Imaging of Gastrointestinal Tract Ailments
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. X-ray/CT
1.2. MRI
1.3. PET/SPECT
1.4. Ultrasound
1.5. Photoacoustic Tomography
2. Imaging of Gastrointestinal Diseases
2.1. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
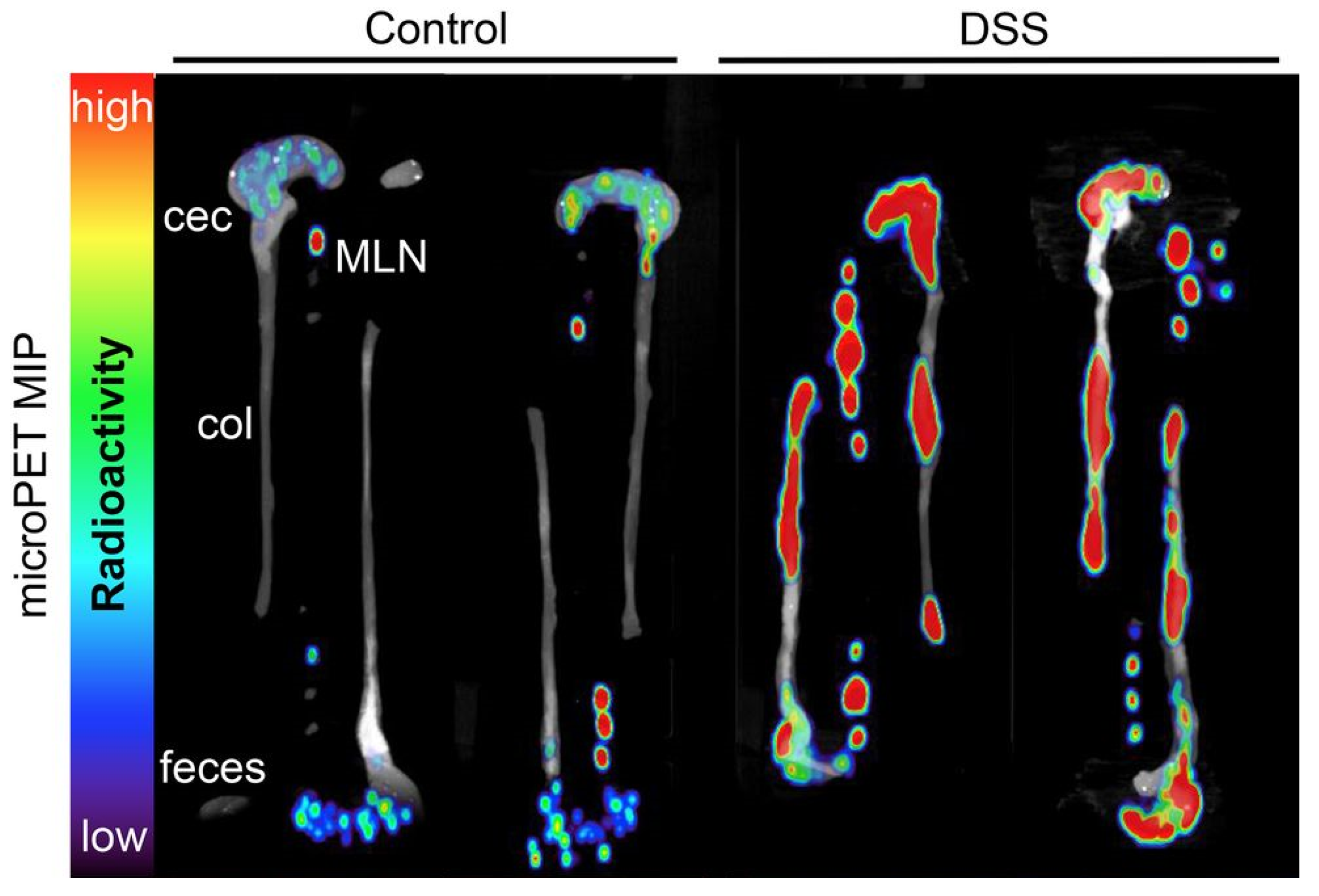
2.1.1. PET Image of IBD
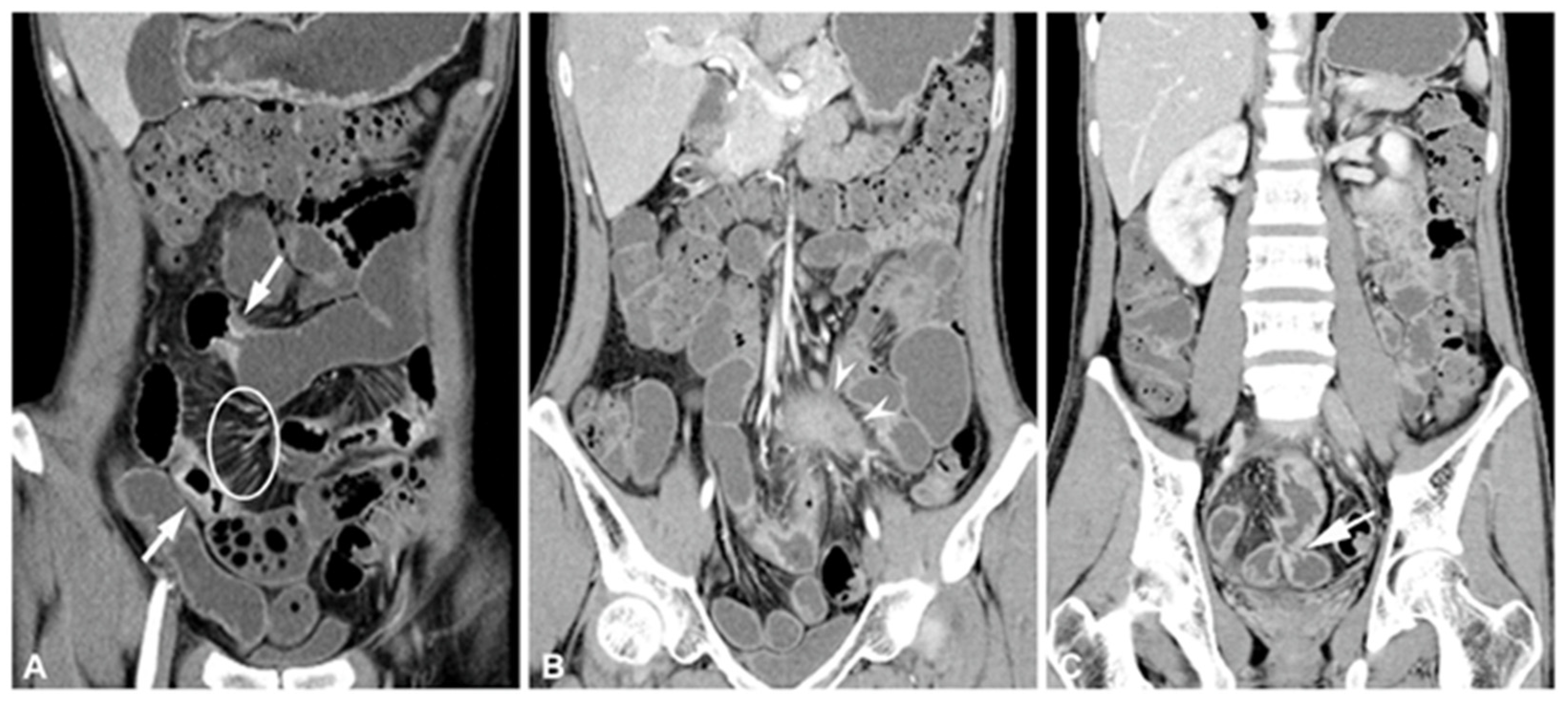
2.1.2. CT and CTE of IBD
2.1.3. PET/CT of IBD
2.1.4. MRI for IBD
2.1.5. Others: Ultrasonography and Scintigraphy Image for IBD
2.2. Appendicitis
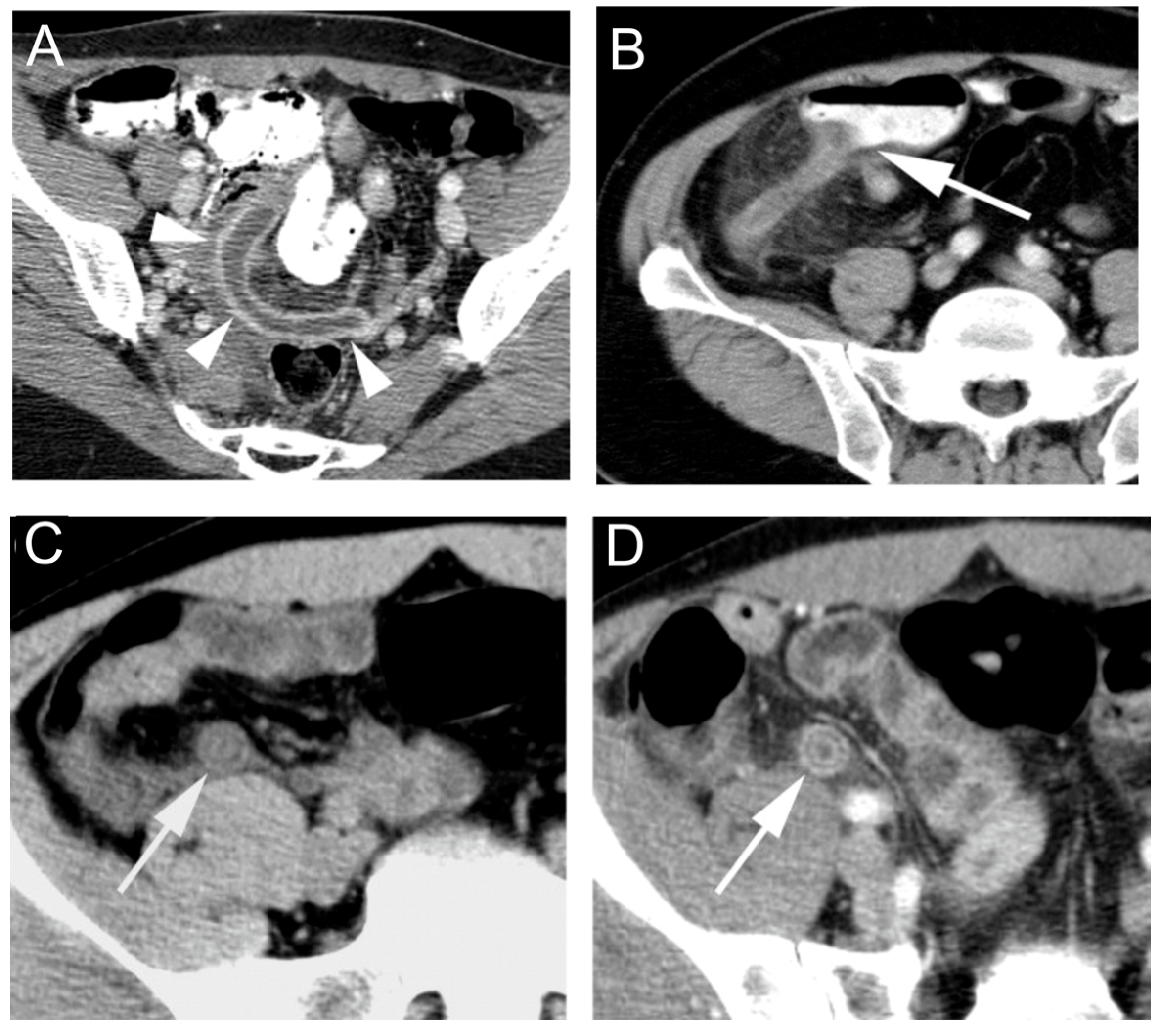
2.2.1. CT for Appendicitis
2.2.2. Ultrasound of Appendicitis
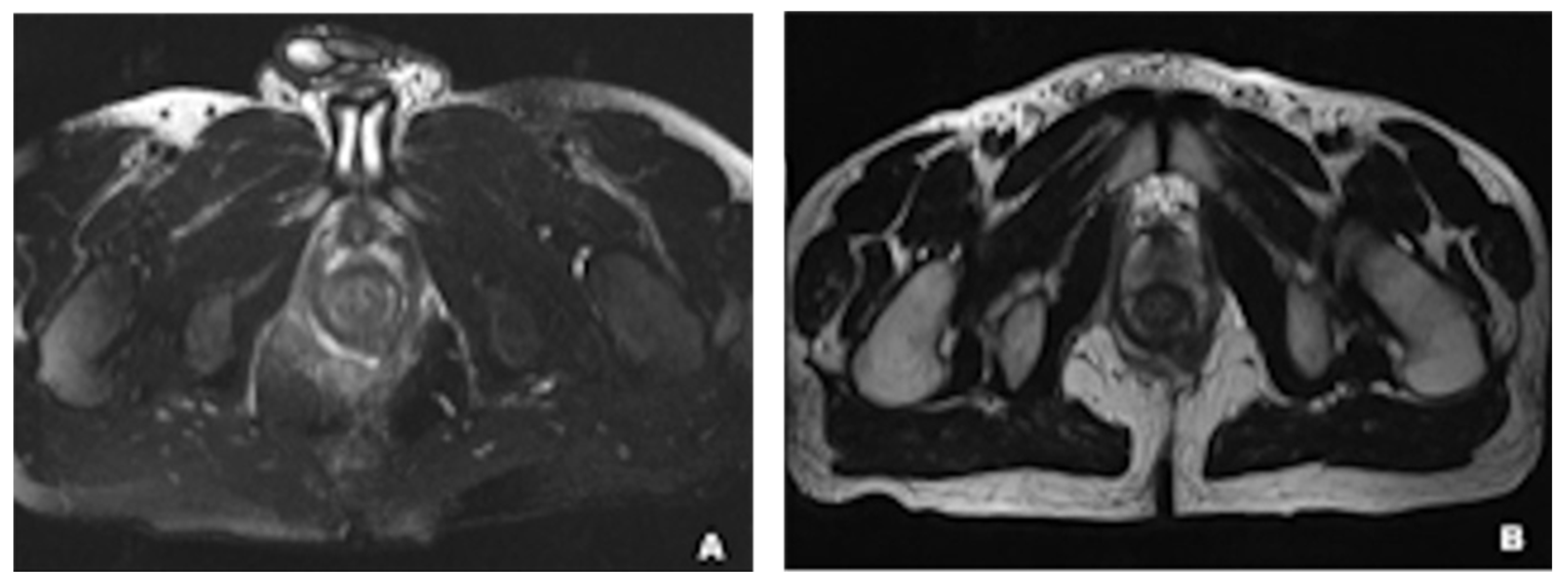
2.2.3. MRI for Appendicitis
2.2.4. Other
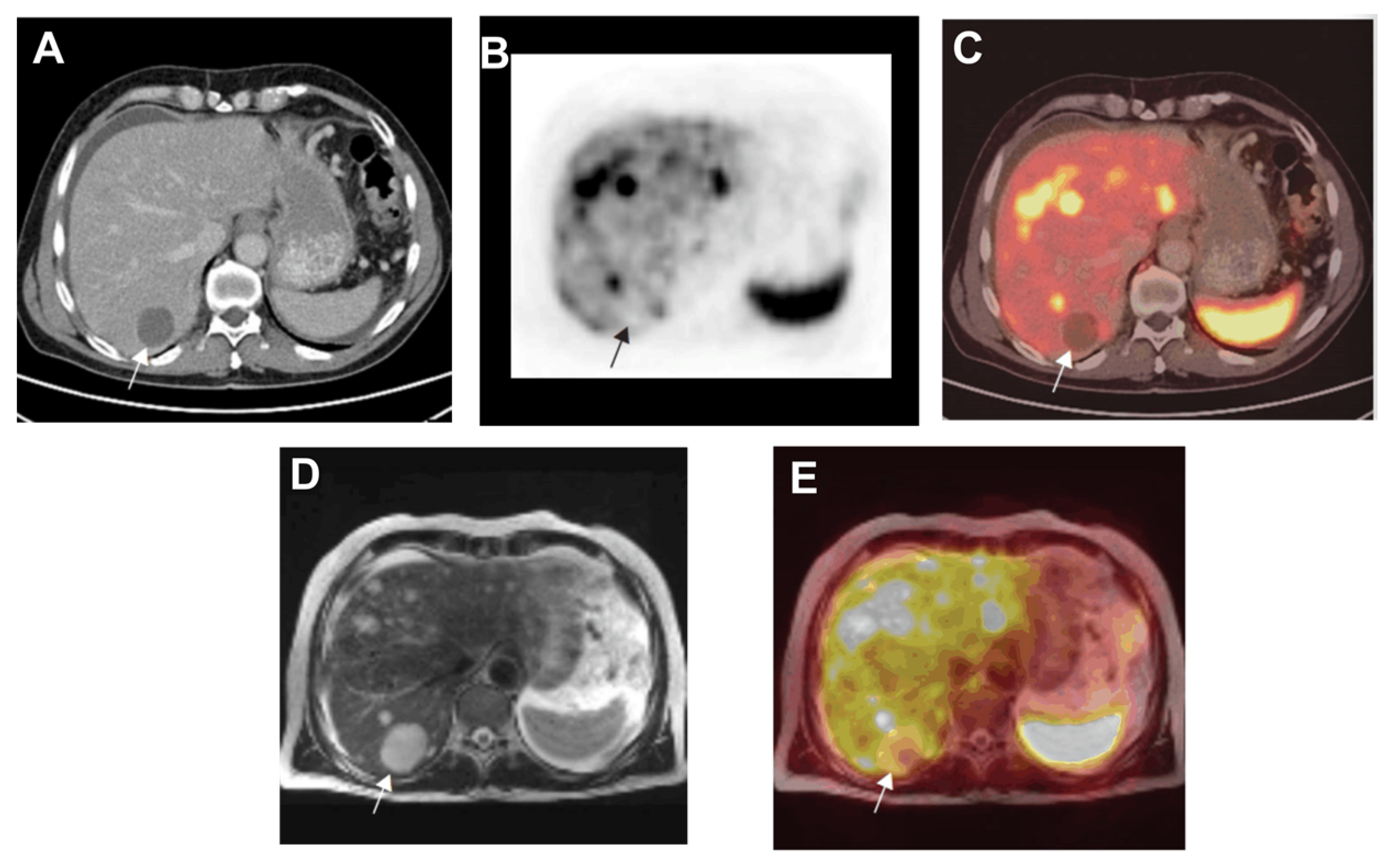
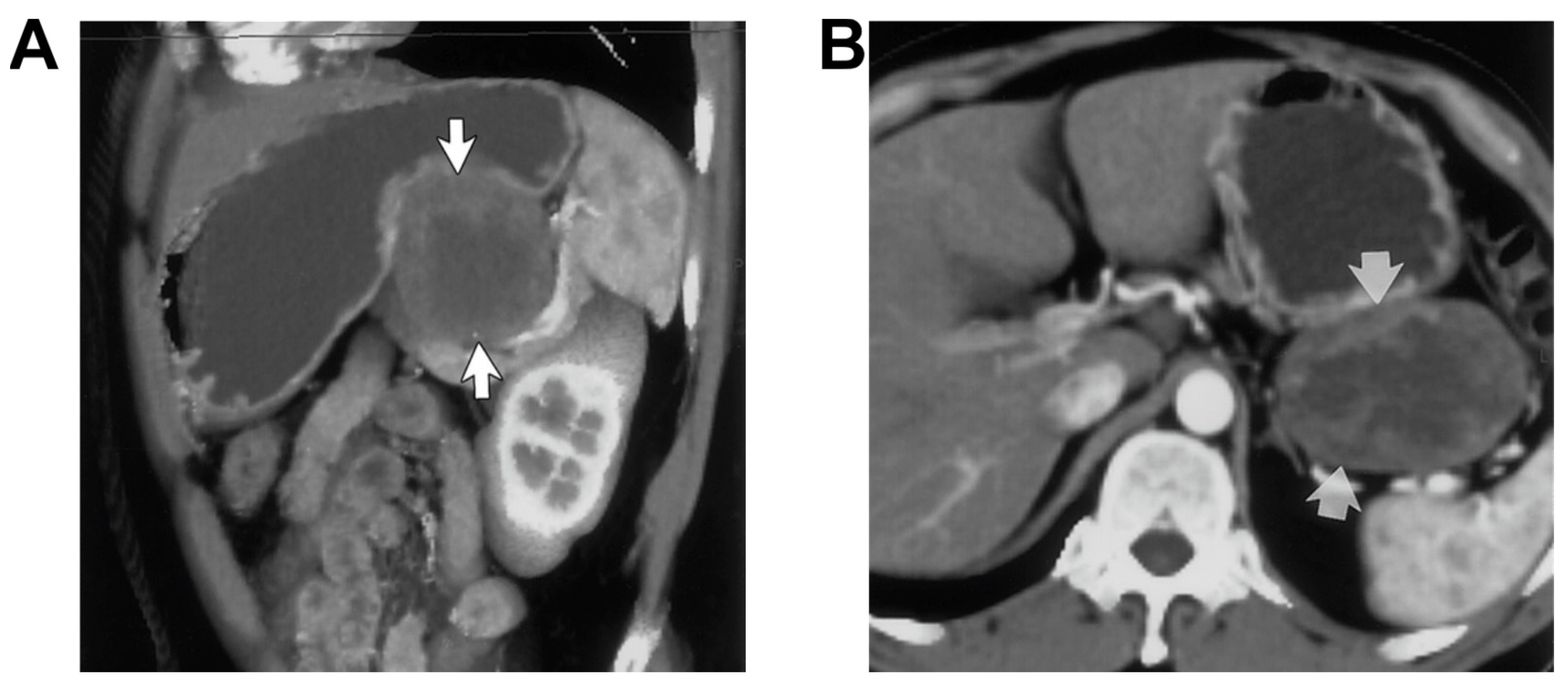
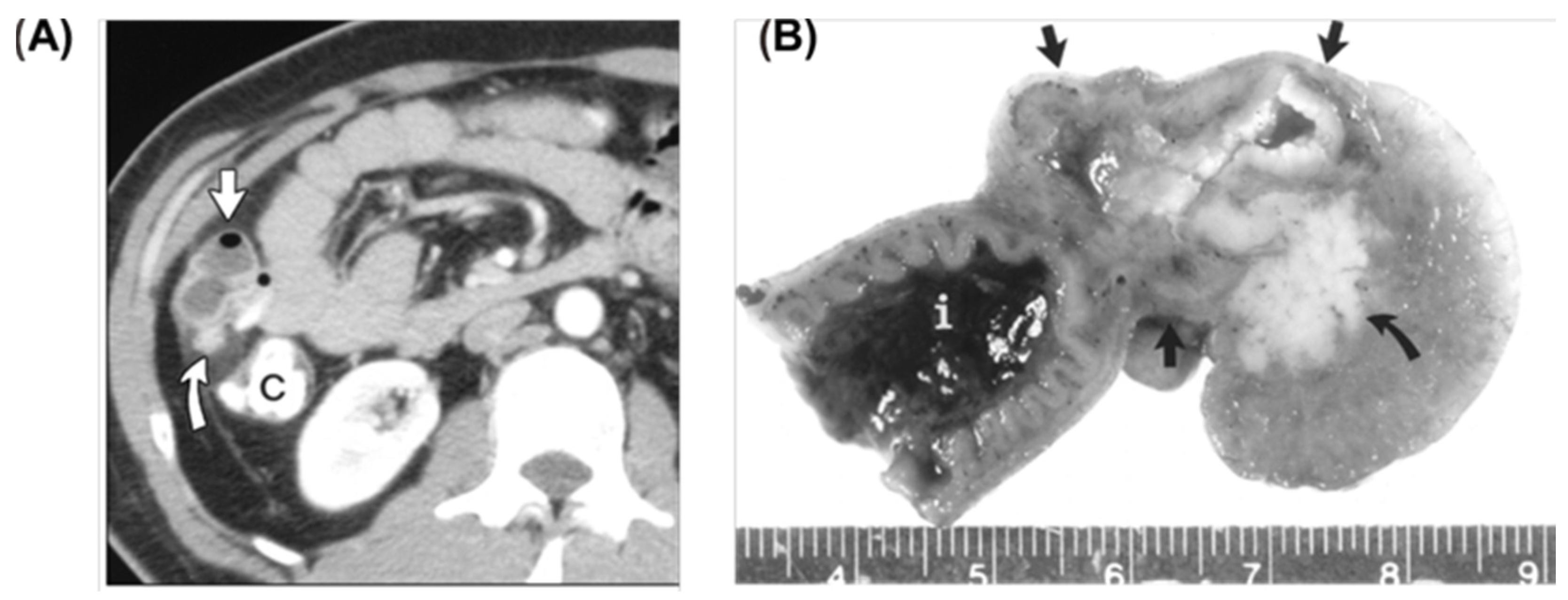
2.3. Carcinoid Tumors and Colorectal Cancer
2.4. Gastric Diseases
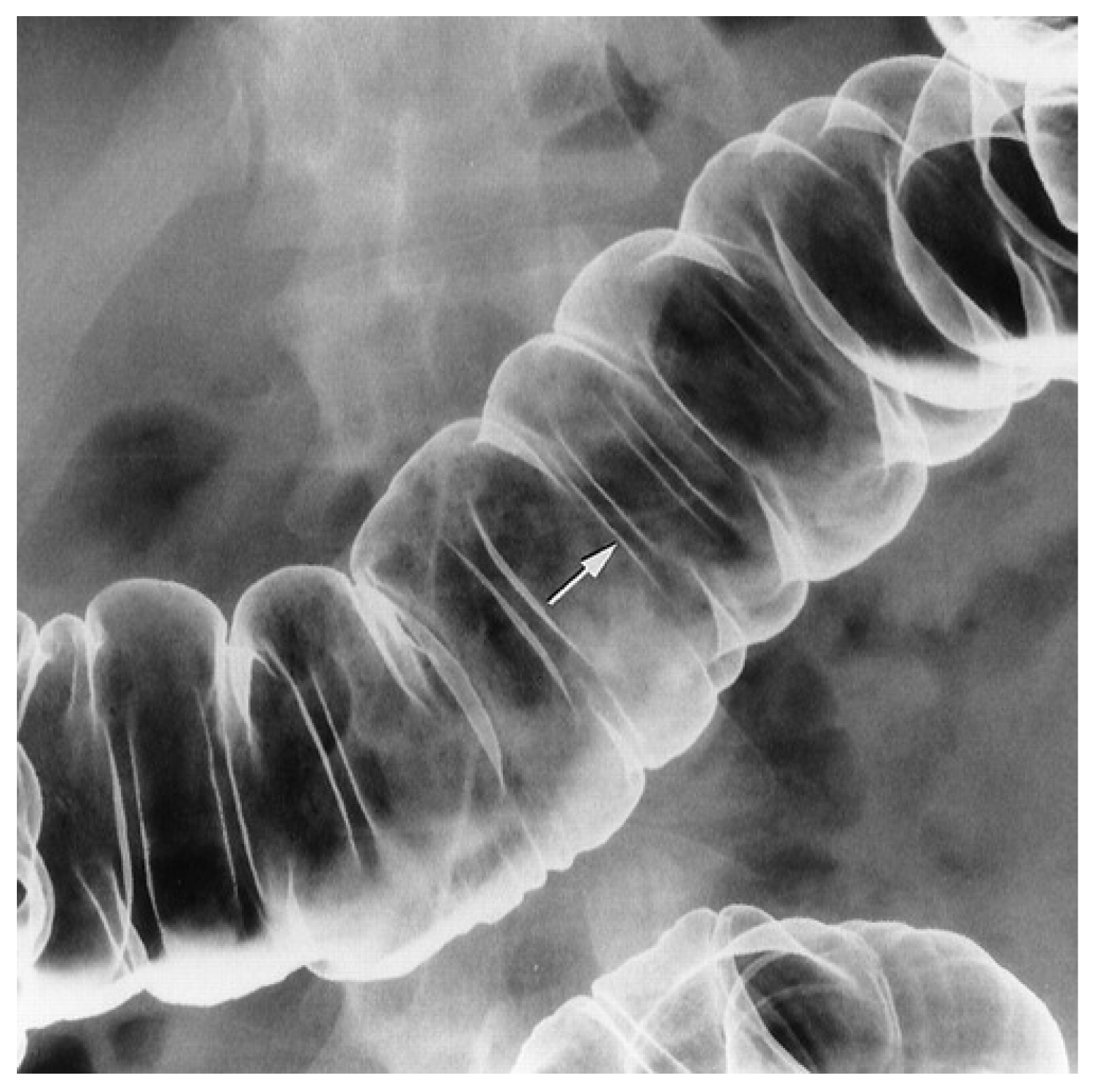
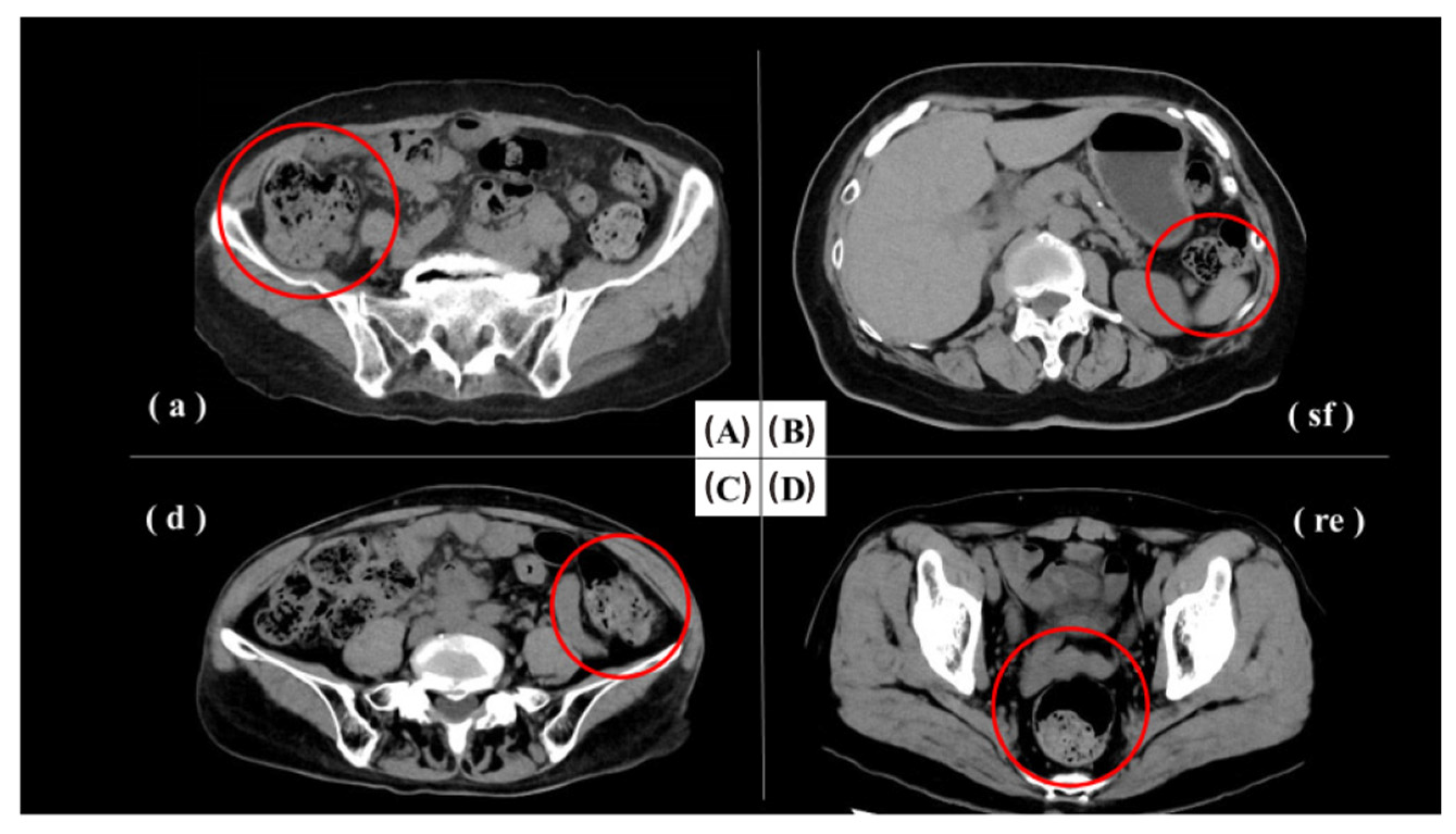
2.5. Meckel’s Diverticulum
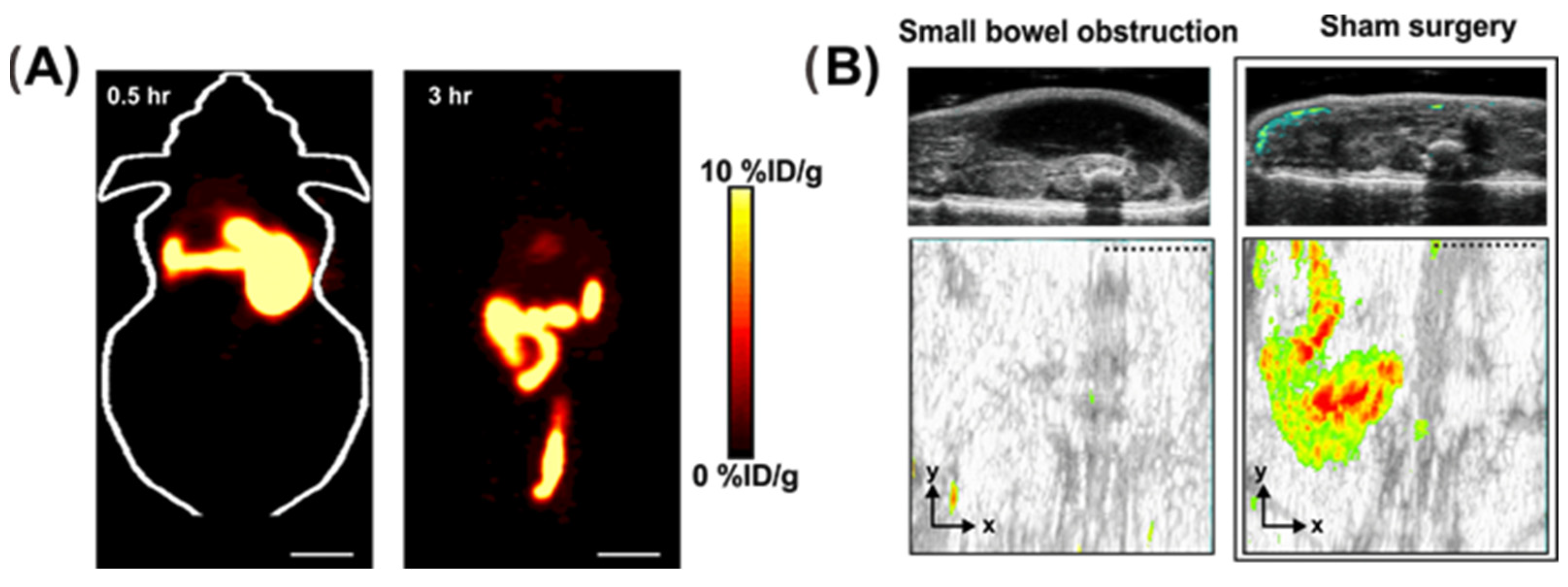
2.6. Intestinal Obstruction
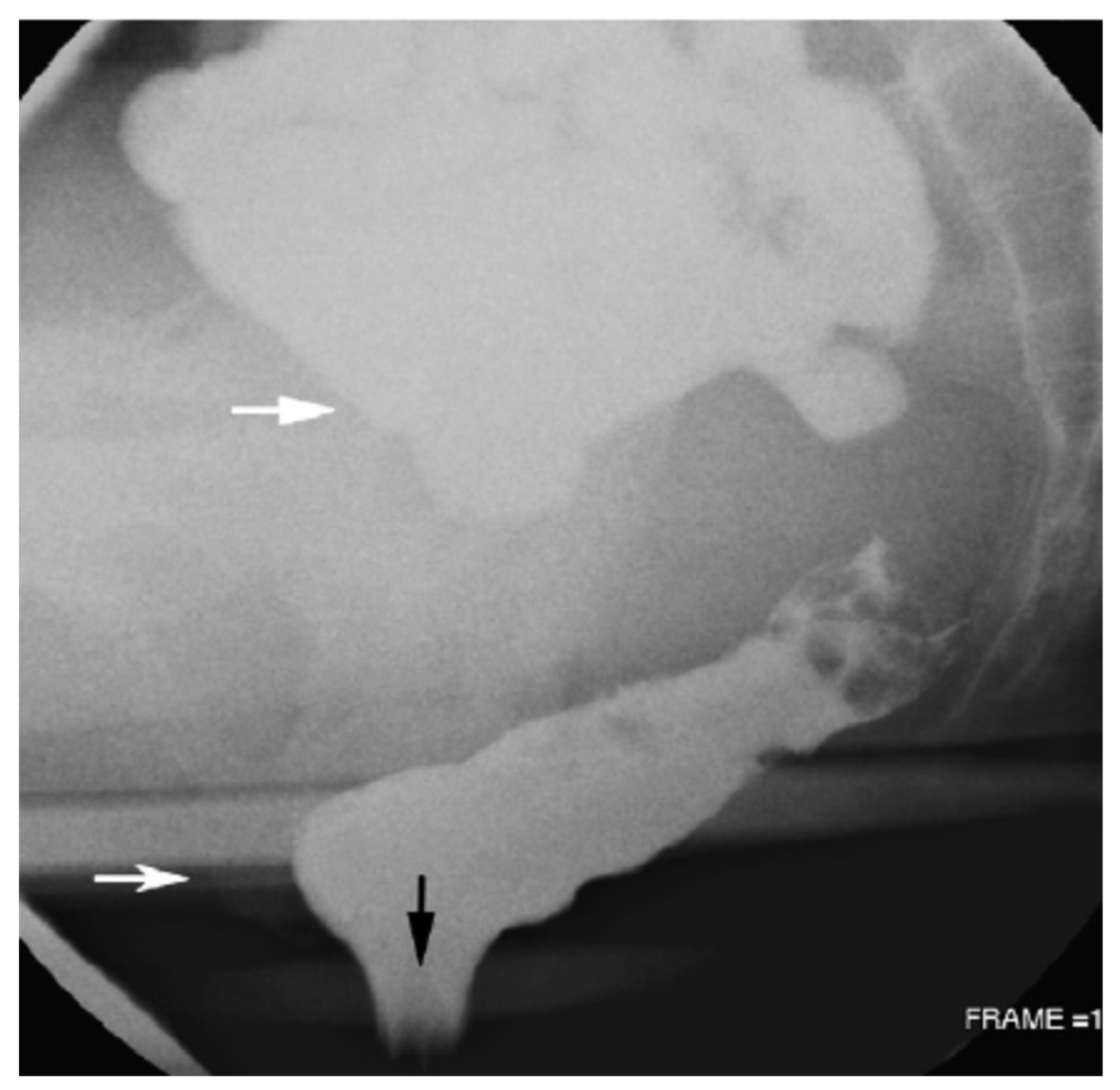
2.7. Pelvic Floor Abnormalities (Constipation)
3. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kappelman, M.D.; Moore, K.R.; Allen, J.K.; Cook, S.F. Recent Trends in the Prevalence of Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis in a Commercially Insured US Population. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 58, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molodecky, N.A.; Soon, I.S.; Rabi, D.M.; Ghali, W.A.; Ferris, M.; Chernoff, G.; Benchimol, E.I.; Panaccione, R.; Ghosh, S.; Barkema, H.W.; et al. Increasing Incidence and Prevalence of the Inflammatory Bowel Diseases with Time, Based on Systematic Review. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gee, M.S.; Harisinghani, M.G. MRI in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2011, 33, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costamagna, G.; Shah, S.K.; Riccioni, M.E.; Foschia, F.; Mutignani, M.; Perri, V.; Vecchioli, A.; Brizi, M.G.; Picciocchi, A.; Marano, P. A prospective trial comparing small bowel radiographs and video capsule endoscopy for suspected small bowel disease. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchman, A.L.; Miller, F.H.; Wallin, A.; Chowdhry, A.A.; Ahn, C. Vidcocapsulc endoscopy versus barium contrast studies for the diagnosis of Crohn’s disease recurrence involving the small intestine. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 99, 2171–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carucci, L.R.; Levine, M.S. Radiographic imaging of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2002, 31, 93–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, K.A.; Fishman, E.K. The current status of multidetector row CT and three-dimensional imaging of the small bowel. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2003, 41, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, S.R.; Huprich, J.E.; Fletcher, J.G.; Booya, F.; Young, B.M.; Fidler, J.L.; Johnson, C.D.; Barlow, J.M.; Earnest, F. CT enterography as a diagnostic tool in evaluating small bowel disorders: Review of clinical experience with over 700 cases. Radiographics 2006, 26, 641–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadayakkara, D.K.; Ranganathan, S.; Young, W.B.; Ahrens, E.T. Assaying macrophage activity in a murine model of inflammatory bowel disease using fluorine-19 MRI. Lab. Investig. 2012, 92, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Sun, B.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H.; Ren, H.; Zhang, H.; Lu, T.; Ren, X.; Wei, W.; Wang, X. Surfactant-Stripped Micelles with Aggregation-Induced Enhanced Emission for Bimodal Gut Imaging In Vivo and Microbiota Tagging Ex Vivo. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2100356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Park, B.; Ye, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, G.; Yang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Han, M.; Fan, Y.; Song, J.; et al. Surfactant-Stripped Semiconducting Polymer Micelles for Tumor Theranostics and Deep Tissue Imaging in the NIR-II Window. Small 2022, 18, e2104132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Lovell, J.F.; Zhang, Y. Ingestible Contrast Agents for Gastrointestinal Imaging. Chembiochem 2019, 20, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Goel, S.; Sun, B.; Chitgupi, U.; Geng, J.; Sun, H.; Barnhart, T.E.; Cai, W.; Xia, J. Surfactant-stripped frozen pheophytin micelles for multimodal gut imaging. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 8524–8530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Jeon, M.; Rich, L.J.; Hong, H.; Geng, J.M.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, S.X.; Barnhart, T.E.; Alexandridis, P.; Huizinga, J.D.; et al. Non-invasive multimodal functional imaging of the intestine with frozen micellar naphthalocyanines. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, P.J.; Bouman, C.; Carmignato, S.; Cnudde, V.; Grimaldi, D.; Hagen, C.K.; Maire, E.; Manley, M.; Du Plessis, A.; Stock, S.R. X-ray computed tomography. Nat. Rev. Methods Prim. 2021, 1, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naha, P.C.; Hsu, J.C.; Kim, J.; Shah, S.; Bouché, M.; Si-Mohamed, S.; Rosario-Berrios, D.N.; Douek, P.; Hajfathalian, M.; Yasini, P. Dextran-coated cerium oxide nanoparticles: A computed tomography contrast agent for imaging the gastrointestinal tract and inflammatory bowel disease. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 10187–10197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patenaude, Y.; Pugash, D.; Lim, K.; Morin, L.; Bly, S.; Butt, K.; Cargill, Y.; Davies, G.; Denis, N.; Hazlitt, G. The use of magnetic resonance imaging in the obstetric patient. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Can. 2014, 36, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buisson, A.; Joubert, A.; Montoriol, P.F.; Ines, D.; Hordonneau, C.; Pereira, B.; Garcier, J.M.; Bommelaer, G.; Petitcolin, V. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for detecting and assessing ileal inflammation in C rohn’s disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 37, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katti, G.; Ara, S.A.; Shireen, A. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)—A review. Int. J. Dent. Clin. 2011, 3, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Gilja, O.H.; Hatlebakk, J.G.; Ødegaard, S.; Berstad, A.; Viola, I.; Giertsen, C.; Hausken, T.; Gregersen, H. Advanced imaging and visualization in gastrointestinal disorders. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, E.; Stadlbauer, A.; Windischberger, C.; Quick, H.H.; Ladd, M.E. Magnetic resonance imaging methodology. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2009, 36, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.R.; Danrad, R.; Herrmann, K.; Semelka, R.C.; Hussain, S.M. Magnetic resonance imaging of the gastrointestinal tract. Top. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2005, 16, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masselli, G.; Gualdi, G. MR Imaging of the Small Bowel. Radiology 2012, 264, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieffel, J.; Chitgupi, U.; Lovell, J.F. Recent Advances in Higher-Order, Multimodal, Biomedical Imaging Agents. Small 2015, 11, 4445–4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmim, A.; Zaidi, H. PET versus SPECT: Strengths, limitations and challenges. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2008, 29, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteves, F.P.; Schuster, D.M.; Halkar, R.K. Gastrointestinal tract malignancies and positron emission tomography: An overview. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2006, 36, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaprakasam, V.S.; Paroder, V.; Schöder, H. Variants and pitfalls in PET/CT imaging of gastrointestinal cancers. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2021, 51, 485–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidekker, M.A. Medical Imaging Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Panes, J.; Bouhnik, Y.; Reinisch, W.; Stoker, J.; Taylor, S.A.; Baumgart, D.C.; Danese, S.; Halligan, S.; Marincek, B.; Matos, C.; et al. Imaging techniques for assessment of inflammatory bowel disease: Joint ECCO and ESGAR evidence-based consensus guidelines. J. Crohns Colitis 2013, 7, 556–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.V.; Yao, J. A practical guide to photoacoustic tomography in the life sciences. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upputuri, P.K.; Pramanik, M. Recent advances toward preclinical and clinical translation of photoacoustic tomography: A review. J. Biomed. Opt. 2017, 22, 41006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Lovell, J.F.; Zhang, Y. Design and application of organic contrast agents for molecular imaging in the second near infrared (NIR-II) window. Photoacoustics 2022, 28, 100426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Hu, J.; Yang, P.; Ding, S.; Zhu, R. Photoacoustic Tomography Imaging: An Emerging Detection Way. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2013, 50, 040005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, L.; Grobmyer, S.R.; Wu, L.; Chen, R.; Zhou, G.; Gutwein, L.G.; Sun, J.; Liao, W.; Zhou, Q.; Xie, H.; et al. Evaluation of breast tumor margins in vivo with intraoperative photoacoustic imaging. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 8726–8731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhong, X.; Lei, H.; Yang, N.; Gao, X.; Cheng, L. Tumor microenvironment-responsive contrast agents for specific cancer imaging: A narrative review. J. Bio-X Res. 2020, 3, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cao, Y.; Liu, H.; Peng, D.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, K.; Tian, J. High-speed and 128-channel multi-spectral photoacoustic tomography system for small animal. Laser Technol. 2017, 41, 669–674. [Google Scholar]
- Na, S.; Russin, J.J.; Lin, L.; Yuan, X.; Hu, P.; Jann, K.B.; Yan, L.; Maslov, K.; Shi, J.; Wang, D.J.; et al. Massively parallel functional photoacoustic computed tomography of the human brain. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 6, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geboes, K. Pathology of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD): Variability with time and treatment. Color. Dis. Off. J. Assoc. Coloproctol. Great Br. Irel. 2001, 3, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podolsky, D.K. Inflammatory bowel disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharzik, T.; Tielbeek, J.; Carter, D.; Taylor, S.A.; Tolan, D.; Wilkens, R.; Bryant, R.V.; Hoeffel, C.; De Kock, I.; Maaser, C.; et al. ECCO-ESGAR Topical Review on Optimizing Reporting for Cross-Sectional Imaging in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2022, 16, 523–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKalski, B.A.; Bernstein, C.N. Diagnostic imaging tools for inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2006, 55, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, R.A.; Hoh, C.; Glaspy, J.; Choi, Y.; Dahlbom, M.; Rege, S.; Messa, C.; Nietszche, E.; Hoffman, E.; Seeger, L. The role of positron emission tomography in oncology and other whole-body applications. Semin. Nucl. Med. 1992, 22, 268–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicik, I.; Bauerfeind, P.; Breitbach, T.; von Schulthess, G.K.; Fried, M. Inflammatory bowel disease activity measured by positron-emission tomography. Lancet 1997, 350, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtmann, M.H.; Uenzen, M.; Helisch, A.; Dahmen, A.; Mudter, J.; Goetz, M.; Schreckenberger, M.; Galle, P.R.; Bartenstein, P.; Neurath, M.F. F-18-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron-Emission Tomography (PET) Can Be Used to Assess Inflammation Non-invasively in Crohn’s Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 2658–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthold, L.D.; Steiner, D.; Scholz, D.; Alzen, G.; Zimmer, K.P. Imaging of Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Disease with 18F-FDG PET in Children and Adolescents. Klin. Padiatr. 2013, 225, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treglia, G.; Sadeghi, R.; Viccaro, A.; Muoio, B.; Giovanella, L. Clinical role and accuracy of F-18-FDG PET in evaluating disease activity in patients with chronic inflammatory bowel disease: An updated systematic review and a bivariate meta-analysis. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2017, 5, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovinfosse, P.; Hustinx, R. The role of PET imaging in inflammatory bowel diseases: State-of-the-art review. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 66, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.; Kim, Y.; Ye, B.D.; Park, S.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Jung, J.H.; Hwang, S.W.; Chae, S.Y.; Lee, D.Y.; Lee, S.J.; et al. PET Imaging of System xC- in Immune Cells for Assessment of Disease Activity in Mice and Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, D.R.B.; Smith, C.C.; Bixby, L.M.; Glatt, D.M.; Dunn, S.S.; Saito, R.; Kim, W.Y.; Serody, J.S.; Vincent, B.G.; Parrott, M.C. Immuno-PET imaging of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes using zirconium-89 radiolabeled anti-CD3 antibody in immune-competent mice bearing syngeneic tumors. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freise, A.C.; Zettlitz, K.A.; Salazar, F.B.; Tavare, R.; Tsai, W.T.K.; Chatzlioannou, A.F.; Rozengurt, N.; Braun, J.; Wu, A.M. Immuno-PET in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Imaging CD4-Positive T Cells in a Murine Model of Colitis. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 980–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmochowska, N.; Tieu, W.; Keller, M.D.; Wardill, H.R.; Mavrangelos, C.; Campaniello, M.A.; Takhar, P.; Hughes, P.A. Immuno-PET of Innate Immune Markers CD11b and IL-1 beta Detects Inflammation in Murine Colitis. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Wang, X.Y.; Fan, Y.L.; Lin, J.H.; Yan, J.J.; Wang, L.Z.; Pan, D.H.; Xu, Y.P.; Yang, M. Immuno-PET Imaging of TNF-alpha in Colitis Using 89Zr-DFO-infliximab. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 3632–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusic, H.; Grinstaff, M.W. X-ray-Computed Tomography Contrast Agents. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 1641–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gore, R.M.; Ghahremani, G.G. Radiologic investigation of acute inflammatory and infectious bowel disease. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 1995, 24, 353–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.Y.; Fu, X.P.; Kuang, K.; Fan, D. Artificial Intelligence Algorithm-Based Differential Diagnosis of Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis by CT Image. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 3871994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raptopoulos, V.; Schwartz, R.K.; McNicholas, M.M.; Movson, J.; Pearlman, J.; Joffe, N. Multiplanar helical CT enterography in patients with Crohn’s disease. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1997, 169, 1545–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.J.; Lim, J.S. Computed tomography enterography for evaluation of inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. Endosc. 2013, 46, 327–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booya, F.; Fletcher, J.G.; Huprich, J.E.; Barlow, J.M.; Johnson, C.D.; Fidler, J.L.; Solem, C.A.; Sandborn, W.J.; Loftus, E.V.; Harmsen, W.S. Active Crohn disease: CT findings and interobserver agreement for enteric phase CT enterography. Radiology 2006, 241, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, H.I.; Sharatz, S.M.; Taphey, M.; Bradley, W.F.; Nimkin, K.; Gee, M.S. Comparison of CT enterography and MR enterography imaging features of active Crohn disease in children and adolescents. Pediatr. Radiol. 2017, 47, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.S.; Kim, A.Y.; Yang, S.K.; Chung, J.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, S.H.; Ha, H.K. Crohn Disease of the Small Bowel: Comparison of CT Enterography, MR Enterography, and Small-Bowel Follow-Through as Diagnostic Techniques. Radiology 2009, 251, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minordi, L.M.; Bevere, A.; Papa, A.; Larosa, L.; Manfredi, R. CT and MRI Evaluations in Crohn’s Complications: A Guide for the Radiologist. Acad. Radiol. 