VICO-DR: A Collaborative Virtual Dressing Room for Image Consulting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background
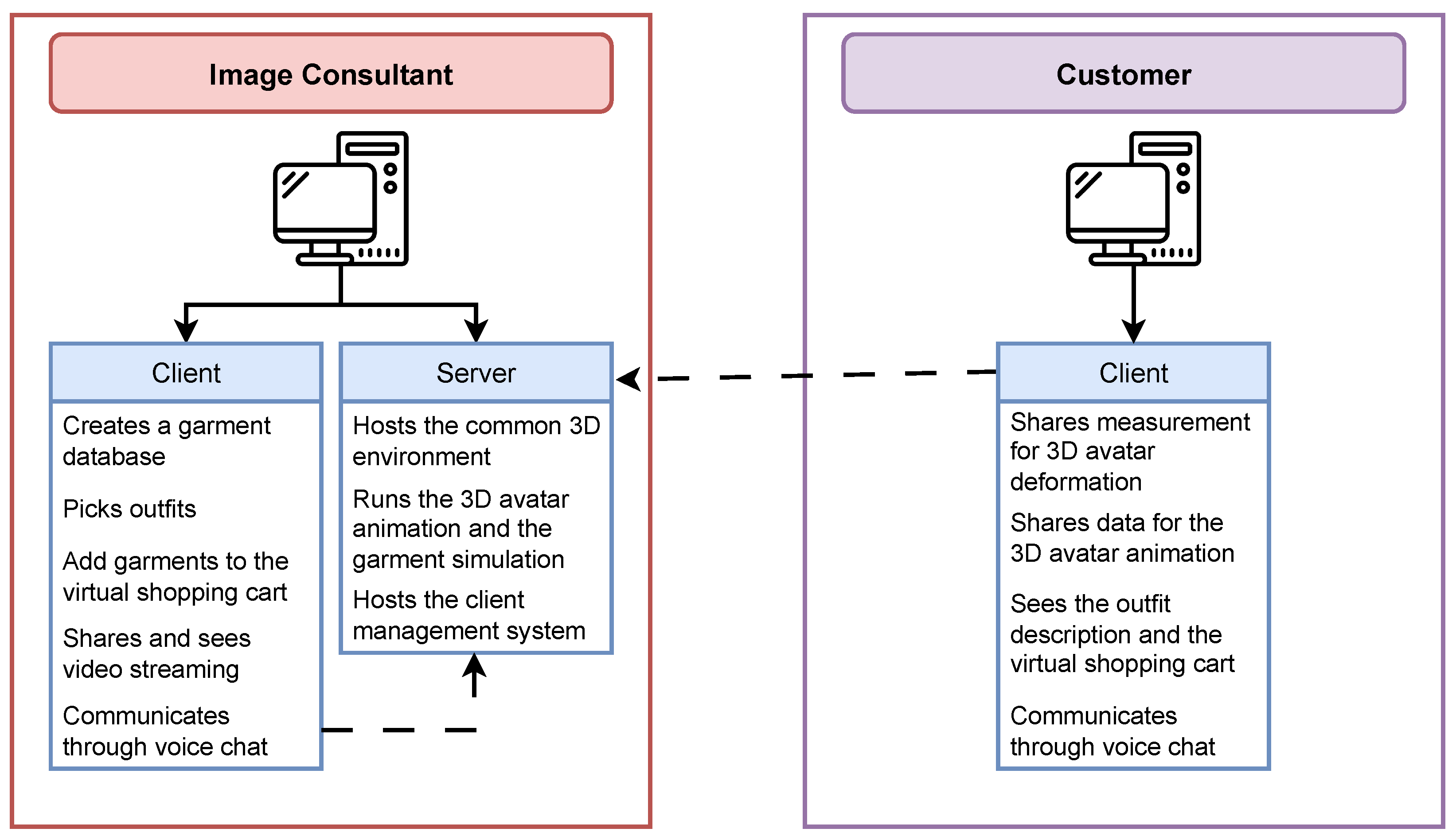
3. System Architecture Overview
4. Image Consultant Application
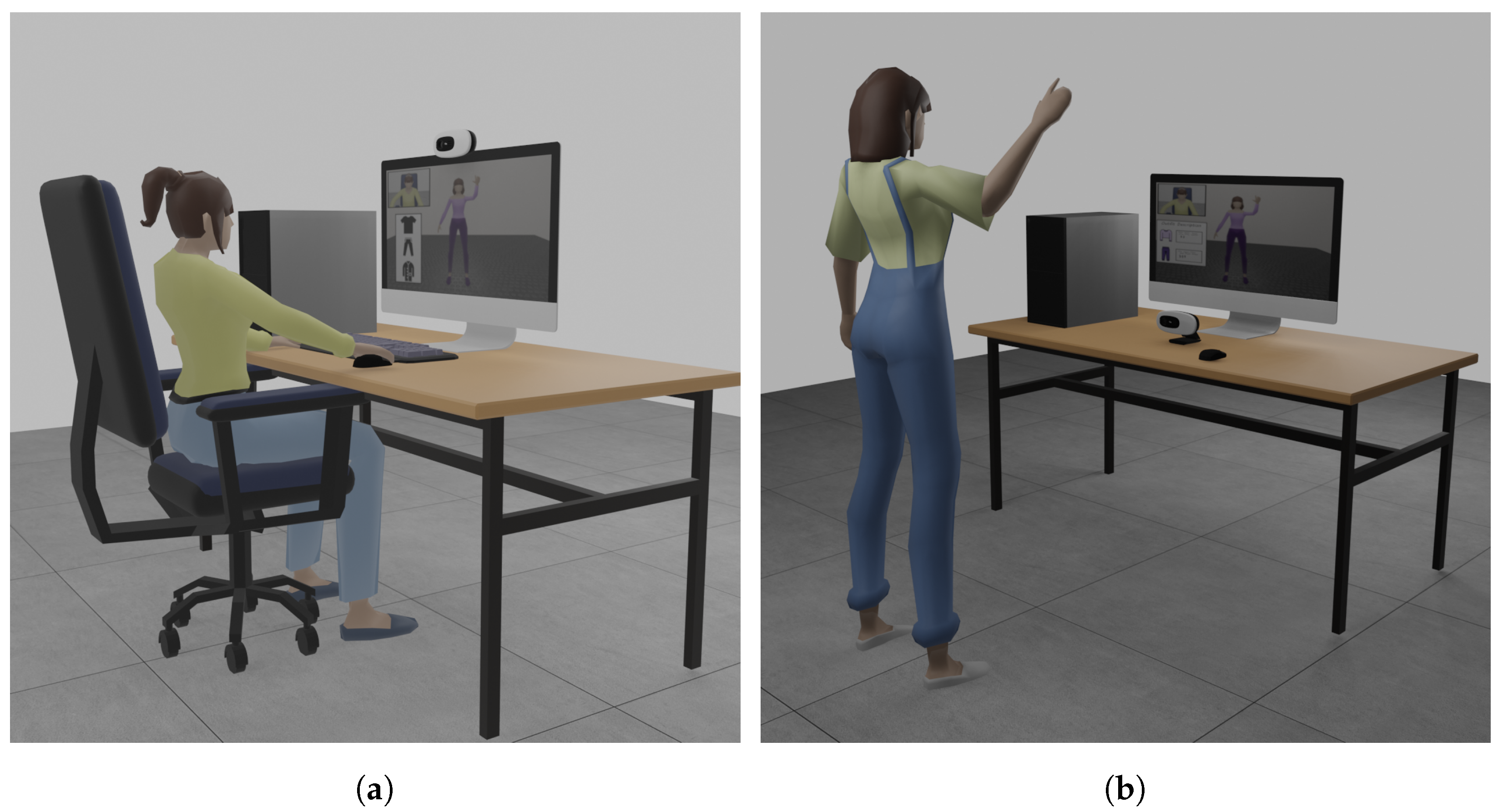
4.1. Setup
4.2. Server Side
4.2.1. Virtual Environment Configuration
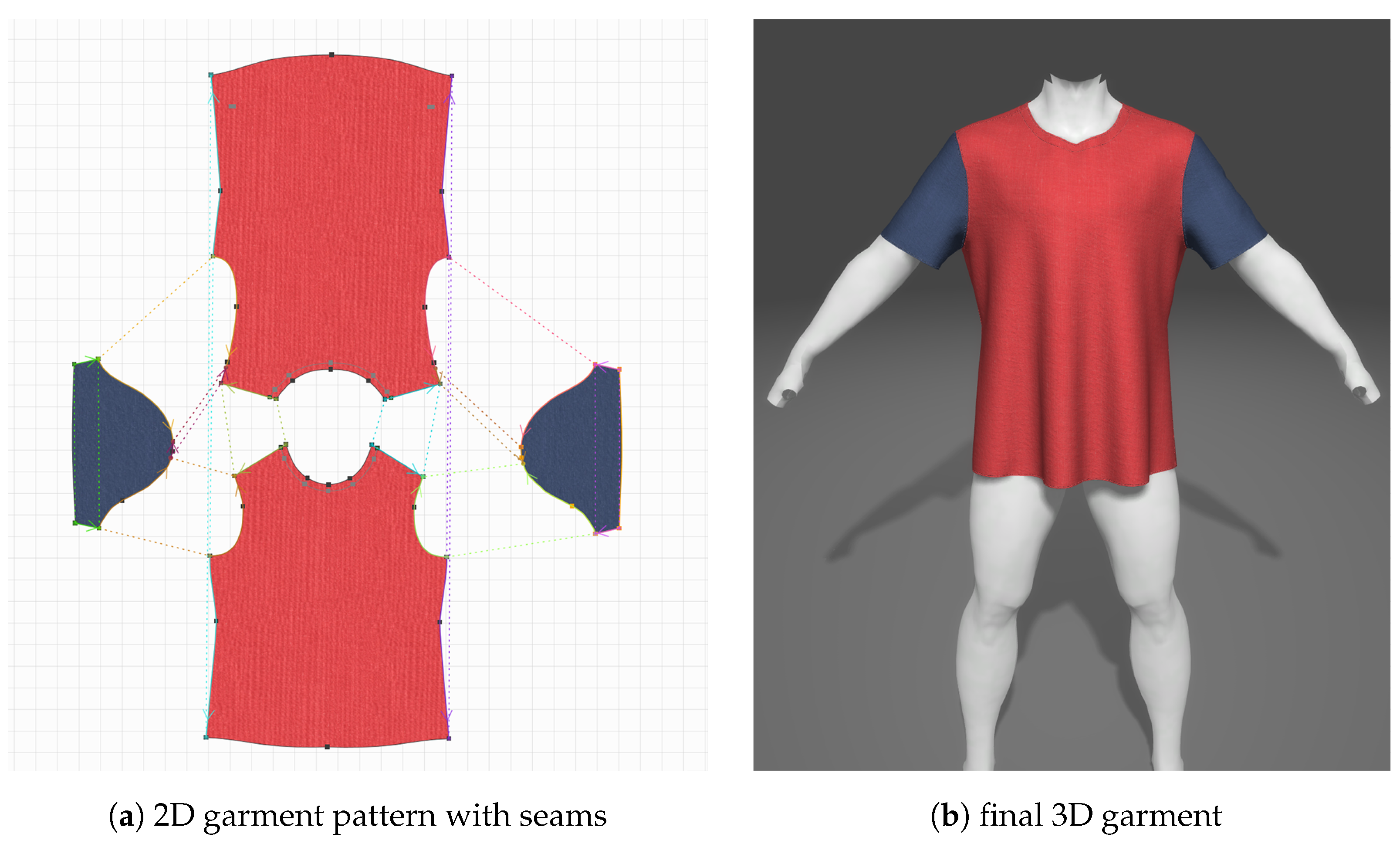
4.2.2. Garment Physical Simulation
4.2.3. Garment Database Creation
4.2.4. Audio–Video Chat System
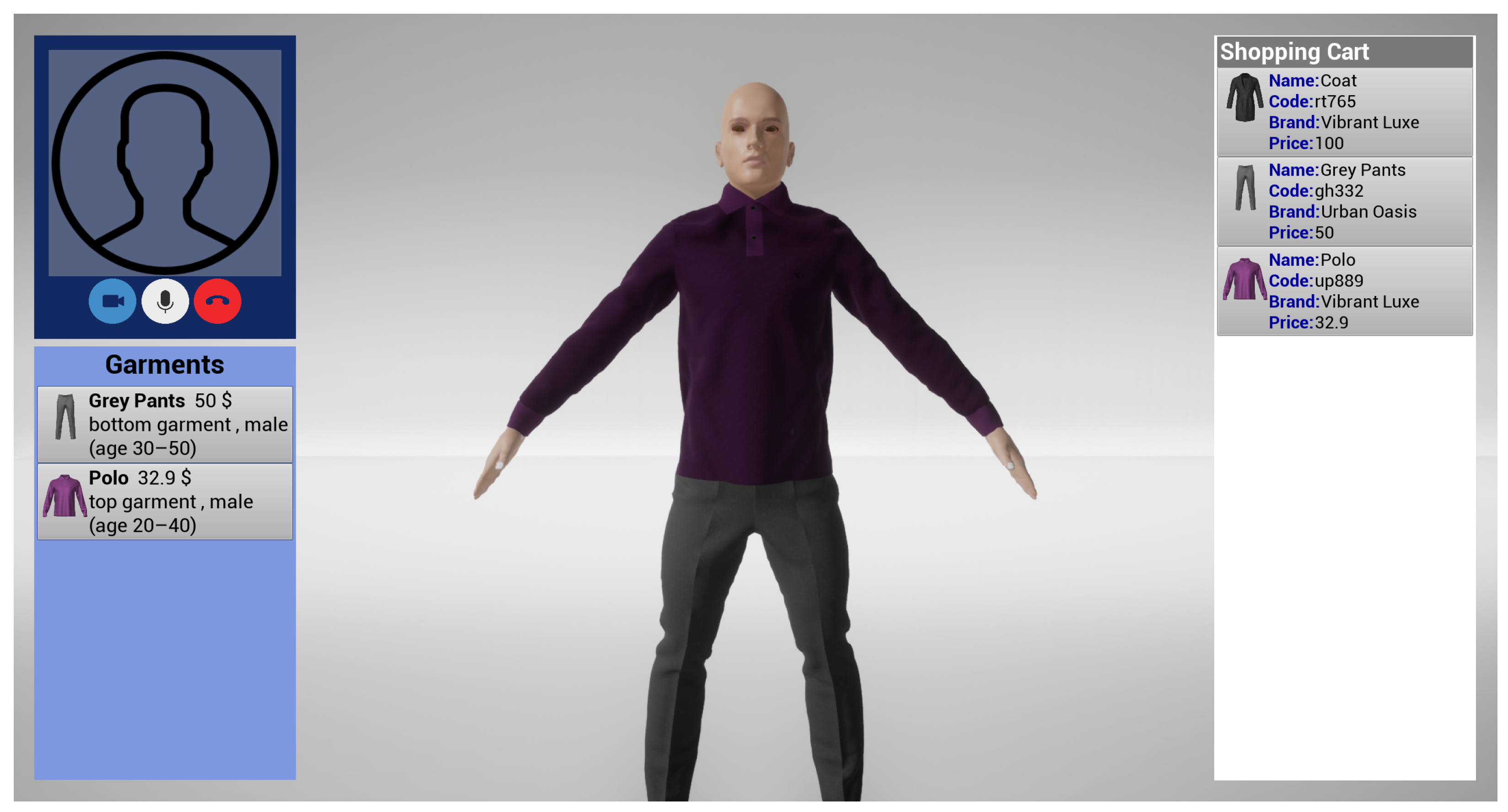
4.2.5. Customer Management System
4.3. Client Side
