrogel for rapid self-healing and high adhesion of tissue adhesion and wound dressings. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 316, 121083. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Huang, S.; Xu, A.; Xue, W. Injectable Adhesive Self-Healing Multiple-Dynamic-Bond Crosslinked Hydrogel with Photothermal Antibacterial Activity for Infected Wound Healing. Chem. Mater. 2022, 34, 2655–2671. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, D.; Xu, T.; Xing, W.; Ge, X.; Fang, L.; Wang, K.; Ren, F.; Lu, X. Mussel-Inspired Contact-Active Antibacterial Hydrogel with High Cell Affinity, Toughness, and Recoverability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 29, 1805964. [Google Scholar]
- Du, D.; Chen, X.; Shi, C.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, D.; Kaneko, D.; Kaneko, T.; Hua, Z. Mussel-Inspired Epoxy Bioadhesive with Enhanced Interfacial Interactions for Wound Repair. Acta Biomater. 2021, 136, 223–232. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.; Wu, L.; Yan, H.; Qu, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Ren, S.; Kong, D.; Wang, L. Multifunctional Hydrogel Patch with Toughness, Tissue Adhesiveness, and Antibacterial Activity for Sutureless Wound Closure. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 2610–2620. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Lu, W.; Shen, S.; Wei, L. Chitosan derivative-based mussel-inspired hydrogels as the dressings and drug delivery systems in wound healing. Cellulose 2021, 28, 11429–11450. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Hu, T.; Han, Y.; Guo, B. Mussel-inspired, antibacterial, conductive, antioxidant, injectable composite hydrogel wound dressing to promote the regeneration of infected skin. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2019, 556, 514–528. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Fan, X.; Lu, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y. Mussel-Inspired Adhesive, Antibacterial, and Stretchable Composite Hydrogel for Wound Dressing. Macromol. Biosci. 2023, 23, e2200370. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Q.; Zhang, W.; Qi, J.; Liao, H.; Guo, H.; Tan, X.; Chi, B. Laponite stabilized endogenous antibacterial hydrogel as wet-tissue adhesive. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2023, 145, 106009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, Z. Effects of gelatin-polyphenol and gelatin–genipin cross-linking on the structure of gelatin hydrogels. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 20, S2822–S2832. [Google Scholar]
- Andreazza, R.; Morales, A.; Pieniz, S.; Labidi, J. Gelatin-Based Hydrogels: Potential Biomaterials for Remediation. Polymers 2023, 15, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Shi, C.; Zi, Y.; Gong, H.; Chen, L.; Kan, G.; Wang, X.; Zhong, J. Effects of polyphenol and gelatin types on the physicochemical properties and emulsion stabilization of polyphenol-crosslinked gelatin conjugates. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Wang, J.; Hao, Z.; Zhao, D. Gelatin-based biomaterials and gelatin as an additive for chronic wound repair. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1398939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Chaieb, S.; Hemar, Y. Gelatin-Based Nanocomposites: A Review. Polym. Rev. 2021, 61, 765–813. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, S.; Shaikh, A.B.; Yang, L.; Lai, Y.; Ouyang, H.; Zhu, W. Bioinspired, injectable, tissue-adhesive and antibacterial hydrogel for multiple tissue regeneration by minimally invasive therapy. Appl. Mater. Today 2022, 26, 101290. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Bai, Q.; Zeng, Q.; Sun, N.; Zheng, C.; Wu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, T. A multifunctional mussel-inspired hydrogel with antioxidant, electrical conductivity and photothermal activity loaded with mupirocin for burn healing. Mater. Des. 2022, 217, 110598. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.; Shi, Z.; Yue, K.; Huang, X.; Xu, Y.; Gao, C.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, Y.S.; Wang, J. Sprayable hydrogel dressing accelerates wound healing with combined reactive oxygen species-scavenging and antibacterial abilities. Acta Biomater. 2021, 124, 219–232. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Xiao, D.; Quan, L.; Chai, H.; Sui, X.; Wang, B.; Xu, H.; Mao, Z. Mussel-inspired adhesive gelatin-polyacrylamide hydrogel wound dressing loaded with tetracycline hydrochloride to enhance complete skin regeneration. Soft Matter 2022, 18, 662–674. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, J.; Bai, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lang, S.; Li, J.; Ji, Y.; Peng, B.; Liu, G. A zwitterionic silver nanoparticle-incorporating injectable hydrogel with a durable and efficient antibacterial effect for accelerated wound healing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 7979–7994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Hong, Y.; Ren, S. Mussel-inspired near-infrared light-responsive gelatin-based hydrogels for enhancing MRSA-infected wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 263, 129887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Wang, H.; Gao, J.; Liu, X.; Li, M.; Wu, D.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Tang, P. First-Aid Hydrogel Wound Dressing with Reliable Hemostatic and Antibacterial Capability for Traumatic Injuries. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, e2300312. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, K.; Yao, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Bioinspired sequentially crosslinked nanofibrous hydrogels with robust adhesive and stretchable capability for joint wound dressing. Compos. Commun. 2021, 26, 100785. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, W.; Zhang, W.; Tang, H.; Yuan, W.E. In situ forming ROS-scavenging hybrid hydrogel loaded with polydopamine-modified fullerene nanocomposites for promoting skin wound healing. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 129. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Peng, W.; Dong, Y.; Fan, B.; Qian, W.; Ji, X.; Lu, X.; Gan, D.; Liu, P. Mussel-Inspired PEDOT-Incorporated Gelatin-Based Conductive Hydrogel with Flexibility and Electroactivity to Accelerate Wound Healing In Vitro. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 4233–4243. [Google Scholar]
- Necas, J.; Bartosikova, L.; Brauner, P.; Kolar, J. Hyaluronic acid (hyaluronan): A review. Veterinární Medicína 2008, 53, 397–411. [Google Scholar]
- Graça, M.F.P.; Miguel, S.P.; Cabral, C.S.D.; Correia, I.J. Hyaluronic acid—Based wound dressings: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 241, 116364. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Huang, H. Application of hyaluronic acid as carriers in drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 766–772. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Shi, K.; Yu, Y.; Gao, N.; Chen, H.; et al. Mussel-inspired “plug-and-play” hydrogel glue for postoperative tumor recurrence and wound infection inhibition. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2023, 650, 1907–1917. [Google Scholar]
- An, S.; Jeon, E.J.; Han, S.Y.; Jeon, J.; Lee, M.J.; Kim, S.; Shin, M.; Cho, S.W. pH-Universal Catechol-Amine Chemistry for Versatile Hyaluronic Acid Bioadhesives. Small 2022, 18, e2202729. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Y.; Cai, F.; He, Y.; Li, L.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, X. Multi-crosslinked hydrogels with strong wet adhesion, self-healing, antibacterial property, reactive oxygen species scavenging activity, and on-demand removability for seawater-immersed wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2023, 159, 95–110. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Liu, L.; He, X.; Xia, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Xi, Z.; Yu, J.; Wang, J. Dynamic Crosslinked Injectable Mussel-Inspired Hydrogels with Adhesive, Self-Healing, and Biodegradation Properties. Polymers 2023, 15, 1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.H.; Zhang, C.M.; Jiang, Z.W.; Qin, S.Y.; Zhang, A.Q. Mussel-Inspired Adhesive Polydopamine-Functionalized Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel with Potential Bacterial Inhibition. Glob. Chall. 2020, 4, 1900068. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Song, J.; Jiang, Y.; Li, M.; Wei, J.; Qin, J.; Peng, W.; Lopez Lasaosa, F.; He, Y.; Mao, H.; et al. Injectable Adhesive Self-Healing Multicross-Linked Double-Network Hydrogel Facilitates Full-Thickness Skin Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 57782–57797. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, M.P.; Neto, A.I.; Correia, T.R.; Miguel, S.P.; Matsusaki, M.; Correia, I.J.; Mano, J.F. Bioinspired multilayer membranes as potential adhesive patches for skin wound healing. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 1962–1975. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Duan, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, R.; Zhu, C.; Fan, D. Instantaneous self-healing and strongly adhesive self-adaptive hyaluronic acid-based hydrogel for controlled drug release to promote tendon wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 125001. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Ren, Y.; Wang, P.; Pu, Y.; Yang, R.; Wang, X.; Tan, X.; Ye, Z.; Maurizot, V.; et al. Mussel-Inspired Dual-Cross-linking Hyaluronic Acid/epsilon-Polylysine Hydrogel with Self-Healing and Antibacterial Properties for Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 27876–27888. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aziz, T.; Haq, F.; Farid, A.; Kiran, M.; Faisal, S.; Ullah, A.; Ullah, N.; Bokhari, A.; Mubashir, M.; Chuah, L.F.; et al. Challenges associated with cellulose composite material: Facet engineering and prospective. Environ. Res. 2023, 223, 115429. [Google Scholar]
- Seddiqi, H.; Oliaei, E.; Honarkar, H.; Jin, J.; Geonzon, L.C.; Bacabac, R.G.; Klein-Nulend, J. Cellulose and its derivatives: Towards biomedical applications. Cellulose 2021, 28, 1893–1931. [Google Scholar]
- Shaghaleh, H.; Xu, X.; Wang, S. Current progress in production of biopolymeric materials based on cellulose, cellulose nanofibers, and cellulose derivatives. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 825–842. [Google Scholar]
