Abstract
Researchers have a long history in the conduct of evaluations of road safety countermeasures. However, despite the strengths of some evaluative road safety evaluations that align with previous and current thinking on program evaluation, few published road safety evaluations have followed standard conceptualization and methodology outlined in numerous program evaluation textbooks, journal articles and Web-based handbooks. However, conceptual and methodological challenges inherent in many evaluations of road safety countermeasures can affect causal attribution. Valid determination of causal attribution is enhanced by use of relevant theory or hypotheses on the putative mechanisms or pathways of change and by the use of a process evaluation to assess the actual implementation process. This article provides a detailed description of the constructs of causal chain, program logic models and process evaluation. This article provides an example of how these standard methods of theory-driven evaluation can improve the interpretation of outcomes and enhance causal attribution of a road safety countermeasure.
1. Introduction
Researchers have a long history in the conduct of evaluations of road safety countermeasures. Researchers also have a long history in the use of innovative methods to conduct outcome evaluations of road safety countermeasures. Ross et al. [1], in their evaluation of the British Road Safety Act of 1967, used the statistical method and research design of time series analysis for the evaluation of road safety legislation, which has subsequently been described in many seminal program evaluation textbooks and articles as a strong quasi-experimental method of choice in evaluation [2,3,4,5,6]. Additionally, some road safety evaluations have used a theory-driven or theory-based approach, advocated by many program evaluation textbooks [6,7,8,9]. For example, Ross’s [10] evaluative research focused on using deterrence theory as the guiding framework. Hall and O’Day [11] introduced the causal chain approach to evaluate road safety countermeasures that is a foundational construct to theory-driven program evaluation [9,12,13,14,15,16,17]. However, despite the strengths of some road safety evaluations that align with previous and current thinking on program evaluation, road safety evaluations are still being published that have not followed standard conceptualization and methodology outlined in numerous program evaluation textbooks, journal articles and Web-based handbooks [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. However, conceptual and methodological challenges inherent in many evaluations of road safety countermeasures can affect causal attribution.
2. Conceptual Problems
Valid determination of causal attribution is enhanced by use of relevant theory on the putative mechanisms or pathways of change. Theory can provide a structure within which to test hypotheses and can identify constructs that influence behaviour or system change [21], although it is also important to point out that the commonly used multidisciplinary approach (a good development) to road safety intervention evaluations can be a challenge for the identification and utilization of theory/theories because different disciplines can have varied understanding of and approaches to theory testing. Identification of a theory can also be problematic when interventions are complex with multiple causal pathways. Moreover, different forms of theory-driven evaluation exist ranging from linear models to models that are more nuanced, contextualized, comprehensive and ecological in which outcomes are explained within a constellation of other mechanisms and pre-existing economic, historical, social, cultural and definitional conditions [22,23]. That said, most evaluations of road safety countermeasures do not use theories by which to conceptualize and design the intervention and its evaluation, and to interpret results [14,24]. From a conceptual standpoint, programs, interventions, treatments and policies are based on the validity of underlying assumptions about how and why they are supposed to work [7,8,9,12,13,25,26,27,28,29,30]. However, as Elvik [13] writes: “Most road safety evaluation studies evaluate the effects of a certain road safety measure on the number of accidents, accident rate or the severity of injuries without describing how and why a certain safety measure produces the observed changes in accident occurrence or injury severity” (p. 741).
Valid determination of causal attribution also requires information on the intervention—what was provided, to whom, in what amount, in what way [8,31]. Without a detailed process (implementation) evaluation to document whether an intervention was implemented as it was supposed to be implemented, evaluations can commit what is called in evaluation literature a Type III error—evaluation of an inadequately delivered intervention [31,32]. Many evaluations of road safety countermeasures do not examine the “process”; that is, whether the intervention was actually delivered as per objectives. These types of evaluations, which only focus on outcomes with no examination of process and the theory-driven cause-and-effect sequence through which the outcomes are presumed to be produced, are called “blackbox” evaluations; they have been highly criticized in the evaluation literature [7,13,26,33]. A few scholars argue that knowledge of how and why a countermeasure worked is not necessary [22,34]. However, blackbox evaluations can limit the interpretation of findings as these evaluations cannot identify whether lack of positive outcomes are due to poor conceptual foundations of the intervention or due to a poorly implemented intervention [16,35].
