Pruritus in Chronic Kidney Disease: An Update
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology of CKDaP
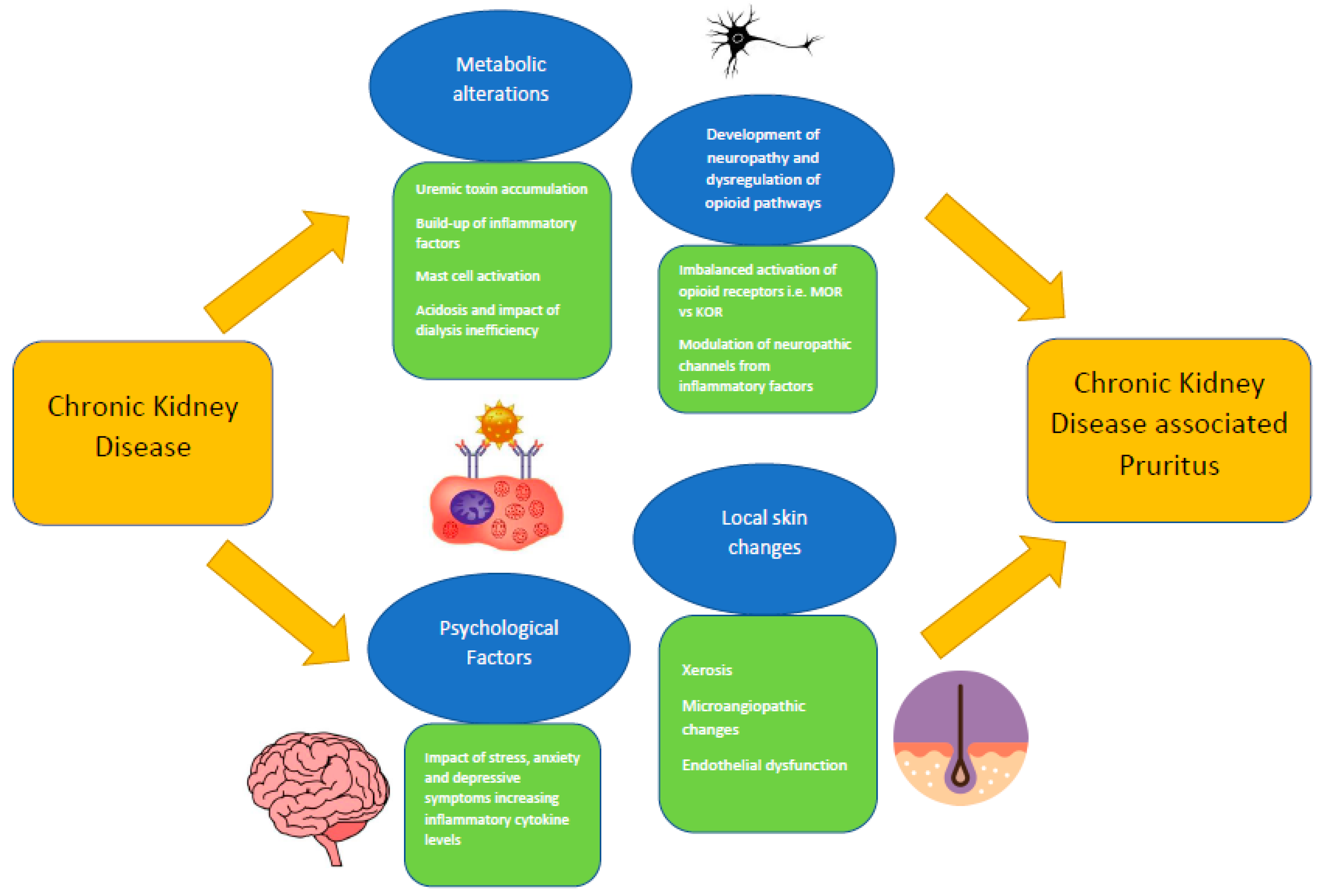
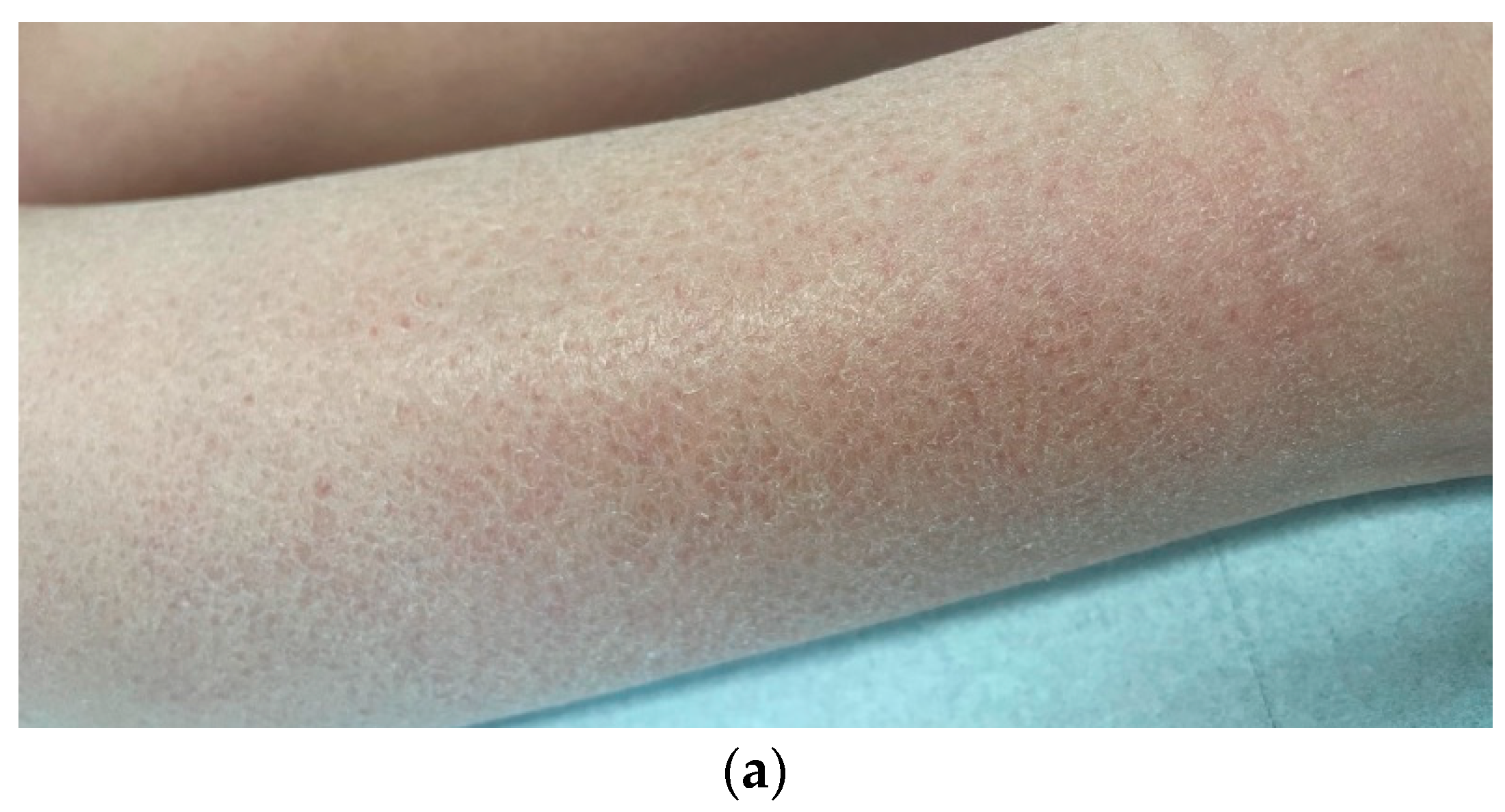
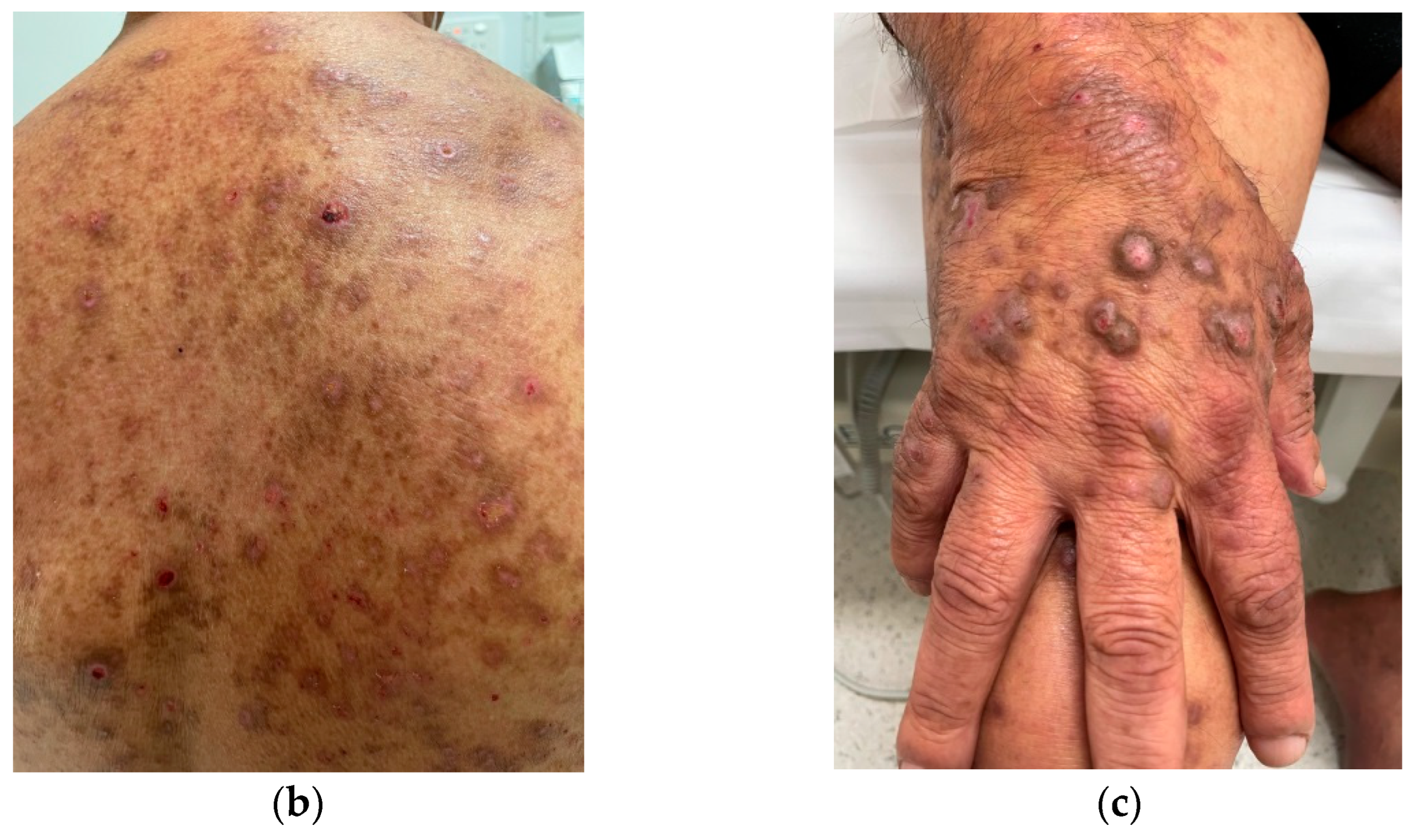
3. Pathophysiology of CKDaP
4. Clinical Assessment and Diagnosis of CKDaP
5. Prevention and Treatment of CKDaP
6. Future Directions for Patient-Centered Care in CKDaP
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levin, A.; Stevens, P.E.; Bilous, R.W.; Coresh, J.; De Francisco, A.L.; De Jong, P.E.; Griffith, K.E.; Hemmelgarn, B.R.; Iseki, K.; Lamb, E.J.; et al. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2013, 3, 1–50. [Google Scholar]
- Romagnani, P.; Remuzzi, G.; Glassock, R.; Levin, A.; Jager, K.J.; Tonelli, M.; Massy, Z.; Wanner, C.; Anders, H.J. Chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, H.J.; Huber, T.B.; Isermann, B.; Schiffer, M. CKD in diabetes: Diabetic kidney disease versus nondiabetic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foreman, K.J.; Marquez, N.; Dolgert, A.; Fukutaki, K.; Fullman, N.; McGaughey, M.; Pletcher, M.A.; Smith, A.E.; Tang, K.; Yuan, C.W.; et al. Forecasting life expectancy, years of life lost, and all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 250 causes of death: Reference and alternative scenarios for 2016–40 for 195 countries and territories. Lancet 2018, 392, 2052–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Jafar, T.H.; Nitsch, D.; Neuen, B.L.; Perkovic, V. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet 2021, 398, 786–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefaniak, A.A.; Agelopoulos, K.; Bednarska-Chabowska, D.; Mazur, G.; Ständer, S.; Szepietowski, J.C. Small-fibre Neuropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and its Relationship with Diabetic Itch: Preliminary Results. Acta Derm. Vener. 2022, 102, adv00719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Renal Data System. USRDS 2021 Annual Data Report: End Stage Renal Disease; National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2021; Volume 2021.
