Allergenicity and Conformational Diversity of Allergens
Abstract
1. Introduction and Background to IgE Mediated Allergic Reaction

2. Structural Characterization and Cross-Reactivities—What Makes a Protein an Allergen?
3. Conformational Diversity and NMR
4. Epitope Conservation and Structural Motifs
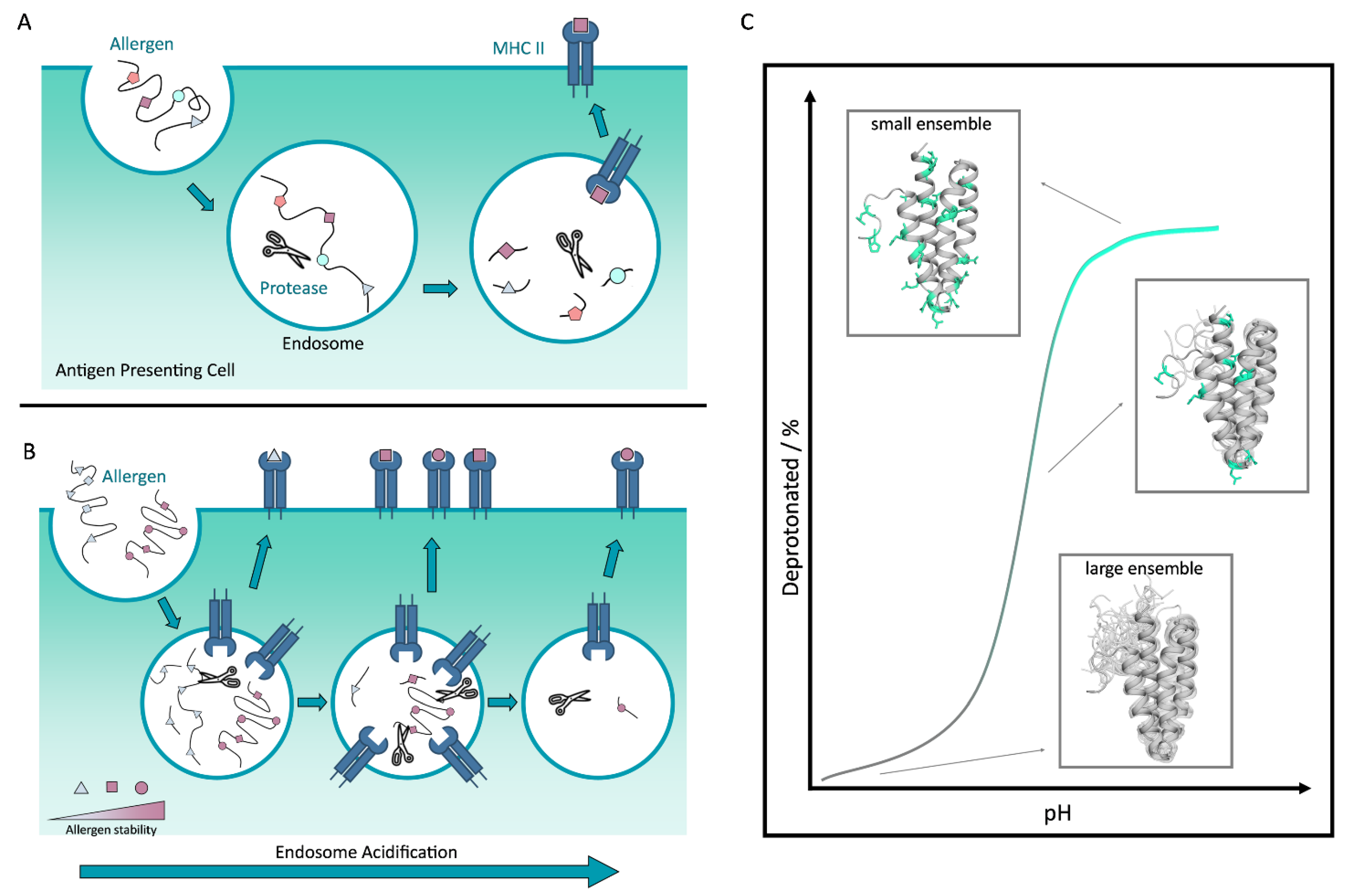
5. Allergen Proteolytic Susceptibility and pH-Dependency
| Family | Route of Exposure | Name | Origin | PDB Accession Code | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bet v 1 family | Airway | Bet v 1 | European white birch | 4A88 | [69] |
| Airway | Bet v 1 | European white birch | 1FM4 | ||
| Airway | Bet v 1 | European white birch | - | ||
| Profilin | Airway | Amb a 8 | Short ragweed | 5EVE | [42] |
| Airway Airway | Art v 4 Bet v 2 | Mugwort European white birch | 5EM0 5NZB | ||
| Group 5/6 grass pollen allergen | Airway | Phl p 6 | Timothy grass | 1NLX | [43] |
6. Discussion and Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fogarty, A.W. What have studies of non-industrialized countries told us about the cause of allergic disease? Clin. Exp. Allergy 2015, 45, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenta, R.; Kraft, D. From allergen structure to new forms of allergen-specific immunotherapy. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2002, 14, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenta, R.; Ferreira, F.; Focke-Tejkl, M.; Linhart, B.; Niederberger, V.; Swoboda, I.; Vrtala, S. From allergen genes to allergy vaccines. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 28, 211–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Kayale, L.; Ling, J.; Henderson, E.; Carter, N. The influence of cultural attitudes to nut exposure on reported nut allergy: A pilot cross sectional study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdanbakhsh, M.; Kremsner, P.G.; Van Ree, R. Allergy, parasites, and the hygiene hypothesis. Science 2002, 296, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdis, C.A. Does the epithelial barrier hypothesis explain the increase in allergy, autoimmunity and other chronic conditions? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.H.; Murphy, J.R. Hygiene hypothesis: Fact or fiction? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maizels, R.M.; McSorley, H.J.; Smyth, D. Helminths in the hygiene hypothesis: Sooner or later? Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2014, 177, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomfield, S.F.; Stanwell-Smith, R.; Crevel, R.W.R.; Pickup, J. Too clean, or not too clean: The hygiene hypothesis and home hygiene. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2006, 36, 402–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, C.; Link, E.; Koletzko, S.; Lehmann, I.; Heinrich, J.; Wichmann, H.-E.; Bauer, C.-P.; Berg, A.V.; Berdel, D.; Herbarth, O. The hygiene hypothesis does not apply to atopic eczema in childhood. In New Trends in Allergy and Atopic Eczema; Karger Publishers: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 96, pp. 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Suhrkamp, I.; Scheffold, A.; Heine, G. T-cell subsets in allergy and tolerance induction. Eur. J. Immunol. 2023, 53, 2249983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, M.D.; Pomés, A.; Breiteneder, H.; Ferreira, F. Nomenclature and structural biology of allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 119, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schein, C.H.; Negi, S.S.; Braun, W. Still SDAPing Along: 20 Years of the Structural Database of Allergenic Proteins. Front. Allergy 2022, 3, 863172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radauer, C.; Bublin, M.; Wagner, S.; Mari, A.; Breiteneder, H. Allergens are distributed into few protein families and possess a restricted number of biochemical functions. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 847–852.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraballo, L.; Valenta, R.; Puerta, L.; Pomés, A.; Zakzuk, J.; Fernandez-Caldas, E.; Acevedo, N.; Sanchez-Borges, M.; Ansotegui, I.; Zhang, L. The allergenic activity and clinical impact of individual IgE-antibody binding molecules from indoor allergen sources. World Allergy Organ. J. 2020, 13, 100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakib, F.; Ghaemmaghami, A.M.; Sewell, H.F. The molecular basis of allergenicity. Trends Immunol. 2008, 29, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tao, A. Antigenicity, immunogenicity, allergenicity. Allergy Bioinform. 2015, 8, 175–186. [Google Scholar]
