Thangka Image Captioning Based on Semantic Concept Prompt and Multimodal Feature Optimization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- 1.
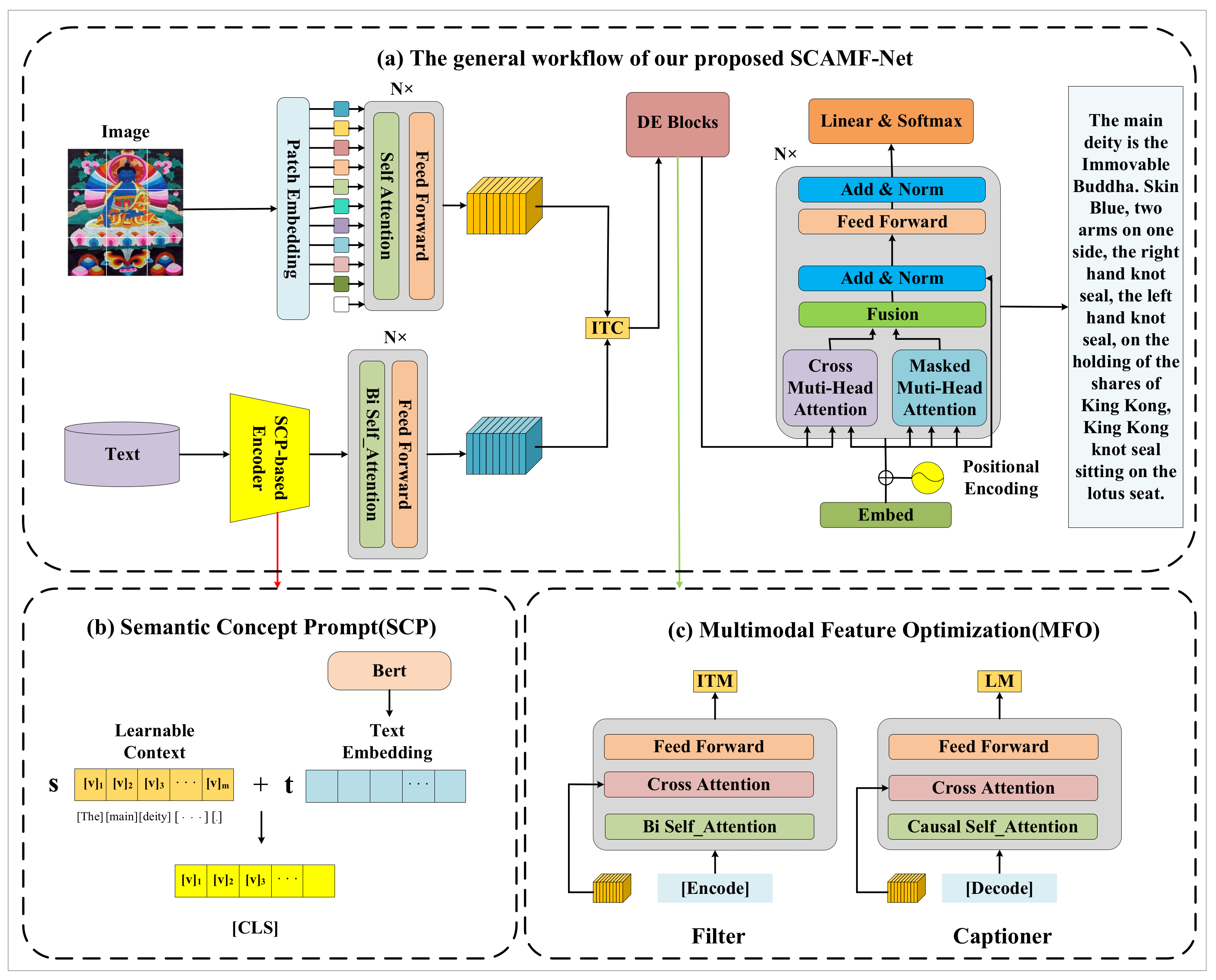
- We proposed the Semantic Concept Prompt (SCP) method, which introduces context prompts on top of traditional text features. This enables the model to learn abstract concepts embedded in Thangka images, such as cultural connotations and domain-specific knowledge, within the closed visual concept space and enriches the generated captions. The SCP method improves the accuracy and richness of generated Thangka captions.
