A Dataset for Temporal Semantic Segmentation Dedicated to Smart Mobility of Wheelchairs on Sidewalks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work and Motivations
2.1. Datasets
2.2. Semantic Segmentation by Convolutional Neural Networks
2.2.1. Fixed Image Models
2.2.2. Image Sequence Models
2.2.3. Need for Real-Time Processing
3. Description of Our Dataset and Test with a Semantic Segmentation Model
3.1. Generation of a Virtual Dataset
3.1.1. Overview
- Addition of a varying density of pedestrians along the roads;
- Addition of vehicles on the roads (cars, bikes, motorcycles, vans, trucks, etc.);
- Variation of the weather conditions (amount of clouds, rain, puddles and wind);
- Variation of the time of day by modifying the position of the sun in the sky.
3.1.2. Data Cleaning and Preprocessing
3.1.3. Additional Data
3.2. Model Description
3.2.1. Architecture of the Network
3.2.2. Loss Function
3.2.3. Data Augmentation and Normalization
3.2.4. Class Balancing
3.2.5. Other Implementation Details
4. Results
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADAPT | Assistive Devices for disAbled People using robotic Technology |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Networks |
| EW | Electric Wheelchair |
| FPS | Frames Per Second |
| mIoU | mean Intersection over Union |
References
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Ros, G.; Codevilla, F.; López, A.; Koltun, V. CARLA: An Open Urban Driving Simulator. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.03938. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2018, 11211, 833–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordts, M.; Omran, M.; Ramos, S.; Rehfeld, T.; Enzweiler, M.; Benenson, R.; Franke, U.; Roth, S.; Schiele, B. The Cityscapes Dataset for Semantic Urban Scene Understanding. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brostow, G.; Shotton, J.; Fauqueur, J.; Cipolla, R. Segmentation and Recognition Using Structure from Motion Point Clouds. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 44–57. [Google Scholar]
- Silberman, N.; Hoiem, D.; Kohli, P.; Fergus, R. Indoor Segmentation and Support Inference from RGBD Images. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 746–760. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, L.; Terwilliger, J.; Sherony, R.; Reimer, B.; Fridman, L. Value of Temporal Dynamics Information in Driving Scene Segmentation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.00758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.; Sirlantzis, K.; Howells, G. A pixel-wise annotated dataset of small overlooked indoor objects for semantic segmentation applications. Data Brief 2022, 40, 107791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, S.R.; Vineet, V.; Roth, S.; Koltun, V. Playing for Data: Ground Truth from Computer Games. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2016, 9906, 102–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros, G.; Sellart, L.; Materzynska, J.; Vazquez, D.; Lopez, A. The SYNTHIA Dataset: A Large Collection of Synthetic Images for Semantic Segmentation of Urban Scenes. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3234–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidon, A.; Wang, Q.; Cabon, Y.; Vig, E. Virtual Worlds as Proxy for Multi-object Tracking Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4340–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaranarayanan, S.; Balaji, Y.; Jain, A.; Lim, S.N.; Chellappa, R. Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Semantic Segmentation with GANs. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.06969. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Dai, D.; Hoyer, L.; Fink, O.; Gool, L.V. Domain Adaptive Semantic Segmentation with Self-Supervised Depth Estimation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.13613. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan, R. Deep Deconvolutional Networks for Scene Parsing. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.4101. [Google Scholar]
- Farabet, C.; Couprie, C.; Najman, L.; LeCun, Y. Learning Hierarchical Features for Scene Labeling. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 1915–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, P.H.O.; Collobert, R. Recurrent Convolutional Neural Networks for Scene Labeling. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Bejing, China, 22–24 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mostajabi, M.; Yadollahpour, P.; Shakhnarovich, G. Feedforward semantic segmentation with zoom-out features. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.0774. [Google Scholar]
- Noh, H.; Hong, S.; Han, B. Learning Deconvolution Network for Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.04366. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.04597. [Google Scholar]
- Shelhamer, E.; Long, J.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. SegNet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid Scene Parsing Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6230–6239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, A.; Badrinarayanan, V.; Cipolla, R. Bayesian SegNet: Model Uncertainty in Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architectures for Scene Understanding. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference 2017, London, UK, 4–7 September 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Kun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Yang, K. DenseASPP for Semantic Segmentation in Street Scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA, 18–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, H.; Han, L.; Tong, Y.; Yang, K. GFF: Gated Fully Fusion for Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1904.01803. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual Attention Network for Scene Segmentation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1809.02983. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Huang, L.; Guo, J.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, J. OCNet: Object Context Network for Scene Parsing. arXiv 2021, arXiv:1809.00916. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Shi, J.; Loy, C.C.; Lin, D.; Jia, J. PSANet: Point-wise Spatial Attention Network for Scene Parsing. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 270–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Dana, K.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Tyagi, A.; Agrawal, A. Context Encoding for Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.08904. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Hong, Z.; Liu, J.; Ma, F.; Han, J.; Ding, E. ACFNet: Attentional Class Feature Network for Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.09408. [Google Scholar]
