Noise Reduction for a Virtual Grid Using a Generative Adversarial Network in Breast X-ray Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Compliance with Ethical Standards
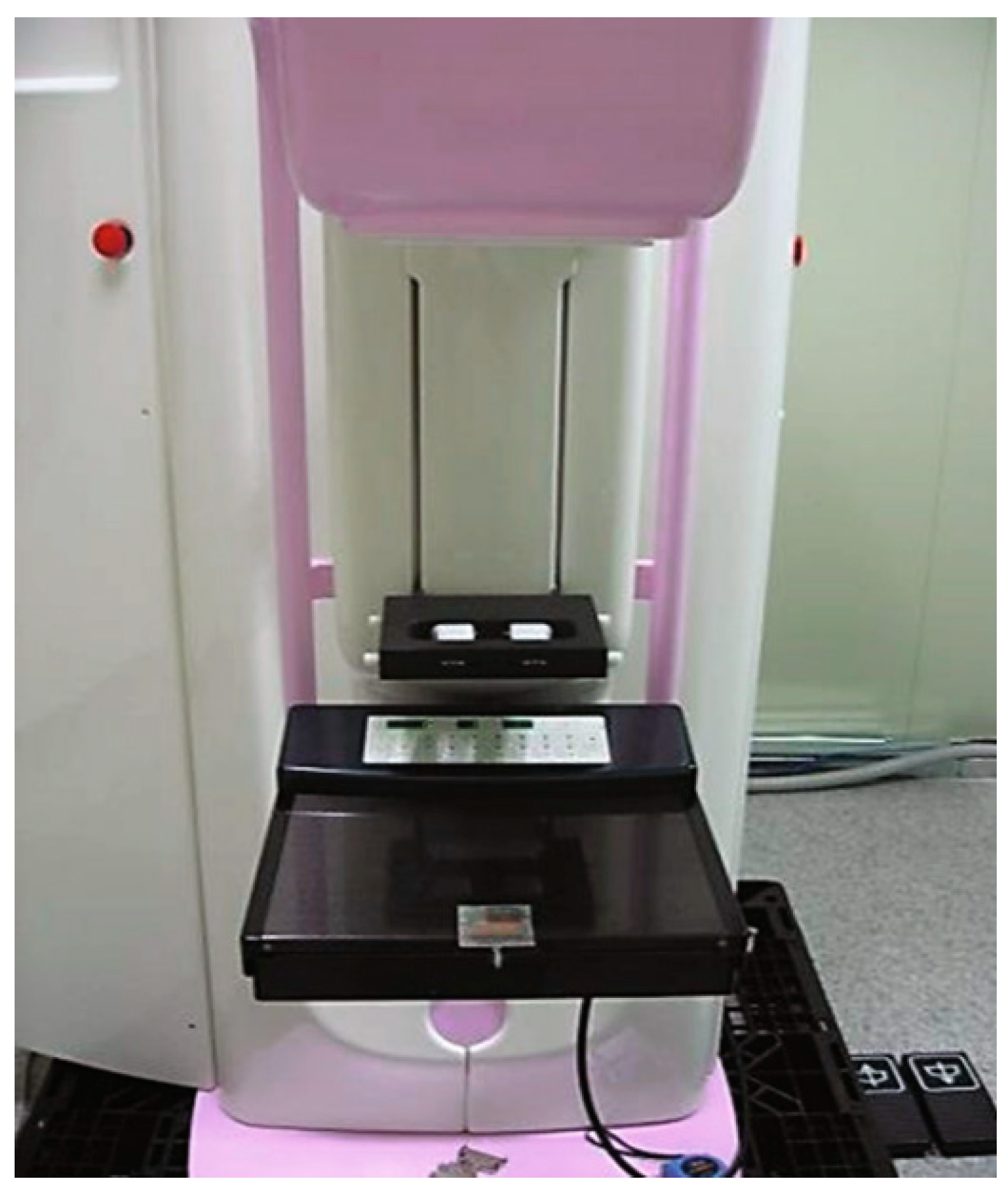
2.2. Acquisition of Breast X-ray Images
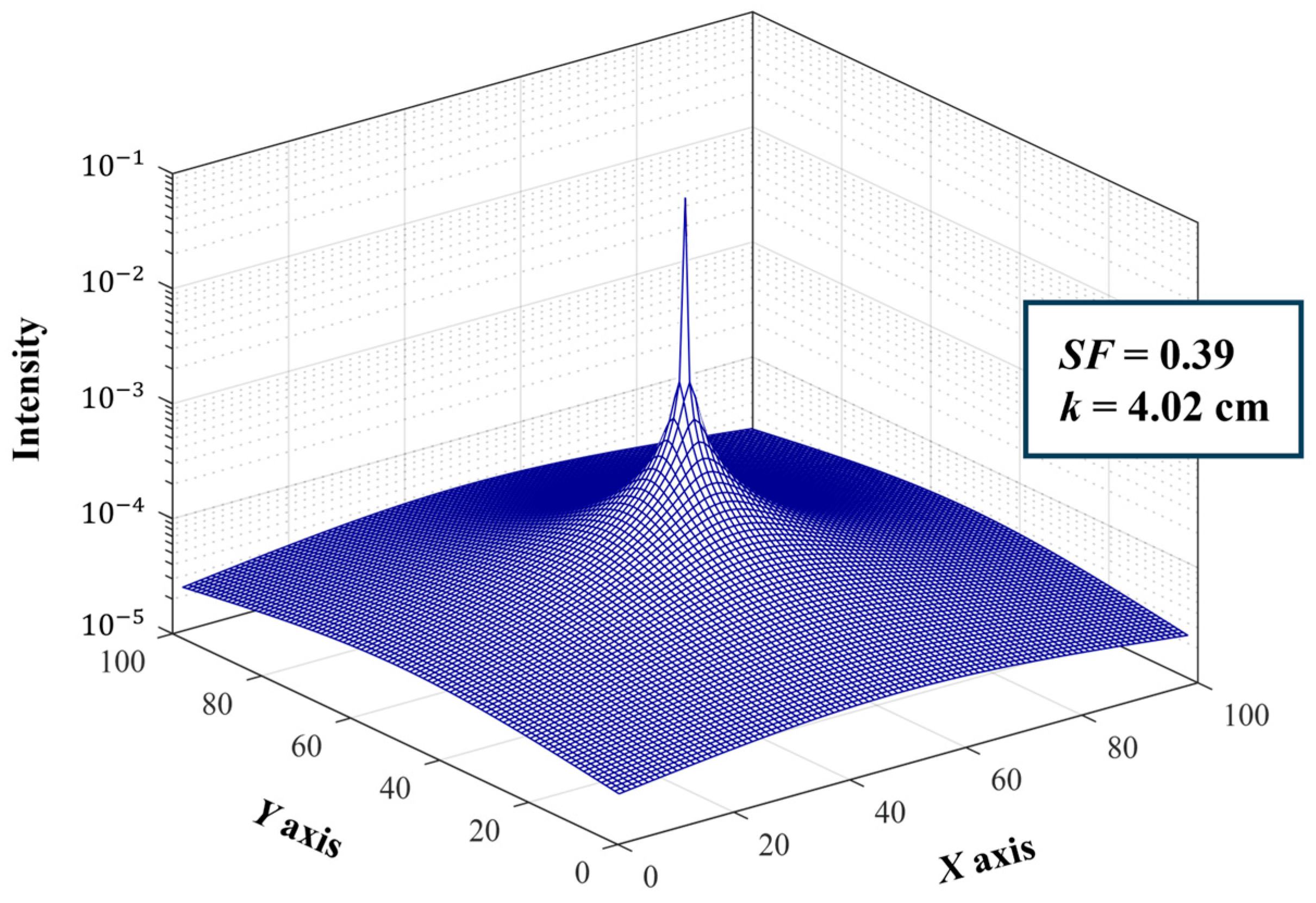
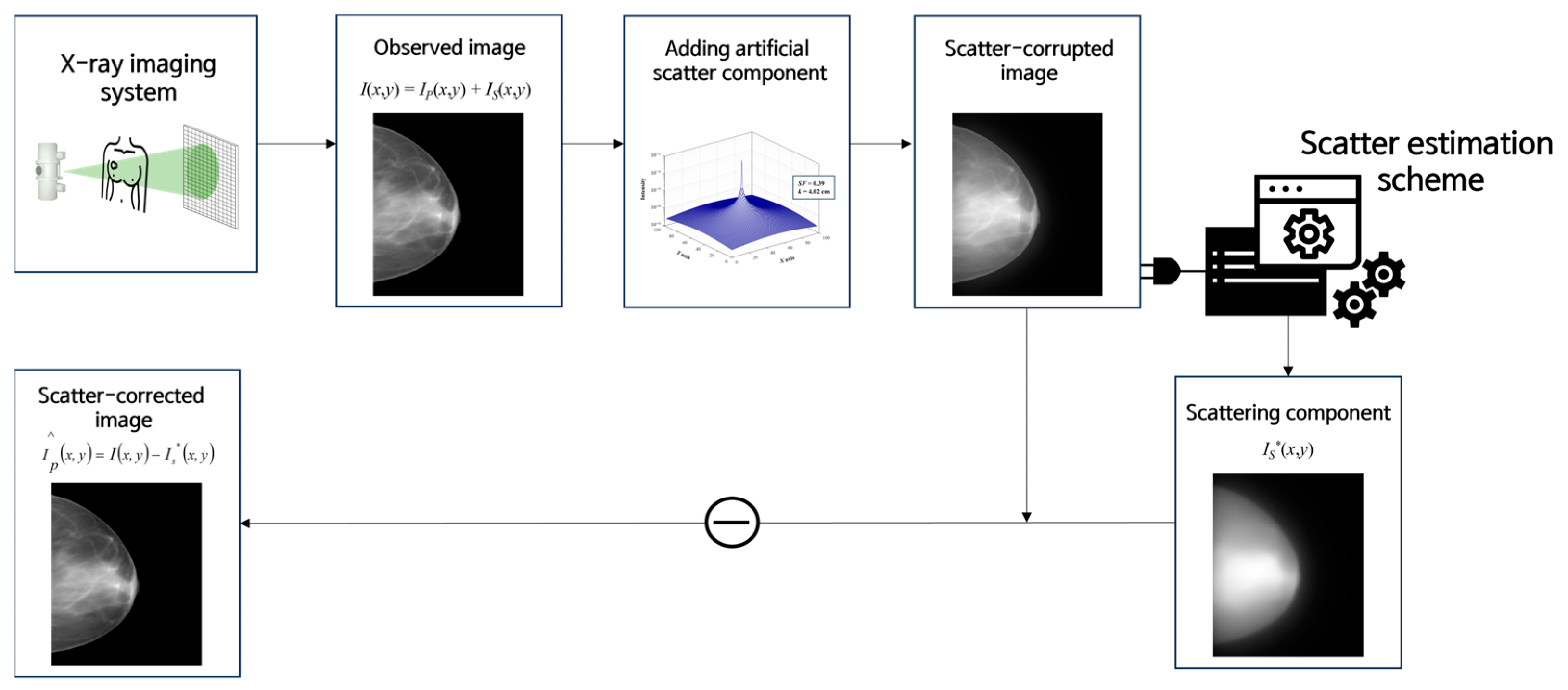
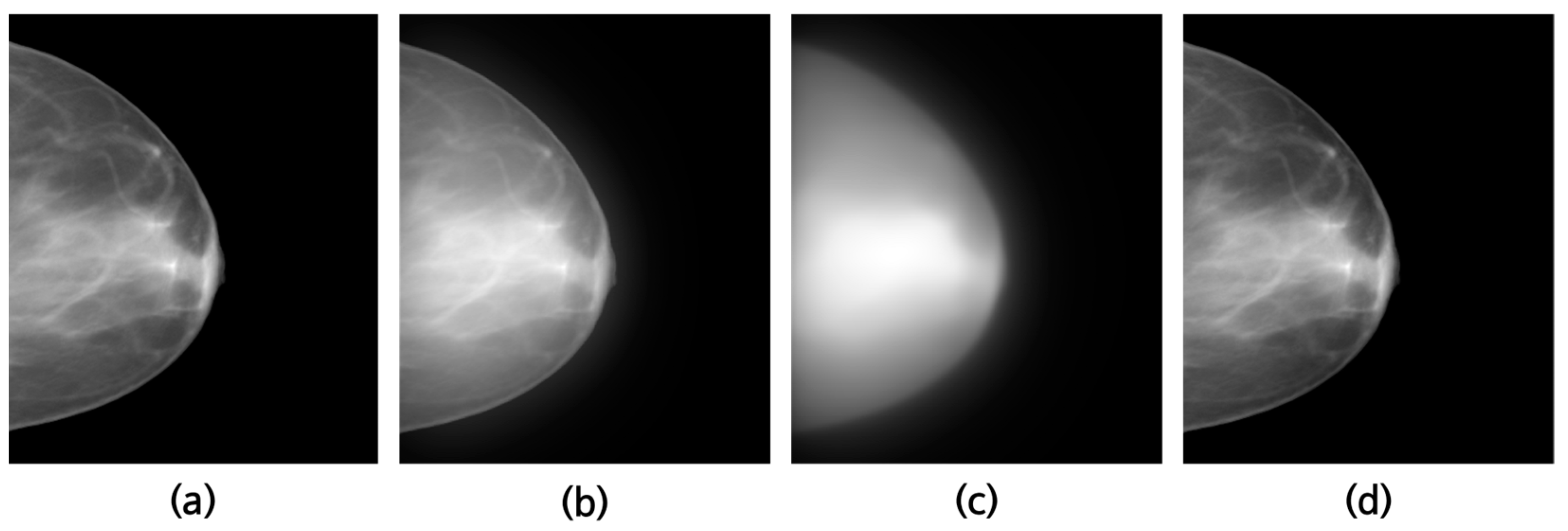
2.3. Scatter Correction Using a Virtual Grid
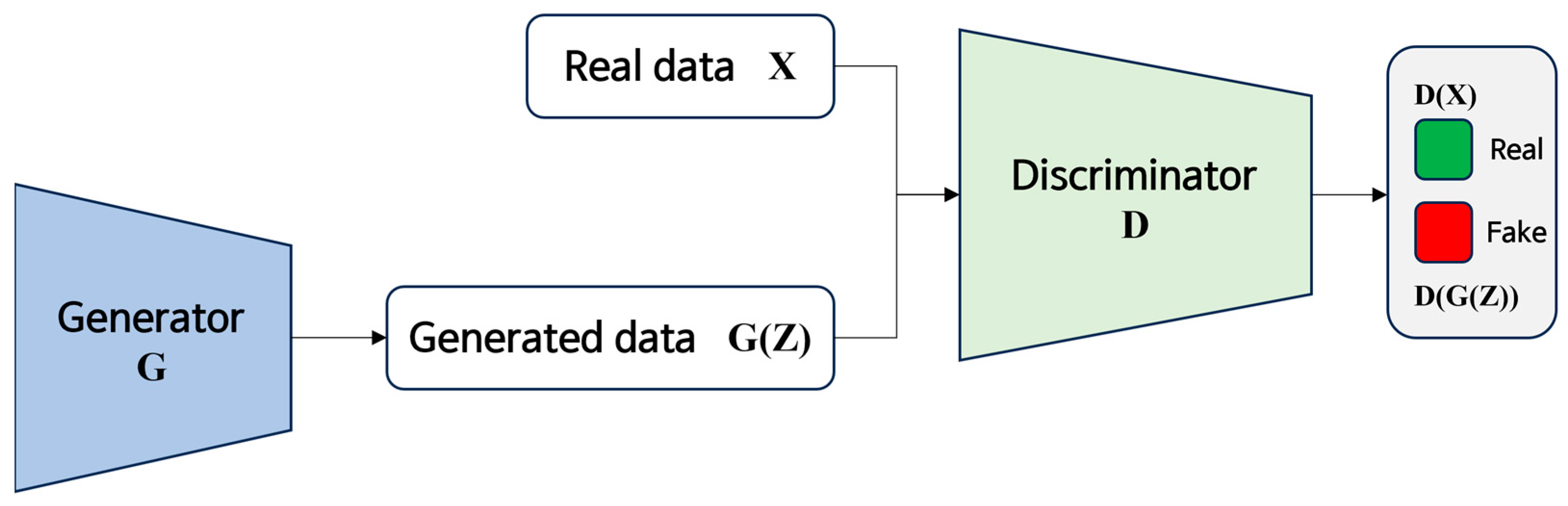
2.4. Noise Suppression Using GANs
2.4.1. Noise Level Quantification
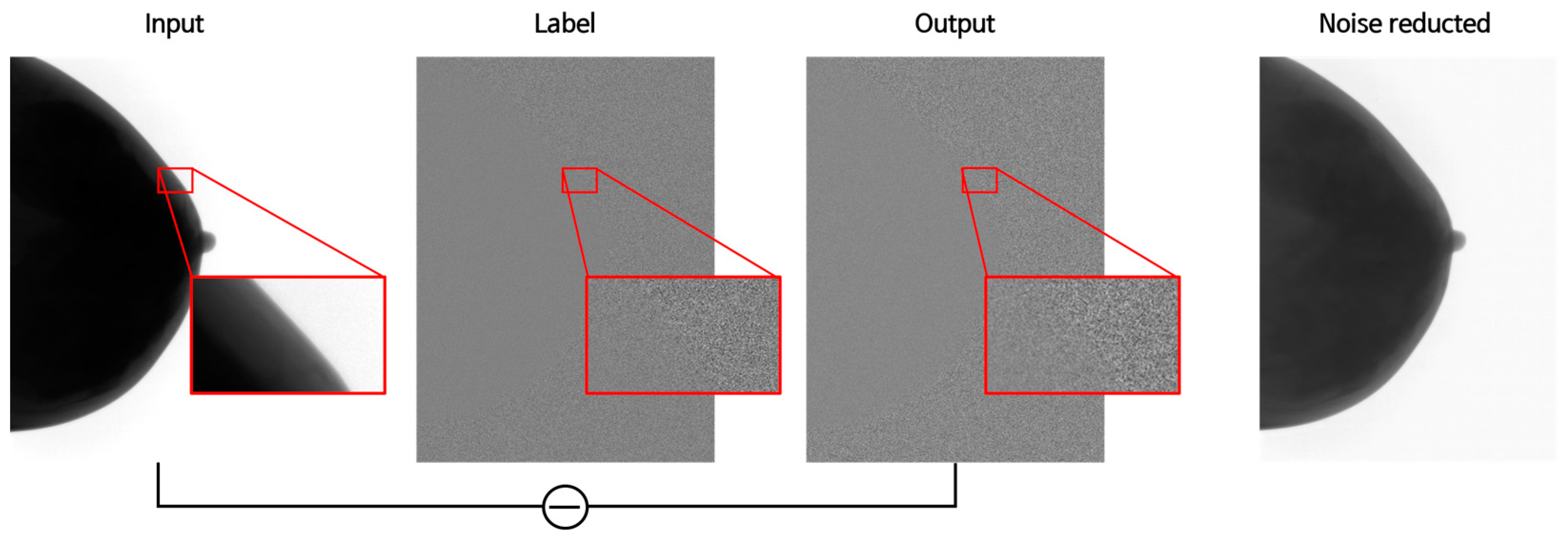
2.4.2. GAN Training
2.5. Quantitative Evaluation of the Noise-Reduced Image
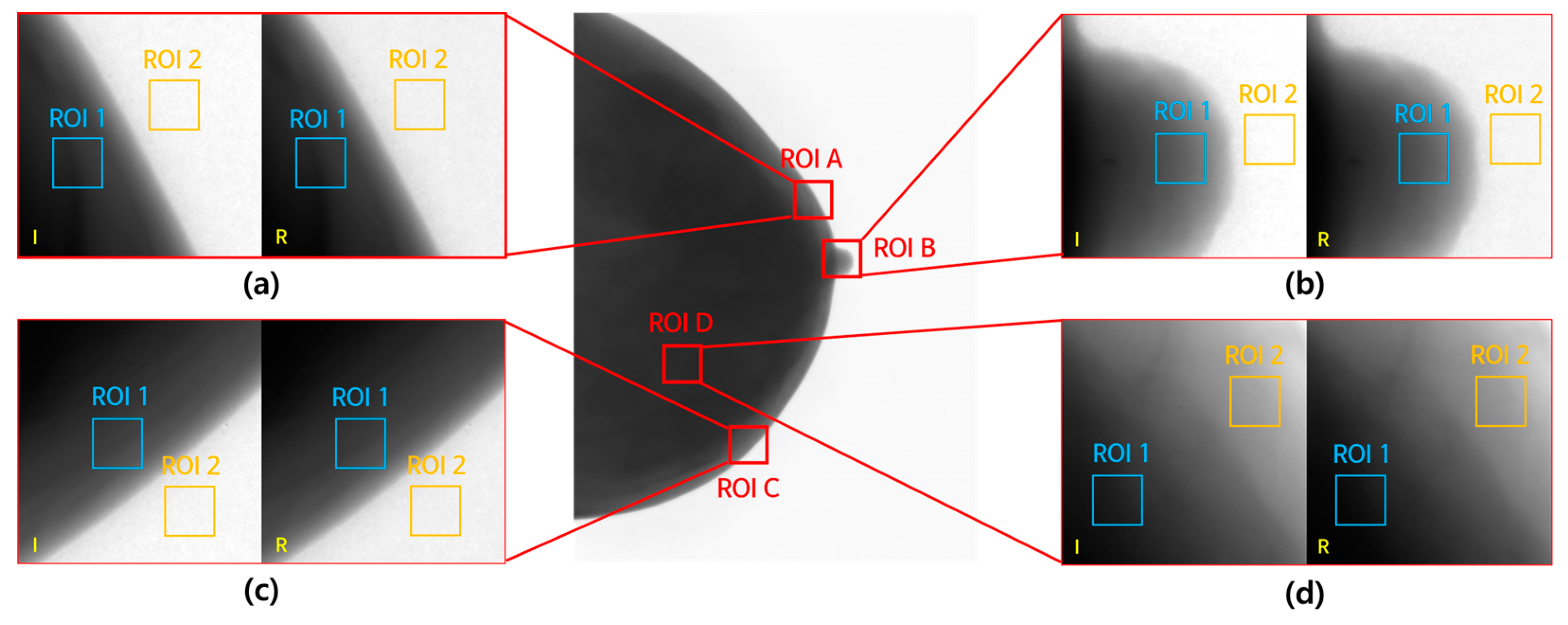
2.5.1. CNR and COV
2.5.2. NNPS
3. Results
3.1. Training Results Image
3.2. Quantitative Evaluation Results
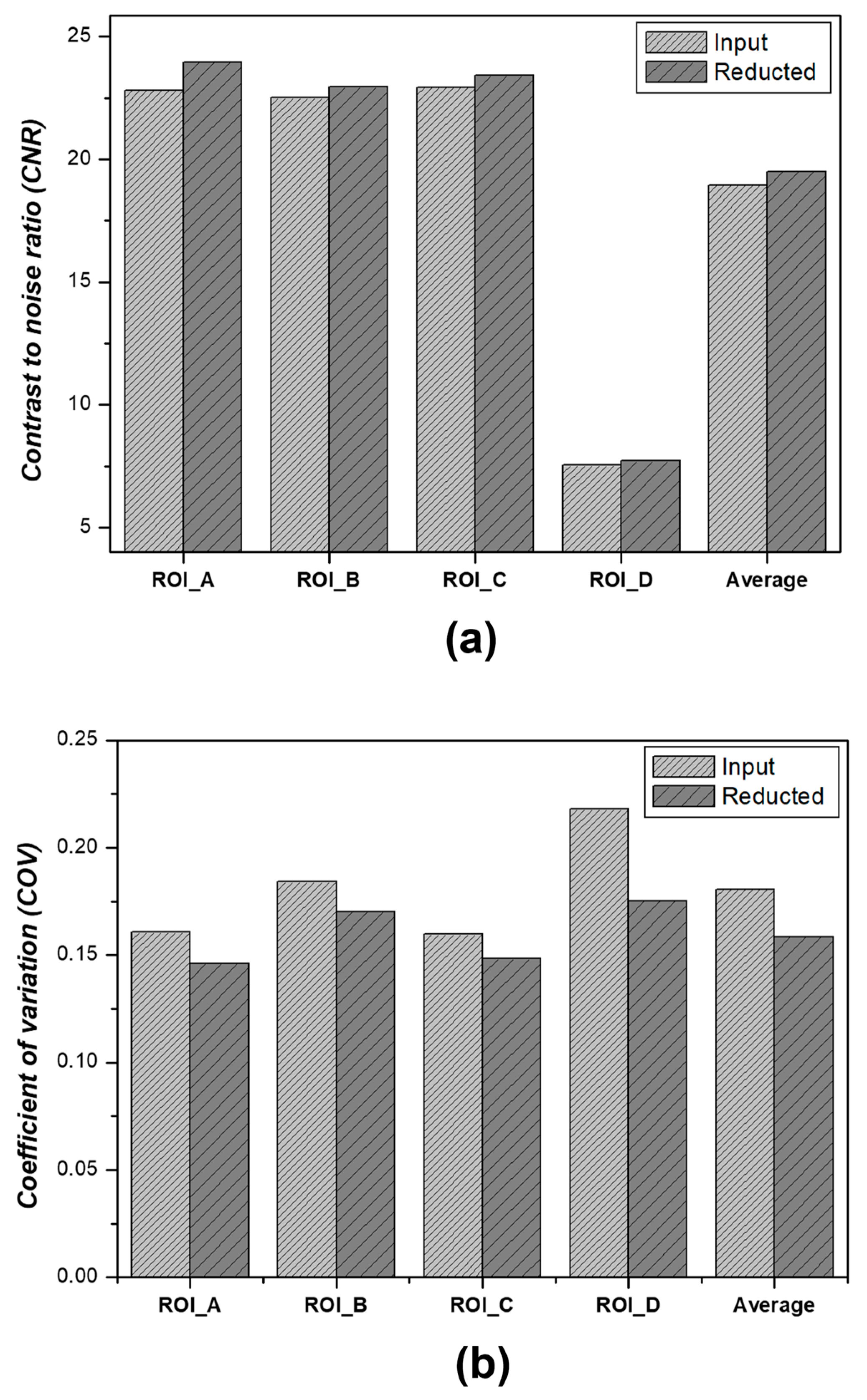
3.2.1. CNR and COV Measurement Results
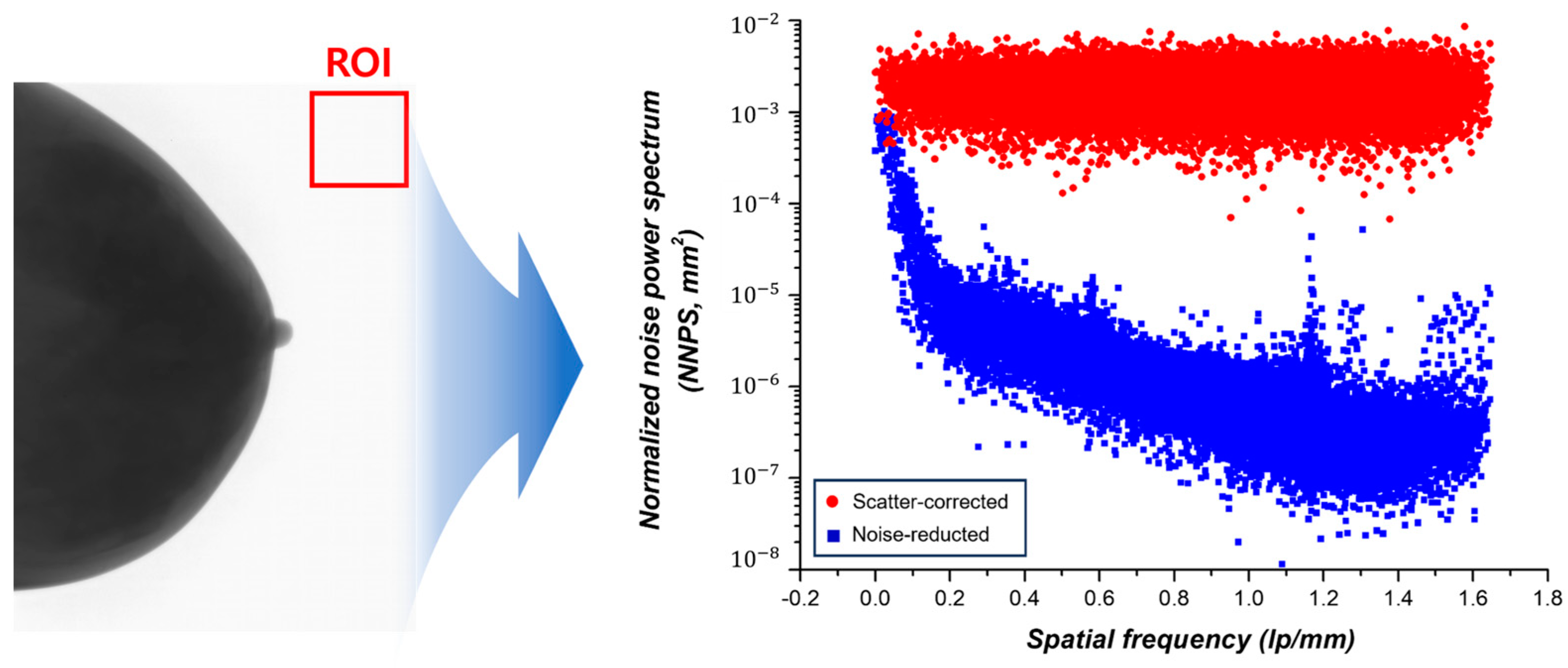
3.2.2. NNPS Measurement Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moore, C.S.; Wood, T.J.; Avery, G.; Balcam, S.; Needler, L.; Smith, A.; Saunderson, J.R.; Beavis, A.W. Investigating the use of an antiscatter grid in chest radiography for average adults with a computed radiography imaging system. Br. Inst. Radiol. 2015, 88, 20140613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentrup, D.; Jockel, S.; Menser, B.; Neitzel, U. Iterative scatter correction for grid-less bedside chest radiography: Performance for a chest phantom. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2016, 169, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossye, T.; Buytaert, D.; Smeets, P.V.; Morbee, L.; Wilde, C.D.; Vermeriren, K.; Achten, E.; Bacher, K. Evaluation of Virtual Grid Processed Clinical Chest Radiographs. Investig. Radiol. 2022, 57, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossye, T.; Smeets, P.V.; Achten, E.; Bacher, K. Impact of Software Parameter Settings on Image Quality of Virtual Grid Processed Radiography Images: A Contrast-Detail Phantom Study. Investig. Radiol. 2020, 55, 374–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.Y.; Chae, K.J.; Goo, J.M. The Potential Role of Grid-Like Software in Bedside Chest Radiography in Improving Image Quality and Dose Reduction: An Observer Preference Study. Korean J. Radiol. 2018, 19, 526–533. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Xing, L. Noise suppression in scatter correction for cone-beam CT. Med. Phys. 2009, 36, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, K.J.; Hermann, C.; Zeitler, G. X-ray scattering in single- and dual-source CT. Med. Phys. 2008, 35, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.T.; Park, S.J.; Jeon, J.M.; Lee, M.H.; Ryu, D.Y.; Lee, E.B.; Kang, S.-H.; Lee, Y.J. Noise removal in medical mammography images using fast non-local means denoising algorithm for early breast cancer detection: A phantom study. Optik 2019, 180, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechria, H.; Hassine, K.; Gouider, M.S. Effect of Denoising on Performance of Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Mammogram Images Classification. