FRNet V2: A Lightweight Full-Resolution Convolutional Neural Network for OCTA Vessel Segmentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We design a new lightweight network for OCTA image segmentation, eschewing any upsampling–downsampling process. Employing the ConvNeXt V2 module as the core, along with deep separable convolutions and a recursive mechanism, this network bolsters the model’s feature extraction ability, slashes the number of parameters, and accelerates the model’s segmentation speed.
- We designed DWAM, a lightweight hybrid adaptive attention mechanism. It is divided into channel and spatial self-attention blocks. By introducing deep separable convolutions and recursive mechanisms, the mechanism becomes lighter, with faster feature extraction.
- Comprehensive tests on two renowned retinal image datasets, OCTA-500 and ROSSA, show the robustness of our proposed method. The model’s lightweight design and segmentation speed demonstrates its computational efficiency and potential for broader application across various scenarios.
2. Research Methods
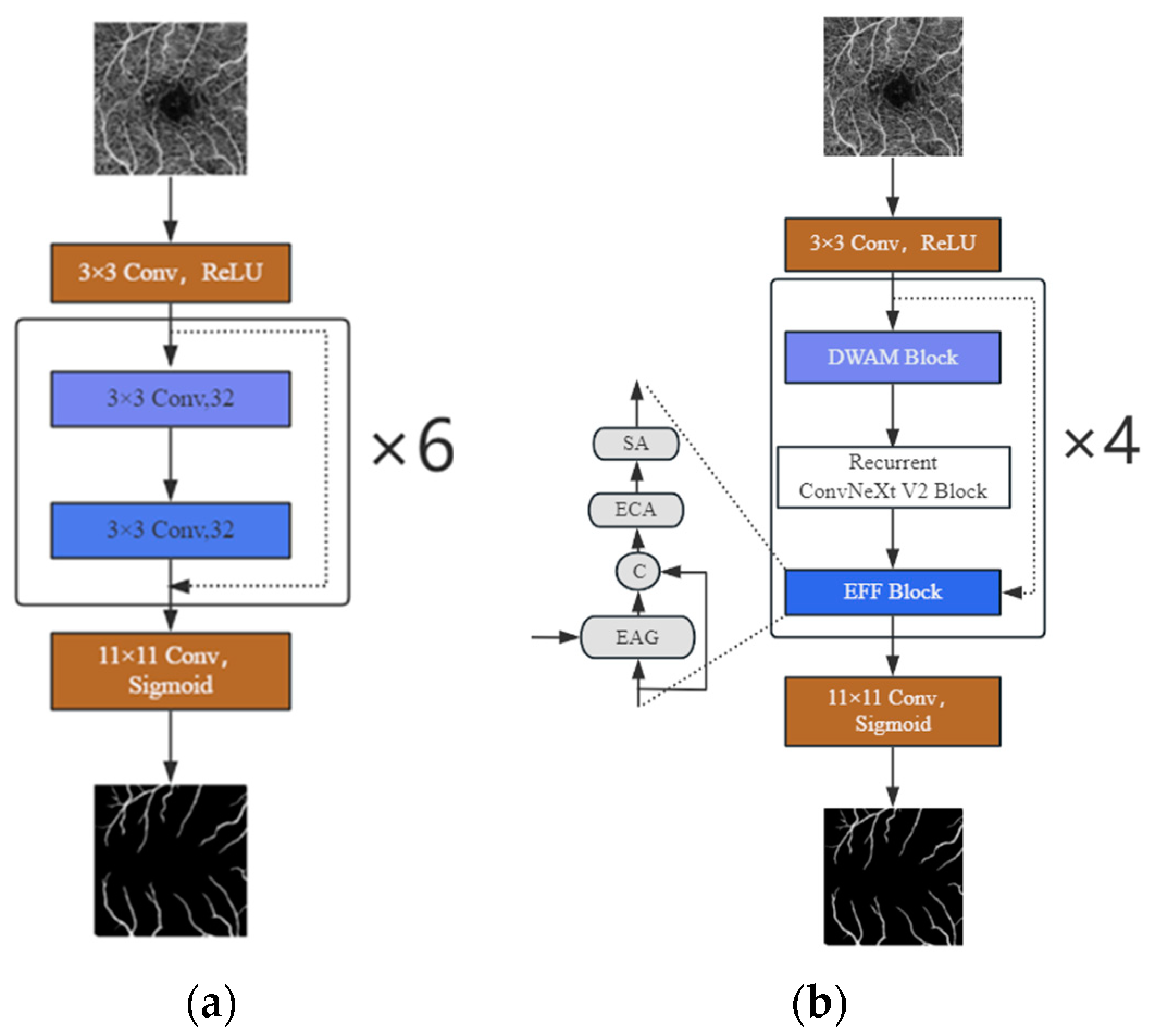
2.1. Model Architecture Description
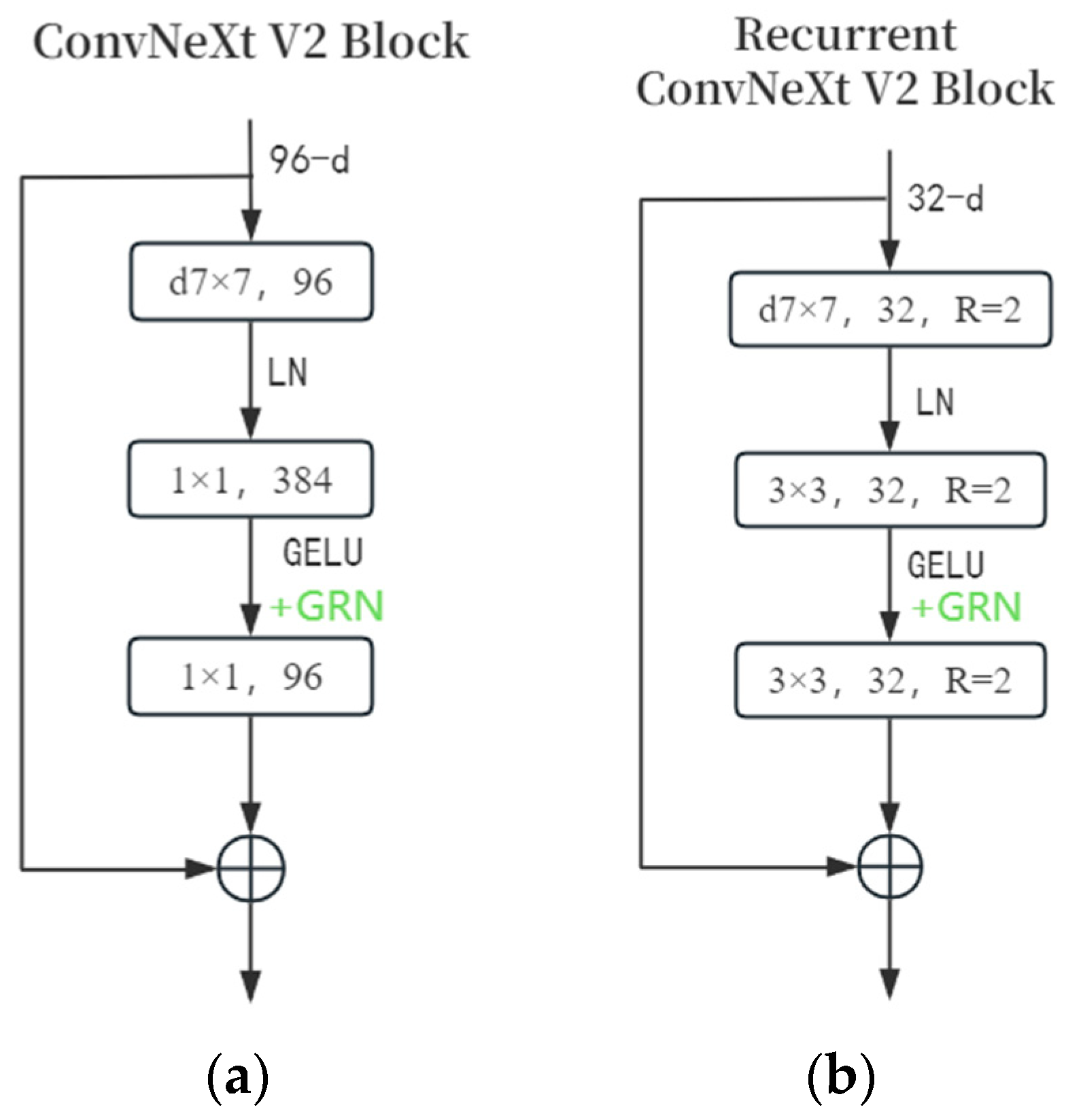
2.2. Improved ConvNeXt V2 Block
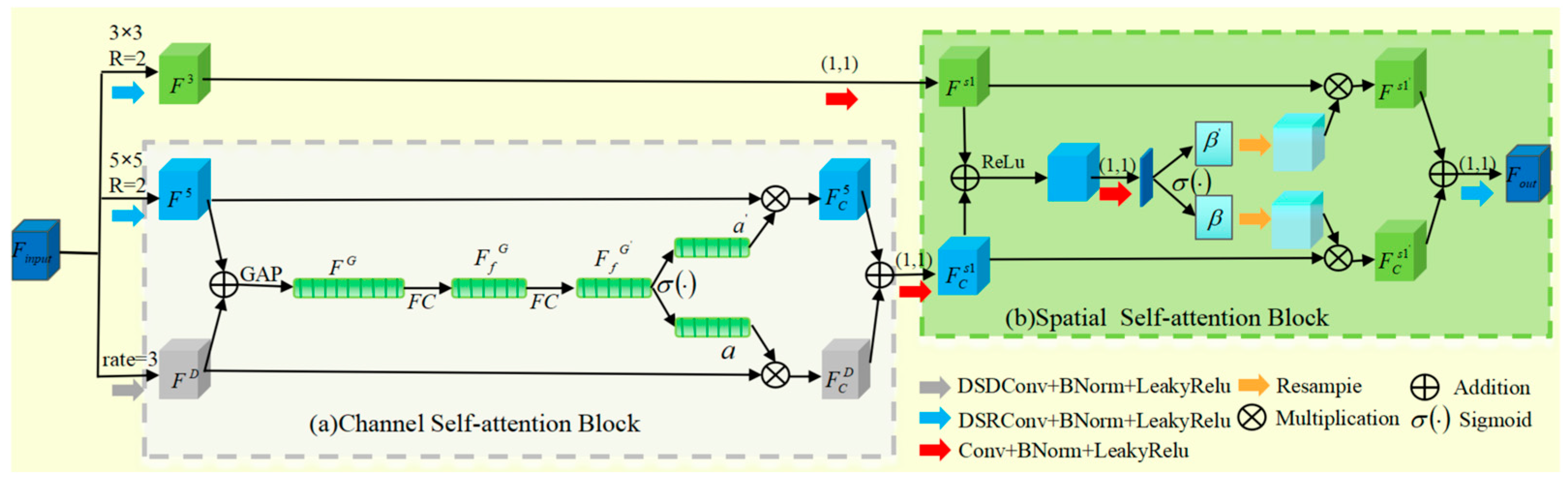
2.3. DWAM Attention Mechanism
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Experimental Environment and Hyperparameter Setting
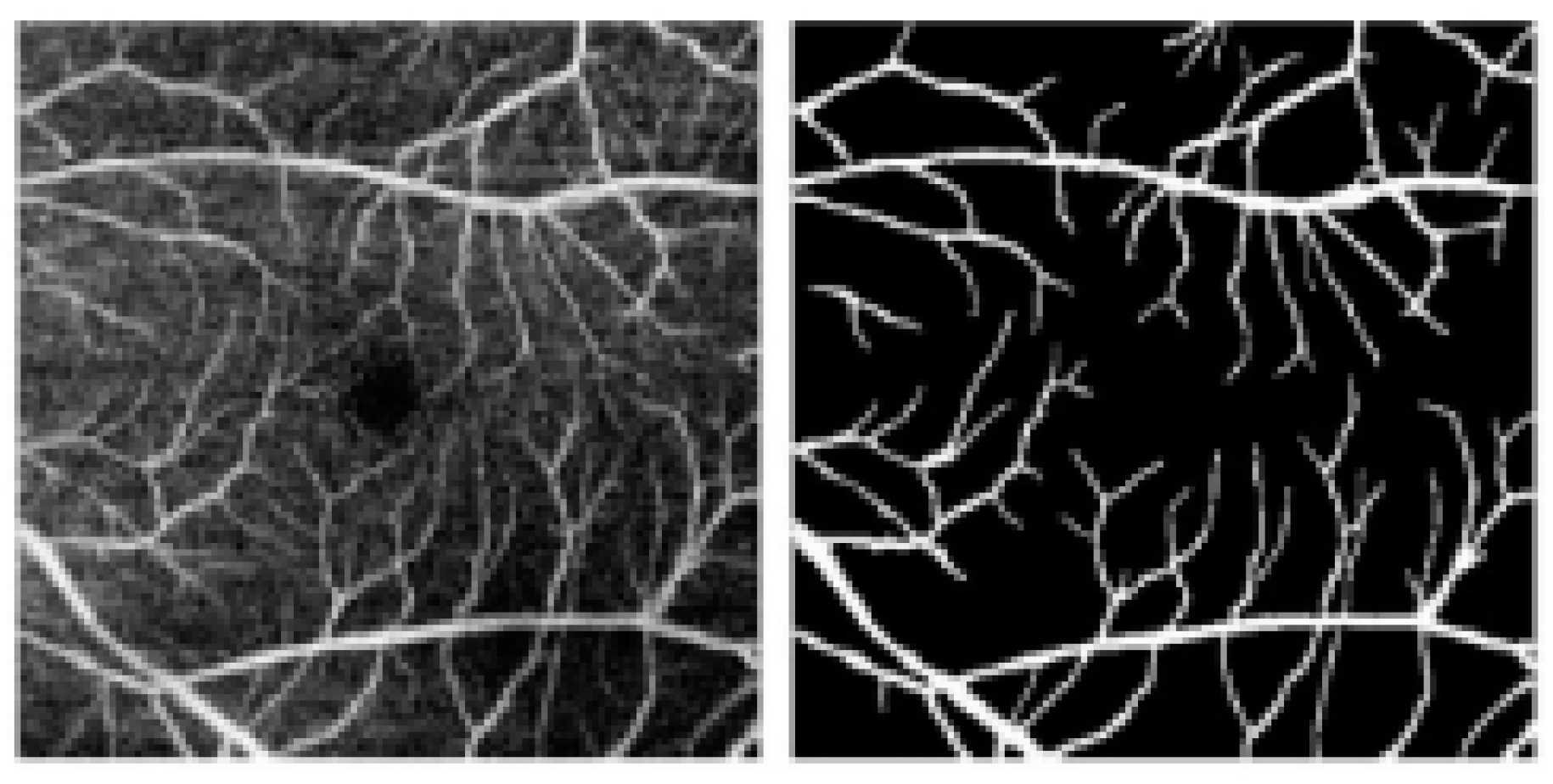
3.2. Experimental Data
3.3. Evaluation Indicators
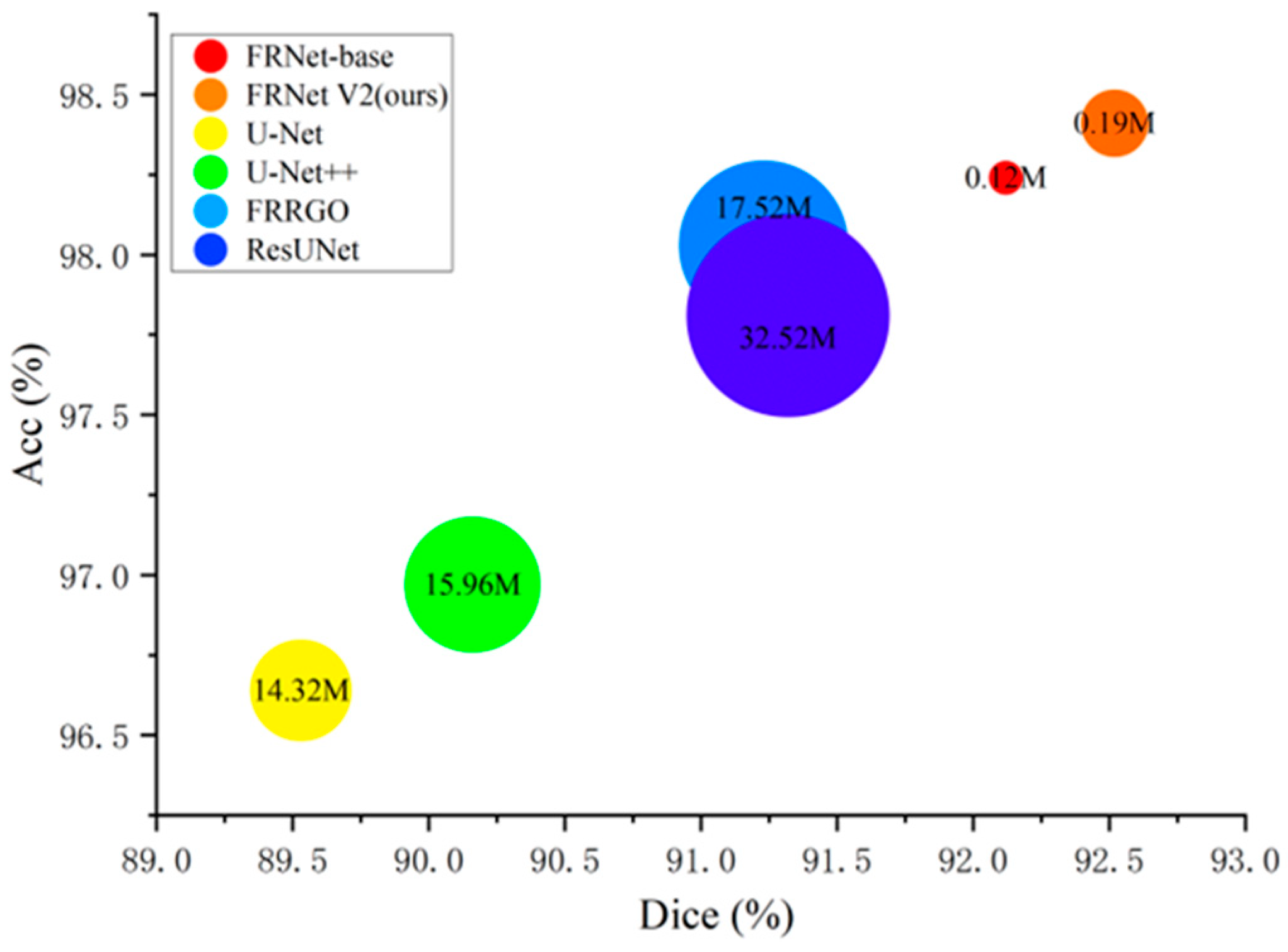
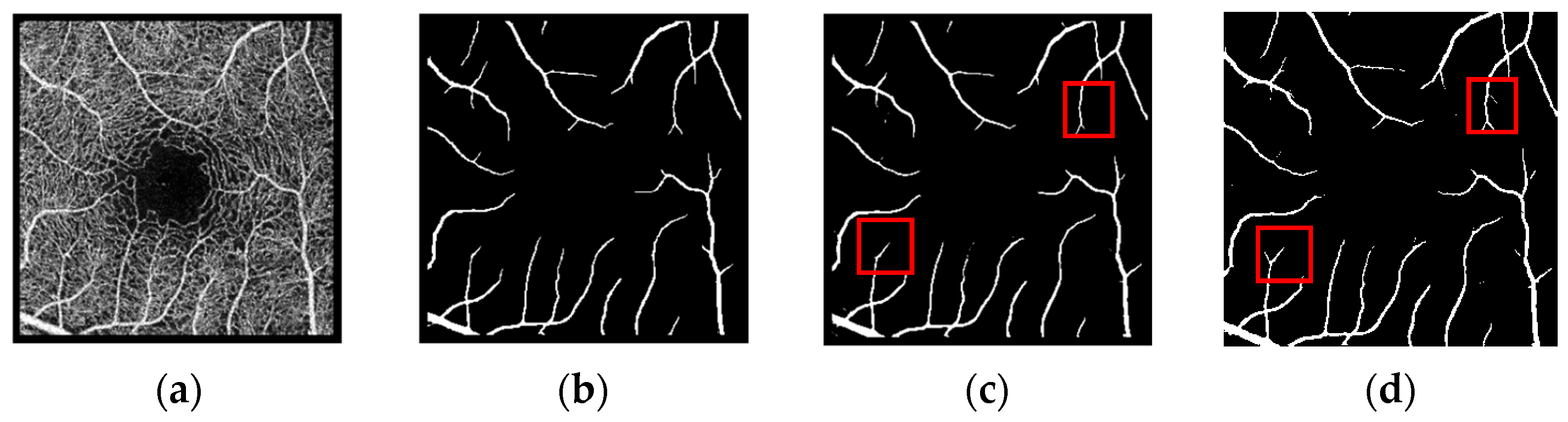
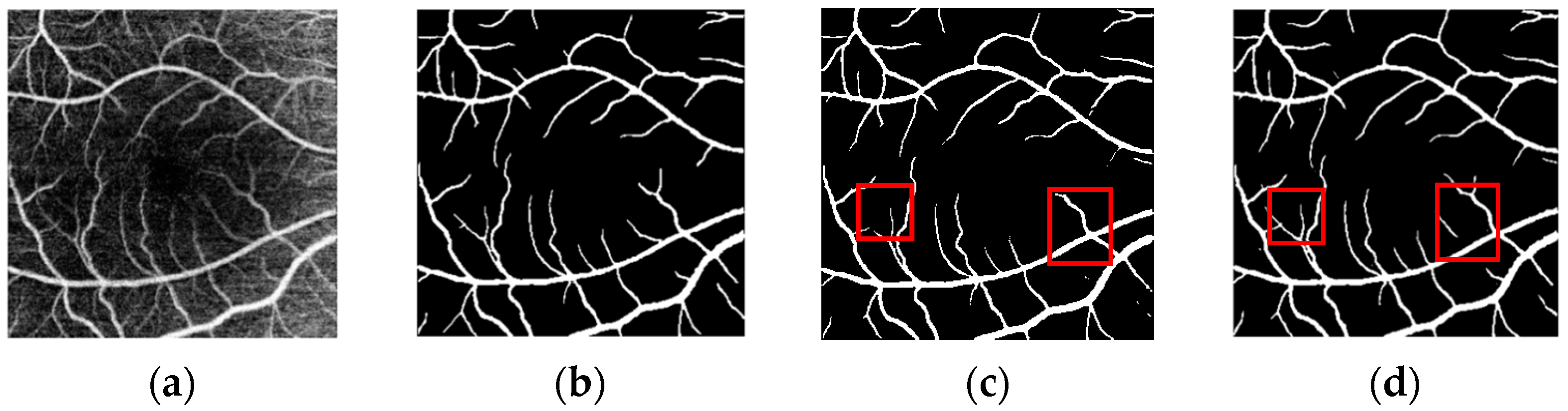
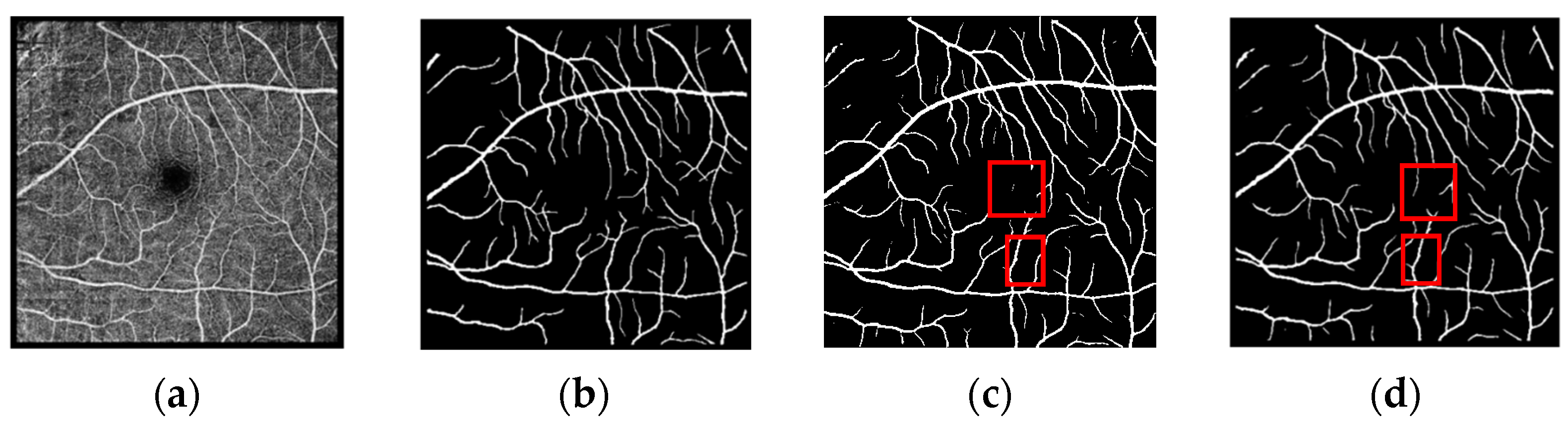