- Shuai, B.; Zuo, Z.; Wang, B.; Wang, G. Scene Segmentation with DAG-Recurrent Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 1480–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Ouyang, W.; Wang, X.; Sebe, N. PAD-Net: Multi-Tasks Guided Prediction-and-Distillation Network for Simultaneous Depth Estimation and Scene Parsing. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.04409. [Google Scholar]
- Chennupati, S.; Sistu, G.; Yogamani, S.; Rawashdeh, S. AuxNet: Auxiliary Tasks Enhanced Semantic Segmentation for Automated Driving. In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications, Prague, Czech Republic, 25–27 February 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takikawa, T.; Acuna, D.; Jampani, V.; Fidler, S. Gated-SCNN: Gated Shape CNNs for Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.05740. [Google Scholar]
- Ranzato, M.; Szlam, A.; Bruna, J.; Mathieu, M.; Collobert, R.; Chopra, S. Video (language) modeling: A baseline for generative models of natural videos. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6604. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donahue, J.; Hendricks, L.A.; Rohrbach, M.; Venugopalan, S.; Guadarrama, S.; Saenko, K.; Darrell, T. Long-Term Recurrent Convolutional Networks for Visual Recognition and Description. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, D.; Sminchisescu, C. Semantic Video Segmentation by Gated Recurrent Flow Propagation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1612.08871. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Yeung, D.Y.; kin Wong, W.; chun Woo, W. Convolutional LSTM Network: A Machine Learning Approach for Precipitation Nowcasting. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.04214. [Google Scholar]
- Ballas, N.; Yao, L.; Pal, C.; Courville, A. Delving Deeper into Convolutional Networks for Learning Video Representations. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.06432. [Google Scholar]
- Fayyaz, M.; Saffar, M.H.; Sabokrou, M.; Fathy, M.; Klette, R.; Huang, F. STFCN: Spatio-Temporal FCN for Semantic Video Segmentation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1608.05971. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Qi, X.; Shen, X.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. ICNet for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation on High-Resolution Images. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2018, 11207, 418–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilg, E.; Mayer, N.; Saikia, T.; Keuper, M.; Dosovitskiy, A.; Brox, T. FlowNet 2.0: Evolution of Optical Flow Estimation with Deep Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Xiong, Y.; Dai, J.; Yuan, L.; Wei, Y. Deep Feature Flow for Video Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Sapra, K.; Reda, F.A.; Shih, K.J.; Newsam, S.; Tao, A.; Catanzaro, B. Improving Semantic Segmentation via Video Propagation and Label Relaxation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1812.01593. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Shi, J.; Lin, D. Low-Latency Video Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Wang, X.; Gonzalez, J.E. Accel: A Corrective Fusion Network for Efficient Semantic Segmentation on Video. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadde, R.; Jampani, V.; Gehler, P.V. Semantic Video CNNs through Representation Warping. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1708.03088. [Google Scholar]
