Predicting Intoxication Using Motorcycle and Head Movements of Riders Wearing Alcohol Intoxication Goggles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Method
2.1. Experiment 1: MC Movement
2.1.1. Participants
2.1.2. Experimental Set-Up
2.1.3. Experimental Design and Procedure
2.2. Experiment 2: Head Movement
2.2.1. Participants
2.2.2. Experimental Set-Up
2.2.3. Experimental Design and Procedure
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.3.1. Classifier
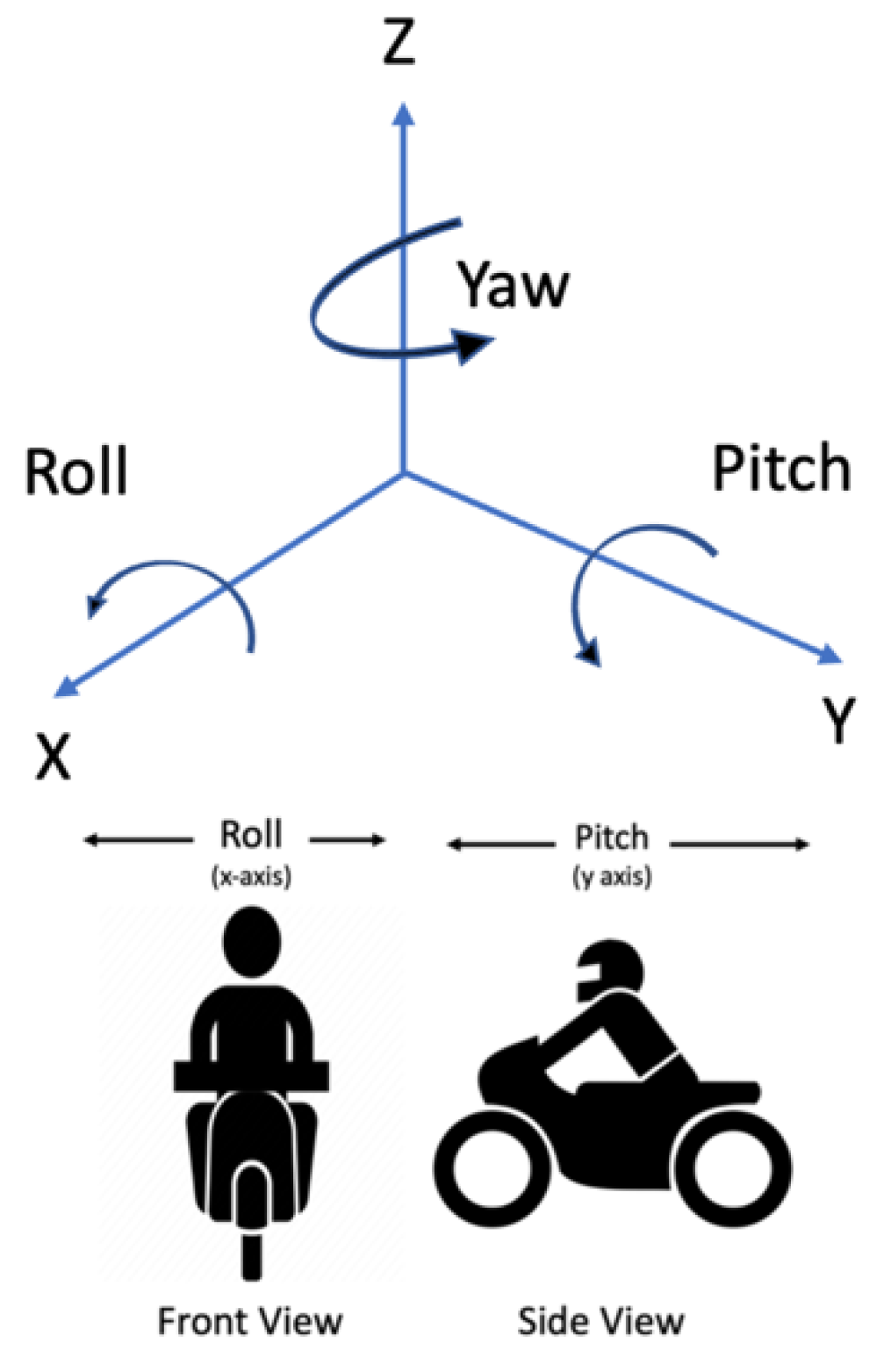
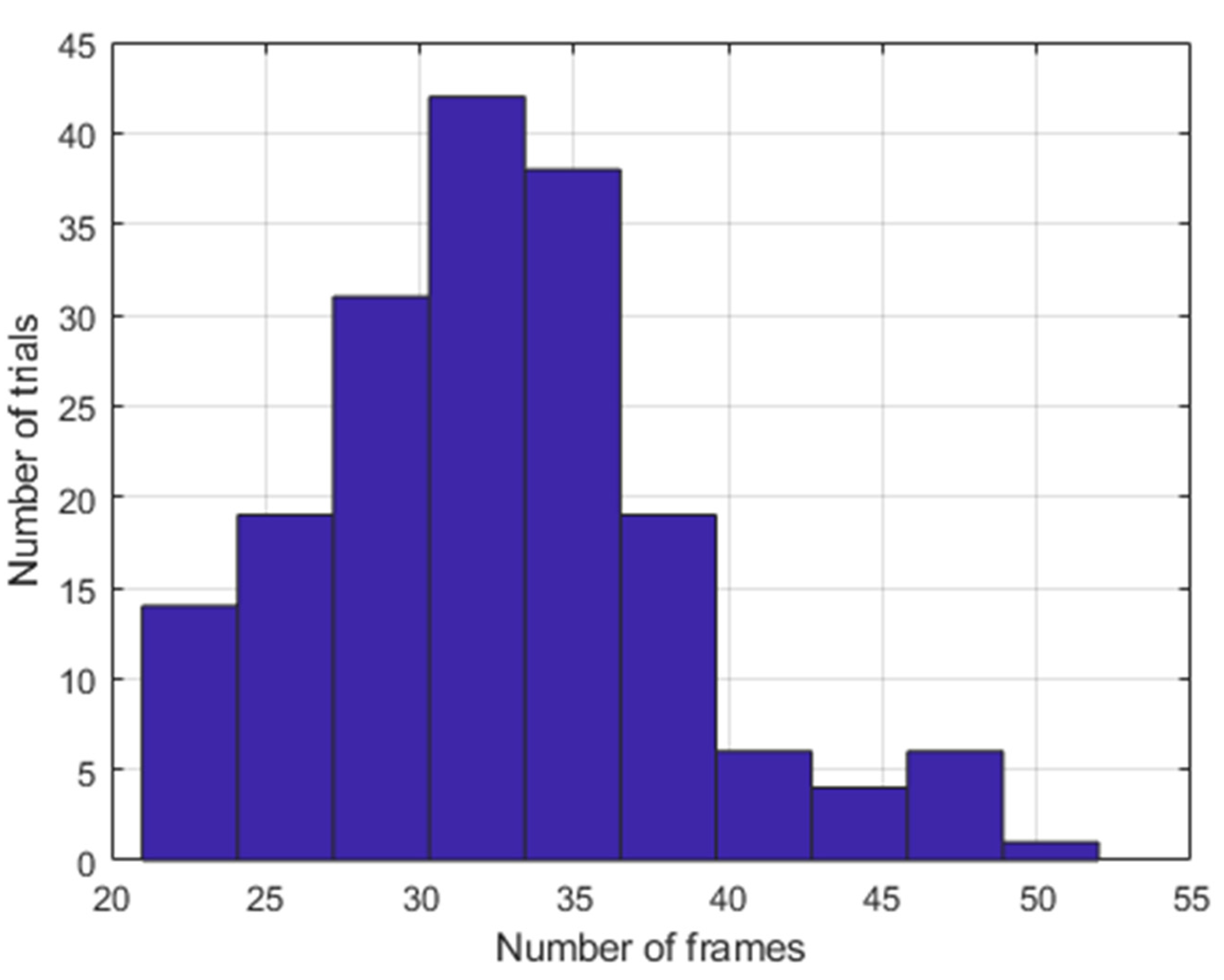
2.3.2. Input Sequence Representation for MC Movement Experiment
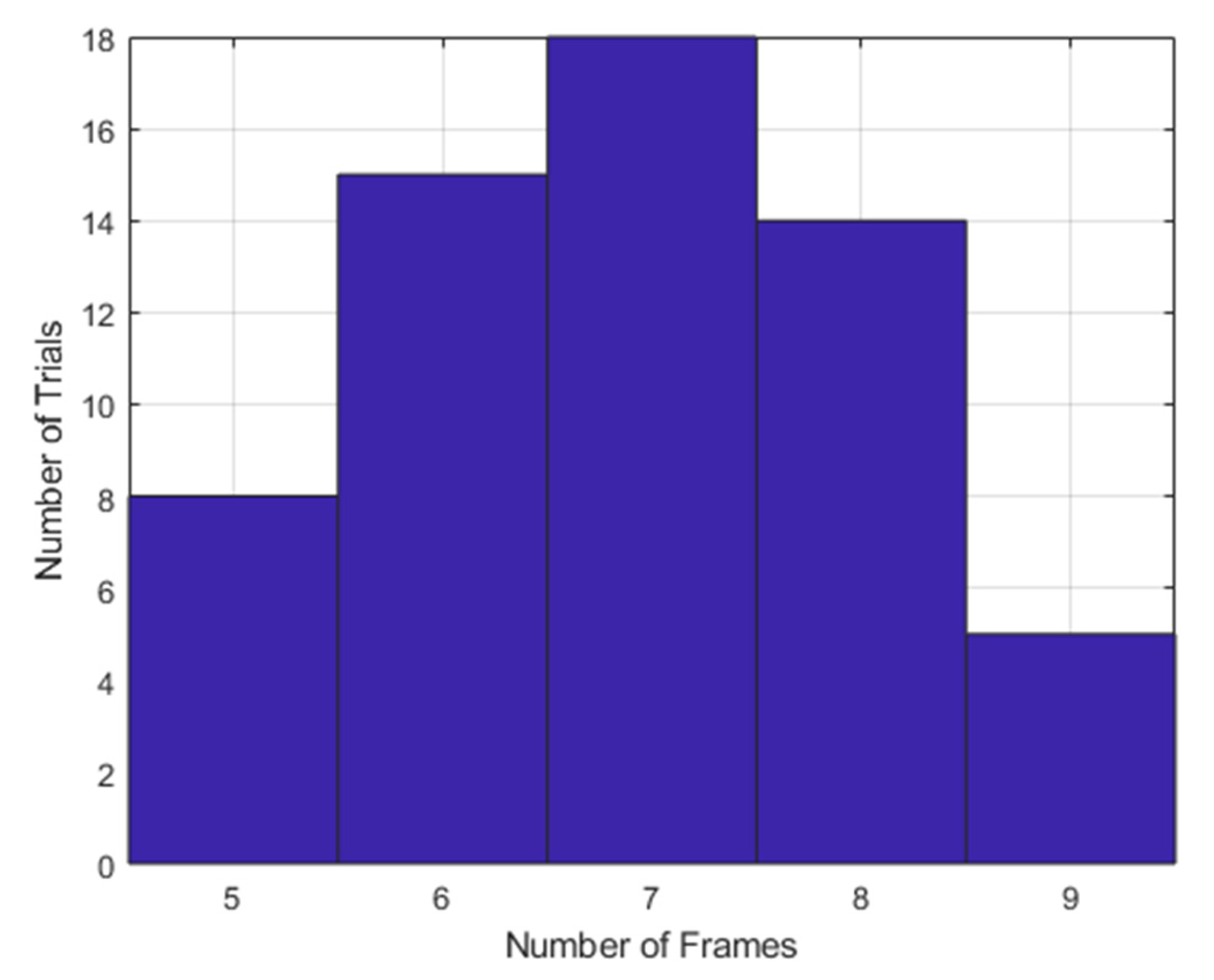
2.3.3. Input Sequence Representation for Head Movement Experiment
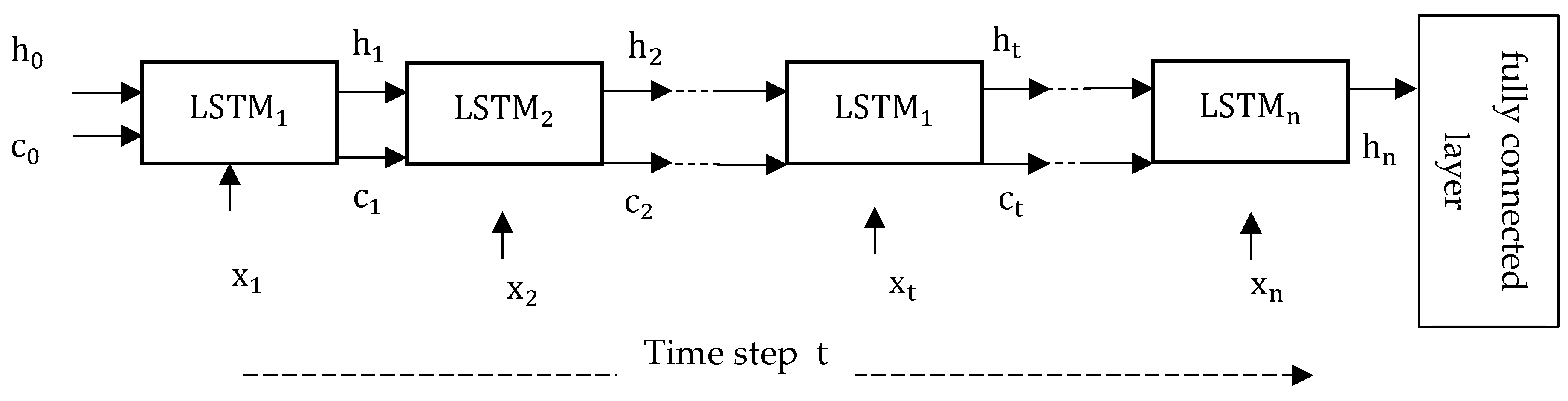
2.3.4. LSTM Block and Training Configuration and Performance
3. Results
3.1. MC Movement Characteristics
3.2. Head Movement Characteristics
3.3. Deep LSTM Training Configuration and Performance
3.3.1. MC Movement Experiment