3.4. Segmentation Results
4. Ablation Experiment
- Row 1: Uses only the same modules as FRNet-base.
- Row 2: Replaces the preceding module with the ConvNeXt V2 block. Parameter reduction is due to its deep separable convolution.
- Row 3: Replaces 1 × 1 convolution in the ConvNeXt V2 block with 3 × 3 convolution. Accuracy increases as parameters increase.
- Row 4: Applies recursive convolution, achieving the best accuracy. It does not increase parameters but increases inference time.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spaide, R.F.; Fujimoto, J.G.; Waheed, N.K.; Sadda, S.R.; Staurenghi, G. Optical coherence tomography angiography. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2018, 64, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, W.S.; Teixeira, J.V.; Ren, T.I.; Cavalcanti, G.D.; Sijbers, J. Unsupervised Retinal Vessel Segmentation Using Combined Filters. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149943. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulsahib, A.A.; Mahmoud, M.A.; Mohammed, M.A.; Rasheed, H.H.; Mostafa, S.A.; Maashi, M.S. Comprehensive review of retinal blood vessel segmentation and classification techniques: Intelligent solutions for green computing in medical images, current challenges, open issues, and knowledge gaps in fundus medical images. Netw. Model. Anal. Health Inform. Bioinform. 2021, 10, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 640–651. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. Med. Image Comput. Comput.-Assist. Interv. 2015, 9351, 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Rahman Siddiquee, M.M.