5. Customer Application
5.1. Setup
5.2. Client Side
5.2.1. Avatar Customization System
5.2.2. Motion Tracking System
5.2.3. Interface
6. Experimental Results
6.1. Qualitative Analysis
- G-Q1
- The VICO-DR application was easy to use and navigate.
- G-Q2
- The garment simulation algorithm in VICO-DR accurately simulated the movement and behavior of real clothing.
- G-Q3
- I found the motion tracking feature in VICO-DR to be accurate and reliable.
- G-Q4
- The motion tracking feature in VICO-DR helped me to visualize how different clothes would move and fit on the 3D avatar.
- G-Q5
- The anthropometric measurements algorithm creates a realistic 3D avatar.
- G-Q6
- The shopping cart is useful to take a trace of/purchase the selected garments.
- G-Q7
- I recommend the VICO-DR application to others.
- IC-Q1
- The customer management system in the image consultant application was easy to use and helped me keep track of customers’ information and preferences.
- IC-Q2
- Creating a new customer profile was easy to do.
- IC-Q3
- Linking a customer to a new session was straightforward.
- IC-Q4
- The garment database in the image consultant application is easy to search and navigate.
- IC-Q5
- The video-chat system helped me to better understand the customer’s needs and preferences.
- C-Q1
- I found the list of my previous sessions to be useful in remembering the outfits I tried on.
- C-Q2
- The 3D avatar accurately represents my body shape and proportions.
- C-Q3
- The 3D avatar accurately follows my movements.
- C-Q4
- The information displayed in the panel about the tried-on outfits was accurate and helpful.
- C-Q5
- The video-chat system allowed me to have a productive consultation with my image consultant.