3.3.2. Head Movement Experiment
4. Discussion
4.1. MC Movement Experiment
4.2. Head Movement Experiment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.; Guo, X.; Xu, M.; Wang, L.; Lord, D. Alcohol-impaired motorcyclists versus car drivers: A comparison of crash involvement and legal consequence from adjudication data. J. Saf. Res. 2021, 79, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.A.; Chan, C.W.; Wiratama, B.S.; Chen, P.L.; Wang, M.H.; Chao, C.J.; Saleh, W.; Huang, H.C.; Pai, C.W. Evaluating the effect of drunk driving on fatal injuries among vulnerable road users in Taiwan: A population-based study. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamann, C.J.; Wendt, L.; Davis, J.; Peek-Asa, C.; Jansson, S.; Cavanaugh, J.E. Should we throw the book at ‘em? Charge combinations and conviction rates among alcohol-influenced drivers involved in motorcycle crashes. J. Saf. Res. 2022, 83, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.Y.; Li, J.S.; Pai, C.W.; Chien, W.C.; Huang, W.C.; Hsu, C.W.; Wu, C.C.; Yu, S.H.; Chiu, W.T.; Lam, C. Environmental Factors Associated with Severe Motorcycle Crash Injury in University Neighborhoods: A Multicenter Study in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, C.; Wiratama, B.S.; Chang, W.-H.; Chen, P.-L.; Chiu, W.-T.; Saleh, W.; Pai, C.-W. Effect of motorcycle helmet types on head injuries: Evidence from eight level-I trauma centres in Taiwan. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.L.; Herbosa, T.J.; Lu, S.F. Analysis of Transport and Vehicular Road Crash Cases in Metro Manila from 2016 to 2020. Acta Med. Philipp. 2022, 56, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elder, R.; Shults, R.; Sleet, D.; Nichols, J.; Zaza, S.; Thompson, R. Effectiveness of Sobriety Checkpoints for Reducing Alcohol-Involved Crashes. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2002, 3, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downey, L.A.; Hayley, A.C.; Porath-Waller, A.J.; Boorman, M.; Stough, C. The Standardized Field Sobriety Tests (SFST) and measures of cognitive functioning. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2016, 86, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marczinski, C.A.; Mearns, C.L. Automated assessment of alcohol-induced impairment of balance in male and female social drinkers. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2020, 28, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafström, A.; Modig, F.; Magnusson, M.; Fransson, P.A. Effectuation of adaptive stability and postural alignment strategies are decreased by alcohol intoxication. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2014, 35, 30–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudin-Brown, C.M.; Belinda, C.; Amy, A.; Christine, M.; Ashleigh, F. Do Drinking and Riding Mix? Effects of Legal Doses of Alcohol on Balance Ability in Experienced Motorcyclists. 2016. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/2134/23006 (accessed on 10 January 2021).
