MSBiLSTM-Attention: EEG Emotion Recognition Model Based on Spatiotemporal Feature Fusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
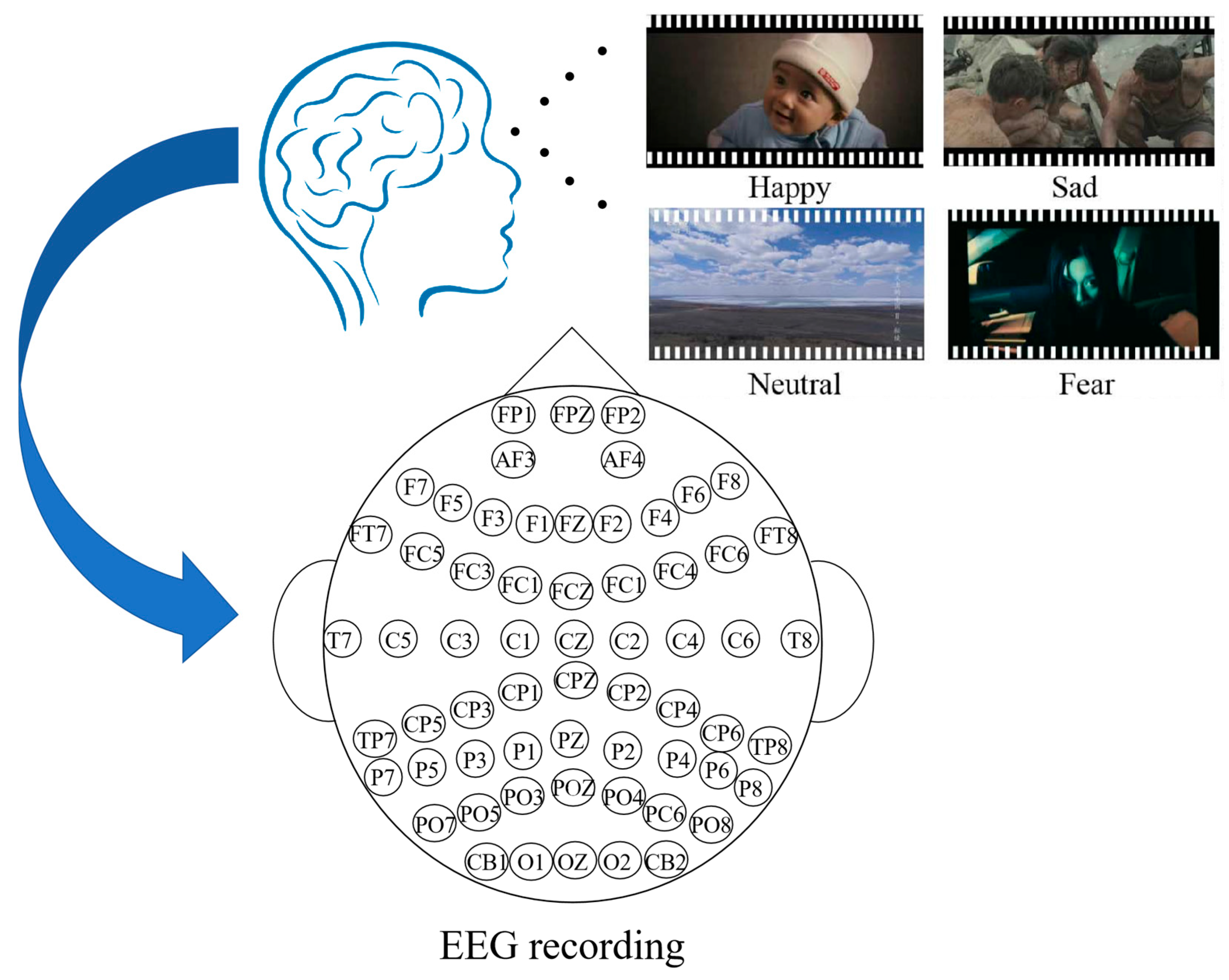
2.1. SEED Dataset
2.2. CNN-Bi-LSTM-Attention Model
2.2.1. Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
2.2.2. Multi-Scale Networks
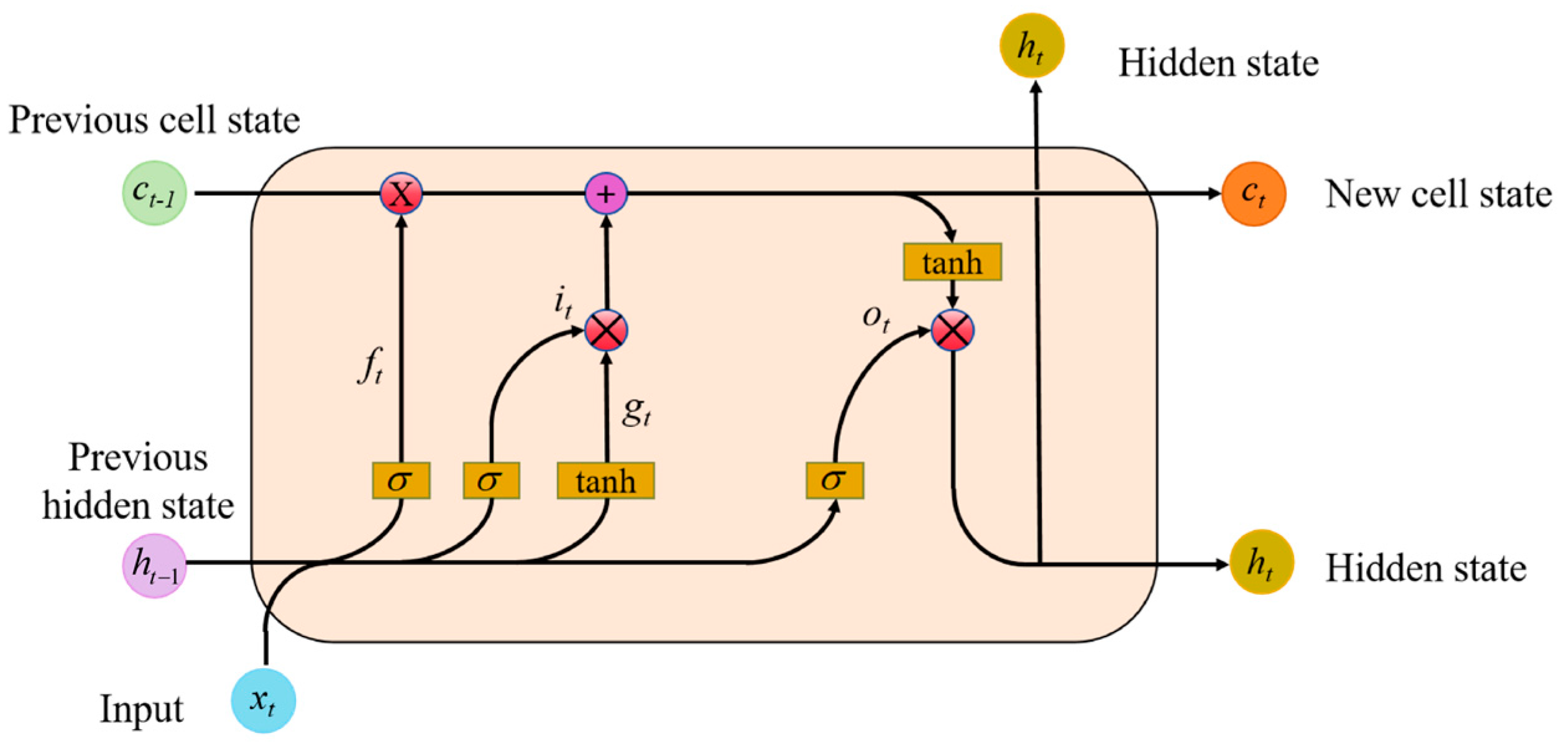
2.2.3. Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory
2.2.4. Fully Connected Layer (FC Layer)
2.2.5. Attention Mechanism
2.3. Evaluation Indexes
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.2. Single Test Result of MSBiLSTM-Attention Model
3.3. 10-Fold Cross-Validation Results of MSBiLSTM-Attention Model
3.4. Ablation Experiment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dolan, R.J. Emotion, cognition, and behavior. Science 2002, 298, 1191–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Su, C.; Zhang, J.; Cui, G.; Cichocki, A.; Zhou, C.; Li, J. EEG-based approach for recognizing human social emotion perception. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2020, 46, 101191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, R.M.; Yang, H.J.; Kim, S.H. Children emotion regulation: Development of neural marker by investigating human brain signals. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 70, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Romero, D.J.; Rincon, A.M.R.; Miguel-Cruz, A.; Yee, N.; Stroulia, E. Recognizing emotional states with wearables while playing a serious game. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolphs, R. Recognizing emotion from facial expressions: Psychological and neurological mechanisms. Behav. Cogn. Neurosci. Rev. 2002, 1, 21–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinsmith, A.; Bianchi-Berthouze, N. Affective body expression perception and recognition: A survey. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2012, 4, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleymani, M.; Pantic, M.; Pun, T. Multimodal emotion recognition in response to videos. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2011, 3, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrushin, V. Emotion in speech: Recognition and application to call centers. In Proceedings of the Artificial Neural Networks in Engineering, St. Louis, MO, USA, 7–10 November 1999; Volume 710. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.; Chen, F.; Xia, X.; Liu, Y. EEG Emotion Classification Based on Graph Convolutional Network. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindquist, K.A. and Barrett, L.F. A functional architecture of the human brain: Emerging insights from the science of emotion. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2012, 16, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Meng, Y.; Qiu, S.; Lv, Y.; Liu, Q. EEG Emotion Recognition by Fusion of Multi-Scale Features. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, W.; Dai, Y. A model for EEG-based emotion recognition: CNN-BI-LSTM with attention mechanism. Electronics 2023, 12, 3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wu, B.; Fang, J.; Lu, Z. Four types of expression-assisted EEG signal recognition methods using improved cospatial mode algorithm. J. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. 2022, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Hussain, A.A.; Lal, S.; Guesgen, H.W. A comprehensive review on critical issues and possible solutions of motor imagery based electroencephalography brain-computer interface. Sensors 2021, 21, 2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, H.; Chowdhury, A.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Samothrakis, S. Single-trial EEG classification with EEGNet and neural structured learning for improving BCI performance. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Glasgow, UK, 19–24 July 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.Y. and Hsieh, S. Classifying different emotional states by means of EEG-based functional connectivity patterns. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95415. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Z.; Sourina, O.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y. Real-time EEG-based emotion monitoring using stable features. Vis. Comput. 2016, 32, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, Z.; Frounchi, J.; Amiri, M. Wavelet-based emotion recognition system using EEG signal. Neural Comput. Appl. 2017, 28, 1985–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.Y.; Yoon, H.J. Affective classification using Bayesian classifier and supervised learning. In Proceedings of the 2012 12th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems, Jeju, Republic of Korea, 17–21 October 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatti, A.M.; Majid, M.; Anwar, S.M.; Khan, B. Human emotion recognition and analysis in response to audio music using brain signals. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 65, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Fu, B.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Y. Eeg-based emotion recognition using spatial-temporal-connective features via multi-scale CNN. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 41859–41867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, Y.; Banville, H.; Albuquerque, I.; Gramfort, A.; Falk, T.H.; Faubert, J. Deep learning-based electroencephalography analysis: A systematic review. J. Neural Eng. 2019, 16, 051001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xie, L.; Chai, B.