The use of theory in evaluation to identify causal mechanisms or chains (also called processes, links, assumptions, pathways or models), through which an intervention is expected to achieve better outcomes and the use of process evaluation has been widely adopted for health, human, and community services, and a range of international development programs, such as the World Bank for evaluating humanitarian services [17,19,21,25,26,27,28,29,30,35,36,37,38,39]. For example, the International Initiative for Impact Evaluation (3ie) guide states: “Studies should clearly lay out how it is that the intervention (inputs) is expected to affect final outcomes, and test each link (assumption) from inputs to outcomes (sometimes referred to as the program theory). The evaluation design should incorporate analysis of the causal chain from inputs to impacts. Hence the study needs to engage in process evaluation questions in order to analyze causes of success or failure” [27] (p. 2). However, the use of the term causal chain or model in evaluation is not to be confused with the statistical use of the term [40], although causal chains or models used in evaluation research to represent the putative mechanisms or pathways of change can form the basis of a measurement model in statistical analyses [41].
Theories in evaluation can be classified into two types: the intervention’s change theory or model (also known as program theory or theory of cause and effect) and the intervention’s action theory or model (also known as implementation theory) [7,8,9,12,26,35,42]. The intervention’s change theory should conceptualize the underlying logic of how and why an intervention could “cause” specific outcomes and focus on what changes are expected to occur in the recipients of the countermeasure to effect the desired positive outcomes [8,9,12,27,43,44]. Unfortunately, this seemingly simple question of how and why an intervention should work can often be a challenge to answer because most interventions are causally complex. That is, the causal mechanisms to conceptualize how an intervention should work may include many components that are extended over different periods of time involving “long chains of cascading direct and indirect effects” that are context dependent and may have delayed, diffuse and subtle outcomes [45] (p. 8). Deterrence theory, safety culture theory, theory of planned behaviour and problem behaviour theory are some examples of change theories that can identify a set of putative causal processes through which a person would engage in safer driving behaviour [24,46,47,48,49,50]. For example, Warner and Äberg [49] found that the theory of planned behaviour predicted speeding behaviour. Similarly, Poulter et al. [50] identified pathways from the theory of planned behaviour that predicted truck driver behaviour and compliance with regulation and possible interventions to tackle these behaviours.
An intervention’s action theory identifies the theoretical basis and research evidence for the strategy chosen to tackle the problem [7,8,9,12]. For example, little theoretical basis and evidence exists that driver education is an effective road safety countermeasure; that is, that driver education produces safer drivers who are involved in fewer collisions and violations, compared to drivers who have not taken driver education courses [51,52]. Numerous blackbox evaluations of graduated licensing programs, however, have shown their effectiveness in reducing novice driver fatality rates [52,53,54,55,56]. Some explanation on how and why graduated licensing programs could work has been offered (driving restrictions increase driving exposure of novice drivers under safer driving conditions) and different graduated licensing systems have been ranked on their restrictive policies and correlated to fatality rates [54,55,56]. Gregersen et al. [57], in their evaluation of Sweden’s graduated licensing system reform with a prolonged supervised driving option, offer an elaborated theoretical basis for positive road safety findings related to the three levels of skill acquisition and behavioural control that need to be addressed for safe driving. The first level of behavioural control is the knowledge based level, which is related to the substantive cognitive effort allocated to learning to perform different tasks within the act of driving. The second level is the rule based level, during which the novice driver, through driving experience, develops cognitive rules in which the driver can “combine several steps of different solutions” to “gain control over long behaviour sequences” (p. 26). The final stage, skill based level, moves beyond, “how” to apply a skill to “when” to apply a skill. At this level, the driver shifts attention and decision making from the driving task to the driving environment and its inherent hazards. Gregersen et al. [57] argue that traditional driver education courses do not provide much driving experience by which a novice driver can move through the three levels; graduated licensing programs, as opposed to traditional driver’s education programs, do offer an extended period of time of driving under mandatory supervision during which all three levels of skills can be developed, although unfortunately their evaluation did not evaluate actual changes in skill levels.
An intervention’s action theory also focuses on whether the program is actually implemented as intended [7,8,9,12]. Typically called process, implementation, progress, monitoring, fidelity or formative evaluation, this evaluation examines both the program’s delivery and coverage [6,9,58,59,60]. The rationale for a process evaluation is that interventions are rarely delivered as per objectives, and as intended [5,9]. Without knowledge of what and how much was actually delivered in the intervention, it is difficult to attribute the intervention to outcome. Gregersen et al. [57] also included a “process evaluation…to analyse how the new age limit was used and by whom” (p. 27). Since a key component of implementation of the graduated licensing system is for novice drivers to engage in substantive practice in supervised driving before application for full licence, the process evaluation included an examination of the amount of practice in which learner drivers actually engaged, based on logbooks and questionnaires. The process evaluation data on the increased amount of actual practice of the graduated licence drivers provided additional information on potential pathways by which graduated licence reform achieved the statistically significant reductions in collision involvement.
