Distinct Animal Food Allergens Form IgE-Binding Amyloids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Food Allergic Patient Sera
2.3. In Silico Studies
2.4. Food Allergens
2.5. Amyloid Fibril Preparation
2.6. Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy
2.7. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
2.8. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate–Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.9. Dot Blot Analysis
3. Results
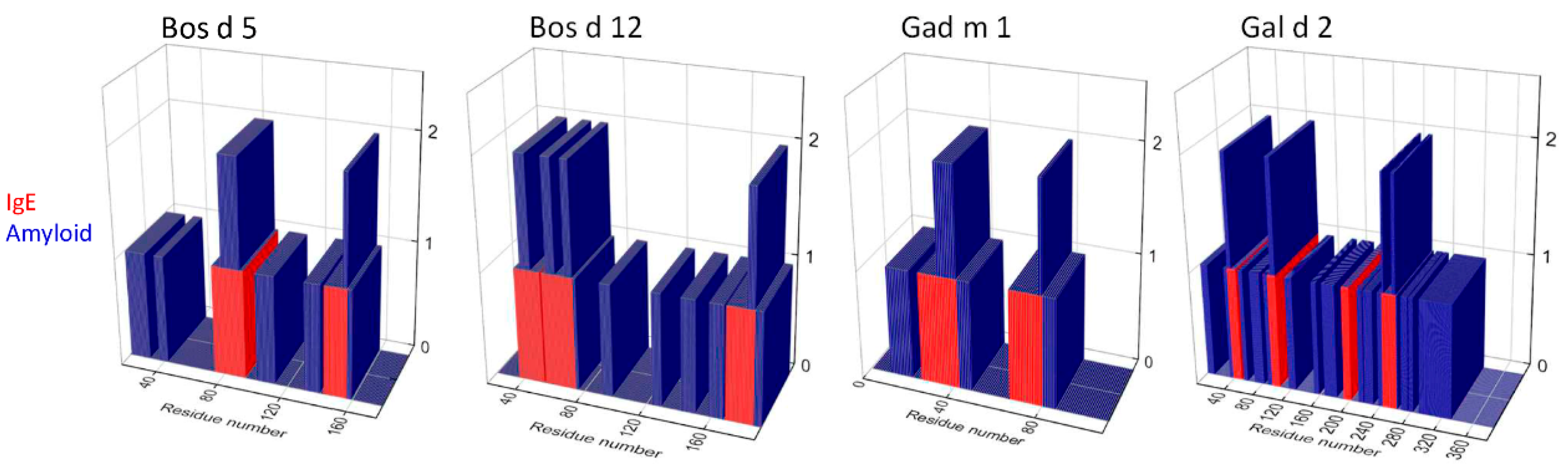
3.1. Relation between IgE-Binding and Amyloid-Forming Regions of Milk and Egg Allergens
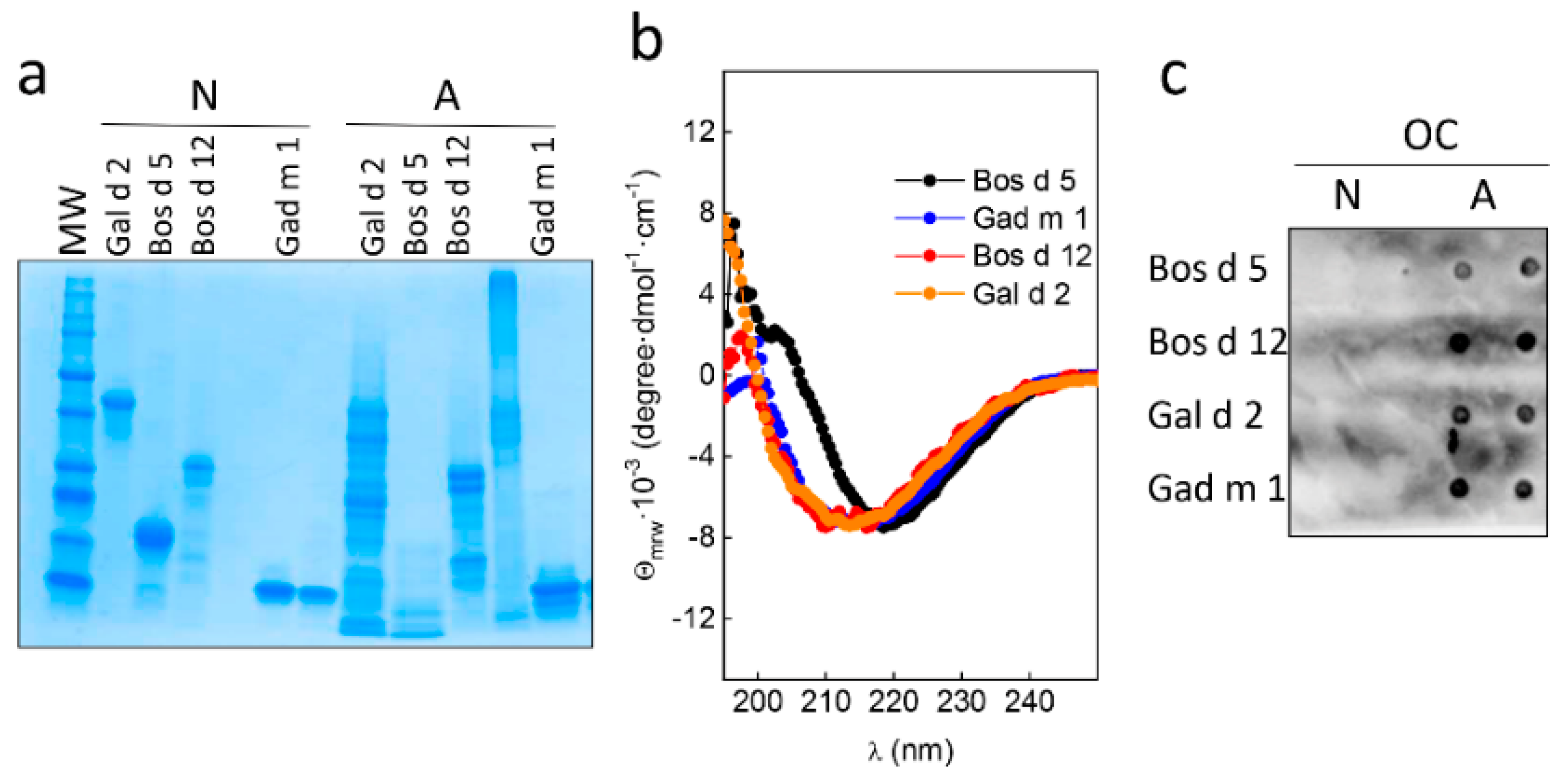
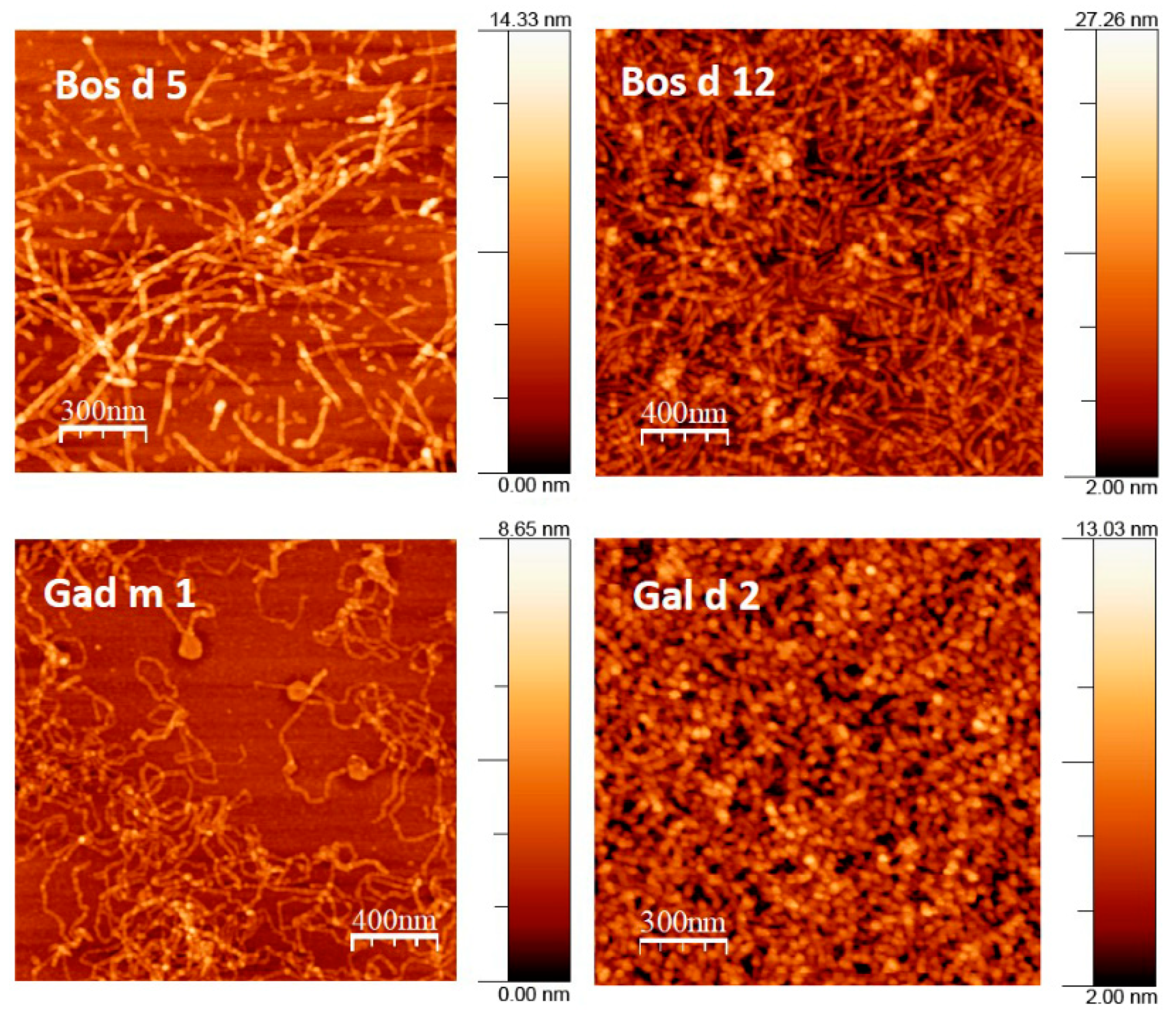
3.2. Native and Amyloid Folds of Milk, Egg and Fish Allergens
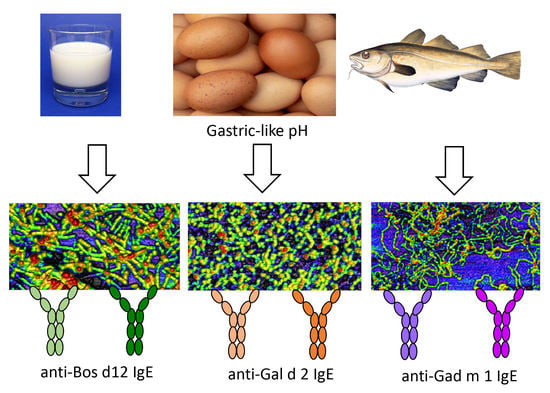
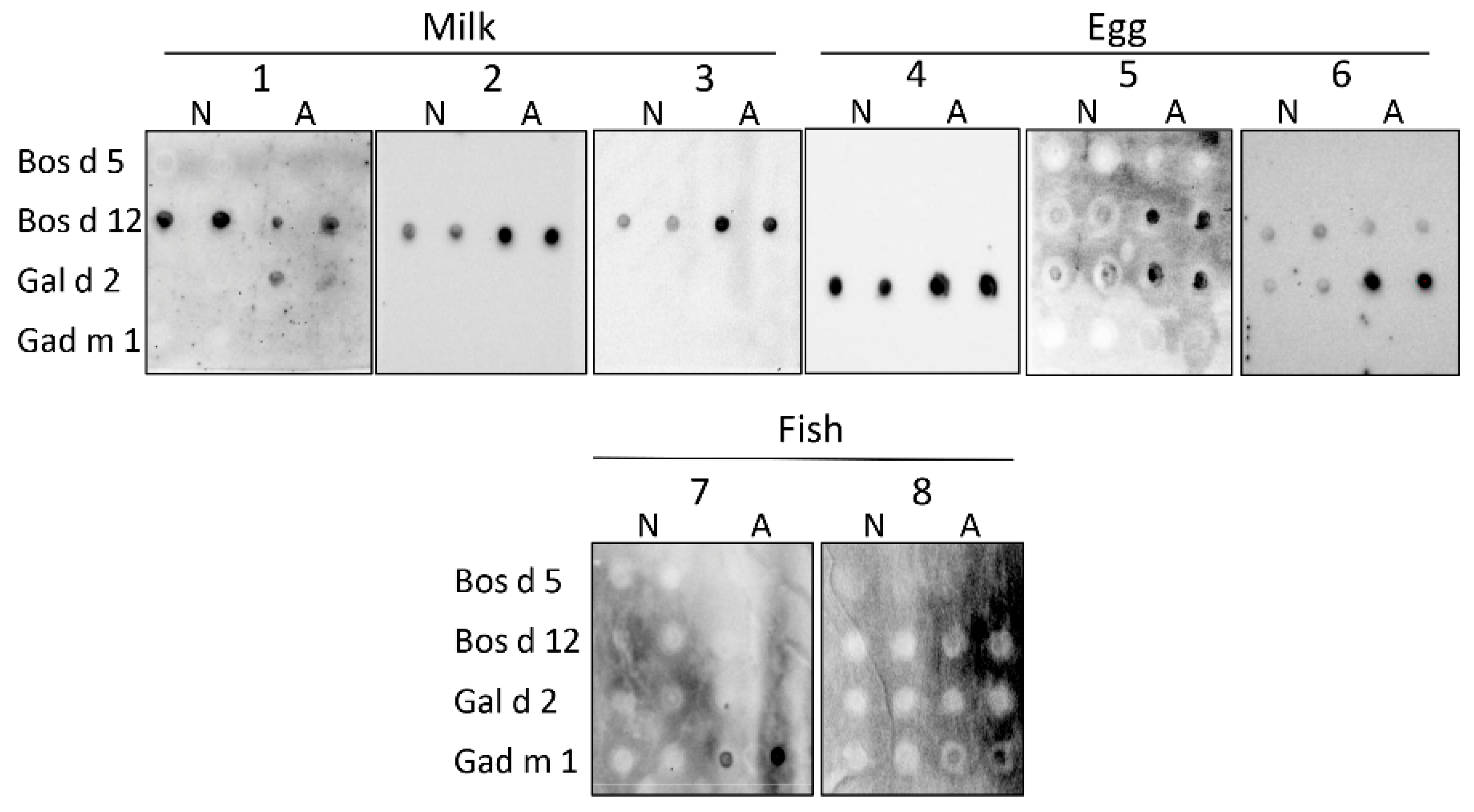
3.3. Interaction of the Amyloids with the IgE of Sera of Milk, Egg and Fish Allergic Patients
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burks, W.; Tang, M.; Sicherer, S.; Muraro, A.; Eigenmann, P.A.; Ebisawa, M.; Fiocchi, A.; Chiang, W.; Beyer, K.; Wood, R.; et al. ICON: Food allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 906–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sicherer, S.H.; Sampson, H.A. Food allergy: A review and update on epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, prevention, and management. J. Allergy Clin. Inmunol. 