- HanchaoHe, X.; Zhu, X.; Liu, J. Dynamic Warping Network for Semantic Video Segmentation. Complexity 2021, 2021, 6680509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, B.; Shi, J.; Lu, Z.; Luo, P. Every Frame Counts: Joint Learning of Video Segmentation and Optical Flow. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.12739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shen, C.; Yu, C.; Wang, J. Efficient Semantic Video Segmentation with Per-frame Inference. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.11433. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Oord, A.; Dieleman, S.; Zen, H.; Simonyan, K.; Vinyals, O.; Graves, A.; Kalchbrenner, N.; Senior, A.; Kavukcuoglu, K. WaveNet: A Generative Model for Raw Audio. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.03499. [Google Scholar]
- Waibel, A.; Hanazawa, T.; Hinton, G.; Shikano, K.; Lang, K. Phoneme recognition using time-delay neural networks. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. IEEE Trans. 1989, 37, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Kolter, J.Z.; Koltun, V. An Empirical Evaluation of Generic Convolutional and Recurrent Networks for Sequence Modeling. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.01271. [Google Scholar]
- Sibechi, R.; Booij, O.; Baka, N.; Bloem, P. Exploiting Temporality for Semi-Supervised Video Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW), Seoul, Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.W.; Lee, J.Y.; Xu, N.; Kim, S.J. Video Object Segmentation using Space-Time Memory Networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.00607. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, J. Temporal Memory Attention for Video Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.08643. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, M.; Mayer, C.; Van Gool, L.; Timofte, R. Efficient Video Semantic Segmentation with Labels Propagation and Refinement. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Snowmass Village, CO, USA, 1–5 March 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Caba, F.; Wang, O.; Lin, Z.; Sclaroff, S.; Perazzi, F. Temporally Distributed Networks for Fast Video Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.S.; Fu, T.J.; Yang, H.K.; Lee, C.Y. Dynamic Video Segmentation Network. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.00931. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.P.; Chen, S.C.; Peng, W.H. GSVNet: Guided Spatially-Varying Convolution for Fast Semantic Segmentation on Video. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.08834. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, P.; Perazzi, F.; Heilbron, F.C.; Wang, O.; Lin, Z.; Saenko, K.; Sclaroff, S. Real-time Semantic Segmentation with Fast Attention. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.03815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, M.; Shin, J. Semantic video segmentation with dynamic keyframe selection and distortion-aware feature rectification. Image Vis. Comput. 