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. UNet++: A Nested U-Net Architecture for Medical Image Segmentation. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2018, 11045, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Folgoc, L.L.; Lee, M.; Heinrich, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; McDonagh, S.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Kainz, B.; et al. Attention U-Net: Learning Where to Look for the Pancreas. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03999. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Yan, X.; Wang, S.; Xiao, G. DA-Net: Dual-attention Network for Multivariate Time Series Classification. Inf. Sci. 2022, 610, 472–487. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.; Lian, S.; Luo, Z.; Li, S. Weighted Res-UNet for High-Quality Retina Vessel Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 9th International Conference on Information Technology in Medicine and Education (ITME), Hangzhou, China, 19–21 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- De Jesus, D.A.; Brea, L.S.; Breda, J.B.; Fokkinga, E.; Ederveen, V.; Borren, N.; Bekkers, A.; Pircher, M.; Stalmans, I.; Klein, S.; et al. OCTA Multilayer and Multisector Peripapillary Microvascular Modeling for Diagnosing and Staging of Glaucoma. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phansalkar, N.; More, S.; Sabale, A.; Joshi, M. Adaptive Local Thresholding for Detection of Nuclei in Diversity Stained Cytology Images. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Communications and Signal Processing, Kerala, India, 10–12 February 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chavan, A.; Mago, G.; Balaji, J.J.; Lakshminarayanan, V. A new method for quantification of retinal blood vessel characteristics. Soc. Photo-Opt. Instrum. Eng. (SPIE) Conf. Ser. 2021, 11623, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Khansari, M.M.; O’Neill, W.; Lim, J.; Shahidi, M. Method for Quantitative Assessment of Retinal Vessel Tortuosity in Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Applied to Sickle Cell Retinopathy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 3796. [Google Scholar]
- Eladawi, N.; Elmogy, M.; Helmy, O.; Aboelfetouh, A.; Riad, A.; Sandhu, H.; Schaal, S.; El-Baz, A. Automatic blood vessels segmentation based on different retinal maps from OCTA scans. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 89, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.; Chua, J.; Tan, B.; Yao, X.; Chong, R.; Sng, C.C.; Husain, R.; Aung, T.; Garway-Heath, D.; Schmetterer, L. Combining OCT and OCTA for Focal Structure-Function Modeling in Early Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2021, 62, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image is Worth 16 × 16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. arXiv 2010, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer Using Shifted Windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chung, A.C. Retinal Vessel Segmentation by A Transformer-U-Net Hybrid Model with Dual-Path Decoder. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2024, 28, 5347–5359. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Huang, X.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q. Stimulus-guided Adaptive Transformer Network for Retinal Blood Vessel Segmentation in Fundus Images. Med. Image Anal. 2023, 89, 102929. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Mao, H.; Wu, C.Y.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Darrell, T.; Xie, S. A ConvNet for the 2020S. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 11966–11976. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, L.; Lin, L.; Cheng, P.; Wang, Z.; Tang, X. FARGO: A Joint Framework for FAZ and RV Segmentation from OCTA Images. Med. Image Comput. Comput.-Assist. Interv. 2021, 12970, 42–51. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, J.U.; Makhdoom, F.; Lu, D. ASU-CNN: An Efficient Deep Architecture for Image Classification and Feature Visualizations. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.19146. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Debnath, S.; Hu, R.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Kweon, I.S.; Xie, S. ConvNeXt V2: Co-designing and Scaling ConvNets with Masked Autoencoders. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 16133–16142. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, H.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Li, S. An Accurate and Efficient Neural Network for OCTA Vessel Segmentation and a New Dataset. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 14–19 April 2024; pp. 1966–1970. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Qin, X.; Huang, C.; Lu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, O.; Shuai, J.; Yuan, C.A. SUnet: A Multi-Organ Segmentation Network Based on Multiple Attention. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 167, 107596. [Google Scholar]
- Alom, M.Z.; Hasan, M.; Yakopcic, C.; Taha, T.M.; Asari, V.K. Recurrent Residual Convolutional Neural Network based on U-Net (R2U-Net) for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.06955. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Li, L.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yap, M.H. AAU-Net: An Adaptive Attention U-Net for Breast Lesions Segmentation in Ultrasound Images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2022, 42, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, Z.; Xie, K.; Yuan, S.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Q. IPN-V2 and OCTA-500: Methodology and Dataset for Retinal Image Segmentation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.07261. [Google Scholar]
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.C.; Lo, W.Y.; et al. Segment Anything. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, J.U.; Makhdoom, F.; Lu, D. Amplifying Sine Unit: An Oscillatory Activation Function for Deep Neural Networks to Recover Nonlinear Oscillations Efficiently. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.09759. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, J.U.; Zulfiqar, R.; Khan, A. SwishReLU: A Unified Approach to Activation Functions for Enhanced Deep Neural Networks Performance. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.08232. [Google Scholar]
| Dataset | OCTA-500 | ROSSA |
|---|---|---|
| Number of images | 500 | 918 |
| Subdatasets | OCTA_6M and OCTA_3M | Train, Test, and Val |
| Num of train/test/val | 320/150/30 | 718/100/100 |
| Size | 400 × 400 (OCTA_6M) 304 × 304 (OCTA_3M) | 320 × 320 |