2018, 141, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matricardi, P.M.; Kleine-Tebbe, J.; Hoffmann, H.J.; Valenta, R.; Hilger, C.; Hofmaier, S.; Aalberse, R.C.; Agache, I.; Asero, R.; Ballmer-Weber, B.; et al. EAACI Molecular Allergology User’s Guide. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 27, 1–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plunkett, C.H.; Nagler, C.R. The influence of the microbiome on allergic sensitization to food. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannon, G.A. What makes a food protein an allergen? Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2004, 4, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, M.D.; Pomés, A.; Breiteneder, H.; Ferreira, F. Nomenclature and structural biology of allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 119, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiteneder, H.; Mills, E.N. Molecular properties of food allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, J.A.; Breiteneder, H.; Mills, E.N. Evolutionary distance from human homologs reflects allergenicity of animal food proteins. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekar, J.; Re, D.; Untersmayr, E. Stability of allergens. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 100, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guijarro, J.I.; Sunde, M.; Jones, J.A.; Campbell, I.D.; Dobson, C.M. Amyloid fibril formation by an SH3 domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 4224–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiti, F.; Dobson, C.M. Protein Misfolding, Amyloid Formation, and Human Disease: A Summary of Progress over the Last Decade. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 27–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riek, R.; Eisenberg, D.S. The activities of amyloids from a structural perspective. Nature 2016, 539, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tayeb-Fligelman, E.; Tabachnikov, O.; Moshe, A.; Goldshmidt-Tran, O.; Sawaya, M.R.; Coquelle, N.; Colletier, J.P.; Landau, M. The cytotoxic Staphylococcus aureus PSMα3 reveals a cross-α amyloid-like fibril. Science 2017, 355, 831–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, J.; Sánchez, R.; Castellanos, M.; Fernández-Escamilla, A.M.; Vázquez-Cortés, S.; Fernández-Rivas, M.; Gasset, M. Fish β-parvalbumin acquires allergenic properties by amyloid assembly. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2015, 145, w14128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez, R.; Martínez, J.; Castro, A.; Pedrosa, M.; Quirce, S.; Rodríguez-Pérez, R.; Gasset, M. The amyloid fold of Gad m 1 epitopes governs IgE binding. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, R.; Martínez, J.; Montoya, L.; Castellanos, M.; Gasset, M. Mapping Amyloid Regions in Gad m 1 with Peptide Arrays. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1779, 197–207. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Mezzenga, R. Food protein amyloid fibrils: Origin, structure, formation, characterization, applications and health implications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 269, 334–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goers, J.; Permyakov, S.E.; Permyakov, E.A.; Uversky, V.N.; Fink, A.L. Conformational prerequisites for alpha-lactalbumin fibrillation. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 12546–12551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorn, D.C.; Ecroyd, H.; Sunde, M.; Poon, S.; Carver, J.A. Amyloid fibril formation by bovine milk alpha(s2)-casein occurs under physiological conditions yet is prevented by its natural counterpart, alpha(s1)-casein. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 3926–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, K.; Zhong, Q.X. Amyloid-like fibrils formed from intrinsically disordered caseins: Physicochemical and nanomechanical properties. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 5898–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaudov, L.N.; de Vries, R. Thermally induced fibrillar aggregation of hen egg white lysozyme. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krebs, M.R.H.; Wilkins, D.K.; Chung, E.W.; Pitkeathly, M.C.; Chamberlain, A.K.; Zurdo, J.; Robinson, C.V.; Dobson, C.M. Formation and seeding of amyloid fibrils from wild-type hen lysozyme and a peptide fragment from the beta-domain. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 300, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raynes, J.K.; Day, L.; Crepin, P.; Horrocks, M.H.; Carver, J.A. Coaggregation of κ-Casein and β-Lactoglobulin Produces Morphologically Distinct Amyloid Fibrils. Small 2017, 13, 1603591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UniProtKB data base. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/ (accessed on 14 July 2020).
- Cerecedo, I.; Zamora, J.; Shreffler, W.G.; Lin, J.; Bardina, L.; Dieguez, M.C.; Wang, J.; Muriel, A.; de la Hoz, B.; Sampson, H.A. Mapping of the IgE and IgG4 sequential epitopes of milk allergens with a peptide microarray-based immunoassay. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 122, 589e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lin, J.; Bardina, L.; Goldis, M.; Nowak-Węgrzyn, A.; Shreffler, W.G.; Sampson, H.A. Correlation of IgE/IgG4 milk epitopes and affinity of milk-specific IgE antibodies with different phenotypes of clinical milk allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mine, Y.; Rupa, P. Fine mapping and structural analysis of immunodominant IgE allergenic epitopes in chicken egg ovalbumin. Protein Eng. 2003, 16, 747e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuo, H.; Yokooji, T.; Taogoshi, T. Common food allergens and their IgE-binding epitopes. Allergol. Int. 2015, 64, 332e343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ZipperDB data base. Available online: https://services.mbi.ucla.edu/zipperdb/ (accessed on 14 July 2020).