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 207, 2345–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, D.L. De-noising by soft-thresholding. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1995, 41, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tanaka, M.; Okutomi, M. Single-image noise level estimation for blind denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 5226–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foi, A.; Trimeche, M.; Katkovnik, V.; Egiazarian, K. Practical Poissonian-Gaussian noise modeling and fitting for single-image raw-data. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2008, 17, 1737–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutour, C.; Deledalle, C.-A.; Aujol, J.-F. Estimation of the noise level function based on a non-parametric detection of homogeneous image regions. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2015, 8, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. A new measure of rank correlation. Biometrika 1938, 30, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. The treatment of ties in ranking problems. Biometrika 1945, 33, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, U.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, B.; Antalek, M.; Keles, E.; Jha, D.; Borhani, A.; Ladner, D.; Bagci, U. Transformer based Generative Adversarial Network for Liver Segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Analysis and Processing, Bordeaux, France, 16–19 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Creswell, A.; White, T.; Dumoulin, V.; Arukumaran, K.; Sengupta, B.; Bharath, A.A. Generative Adversarial Networks: An Overview. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2017, 35, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossmann, K. Point Spread-Function, Line Spread-Function, and Modulation Transfer Function. Radiology 1969, 93, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducote, J.L.; Molloi, S. Scatter correction in digital mammography based on image deconvolution. Phys. Med. Biol. 2010, 55, 1295–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Kang, S.; Kim, W.; Park, C.; Lee, D.; Cho, H.; Kang, W.; Park, S.; Kim, G.; Lim, H.; et al. A new software scheme for scatter correction based on a simple radiographic scattering model. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2019, 57, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.-H.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, Y.J. Experimental study of noise level optimization in brain single-photon emission computed tomography images using non-local means approach with various reconstruction methods. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2023, 55, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.