| Method | Dice (↑) | Acc (↑) | Param (↓) | Time (↓) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OCTA_6M | ||||
| U-Net | 85.03 | 95.21 | 14.32 M | 20.2 ms |
| U-Net + + | 85.67 | 95.73 | 15.96 M | 25.7 ms |
| ResUNet | 88.10 | 96.03 | 32.52 M | 32.4 ms |
| FARGO | 89.01 | 98.12 | 17.52 M | 29.6 ms |
| FRNet-base | 88.85 | 98.02 | 0.12 M | 15.3 ms |
| FRNet V2 | 89.10 | 98.20 | 0.19 M | 21.8 ms |
| OCTA_3M | ||||
| U-Net | 88.35 | 95.45 | 14.32 M | 17.4 ms |
| U-Net + + | 88.64 | 95.98 | 15.96 M | 21.2 ms |
| ResUNet | 90.03 | 96.18 | 32.52 M | 26.3 ms |
| FRRGO | 91.21 | 98.12 | 17.52 M | 24.5 ms |
| FRNet-base | 91.15 | 98.84 | 0.12 M | 12.1 ms |
| FRNet V2 | 91.63 | 98.97 | 0.19 M | 13.5 ms |
| ROSSA | ||||
| U-Net | 89.53 | 96.64 | 14.32 M | 18.9 ms |
| U-Net + + | 90.16 | 96.97 | 15.96 M | 23.9 ms |
| ResUNet | 91.32 | 97.81 | 32.52 M | 28.7 ms |
| FRRGO | 91.23 | 98.03 | 17.52 M | 27.5 ms |
| FRNet-base | 92.12 | 98.24 | 0.12 M | 13.8 ms |
| FRNet V2 | 92.52 | 98.41 | 0.19 M | 14.9 ms |
| Component | Dice | ACC | Param | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residual Block | 91.89 | 98.28 | 0.11 M | 9.1 ms |
| ConvNeXt V2 Block | 91.23 | 97.91 | 0.07 M | 7.5 ms |
| 1 × 1⇒3 × 3 | 91.97 | 98.36 | 0.12 M | 10.5 ms |
| +Recurrent | 92.27 | 98.38 | 0.12 M | 11.6 ms |
| Component | Dice | ACC | Param | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without Attention | 92.27 | 98.38 | 0.12 M | 11.6 ms |
| With HAAM | 92.39 | 98.39 | 0.59 M | 18.4 ms |
| With CBAM | 92.29 | 98.38 | 0.18 M | 13.2 ms |
| With DWAM | 92.52 | 98.41 | 0.19 M | 14.9 ms |