2021, 110, 104184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wen, Z.; Zhao, S.; Huang, K. Video semantic segmentation via feature propagation with holistic attention. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 104, 107268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.; Sirlantzis, K.; Howells, G. Indoor/Outdoor Semantic Segmentation Using Deep Learning for Visually Impaired Wheelchair Users. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 147914–147932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, H.; Sun, Y.; He, T.; Mueller, J.; Manmatha, R.; et al. ResNeSt: Split-Attention Networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.08955. [Google Scholar]
- Jadon, S. A survey of loss functions for semantic segmentation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.14822. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollar, P. Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2999–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszke, A.; Chaurasia, A.; Kim, S.; Culurciello, E. ENet: A Deep Neural Network Architecture for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.02147. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, R.; Kornblith, S.; Hinton, G.E. When Does Label Smoothing Help? In Proceedings of the Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2019, NeurIPS 2019, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]

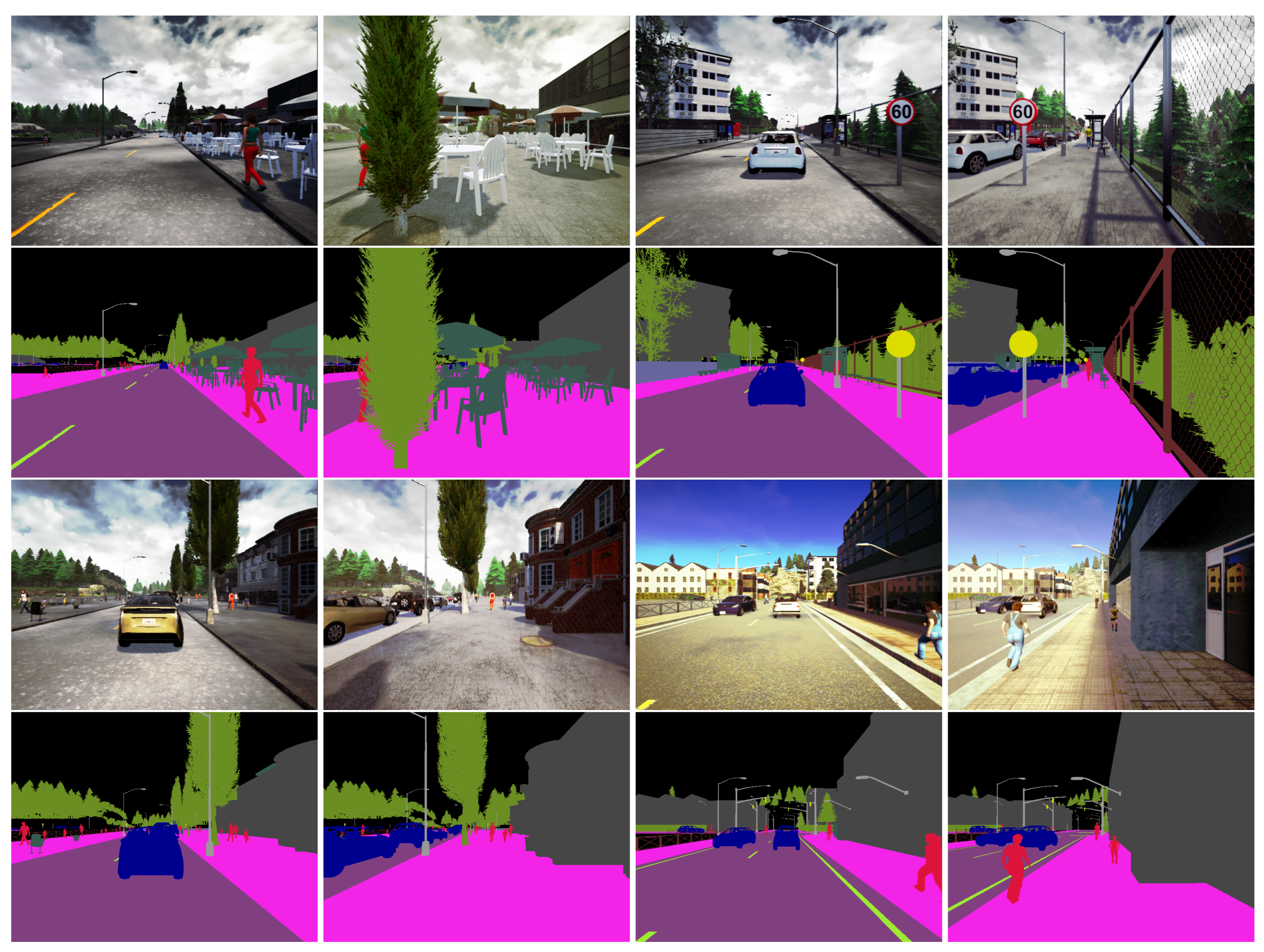
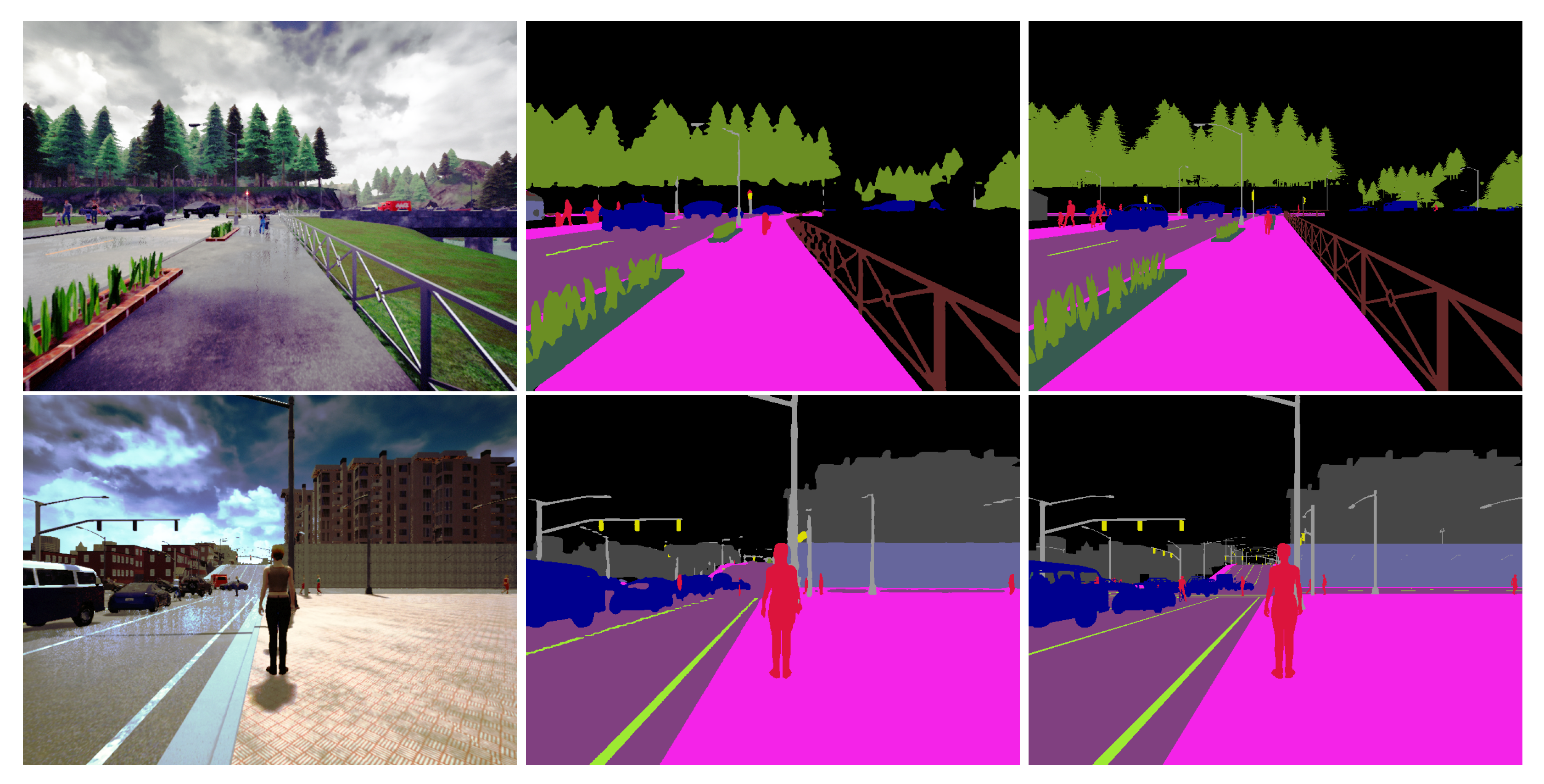
| Classes | Unlabeled | Building | Fence | Other | Pedestrian | Pole | Road Line |
| Weights | 8.7140 | 31.2160 | 30.7612 | 27.5623 | 27.9024 | 37.7695 | 8.1916 |
| Classes | Road | Sidewalk | Vegetation | Vehicle | Wall | Traffic Sign | |
| Weights | 4.9276 | 6.8403 | 33.7536 | 17.6963 | 46.7649 | 3.3284 | - |
| Test on ADRoad | Test on ADSidewalk | |
|---|---|---|
| learn on ADRoad | 61.51% | 30.58% |
| learn on ADSidewalk | 51.32% | 62.23% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Decoux, B.; Khemmar, R.; Ragot, N.; Venon, A.; Grassi-Pampuch, M.; Mauri, A.; Lecrosnier, L.; Pradeep, V. A Dataset for Temporal Semantic Segmentation Dedicated to Smart Mobility of Wheelchairs on Sidewalks. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging8080216
Decoux B, Khemmar R, Ragot N, Venon A, Grassi-Pampuch M, Mauri A, Lecrosnier L, Pradeep V. A Dataset for Temporal Semantic Segmentation Dedicated to Smart Mobility of Wheelchairs on Sidewalks. Journal of Imaging. 2022; 8(8):216. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging8080216
Chicago/Turabian StyleDecoux, Benoit, Redouane Khemmar, Nicolas Ragot, Arthur Venon, Marcos Grassi-Pampuch, Antoine Mauri, Louis Lecrosnier, and Vishnu Pradeep. 2022. "A Dataset for Temporal Semantic Segmentation Dedicated to Smart Mobility of Wheelchairs on Sidewalks" Journal of Imaging 8, no. 8: 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging8080216
APA StyleDecoux, B., Khemmar, R., Ragot, N., Venon, A., Grassi-Pampuch, M., Mauri, A., Lecrosnier, L., & Pradeep, V. (2022). A Dataset for Temporal Semantic Segmentation Dedicated to Smart Mobility of Wheelchairs on Sidewalks. Journal of Imaging, 8(8), 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging8080216