- 2.
- We designed the Multimodal Feature Optimization (MFO) module, which includes the Filter that removes the noisy data in the Thangka image–text pairs during the model training process and the Captioner that enriches the text features of Thangka images and optimizes the data source, thereby improving the accuracy and stability of the image captioning model and making the generated Thangka image captions better match the Thangka images.
- 3.
- This paper proposed a Thangka image captioning method based on Semantic Concept Prompt and Multimodal Feature Optimization, called SCAMF-Net. We also construct a new Thangka dataset, providing essential resources for further research.
2. Related Work
2.1. Visual Language Pre-Training
2.1.1. Language Modeling Methods
2.1.2. Image–Text Contrastive Learning Methods
2.2. Prompt Learning
2.3. Knowledge Distillation
3. Methodology
3.1. Semantic Concept Prompt (SCP)
3.2. Multimodal Feature Optimization (MFO)
3.3. Loss Function
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.1. Dataset and Experiment Setup
4.2. Evaluation Indicators
4.3. Quantitative Evaluation
4.4. Qualitative Evaluation
4.5. Ablation Experiments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thanka Introduction. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki (accessed on 7 January 2021).
- Wang, W.; Qian, J.; Lu, X. Research outline and progress of digital protection on thangka. Adv. Top. Multimed. Res. 2012, 2, 67. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, G.; Premraj, V.; Ordonez, V.; Dhar, S.; Li, S.; Choi, Y.; Berg, A.C.; Berg, T.L. Babytalk: Understanding and generating simple image descriptions. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 2891–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhadi, A.; Hejrati, M.; Sadeghi, M.A.; Young, P.; Rashtchian, C.; Hockenmaier, J.; Forsyth, D. Every picture tells a story: Generating sentences from images. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Heraklion, Greece, 5–11 September 2010; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 15–29. [Google Scholar]
- Ordonez, V.; Kulkarni, G.; Berg, T.L. Im2text: Describing images using 1 million captioned photographs. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Sierra Nevada, Spain, 16–17 December 2011; pp. 1143–1151. [Google Scholar]
- Socher, R.; Karpathy, A.; Le, Q.V.; Manning, C.D.; Ng, A.Y. Grounded compositional semantics for finding and describing images with sentences. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2014, 2, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, R.; Charniak, E. Nonparametric Method for Data-driven Image Captioning. In Proceedings of the Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Baltimore, MD, USA, 22–27 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, H.; Gupta, S.; Iandola, F.N.; Srivastava, R.K.; Deng, L.; Dollár, P.; Gao, J.; He, X.; Mitchell, M.; Platt, J.C.; et al. From Captions to Visual Concepts and Back. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; pp. 1473–1482. [Google Scholar]
- Herdade, S.; Kappeler, A.; Boakye, K.; Soares, J. Image captioning: Transforming objects into words. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.S.; Xiong, C.M.; Parikh, D.; Socher, R. Knowing when to look: Adaptive attention via a visual sentinel for image captioning. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; pp. 3242–3250. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Yao, T.; Li, Y.; Mei, T. X-linear attention networks for image captioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 10971–10980. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Ba, J.; Kiros, R.; Cho, K.; Courville, A.; Salakhudinov, R.; Zemel, R.; Bengio, Y. Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 2048–2057. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, P.; He, X.; Buehler, C.; Teney, D.; Johnson, M.; Gould, S.; Zhang, L. Bottom-up and top-down attention for image captioning and visual question answering. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6077–6086. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.14030. [Google Scholar]