- Australian and New Zealand Dialysis and Transplant Registry. Dialysis Centre Report 2015–2020; ANZDATA Registry: Adelaide, SA, Australia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Fox, C.H.; Vassalotti, J.; Choi, M. Complications of progression of CKD. Adv. Chronic. Kidney Dis. 2011, 18, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Pollock, C. Epidemiology and burden of chronic kidney disease-associated pruritus. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, i1–i7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Sang, Y.; Yang, M.; Chen, X.; Tang, W. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease-associated pruritus among adult dialysis patients: A meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies. Medicine 2018, 97, e10633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevikbas, F.; Lerner, E.A. Physiology and pathophysiology of itch. Physiol. Rev. 2020, 100, 945–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, A.E.; Feramisco, J.; Reeh, P.W.; Beuers, U.; Elferink, R.P. Receptors, cells and circuits involved in pruritus of systemic disorders. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2014, 1842, 869–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.E.; Clotet-Freixas, S.; Farragher, J.F.; Hundemer, G.L. Have we just scratched the surface? A narrative review of uremic pruritus in 2020. Can. J. Kidney Health Dis. 2020, 7, 2054358120954024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schricker, S.; Kimmel, M. Unravelling the pathophysiology of chronic kidney disease-associated pruritus. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, i23–i31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisshaar, E.; Szepietowski, J.C.; Dalgard, F.J.; Garcovich, S.; Gieler, U.; Giménez-Arnau, A.M.; Lambert, J.; Leslie, T.; Mettang, T.; Misery, L.; et al. European S2k guideline on chronic pruritus. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2019, 99, 469–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manenti, L.; Leuci, E. Do you feel itchy? A guide towards diagnosis and measurement of chronic kidney disease-associated pruritus in dialysis patients. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, i8–i15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelidis, N.; Sautenet, B.; Madero, M.; Tong, A.; Ashuntantang, G.; Sanabria, L.C.; de Boer, I.H.; Fung, S.; Gallego, D.; Levey, A.S.; et al. Standardised Outcomes in Nephrology–Chronic Kidney Disease (SONG-CKD): A protocol for establishing a core outcome set for adults with chronic kidney disease who do not require kidney replacement therapy. Trials 2021, 22, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishbane, S.; Jamal, A.; Munera, C.; Wen, W.; Menzaghi, F. A phase 3 trial of difelikefalin in hemodialysis patients with pruritus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisoni, R.L.; Wikström, B.; Elder, S.J.; Akizawa, T.; Asano, Y.; Keen, M.L.; Saran, R.; Mendelssohn, D.C.; Young, E.W.; Port, F.K. Pruritus in haemodialysis patients: International results from the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS). Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2006, 21, 3495–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, H.C.; Larkina, M.; Wang, M.; Graham-Brown, M.; van der Veer, S.N.; Ecder, T.; Hasegawa, T.; Kleophas, W.; Bieber, B.A.; Tentori, F.; et al. International comparisons of prevalence, awareness, and treatment of pruritus in people on hemodialysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 2000–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukul, N.; Karaboyas, A.; Csomor, P.A.; Schaufler, T.; Wen, W.; Menzaghi, F.; Rayner, H.C.; Hasegawa, T.; Al Salmi, I.; Al-Ghamdi, S.M.; et al. Self-reported pruritus and clinical, dialysis-related, and patient-reported outcomes in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Med. 2021, 3, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukul, N.; Speyer, E.; Tu, C.; Bieber, B.A.; Li, Y.; Lopes, A.A.; Asahi, K.; Mariani, L.; Laville, M.; Rayner, H.C.; et al. Pruritus and patient reported outcomes in non-dialysis CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, M.; Mettang, T.; Tschulena, U.; Passlick-Deetjen, J.; Weisshaar, E. Prevalence of chronic itch and associated factors in haemodialysis patients: A representative cross-sectional study. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2015, 95, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aresi, G.; Rayner, H.C.; Hassan, L.; Burton, J.O.; Mitra, S.; Sanders, C.; van der Veer, S.N. Reasons for underreporting of uremic pruritus in people with chronic kidney disease: A qualitative study. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2019, 58, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.Y.; Huang, J.W.; Tsai, W.C.; Peng, Y.S.; Chen, H.Y.; Yang, J.Y.; Hsu, S.P.; Pai, M.F.; Ko, M.J.; Hung, K.Y.; et al. Prognostic importance and determinants of uremic pruritus in patients receiving peritoneal dialysis: A prospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.W.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y.O.; Jin, D.C.; Song, H.C.; Choi, E.J.; Kim, Y.L.; Kim, Y.S.; Kang, S.W.; Kim, N.H.; et al. Comparison of uremic pruritus between patients undergoing hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2016, 35, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishnan, K.; Bond, T.C.; Claxton, A.; Sood, V.C.; Kootsikas, M.; Agnese, W.; Sibbel, S. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of end-stage renal disease patients with self-reported pruritus symptoms. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc. Dis. 2014, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Afsar, B.; Afsar, R.E. HbA1c is related with uremic pruritus in diabetic and nondiabetic hemodialysis patients. Renal. Fail. 2012, 34, 1264–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisshaar, E.; Weiss, M.; Passlick-Deetjen, J.; Tschulena, U.; Maleki, K.; Mettang, T. Laboratory and dialysis characteristics in hemodialysis patients suffering from chronic itch-results from a representative cross-sectional study. BMC Nephrol. 2015, 16, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefaniak, A.A.; Krajewski, P.K.; Bednarska-Chabowska, D.; Bolanowski, M.; Mazur, G.; Szepietowski, J.C. Itch in Adult Population with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Clinical Profile, Pathogenesis and Disease-Related Burden in a Cross-Sectional Study. Biology 2021, 10, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, V.S.; Lindberg, J.; Germain, M.; Block, G.; Tumlin, J.; Smith, M.; Grewal, M.; McGuire, D.; ITCH National Registry Investigators. A longitudinal study of uremic pruritus in hemodialysis patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 1410–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.H.; Zhu, Q.S.; Li, Y.W.; Wang, L.L. Determinants of the intensity of uremic pruritus in patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis: A cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozen, N.; Cinar, F.I.; Askin, D.; Mut, D. Uremic pruritus and associated factors in hemodialysis patients: A multi-center study. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 37, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Chiu, Y.L.; Hsu, S.P.; Pai, M.F.; Lai, C.F.; Yang, J.Y.; Peng, Y.S.; Tsai, T.J.; Wu, K.D. Elevated C-reactive protein level in hemodialysis patients with moderate/severe uremic pruritus: A potential mediator of high overall mortality. Q. J. Med. 2010, 103, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grochulska, K.; Ofenloch, R.; Mettang, T.; Weisshaar, E. Mortality of Haemodialysis Patients with and without Chronic Itch: A Follow-up Study of the German Epidemiological Hemodialysis Itch Study (GEHIS). Acta Derm. Venereol. 2019, 99, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plewig, N.; Ofenloch, R.; Mettang, T.; Weisshaar, E. The course of chronic itch in hemodialysis patients: Results of a 4-year follow-up study of GEHIS (German Epidemiological Hemodialysis Itch Study). J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, 1429–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, I.U.; Lai, P.S.; Kun, L.S.; Lee, L.H.; Chan, K.G.; Khan, T.M. Chronic kidney disease-associated pruritus and quality of life in Malaysian patients undergoing hemodialysis. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2020, 24, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikonomou, M.; Skapinakis, P.; Balafa, O.; Eleftheroudi, M.; Damigos, D.; Siamopoulos, K.C. The impact of socioeconomic factors on quality of life of patients with chronic kidney disease in Greece. J. Renal. Care 2015, 41, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seng, J.J.; Tan, J.Y.; Yeam, C.T.; Htay, H.; Foo, W.Y. Factors affecting medication adherence among pre-dialysis chronic kidney disease patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of literature. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2020, 52, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weldegiorgis, M.; Smith, M.; Herrington, W.G.; Bankhead, C.; Woodward, M. Socioeconomic disadvantage and the risk of advanced chronic kidney disease: Results from a cohort study with 1.4 million participants. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 1562–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stander, S.; Weisshaar, E.; Mettang, T.; Szepietowski, J.C.; Carstens, E.; Ikoma, A.; Bergasa, N.V.; Gieler, U.; Misery, L.; Wallengren, J.; et al. Clinical classification of itch: A position paper of the International Forum for the Study of Itch. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2007, 87, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, E.A.; Hassan, S.I.; Youssef, N.M. Cutaneous disorders in uremic patients on hemodialysis: An Egyptian case-controlled study. Int. J. Dermatol. 2010, 49, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurban, M.S.; Boueiz, A.; Kibbi, A.G. Cutaneous manifestations of chronic kidney disease. Clin. Dermatol. 2008, 26, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szepietowski, J.C.; Reich, A.; Schwartz, R.A. Uraemic xerosis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2004, 19, 2709–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojtowicz-Prus, E.; Kilis-Pstrusinska, K.; Reich, A.; Zachwieja, K.; Miklaszewska, M.; Szczepanska, M.; Szepietowski, J.C. Disturbed skin barrier in children with chronic kidney disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2015, 30, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosipovitch, G.; Reis, J.; Tur, E.; Sprecher, E.; Yarnitsky, D.; Boner, G. Sweat secretion, stratum corneum hydration, small nerve function and pruritus in patients with advanced chronic renal failure. Br. J. Dermatol. 1995, 133, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorążyczewska, W.; Reich, A.; Szepietowski, J.C. Lipid content and barrier function analysis in uraemic pruritus. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2016, 96, 402–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prommer, H.U.; Maurer, J.; von Websky, K.; Freise, C.; Sommer, K.; Nasser, H.; Samapati, R.; Reglin, B.; Guimarães, P.; Pries, A.R.; et al. Chronic kidney disease induces a systemic microangiopathy, tissue hypoxia and dysfunctional angiogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilchrest, B.A.; Rowe, J.W.; Mihm, M.C., Jr. Clinical and histological skin changes in chronic renal failure: Evidence for a dialysis-resistant, transplant-responsive microangiopathy. Lancet 1980, 2, 1271–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, C.; Shah, S.V.; Karaduta, O.K.; Kaushal, G.P. Carbamylated low-density lipoprotein (cLDL)-mediated induction of autophagy and its role in endothelial cell injury. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querfeld, U.; Mak, R.H.; Pries, A.R. Microvascular disease in chronic kidney disease: The base of the iceberg in cardiovascular comorbidity. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 1333–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhlough, A.; Emadi, N.; Sedighi, O.; Khademloo, M.; Bicmohamadi, A.R. Relationship between serum intact parathyroid hormone and pruritus in hemodialysis patients. Iran. J. Kidney Dis. 2013, 7, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duque, M.I.; Thevarajah, S.; Chan, Y.H.; Tuttle, A.B.; Freedman, B.I.; Yosipovitch, G. Uremic pruritus is associated with higher Kt/V and serum calcium concentration. Clin. Nephrol. 2006, 66, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dashti-Khavidaki, S.; Khalili, H.; Vahedi, S.M.; Lessan-Pezeshki, M. Serum zinc concentrations in patients on maintenance hemodialysis and its relationship with anemia, parathyroid hormone concentrations and pruritus severity. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2010, 21, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Narita, I.; Alchi, B.; Omori, K.; Sato, F.; Ajiro, J.; Saga, D.; Kondo, D.; Skatsume, M.; Maruyama, S.; Kazama, J.J.; et al. Etiology and prognostic significance of severe uremic pruritus in chronic hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 1626–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momose, A.; Kudo, S.; Sato, M.; Saito, H.; Nagai, K.; Katabira, Y.; Funyu, T. Calcium ions are abnormally distributed in the skin of haemodialysis patients with uraemic pruritus. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2004, 19, 2061–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, F.F.; Ho, J.C.; Huang, S.C.; Sheen-Chen, S.M. A study on pruritus after parathyroidectomy for secondary hyperparathyroidism. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2000, 190, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganz, T.; Nemeth, E. Iron balance and the role of hepcidin in chronic kidney disease. Semin. Nephrol. 