Endoscopic Dilation for Fibrostenotic Complications in Eosinophilic Esophagitis—A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Evaluation of Esophageal Fibrostenotic Complications in Eosinophilic Esophagitis
2.1. Endoscopic Features of Inflammation and Fibrosis in Eosinophilic Esophagitis
2.2. Association Between Obstructive Symptoms and Quality of Life
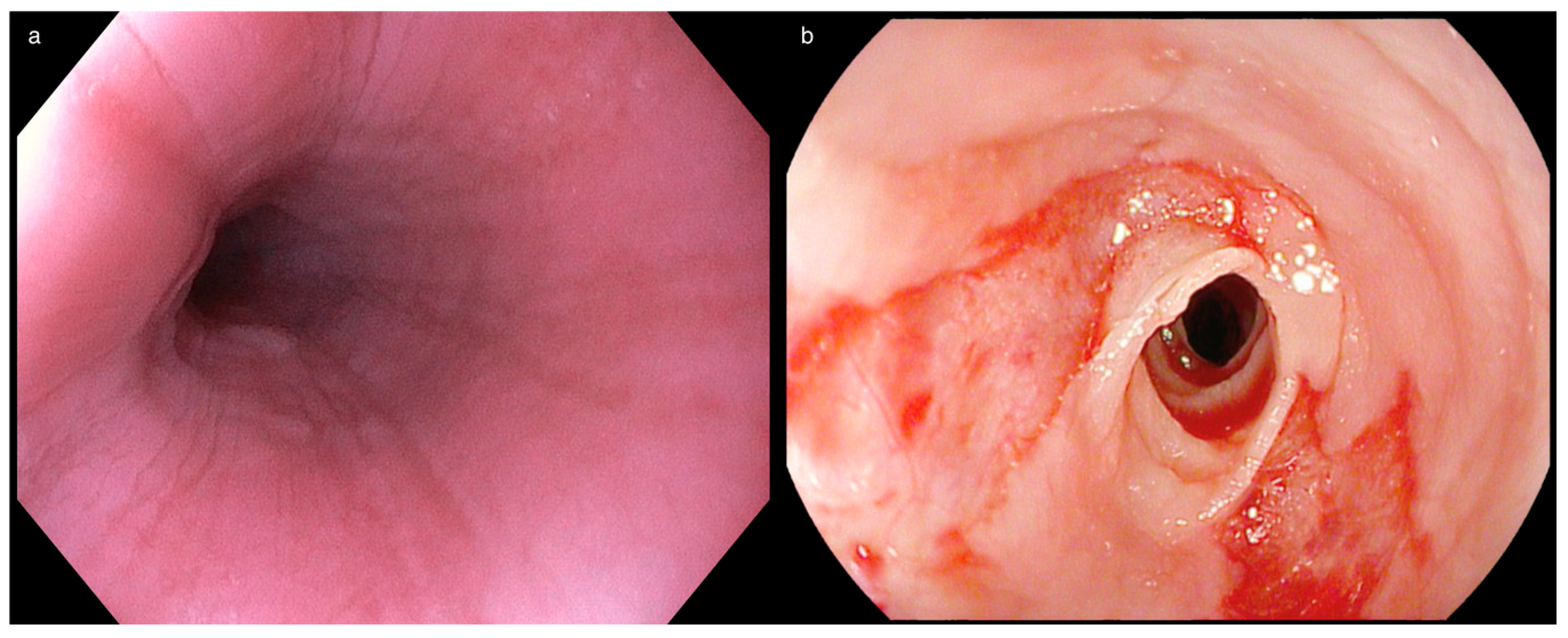
2.3. Definition and Grading of Esophageal Rings and Strictures
2.4. Methods to Assess Fibrostenotic Complications of EoE
2.4.1. Endoscopy and Radiology
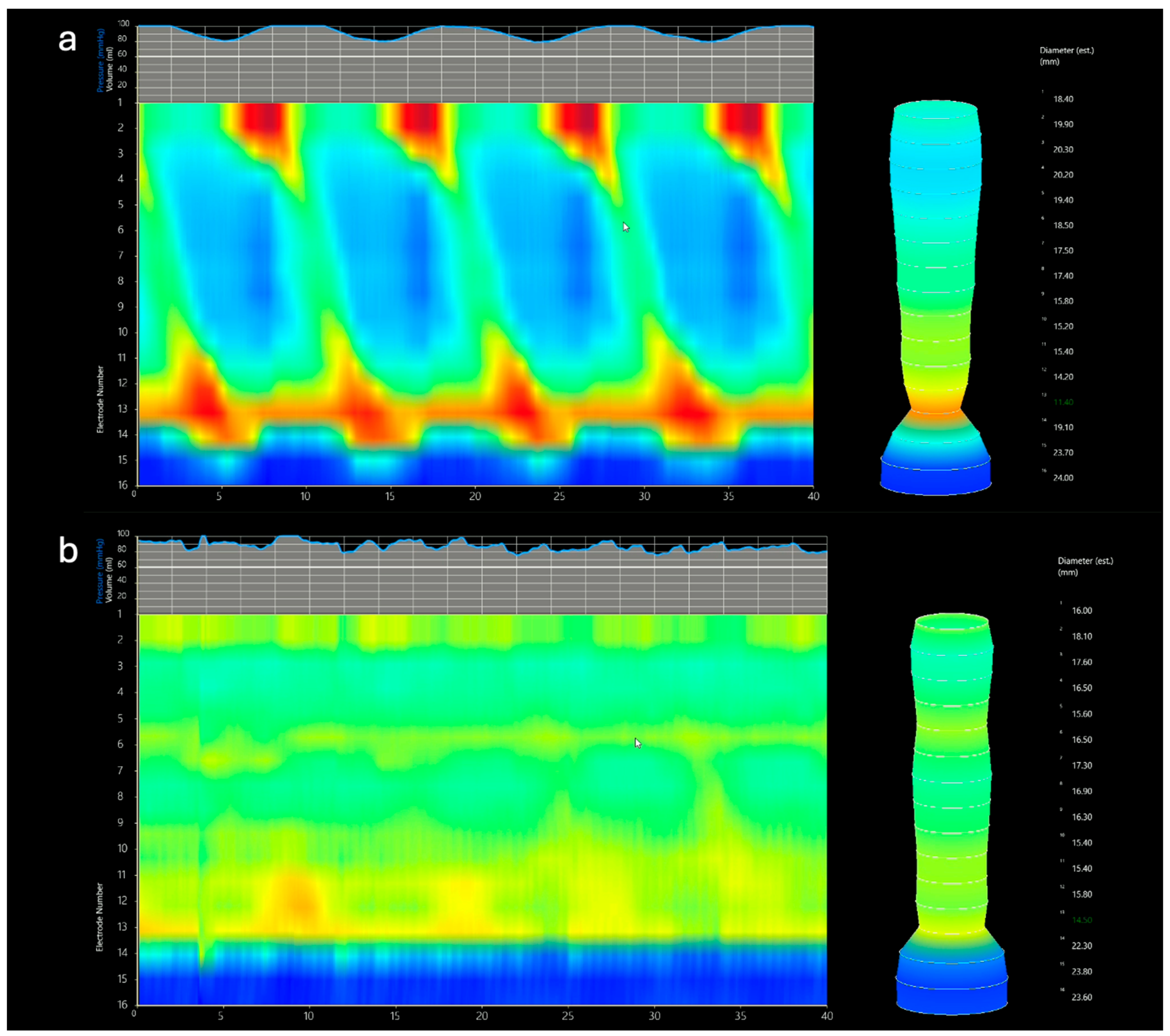
2.4.2. Functional Luminal Imaging Probe (FLIP)
3. Endoscopic Dilation of Fibrostenotic Complications in Eosinophilic Esophagitis
3.1. Role of Endoscopic Dilation in Eosinophilic Esophagitis
3.2. Practical Considerations for Esophageal Dilation
3.3. Informed Consent, Setting and Dilation Methods
3.3.1. Informed Consent
3.3.2. Setting (Fluoroscopy and Anesthesia)
3.4. Endoscopic Dilators for Eosinophilic Esophagitis
3.5. Mechanical Dilators (Savary–Gilliard Bougie, BougieCap)
3.6. Balloon Dilation
EsoFLIP (Functional Luminal Imaging Probe)
3.7. Post-Dilation Clinical Management
3.8. Management of Esophageal Complications After Dilation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CT | Computer tomography |
| EGD | Esophagogastroduodenoscopy |
| EoE | eosinophilic esophagitis |
| EREFS | EoE Endoscopic Reference Score |
| FLIP | Functional luminal imaging probe |
| TTS | through-the-scope |
References
- Kim, H.P.; Vance, R.B.; Shaheen, N.J.; Dellon, E.S. The prevalence and diagnostic utility of endoscopic features of eosinophilic esophagitis: A meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 988–996.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorge, A.; Aldinio, G.; Marinoni, B.; Visaggi, P.; Penagini, R.; Maniero, D.; Ghisa, M.; Marabotto, E.; de Bortoli, N.; Pasta, A.; et al. Distribution of esophageal inflammation in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis and its impact on diagnosis and outcome. Dig. Liver Dis. 2025, 57, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bortoli, N.; Visaggi, P.; Penagini, R.; Annibale, B.; Baiano Svizzero, F.; Barbara, G.; Bartolo, O.; Battaglia, E.; Di Sabatino, A.; De Angelis, P.; et al. The 1st EoETALY Consensus on the Diagnosis and Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis—Definition, Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2024, 56, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bortoli, N.; Visaggi, P.; Penagini, R.; Annibale, B.; Baiano Svizzero, F.; Barbara, G.; Bartolo, O.; Battaglia, E.; Di Sabatino, A.; De Angelis, P.; et al. The 1st EoETALY Consensus on the Diagnosis and Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis-Current Treatment and Monitoring. Dig. Liver Dis. 2024, 56, 1173–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; Neilson, E.G. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for fibrosis. J. Clin. Invest. 2003, 112, 1776–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-González, L.; Rodríguez-Alcolado, L.; Laserna-Mendieta, E.J.; Navarro, P.; Lucendo, A.J.; Grueso-Navarro, E. Fibrous Remodeling in Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Clinical Facts and Pathophysiological Uncertainties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colizzo, J.M.; Clayton, S.B.; Richter, J.E. Intrabolus pressure on high-resolution manometry distinguishes fibrostenotic and inflammatory phenotypes of eosinophilic esophagitis. Dis. Esophagus 2016, 29, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visaggi, P.; Ghisa, M.; Marabotto, E.; Venturini, A.; Stefani