Combining CNNs and Markov-like Models for Facial Landmark Detection with Spatial Consistency Estimates
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (i)
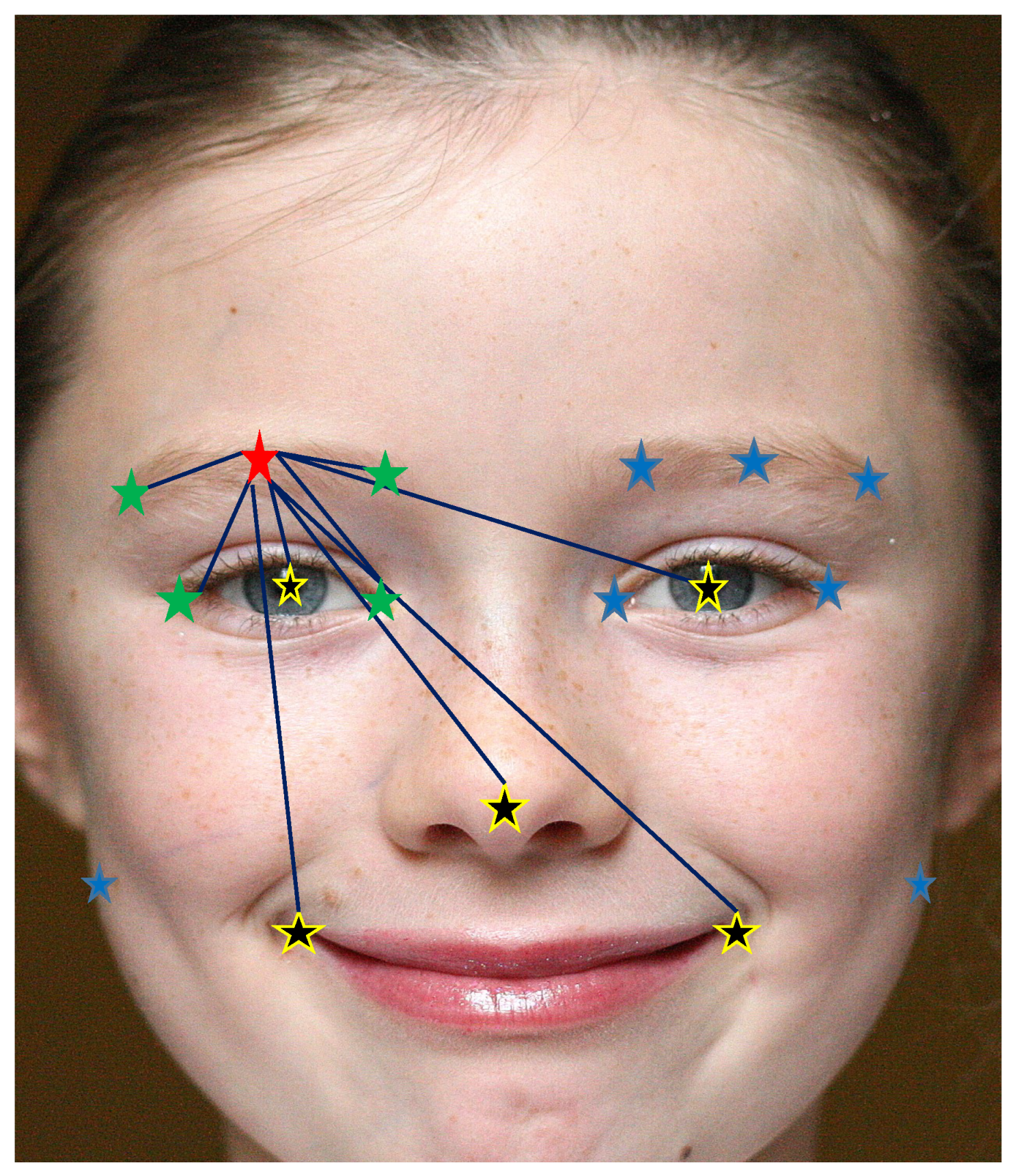
- The model was trained exclusively on 17 carefully selected landmarks preserving the global shape of the face. Additionally, these landmarks placed more emphasis on the pupil region, with 12 landmarks specifically positioned on the eyebrows and eyes, as demonstrated in Figure 3.