2016, 36, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, M.; Alscher, D.M.; Dunst, R.; Braun, N.; Machleidt, C.; Kiefer, T.; Stülten, C.; van der Kuip, H.; Pauli-Magnus, C.; Raub, U.; et al. The role of micro-inflammation in the pathogenesis of uraemic pruritus in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2006, 21, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahzadeh, M.K.; Roozbeh, J.; Geramizadeh, B.; Namazi, M.R. Interleukin-2 serum levels are elevated in patients with uremic pruritus: A novel finding with practical implications. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 3338–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, M.J.; Peng, Y.S.; Chen, H.Y.; Hsu, S.P.; Pai, M.F.; Yang, J.Y.; Wen, S.Y.; Jee, S.H.; Wu, H.Y.; Chiu, H.C. Interleukin-31 is associated with uremic pruritus in patients receiving hemodialysis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 71, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szepietowski, J.; Thepen, T.; Van Vloten, W.A.; Szepietowski, T.; Bihari, I.C. Pruritus and mast cell proliferation in the skin of haemodialysis patients. Inflamm. Res. 1995, 44, S84–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.M.; Huang, C.; Peng, Z.; Han, S.L.; Li, W.G.; Zhu, M.X.; Xu, T.L. Acidosis counteracts itch tachyphylaxis to consecutive pruritogen exposure dependent on acid-sensing ion channel 3. Mol. Pain. 2017, 13, 1744806917721114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Li, W.G.; Huang, C.; Jiang, Y.M.; Wang, X.; Zhu, M.X.; Cheng, X.; Xu, T.L. ASIC3 mediates itch sensation in response to coincident stimulation by acid and nonproton ligand. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Malekmakan, L.; Malekmakan, A.; Sayadi, M.; Pakfetrat, M.; Sepaskhah, M.; Roozbeh, J. Association of high-sensitive C-reactive protein and dialysis adequacy with uremic pruritus. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2015, 26, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ko, M.J.; Wu, H.Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Chiu, Y.L.; Hsu, S.P.; Pai, M.F.; Lai, C.F.; Lu, H.M.; Huang, S.C.; Yang, S.Y.; et al. Uremic pruritus, dialysis adequacy, and metabolic profiles in hemodialysis patients: A prospective 5-year cohort study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reszke, R.; Szepietowski, J.C. End-stage renal disease chronic itch and its management. Dermatol. Clin. 2018, 36, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakrzewska-Pniewska, B.; Jedras, M. Is pruritus in chronic uremic patients related to peripheral somatic and autonomic neuropathy? Study by R-R interval variation test (RRIV) and by sympathetic skin response (SSR). Neurophysiol. Clin. 2001, 31, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettang, T.; Kremer, A.E. Uremic pruritus. Kidney Int. 2015, 87, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, L.B.; Mei, B.Q. Itch: Mechanisms and Treatment; Akiyama, T., Carstens, E., Eds.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Schulze, E.; Witt, M.; Fink, T.; Hofer, A.; Funk, R.H. Immunohistochemical detection of human skin nerve fibers. Acta Histochem. 1997, 99, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ständer, S.; Gunzer, M.; Metze, D.; Luger, T.; Steinhoff, M. Localization of μ-opioid receptor 1A on sensory nerve fibers in human skin. Regul. Pept. 2002, 110, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labuz, D.; Berger, S.; Mousa, S.A.; Zöllner, C.; Rittner, H.L.; Shaqura, M.A.; Segovia-Silvestre, T.; Przewlocka, B.; Stein, C.; Machelska, H. Peripheral antinociceptive effects of exogenous and immune cell-derived endomorphins in prolonged inflammatory pain. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 4350–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma–Gandhu, M.; Bercik, P.; Motomura, Y.; Verdu, E.F.; Khan, W.I.; Blennerhassett, P.A.; Wang, L.; El–Sharkawy, R.T.; Collins, S.M. CD4+ T-cell modulation of visceral nociception in mice. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 1721–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousa, S.A.; Machelska, H.; Schäfer, M.; Stein, C. Immunohistochemical localization of endomorphin-1 and endomorphin-2 in immune cells and spinal cord in a model of inflammatory pain. J. Neuroimmunol. 2002, 126, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.M. Opioid peptides in immune cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2003, 521, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wieczorek, A.; Krajewski, P.; Kozioł-Gałczyńska, M.; Szepietowski, J.C. Opioid receptors expression in the skin of haemodialysis patients suffering from uraemic pruritus. J. Eur. Acad. Derm. Venereol. 2020, 34, 2368–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Świerczyńska, K.; Krajewski, P.K.; Nowicka-Suszko, D.; Białynicki-Birula, R.; Krajewska, M.; Szepietowski, J.C. The Serum Level of IL-31 in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease-Associated Pruritus: What Can We Expect? Toxins 2022, 14, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippe, D.; Dubuquoy, L.; Groux, H.; Brun, V.; Van Chuoï-Mariot, M.T.; Gaveriaux-Ruff, C.; Colombel, J.F.; Kieffer, B.L.; Desreumaux, P. Anti-inflammatory properties of the μ opioid receptor support its use in the treatment of colon inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegeder, I.; Geisslinger, G. Opioids as modulators of cell death and survival—unraveling mechanisms and revealing new indications. Pharmacol. Rev. 2004, 56, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schricker, S.; Heider, T.; Schanz, M.; Dippon, J.; Alscher, M.D.; Weiss, H.; Mettang, T.; Kimmel, M. Strong associations between inflammation, Pruritus and mental health in dialysis patients. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2019, 99, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taraz, M.; Taraz, S.; Dashti-Khavidaki, S. Association between depression and inflammatory/anti-inflammatory cytokines in chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease patients: A review of literature. Hemodial. Int. 2015, 19, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Hayashino, Y.; Yamazaki, S.; Akiba, T.; Akizawa, T.; Asano, Y.; Saito, A.; Kurokawa, K.; Miyachi, Y.; Fukuhara, S. Depressive symptoms predict the future risk of severe pruritus in haemodialysis patients: Japan Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009, 161, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reamy, B.V.; Bunt, C.W.; Fletcher, S. A diagnostic approach to pruritus. Am. Fam. Physician. 2011, 84, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stefaniak, A.A.; Pereira, M.P.; Zeidler, C.; Ständer, S. Pruritus in Pregnancy. Am. J. Clin Dermatol. 2022, 23, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combs, S.A.; Teixeira, J.P.; Germain, M.J. Pruritus in kidney disease. Semin. Nephrol. 2015, 35, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry. Patient-Reported Outcome Measures: Use in Medical Product Development to Support Labeling Claims. 2009. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/patient-reported-outcome-measures-use-medical-product-development-support-labeling-claims (accessed on 6 May 2022).