- Girard, V.D.; Chaussé, J.; Vermette, P. Bacterial cellulose: A comprehensive review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 141, e55163. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Shi, G.; Wang, R.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Q.; Yu, A.; Lu, A. Bioinspired wet adhesive carboxymethyl cellulose-based hydrogel with rapid shape adaptability and antioxidant activity for diabetic wound repair. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 334, 122014. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Huang, R.; Zheng, B.; Guo, W.; Li, C.; He, W.; Wei, Y.; Du, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, D.; et al. Highly Stretchable, Adhesive, Biocompatible, and Antibacterial Hydrogel Dressings for Wound Healing. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2003627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Mensaha, A.; Li, D.; Wang, Q.; Wei, Q. A plant-inspired long-lasting adhesive bilayer nanocomposite hydrogel based on redox-active Ag/Tannic acid-Cellulose nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 255, 117508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khamrai, M.; Banerjee, S.L.; Paul, S.; Ghosh, A.K.; Sarkar, P.; Kundu, P.P. A Mussel Mimetic, Bioadhesive, Antimicrobial Patch Based on Dopamine-Modified Bacterial Cellulose/rGO/Ag NPs: A Green Approach toward Wound-Healing Applications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 12083–12097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Wang, J.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xi, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Guo, X. A mussel-inspired carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogel with enhanced adhesiveness through enzymatic crosslinking. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 179, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wu, M.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhong, S.; Gao, Y.; Cui, X. Fe3+-induced coordination cross-linking gallic acid-carboxymethyl cellulose self-healing hydrogel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 267, 131626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Zhang, X.; Tang, Z.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, M.; Liu, K.; Chen, L.; Huang, L.; Ni, Y.; Wu, H. Mussel-inspired blue-light-activated cellulose-based adhesive hydrogel with fast gelation, rapid haemostasis and antibacterial property for wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 129329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suneetha, M.; Rao, K.M.; Han, S.S. Cell/Tissue Adhesive, Self-Healable, Biocompatible, Hemostasis, and Antibacterial Hydrogel Dressings for Wound Healing Applications. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2102369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varaprasad, K.; Jayaramudu, T.; Kanikireddy, V.; Toro, C.; Sadiku, E.R. Alginate-based composite materials for wound dressing application:A mini review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 116025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, H.; Srebnik, S. Structural Characterization of Sodium Alginate and Calcium Alginate. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 2160–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Shen, P.; Peng, Q. Structures, properties and application of alginic acid: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reakasame, S.; Boccaccini, A.R. Oxidized Alginate-Based Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications: A Review. Biomacromolecules 2017, 19, 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Rastogi, P.; Kandasubramanian, B. Review of alginate-based hydrogel bioprinting for application in tissue engineering. Biofabrication 2019, 11, 042001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Jiang, T.; Song, P.; Wang, B.; Zhao, X. Mussel-inspired nanocomposite hydrogel based on alginate and antimicrobial peptide for infected wound repair. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 219, 1087–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Chen, Y.; Rehman, H.U.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, M.; Li, H.; Liu, H. Ultratough, Self-Healing, and Tissue-Adhesive Hydrogel for Wound Dressing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 33523–33531. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.; Huang, B.; Wang, Q.; Wu, W.; Coates, P.; Sefat, F.; Lu, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X. A Mussel-Inspired Antibacterial Hydrogel with High Cell Affinity, Toughness, Self-Healing, and Recycling Properties for Wound Healing. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 3070–3082. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Z.; Dan, W.; Yu, G.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yang, C.; Dan, N. Tough and tissue-adhesive polyacrylamide/collagen hydrogel with dopamine-grafted oxidized sodium alginate as crosslinker for cutaneous wound healing. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 42123–42132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.H.; Shin, M.; Park, E.; Ryu, J.H.; Burdick, J.A.; Lee, H. Alginate-Boronic Acid: pH-Triggered Bioinspired Glue for Hydrogel Assembly. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 30, 1908497. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Wang, C.; Yuan, W.; Xie, X.; Song, Y. Highly Adhesive, Conductive, and Self-Healing Hydrogel with Triple Cross-Linking Inspired by Mussel and DNA for Wound Adhesion and Human Motion Sensing. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 6586–6597. [Google Scholar]