- Nassi, B.; Shams, J.; Rokach, L.; Elovici, Y. Virtual Breathalyzer: Towards the Detection of Intoxication Using Motion Sensors of Commercial Wearable Devices. Sensors 2022, 22, 3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creaser, J.; Ward, N.; Rakauskas, M.; Shankwitz, C.; Boer, E. Effects of alcohol impairment on motorcycle riding skills. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2009, 41, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modig, F.; Fransson, P.-A.; Magnusson, M.; Patel, M. Blood alcohol concentration at 0.06 and 0.10% causes a complex multifaceted deterioration of body movement control. Alcohol 2011, 46, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.S.-K.; Ng, T.C.-K. Development of a Chinese Motorcycle Rider Driving Violation Questionnaire. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2010, 42, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafström, A.; Patel, M.; Modig, F.; Magnusson, M.; Fransson, P.A. Acute alcohol intoxication impairs segmental body alignment in upright standing. J. Vestib. Res. 2014, 24, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCartney, D.; Desbrow, B.; Irwin, C. Using alcohol intoxication goggles (Fatal Vision® goggles) to detect alcohol related impairment in simulated driving. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2017, 18, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goebel, J.A.; Dunham, D.N.; Rohrbaugh, J.W.; Fischel, D.; Stewart, P.A. Dose-related effects of alcohol on dynamic posturography and oculomotor measures. Acta Otolaryngol. Suppl. 1995, 520 Pt 1, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Y.A.; Imaduddin, S.; Singh, Y.P.; Wajid, M.; Usman, M.; Abbas, M. Artificial Intelligence Based Approach for Classification of Human Activities Using MEMS Sensors Data. Sensors 2023, 23, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, V.; Yadav, H.; Semwal, V.B.; Roy, B.; Choubey, D.K.; Mallick, D.K. (Eds.) A Novel Smartphone-Based Human Activity Recognition Using Deep Learning in Health care. In Machine Learning, Image Processing, Network Security and Data Sciences; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The MathWorks Inc. MATLAB; Version 2022a; The MathWorks Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kishida, T.; Kageyama, I. A Study on Riding Simulator for Motorcycle. 2007. Available online: http://www.nads-sc.uiowa.edu/dscna/2007/papers/Section%203B%20-%20Simulator%20Characteristics%20-%20Applications%20II/Kishinda.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2023).
- Collings, R.; Paton, J.; Glasser, S.; Marsden, J. The effect of vision impairment on dynamic balance. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2015, 8, A6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomomitsu, M.S.; Alonso, A.C.; Morimoto, E.; Bobbio, T.G.; Greve, J.M. Static and dynamic postural control in low-vision and normal-vision adults. Clinics 2013, 68, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, E.B. Sensation and Perception, 8th ed.; Wadsworth/Thomson Learning: Belmont, CA, USA, 2010; p. 459. [Google Scholar]
- Sarker, I.H. Deep Learning: A Comprehensive Overview on Techniques, Taxonomy, Applications and Research Directions. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmis, M.A.; Pardhan, S. The Effect of Central Visual Impairment on Manual Prehension When Tasked with Transporting-to-Place an Object Accurately to a New Location. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 2812–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlob, I.; Wizov, S.S.; Reinecke, R.D. Head and eye movements in children with low vision. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 1996, 234, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivers, S. Alcohol Detection Sensor Might Be the Next Big Controversial Safety Feature to Be Required in Every New Car. 2022. Available online: https://www.carscoops.com/2022/03/alcohol-detection-sensor-might-be-the-next-big-controversial-safety-feature-to-be-required-in-every-new-car/ (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Arachchige, U.; Jayasinghe, S. A smart helmet with a built-in drowsiness and alcohol detection system. J. Res. Technol. Eng. 2020, 1, 76–81. [Google Scholar]
- International Motorcycle Manufacturers Association (IMMA). Motorcycle Safety: IMMA’s Contribution to the Decade of Action for Safety 2011–2020; International Motorcycle Manufacturers Association (IMMA): Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; Available online: https://www.jama.or.jp/operation/motorcycle/imma_report/pdf/attached04.pdf (accessed on 21 April 2023).