- Morton, C.A.; Lafferty, M.; Hau, C.; Henderson, I.; Jones, M.; Lowe, J.G. Pruritus and skin hydration during dialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1996, 11, 2031–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, A.; Chatzigeorkidis, E.; Zeidler, C.; Osada, N.; Furue, M.; Takamori, K.; Ebata, T.; Augustin, M.; Szepietowski, J.C.; Ständer, S. Tailoring the cut-off values of the visual analogue scale and numeric rating scale in itch assessment. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2017, 97, 759–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storck, M.; Sandmann, S.; Bruland, P.; Pereira, M.P.; Steinke, S.; Riepe, C.; Soto-Rey, I.; Garcovich, S.; Augustin, M.; Blome, C.; et al. Pruritus intensity scales across Europe: A prospective validation study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, R.D.; Kallich, J.D.; Mapes, D.L.; Coons, S.J.; Carter, W.B. Development of the kidney disease quality of life (KDQOLTM) instrument. Qual. Life Res. 1994, 3, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elman, S.; Hynan, L.S.; Gabriel, V.; Mayo, M.J. The 5-D itch scale: A new measure of pruritus. Br. J. Dermatol. 2010, 162, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suseł, J.; Batycka-Baran, A.; Reich, A.; Szepietowski, J.C. Uraemic pruritus markedly affects the quality of life and depressive symptoms in haemodialysis patients with end-stage renal disease. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2014, 94, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeski, C.J.; Johnson, J.A.; Davison, S.N.; Lauzon, G.J. Itch Severity Scale: A self-report instrument for the measurement of pruritus severity. Br. J. Dermatol. 2007, 156, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bender, B.G.; Leung, S.B.; Leung, D.Y. Actigraphy assessment of sleep disturbance in patients with atopic dermatitis: An objective life quality measure. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval, L.F.; Huang, K.; O’Neill, J.L.; Gustafson, C.J.; Hix, E.; Harrison, J.; Clark, A.; Buxton, O.M.; Feldman, S.R. Measure of atopic dermatitis disease severity using actigraphy. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2014, 18, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikoma, A.; Ebata, T.; Chantalat, L.; Takemura, K.; Mizzi, F.; Poncet, M.; Leclercq, D. Measurement of Nocturnal Scratching in Patients with Pruritus Using a Smartwatch: Initial Clinical Studies with the Itch Tracker App. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2019, 99, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipman, Z.M.; Paramasivam, V.; Yosipovitch, G.; Germain, M.J. Clinical management of chronic kidney disease-associated pruritus: Current treatment options and future approaches. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, i16–i22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, K.; Matsumoto, K. Effect of skin care with an emollient containing a high water content on mild uremic pruritus. Therapher. Dial. 2004, 8, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaskas, E.; Szepietowski, J.C.; Bessis, D.; Ioannides, D.; Ponticelli, C.; Ghienne, C.; Taberly, A.; Dupuy, P. Randomized, double-blind study with glycerol and paraffin in uremic xerosis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 748–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouhari, A.; Moghtaderi, M.; Raeisi, S.; Shahidi, S.; Parin Hedayati, Z.; Zaboliyan, J.; Ani, S.; Moeinzadeh, F.; Mortazavi, M. Pruritus-reducing effects of omega-3 fatty acids in hemodialysis patients: A cross-over randomized clinical trial. Hemodial. Int. 2022, in press. [CrossRef]
- Panahi, Y.; Dashti-Khavidaki, S.; Farnood, F.; Noshad, H.; Lotfi, M.; Gharekhani, A. Therapeutic effects of omega-3 fatty acids on chronic kidney disease-associated pruritus: A literature review. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 6, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pele, M.; Waluyo, A. Use of olive oil and warm water in bathing intervention in preventing risk of skin integrity damage in total care patients with chronic disease: A case study. J. Pendidik. Keperawatan Indo. 2019, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmariah, S.B.; Lerner, E.A. Topical therapies for pruritus. Semin. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2011, 30, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.J.; Cao, G.; Tang, W.X.; Lv, X.Y.; Huang, S.M.; Qin, W.; Ping, F.; Ye, T. A randomized controlled trial of high-permeability haemodialysis against conventional haemodialysis in the treatment of uraemic pruritus. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2009, 34, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotch, F.A.; Sargent, J.A.; Keen, M.L. Whither goest kt/v? Kidney Int. 2000, 58, S3–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlSahow, A.; Muenz, D.; Al-Ghonaim, M.A.; Al Salmi, I.; Hassan, M.; Al Aradi, A.H.; Hamad, A.; Al-Ghamdi, S.M.; Shaheen, F.A.; Alyousef, A.; et al. Kt/V: Achievement, predictors and relationship to mortality in hemodialysis patients in the Gulf Cooperation Council countries: Results from DOPPS (2012–18). Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eloot, S.; Van Biesen, W.; Glorieux, G.; Neirynck, N.; Dhondt, A.; Vanholder, R. Does the adequacy parameter kt/v urea reflect uremic toxin concentrations in hemodialysis patients? PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajewski, P.K.; Krajewska, M.; Szepietowski, J.C. Pruritus in renal transplant recipients: Current state of knowledge. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020, 29, 769–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panuccio, V.; Tripepi, R.; Bellantoni, M.; Saporito, L.; Quattrone, S.; Lacava, V.; Parlongo, G.; Tripepi, G.; Mallamaci, F.; Zoccali, C. Pruritus and quality of life in renal transplant patients. Clin. Transplant. 2017, 31, e12893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schricker, S.; Weisshaar, E.; Kupfer, J.; Mettang, T. Prevalence of pruritus in a single cohort of long-term kidney transplant recipients. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2020, 100, adv00066. [Google Scholar]