- Nezhad-Mokhtari, P.; Hamishehkar, H.; Farahpour, M.R.; Mehdipour, A.; Rahbarghazi, R.; Milani, M.; Mehrali, M. Engineered bioadhesive Self-Healing nanocomposite hydrogel to fight infection and accelerate cutaneous wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 489, 150992. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Y.; Su, X.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Yan, Q.; Qian, Q.; Zhao, J.; Li, P.; Wang, S. Mussel-inspired “all-in-one” sodium alginate/carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel patch promotes healing of infected wound. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 261, 129828. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, S.; Gu, Y. Rapidly degrading and mussel-inspired multifunctional carboxymethyl chitosan/montmorillonite hydrogel for wound hemostasis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhong, K.; Zong, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, H.; Zhen, L.; Tao, S.; Sun, L.; Yang, J.; Li, J. A mussel-inspired wet-adhesion hydrogel with hemostasis and local anti-inflammation for managing the development of acute wounds. Mater. Des. 2022, 213, 110347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhu, D.; Li, Q.; Wang, C.; Cui, J.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, X. Mechanically Reinforced and Injectable Universal Adhesive Based on a PEI-PAA/Alg Dual-Network Hydrogel Designed by Topological Entanglement and Catechol Chemistry. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 59826–59837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Liu, L.; Han, H.; Shi, W.; Yang, W.; Lu, X. Bioinspired and Microgel-Tackified Adhesive Hydrogel with Rapid Self-Healing and High Stretchability. Macromolecules 2018, 52, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huangfu, Y.; Li, S.; Deng, L.; Zhang, J.; Huang, P.; Feng, Z.; Kong, D.; Wang, W.; Dong, A. Skin-Adaptable, Long-Lasting Moisture, and Temperature-Tolerant Hydrogel Dressings for Accelerating Burn Wound Healing without Secondary Damage. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 59695–59707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argenziano, R.; Viggiano, S.; Esposito, R.; Schibeci, M.; Gaglione, R.; Castaldo, R.; Fusaro, L.; Boccafoschi, F.; Arciello, A.; Della Greca, M.; et al. All natural mussel-inspired bioadhesives from soy proteins and plant derived polyphenols with marked water-resistance and favourable antibacterial profile for wound treatment applications. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2023, 652, 1308–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, Q.; Pan, W.; Huang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Dong, W.; Qi, X.; Shen, J. Mussel-inspired agarose hydrogel scaffolds for skin tissue engineering. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yu, F.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L. Biomimetic poly(thioctic acid)-based bioadhesive hydrogels for wet adhesion, expeditious hemostasis and enhanced wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 283, 137108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Qiu, W.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Qin, X.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Li, B.; Li, F.; Huang, L.; et al. Conductive hydrogel dressings based on cascade reactions with photothermal effect for monitoring and treatment of diabetic wounds. Compos. Part. B Eng. 2022, 242, 110098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Kang, X.; Gao, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Fan, C.; Shen, H.; Chen, Y.; Dai, J. Biomimetic Natural Biopolymer-Based Wet-Tissue Adhesive for Tough Adhesion, Seamless Sealed, Emergency/Nonpressing Hemostasis, and Promoted Wound Healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 33, 2211340. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, H.; Yoshihara, D.; Tottori, S.; Nishizawa, M. Mussel-inspired thermo-switchable underwater adhesive based on a Janus hydrogel. NPG Asia Mater. 2024, 16, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DFullenkamp, E.; Rivera, J.G.; Gong, Y.-K.; Lau, K.H.A.; He, L.; Varshney, R.; Messersmith, P.B. Mussel-inspired silver-releasing antibacterial hydrogels. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3783–3791. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, X.; Mi, H.-Y.; Napiwocki, B.N.; Peng, X.-F.; Turng, L.-S. Mussel-inspired electroactive chitosan/graphene oxide composite hydrogel with rapid self-healing and recovery behavior for tissue engineering. Carbon 2017, 125, 557–570. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, K.; Senturk, B.; Matter, M.T.; Wu, X.; Herrmann, I.K.; Rottmar, M.; Toncelli, C. Mussel-Inspired Injectable Hydrogel Adhesive Formed under Mild Conditions Features Near-Native Tissue Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 47707–47719. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.H.; Rong, L.H.; Ge, J.; Tiu, B.D.B.; Cao, P.F.; Advincula, R.C. Mussel-Inspired Hydrogel Composite with Multi-Stimuli Responsive Behavior. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2019, 304, 1800720. [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Cui, P.; Lu, S. Mussel-Inspired Hydrogel Applied to Wound Healing: A Review and Future Prospects. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10040206
Chen Y, Cao Y, Cui P, Lu S. Mussel-Inspired Hydrogel Applied to Wound Healing: A Review and Future Prospects. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(4):206. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10040206
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yanai, Yijia Cao, Pengyu Cui, and Shenzhou Lu. 2025. "Mussel-Inspired Hydrogel Applied to Wound Healing: A Review and Future Prospects" Biomimetics 10, no. 4: 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10040206
APA StyleChen, Y., Cao, Y., Cui, P., & Lu, S. (2025). Mussel-Inspired Hydrogel Applied to Wound Healing: A Review and Future Prospects. Biomimetics, 10(4), 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10040206