| Component | Dice | ACC | Param | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without Attention | 92.27 | 98.38 | 0.12 M | 11.6 ms |
| With HAAM | 92.39 | 98.39 | 0.59 M | 18.4 ms |
| Conv⇒DSConv | 92.45 | 98.40 | 0.19 M | 11.9 ms |
| +Recurrent | 92.52 | 98.41 | 0.19 M | 14.9 ms |
| Model Layers | Dice | ACC | Param | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layer two | 92.27 | 98.34 | 0.09 M | 7.2 ms |
| Layer three | 92.33 | 98.38 | 0.14 M | 11.1 ms |
| Layer four | 92.52 | 98.41 | 0.19 M | 14.9 ms |
| Layer five | 92.37 | 98.40 | 0.24 M | 19.0 ms |
| Layer six | 92.54 | 98.42 | 0.29 M | 24.5 ms |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, D.; Wang, L.; Fang, Y.; Jiang, D.; Zheng, Y. FRNet V2: A Lightweight Full-Resolution Convolutional Neural Network for OCTA Vessel Segmentation. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10040207
Gao D, Wang L, Fang Y, Jiang D, Zheng Y. FRNet V2: A Lightweight Full-Resolution Convolutional Neural Network for OCTA Vessel Segmentation. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(4):207. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10040207
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Dongxu, Liang Wang, Youtong Fang, Du Jiang, and Yalin Zheng. 2025. "FRNet V2: A Lightweight Full-Resolution Convolutional Neural Network for OCTA Vessel Segmentation" Biomimetics 10, no. 4: 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10040207
APA StyleGao, D., Wang, L., Fang, Y., Jiang, D., & Zheng, Y. (2025). FRNet V2: A Lightweight Full-Resolution Convolutional Neural Network for OCTA Vessel Segmentation. Biomimetics, 10(4), 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10040207