The most commonly used method in evaluation research for conceptualizing the change and action theories is through the development of a causal chain (also called model, link, attribution or pathway) [6,11,15] from which a program logic model is developed, although often the terms causal chain or model and logic models are used interchangeably [4,8,12,26,39,61,62,63,64,65,66,67]. The causal chain represents a series of steps of causal assumptions along a continuum that reflect the change theory underlying the intervention [5,6,11,15]. Sometimes the causal steps are linearly presented but often with complex interventions a causal chain or logic model can show steps with simultaneous causal pathways [22,39]. The focus of the causal chain is on the recipient of the intervention and reflects the process of change to positive outcomes that is assumed to occur with the person or system (if the system is the recipient of the intervention) [43]. The focus of the program logic model, on the other hand, is on the intervention inputs, activities, and outputs that are expected to occur to cause change to each of the steps of the recipient’s causal chain for the short and longer outcomes. Program logic models present a schema for understanding how resources for an intervention are used to implement key strategies and activities and how their implementation contributes to expected short and longer-term outcomes [44,61,66]. All causal chains and logic models utilize a series of if-then statements to illustrate how activities will affect a cascade of changes [8,67]. Figure 1 presents a generic logic model. It is important to point out that the right hand side of the model (outcomes) is dependent on the left hand side (input, output) so that the full chain consists of Input-Output-Outcome, with each specific output constructed to affect specific outcomes.
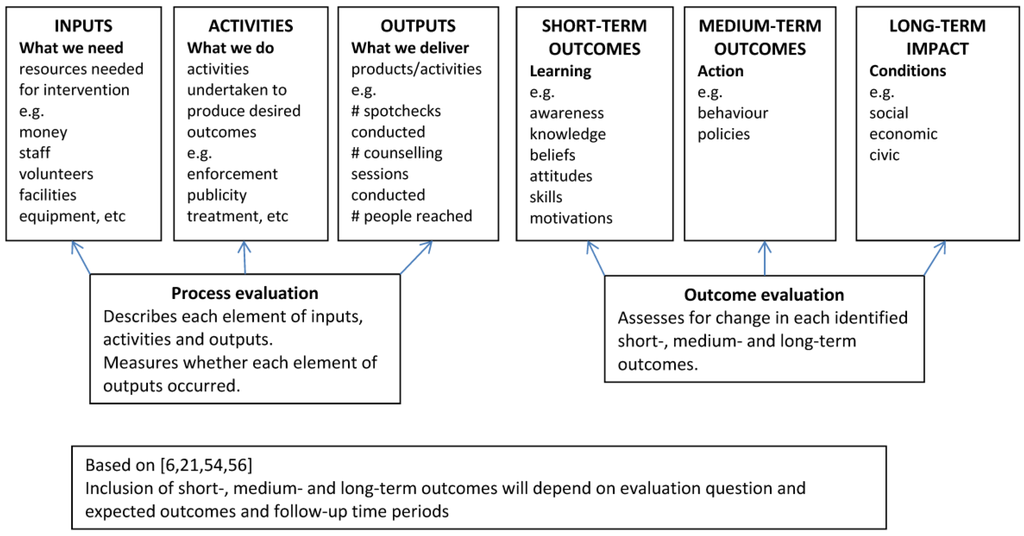
Figure 1.
Generic logic model.
Blackbox evaluations are still common, particularly for evaluations of legislative or administrative regulations, for example, administrative licence suspension laws which typically use time series analysis to evaluate the effect of these laws on collisions and/or fatalities [68,69,70]. A recent example is Wagenaar and Maldonado-Molina’s [70] evaluation of the effects of mandatory pre-conviction and post-conviction licence suspension laws for impaired driving for 46 US states. They did present three potential mechanisms by which licence suspensions could affect collision rates, based on deterrence theory and incapacitation. Specifically, they argued that for jurisdictions that introduced pre-conviction “immediate” administrative licence suspension laws, a greater deterrent effect should occur compared to jurisdictions with court imposed licence suspensions because the close pairing of the offence and punishment supports one of the tenets of deterrence theory. Using time series analyses, they found that of the 38 states that implemented administrative licence suspension laws, 24 showed declines in single vehicle night time crashes but only nine were statistically significant, 27 showed declines in crashes for drivers with Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) of 0.08–0.14 g/dL with six statistically significant and 25 showed declines in crashes for drivers with BAC of ≥0.15 g/dL with six statistically significant. Examination of the 24 states with court imposed licence suspension laws found that 15 showed declines in single vehicle night time crashes with five statistically significant, 10 showed declines in crashes for drivers with BAC of 0.08–0.14 g/dL with one statistically significant and 13 showed declines in crashes for drivers with BAC of ≥0.15 g/dL, none statistically significant. In other words, for the majority of states, no statistically significant changes were found, although ad hoc pooled analyses, using methods from the meta-analysis literature, suggested “effectiveness” of administrative licence suspension laws. However, it is fair to assume that conceptually for the laws to have a potential to deter drinking driving behaviour, the public should be aware of the new laws and their consequences, and the new laws should enforced. However, this evaluation did not include a process evaluation by which to assess the degree of implementation of the laws or whether the public even knew about the laws. Hence, it is not possible to assess how and why the administrative laws did or did not work in the various jurisdictions so that improvements could be made for better outcomes.