6.2. Quantitative Analysis
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vaidya, G.M.; Loya, Y.; Dudhe, P.; Sawarkar, R.; Chanekar, S. Visualization Of Furniture Model Using Augmented Reality. In Proceedings of the 2022 Fifth International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Communication Technologies (CCICT), Sonepat, India, 8–9 July 2022; pp. 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, S.; Sanagavarapu, S. Instant Tracking-Based Approach for Interior Décor Planning with Markerless AR. In Proceedings of the 2020 Zooming Innovation in Consumer Technologies Conference (ZINC), Novi Sad, Serbia, 26–27 May 2020; pp. 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour Rahimian, F.; Chavdarova, V.; Oliver, S.; Chamo, F.; Potseluyko Amobi, L. OpenBIM-Tango integrated virtual showroom for offsite manufactured production of self-build housing. Autom. Constr. 2019, 102, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kips, R.; Jiang, R.; Ba, S.; Phung, E.; Aarabi, P.; Gori, P.; Perrot, M.; Bloch, I. Deep Graphics Encoder for Real-Time Video Makeup Synthesis From Example. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Online, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 3889–3893. [Google Scholar]
- Soares Borges, A.d.F.; Morimoto, C.H. A Virtual Makeup Augmented Reality System. In Proceedings of the 2019 21st Symposium on Virtual and Augmented Reality (SVR), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 28–31 October 2019; pp. 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adikari, S.; Ganegoda, N.; Meegama, R.; Wanniarachchi, W.K. Applicability of a Single Depth Sensor in Real-Time 3D Clothes Simulation: Augmented Reality Virtual Dressing Room Using Kinect Sensor. Adv. Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2020, 2020, 1314598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Cohen, F. In-Home Application (App) for 3D Virtual Garment Fitting Dressing Room. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 5203–5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erra, U.; Scanniello, G.; Colonnese, V. Exploring the effectiveness of an augmented reality dressing room. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 25077–25107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, K.W.; Wong, C.T.; Choi, S.K.; Zhang, L.M. Design and development of virtual dressing room system based on kinect. IJ Inf. Technol. Comput. Sci. 2018, 9, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, G.; Capece, N.; Erra, U.; Gilio, G.; Baldi, V.; Di Domenico, S.G. TryItOn: A Virtual Dressing Room with Motion Tracking and Physically Based Garment Simulation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Extended Reality, Lecce, Italy, 6–8 July 2022; pp. 63–76. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, L.; Parker, C.J.; Hart, C. How to design fashion retail’s virtual reality platforms. Int. J. Retail Distrib. Manag. 2020, 48, 1057–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obermeier, G.; Jain, S.; Auinger, A.; Werth, D. The Impact of Prior Experience on Customers Using a Mixed-Reality Shopping Assistant. In Using Optical See-through Mixed Reality for Enhanced Shopping Experience in Omnichannel Retail; Association for Information Systems: Atlanta, Georgia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann, R.; Mora, D.; Cirqueira, D.; Helfert, M.; Bezbradica, M.; Werth, D.; Weitzl, W.J.; Riedl, R.; Auinger, A. Enhancing brick-and-mortar store shopping experience with an augmented reality shopping assistant application using personalized recommendations and explainable artificial intelligence. J. Res. Interact. Mark. 2022, 17, 2040–7122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akay, K.; Kandemir, Ü.; Dalkilıç, F. Android-Based Personalized Shopping Assistant with Navigation and Augmented Reality Support. In Proceedings of the 2022 Innovations in Intelligent Systems and Applications Conference (ASYU), Antalya, Turkey, 7–9 September 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.C.; Hu, S.Y.; Wang, S.T.; Huang, S.C.C. Exploration of virtual reality-based online shopping platform. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, Orlando, FL, USA, 26–31 July 2019; pp. 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Morotti, E.; Stacchio, L.; Donatiello, L.; Roccetti, M.; Tarabelli, J.; Marfia, G. Exploiting fashion x-commerce through the empowerment of voice in the fashion virtual reality arena. Virtual Real. 2022, 26, 871–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, W.; Craig, A. Understanding Virtual Reality—Interface, Application, and Design; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Burova, A.; Mäkelä, J.; Heinonen, H.; Palma, P.B.; Hakulinen, J.; Opas, V.; Siltanen, S.; Raisamo, R.; Turunen, M. Asynchronous industrial collaboration: How virtual reality and virtual tools aid the process of maintenance method development and documentation creation. Comput. Ind. 2022, 140, 103663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.; Combe, T.; Chardonnet, J.R.; Ovtcharova, J. Asynchronous Manual Work in Mixed Reality Remote Collaboration; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, A.; Reis, G.; Stricker, D. A Survey on Synchronous Augmented, Virtual, andMixed Reality Remote Collaboration Systems. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 55, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikumar, P.; Collins, M.; Bai, H.; Billinghurst, M. XRTB: A Cross Reality Teleconference Bridge to incorporate 3D interactivity to 2D Teleconferencing. In Proceedings of the Extended Abstracts of the 2021 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Yokohama, Japan, 8–13 May 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, R.; Chang, K.C.; Weller, R.; Zachmann, G. Volumetric medical data visualization for collaborative VR environments. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality, Valencia, Spain, 25–27 November 2020; pp. 178–191. [Google Scholar]
- Chheang, V.; Saalfeld, P.; Joeres, F.; Boedecker, C.; Huber, T.; Huettl, F.; Lang, H.; Preim, B.; Hansen, C. A collaborative virtual reality environment for liver surgery planning. Comput. Graph. 2021, 99, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.H.; Wu, F.; Liang, C.J.; Li, Y.F.; Tseng, C.M.; Kang, S.C. A virtual reality tool for training in global engineering collaboration. Univers. Access Inf. Soc. 2019, 18, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unreal Engine Documentation. Available online: https://docs.unrealengine.com/4.26/en-US/InteractiveExperiences/Networking/Overview/ (accessed on 29 January 2023).