Donati, D.; Bellini, M.; Savarino, V.; de Bortoli, N.; Savarino, E. Esophageal dysmotility in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis: Pathogenesis, assessment tools, manometric characteristics, and clinical implications. Esophagus 2023, 20, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visaggi, P.; Del Corso, G.; Solinas, I.; Ovidi, F.; Adamo, G.; Dulmin, I.; Svizzero, F.B.; Bellini, M.; Savarino, E.V.; de Bortoli, N. Adaptive Behaviors, Esophageal Anxiety and Hypervigilance Modify the Association Between Dysphagia Perception and Histological Disease Activity in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visaggi, P.; Ghisa, M.; Vespa, E.; Barchi, A.; Mari, A.; Pasta, A.; Marabotto, E.; de Bortoli, N.; Savarino, E.V. Optimal Assessment, Treatment, and Monitoring of Adults with Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Strategies to Improve Outcomes. Immunotargets Ther. 2024, 13, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laserna-Mendieta, E.J.; Navarro, P.; Casabona-Francés, S.; Savarino, E.V.; Pérez-Martínez, I.; Guagnozzi, D.; Barrio, J.; Perello, A.; Guardiola-Arévalo, A.; Betoré-Glaria, M.E.; et al. Differences between childhood- and adulthood-onset eosinophilic esophagitis: An analysis from the EoE connect registry. Dig. Liver Dis. 2023, 55, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visaggi, P.; Savarino, E.; Sciume, G.; Chio, T.D.; Bronzini, F.; Tolone, S.; Frazzoni, M.; Pugno, C.; Ghisa, M.; Bertani, L.; et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: Clinical, endoscopic, histologic and therapeutic differences and similarities between children and adults. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2021, 14, 1756284820980860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoepfer, A.M.; Safroneeva, E.; Bussmann, C.; Kuchen, T.; Portmann, S.; Simon, H.U.; Straumann, A. Delay in diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis increases risk for stricture formation in a time-dependent manner. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 1230–1236.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, N.; Tapper, E.B.; Corban, C.; Sommers, T.; Leffler, D.A.; Lembo, A.J. The clinical predictors of aetiology and complications among 173 patients presenting to the Emergency Department with oesophageal food bolus impaction from 2004–2014. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 42, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperry, S.L.; Crockett, S.D.; Miller, C.B.; Shaheen, N.J.; Dellon, E.S. Esophageal foreign-body impactions: Epidemiology, time trends, and the impact of the increasing prevalence of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2011, 74, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenti, M.V.; Savarino, E.; Mauro, A.; Penagini, R.; Racca, F.; Ghisa, M.; Laserra, G.; Merli, S.; Arsiè, E.; Longoni, V.; et al. Diagnostic delay and misdiagnosis in eosinophilic oesophagitis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2021, 53, 1632–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Molina-Infante, J.; Arias, Á.; von Arnim, U.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Bussmann, C.; Amil Dias, J.; Bove, M.; González-Cervera, J.; Larsson, H.; et al. Guidelines on eosinophilic esophagitis: Evidence-based statements and recommendations for diagnosis and management in children and adults. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2017, 5, 335–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, A.; Haboubi, H.N.; Attwood, S.E.; Auth, M.K.H.; Dunn, J.M.; Sweis, R.; Morris, D.; Epstein, J.; Novelli, M.R.; Hunter, H.; et al. British Society of Gastroenterology (BSG) and British Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (BSPGHAN) joint consensus guidelines on the diagnosis and management of eosinophilic oesophagitis in children and adults. Gut 2022, 71, 1459–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visaggi, P.; Del Corso, G.; Baiano Svizzero, F.; Ghisa, M.; Bardelli, S.; Venturini, A.; Stefani Donati, D.; Barberio, B.; Marciano, E.; Bellini, M.; et al. Artificial Intelligence Tools for the Diagnosis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Adults Reporting Dysphagia: Development, External Validation, and Software Creation for Point-of-Care Use. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2024, 12, 1008–1016.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorge, A.; Coletta, M.; Elli, L.; Bredenoord, A.J. Clinical practices and adherence to guidelines for eosinophilic esophagitis: A European survey. Dig. Liver Dis. 2024, 56, 1196–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, P.; Safroneeva, E.; Schoepfer, A.; Greuter, T.; Biedermann, L.; Schlag, C.; Labenz, J.; Auth, M.K.H.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Chang, J.W.; et al. Management of eosinophilic esophagitis associated food impaction in Europe and the United States. Dis. Esophagus 2022, 35, doac003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.W.; Olson, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Dolan, R.; Greenson, J.; Sanders, G.; Rubenstein, J.H. Loss to follow-up after food impaction among patients with and without eosinophilic esophagitis. Dis. Esophagus 2019, 32, doz056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Ochiai, Y.; Hosoi, A.; Okamura, T.; Hayasaka, J.; Mitsunaga, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Odagiri, H.; Nomura, K.; Yamashita, S.; et al. Mucosal and Submucosal Thickening of Esophageal Wall Is a Promising Factor in the Development of Symptoms in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gut Liver 2024, 18, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straumann, A.; Conus, S.; Degen, L.; Frei, C.; Bussmann, C.; Beglinger, C.; Schoepfer, A.; Simon, H.U. Long-term budesonide maintenance treatment is partially effective for patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 400–409.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoepfer, A.M.; Simko, A.; Bussmann, C.; Safroneeva, E.; Zwahlen, M.; Greuter, T.; Biedermann, L.; Vavricka, S.; Godat, S.; Reinhard, A.; et al. Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Relationship of Subepithelial Eosinophilic Inflammation With Epithelial Histology, Endoscopy, Blood Eosinophils, and Symptoms. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, I. Clinical relevance of esophageal subepithelial activity in eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moawad, F.J.; Cheatham, J.G.; DeZee, K.J. Meta-analysis: The safety and efficacy of dilation in eosinophilic oesophagitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 38, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, D.A.; Hirano, I. Narrow-caliber esophagus of eosinophilic esophagitis: Difficult to define, resistant to remedy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2016, 83, 1149–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hirano, I.; Moy, N.; Heckman, M.G.; Thomas, C.S.; Gonsalves, N.; Achem, S.R. Endoscopic assessment of the oesophageal features of eosinophilic oesophagitis: Validation of a novel classification and grading system. Gut 2013, 62, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, J.B.; Bolton, S.M.; Amsden, K.; Wershil, B.K.; Hirano, I.; Kagalwalla, A.F. Eosinophilic Esophagitis Reference Score Accurately Identifies Disease Activity and Treatment Effects in Children. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellon, E.S.; Cotton, C.C.; Gebhart, J.H.; Higgins, L.L.; Beitia, R.; Woosley, J.T.; Shaheen, N.J. Accuracy of the Eosinophilic Esophagitis Endoscopic Reference Score in Diagnosis and Determining Response to Treatment. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellon, E.S.; Muir, A.B.; Katzka, D.A.; Shah, S.C.; Sauer, B.G.; Aceves, S.S.; Furuta, G.T.; Gonsalves, N.; Hirano, I. ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2025, 120, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aceves, S.S.; Alexander, J.A.; Baron, T.H.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Day, L.; Dellon, E.S.; Falk, G.W.; Furuta, G.T.; Gonsalves, N.; Hirano, I.; et al. Endoscopic approach to eosinophilic esophagitis: American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Consensus Conference. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2022, 96, 576–592.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagula, S.; Parasa, S.; Laine, L.; Shah, S.C. AGA Clinical Practice Update on High-Quality Upper Endoscopy: Expert Review. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 22, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukkada, V.; Falk, G.W.; Eichinger, C.S.; King, D.; Todorova, L.; Shaheen, N.J. Health-Related Quality of Life and Costs Associated With Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Systematic Review. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 495–503.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, E.; Taft, T.; Zalewski, A.; Gonsalves, N.; Hirano, I. Prospective assessment of disease-specific quality of life in adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Dis. Esophagus 2018, 31, dox128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewett, R.; Alexakis, C.; Farmer, A.D.; Ainley, J.; Chhaya, V.; Hayat, J.O.; Poullis, A.; Kang, J.Y. Effects of eosinophilic oesophagitis on quality of life in an adult UK population: A case control study. Dis. Esophagus 2017, 30, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Arias-González, L.; Molina-Infante, J.; Arias, Á. Systematic review: Health-related quality of life in children and adults with eosinophilic oesophagitis-instruments for measurement and determinant factors. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 46, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.W.; Pandolfino, J.E.; Lin, Z.; Ciolino, J.D.; Gonsalves, N.; Kahrilas, P.J.; Hirano, I. Severity of endoscopically identified esophageal rings correlates with reduced esophageal distensibility in eosinophilic esophagitis. Endoscopy 2016, 48, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siersema, P.D. How to Approach a Patient With Refractory or Recurrent Benign Esophageal Stricture. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eluri, S.; Runge, T.M.; Cotton, C.C.; Burk, C.M.; Wolf, W.A.; Woosley, J.T.; Shaheen, N.J.; Dellon, E.S. The extremely narrow-caliber esophagus is a treatment-resistant subphenotype of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2016, 83, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Huprich, J.; Kujath, C.; Ravi, K.; Enders, F.; Smyrk, T.C.; Katzka, D.A.; Talley, N.J.; Alexander, J.A. Esophageal diameter is decreased in some patients with eosinophilic esophagitis and might increase with topical corticosteroid therapy. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visaggi, P.; Dellon, E.S. The Esophageal Mucosa: Clues to Underlying Pathology. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2025; in press, corrected proof. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorge, A.; Masclee, G.M.C.; Bredenoord, A.J. Endoscopic Diagnosis and Response Evaluation in Patients with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2023, 21, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugazza, A.; Repici, A. Endoscopic Management of Refractory Benign Esophageal Strictures. Dysphagia 2021, 36, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, N.; Katzka, D.; Ravi, K.; Trenkner, S.; Enders, F.; Killian, J.; Kryzer, L.; Talley, N.J.; Alexander, J. Oesophageal narrowing is common and frequently under-appreciated at endoscopy in patients with oesophageal eosinophilia. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 40, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.J.; Miller, F.H.; Moy, N.; Zalewski, A.; Gonsalves, N.; Gregory, D.L.; Hirano, I. Comparison of endoscopy and radiographic imaging for detection of esophageal inflammation and remodeling in adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 87, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menard-Katcher, C.; Swerdlow, M.P.; Mehta, P.; Furuta, G.T.; Fenton, L.Z. Contribution of Esophagram to the Evaluation of Complicated Pediatric Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 61, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnan, E.N.; Pandolfino, J.E. EndoFLIP in the Esophagus: Assessing Sphincter Function, Wall Stiffness, and Motility to Guide Treatment. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 2020, 49, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarino, E.; di Pietro, M.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Carlson, D.A.; Clarke, J.O.; Khan, A.; Vela, M.F.; Yadlapati, R.; Pohl, D.; Pandolfino, J.E.; et al. Use of the Functional Lumen Imaging Probe in Clinical Esophagology. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 1786–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desprez, C.; Roman, S.; Leroi, A.M.; Gourcerol, G. The use of impedance planimetry (Endoscopic Functional Lumen Imaging Probe, EndoFLIP(®)) in the gastrointestinal tract: A systematic review. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 32, e13980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, D.A.; Kou, W.; Lin, Z.; Hinchcliff, M.; Thakrar, A.; Falmagne, S.; Prescott, J.; Dorian, E.; Kahrilas, P.J.; Pandolfino, J.E. Normal Values of Esophageal Distensibility and Distension-Induced Contractility Measured by Functional Luminal Imaging Probe Panometry. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 674–681.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicodème, F.; Hirano, I.; Chen, J.; Robinson, K.; Lin, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Gonsalves, N.; Kwasny, M.J.; Kahrilas, P.J.; Pandolfino, J.E. Esophageal distensibility as a measure of disease severity in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, 1101–1107.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo, I.K.; Shehata, C.; Hirano, I.; Gonsalves, N.; Kahrilas, P.J.; Tetreault, M.P.; Schauer, J.M.; Farina, D.; Peterson, S.; Kou, W.; et al. The Severity of Reduced Esophageal Distensibility Parallels Eosinophilic Esophagitis Disease Duration. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 22, 513–522.