However, previously published research on administrative licence suspension laws has found that road safety impact can be limited when public awareness and enforcement are limited. An evaluation of the impact of the 12-h Administrative Licence Suspension Law in Ontario, Canada [71], based on deterrence theory, developed and evaluated a causal chain (Figure 2) that presented a series of steps hypothesized to be necessary for the legislation to have an effect on alcohol-related collision casualties [71]. First, for the new law to be effective, evidence of enforcement and publicity of the new law would be required, as the public cannot be deterred by laws about which they know nothing and that are not being enforced. Next, it was posited that if the 12-h Administrative Licence Suspension Law was properly delivered, the public in the intervention jurisdiction should be more aware of and knowledgeable about the law and the consequences of impaired driving. If the public became aware of consequences of the new law, then this should lead to increased risk perception of getting caught by police spot-checks and sanctioned with a swiftly meted out administrative licence suspension. This increased risk perception should lead to decreased drinking-driving behaviour, which should lead to reduced alcohol-related fatalities.
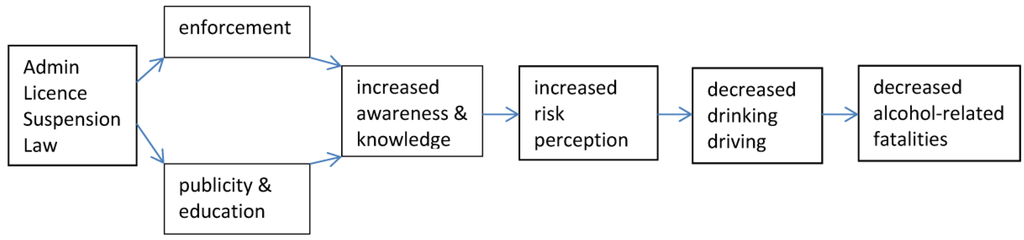
Figure 2.
Causal chain based on deterrence theory used in Vingilis et al. [71].
The evaluation indicated a significant reduction in alcohol-related motor vehicle collision fatalities for the first three months of the law’s existence, which was not found for the comparison jurisdictions [71]. A process evaluation found very limited media coverage (a few short articles for first three months) and enforcement capacity among the municipal, regional and provincial police forces [71]. The outcome evaluation measured the other components along the causal chain and found limited awareness of the new law and no pre-post changes for knowledge and for risk perception (personal and average person’s risk of getting caught by police for drinking-driving) [71]. Thus, the short-term reduction of alcohol-related motor vehicle collision fatalities for the first three months that regressed to baseline levels could be explained by the lack of publicity campaign, no pre–post change in knowledge and risk perception of getting caught in relation to the new law and lack of enforcement capacity for the new law [71]. This earlier study suggests that risk perception is an important component of deterrence. Additionally, the process evaluation helped explain the short-term effect of the new law by identifying the potential importance of publicity and enforcement capacity if new laws are to have any potential of success.
A recent evaluation of a new law with an administrative licensing regulation demonstrates the use of theory to formulate a causal chain and the inclusion of a process evaluation in addition to an outcome evaluation to understand how and why an intervention may have worked. Meirembayeva and colleagues [48,72] evaluated the effect of new street racing and stunt driving legislation on extreme speeding convictions and speeding related casualties. The legislation, based on deterrence theory, provided a swift and certain penalty of an immediate seven-day administrative licence suspension and vehicle impoundment, a fine of $2000–10,000 CDN, six demerit points and possible imprisonment. Similar to Figure 2 above, the causal chain included enforcement, publicity, speeding behaviour, convictions and collision casualties. For process evaluation, licence suspension data were tracked to determine how many drivers actually received this new penalty since the law’s inception. The results indicated over 25,000 administrative licence suspensions during the four-year evaluation period. Evidence also indicated that in Ontario, mass media reported substantively on the legislation because of controversial issues with the legislation [73]. Time series analyses of highway speed data, taken from three speed counting stations, indicated that median speed significantly decreased after the new legislation. As hypothesized, significant intervention effects were found for reductions in extreme speeding convictions and speeding-related motor vehicle casualties for male drivers compared to female drivers, with the interrupted time series analysis indicating an average monthly decrease of 58 fewer speeding-related motor vehicle casualties of males aged 16–25 years old after implementation of the new legislation. Thus, the causal attribution of the evaluation of this legislative change is enhanced by use of relevant theory on the putative mechanisms or pathways of change and by the examination of the degree of implementation of the legislation.