- Doneva, N.; Doytchinova, I.; Dimitrov, I. Predicting immunogenicity risk in biopharmaceuticals. Symmetry 2021, 13, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, N.D.; Mayrose, I.; Martz, E.; Pupko, T. Epitopia: A web-server for predicting B-cell epitopes. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayrose, I.; Penn, O.; Erez, E.; Rubinstein, N.D.; Shlomi, T.; Freund, N.T.; Bublil, E.M.; Ruppin, E.; Sharan, R.; Gershoni, J.M. Pepitope: Epitope mapping from affinity-selected peptides. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 3244–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarenko, J.; Bui, H.-H.; Li, W.; Fusseder, N.; Bourne, P.E.; Sette, A.; Peters, B. ElliPro: A new structure-based tool for the prediction of antibody epitopes. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Zheng, D.; Standley, D.M.; Yao, B.; Zacharias, M.; Zhang, C. EPSVR and EPMeta: Prediction of antigenic epitopes using support vector regression and multiple server results. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, I.; Naneva, L.; Doytchinova, I.; Bangov, I. AllergenFP: Allergenicity prediction by descriptor fingerprints. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chruszcz, M.; Kapingidza, A.B.; Dolamore, C.; Kowal, K. A robust method for the estimation and visualization of IgE cross-reactivity likelihood between allergens belonging to the same protein family. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, J.S.; Warrington, R.; Watson, W.; Kim, H.L. An introduction to immunology and immunopathology. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sindher, S.B.; Long, A.; Acharya, S.; Sampath, V.; Nadeau, K.C. The use of biomarkers to predict aero-allergen and food immunotherapy responses. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 55, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corry, D.B.; Kheradmand, F. Induction and regulation of the IgE response. Nature 1999, 402, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodfolk, J.A.; Commins, S.P.; Schuyler, A.J.; Erwin, E.A.; Platts-Mills, T.A. Allergens, sources, particles, and molecules: Why do we make IgE responses? Allergol. Int. 2015, 64, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaswamy, J.K.; Alsén, S.; Yrlid, U.; Eisenbarth, S.C.; Williams, A. Determination of T follicular helper cell fate by dendritic cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-B. Regulation of IgE-mediated food allergy by IL-9 producing mucosal mast cells and type 2 innate lymphoid cells. Immune Netw. 2016, 16, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, H.A.; O’Mahony, L.; Burks, A.W.; Plaut, M.; Lack, G.; Akdis, C.A. Mechanisms of food allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenta, R.; Hochwallner, H.; Linhart, B.; Pahr, S. Food allergies: The basics. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 1120–1131.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, L.A.; Leung, D.Y. Allergen sensitization through the skin induces systemic allergic responses. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 106, S258–S263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, T.P. The external exposome and food allergy. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2020, 20, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulis, M.D.; Smeekens, J.M.; Immormino, R.M.; Moran, T.P. The airway as a route of sensitization to peanut: An update to the dual allergen exposure hypothesis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallinich, T.; Beier, K.C.; Wahn, U.; Stock, P.; Hamelmann, E. T-cell co-stimulatory molecules: Their role in allergic immune reactions. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 29, 1246–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharpe, A.H.; Freeman, G.J. The B7–CD28 superfamily. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheurer, S.; Toda, M.; Vieths, S. What makes an allergen? Clin. Exp. Allergy 2015, 45, 1150–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, G.A.; Maleki, S.J.; Pedersen, L.C. The molecular basis of peanut allergy. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2014, 14, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnhammer, E.L.; Eddy, S.R.; Durbin, R. Pfam: A comprehensive database of protein domain families based on seed alignments. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 1997, 28, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Führer, S.; Unterhauser, J.; Zeindl, R.; Eidelpes, R.; Fernández-Quintero, M.L.; Liedl, K.R.; Tollinger, M. The structural flexibility of PR-10 food allergens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, F.; Fischer, A.-L.; Kamenik, A.S.; Waibl, F.; Fernández-Quintero, M.L.; Liedl, K.R. pH-dependent structural diversity of profilin allergens determines thermal stability. Front. Allergy 2022, 3, 1007000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofer, F.; Dietrich, V.; Kamenik, A.S.; Tollinger, M.; Liedl, K.R. pH-Dependent protonation of the Phl p 6 pollen allergen studied by NMR and cpH-aMD. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2019, 15, 5716–5726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popescu, F.-D. Cross-reactivity between aeroallergens and food allergens. World J. Methodol. 2015, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamath, S.D.; Bublin, M.; Kitamura, K.; Matsui, T.; Ito, K.; Lopata, A.L. Cross-reactive epitopes and their role in food allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, 1178–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahaman, T.; Vasiljevic, T.; Ramchandran, L. Effect of processing on conformational changes of food proteins related to allergenicity. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 49, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, J.; Liang, R.; Huang, H.; Ma, X. Maillard reaction induced changes in allergenicity of food. Foods 2022, 11, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foo, A.C.; Mueller, G.A. Abundance and stability as common properties of allergens. Front. Allergy 2021, 2, 769728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnyder, B.; Brockow, K. Pathogenesis of drug allergy–current concepts and recent insights. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2015, 45, 1376–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Trincado, J.L.; Gomez-Perosanz, M.; Reche, P.A. Fundamentals and methods for T-and B-cell epitope prediction. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 2680160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomés, A.; Mueller, G.A.; Chruszcz, M. Structural aspects of the allergen-antibody interaction. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, Y.; Freier, R.; Scheiblhofer, S.; Thalhamer, T.; Mayr, M.; Briza, P.; Grutsch, S.; Ahammer, L.; Fuchs, J.E.; Wallnoefer, H.G. Fold stability during endolysosomal acidification is a key factor for allergenicity and immunogenicity of the major birch pollen allergen. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamath, S.D.; Scheiblhofer, S.; Johnson, C.M.; Machado, Y.; McLean, T.; Taki, A.C.; Ramsland, P.A.; Iyer, S.; Joubert, I.; Hofer, H. Effect of structural stability on endolysosomal degradation and T-cell reactivity of major shrimp allergen tropomyosin. Allergy 2020, 75, 2909–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeindl, R.; Unterhauser, J.; Röck, M.; Eidelpes, R.; Führer, S.; Tollinger, M. Structural characterization of food allergens by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. In Food Allergens: Methods and Protocols; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 159–173. [Google Scholar]