| Stage | Type | Activation | Learnable Parameters | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Input Sequence | 32 | ||
| 2 | LSTM | 50 | Input Weights Recurrent Weights Bias | 200 × 32 200 × 50 200 × 1 |
| 3 | Fully Connected | 2 | Weights Bias | 2 × 50 2 × 1 |
| 4 | Softmax | 2 | ||
| 5 | Classification Cross entropy with class “Drunk” and “Not Drunk” | |||
| Mean ± SD | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variable\BAC Level | 0% BAC | 0.05% BAC | 0.08% BAC |
| Pitch frequency | 11.0 ± 8.5 | 12.2 ± 11.265 | 16.2 ± 8.7 |
| Roll frequency | 30.0 ± 9.0 | 28.2± 11.004 | 24.8 ± 9.0 |
| Pitch amplitude (deg) | 1.2 ± 0.4 | 0.8 ± 0.3 | 0.6 ± 0.2 |
| Roll amplitude (deg) | 0.14 ± 0.1 | 0.2± 0.097 | 0.2 ± 0.1 |
| Mean ± SD | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | 0% BAC | 0.05% BAC | p-Value |
| Pitch frequency | 50.7 ± 11.5 | 57.3 ± 14.5 | 0.00 |
| Roll frequency | 50.0 ± 10.7 | 54.6 ± 13.0 | 0.03 |
| Pitch amplitude (deg) | 4.0 ± 1.0 | 3.7 ± 0.9 | 0.10 |
| Roll amplitude (deg) | 1.7 ± 0.9 | 1.7 ± 0.8 | 0.40 |
| Model | Confusion Matrix | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roll Only | 20 | 0 | 72% | 100% | 71% | 83% |
| 8 | 2 | |||||
| Pitch Only | 4 | 16 | 43% | 20% | 80% | 32% |
| 1 | 9 | |||||
| Roll-Pitch | 19 | 1 | 77% | 95% | 76% | 84% |
| 6 | 4 | |||||
| Model | Confusion Matrix | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roll Only | 4 | 11 | 37% | 27% | 33% | 30% |
| 8 | 7 | |||||
| Pitch Only | 14 | 1 | 67% | 93% | 61% | 74% |
| 9 | 6 | |||||
| Roll-Pitch | 6 | 9 | 60% | 40% | 67% | 50% |
| 3 | 12 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seva, R.; del Rosario, I.L.; Peñafiel, L.M.; Young, J.M.; Sybingco, E. Predicting Intoxication Using Motorcycle and Head Movements of Riders Wearing Alcohol Intoxication Goggles. Safety 2023, 9, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/safety9020029
Seva R, del Rosario IL, Peñafiel LM, Young JM, Sybingco E. Predicting Intoxication Using Motorcycle and Head Movements of Riders Wearing Alcohol Intoxication Goggles. Safety. 2023; 9(2):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/safety9020029
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeva, Rosemary, Imanuel Luir del Rosario, Lorenzo Miguel Peñafiel, John Michael Young, and Edwin Sybingco. 2023. "Predicting Intoxication Using Motorcycle and Head Movements of Riders Wearing Alcohol Intoxication Goggles" Safety 9, no. 2: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/safety9020029
APA StyleSeva, R., del Rosario, I. L., Peñafiel, L. M., Young, J. M., & Sybingco, E. (2023). Predicting Intoxication Using Motorcycle and Head Movements of Riders Wearing Alcohol Intoxication Goggles. Safety, 9(2), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/safety9020029









