Development of Acellular Hepatic Scaffolds Through a Low-Cost Gravity-Assisted Perfusion Decellularization Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Model and Ethical Considerations
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Liver Harvesting Procedure
2.4. Decellularization Protocols
2.4.1. Immersion Method
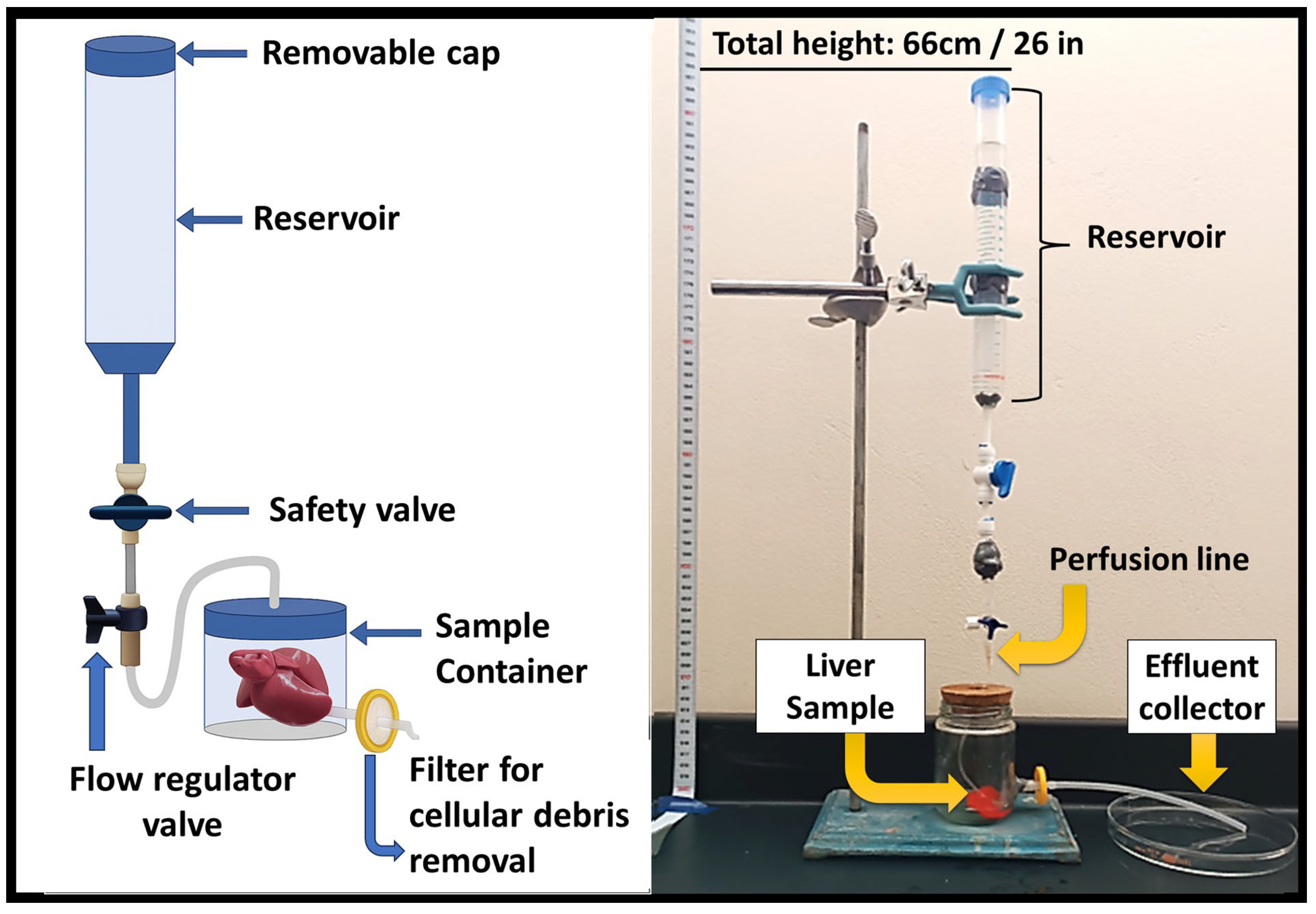
2.4.2. Gravity-Assisted Perfusion Method
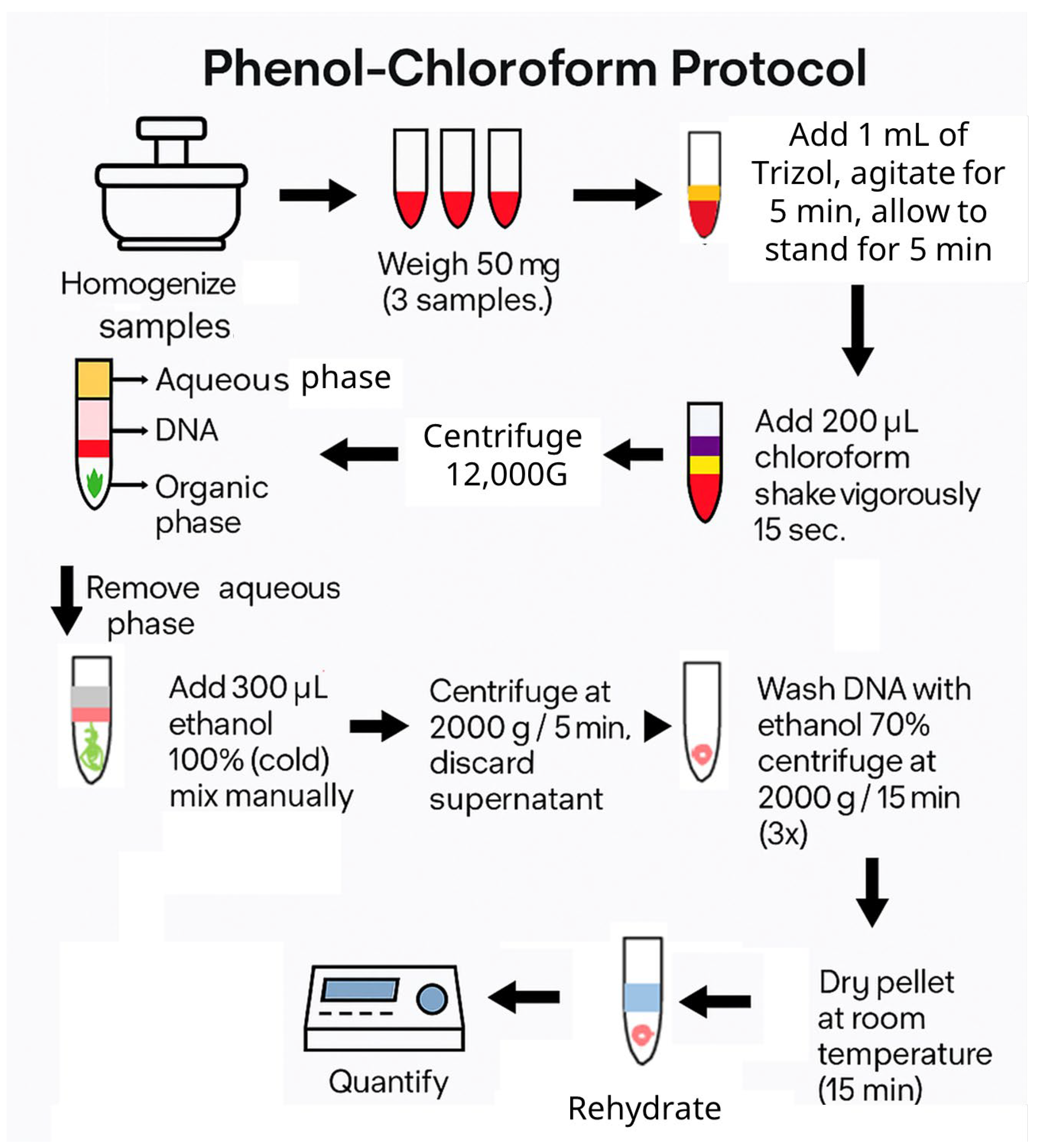
2.4.3. DNA Extraction and Quantification
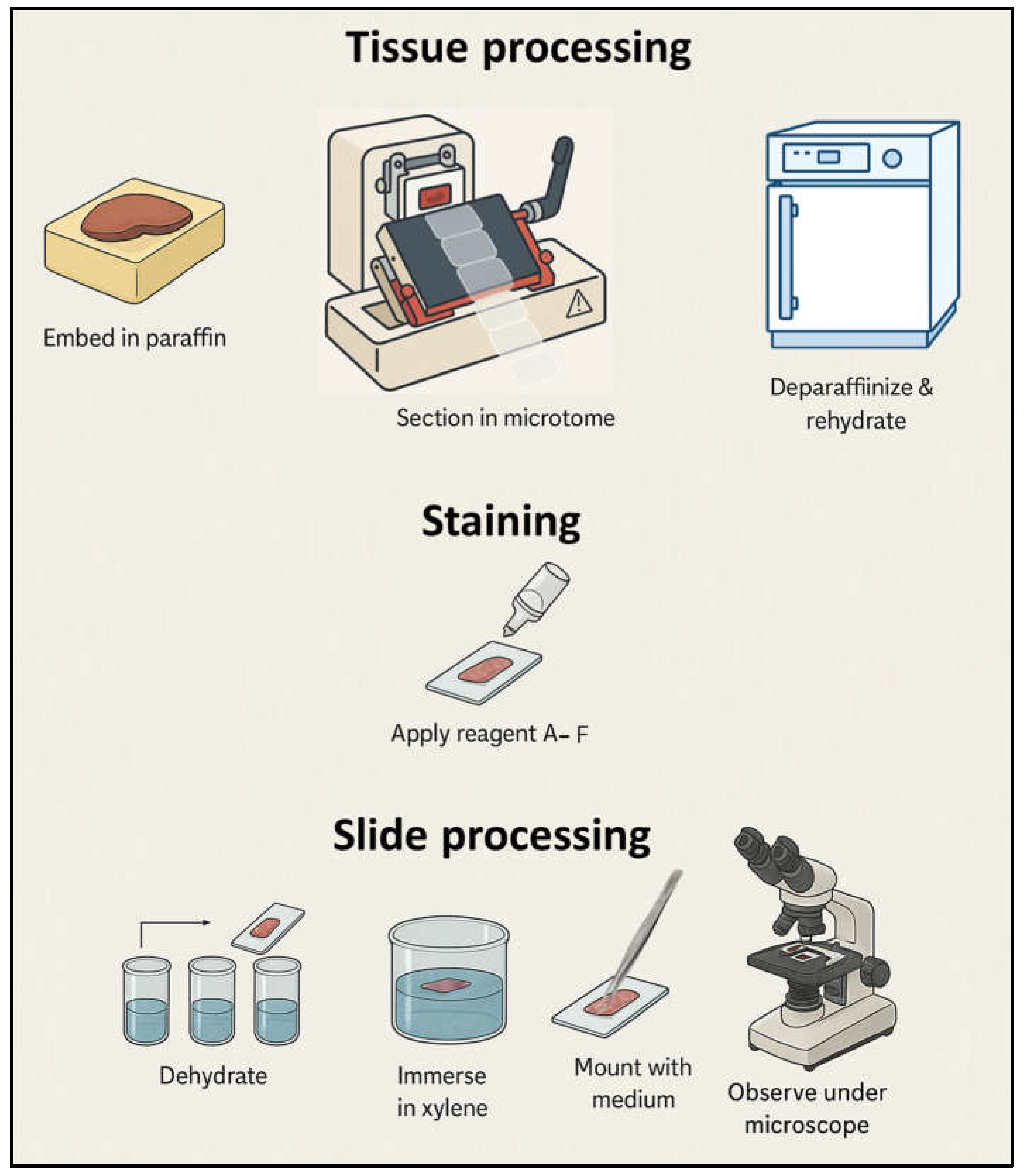
2.4.4. Histological Evaluation
3. Results
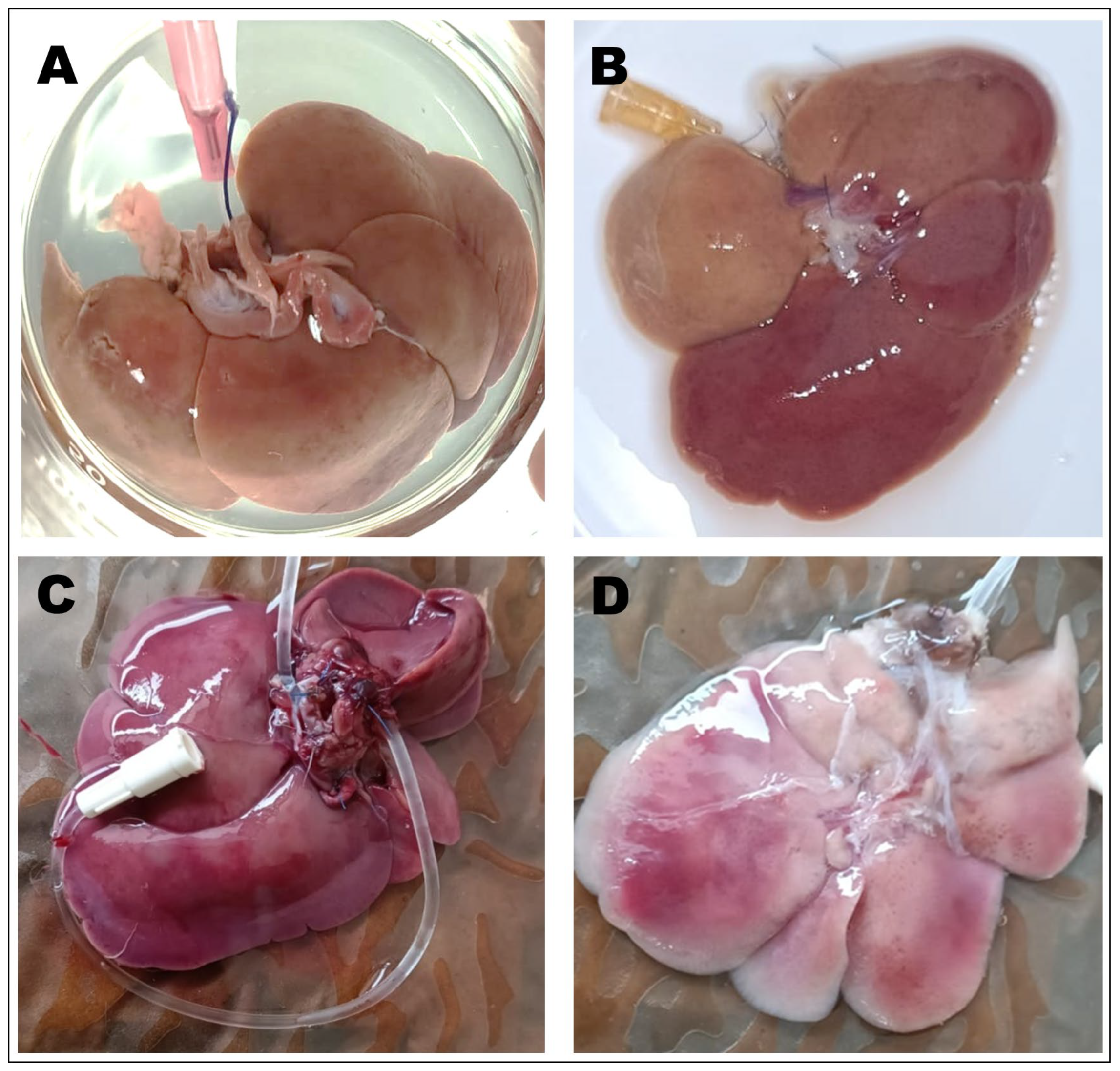
3.1. Macroscopic Analysis
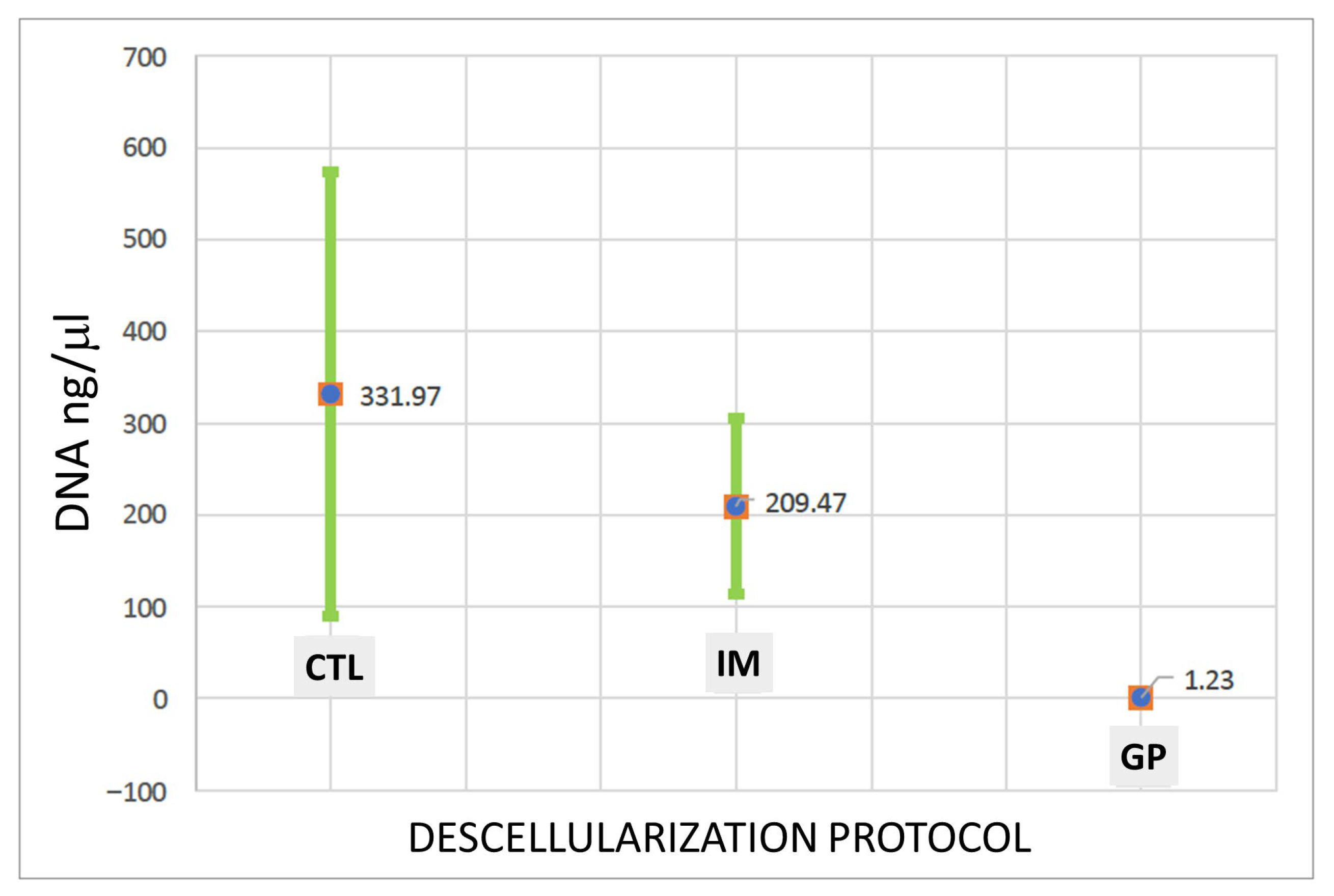
3.2. DNA Quantification
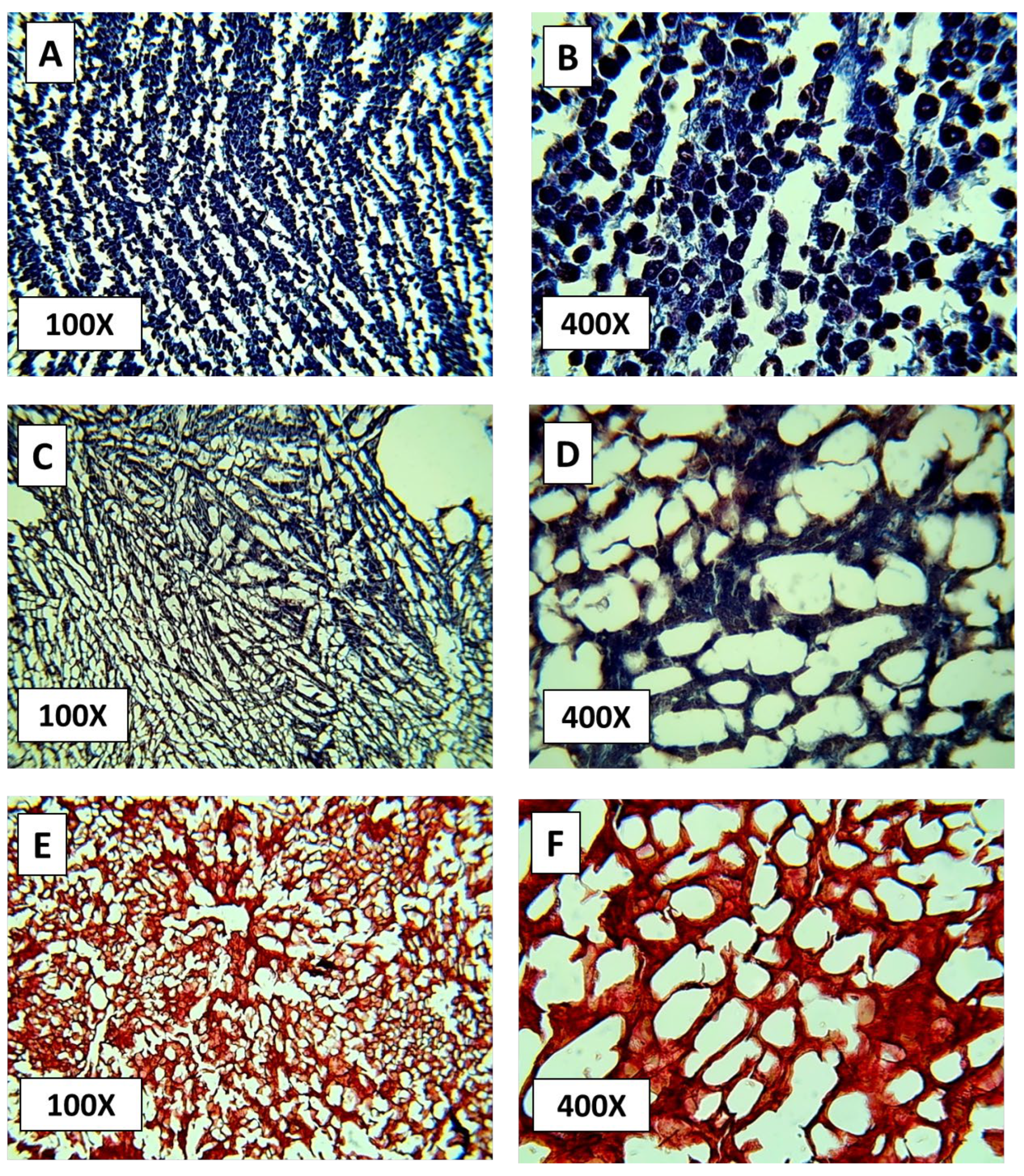
3.3. Histological Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nair, D.G.; Weiskirchen, R. Recent Advances in Liver Tissue Engineering as an Alternative and Complementary Approach for Liver Transplantation. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 46, 262–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Jiang, W.; Huang, F.; Song, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, H. Recent Advances in Liver Engineering with Decellularized Scaffold. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 831477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Assiri, A.; Dhar, D.; Broering, D. A Promising Approach to Develop Functional Liver Surrogates. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 1759–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Kock, J.; Ceelen, L.; De Spiegelaere, W.; Casteleyn, C.; Claes, P.; Vanhaecke, T.; Rogiers, V. Simple and Quick Method for Whole-Liver Decellularization: A Novel In Vitro Three-Dimensional Bioengineering Tool? Arch. Toxicol. 2011, 85, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS). Organ Donation Statistics. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Available online: https://www.organdonor.gov/learn/organ-donation-statistics (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- González, F.X.; Cordero, E.; López, R. Deceased Donation and Organ Transplantation in Mexico. Transplant. Proc. 2016, 48, 675–680. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32538984/ (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- Centro Nacional de Trasplantes (CENATRA). Informe Estadístico de Donación y Trasplantes en México. 2024. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cenatra (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- Morawski, M.; Krasnodębski, M.; Rochoń, J.; Kubiszewski, H.; Marzęcki, M.; Topyła, D.; Murat, K.; Staszewski, M.; Szczytko, J.; Maleszewski, M.; et al. Decellularized Liver Matrices for Expanding the Donor Pool—An Evaluation of Existing Protocols and Future Trends. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Callanan, A. Comparison of Methods for Whole-Organ Decellularization in Tissue Engineering of Bioartificial Organs. J. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2012, 19, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.K.C.; Ekser, B.; Tector, A.J. A Brief History of Clinical Xenotransplantation. Int. J. Surg. 2015, 23, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupon, E.; Acun, A.; Taveau, C.B.; Oganesyan, R.; Lancia, H.H.; Andrews, A.R.; Randolph, M.A.; Cetrulo, C.L.; Lellouch, A.G.; Uygun, B.E. Optimized Decellularization of a Porcine Fasciocutaneous Flap. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hengel, E.V.A.; van der Laan, L.J.W.; de Jonge, J.; Verstegen, M.M.A. Towards Safety and Regulation Criteria for Clinical Applications of Decellularized Organ-Derived Matrices. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struecker, B.; Butter, A.; Hillebrandt, K.; Polenz, D.; Reutzel-Selke, A.; Tang, P.; Lippert, S.; Leder, A.; Rohn, S.; Geisel, D.; et al. Improved Rat Liver Decellularization by Arterial Perfusion under Oscillating Pressure Conditions. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2017, 11, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, K.T.; Prasad, P.R.; Sandhu, J.S.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, N.A.N.; Shridhar, N.B.; Bisht, B.; Paul, M.K. Decellularization Techniques: Unveiling the Blueprint for Tracheal Tissue Engineering. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2025, 13, 1518905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.S.; D’Elia, A.; Hadzimustafic, N.; Adil, A.; Karoubi, G.; Waddell, T.K.; Haykal, S. Bioengineering of Vascularized Porcine Flaps Using Perfusion–Recellularization. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croce, S.; Peloso, A.; Zoro, T.; Avanzini, M.A.; Cobianchi, L. A Hepatic Scaffold from Decellularized Liver Tissue. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toprakhisar, B.; Verfaillie, C.M.; Kumar, M. Advances in Recellularization of Decellularized Liver Grafts with Different Liver (Stem) Cells: Towards Clinical Applications. Cells 2023, 12, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meșină, M.; Mîndrilă, I.; Meșină, C.; Obleagă, C.V.; Istrătoaie, O. A Perfusion Decellularization Heart Model—An Interesting Tool for Cell–Matrix Interaction Studies. J. Mind Med. Sci. 2019, 6, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchuk, O.I.; Korcheva, V.V.; Moskalenko, N.S.; Kyryk, V.M.; Kot, K.V.; Krasnienkov, D.S. Application of Decellularization Methods for Scaffold Production: Advantages, Disadvantages, Biosafety, and Modifications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2025, 13, 1621641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diedrich, A.M.; Daneshgar, A.; Tang, P.; Klein, O.; Mohr, A.; Onwuegbuchulam, O.A.; von rueden, S.; Menck, K.; Bleckmann, A.; Juratli, M.A.; et al. Proteomic Analysis of Decellularized Mice Liver and Kidney Extracellular Matrces. J. Biol. Eng. 2024, 18, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.A.; Kren, S.M.; Rhett, K.; Robertson, M.J.; Morrissey, J.; Rodriguez, O.E.; Virk, H.; Chacon-Alberty, L.; da Costa, E.C.; Mesquita, F.C.P.; et al. Characterization of Perfusion-Decellularized Whole Animal Body, Isolated Organs, and Multi-Organ Systems for Tissue Engineering Applications. Physiol. Rep. 2021, 9, e14817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X. The Prospect of Hepatic Decellularized Extracellular Matrix as a Bioink for Liver 3D Bioprinting. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Guerrero, N.A.; Varela-Echavarría, A.; Lozano-Flores, C.; Vázquez-Cuevas, F.G.; Velázquez-Miranda, E.; Reyes-López, J.V.; García-Solís, P.; Solís-S, J.C.; Hernandez-Montiel, H.L. A New Strategy for the Decellularization of Whole Organs by Hydrostatic Pressure. Biotechnol. Prog. 2022, 38, e3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubarevich, A.; Osswald, A.; Amanov, L.; Rad, A.A.; Schmack, B.; Ruhparwar, A.; Weymann, A. Development and Evaluation of a Novel Combined Perfusion Decellularization Heart–Lung Model for Tissue Engineering of Bioartificial Heart–Lung Scaffolds. Artif. Organs 2023, 47, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NOM-062-ZOO-1999; Especificaciones Técnicas Para la Producción, Cuidado y uso de los Animales de Laboratorio. Secretaría de Agricultura, Ganadería, Desarrollo Rural, Pesca y Alimentación (SAGARPA): Ciudad de México, México, 1999.
- NOM-087-SEMARNAT-SSA1-2002; Protección Ambiental—Residuos Peligrosos Biológico-Infecciosos—Clasificación y Especificaciones de Manejo. Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales (SEMARNAT) y Secretaría de Salud: Ciudad de México, México, 2002.