- (ii)
- Different image scales were run through the same layers instead of assigning a new convolution layer for each scale.
- (iii)
- runs only a subset of the available landmarks to validate their spatial consistency, instead of running the full set of them.
2. Related Work
2.1. CNN Characteristics
2.2. Postprocessing by Generative Models
3. Materials and Methods
- (i)
- High-level features generated from a sufficiently deep network to encode high-level object knowledge;
- (ii)
- Fine spatial details around the object in order to learn its discriminativeness;
- (iii)
- An explicit internal representation of entities and their relationship to associate components with one another.
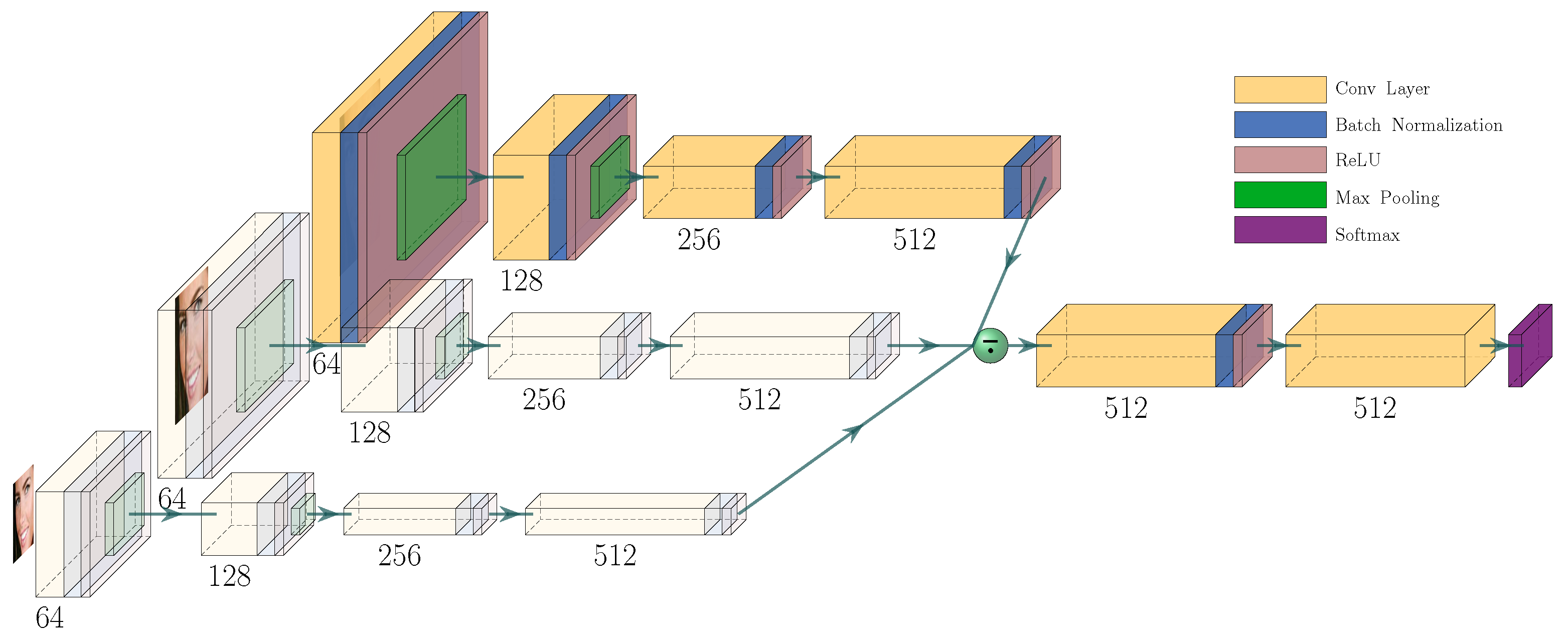
3.1. Landmark Detector
- (S1)
- Each image is processed on three different scales by four consecutive convolutional blocks, which essentially extract low-order features.