- Mittermaier, A.K.; Kay, L.E. Observing biological dynamics at atomic resolution using NMR. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2009, 34, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grutsch, S.; Fuchs, J.E.; Freier, R.; Kofler, S.; Bibi, M.; Asam, C.; Wallner, M.; Ferreira, F.; Brandstetter, H.; Liedl, K.R. Ligand binding modulates the structural dynamics and compactness of the major birch pollen allergen. Biophys. J. 2014, 107, 2972–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Patiyal, S.; Dhall, A.; Pande, A.; Arora, C.; Raghava, G.P. AlgPred 2.0: An improved method for predicting allergenic proteins and mapping of IgE epitopes. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, C.; Moriyama, T.; Ogawa, T. Identification of cyclophilin as an IgE-binding protein from carrots. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2001, 125, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buyuktiryaki, B.; Masini, M.; Mori, F.; Barni, S.; Liccioli, G.; Sarti, L.; Lodi, L.; Giovannini, M.; du Toit, G.; Lopata, A.L. IgE-mediated fish allergy in children. Medicina 2021, 57, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiteneder, H. Mapping of Conformational IgE Epitopes of Food Allergens; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; Volume 73, pp. 2107–2109. ISBN 0105-4538. [Google Scholar]
- Calvani, M.; Bianchi, A.; Reginelli, C.; Peresso, M.; Testa, A. Oral food challenge. Medicina 2019, 55, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, Y.; Urisu, A. Oral allergy syndrome. Allergol. Int. 2009, 58, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muluk, N.B.; Cingi, C. Oral allergy syndrome. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2018, 32, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanciuc, O.; Garcia, T.; Torres, M.; Schein, C.H.; Braun, W. Characteristic motifs for families of allergenic proteins. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blankestijn, M.A.; Knulst, A.C.; Knol, E.F.; Le, T.-M.; Rockmann, H.; Otten, H.G.; Klemans, R.J. Sensitization to PR-10 proteins is indicative of distinctive sensitization patterns in adults with a suspected food allergy. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2017, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, C. Latex-fruit syndrome. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2003, 3, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flower, D.R.; North, A.C.; Sansom, C.E. The lipocalin protein family: Structural and sequence overview. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 2000, 1482, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freier, R.; Dall, E.; Brandstetter, H. Protease recognition sites in Bet v 1a are cryptic, explaining its slow processing relevant to its allergenicity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenik, A.S.; Hofer, F.; Handle, P.H.; Liedl, K.R. Dynamics rationalize proteolytic susceptibility of the major birch pollen allergen Bet v 1. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hehir, R.E.; Prickett, S.R.; Rolland, J.M. T cell epitope peptide therapy for allergic diseases. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-B.; Dammer, E.B.; Ren, R.-J.; Wang, G. The endosomal-lysosomal system: From acidification and cargo sorting to neurodegeneration. Transl. Neurodegener. 2015, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grutsch, S.; Fuchs, J.E.; Ahammer, L.; Kamenik, A.S.; Liedl, K.R.; Tollinger, M. Conformational flexibility differentiates naturally occurring Bet v 1 isoforms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, F.; Kamenik, A.S.; Fernández-Quintero, M.L.; Kraml, J.; Liedl, K.R. pH-induced local unfolding of the Phl p 6 pollen allergen from cpH-MD. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 7, 603644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Jürets, A.; Wallner, M.; Briza, P.; Ruzek, S.; Hainzl, S.; Pichler, U.; Kitzmüller, C.; Bohle, B.; Huber, C.G. Assessing protein immunogenicity with a dendritic cell line-derived endolysosomal degradome. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheiblhofer, S.; Laimer, J.; Machado, Y.; Weiss, R.; Thalhamer, J. Influence of protein fold stability on immunogenicity and its implications for vaccine design. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2017, 16, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Zhou, H.-X. Protein allostery and conformational dynamics. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 6503–6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, V. Conformational dynamics and ensembles in protein folding. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2007, 36, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traidl-Hoffmann, C.; Jakob, T.; Behrendt, H. Determinants of allergenicity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatri, K.; Richardson, C.M.; Glesner, J.; Kapingidza, A.B.; Mueller, G.A.; Zhang, J.; Dolamore, C.; Vailes, L.D.; Wünschmann, S.; Peebles Jr, R.S. Human IgE monoclonal antibody recognition of mite allergen Der p 2 defines structural basis of an epitope for IgE cross-linking and anaphylaxis in vivo. PNAS Nexus 2022, 1, pgac054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, G.A. Contributions and future directions for structural biology in the study of allergens. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 174, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomés, A.; Chruszcz, M.; Gustchina, A.; Minor, W.; Mueller, G.A.; Pedersen, L.C.; Wlodawer, A.; Chapman, M.D. 100 Years later: Celebrating the contributions of x-ray crystallography to allergy and clinical immunology. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 29–37.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, L.C.; Tawfik, D.S. Conformational diversity and protein evolution–a 60-year-old hypothesis revisited. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2003, 28, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauling, L. A theory of the structure and process of formation of antibodies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1940, 62, 2643–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foote, J.; Milstein, C. Conformational isomerism and the diversity of antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 10370–10374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Quintero, M.L.; Loeffler, J.R.; Waibl, F.; Kamenik, A.S.; Hofer, F.; Liedl, K.R. Conformational selection of allergen-antibody complexes—Surface plasticity of paratopes and epitopes. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2019, 32, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gieras, A.; Cejka, P.; Blatt, K.; Focke-Tejkl, M.; Linhart, B.; Flicker, S.; Stoecklinger, A.; Marth, K.; Drescher, A.; Thalhamer, J. Mapping of conformational IgE epitopes with peptide-specific monoclonal antibodies reveals simultaneous binding of different IgE antibodies to a surface patch on the major birch pollen allergen, Bet v 1. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 5333–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhoeckx, K.C.; Vissers, Y.M.; Baumert, J.L.; Faludi, R.; Feys, M.; Flanagan, S.; Herouet-Guicheney, C.; Holzhauser, T.; Shimojo, R.; van der Bolt, N. Food processing and allergenicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 80, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X.; Zhou, X.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Li, X.; Yang, A.; Tong, P.; Wu, Z.; Chen, H. Effect of processing on the structure and allergenicity of peanut allergen Ara h 2 roasted in a matrix. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, M.; Xu, Z.; Tan, H.; Yang, F.; Yuan, J.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yang, A.; Chen, H.; Li, X. Allergenicity reduction of cow milk treated by alkaline protease combined with Lactobacillus Plantarum and Lactobacillus helveticus based on epitopes. Food Chem. 2023, 421, 136180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazebrouck, S.; Patil, S.U.; Guillon, B.; Lahood, N.; Dreskin, S.C.; Adel-Patient, K.; Bernard, H. Immunodominant conformational and linear IgE epitopes lie in a single segment of Ara h 2. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 150, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, G.A.; Glesner, J.; Daniel, J.L.; Zhang, J.; Hyduke, N.; Richardson, C.M.; DeRose, E.F.; Chapman, M.D.; Peebles, R.S.; A Smith, S. Mapping human monoclonal IgE epitopes on the major dust mite allergen Der p 2. J. Immunol. 2020, 205, 1999–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Quintero, M.L.; Kokot, J.; Waibl, F.; Fischer, A.-L.M.; Quoika, P.K.; Deane, C.M.; Liedl, K.R. Challenges in antibody structure prediction. In Proceedings of the MAbs; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2023; Volume 15, p. 2175319. [Google Scholar]