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H. Spatial-frequency convolutional self-attention network for EEG emotion recognition. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 122, 108740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, W.; Cui, Z.; Zong, Y.; Ge, S. EEG emotion recognition based on graph regularized sparse linear regression. Neural Process. Lett. 2019, 49, 555–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Li, C.; Song, R.; Cheng, J.; Liu, Y.; Wan, F.; Chen, X. EEG-based emotion recognition via channel-wise attention and self attention. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2020, 14, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Gu, Z.; Qi, F.; Sun, C.; Guo, H.; Sun, L. CMLP-Net: A convolution-multilayer perceptron network for EEG-based emotion recognition. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 96, 106620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Xie, H.; Tao, J.; Li, Y.; Pei, G.; Li, T.; Lv, Z. ICaps-ResLSTM: Improved capsule network and residual LSTM for EEG emotion recognition. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 87, 105422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.L.; Lu, B.L. Investigating critical frequency bands and channels for EEG-based emotion recognition with deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Auton. Ment. Dev. 2015, 7, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.N.; Zhu, J.Y.; Lu, B.L. Differential entropy feature for EEG-based emotion classification. In Proceedings of the 2013 6th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER), San Diego, CA, USA, 6–8 November 2013; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.L.; Liu, W.; Lu, Y.; Lu, B.L.; Cichocki, A. Emotionmeter: A multimodal framework for recognizing human emotions. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2018, 49, 1110–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, A.L.; Hannun, A.Y.; Ng, A.Y. Rectifier nonlinearities improve neural network acoustic models. In Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–21 June 2013; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Q. Dual-modal and multi-scale deep neural networks for sleep staging using EEG and ECG signals. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 66, 102455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharan, B.; Arbeláez, P.; Girshick, R.; Malik, J. Hypercolumns for object segmentation and fine-grained localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Ma, W.; Dang, X. Motor imagery EEG recognition based on conditional optimization empirical mode decomposition and multi-scale convolutional neural network. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 149, 113285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Zhou, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, N. HS-CNN: A CNN with hybrid convolution scale for EEG motor imagery classification. J. Neural Eng. 2020, 17, 016025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, CO, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lawhern, V.J.; Solon, A.J.; Waytowich, N.R.; Gordon, S.M.; Hung, C.P.; Lance, B.J. EEGNet: A compact convolutional neural network for EEG-based brain–computer interfaces. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 056013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini MS, K.; Firoozabadi, S.M.; Badie, K.; Azadfallah, P. Personality-based emotion recognition using EEG signals with a CNN-LSTM network. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, S. Transformer help CNN see better: A lightweight hybrid apple disease identification model based on transformers. Agriculture 2022, 12, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, C.; Zhao, L.; Wang, S. EEG Emotion Recognition Network Based on Attention and Spatiotemporal Convolution. Sensors 2024, 24, 3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| epoch number | 100 |
| learning rate | 0.001 |
| batch size | 1024 |
| optimizer | Adam |
| loss function | categorical_cross-entropy |
| convolution kernel | 32 |
| activation function | ReLU |
| multi-scale convolution | 1 × 1, 1 × 3 |
| Bi-LSTM | 32 |
| FC1 | 64 |
| FC2 | 32 |
| classifier | Softmax |
| random seed | 42 |
| Methods | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | MCC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN-GRU | 70.38 | 70.42 | 70.38 | 70.32 | 55.64 |
| CNN-LSTM | 94.65 | 94.67 | 94.65 | 94.65 | 92.00 |
| 1D CAE | 96.01 | 96.06 | 96.01 | 96.01 | 94.05 |
| 1D InceptionV1 | 86.65 | 86.71 | 86.65 | 86.64 | 80.01 |
| EEGNet | 37.56 | 36.65 | 37.56 | 36.17 | 6.5 |
| VGG16-LSTM | 98.01 | 98.02 | 98.01 | 98.01 | 97.02 |
| Adaboost | 54.29 | 55.03 | 54.29 | 53.99 | 31.86 |
| Bayes | 40.95 | 42.97 | 40.95 | 35.88 | 13.77 |
| MSBiLSTM- Attention | 99.44 | 99.44 | 99.44 | 99.43 | 99.16 |
| Methods | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | MCC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN-GRU | 56.94 | 57.54 | 56.94 | 56.70 | 42.85 |
| CNN-LSTM | 84.90 | 84.97 | 84.90 | 84.89 | 79.90 |
| 1D CAE | 88.45 | 88.54 | 88.45 | 88.46 | 84.62 |
| 1D InceptionV1 | 77.96 | 78.14 | 77.96 | 77.94 | 70.68 |
| EEGNet | 26.45 | 26.59 | 26.45 | 25.29 | 2.1 |
| VGG16-LSTM | 96.79 | 96.83 | 96.79 | 96.79 | 95.21 |
| Adaboost | 37.49 | 37.52 | 37.49 | 37.41 | 16.69 |
| Bayes | 26.10 | 30.44 | 26.10 | 17.39 | 2.46 |
| MSBiLSTM- Attention | 99.85 | 99.85 | 99.85 | 99.85 | 99.80 |
| Methods | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | MCC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN-GRU | 81.67 | 81.82 | 81.67 | 81.67 | 72.57 |