2022, 29, 1206–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charron, M.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Kocoshis, S. CT and Tc-99m-WBC vs colonoscopy in the evaluation of inflammation and complications of inflammatory bowel diseases. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 37, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scotiniotis, I.; Rubesin, S.E.; Ginsberg, G.G. Imaging modalities in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 1999, 28, 391–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabra, A.A.; Fishman, E.K.; Taylor, G.A. CT findings in inflammatory bowel disease in children. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1994, 162, 975–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gore, R.M.; Balthazar, E.J.; Ghahremani, G.G.; Miller, F.H. CT features of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1996, 167, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, J.R.; Pozzuto, J.; Morrison, S.; Obuchowski, N.; Davros, W. Comparison of Gonadal Radiation Doses from CT Enterography and Small-Bowel Follow-Through in Pediatric Patients. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatlin, J.L.; Brown, K.; Tang, S.J.; Sebastian, S. Beyond routine abdominal CT in the ER: A patient with indeterminate recurrent abdominal pain benefits from CT enterography. Clin. Imaging 2012, 36, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruining, D.H. CT Enterography: Is It the Current State-of-the-Art for Small Bowel Diagnostics? Dig. Dis. 2010, 28, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, K. Crohn’s disease: New imaging techniques. Baillieres Clin. Gastroenterol. 1998, 12, 35–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, H.E.; Frush, D.P.; Farmer, D.; Waldhausen, J.H.; Comm, A.E. Review of radiation risks from computed tomography: Essentials for the pediatric surgeon. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2007, 42, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, D.J.; Elliston, C.D.; Hall, E.J.; Berdon, W.E. Estimates of the cancer risks from pediatric CT radiation are not theoretical: Comment on “Point/Counterpoint: In x-ray computed tomography, technique factors should be selected appropriate to size. Against the Proposition” [Med. Phys. 28, 1543-1545 (2001)]. Med. Phys. 2001, 28, 2387–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govani, S.M.; Higgins, P.D.R.; Rubenstein, J.H.; Stidham, R.W.; Waljee, A.K. CT utilization abruptly increases at age 18 among patients with inflammatory bowel diseases in the hospital. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treglia, G.; Quartuccio, N.; Sadeghi, R.; Farchione, A.; Caldarella, C.; Bertagna, F.; Fania, P.; Cistaro, A. Diagnostic performance of Fluorine-18-Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in patients with chronic inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review and a meta-analysis. J. Crohns Colitis 2013, 7, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattaru, A.; Borja, A.; Zhang, V.; Rojulpote, K.V.; Werner, T.; Alavi, A.; Revheim, M.E. FDG-PET/CT as the superior imaging modality for inflammatory bowel disease. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 1159. [Google Scholar]
- Perlman, S.B.; Hall, B.S.; Reichelderfer, M. PET/CT Imaging of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2013, 43, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoch, G.; Saoudi, N.; Kuehl, H.; Dahmen, G.; Mueller, S.P.; Beyer, T.; Bockisch, A.; Debatin, J.F.; Freudenberg, L.S. Accuracy of whole-body dual-modality fluorine-18-2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography and computed tomography (FDG-PET/CT) for tumor staging in solid tumors: Comparison with CT and PET. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 4357–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, C.J.; Makharia, G.; Kumar, R.; Chawla, M.; Goswami, P.; Sharma, R.; Malhotra, A. PET-CT enteroclysis: A new technique for evaluation of inflammatory diseases of the intestine. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2007, 34, 2106–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapp, R.T.; Spier, B.J.; Perlman, S.B.; Jaskowiak, C.J.; Reichelderfer, M. Clinical Utility of Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2011, 13, 573–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpenny, D.F.; Burke, J.P.; Lawlor, G.O.; O’Connell, M. Role of PET and Combination PET/CT in the Evaluation of Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2009, 15, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaudemans, A.W.; de Vries, E.F.; Galli, F.; Dierckx, R.A.; Slart, R.H.; Signore, A. The use of (18)F-FDG-PET/CT for diagnosis and treatment monitoring of inflammatory and infectious diseases. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 623036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spier, B.J.; Perlman, S.B.; Jaskowiak, C.J.; Reichelderfer, M. PET/CT in the evaluation of inflammatory bowel disease: Studies in patients before and after treatment. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2010, 12, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuelhia, E.; Alghamdi, A. Evaluation of arising exposure of ionizing radiation from computed tomography and the associated health concerns. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2020, 13, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Ren, Y. Application progresses of MRI in diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease. Chin. J. Med. Imaging Technol. 2018, 34, 1736–1739. [Google Scholar]
- Deepak, P.; Axelrad, J.E.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N. The Role of the Radiologist in Determining Disease Severity in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 29, 447–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, J.C.; Echarri, A. Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the management of perianal Crohn’s disease. Insights Imaging 2018, 9, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcı, S.; Onur, M.R.; Karaosmanoğlu, A.D.; Karçaaltıncaba, M.; Akata, D.; Konan, A.; Özmen, M.N. MRI evaluation of anal and perianal diseases. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 25, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reginelli, A.; Vacca, G.; Giovine, S.; Izzo, A.; Agostini, A.; Belfiore, M.P.; Cellina, M.; Floridi, C.; Borgheresi, A.; Palumbo, P.; et al. MRI of perianal fistulas in Crohn’s disease. Acta Bio-Med. Atenei Parm. 2020, 91, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudoł-Szopińska, I.; Kołodziejczak, M.; Aniello, G.S. A novel template for anorectal fistula reporting in anal endosonography and MRI—A practical concept. Med. Ultrason. 2019, 21, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, J.; Guggenberger, R.; Del Grande, F. Rapid Musculoskeletal MRI in 2021: Clinical Application of Advanced Accelerated Techniques. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2021, 216, 718–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laudicella, R.; Davidzon, G.; Vasanawala, S.; Baldari, S.; Iagaru, A. F-18-FDG PET/MR Refines Evaluation in Newly Diagnosed Metastatic Urethral Adenocarcinoma. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 53, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, O.A.; Wu, V.; Mahmood, U.; Signore, A.; Vangel, M.; Soricelli, A.; Salvatore, M.; Gervais, D.; Rosen, B.R. Diagnostic performance of PET/MR in the evaluation of active inflammation in Crohn disease. Am. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 8, 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Paolantonio, P.; Ferrari, R.; Vecchietti, F.; Cucchiara, S.; Laghi, A. Current status of MR imaging in the evaluation of IBD in a pediatric population of patients. Eur. J. Radiol. 2009, 69, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidler, J.L.; Guimaraes, L.; Einstein, D.M. MR Imaging of the Small Bowel. Radiographics 2009, 29, 1811–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreyer, A.G.; Geissler, A.; Albrich, H.; Scholmerich, J.; Feuerbach, S.; Rogler, G.; Volk, M.; Herfarth, H. Abdominal MRI After Enteroclysis or with Oral Contrast in Patients with Suspected or Proven Crohn’s Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2004, 2, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negaard, A.; Paulsen, V.; Sandvik, L.; Berstad, A.E.; Borthne, A.; Try, K.; Lygren, I.; Storaas, T.; Klow, N.E. A prospective randomized comparison between two MRI studies of the small bowel in Crohn’s disease, the oral contrast method and MR enteroclysis. Eur. Radiol. 