Indeed, process evaluation can also enhance interpretation of non-results. A National Institutes of Health (NIH)-funded evaluation of the road safety impact of extended drinking hours of alcohol sales and service in licensed establishments in Ontario, Canada was conducted [74,75]. The study used a quasi-experimental design with interrupted time series analyses of BAC-positive fatalities for the different time windows and days (11 p.m.–4 a.m., Sunday–Wednesday and Thursday–Saturday) over which the extended drinking would have occurred for the intervention (Ontario), compared to control jurisdictions (Michigan and New York). The study also included a survey of licensed establishments as a process evaluation to determine whether the licensed establishments actually extended their hours of sales. Three competing hypotheses were tested: (1) availability theory; (2) power drinking hypothesis; and (3) temporal shift in drinking patterns hypothesis. The total driver fatalities over the 11 p.m.–4 a.m. time window indicated no significant changes between the intervention and control jurisdictions while for BAC-positive driver fatalities, near significant downward trends were found for the intervention jurisdiction and one significant downward trend for the control jurisdiction. These findings did not support availability theory that would posit that an extra hour from 1 a.m. to 2 a.m. of sales and service of alcohol in licensed establishments should lead to increased alcohol-related harms, such as increased BAC-positive motor vehicle fatalities. Interrupted time series examination of the key time periods of 1–2 a.m. and 2–3 a.m. also did not show patterns supportive of availability theory. However, the process evaluation provided additional information by which to interpret the results. Only about 16% of licensed establishment survey respondents reported extending their closing hours from 1 a.m. to 2 a.m. on Sunday through Wednesday and about 29% respondents reported extending their closing hours from 1 a.m. to 2 a.m. on Thursday through Saturday. Thus, for the vast majority of licensed establishments, the “intervention” was not implemented.
3. Conclusions
Although the use of a theory-driven approach with inclusion of process evaluation is not necessary for the conduct of road safety evaluations, seminal program evaluation textbooks, journal articles and Web-based handbooks pontificate on the importance of theory-driven evaluations with the use of causal chains and/or logic models to articulate hypothesized intermediate steps reflecting causal pathways, and of the inclusion of process evaluations (e.g., [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20]). Most theory-driven evaluation approaches share three fundamental characteristics: (a) clearly present the theory of an intervention by describing the expected relationships among inputs, mediating processes, and short- and long-term outcomes; (b) measure all of the hypothesized constructs in the theory; and (c) analyze the data to assess the extent to which the hypothesized relationships actually occurred [76]. Shadish et al. [76] further state that “theoretical exploration is important” because it “can clarify general issues with treatments of a particular type, suggest specific research questions, describe how the intervention functions, spell out mediating processes, locate opportunities to remedy implementation failures”(p. 501). Unfortunately, various blackbox evaluations of road safety countermeasures provide limited information on how the intervention functions, on mediating processes or on how to improve the effects of the countermeasure. For example, the evaluation described above on the road safety effects of mandatory pre-conviction and post-conviction licence suspension laws for 46 US states may be eliciting more questions than answers. The study found that less than one-quarter of the states with licence suspension laws demonstrated any statistically significant reductions on different alcohol-related crash measures [70]. The results of this study provide limited useful information for decision makers for policy formulation on how and why licence suspension legislation works, for whom, and under what conditions. Assessment of implementation of the legislation in the different states, based on some casual model conceptualization of how and why the new law could work, could provide some insight on mechanisms, although it is also possible that other factors contributed to the limited success of the legislation in the different jurisdictions.
It is important to point out that the use of theory and process evaluation is not a panacea for the conduct of all evaluations. For certain interventions with a simple direct causal effect, blackbox evaluations are perfectly adequate. If a significant outcome is found with the use of rigorous design and methodology, causal inference is possible. The problem arises, however, when no significant results are found, despite the use of rigorous design and methodology. Blackbox or methods-driven research that can make it a challenge for policy makers to understand how and why an intervention does or does not work and to identify the key elements for successful implementation [7,16,26,30,59].