- Ketteler, M.; Block, G.A.; Evenepoel, P.; Fukagawa, M.; Herzog, C.A.; McCann, L.; Moe, S.M.; Shroff, R.; Tonelli, M.A.; Toussaint, N.D.; et al. Executive summary of the 2017 KDIGO Chronic Kidney Disease–Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD) Guideline Update: What’s changed and why it matters. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apetrii, M.; Goldsmith, D.; Nistor, I.; Siriopol, D.; Voroneanu, L.; Scripcariu, D.; Vervloet, M.; Covic, A. Impact of surgical parathyroidectomy on chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD)–a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amro, A.; Waldum-Grevbo, B.; von der Lippe, N.; Brekke, F.B.; Miaskowski, C.; Os, I. Symptom clusters from dialysis to renal transplantation: A five-year longitudinal study. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2016, 51, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirazian, S.; Aina, O.; Park, Y.; Chowdhury, N.; Leger, K.; Hou, L.; Miyawaki, N.; Mathur, V.S. Chronic kidney disease-associated pruritus: Impact on quality of life and current management challenges. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc. Dis. 2017, 10, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yosipovitch, G.; Rosen, J.D.; Hashimoto, T. Itch: From mechanism to (novel) therapeutic approaches. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 1375–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakhaee, S.; Nasiri, A.; Waghei, Y.; Morshedi, J. Comparison of Avena sativa, vinegar, and hydroxyzine for uremic pruritus of hemodialysis patients: A crossover randomized clinical trial. Iran J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 9, 316–322. [Google Scholar]
- Weisshaar, E.; Dunker, N.; Röhl, F.W.; Gollnick, H. Antipruritic effects of two different 5HT3 receptor antagonists and an antihistamine in haemodialysis patients. Exp. Dermatol. 2004, 13, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, E.; Yosipovitch, G. Chronic itch management: Therapies beyond those targeting the immune system. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019, 123, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehrenbacher, J.C.; Taylor, C.P.; Vasko, M.R. Pregabalin and gabapentin reduce release of substance P and CGRP from rat spinal tissues only after inflammation or activation of protein kinase, C. Pain 2003, 105, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofal, E.; Farag, F.; Nofal, A.; Eldesouky, F.; Alkot, R.; Abdelkhalik, Z. Gabapentin: A promising therapy for uremic pruritus in hemodialysis patients: A randomized-controlled trial and review of literature. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2016, 27, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Jiao, S.; Xiao, Y.; Ren, W.; Zhao, T.; Meng, J. Comparison of pregabalin with ondansetron in treatment of uraemic pruritus in dialysis patients: A prospective, randomized, double-blind study. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2015, 47, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.A.; Patel, T.S.; Camacho, F.; Clark, A.; Freedman, B.I.; Kaur, M.; Fountain, J.; Williams, L.L.; Yosipovitch, G.; Fleischer, A.B., Jr. A pramoxine-based anti-itch lotion is more effective than a control lotion for the treatment of uremic pruritus in adult hemodialysis patients. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2009, 20, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breneman, D.L.; Cardone, J.S.; Blumsack, R.F.; Lather, R.M.; Searle, E.A.; Pollack, V.E. Topical capsaicin for treatment of hemodialysis-related pruritus. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1992, 26, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarng, D.C.; Cho, Y.L.; Liu, H.N.; Huang, T.P. Hemodialysis-related pruritus: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study of capsaicin 0.025% cream. Nephron 1996, 72, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duque, M.I.; Yosipovitch, G.; Fleischer, A.B., Jr.; Willard, J.; Freedman, B.I. Lack of efficacy of tacrolimus ointment 0.1% for treatment of hemodialysis-related pruritus: A randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2005, 52, 519–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szepietowski, J.; Szepietowski, T.; Reich, A. Efficacy and tolerance of the cream containing structured physiological lipids with endocannabinoids in the treatment of uremic pruritus: A preliminary study. Acta Dermatovenerol. Croat. 2005, 13, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, K.Y.; Li, C.W.; Wong, H.; Yip, T.; Chan, M.L.; Cheng, H.W.; Sham, M.K. Use of sertraline for antihistamine-refractory uremic pruritus in renal palliative care patients. J. Palliat. Med. 2013, 16, 966–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakfetrat, M.; Malekmakan, L.; Hashemi, N.; Tadayon, T. Sertraline can reduce uremic pruritus in hemodialysis patient: A double blind randomized clinical trial from Southern Iran. Hemodial. Int. 2018, 22, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, M.W. Itch in systemic disease: Therapeutic options. Dermatol. Ther. 2005, 18, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Andoh, T.; Zhang, Q.; Uta, D.; Kuraishi, Y. β2-Microglobulin, interleukin-31, and arachidonic acid metabolites (leukotriene B4 and thromboxane A2) are involved in chronic renal failure-associated itch-associated responses in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 847, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikström, B.; Gellert, R.; Ladefoged, S.D.; Danda, Y.; Akai, M.; Ide, K.; Ogasawara, M.; Kawashima, Y.; Ueno, K.; Mori, A.; et al. κ-Opioid system in uremic pruritus: Multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical studies. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 3742–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, H.; Ebata, T.; Takamori, K.; Muramatsu, T.; Nakamoto, H.; Suzuki, H. Effect of a novel kappa-receptor agonist, nalfurafine hydrochloride, on severe itch in 337 haemodialysis patients: A Phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozono, H.; Yoshitani, H.; Nakano, R. Post-marketing surveillance study of the safety and efficacy of nalfurafine hydrochloride (Remitch(®) capsules 2.5μg) in 3,762 hemodialysis patients with intractable pruritus. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc Dis. 2018, 11, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawi, A.; Alcorn, H.; Berg, J.; Hines, C.; Hait, H.; Sciascia, T. Pharmacokinetics of nalbuphine hydrochloride extended release tablets in hemodialysis patients with exploratory effect on pruritus. BMC Nephrol. 2015, 16, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, V.S.; Kumar, J.; Crawford, P.W.; Hait, H.; Sciascia, T.; TR02 Study Investigators. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of nalbuphine ER tablets for uremic pruritus. Am. J. Nephrol. 2017, 46, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, L.W.; Friedberg, M.; Lokkegaard, N. Naloxone in the treatment of uremic pruritus: A case history. Clin. Nephrol. 1984, 21, 355–356. [Google Scholar]