- Sawaya, M.R.; Sambashivan, S.; Nelson, R.; Ivanova, M.I.; Sievers, S.A.; Apostol, M.I.; Thompson, M.J.; Balbirnie, M.; Wiltzius, J.J.; McFarlane, H.T.; et al. Atomic structures of amyloid cross-beta spines reveal varied steric zippers. Nature 2007, 447, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Tavarez, R.; Carrera, M.; Pedrosa, M.; Quirce, S.; Rodríguez-Pérez, R.; Gasset, M. Reconstruction of fish allergenicity from the content and structural traits of the component β-parvalbumin isoforms. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eisenberg, D.S.; Sawaya, M.R. Implications for Alzheimer’s disease of an atomic resolution structure of amyloid-β (1–42) fibrils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9398–9400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holland, J.W.; Deeth, H.C.; Alewood, P.F. Analysis of O-glycosylation site occupancy in bovine kappa-casein glycoforms separated by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Proteomics 2005, 5, 990–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldschmidt, L.; Teng, P.K.; Riek, R.; Eisenberg, D. Identifying the amylome, proteins capable of forming amyloid-like fibrils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 3487–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uversky, V.N. Amyloidogenesis of natively unfolded proteins. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2008, 5, 260–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, C.M. Protein misfolding: Evolution and disease. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1999, 24, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, A.H.; Ackerbauer, D.; Kostadinova, M.; Bublin, M.; de Oliveira, G.A.; Ferreira, F.; Almeida, F.C.; Breiteneder, H.; Valente, A.P. Solution and high-pressure NMR studies of the structure, dynamics, and stability of the cross-reactive allergenic cod parvalbumin Gad m 1. Proteins 2014, 82, 3032–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Patient | Offending Food | Sex (M/F) | Age (year) | Symptoms a | IgE (kU/L) b | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Milk | Bos d 5 | Bos d 12 | Egg-White | Gal d 2 | Hake | Cod | |||||
| 1 | milk | F | 16 | OAS, AE | 391 | 7.1 | 0.2 | 0.7 | <0.4 | nd | nd | nd |
| 2 | milk | M | 15 | A | 648 | 22.8 | 2.5 | 23.8 | 0.4 | 0.3 | nd | nd |
| 3 | milk | F | 19 | A | 1323 | 354 | 70.2 | 461 | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| 4 | egg | M | 20 | RD | 850 | nd | nd | nd | 325 | 62.1 | nd | nd |
| 5 | egg | F | 14 | E | 5774 | nd | 0.1 | 0.1 | 3.2 | 3.9 | nd | nd |
| 6 | egg | M | 15 | E, A | 3017 | nd | nd | nd | 6.1 | 5.6 | nd | nd |
| 7 | hake | M | 35 | A | 124 | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | 2.7 | 1.0 |
| 8 | hake | F | 18 | RD | 222 | nd | nd | 0.1 | nd | 0.01 | 17.4 | nd |
| Allergen | Sequence Regions. |
|---|---|
| Bos d 5 | 74LQKWENGECAQKKIIAEKTK93 131QSLACQCLVRTPEVDDEALEKFDKALKAL159 |
| Bos d 12 | 37RFFSDKIAKYIPIQYVL53 55RYPSYGLNYYQQKPVALINNQF76 159AVESTVATLEDSPEVIESPPEINTVQVTSTAV190 |
| Gad m 1 | 25FDHKAFFTKVGLAAKSSADIKKVF48 67FLQNFSAGARALSDAETKVF86 |
| Gal d 2 | 39AIMSALAMVYLGAKDSTRTQINKVV68 88LNQITKPNDVYSFSLAS104 238GTMSMLVLLPDEVSGLEQLESIINFE263 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez-Tavarez, R.; Castellanos, M.; Loli-Ausejo, D.; Pedrosa, M.; Hurtado, J.L.; Rodriguez-Pérez, R.; Gasset, M. Distinct Animal Food Allergens Form IgE-Binding Amyloids. Allergies 2021, 1, 22-32. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies1010002
Pérez-Tavarez R, Castellanos M, Loli-Ausejo D, Pedrosa M, Hurtado JL, Rodriguez-Pérez R, Gasset M. Distinct Animal Food Allergens Form IgE-Binding Amyloids. Allergies. 2021; 1(1):22-32. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies1010002
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez-Tavarez, Raquel, Milagros Castellanos, David Loli-Ausejo, María Pedrosa, José Luis Hurtado, Rosa Rodriguez-Pérez, and María Gasset. 2021. "Distinct Animal Food Allergens Form IgE-Binding Amyloids" Allergies 1, no. 1: 22-32. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies1010002
APA StylePérez-Tavarez, R., Castellanos, M., Loli-Ausejo, D., Pedrosa, M., Hurtado, J. L., Rodriguez-Pérez, R., & Gasset, M. (2021). Distinct Animal Food Allergens Form IgE-Binding Amyloids. Allergies, 1(1), 22-32. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies1010002