- (S2)
- Subsequently, the average of the results of the previous subpart represents the input for the remaining convolution layers, which extract the higher-order features to ultimately generate ’s output.
3.1.1. Scale Variance Handling
3.1.2. Low-/High-order Feature Compromise
3.2. Spatial Model
3.2.1. Learned Conditional Distribution
3.2.2. Neighborhood Space Definition
- presents the local consistency challenge that prioritizes the nearest neighbors over farther ones and provides an image of the local state around the subject landmark.
- presents the global structure of the human face that prioritizes some landmarks, which we call central landmarks, over others. roughly indicates the smallest set that describes most of the face structure.
3.2.3. Landmark-Specific Graph Definition
3.2.4. SpatialModel Implementation
3.3. Loss Function
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Data Enhancement
4.2. Model Training
4.3. Model Evaluation
4.3.1. Effect of Filtering on LandmarkDetector
4.3.2. Quantitative Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lorenz, B.; Strohmayr, E.; Zahn, S.; Friedburg, C.; Kramer, M.; Preising, M.; Stieger, K. Chromatic pupillometry dissects function of the three different light-sensitive retinal cell populations in RPE65 deficiency. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. IOVS 2012, 53, 5641–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takács, B.; Wechsler, H. Detection of faces and facial landmarks using iconic filter banks. Pattern Recognit. 1997, 30, 1623–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cootes, T.F.; Edwards, G.J.; Taylor, C.J. Active appearance models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2001, 23, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopaczka, M.; Acar, K.; Merhof, D. Robust Facial Landmark Detection and Face Tracking in Thermal Infrared Images using Active Appearance Models. In Proceedings of the VISIGRAPP, Rome, Italy, 27–29 February 2016; pp. 150–158. [Google Scholar]
- Cootes, T.F.; Taylor, C.J.; Cooper, D.H.; Graham, J. Active shape models-their training and application. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 1995, 61, 38–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.C.; Huang, Y.S.; Cheng, F.H. A novel ASM-based two-stage facial landmark detection method. In Proceedings of the Pacific-Rim Conference on Multimedia (PCM), Shanghai, China, 21–24 September 2010; pp. 526–537. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Hassner, T.; Kim, K.; Medioni, G.; Natarajan, P. Facial landmark detection with tweaked convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 3067–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merget, D.; Rock, M.; Rigoll, G. Robust facial landmark detection via a fully-convolutional local-global context network. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 781–790. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, K.; Attique, M.; Khan, R.U.; Syed, I.; Chung, T.S. A multi-task framework for facial attributes classification through end-to-end face parsing and deep convolutional neural networks. Sensors 2020, 20, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Liu, Q.; Yang, J.; Tao, D. M3 csr: Multi-view, multi-scale and multi-component cascade shape regression. Image Vis. Comput. 2016, 47, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, J.; Deng, J.; Zhang, K. Robust facial landmark tracking via cascade regression. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 66, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liao, M.; Li, P.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Z. Bifurcation properties for fractional order delayed BAM neural networks. Cogn. Comput. 2021, 13, 322–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Mu, D.; Liu, Z.; Pang, Y.; Liao, M.; Li, P.; Yao, L.; Qin, Q. Comparative exploration on bifurcation behavior for integer-order and fractional-order delayed BAM neural networks. Nonlinear Anal. Model. Control 2022, 27, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, W.; Aouiti, C.; Liu, Z.; Yao, L. Bifurcation insight for a fractional-order stage-structured predator–prey system incorporating mixed time delays. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2023, 118, 107043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liu, Z.; Li, P.; Yan, J.; Yao, L. Bifurcation Mechanism for Fractional-Order Three-Triangle Multi-delayed Neural Networks. Neural Process Lett. 2022, 118, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Mu, D.; Liu, Z.; Pang, Y.; Liao, M.; Aouiti, C. New insight into bifurcation of fractional-order 4D neural networks incorporating two different time delays. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2023, 118, 107043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medley, D.O.; Santiago, C.; Nascimento, J.C. Deep active shape model for robust object fitting. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 29, 2380–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovanu, S.; Toporaș, L.P.; Biswas, A.; Moraru, L. Combining sparse and dense features to improve multi-modal registration for brain DTI images. Entropy 2020, 22, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Su, H.; Ji, Q. Deep structured prediction for facial landmark detection. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 2450–2460. [Google Scholar]