| CNN-LSTM | 94.86 | 94.87 | 94.86 | 94.85 | 92.30 |
| 1D CAE | 93.65 | 93.67 | 93.65 | 93.65 | 90.49 |
| 1D InceptionV1 | 88.32 | 88.37 | 88.32 | 88.31 | 82.51 |
| EEGNet | 45.46 | 46.34 | 45.47 | 44.91 | 18.62 |
| VGG16-LSTM | 93.98 | 94.01 | 93.98 | 93.99 | 90.98 |
| Adaboost | 52.63 | 53.38 | 52.64 | 52.35 | 29.35 |
| Bayes | 41.79 | 42.23 | 41.79 | 38.82 | 13.75 |
| MSBiLSTM- Attention | 99.49 | 99.50 | 99.49 | 99.49 | 99.24 |
| Methods | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | MCC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN-GRU | 58.55 | 58.87 | 58.55 | 58.43 | 44.88 |
| CNN-LSTM | 84.13 | 84.18 | 84.13 | 84.12 | 78.86 |
| 1D CAE | 84.13 | 84.21 | 84.13 | 84.13 | 78.87 |
| 1D InceptionV1 | 76.55 | 76.68 | 76.55 | 76.54 | 68.78 |
| EEGNet | 41.94 | 46.79 | 41.93 | 40.67 | 23.75 |
| VGG16-LSTM | 98.28 | 98.28 | 98.28 | 98.28 | 97.71 |
| Adaboost | 35.93 | 35.98 | 35.93 | 35.82 | 14.61 |
| Bayes | 25.77 | 28.84 | 25.77 | 17.34 | 1.66 |
| MSBiLSTM- Attention | 99.70 | 99.70 | 99.70 | 99.70 | 99.60 |
| Methods | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | MCC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Block1 | 98.24 | 98.25 | 98.24 | 98.24 | 97.37 |
| Block2 | 99.04 | 99.04 | 99.04 | 99.04 | 98.56 |
| MSBiLSTM- Attention | 99.49 | 99.50 | 99.49 | 99.49 | 99.24 |
| Methods | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | MCC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Block1 | 97.50 | 97.50 | 97.49 | 97.49 | 96.67 |
| Block2 | 98.22 | 98.22 | 98.22 | 98.22 | 97.63 |
| MSBiLSTM- Attention | 99.70 | 99.70 | 99.70 | 99.70 | 99.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Huang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y. MSBiLSTM-Attention: EEG Emotion Recognition Model Based on Spatiotemporal Feature Fusion. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10030178
Ma Y, Huang Z, Yang Y, Chen Z, Dong Q, Zhang S, Li Y. MSBiLSTM-Attention: EEG Emotion Recognition Model Based on Spatiotemporal Feature Fusion. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(3):178. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10030178
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yahong, Zhentao Huang, Yuyao Yang, Zuowen Chen, Qi Dong, Shanwen Zhang, and Yuan Li. 2025. "MSBiLSTM-Attention: EEG Emotion Recognition Model Based on Spatiotemporal Feature Fusion" Biomimetics 10, no. 3: 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10030178
APA StyleMa, Y., Huang, Z., Yang, Y., Chen, Z., Dong, Q., Zhang, S., & Li, Y. (2025). MSBiLSTM-Attention: EEG Emotion Recognition Model Based on Spatiotemporal Feature Fusion. Biomimetics, 10(3), 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10030178