- Aalberse, R.C.; Crameri, R. IgE-binding epitopes: A reappraisal. Allergy 2011, 66, 1261–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.A.; Chruszcz, M.; Chapman, M.D.; Pomés, A. Human Monoclonal IgE Antibodies—A Major Milestone in Allergy. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2023, 23, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orengo, J.M.; Radin, A.R.; Kamat, V.; Badithe, A.; Ben, L.H.; Bennett, B.L.; Zhong, S.; Birchard, D.; Limnander, A.; Rafique, A. Treating cat allergy with monoclonal IgG antibodies that bind allergen and prevent IgE engagement. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padavattan, S.; Flicker, S.; Schirmer, T.; Madritsch, C.; Randow, S.; Reese, G.; Vieths, S.; Lupinek, C.; Ebner, C.; Valenta, R. High-affinity IgE recognition of a conformational epitope of the major respiratory allergen Phl p 2 as revealed by X-ray crystallography. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 2141–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atanasio, A.; Franklin, M.C.; Kamat, V.; Hernandez, A.R.; Badithe, A.; Ben, L.-H.; Jones, J.; Bautista, J.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Olson, W. Targeting immunodominant Bet v 1 epitopes with monoclonal antibodies prevents the birch allergic response. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitropoulou, A.N.; Bowen, H.; Dodev, T.S.; Davies, A.M.; Bax, H.J.; Beavil, R.L.; Beavil, A.J.; Gould, H.J.; James, L.K.; Sutton, B.J. Structure of a patient-derived antibody in complex with allergen reveals simultaneous conventional and superantigen-like recognition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8707–E8716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Führer, S.; Kamenik, A.S.; Zeindl, R.; Nothegger, B.; Hofer, F.; Reider, N.; Liedl, K.R.; Tollinger, M. Inverse relation between structural flexibility and IgE reactivity of Cor a 1 hazelnut allergens. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swails, J.M.; Roitberg, A.E. Enhancing conformation and protonation state sampling of hen egg white lysozyme using pH replica exchange molecular dynamics. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2012, 8, 4393–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, A.M.; Martel, P.J.; Petersen, S.B. Simulation of protein conformational freedom as a function of pH: Constant-pH molecular dynamics using implicit titration. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 1997, 27, 523–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seidler, C.A.; Zeindl, R.; Fernández-Quintero, M.L.; Tollinger, M.; Liedl, K.R. Allergenicity and Conformational Diversity of Allergens. Allergies 2024, 4, 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies4010001
Seidler CA, Zeindl R, Fernández-Quintero ML, Tollinger M, Liedl KR. Allergenicity and Conformational Diversity of Allergens. Allergies. 2024; 4(1):1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies4010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeidler, Clarissa A., Ricarda Zeindl, Monica L. Fernández-Quintero, Martin Tollinger, and Klaus R. Liedl. 2024. "Allergenicity and Conformational Diversity of Allergens" Allergies 4, no. 1: 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies4010001
APA StyleSeidler, C. A., Zeindl, R., Fernández-Quintero, M. L., Tollinger, M., & Liedl, K. R. (2024). Allergenicity and Conformational Diversity of Allergens. Allergies, 4(1), 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies4010001