- Tompson, J.J.; Jain, A.; LeCun, Y.; Bregler, C. Joint training of a convolutional network and a graphical model for human pose estimation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27. Available online: https://papers.nips.cc/paper_files/paper/2014/hash/e744f91c29ec99f0e662c9177946c627-Abstract.html (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Yue-Hei Ng, J.; Yang, F.; Davis, L.S. Exploiting local features from deep networks for image retrieval. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 53–61. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Deep convolutional network cascade for facial point detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 3476–3483. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, E.; Mo, Y.; Liu, J.; Cao, Z. Delving deep into coarse-to-fine framework for facial landmark localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 142–149. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Luo, P.; Loy, C.C.; Tang, X. Facial landmark detection by deep multi-task learning. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 94–108. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Kan, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Shan, S. A fully end-to-end cascaded cnn for facial landmark detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 12th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG), Washington, DC, USA, 30 May–3 June 2017; pp. 200–207. [Google Scholar]
- Gogić, I.; Ahlberg, J.; Pandžić, I.S. Regression-based methods for face alignment: A survey. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2021, 178, 107755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springenberg, J.T.; Dosovitskiy, A.; Brox, T.; Riedmiller, M. Striving for simplicity: The all convolutional net. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6806. [Google Scholar]
- Hannane, R.; Elboushaki, A.; Afdel, K. A divide-and-conquer strategy for facial landmark detection using dual-task CNN architecture. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 107, 107504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention (MICCAI), Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, A.; Yang, K.; Deng, J. Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; pp. 483–499. [Google Scholar]
- Bulat, A.; Tzimiropoulos, G. Human pose estimation via convolutional part heatmap regression. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; pp. 717–732. [Google Scholar]
- Erhan, D.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y.; Vincent, P. Why does unsupervised pre-training help deep learning? In Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS)—JMLR Workshop and Conference Proceedings, Sardinia, Italy, 13–15 May 2010; pp. 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, W.; Pang, J.; Yan, Q.; Tai, Y.W.; Xu, L. Accurate single stage detector using recurrent rolling convolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5420–5428. [Google Scholar]
- Van Noord, N.; Postma, E. Learning scale-variant and scale-invariant features for deep image classification. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 61, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xiao, T.; Zhang, J.; Yang, K.; Zhang, Z. Scale-invariant convolutional neural networks. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.6369. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.W.; Kook, H.K.; Sun, J.Y.; Kang, M.C.; Ko, S.J. Parallel feature pyramid network for object detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 234–250. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, A.; Tompson, J.; Andriluka, M.; Taylor, G.W.; Bregler, C. Learning human pose estimation features with convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 2–4 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Moraru, L.; Moldovanu, S.; Dimitrievici, L.T.; Dey, N.; Ashour, A.S.; Shi, F.; Fong, S.J.; Khan, S.; Biswas, A. Gaussian mixture model for texture characterization with application to brain DTI images. J. Adv. Res. 2019, 16, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felzenszwalb, P.F.; Huttenlocher, D.P. Efficient belief propagation for early vision. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2006, 70, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bo, L.; Fuxin, L. Adaptive wing loss for robust face alignment via heatmap regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6971–6981. [Google Scholar]