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amil-Dias, J.; Oliva, S.; Papadopoulou, A.; Thomson, M.; Gutiérrez-Junquera, C.; Kalach, N.; Orel, R.; Auth, M.K.; Nijenhuis-Hendriks, D.; Strisciuglio, C.; et al. Diagnosis and management of eosinophilic esophagitis in children: An update from the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (ESPGHAN). J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2024, 79, 394–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runge, T.M.; Eluri, S.; Cotton, C.C.; Burk, C.M.; Woosley, J.T.; Shaheen, N.J.; Dellon, E.S. Outcomes of Esophageal Dilation in Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Safety, Efficacy, and Persistence of the Fibrostenotic Phenotype. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visaggi, P.; Barberio, B.; Del Corso, G.; de Bortoli, N.; Black, C.J.; Ford, A.C.; Savarino, E. Comparison of drugs for active eosinophilic oesophagitis: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. Gut 2023, 72, 2019–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cini, L.; Marinoni, B.; Coletta, M. Persistent dysphagia in stricture-free eosinophilic esophagitis in histological remission: Effectiveness of empirical dilation. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2024, 12, 708. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, D.A.; Hirano, I.; Zalewski, A.; Gonsalves, N.; Lin, Z.; Pandolfino, J.E. Improvement in Esophageal Distensibility in Response to Medical and Diet Therapy in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2017, 8, e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, M.; Mutlu, E.A.; Jakate, S.; Bruninga, K.; Losurdo, J.; Losurdo, J.; Keshavarzian, A. Endoscopy in eosinophilic esophagitis: “feline” esophagus and perforation risk. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2003, 1, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucendo, A.J.; De Rezende, L. Endoscopic dilation in eosinophilic esophagitis: A treatment strategy associated with a high risk of perforation. Endoscopy 2007, 39, 376, author reply 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, M.; Runge, T.M.; Eluri, S.; Dellon, E.S. Esophageal dilation with either bougie or balloon technique as a treatment for eosinophilic esophagitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2017, 86, 581–591.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rank, M.A.; Sharaf, R.N.; Furuta, G.T.; Aceves, S.S.; Greenhawt, M.; Spergel, J.M.; Falck-Ytter, Y.T.; Dellon, E.S. Technical review on the management of eosinophilic esophagitis: A report from the AGA institute and the joint task force on allergy-immunology practice parameters. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020, 124, 424–440.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moawad, F.J.; Molina-Infante, J.; Lucendo, A.J.; Cantrell, S.E.; Tmanova, L.; Douglas, K.M. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Endoscopic dilation is highly effective and safe in children and adults with eosinophilic oesophagitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 46, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias-González, L.; Rey-Iborra, E.; Ruiz-Ponce, M.; Laserna-Mendieta, E.J.; Arias, Á.; Lucendo, A.J. Esophageal perforation in eosinophilic esophagitis: A systematic review on clinical presentation, management and outcomes. Dig. Liver Dis. 2020, 52, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.P.; Weingart, G.; Hiramoto, B.; Gregory, D.L.; Gonsalves, N.; Hirano, I. Clinical outcomes of adults with eosinophilic esophagitis with severe stricture. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 92, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, S.; Chang, N.C.; Corder, S.R.; Reed, C.C.; Eluri, S.; Dellon, E.S. Dilation-predominant approach versus routine care in patients with difficult-to-treat eosinophilic esophagitis: A retrospective comparison. Endoscopy 2022, 54, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safroneeva, E.; Pan, Z.; King, E.; Martin, L.J.; Collins, M.H.; Yang, G.Y.; Capocelli, K.E.; Arva, N.C.; Abonia, J.P.; Atkins, D.; et al. Long-Lasting Dissociation of Esophageal Eosinophilia and Symptoms After Dilation in Adults With Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 766–775.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoepfer, A.M.; Gonsalves, N.; Bussmann, C.; Conus, S.; Simon, H.U.; Straumann, A.; Hirano, I. Esophageal dilation in eosinophilic esophagitis: Effectiveness, safety, and impact on the underlying inflammation. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 1062–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, I. How to Approach a Patient With Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, J.E. Eosinophilic Esophagitis Dilation in the Community—Try It—You will Like It—But Start Low and Go Slow. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 214–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, S.M.; Triantafyllou, K.; Hassan, C.; Mergener, K.; Tham, T.C.; Almeida, N.; Antonelli, G.; Axon, A.; Bisschops, R.; Bretthauer, M.; et al. Informed consent for endoscopic procedures: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Position Statement. Endoscopy 2023, 55, 952–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortoluzzi, F.; Sorge, A.; Vassallo, R.; Montalbano, L.M.; Monica, F.; La Mura, S.; Canova, D.; Checchin, D.; Fedeli, P.; Marmo, R.; et al. Sustainability in gastroenterology and digestive endoscopy: Position Paper from the Italian Association of Hospital Gastroenterologists and Digestive Endoscopists (AIGO). Dig. Liver Dis. 2022, 54, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, U.D.; Banerjee, S.; Barth, B.; Chauhan, S.S.; Gottlieb, K.T.; Konda, V.; Maple, J.T.; Murad, F.M.; Pfau, P.R.; Pleskow, D.K.; et al. Tools for endoscopic stricture dilation. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2013, 78, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, L.V.; Jacobson, J.W.; Harris, M.S. Comparison among the perforation rates of Maloney, balloon, and savary dilation of esophageal strictures. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2000, 51, 460–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hussaini, A. Savary Dilation Is Safe and Effective Treatment for Esophageal Narrowing Related to Pediatric Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 63, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoepfer, A.M.; Henchoz, S.; Biedermann, L.; Schreiner, P.; Greuter, T.; Reinhard, A.; Senn, J.; Franke, A.; Burri, E.; Juillerat, P.; et al. Technical feasibility, clinical effectiveness, and safety of esophageal stricture dilation using a novel endoscopic attachment cap in adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 94, 912–919.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.Y.; Tabibian, N.; Schwartz, J.T.; Smith, J.L. Evaluation of the effectiveness of through-the-scope balloons as dilators of benign and malignant gastrointestinal strictures. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1987, 33, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, J.A.; Barkin, J.S. Comparison of the diameter consistency and dilating force of the controlled radial expansion balloon catheter to the conventional balloon dilators. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 3423–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskins, B.; Almazan, E.; Hohl, B.; Ng, K. Esophageal dilation with EsoFLIP is faster than CRE balloon dilation combined with EndoFLIP in children. Surg. Endosc. 