-R.; Kang, S.-H.; Lee, Y.J. Feasibility of Total Variation Noise Reduction Algorithm According to Various MR-Based PET Images in a Simultaneous PET/MR System: A Phantom Study. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, R.; Kirkland, A.I. Chapter One—Direct Digital Electron Detectors. Adv. Imaging Electron. Phys. 2016, 198, 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, R. Noise Power Spectral Density Estimation Based on Optimal Smoothing and Minimum Statistics. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 2001, 9, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, M.; Knapp, K.M.; Fulford, J.; Heales, C.; Alqahtani, S.J. The principles and effectiveness of X-ray scatter correction software for diagnostic X-ray imaging: A-scoping review. Eur. J. Radiol. 2023, 158, 110600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bednarek, D.R.; Rudin, S.; Wong, R. Artifacts Produced by Moving Grids. Radiology 1983, 147, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.S. Principles of Diagnoistic Radiation; Daihakseorim: Busan, Republic of Korea, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Cannistraci, C.V.; Montevecchi, F.M.; Alessio, M. Median-modified Wiener filter provides efficient denoising, preserving spot edge and morphology in 2-DE image processing. Proteomics 2009, 9, 4908–4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Q.; Chen, X.; Lin, C. A Novel VLSI Architecture for Multidimensional Discrete Wavelet Transform. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2004, 14, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camara, J.R.; Tomihama, R.T.; Pop, A.; Shedd, M.P.; Dobrowski, B.S.; Knox, C.J.; Jr, A.M.A.-Z.; Kiang, S.C. Development of a convolutional neural network to detect abdominal aortic aneurysms. J. Vasc. Surg. Cases Innov. Tech. 2002, 8, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinayahalingam, S.; Berends, B.; Baan, F.; Moin, D.A.; Lujin, R.V.; Berge, S.; Xi, T. Deep learning for automated segmentation of the temporomandibular joint. J. Densitry 2023, 132, 104475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, S.; Khan, M.S.; Bibi, A.; Khandakar, A.; Ayari, M.A.; Chowdhury, M.E.H. Deep learning techniques for liver and liver tumor segmentation: A review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 147, 105620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhivya, S.; Subramaniam, M.; Subbaraj, K.; Shivani, S.; Mageswari, R. GAN based Data Augmentation for Enhanced Tumor Classification. In Proceedings of the 2020 4th International Conference on Computer, Communication and Signal Processing (ICCCSP), Chennai, India, 28–29 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, P.; Muhammad, K.; Ser, J.D. Vessel-GAN: Angiographic reconstructions from myocardial CT perfusion with explainable generative adversarial networks. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2022, 130, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledig, C.; Theis, L.; Huszar, F.; Caballero, J.; Cunningham, A.; Acosta, A.; Aitken, A.; Tejani, A.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Photo-Realistic Single Image Super-Resolution Using a Generative Adversarial Network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–25 July 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, M.H.; Alhwaiti, Y. Signal-to-Noise Ratio Comparison of Several Filters against Phantom Image. J. Healthc. Eng. 2022, 2022, 4724342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havariyoun, G.; Massimi, L.; Hagen, C.; Endrizzi, M.; Olivo, A. Modulation transfer function (MTF) evaluation for x-ray phase imaging system employing attenuation masks. Phys. Med. Biol. 2023, 68, 09NT02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Park, M.; Kim, H.; Kang, S.-H.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, Y.J. Optimization of Median Modified Wiener Filter for Improving Lung Segmentation Performance in Low-Dose Computed Tomography Images. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Xing, S.; Jarayathne, U.; Pardasani, U.; Peters, T.; Chen, E. X-ray image decomposition for improved magnetic navigation. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2023, 18, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter | Dimension |
|---|---|
| Size of input and output images | 256 256 |
| Number of training patches | 54,686 |
| Number of validating patches | 6100 |
| Number of testing patches | 2128 |
| Number of epochs | 200 |
| Size of batch | 16 |
| Number of channels | 128, 256, 512, and 1024 |
| Learning rate | 5 × 10−4 |
| Objective function | Mean Squared Error Loss |
| Optimization solver | Adaptive momentum estimation (Adam) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, S.; Nam, H.; Shin, H.; Jeong, S.; Kim, K.; Lee, Y. Noise Reduction for a Virtual Grid Using a Generative Adversarial Network in Breast X-ray Images. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9120272
Lim S, Nam H, Shin H, Jeong S, Kim K, Lee Y. Noise Reduction for a Virtual Grid Using a Generative Adversarial Network in Breast X-ray Images. Journal of Imaging. 2023; 9(12):272. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9120272
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Sewon, Hayun Nam, Hyemin Shin, Sein Jeong, Kyuseok Kim, and Youngjin Lee. 2023. "Noise Reduction for a Virtual Grid Using a Generative Adversarial Network in Breast X-ray Images" Journal of Imaging 9, no. 12: 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9120272
APA StyleLim, S., Nam, H., Shin, H., Jeong, S., Kim, K., & Lee, Y. (2023). Noise Reduction for a Virtual Grid Using a Generative Adversarial Network in Breast X-ray Images. Journal of Imaging, 9(12), 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9120272