The use of this approach is not new to road safety. Indeed, renowned road safety scholars, such as Shope [77] have also argued for the inclusion of these evaluation components: “Evaluation of interventions is essential and should include process evaluation as well as evaluation of the impact (on the intermediate measure of interest) and the outcome (driving behavior or crash)…Doing so will require developing sound programs based on a conceptual framework such as that presented” (p. i13). Curiously, historical documents for the conduct of evaluations of road safety countermeasures identified the use of causal chains, and process evaluations (e.g., [11,78]); yet these methods have fallen by the wayside in many road safety evaluations. The time has come for road safety researchers to use standard practice from the evaluation literature and historical road safety countermeasure evaluation literature in the conduct of evaluations of road safety countermeasures.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Ross, H.L.; Campbell, D.T.; Glass, G.V. Determining the social effects of a legal reform: The British breathalyzer crackdown of 1967. Am. Behav. Sci. 1970, 13, 494–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, T.D.; Campbell, D.T. Quasi-Experimentation Design and Analysis Issues for Field Settings; Houghton Mifflin Company: Boston, MA, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Eccles, M.; Grimshaw, J.; Campbell, M.; Ramsay, C. Research designs for studies evaluating the effectiveness of change and improvement strategies. Qual. Saf. Health Care 2003, 12, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDavid, J.C.; Hawthorn, L.R. Program Evaluation and Performance Measurement: An Introduction to Practice; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, P.H.; Freeman, H.E. Evaluation a Systematic Approach, 5th ed.; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, P.H.; Freeman, H.E.; Lipsey, M.W. Evaluation a Systematic Approach, 6th ed.; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.-T. Theory-Driven Evaluations; Sage Publications: Newbury Park, CA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Grembowski, D. The Practice of Health Program Evaluation; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, C.H. Evaluation, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, L.H. Deterring the Drinking Driver, Legal Policy and Social Control; Lexington Books: Lexington, MA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, W.K.; O’Day, J. Causal chain approaches to evaluation of highway safety countermeasures. J. Saf. Res. 1971, 3, 9–20. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, J.E.H.; Vingilis, E. Development of a framework for comprehensive evaluation of client outcomes in community mental health services. Can. J. Progr. Eval. 2006, 21, 133–180. [Google Scholar]
- Elvik, R. Assessing the validity of road safety evaluation studies by analysing causal chains. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2003, 35, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvik, R. To what extent can theory account for the findings of road safety evaluation studies? Accid. Prev. Anal. 2004, 36, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrosino, A. Answering the why question in evaluation: The causal-model approach. Can. J. Progr. Eval. 2000, 15, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Vingilis, E.; Pederson, L. Using the right tools to answer the right questions: The importance of evaluative research techniques for health services evaluation research in the 21st century. Can. J. Progr. Eval. 2001, 16, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- White, H. Theory-based impact evaluation: Principles and practice. J. Dev. Eff. 2009, 1, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E.J. Evaluation Methodology Basics; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson, S.I. Program Theory-Driven Evaluation Science; Lawrence Erlbaum Assoc: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- W. K. Kellogg Foundation Evaluation Handbook. 2004. Available online: https://www.wkkf.org/resource-directory/resource/2010/w-k-kellogg-foundation-evaluation-handbook (accessed on 20 February 2016).
- Prestwich, A.; Webb, T.L.; Conner, M. Using theory to develop and test interventions to promote changes in health behaviour: Evidence, issues and recommendations. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2015, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coryn, C.L.S.; Noakes, L.A.; Westine, C.D.; Schtöter, D.C. A systematic review of theory-driven evaluation practice from 1990 to 2009. Am. J. Eval. 2011, 32, 199–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazi, M. Realist evaluation for practice. Br. J. Soc. Work 2003, 33, 803–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, S.; Watson, B. Work-related driving safety in light vehicle fleets: A review of past research and the development of an intervention framework. Saf. Sci. 2011, 49, 369–381. [Google Scholar]
- Bickman, L. The functions of program theory. New Dir. Progr. Eval. 1987, 33, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-T. Practical Program Evaluation; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- International initiative for Impact Evaluation (3ie). 3ie Impact Evaluation Practice: A Guide for Grantees. Available online: http://www.alnap.org/resources/8130.asp (accessed on 16 December 2015).