2023, 37, 6308–6314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paspatis, G.A.; Arvanitakis, M.; Dumonceau, J.M.; Barthet, M.; Saunders, B.; Turino, S.Y.; Dhillon, A.; Fragaki, M.; Gonzalez, J.M.; Repici, A.; et al. Diagnosis and management of iatrogenic endoscopic perforations: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Position Statement—Update 2020. Endoscopy 2020, 52, 792–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sdralis, E.I.K.; Petousis, S.; Rashid, F.; Lorenzi, B.; Charalabopoulos, A. Epidemiology, diagnosis, and management of esophageal perforations: Systematic review. Dis. Esophagus 2017, 30, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Simple Strictures | Complex Strictures * | |
|---|---|---|
| Allows for passage of a standard gastroscope | Yes | No (typically) |
| Length | Short (<2 cm) | Long (>2 cm) |
| Focal | Yes | No |
| Angulation/Irregularity | Straight | Angulated and irregular |
| Degree of narrowing | Less severe | Severe |
| Etiology | Peptic, Eosinophilic esophagitis, Schatzki’s ring, esophageal web | Post-ESD, Eosinophilic esophagitis, anastomotic, caustic ingestion, radiotherapy-induced |
| Association with fibrosis | Minimal | Significant |
| Fluoroscopy | Optional | Recommended |
| Refractoriness to treatment | Less common | More common |
| Response to medical therapy | Often effective | Limited effectiveness |
| Sizes | Main Advantages | Main Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Savary–Gilliard® | 5–20 mm |
|
|
| Balloon dilators | 6–20 mm |
|
|
| BougieCap | 7–18 mm |
|
|
| Step | Procedure |
|---|---|
| 1. Stricture assessment and guidewire positioning |
|
| 2. Gastroscope removal |
|
| 3. Bougie size selection |
|
| 4. Bougie insertion |
|
| 5. Gradual dilation |
|
| 6. Post-dilation endoscopy check |
|
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1. Stricture assessment and guidewire positioning |
|
| 2a. Guidewire and balloon placement (simple strictures) |
|
| 2b. Guidewire placement (complex strictures) |
|
| 3. Balloon inflation |
|
| 4. Post-dilation examination |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Michelon, M.; Savarino, E.V.; Montori, M.; Argenziano, M.E.; Poortmans, P.J.; Visaggi, P.; Penagini, R.; Tate, D.J.; Coletta, M.; Sorge, A. Endoscopic Dilation for Fibrostenotic Complications in Eosinophilic Esophagitis—A Narrative Review. Allergies 2025, 5, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5020017
Michelon M, Savarino EV, Montori M, Argenziano ME, Poortmans PJ, Visaggi P, Penagini R, Tate DJ, Coletta M, Sorge A. Endoscopic Dilation for Fibrostenotic Complications in Eosinophilic Esophagitis—A Narrative Review. Allergies. 2025; 5(2):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5020017
Chicago/Turabian StyleMichelon, Marco, Edoardo Vincenzo Savarino, Michele Montori, Maria Eva Argenziano, Pieter Jan Poortmans, Pierfrancesco Visaggi, Roberto Penagini, David J. Tate, Marina Coletta, and Andrea Sorge. 2025. "Endoscopic Dilation for Fibrostenotic Complications in Eosinophilic Esophagitis—A Narrative Review" Allergies 5, no. 2: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5020017
APA StyleMichelon, M., Savarino, E. V., Montori, M., Argenziano, M. E., Poortmans, P. J., Visaggi, P., Penagini, R., Tate, D. J., Coletta, M., & Sorge, A. (2025). Endoscopic Dilation for Fibrostenotic Complications in Eosinophilic Esophagitis—A Narrative Review. Allergies, 5(2), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5020017