- MB-Lab. Available online: https://mb-lab-community.github.io/MB-Lab.github.io/ (accessed on 29 January 2023).
- Blender Shape Keys. Available online: https://docs.blender.org/manual/en/latest/animation/shape_keys/index.html (accessed on 29 January 2023).
- Liu, X.H.; Wu, Y.W. A 3D Display System for Cloth Online Virtual Fitting Room. In Proceedings of the 2009 WRI World Congress on Computer Science and Information Engineering, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 31 March–2 April 2009; Volume 7, pp. 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Shiratori, T.; Joo, H. FrankMocap: A Monocular 3D Whole-Body Pose Estimation System via Regression and Integration. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, H.; Neverova, N.; Vedaldi, A. Exemplar Fine-Tuning for 3D Human Pose Fitting Towards In-the-Wild 3D Human Pose Estimation. 3DV 2021, 1, 42–52. [Google Scholar]
- Likert, R. A technique for the measurement of attitudes. Arch. Psychol. 1932, 140, 55. [Google Scholar]








| Adikari et al. [6] | Li et al. [7] | Erra et al. [8] | Mok et al. [9] | VICO-DR (Our) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Game Engine | Unity | No game engine | Unity | Unity | Unreal Engine 4.27 |
| Camera System | Microsoft Kinect V2 (depth sensor) | Common RGB camera | Microsoft Kinect V2 (depth sensor) | Microsoft Kinect (depth sensor) | Common RGB camera |
| Anthropometric measurements | Real (linear and circular) | Not real | Real (only linear) | Real | Real (linear and circular) |
| Measurements calculation | Real-time and automatic | Automatic | Real-time and automatic | Manual | Real-time and automatic |
| Avatar Realism | Real image of user | Not so realistic | Real image of user | Quite realistic | High-fidelity 3D model |
| Avatar Deformation | Manual | Automatic deformation (no anthropometric measurements) | Automatic deformation (only height and width) at runtime | Automatic deformation (by a third-party software) | Automatic deformation at runtime |
| Garment Animation | Keyframe animation | Static fitting without animation | Keyframe animation | Physically-based simulation | Physically-based simulation |
| Body Tracking | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Gesture Recognition | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Collaborative image consulting | No | No | No | No | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manfredi, G.; Gilio, G.; Baldi, V.; Youssef, H.; Erra, U. VICO-DR: A Collaborative Virtual Dressing Room for Image Consulting. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9040076
Manfredi G, Gilio G, Baldi V, Youssef H, Erra U. VICO-DR: A Collaborative Virtual Dressing Room for Image Consulting. Journal of Imaging. 2023; 9(4):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9040076
Chicago/Turabian StyleManfredi, Gilda, Gabriele Gilio, Vincenzo Baldi, Hiba Youssef, and Ugo Erra. 2023. "VICO-DR: A Collaborative Virtual Dressing Room for Image Consulting" Journal of Imaging 9, no. 4: 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9040076
APA StyleManfredi, G., Gilio, G., Baldi, V., Youssef, H., & Erra, U. (2023). VICO-DR: A Collaborative Virtual Dressing Room for Image Consulting. Journal of Imaging, 9(4), 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9040076