- Lipsey, M.W. Theory as methods: Small theories of treatments. New Dir. Progr. Eval. 1993, 57, 5–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, A.J. Confirmatory program evaluation: A method for strengthening causal inference. Am. J. Eval. 1998, 19, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stame, N. Theory-based evaluation and types of complexity. Evaluation 2004, 10, 58–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasson, H. Systematic evaluation of implementation fidelity of complex interventions in health and social care. Implement Sci. 2010, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, D.; Cook, T. Avoiding type III error in program evaluation: Results from a field experiment. Eval. Progr. Plan. 1980, 3, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astbury, B.; Leeuw, F.L. Unpacking black boxes: Mechanisms and theory building in evaluation. Am. J. Eval. 2010, 31, 363–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scriven, M. The fine line between evaluation and explanation. Eval. Pract. 1994, 15, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-T.; Rossi, P.H. Evaluating with sense: The theory-driven approach. Eval. Rev. 1983, 7, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, S.I.; Gooler, L.E. Theory-driven evaluation in action: Lessons from a $20 million statewide Work and Health Initiative. Eval. Progr. Plan. 2003, 26, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, M.J.; Breuer, E.; Lee, L.; Asher, L.; Chowdhary, N.; Lund, C.; Patel, V. Theory of change: A theory-driven approach to enhance the Medical Research Council’s framework for complex interventions. Trials 2014, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michie, S.; Johnston, M.; Francis, J.; Hardeman, W.; Eccles, M. From theory to intervention: Mapping theoretically derived behavioural determinants to behaviour change techniques. Appl. Psychol. Int. Rev. 2008, 57, 660–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, P.J. Using programme theory to evaluate complicated and complex aspects of interventions. Evaluation 2008, 14, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarko, A.P. Use of crash surrogates and exceedance statistics to estimate road safety. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2012, 45, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M. Modelling the effects of road safety measures. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2006, 38, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute. Theory at a Glance, 2nd ed. 2005. Available online: http://sbccimplementationkits.org/demandrmnch/ikitresources/theory-at-a-glance-a-guide-for-health-promotion-practice-second-edition/ (accessed on 23 December 2015).
- Vingilis, E.R. Issues and challenges in community mental health services: Program and policy evaluation. In Applied Research and Evaluation in Community Mental Health Services; Vingilis, E.R., State, S.A., Eds.; McGill-Queen’s University Press: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- W.K. Kellogg Foundation, Using Logic Models to Bring Together Planning, Evaluation and Action: Logic Model Development Guide. 2001. Available online: https://www.wkkf.org/resource-directory/resource/2006/02/wk-kellogg-foundation-logic-model-development-guide (accessed on 23 December 2015).
- Lipsey, M.W. Practice and malpractice in evaluation research. Eval. Pract. 1988, 9, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, C.R.; Shope, J.T. Adolescent problem behavior and problem drinking in young adulthood. J. Adolesc. Res. 2004, 19, 205–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glendon, A.I.; Stanton, N.A. Perspectives on safety culture. Saf. Sci. 2000, 34, 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meirembeyava, A.; Vingilis, E.; McLeod, A.I.; Elzohairy, Y.; Xiao, J.; Zou, G.; Lai, Y. Road safety impact of Ontario’s street racing and stunt driving law. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2014, 71, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallén Warner, H.; Äberg, L. Drivers’ decision to speed: A study inspired by the theory of planned behavior. Transp. Res. F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2006, 9, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulter, D.R.; Chapman, P.; Bibby, P.A.; Clarke, D.D.; Crundall, D. An application of the theory of planned behaviour to truck driving behaviour and compliance with regulations. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2008, 40, 2058–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayhew, D.R. Driver education and graduated licensing in North America: Past, present and future. J. Saf. Res. 2007, 38, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foss, R.D.; Evenson, K.R. Effectiveness of graduated driver licensing in reducing motor vehicle crashes. Am. J. Prev. Med. 1999, 16, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulmer, R.G.; Preusser, D.F.; Williams, A.F.; Ferguson, S.A.; Farmer, C.M. Effect of Florida’s graduated licensing program on the crash rate of teenage drivers. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2000, 32, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, T.S.; Grebowski, D.C.; Morrisey, M.A. Graduated driver licensing and teen fatalities. J. Health Econ. 2005, 24, 571–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrisey, M.A.; Grabowski, D.C.; Dee, T.S.; Campbell, C. The strength of graduated license programs and fatalities among teen drivers and passengers. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2006, 38, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCartt, A.T.; Teoh, E.R.; Fields, M.; Braitman, K.A.; Hellinga, L.A. Graduated licensing laws and fatal crashes of teenage drivers: A national study. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2010, 11, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregersen, N.P.; Berg, H.-Y.; Engström, I.; Nolén, S.; Nyberg, A.; Rimmö, P.-A. Sixteen years age limit for learner drivers in Sweden—An evaluation of safety effects. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2000, 32, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousins, B.J.; Aubry, D.; Smith Fowler, H.; Smith, M. Using key component profiles for the evaluation of program implementation in intensive mental health case management. Eval. Progr. Plan. 2004, 27, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posavac, E.J.; Carey, R.G. Program Evaluation: Methods and Case Studies, 6th ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pullen-Sufert, N.C.; Hall, W.L. The Art of Approriate Evaluation a Guide for Highway Safety Program Managers; U.S. Department of Transportation, National Highway Traffic Safety Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2008.