2007, 17, 2294–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masselli, G.; Casciani, E.; Polettini, E.; Gualdi, G. Comparison of MR enteroclysis with MR enterography and conventional enteroclysis in patients with Crohn’s disease. Eur. Radiol. 2008, 18, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghi, A.; Paolantonio, P.; Iafrate, F.; Altomari, F.; Miglio, C.; Passariello, R. Oral contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging of the bowel. Top. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2002, 13, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomas, D.J.; Graves, M.J. Small bowel MRI using water as a contrast medium. Br. J. Radiol. 1999, 72, 994–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, R.R.; Joubert, I.; Franklin, H.; Doyle, T.; Lomas, D.J. Small bowel MRI: Comparison of a polyethylene glycol preparation and water as oral contrast media. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2002, 15, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, D.A.; Roche, C.J.; Murphy, J.M.P.; McCarthy, P.A. Polyethylene glycol solution as an oral contrast agent for MRI of the small bowel in a patient population. Clin. Radiol. 2006, 61, 966–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghi, A.; Carbone, I.; Paolantonio, P.; Iannaccone, R.; Passariello, R. Polyethylene glycol solution as an oral contrast agent for MR imaging of the small bowel. Acad. Radiol. 2002, 9, S355–S356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnano, G.; Granata, C.; Barabino, A.; Magnaguagno, F.; Rossi, U.; Calevo, M.G.; Toma, P. Polyethylene glycol and contrast-enhanced MRI of Crohn’s disease in children: Preliminary experience. Pediatr. Radiol. 2003, 33, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauenstein, T.C.; Schneemann, H.; Vogt, F.M.; Herborn, C.U.; Ruhm, S.G.; Debatin, J.F. Optimization of oral contrast agents for MR imaging of the small bowel. Radiology 2003, 228, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laghi, A.; Paolantonio, P.; Catalano, C.; Dito, L.; Carbone, L.; Barbato, M.; Tomei, E.; Passariello, R. MR Imaging of the small bowel using polyethylene glycol solution as an oral contrast agent in adults and children with celiac disease: Preliminary observations. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2003, 180, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajaj, W.; Goehde, S.C.; Schneemann, H.; Ruehm, S.G.; Debatin, J.F.; Lauenstein, T.C. Dose optimization of mannitol solution for small bowel distension in MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2004, 20, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, K.A.; Zech, C.J.; Michaely, H.J.; Seiderer, J.; Ochsenkuehn, T.; Reiser, M.F.; Schoenberg, S.O. Comprehensive magnetic resonance imaging of the small and large bowel using intraluminal dual contrast technique with iron oxide solution and water in magnetic resonance enteroclysis. Investig. Radiol. 2005, 40, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boraschi, P.; Braccini, G.; Gigoni, R.; Cartei, F.; Perri, G. MR enteroclysis using iron oxide particles (ferristene) as an endoluminal contrast agent: An open phase III trial. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2004, 22, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreyer, A.G.; Golder, S.; Scheibl, K.; Volk, M.; Lenhart, M.; Timmer, A.; Scholmerich, J.; Feuerbach, S.; Rogler, G.; Herfarth, H.; et al. Dark lumen magnetic resonance enteroclysis in combination with MRI colonography for whole bowel assessment in patients with Crohn’s disease: First clinical experience. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2005, 11, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieber, A.; Aschoff, A.; Nussle, K.; Wruk, D.; Tomczak, R.; Reinshagen, M.; Adler, G.; Brambs, H.J. MRI in the diagnosis of small bowel disease: Use of positive and negative oral contrast media in combination with enteroclysis. Eur. Radiol. 2000, 10, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Gao, C.; Chen, W.; Zhou, K.; Xu, M. Molecular Magnetic Resonance Imaging with Contrast Agents for Assessment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2020, 2020, 4764985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karantanas, A.H.; Papanikolaou, N.; Kalef-Ezra, J.; Challa, A.; Gourtsoyiannis, N. Blueberry juice used per os in upper abdominal MR imaging: Composition and initial clinical data. Eur. Radiol. 2000, 10, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.W.; Zhong, X.Y.; Li, J.X.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, L. Inorganic nanomaterials with rapid clearance for biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 8669–8742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litta, F.; Scaldaferri, F.; Parello, A.; De Simone, V.; Gasbarrini, A.; Ratto, C. Anorectal Function and Quality of Life in IBD Patients with a Perianal Complaint. J. Investg. Surg. 2021, 34, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, N.; Hoad, C.L.; Naim, I.; Alshammari, M.; Radford, S.J.; Clarke, C.; Marciani, L.; Moran, G. Imaging in inflammatory bowel disease: Current and future perspectives. Front. Gastroenterol. 2022, 13, e28–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, C.L.; Maclachlan, J.; Beal, I. Paediatric bowel ultrasound in inflammatory bowel disease. Eur. J. Radiol. 2018, 108, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucharzik, T.; Wittig, B.M.; Helwig, U.; Borner, N.; Rossler, A.; Rath, S.; Maaser, C.; Grp, T.S. Use of Intestinal Ultrasound to Monitor Crohn’s Disease Activity. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 535–542.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worlicek, H.; Lutz, H.; Heyder, N.; Matek, W. Ultrasound findings in Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis: A prospective study. J. Clin. Ultrasound 1987, 15, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Ko, Y.T.; Lee, D.H.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, T.H. Sonography of inflammatory bowel disease: Findings and value in differential diagnosis. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1994, 163, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, T.; Tanami, Y.; Sato, Y.; Nambu, R.; Iwama, I.; Oguma, E. Role of ultrasound in the diagnosis of very early-onset inflammatory bowel disease in children: A report of three cases. Med. Ultrason. 2022, 24, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaser, C.; Petersen, F.; Helwig, U.; Fischer, I.; Roessler, A.; Rath, S.; Lang, D.; Kucharzik, T.; German IBD Study Group; TRUST&UC Study Group. Intestinal ultrasound for monitoring therapeutic response in patients with ulcerative colitis: Results from the TRUST&UC study. Gut 2020, 69, 1629–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharzik, T.; Kannengiesser, K.; Petersen, F. The use of ultrasound in inflammatory bowel disease. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2017, 30, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, D.J.; Ramos, G.P.; Fletcher, J.G.; Bruining, D.H. Imaging Evaluation of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Complications. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 32, 651–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Oostayen, J.A.; Wasser, M.; Griffioen, G.; van Hogezand, R.A.; Lamers, C.; de Roos, A. Activity of Crohn’s disease assessed by measurement of superior mesenteric artery flow with Doppler ultrasound. Neth. J. Med. 1998, 53, S3–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasche, C.; Moser, G.; Turetschek, K.; Schober, E.; Moeschl, P.; Oberhuber, G. Transabdominal bowel sonography for the detection of intestinal complications in Crohn’s disease. Gut 1999, 44, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maaser, C.; Sturm, A.; Vavricka, S.R.; Kucharzik, T.; Fiorino, G.; Annese, V.; Calabrese, E.; Baumgart, D.C.; Bettenworth, D.; Nunes, P.B.; et al. ECCO-ESGAR Guideline for Diagnostic Assessment in IBD Part 1: Initial diagnosis, monitoring of known IBD, detection of complications. J. Crohns Colitis 2019, 13, 144–164K. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esterson, A.; Alpert, E.A.; Gabrieli, S.; Granat, N. Sonographic assessment of inflammatory bowel disease in the emergency department: A case series and review of the literature. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2021, 49, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, T.; Papos, M.; Gyulai, C.; Ambrus, E.; Kardos, L.; Nagy, F.; Palko, A.; Pavics, L.; Lonovics, J. Clinical value of technetium-99m-HMPAO-labeled leukocyte scintigraphy and spiral computed tomography in active Crohn’s disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 96, 1517–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, R.; Rambaldi, P.F.; Di Grezia, G.; Mansi, L.; Cuccurullo, V.; Cirillo, A.; Riegler, G.; Cappabianca, S.; Rotondo, A. Inflammatory bowel disease: Value in diagnosis and management of MDCT-enteroclysis and Tc-99m-HMPAO labeled leukocyte scintigraphy. Abdom. Imaging 2011, 36, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chroustova, D.; El-Lababidi, N.; Trnka, J.; Cerna, L.; Lambert, L. Scintigraphy with Tc-99m-HMPAO labeled leukocytes is still an accurate and convenient tool to rule out suspected inflammatory bowel disease in children. Nucl. Med. Rev. 2019, 22, 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Monsonis, B.; Mandoul, C.; Millet, I.; Taourel, P. Imaging of appendicitis: Tips and tricks. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 130, 109165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.; Bolus, N.E. Appendicitis imaging. Radiol. Technol. 2005, 77, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, M.W.; Lopez, R.A.; Deppen, J.G. Appendicitis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing Copyright© 2023; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Rybkin, A.V.; Thoeni, R.F. Current concepts in imaging of appendicitis. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 45, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajjar, H.; Levy, A. Imaging of appendicitis. S. Afr. Med. J. 2008, 12, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubesin, S.E.; Levine, M.S.; Laufer, I.; Herlinger, H. Double-contrast barium enema examination technique. Radiology 2000, 215, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terasawa, T.; Blackmore, C.C.; Bent, S.; Kohlwes, R.J. Systematic review: Computed tomography and ultrasonography to detect acute appendicitis in adults and adolescents. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 141, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto Leite, N.; Pereira, J.M.; Cunha, R.; Pinto, P.; Sirlin, C. CT evaluation of appendicitis and its complications: Imaging techniques and key diagnostic findings. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2005, 185, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.A. Imaging Acute Appendicitis. Semin. Ultrasound CT MR. 2008, 29, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Old, J.L.; Dusing, R.W.; Yap, W.; Dirks, J. Imaging for suspected appendicitis. Am. Fam. Physician 2005, 71, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Gaskill, C.E.; Simianu, V.V.; Carvell, J.; Hippe, D.S.; Bhargava, P.; Flum, D.R.; Davidson, G.H. Use of Computed Tomography to Determine Perforation in Patients with Acute Appendicitis. Curr. Probl. Diagn. Radiol. 2018, 47, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Malley, M.E.; Halpern, E.; Mueller, P.R.; Gazelle, G.S. Helical CT protocols for the abdomen and pelvis: A survey. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2000, 175, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balthazar, E.J.; Birnbaum, B.A.; Yee, J.; Megibow, A.J.; Roshkow, J.; Gray, C. Acute appendicitis: CT and US correlation in 100 patients. Radiology 1994, 190, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.M.; Rhea, J.T.; Novelline, R.A.; Mostafavi, A.A.; Lawrason, J.N.; McCabe, C.J. Helical CT combined with contrast material administered only through the colon for imaging of suspected appendicitis. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1997, 169, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, S.W.; Labuski, M.R.; Kasales, C.J.; Blebea, J.S.; Meilstrup, J.W.; Holley, G.P.; LaRusso, S.A.; Holliman, J.; Ruggiero, F.M.; Mauger, D. Comparative assessment of CT and sonographic techniques for appendiceal imaging. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2001, 176, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ege, G.; Akman, H.; Sahin, A.; Bugra, D.; Kuzucu, K. Diagnostic value of unenhanced helical CT in adult patients with suspected acute appendicitis. Br. J. Radiol. 2002, 75, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Lppolito, G.; de Mello, G.G.; Szejnfeld, J. The value of unenhanced CT in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis. Sao Paulo Med. J. Rev. Paul. Med. 1998, 116, 1838–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, M.J.; Liu, D.M.; Huynh, M.D.; Jeffrey, R.B.; Mindelzun, R.E.; Katz, D.S. Suspected acute appendicitis: Nonenhanced helical CT in 300 consecutive patients. Radiology 1999, 213, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, A.J. Unenhanced CT in the evaluation of the acute abdomen: The community hospital experience. Semin. Ultrasound CT MRI 1999, 20, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Salminen, P.; Tannaphai, P.; Lee, K.H. Low-Dose Abdominal CT for Evaluating Suspected Appendicitis in Adolescents and Young Adults: Review of Evidence. Korean J. Radiol. 2022, 23, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sippola, S.; Virtanen, J.; Tammilehto, V.; Grönroos, J.; Hurme, S.; Niiniviita, H.; Lietzen, E.; Salminen, P. The Accuracy of Low-dose Computed Tomography Protocol in Patients with Suspected Acute Appendicitis: The OPTICAP Study. Ann. Surg. 2020, 271, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapna, T. A prospective comparative study of Alvarado score and ultrasound imaging in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis. Int. J. Surg. 2021, 5, 301–303. [Google Scholar]
- Guillerman, R.P.; Ng, C.S. Ultrasound of Appendicitis. Ultrasound 2005, 13, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, Y.S.; Gong, N.M. Diagnostic value of ultrasound compared to CT in patients with suspected acute appendicitis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 10, 14377–14385. [Google Scholar]
- Brenner, D.J.; Elliston, C.D.; Hall, E.J.; Berdon, W.E. Estimated risks of radiation-induced fatal cancer from pediatric CT. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2001, 176, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, K.; Tsuda, M. Ultrasound-based decision making in the treatment of acute appendicitis in children. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2004, 39, 1316–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alelyani, M.; Hadadi, I.; Shubayr, N.; Alashban, Y.; Alqahtani, M.; Adam, M.; Almater, H.; Alamri, S. Evaluation of Ultrasound Accuracy in Acute Appendicitis Diagnosis. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdawati, A.; Sari, I. The Evaluation of the Sensitivity and Specificity of Ultrasound Examination in Patients with Suspected Acute Appendicitis. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Sustainable Innovation—Health Science and Nursing (ICoSIHSN), Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 13–14 October 2020; pp. 156–160. [Google Scholar]