- Seshadri, K.; Savvides, M. Robust modified active shape model for automatic facial landmark annotation of frontal faces. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Biometrics: Theory, Applications, and Systems (BTAS), Washington, DC, USA, 28–30 September 2009; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Milborrow, S.; Nicolls, F. Locating facial features with an extended active shape model. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Marseille, France, 12–18 October 2008; pp. 504–513. [Google Scholar]
- Sagonas, C.; Antonakos, E.; Tzimiropoulos, G.; Zafeiriou, S.; Pantic, M. 300 faces in-the-wild challenge: Database and results. Image Vis. Comput. 2016, 47, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.; Brandt, J.; Lin, Z.; Bourdev, L.; Huang, T.S. Interactive facial feature localization. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Florence, Italy, 7–13 October 2012; pp. 679–692. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Qian, C.; Yang, S.; Wang, Q.; Cai, Y.; Zhou, Q. Look at boundary: A boundary-aware face alignment algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 2129–2138. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Ramanan, D. Articulated human detection with flexible mixtures of parts. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 35, 2878–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriluka, M.; Pishchulin, L.; Gehler, P.; Schiele, B. 2d human pose estimation: New benchmark and state of the art analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Colombus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 3686–3693. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Guo, Z.; Rhee, S.M.; Han, S.; Han, J.J. Towards Accurate Facial Landmark Detection via Cascaded Transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 4176–4185. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Yang, S. Leveraging intra and inter-dataset variations for robust face alignment. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 150–159. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, X.; Li, J.; Wu, J.; Chang, J.; Wan, J.; Ma, J. Multi-task adversarial autoencoder network for face alignment in the wild. Neurocomputing 2021, 437, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Shi, D.; Zheng, M.; Sadiq, M. Robust facial landmark detection via occlusion-adaptive deep networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 3486–3496. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, X.; Zhong, S.; Yan, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Y. Learning robust facial landmark detection via hierarchical structured ensemble. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 141–150. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H.; Liao, S.; Shao, L. Pixel-in-pixel net: Towards efficient facial landmark detection in the wild. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 3174–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, A.; Chong Lim, Y.; Baltrusaitis, T.; Morency, L.P. Convolutional experts constrained local model for 3d facial landmark detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2519–2528. [Google Scholar]




| LPc | RPc | NT | LMe | RMe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300 w | 98.1 | 99.03 | 94.3 | 97.1 | 97.6 |
| HELEN | 99.0 | 99.4 | 98.4 | 96.4 | 98.7 |
| WLFW | 95.31 | 96.5 | 93.3 | 92.8 | 91.6 |
| Method | NME (300 w, WFLW) | NME < 90% (300 w) |
|---|---|---|
| LAB [46] | 5.8, 5.27 | 6.5 |
| MERGET [8] | 5.29 (IBUG) | 4.5, 7 (IBUG) |
| DVLN [51] | 4.45, - | 5.5 |
| MTAAE [52] | 4.3, 5.18 | - |
| ODN [53] | 3.56, - | 9 |
| HG-HSLE [54] | 3.28, - | 4.7 |
| PIPNET [55] | 3.19, 4.31 | - |
| CE-CLM [56] | 3.15, - | 4.5 |
| DTLD [50] | 2.96, 4.05 | - |
| OURS | 3.3, 4.1 | 4.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gdoura, A.; Degünther, M.; Lorenz, B.; Effland, A. Combining CNNs and Markov-like Models for Facial Landmark Detection with Spatial Consistency Estimates. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9050104
Gdoura A, Degünther M, Lorenz B, Effland A. Combining CNNs and Markov-like Models for Facial Landmark Detection with Spatial Consistency Estimates. Journal of Imaging. 2023; 9(5):104. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9050104
Chicago/Turabian StyleGdoura, Ahmed, Markus Degünther, Birgit Lorenz, and Alexander Effland. 2023. "Combining CNNs and Markov-like Models for Facial Landmark Detection with Spatial Consistency Estimates" Journal of Imaging 9, no. 5: 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9050104
APA StyleGdoura, A., Degünther, M., Lorenz, B., & Effland, A. (2023). Combining CNNs and Markov-like Models for Facial Landmark Detection with Spatial Consistency Estimates. Journal of Imaging, 9(5), 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9050104