- Cooksy, L.J.; Gill, P.; Kelly, P.A. The program logic model as an integrative framework for a multimethod evaluation. Eval. Progr. Plan. 2001, 24, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, D.A. The utilization of the logic model as a system level planning and evaluation device. Eval. Progr. Plan. 1997, 20, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, D.A.; Jones, A.; Deyo, D. Open systems evaluation and the logic model: Program planning and evaluation tools. Eval. Progr. Plan. 1995, 18, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, S.A.; Garrett, K.E. The use of logic models by community-based initiatives. Eval. Progr. Plan. 2005, 28, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayne, J. Addressing attribution through contribution analysis: Using performance measures sensibly. Can. J. Progr. Eval. 2001, 16, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Gale, J.A.; Coburn, A.F.; Loux, S. Creating Program Logic Models: A Toolkit for State Flex Programs. Population Health and Health Policy, Paper 20, 2006. Available online: http://digitalcommons.usm.maine.edu/healthpolicy/20 (accessed on 16 December 2015).
- University of Wisconsin Extension. Program Development and Evaluation Logic Model. 2003. Paper 20, 2006. Available online: http://www.uwex.edu/ces/pdande/evaluation/evallogicmodel.html (accessed on 9 December 2015).
- Mann, R.E.; Smart, R.G.; Stoduto, G.; Beirness, D.; Lamble, R.; Vingilis, E. The early effects of Ontario’s Administrative Driver’s Licence Suspension Law on driver fatalities with a BAC >80 mg%. Can. J. Public Health 2002, 93, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Asbridge, M.; Mann, R.E.; Smart, R.G.; Stoduto, G.; Beirness, D.; Lamble, R.; Vingilis, E. The effects of Ontario’s driver’s licence suspension law on total driver fatalities: A multiple time series analysis. Drugs Educ. Prev. Policy 2009, 16, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenaar, A.C.; Maldonado-PMolina, M.M. Effects of drivers’ licensen suspension policies on alcohol-related crash involvement: Long-term follow-up in forty-six states. Alcoholism Clin. Exp. Res. 2007, 31, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vingilis, E.; Belfgen, H.; Lei, H.; Sykora, K.; Mann, M.E. An evaluation of the deterrent impact of Ontario’s 12-hour licence suspension law. Accid. Anal. Prev. 1988, 20, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meirambayeva, A.; Vingilis, E.; Zou, G.; Elzohairy, Y.; McLeod, A.I.; Xiao, J.Y. Evaluation of deterrent impact of Ontario’s street racing and stunt driving law on extreme speeding convictions. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2014, 15, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daigle, D.; Seeley, J.; Vingilis, E. Street racing: Content analysis of coverage and framing by Canadian newspapers. In Proceedings of the 24th Multidisciplinary Road Safety Conference; 2014. Available online: http://www.carsp.ca/research/research-papers/proceedings/proceedings-2014-vancouver/ (accessed on 15 December 2015). [Google Scholar]
- Vingilis, E.; Seeley, J.; McLeod, I.A.; Mann, R.E.; Beirness, D.; Compton, C. Road safety impact of the extended drinking hours policy in Ontario. In Contemporary Issues in Road User Behavior and Traffic Safety; Hennessy, D.A., Wiesenthal, D.L., Eds.; Nova Science Publ.: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Vingilis, E.; McLeod, I.A.; Seeley, J.; Mann, R.E.; Beirness, D.; Compton, C. Road safety impact of the extended drinking hours in Ontario. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2005, 37, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadish, W.R.; Cook, T.D.; Campbell, D.T. Experimental and Quasi Experimental Designs for Generalized Causal Inference; Houghton Mifflin Company: Boston, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Shope, J.T. Influences on youthful driving behavior and their potential for guiding interventions to reduce crashes. Inj. Prev. 2006, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vingilis, E.; Salutin, L. A prevention program for drinking driving. Accid. Anal. Prev. 1980, 12, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).