- Khare, Y.; Bagal, V.; Mathew, M.; Devi, A.; Priyakumar, U.D.; Jawahar, C.V. Mmbert: Multimodal bert pretraining for improved medical vqa. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 18th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Nice, France, 13–16 April 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1033–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Batra, D.; Parikh, D.; Lee, S. Vilbert: Pretraining task-agnostic visiolinguistic representations for vision-and-language tasks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.; Bansal, M. Lxmert: Learning cross-modality encoder representations from transformers. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.07490. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.C.; Li, L.; Yu, L.; El Kholy, A.; Ahmed, F.; Gan, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, J. Uniter: Universal image-text representation learning. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 104–120. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Palangi, H.; Zhang, L.; Hu, H.; Corso, J.; Gao, J. Unified vision language pre-training for image captioning and vqa. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 13041–13049. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learn-ing transferable visual models from natural language super-vision. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.00020. [Google Scholar]
- Mokady, R.; Hertz, A.; Bermano, A.H. Clipcap: Clip prefix for image captioning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.09734. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, A.; Attarian, M.; Ichter, B.; Choromanski, K.; Wong, A.; Welker, S.; Tombari, F.; Purohit, A.; Ryoo, M.; Sindhwani, V.; et al. Socratic models: Composing zero-shot multimodal reasoning with language. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.00598. [Google Scholar]
- Furlanello, T.; Lipton, Z.; Tschannen, M.; Itti, L.; An Kumar, A. Born-again neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 1602–1611. [Google Scholar]
- Touvron, H.; Cord, M.; Douze, M.; Massa, F.; Sablayrolles, A.; Jégou, H. Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.12877. [Google Scholar]
- Tsimpoukelli, M.; Menick, J.L.; Cabi, S.; Eslami, S.M.; Vinyals, O.; Hill, F. Multimodal few-shot learning with frozen language models. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Virtual, 6–14 December 2021; Volume 34, pp. 200–212. [Google Scholar]
- Alayrac, J.B.; Donahue, J.; Luc, P.; Miech, A.; Barr, I.; Hasson, Y.; Lenc, K.; Mensch, A.; Millican, K.; Reynolds, M.; et al. Flamingo: A visual language model for few-shot learning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.14198. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Yang, Y. Switchable novel object captioner. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 1162–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petroni, F.; Rocktäschel, T.; Lewis, P.; Bakhtin, A.; Wu, Y.; Miller, A.H.; Riedel, S. Language models as knowledge bases? arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.01066. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Ye, Y.; Gupta, A. Zero-shot recognition via semantic embeddings and knowledge graphs. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 6857–6866. [Google Scholar]
- Sanh, V.; Debut, L.; Chaumond, J.; Wolf, T. Distilbert, a distilled version of bert: Smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.01108. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiang, T.; Hospedales, T.M.; Lu, H. Deep mutual learning. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition CVPR, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4320–4328. [Google Scholar]
- Anil, R.; Pereyra, G.; Passos, A.; Ormandi, R.; Dahl, G.E.; Hinton, G.E. Large scale distributed neural network training through online distillation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Wu, P.; Hoi, S.C.H. Face detection using deep learning: An improved faster RCNN approach. Neurocomputing 2018, 299, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Xu, F.F.; Araki, J.; Neubig, G. How can we know what language models know? Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2020, 8, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrej, K.; Li, F. Deep visual-semantic alignments for generating image descriptions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Papineni, K.; Roukos, S.; Ward, T.; Zhu, W.J. Bleu: A method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 7–12 July 2002; pp. 311–318. [Google Scholar]