- Geerts, S.; Ozer, S.; Jaramillo, M.; Yarmush, M.L.; Uygun, B.E. Nondestructive Methods for Monitoring Cell Removal During Rat Liver Decellularization. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2016, 22, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uygun, B.E.; Price, G.; Saeidi, N.; Izamis, M.-L.; Berendsen, T.; Yarmush, M.; Uygun, K. Decellularization and Recellularization of Whole Livers. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 48, e2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nari, G.A.; Cid, M.; Comín, R.; Reyna, L.; Juri, G.; Taborda, R.; Salvatierra, N.A. Preparación de una matriz extracelular tridimensional por descelularización de hígados de conejos. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2013, 105, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allu, I.; Sahi, A.K.; Koppadi, M.; Gundu, S.; Sionkowska, A. Decellularization Techniques for Tissue Engineering: Towards Replicating Native Extracellular Matrix Architecture in Liver Regeneration. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, D.L.; Rostami, S.; Karoubi, G.; Haykal, S. Perfusion Decellularization for Vascularized Composite Allotransplantation. SAGE Open Med. 2022, 10, 20503121221123893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neishabouri, A.; Soltani Khaboushan, A.; Daghigh, F.; Kajbafzadeh, A.-M.; Majidi Zolbin, M. Decellularization in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine: Evaluation, Modification, and Application Methods. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 805299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, D.; Joshi, A.; Baghel, V.S.; Ananthasuresh, G.K.; Asthana, S.; Homer-Vanniasinkam, S.; Chatterjee, K. Design-encoded dual shape-morphing and shape-memory in 4D printed polymer parts toward cellularized vascular grafts. J. Mater. Chemestry B 2024, 23, 5678–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, G.H.D.R.; da Silva-Júnior, L.N.; Gibin, M.S.; dos Santos, H.; Horvath-Pereira, B.d.O.; Pinho, L.B.M.; Baesso, M.L.; Sato, F.; Hernandes, L.; Long, C.R.; et al. Perfusion and Ultrasonication Produce a Decellularized Porcine Whole-Ovary Scaffold with a Preserved Microarchitecture. Cells 2023, 12, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, T.A.; Alzhrani, A.; Nakamura, M.; Iwanaga, S.; Wani, S.I.; Altuhami, A.; Kazmi, S.; Arai, K.; Shamma, T.; Obeid, D.A.; et al. Whole Liver Derived Acellular Extracellular Matrix for Bioengineering of Liver Constructs: An Updated Review. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duarte-Ortega, M.F.; Enríquez-Sánchez, L.B.; Pérez-Ruiz, M.D.; Nevárez-Rascón, A.; Favila-Pérez, M.A.; Castillo-González, A.R.; Quiñonez-Flores, C.M.; Hinojos-Gallardo, L.C.; Ríos-Barrera, V.A.; Arzate-Quintana, C. Development of Acellular Hepatic Scaffolds Through a Low-Cost Gravity-Assisted Perfusion Decellularization Method. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10110777
Duarte-Ortega MF, Enríquez-Sánchez LB, Pérez-Ruiz MD, Nevárez-Rascón A, Favila-Pérez MA, Castillo-González AR, Quiñonez-Flores CM, Hinojos-Gallardo LC, Ríos-Barrera VA, Arzate-Quintana C. Development of Acellular Hepatic Scaffolds Through a Low-Cost Gravity-Assisted Perfusion Decellularization Method. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(11):777. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10110777
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuarte-Ortega, María Fernanda, Luis Bernardo Enríquez-Sánchez, Manuel David Pérez-Ruiz, Alfredo Nevárez-Rascón, María Alejandra Favila-Pérez, Alva Rocío Castillo-González, Celia María Quiñonez-Flores, Luis Carlos Hinojos-Gallardo, Víctor Adolfo Ríos-Barrera, and Carlos Arzate-Quintana. 2025. "Development of Acellular Hepatic Scaffolds Through a Low-Cost Gravity-Assisted Perfusion Decellularization Method" Biomimetics 10, no. 11: 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10110777
APA StyleDuarte-Ortega, M. F., Enríquez-Sánchez, L. B., Pérez-Ruiz, M. D., Nevárez-Rascón, A., Favila-Pérez, M. A., Castillo-González, A. R., Quiñonez-Flores, C. M., Hinojos-Gallardo, L. C., Ríos-Barrera, V. A., & Arzate-Quintana, C. (2025). Development of Acellular Hepatic Scaffolds Through a Low-Cost Gravity-Assisted Perfusion Decellularization Method. Biomimetics, 10(11), 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10110777