- Conwell, N.K.; Kennedy, N.J.; Quinton, A.E. Diagnostic performance of ultrasound to differentiate perforated from non-perforated paediatric appendicitis: A narrative review. Sonography 2020, 7, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearl, Y.L.; Claudius, I.; Behar, S.; Cooper, J.; Dollbaum, R.; Hardasmalani, M.; Hardiman, K.; Rose, E.; Santillanes, G.; Berdahl, C. Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Ultrasound for Appendicitis in Diagnostic and Nondiagnostic Studies. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2016, 23, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, K. Acute abdominal emergencies associated with pregnancy. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2002, 45, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wi, S.A.; Kim, D.J.; Cho, E.S.; Kim, K.A. Diagnostic performance of MRI for pregnant patients with clinically suspected appendicitis. Abdom. Radiol. 2018, 43, 3456–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspelund, G.; Fingeret, A.; Gross, E.; Kessler, D.; Keung, C.; Thirumoorthi, A.; Oh, P.S.; Behr, G.; Chen, S.; Lampl, B.; et al. Ultrasonography/MRI Versus CT for Diagnosing Appendicitis. Pediatrics 2014, 133, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theilen, L.H.; Mellnick, V.M.; Longman, R.E.; Tuuli, M.G.; Odibo, A.O.; Macones, G.A.; Cahill, A.G. Utility of magnetic resonance imaging for suspected appendicitis in pregnant women. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 212, 345.E1–345.E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufini, V.; Calcagni, M.L.; Baum, R.P. Imaging of neuroendocrine tumors. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2006, 36, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujral, D.M.; Bhattacharyya, S. Cardiac manifestations of gastrointestinal carcinoid tumor. Future Cardiol. 2013, 9, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaltsas, G.A.; Besser, G.M.; Grossman, A.B. The diagnosis and medical management of advanced neuroendocrine tumors. Endocr. Rev. 2004, 25, 458–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Rest, C.; Bomanji, J.B.; Costa, D.C.; Townsend, C.E.; Visvikis, D.; Ell, P.J. Functional imaging of malignant paragangliomas and carcinoid tumours. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2001, 28, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearon, E.R.; Vogelstein, B. A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell 1990, 61, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, M.D.; Meisetschlaeger, G.; Gaa, J.; Rummeny, E.J. Assessment of the extent of metastases of gastrointestinal carcinoid tumors using whole-body PET, CT, MRI, PET/CT and PET/MRI. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2006, 11, 58–65. [Google Scholar]
- Bader, T.R.; Semelka, R.C.; Chiu, V.C.Y.; Armao, D.M.; Woosley, J.T. MRI of carcinoid tumors: Spectrum of appearances in the gastrointestinal tract and liver. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2001, 14, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langman, G.; Patel, A.; Bowley, D.M. Size and Distribution of Lymph Nodes in Rectal Cancer Resection Specimens. Dis. Colon Rectum 2015, 58, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, D.M.; Brown, G.; Temple, L.; Blake, H.; Raja, A.; Toomey, P.; Bett, N.; Farhat, S.; Norman, A.R.; Daniels, I.; et al. Distribution of mesorectal lymph nodes in rectal cancer: In vivo MR imaging compared with histopathological examination. Initial observations. Eur. Radiol. 2005, 15, 1650–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelen, S.M.E.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Lahaye, M.J.; Kessels, A.G.H.; Beets, G.L. Location of involved mesorectal and extramesorectal lymph nodes in patients with primary rectal cancer: Preoperative assessment with MR imaging. EJSO 2008, 34, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, D.M.; George, C.; Temple, L.; Collins, D.J.; Toomey, P.; Raja, A.; Bett, N.; Farhat, S.; Husband, J.E.; Brown, G. Diagnostic Accuracy of Nodal Enhancement Pattern of Rectal Cancer at MRI Enhanced with Ultrasmall Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide: Findings in Pathologically Matched Mesorectal Lymph Nodes. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 194, W505–W513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashir, M.R.; Bhatti, L.; Marin, D.; Nelson, R.C. Emerging Applications for Ferumoxytol as a Contrast Agent in MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 41, 884–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccioni, F.; Almberger, M.; Bruni, A.; Parlanti, S.; Marini, M. Magnetic resonance imaging of an ileal carcinoid tumor correlation with CT and US. Clin. Imaging 2003, 27, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickhardt, P.J.; Hassan, C.; Halligan, S.; Marmo, R. Colorectal Cancer: CT Colonography and Colonoscopy for Detection-Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Radiology 2011, 259, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.B.; Olafsen, T.; Zhang, X.Z.; Cao, Q.Z.; Gambhir, S.S.; Williams, L.E.; Wu, A.M.; Chen, X.Y. PET imaging of colorectal cancer in xenograft-bearing mice by use of an F-18-labeled T84.66 anti-carcinoembryonic antigen diabody. J. Nucl. Med. 2007, 48, 304–310. [Google Scholar]
- Schillaci, O.; Scopinaro, F.; Angeletti, S.; Tavolaro, R.; Danieli, R.; Annibale, B.; Gualdi, G.; Delle Fave, G. SPECT improves accuracy of somatostatin receptor scintigraphy in abdominal carcinoid tumors. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 1996, 37, 1452–1456. [Google Scholar]
- Fishman, E.K.; Urban, B.A.; Hruban, R.H. CT of the stomach: Spectrum of disease. Radiographics 1996, 16, 1035–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asplund, J.; Kauppila, J.H.; Mattsson, F.; Lagergren, J. Survival Trends in Gastric Adenocarcinoma: A Population-Based Study in Sweden. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 25, 2693–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, K.M.; Fishman, E.K. Current role of CT in Imaging of the stomach. Radiographics 2003, 23, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Han, F.; Sun, X. Differential Diagnosis of Spiral CT in Invasive Adenocarcinoma of the Lung and Preinvasive Lesions. Chin. Comput. Med. Imaging 2014, 20, 329–333. [Google Scholar]
- Hori, S.; Tsuda, K.; Murayama, S.; Matsushita, M.; Yukawa, K.; Kozuka, T. CT of gastric carcinoma: Preliminary results with a new scanning technique. Radiographics 1992, 12, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.H.; Ko, Y.T. The role of 3D spiral CT in early gastric carcinoma. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1998, 22, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Ha, H.K. Gastric cancer by multidetector row CT: Preoperative staging. Abdom. Imaging 2005, 30, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.Y.; Liu, S.; Qiao, X.M.; Li, L.; Ji, C.F.; Zhou, Z.Y. Clinicopathological features and CT findings of papillary gastric adenocarcinoma. Abdom. Radiol. 2022, 47, 3698–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buy, J.N.; Moss, A.A. Computed tomography of gastric lymphoma. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1982, 138, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.Q.; Luo, Y.P.; Cao, X.X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F. Spontaneous Regression of Clinically Indolent Lymphomas Revealed by F-18-FDG PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2019, 44, 321–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Huang, X.Y.; Zhang, L.J. Whole body FDG-PET/CT for the assessment of bone marrow infiltration in patients with newly diagnosed lymphoma. Med. Clin. 2020, 154, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, K.M.; Ho, S.K.D.; Wong, B.Y.K.; Gill, H.; Khong, P.L.; Lee, E.Y.P. Beyond the lymph nodes: FDG-PET/CT in primary extranodal lymphoma. Clin. Imaging 2017, 42, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Fu, Q.; Dong, Y.W.; Liu, J.J.; Song, X.Y.; Dai, D.; Zuo, C.; Xu, W.G. (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography comparison of gastric lymphoma and gastric carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 7787–7796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Suman, S.K.; Singh, H.; Sharma, A.; Bal, C.; Malhotra, A.; Kumar, R. Primary gastric lymphoma: Utility of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography-computed tomography for detecting relapse after treatment. Leuk. Lymphoma 2013, 54, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammohan, A.; Sathyanesan, J.; Rajendran, K.; Pitchaimuthu, A.; Perumal, S.K.; Srinivasan, U.P.; Ramasamy, R.; Palaniappan, R.; Govindan, M. A gist of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: A review. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2013, 5, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parab, T.M.; DeRogatis, M.J.; Boaz, A.M.; Grasso, S.A.; Issack, P.S.; Duarte, D.A.; Urayeneza, O.; Vahdat, S.; Qiao, J.H.; Hinika, G.S. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: A comprehensive review. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2019, 10, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Li, J. CT diagnostic value in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Chin. J. Med. Imaging Technol. 2005, 21, 90–92. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Zhai, Z.; Yang, L.; Miao, N.; Zhao, C.; Deng, J. MSCT Diagnosis of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor. Chin. Comput. Med. Imaging 2010, 16, 221–225. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Ye, Z.; Li, X.; Luo, H.; Cui, X.; Wang, H. Clinical value of multislice spiral computed tomography examination on risk assessment of gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Chin. J. Dig. Surg. 2015, 14, 242–247. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Xie, C.; Huang, Z. Multi-slice spiral CT diagnosis of extra-gastrointestinal stromal tumors. J. Pract. Radiol. 2014, 30, 954. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.-f.; Qiu, S.-j.; Song, Y.-d.; Han, L.-j. Value of multi-slice spiral CT in the diagnosis and therapeutic effect evaluation of gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao = J. South. Med. Univ. 2010, 30, 875–877. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrakopoulou-Strauss, A.; Ronellenfitsch, U.; Cheng, C.; Pan, L.; Sachpekidis, C.; Hohenberger, P.; Henzler, T. Imaging therapy response of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) with FDG PET, CT and MRI: A systematic review. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2017, 5, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzei, M.A.; Cioffi Squitieri, N.; Vindigni, C.; Guerrini, S.; Gentili, F.; Sadotti, G.; Mercuri, P.; Righi, L.; Lucii, G.; Mazzei, F.G.; et al. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST): A proposal of a “CT-based predictive model of Miettinen index” in predicting the risk of malignancy. Abdom. Radiol. 2020, 45, 2989–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Ota, S.; Yamasaki, M.; Batsaikhan, B.; Furukawa, A.; Watanabe, Y. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: A comprehensive radiological review. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2022, 40, 1105–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junping, W.; Renju, B.A.I.; Haoran, S.U.N.; Xin, Z.; Yang, J. The Imaging Features of Multi-Spiral CT and MRI in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors and Correlation with Pathology. Tianjin Med. J. 2008, 36, 933–935. [Google Scholar]
- Cannella, R.; La Grutta, L.; Midiri, M.; Bartolotta, T.V. New advances in radiomics of gastrointestinal stromal tumors. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 4729–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urs, A.; Narula, P.; Thomson, M.A. Peptic ulcer disease. Paediatr. Child Health 2014, 24, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cello, J.P. Helicobacter pylori and peptic ulcer disease. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1995, 164, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannis, M.; Dimitra, Z.; Hristos, H.; Ioannis, D. Peptic ulcer perforation: Sonographic imaging of active fluid leakage. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2006, 34, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, S.; Ahmed, A.R.; Johnson, J.; Boss, T.; O’Malley, W. CT scan diagnosis of bleeding peptic ulcer after gastric bypass. Obes. Surg. 2007, 17, 1520–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleem, A.; Shah, H. Gastric Varices. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing Copyright© 2023; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Xiang, M.; Cheng, F.; Shi, H.T.; Gao, J.; He, S.; Mei, Z.C.; Zhang, H. Application of multi-slice spiral CT to assess vascular volume for the diagnosis and treatment of gastric varices. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi = Zhonghua Ganzangbing Zazhi = Chin. J. Hepatol. 2019, 27, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.I.; Fu-rong, L.U.; Qian-hong, M.A. CT study on the blood supply and vein shunt of esophageal and gastric varices. Chin. J. Clin. Anat. 2009, 27, 184–186. [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson, K.G.; Bailey, B.M.; Balint, T.D.; Pofahl, W.E. Meckel’s diverticulum: Review and surgical management. Curr. Surg. 2001, 58, 455–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, P.; Gourtsoyiannis, N.; Bezzi, M.; Raptopoulos, V.; Massa, R.; Capanna, G.; Pedicini, V.; Coe, M. Meckel’s diverticulum: Imaging diagnosis. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1996, 166, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, J.; Kumar, V.; Shah, D.K. Meckel’s diverticulum: A systematic review. J. R. Soc. Med. 2006, 99, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enge, I.; Frimann-Dahl, J. Radiology in acute abdominal disorders due to meckel’s diverticulum. Br. J. Radiol. 1964, 37, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltes, P.; Dray, X.; Riccioni, M.E.; Perez-Cuadrado-Robles, E.; Fedorov, E.; Wiedbrauck, F.; Chetcuti Zammit, S.; Cadoni, S.; Bruno, M.; Rondonotti, E.; et al. Small-bowel capsule endoscopy in patients with Meckel’s diverticulum: Clinical features, diagnostic workup, and findings. A European multicenter I-CARE study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2023, 97, 917–926.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.Y.; Hong, S.S.; Park, H.J.; Lee, H.K.; Shin, H.C.; Choi, G.C. The many faces of Meckel’s diverticulum and its complications. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 61, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigogosyan, M.; Dolinskas, C. CT demonstration of inflamed Meckel diverticulum. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1990, 14, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, G.L.; Birnbaum, B.A.; Balthazar, E.J. CT of Meckel’s diverticulitis in 11 patients. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2004, 182, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russ, P.D.; Friefeld, G.D.; Nauck, C.J.; Wilmouth, R.J. Infarcted Meckel diverticulum detected by CT. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1988, 150, 299–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Singh, P.; Kumari, P.; Kaushik, R. Revisiting the forgotten remnant: Imaging spectrum of Meckel’s diverticulum. SA J. Radiol. 2022, 26, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglinte, D.D.; Elmore, M.F.; Isenberg, M.; Dolan, P.A. Meckel diverticulum: Radiologic demonstration by enteroclysis. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1980, 134, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.E.; Sellink, J.L. Enterocylsis: The small bowel enema. How to succeed and how to fail. Gastrointest. Radiol. 1979, 4, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurley, P.D.; Halliday, K.E.; Somers, J.M.; Al-Daraji, W.I.; Ilyas, M.; Broderick, N.J. Radiological features of Meckel’s diverticulum and its complications. Clin. Radiol. 2009, 64, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayes, K.M.; Menias, C.O.; Harvin, H.J.; Francis, I.R. Imaging manifestations of Meckel’s diverticulum. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 189, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, P.V.; Bartold, S.P.; Fink-Bennett, D.M.; Jolles, P.R.; Lull, R.J.; Maurer, A.H.; Seabold, J.E. Procedure guideline for gastrointestinal bleeding and Meckel’s diverticulum scintigraphy. J. Nucl. Med. 1999, 40, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Connolly, L.P.; Treves, S.T.; Bozorgi, F.; O’Connor, S.C. Meckel’s diverticulum: Demonstration of heterotopic gastric mucosa with technetium-99m-pertechnetate SPECT. J. Nucl. Med. 1998, 39, 1458–1460. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tennant, S.L.; Ganatra, R. Meckel’s diverticulum—An incidental finding on PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2007, 32, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.Y.; Li, X.; Ye, B.X.; Jiang, J.X. A fundic gland polyp and peptic ulcer in Meckel’s diverticulum. Dig. Liver Dis. 2022, 54, 1439–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.B.; Zhuang, P.J.; Chen, G.; Huang, Y.L.; Dong, K.R.; Xiao, X.M.; Zheng, S.; Sun, S. Clinical Characteristics and Management of Colorectal Vascular Malformation in Children: A Retrospective Study of 23 Cases. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefny, A.F.; Corr, P.; Abu-Zidan, F.M. The role of ultrasound in the management of intestinal obstruction. J. Emerg. Trauma Shock 2012, 5, 84–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, W. Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ripamonti, C.I.; Easson, A.M.; Gerdes, H. Management of malignant bowel obstruction. Eur. J. Cancer 2008, 44, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, P.G.; Raiji, M. Evaluation and Management of Intestinal Obstruction. Am. Fam. Physician 2011, 83, 159–165. [Google Scholar]