- Satanjeev, B. METEOR: An Automatic Metric for MT Evaluation with Improved Correlation with Human Judgments. In Proceedings of the ACL-2005, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 25–30 June 2005; pp. 228–231. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.Y.; Och, F.J. Automatic Evaluation of Machine Translation Quality Using Longest Common Subsequence and Skip-Bigram Statistics. In Proceedings of the 42nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Barcelona, Spain, 21–26 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Vedantam, R.; Lawrence Zitnick, C.; Parikh, D. Cider: Consensus-based image description evaluation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 4566–4575. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, P.; Fernando, B.; Johnson, M.; Gould, S. SPICE: Semantic Propositional Image Caption Evaluation. Adapt. Behav. 2016, 11, 382–398. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Wei, X.Y. Attention on attention for image captioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 4634–4643. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Yin, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, P.; Hu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Hu, H.; Dong, L.; Wei, F.; et al. Oscar: Object semantics aligned pre-training for vision-language tasks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 121–137. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Gavves, E.; Fernando, B.; Tuytelaars, T. Guiding long-short term memory for image caption generation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1509.04942. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Gan, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Wang, L. Scaling up vision-language pre-training for image captioning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.12233. [Google Scholar]

| Model | BLEU-1 | BLEU-4 | CIDEr | METEOR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi-LSTM [45] | 42.9 | 36.3 | 299.7 | 28.7 |
| BUTD [13] | 48.8 | 24.3 | 268.5 | 33.9 |
| VLP [20] | 58.8 | 44.8 | 444.6 | 44.5 |
| ClipCap [22] | 51.1 | 48.4 | 390.6 | 38.0 |
| SCAMF (VGG) | 45.5 | 28.3 | 286.4 | 29.4 |
| SCAMF (Inception) | 46.5 | 30.3 | 318.6 | 30.6 |
| SCAMF (EfficientNetV2) | 47.2 | 36.4 | 341.2 | 34.5 |
| SCAMF (Realformer) | 60.5 | 58.6 | 484.5 | 46.3 |
| SCAMF (T5) | 64.5 | 62.3 | 540.6 | 49.4 |
| SCAMF-Net | 70.5 | 63.6 | 562.4 | 52.0 |
| Model | BLEU-4 | METEOR | CIDEr | SPICE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BUTD [13] | 36.3 | 27.7 | 120.1 | 21.4 |
| MMBert [16] | 39.5 | 29.4 | 130.6 | 22.6 |
| ViLBert [17] | 37.3 | 27.9 | 122.3 | 20.9 |
| LXMERT [18] | 37.8 | 26.7 | 124.8 | 21.4 |
| UNITER [19] | 38.4 | 28.7 | 128.4 | 21.8 |
| VLP [20] | 39.5 | 29.3 | 129.8 | 22.4 |
| CLIP [21] | 38.6 | 28.8 | 127.9 | 22.7 |
| ClipCap [22] | 33.5 | 27.4 | 113.1 | 21.1 |
| AoA [43] | 38.9 | 29.1 | 119.8 | 20.4 |
| Oscar [44] | 36.5 | 30.3 | 123.7 | 23.1 |
| LEMON [46] | 40.3 | 30.2 | 133.3 | 23.3 |
| SCAMF-Net | 40.7 | 31.3 | 133.5 | 23.9 |
| Model | BLEU-4 | METEOR | ROUGE | CIDEr | SPICE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 54.9 | 44.1 | 71.3 | 485.8 | 41.8 |
| Baseline + SCP (M = 4) | 57.5 | 43.7 | 61.7 | 443.5 | 40.3 |
| Baseline + SCP (M = 8) | 61.7 | 50.6 | 67.2 | 540.1 | 43.2 |
| Baseline + SCP (M = 16) | 60.7 | 49.6 | 62.2 | 550.1 | 45.2 |
| Baseline + MFO (Captioner) | 60.5 | 49.9 | 77,6 | 541.1 | 46.5 |
| Baseline + MFO (Filter) | 59.7 | 48.8 | 76.7 | 536.2 | 45.5 |
| SCAMF-Net | 63.6 | 52.0 | 79.5 | 562.4 | 47.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, W.; Qiao, L.; Kang, W.; Shi, X. Thangka Image Captioning Based on Semantic Concept Prompt and Multimodal Feature Optimization. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9080162
Hu W, Qiao L, Kang W, Shi X. Thangka Image Captioning Based on Semantic Concept Prompt and Multimodal Feature Optimization. Journal of Imaging. 2023; 9(8):162. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9080162
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Wenjin, Lang Qiao, Wendong Kang, and Xinyue Shi. 2023. "Thangka Image Captioning Based on Semantic Concept Prompt and Multimodal Feature Optimization" Journal of Imaging 9, no. 8: 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9080162
APA StyleHu, W., Qiao, L., Kang, W., & Shi, X. (2023). Thangka Image Captioning Based on Semantic Concept Prompt and Multimodal Feature Optimization. Journal of Imaging, 9(8), 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9080162