- Legroux-Crespel, E.; Clèdes, J.; Misery, L. A comparative study on the effects of naltrexone and loratadine on uremic pruritus. Dermatology 2004, 208, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauli-Magnus, C.; Mikus, G.; Alscher, D.M.; Kirschner, T.; Nagel, W.; Gugeler, N.; Risler, T.; Berger, E.D.; Kuhlmann, U.; Mettang, T. Naltrexone does not relieve uremic pruritus: Results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2000, 11, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ada, S.; Seçkin, D.; Budakoğlu, İ.; Özdemir, F.N. Treatment of uremic pruritus with narrowband ultraviolet B phototherapy: An open pilot study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2005, 53, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherjeena, P.B.; Binitha, M.P.; Rajan, U.; Sreelatha, M.; Sarita, S.; Nirmal, C.; Deepthi, N.S. A controlled trial of narrowband ultraviolet B phototherapy for the treatment of uremic pruritus. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2017, 83, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szepietowski, J.C.; Morita, A.; Tsuji, T. Ultraviolet B induces mast cell apoptosis: A hypothetical mechanism of ultraviolet B treatment for uraemic pruritus. Med. Hypotheses 2002, 58, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Sasaki, J.; Nakamura, M.; Koo, J. Cutaneous carcinogenic risk of phototherapy: An updated comprehensive review. J. Psoriasis Psoriatic Arthrit. 2015, 1, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakfetrat, M.; Basiri, F.; Malekmakan, L.; Roozbeh, J. Effects of turmeric on uremic pruritus in end stage renal disease patients: A double-blind randomized clinical trial. J. Nephrol. 2014, 27, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.H.; Tai, Y.C.; Yu, M.C.; Lin, I.H.; Kuo, K.L. Western and complementary alternative medicine treatment of uremic pruritus: A literature review. Tzu Chi Med. J. 2021, 33, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Min, S.; Kim, K.W.; Jung, W.M.; Lee, M.J.; Kim, Y.K.; Chae, Y.; Lee, H.; Park, H.J. Acupuncture for histamine-induced itch: Association with increased parasympathetic tone and connectivity of putamen-midcingulate cortex. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akça, N.K.; Taşcı, S. Acupressure and transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation for improving uremic pruritus: A randomized, controlled trial. Alternat. Ther. Health Med. 2016, 22, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, I.U.; Ahmed, R.; Rahman, A.U.; Wu, D.B.; Munib, S.; Shah, Y.; Khan, N.A.; Rehman, A.U.; Lee, L.H.; Chan, K.G.; et al. Effectiveness and safety profiling of zolpidem and acupressure in CKD associated pruritus: An interventional study. Medicine 2021, 100, e25995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combs, S. CKD-associated Pruritus. In Proceedings of the KDIGO Clinical Practice Conference, Alexandria, VA, USA, 4 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
| Local skin differential diagnoses Allergic/irritant/contact dermatitis Atopic dermatitis Bullous pemphigoid Dermatitis herpetiformis Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (mycosis fungoides) Dermatophyte infection Folliculitis Lichen planus Lichen simplex chronicus Pediculosis (lice infestation) Psoriasis Scabies Sunburn Urticaria (hives) Xerosis | Systemic differential diagnoses Autoimmune Dermatitis herpetiformis secondary to celiac disease Dermatomyositis Linear IgA disease Sjögren’s syndrome Hematological Hemochromatosis Iron deficiency anemia Mastocytosis Plasma cell dyscrasia Polycythemia vera Hepatobiliary Biliary cirrhosis and sclerosing cholangitis Chronic pancreatitis with biliary tract obstruction Drug-induced cholestasis Hepatitis Systemic infections AIDS Parasites (e.g., giardiasis, onchocerciasis, schistosomiasis) Prion disease Malignancy Leukemia Lymphoma Multiple myeloma Solid tumors with paraneoplastic syndrome Metabolic and Endocrine Carcinoid syndrome Diabetes mellitus Thyroid disease–hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism Hyperparathyroidism Neurological Cerebral abscess Cerebral tumor Multiple sclerosis Stroke Other systemic differentials Drug ingestion Eating disorders with rapid weight loss Neuropsychiatric disorders Pregnancy |
| Regular screening for symptoms associated with CKDaP during every patient consultation and performing skin examination |
| Designing patient-friendly resources (e.g., leaflets, e-resources) to improve awareness of CKDaP for the CKD population |
| Increasing awareness regarding CKDaP among families/carers |
| Creation of easy-to-use electronic scoring systems for diagnosis and severity measurement of CKDaP for use at the bedside or in the community |
| Development of accepted guidelines on the management of CKDaP (in the absence of internationally accepted guidelines these could be locally agreed) |
| Setting up video consultations with a dermatologist as part of care pathways for CKDaP, for example to monitor the response to treatment |
| Improve pathways of communication between nephrologists and dermatologists to increase the effectiveness and flow of care. |
| Involvement of other stakeholders, such as general practitioners, nursing staff etc., to improve awareness of CKDaP |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.C.Y.; Wu, H.H.L.; Ponnusamy, A.; Pye, I.; Woywodt, A. Pruritus in Chronic Kidney Disease: An Update. Allergies 2022, 2, 87-105. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies2030009
Wang CCY, Wu HHL, Ponnusamy A, Pye I, Woywodt A. Pruritus in Chronic Kidney Disease: An Update. Allergies. 2022; 2(3):87-105. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies2030009
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Claire C. Y., Henry H. L. Wu, Arvind Ponnusamy, Isobel Pye, and Alexander Woywodt. 2022. "Pruritus in Chronic Kidney Disease: An Update" Allergies 2, no. 3: 87-105. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies2030009
APA StyleWang, C. C. Y., Wu, H. H. L., Ponnusamy, A., Pye, I., & Woywodt, A. (2022). Pruritus in Chronic Kidney Disease: An Update. Allergies, 2(3), 87-105. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies2030009