- Kwang-baek, K.; Woo, Y.W. Extraction of Intestinal Obstruction in X-ray Images Using PCM. J. Korea Inst. Inf. Commun. Eng. 2020, 24, 1618–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taydas, O.; Unal, E.; Onur, M.R.; Akpinar, E. Role of Computed Tomography in Intestinal Obstruction. Istanb. Med. J. 2018, 19, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, N.; Du, B.; Li, Y. Clinical Significance of 18F-FDG PET/CT in the Etiological Diagnosis of Postoperative Intestinal Obstruction in Patients with Gastrointestinal Cancer. J. China Med. Univ. 2016, 45, 422–425. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhao, Z.; Li, X.L.; Zhao, M.T.; Kefei, H. Appearance of fetal intestinal obstruction on fetalMRI. Prenat. Diagn. 2020, 40, 1398–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Zidan, F.M.; Abdel-Kader, S.; Abusharia, M.I.; Mousa, H. Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the management of intestinal obstruction during the first trimester of pregnancy. ANZ J. Surg. 2018, 88, E683–E684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzal, S.; Ahmad, F.; Farooq, F. Role of Multi-Detector Computed Tomography in the Diagnosis of Intestinal Obstruction. Cureus 2023, 15, e33730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megibow, A.J.; Balthazar, E.J.; Cho, K.C.; Medwid, S.W.; Birnbaum, B.A.; Noz, M.E. Bowel obstruction: Evaluation with CT. Radiology 1991, 180, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.C.; Pimenta, M.; Guimarães, L.S. Small bowel obstruction: What to look for. Radiographics 2009, 29, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H. Ultrasound examination of gastrointestinal tract diseases. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2000, 15, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.B.; Pang, L.; Liu, C.; Chen, X.Y.; Qiao, Q.; Zhang, C. Ultrasonic Diagnosis of Intestinal Obstruction in Neonates-Original Article. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.G.; Dong, P.; Wu, X.S.; Li, M.L.; Ding, Q.C.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J.H.; Weng, H.; Ding, Q.; Tan, Z.J.; et al. Surgical management of patients with bowel obstructions secondary to gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 4559–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, K.; Ryu, S.; Okamoto, A.; Hara, K.; Ishida, K.; Ito, R.; Nakabayashi, Y. Usefulness of blood flow evaluation with indocyanine green fluorescence imaging during laparoscopic surgery for strangulated bowel obstruction: A cohort study. Asian J. Surg. 2022, 45, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, W.F.; Liberman, J.N.; Sandler, R.S.; Woods, M.S.; Stemhagen, A.; Chee, E.; Lipton, R.B.; Farup, C.E. Epidemiology of constipation (EPOC) study in the United States: Relation of clinical subtypes to sociodemographic features. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 94, 3530–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganeshan, A.; Anderson, E.M.; Upponi, S.; Planner, A.C.; Slater, A.; Moore, N.; D’Costa, H.; Bungay, H. Imaging of obstructed defecation. Clin. Radiol. 2008, 63, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, S.S. Imaging of Constipation and Its Complications. In Constipation; Gyula, M., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2018; Chapter 4. [Google Scholar]
- Vitton, V.; Vignally, P.; Barthet, M.; Cohen, V.; Durieux, O.; Bouvier, M.; Grimaud, J.C. Dynamic Anal Endosonography and MRI Defecography in Diagnosis of Pelvic Floor Disorders: Comparison with Conventional Defecography. Dis. Colon Rectum 2011, 54, 1398–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alame, A.M.; Bahna, H. Evaluation of constipation. Clin. Colon Rectal Surg. 2012, 25, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, J.E.; Weishaupt, D.; Wildermuth, S.; Willmann, J.K.; Marincek, B.; Hilfiker, P.R. Experience of 4 years with open MR defecography: Pictorial review of anorectal anatomy and disease. Radiographics 2002, 22, 817–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalwani, N.; El Sayed, R.F.; Kamath, A.; Lewis, S.; Arif, H.; Chernyak, V. Imaging and clinical assessment of functional defecatory disorders with emphasis on defecography. Abdom. Radiol. 2021, 46, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reginelli, A.; Di Grezia, G.; Gatta, G.; Iacobellis, F.; Rossi, C.; Giganti, M.; Coppolino, F.; Brunese, L. Role of conventional radiology and MRi defecography of pelvic floor hernias. BMC Surg. 2013, 13, S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, J.C.; Halligan, S.; Reznek, R.H.; Watson, S.; Bartram, C.I.; Phillips, R.; Armstrong, P. Dynamic MR imaging compared with evacuation proctography when evaluating anorectal configuration and pelvic floor movement. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1997, 169, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodfield, C.A.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Hampton, B.S.; Brody, J.M. Imaging Pelvic Floor Disorders: Trend Toward Comprehensive MRI. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 194, 1640–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, B.J.; Lim, E.; Cook, D.; Hughes, J.; Chow, C.W.; Stanton, M.P.; Bidarkar, S.S.; Southwell, B.R.; Hutson, J.M. Radionuclear transit to assess sites of delay in large bowel transit in children with chronic idiopathic constipation. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2005, 40, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskins, B.; Marek, S. Things We Do for No Reason(™): Obtaining an Abdominal X-ray to Assess for Constipation in Children. J. Hosp. Med. 2020, 15, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraikawa, M.; Takeda, T.; Oki, S.; Hojo, M.; Asaoka, D.; Iwano, T.; Uchida, R.; Utsunomiya, H.; Susuki, N.; Abe, D.; et al. Correlation between Constipation Symptoms and Abdominal CT Imaging: A Cross-Sectional Pilot Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.; Elangovan, A.; Jordan, D.W.; Katz, J.; Cooper, G.S. 10-Year Trend of Abdominal Magnetic Resonance Imaging Compared with Abdominal Computed Tomography Scans in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2022, 28, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Li, L.; Lin, L.; Shi, J.; Wang, L.V. In vivo superresolution photoacoustic computed tomography by localization of single dyed droplets. Light Sci. Appl. 2019, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beard, P. Biomedical photoacoustic imaging. Interface Focus 2011, 1, 602–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, T.; Razansky, D.; Yao, J. Listening to tissues with new light: Recent technological advances in photoacoustic imaging. J. Opt. 2019, 21, 103001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, B.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Lovell, J.F.; Zhang, Y. Imaging of Gastrointestinal Tract Ailments. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9060115
Sun B, Liu J, Li S, Lovell JF, Zhang Y. Imaging of Gastrointestinal Tract Ailments. Journal of Imaging. 2023; 9(6):115. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9060115
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Boyang, Jingang Liu, Silu Li, Jonathan F. Lovell, and Yumiao Zhang. 2023. "Imaging of Gastrointestinal Tract Ailments" Journal of Imaging 9, no. 6: 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9060115
APA StyleSun, B., Liu, J., Li, S., Lovell, J. F., & Zhang, Y. (2023). Imaging of Gastrointestinal Tract Ailments. Journal of Imaging, 9(6), 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9060115







