Scanning X-ray Fluorescence Data Analysis for the Identification of Byzantine Icons’ Materials, Techniques, and State of Preservation: A Case Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
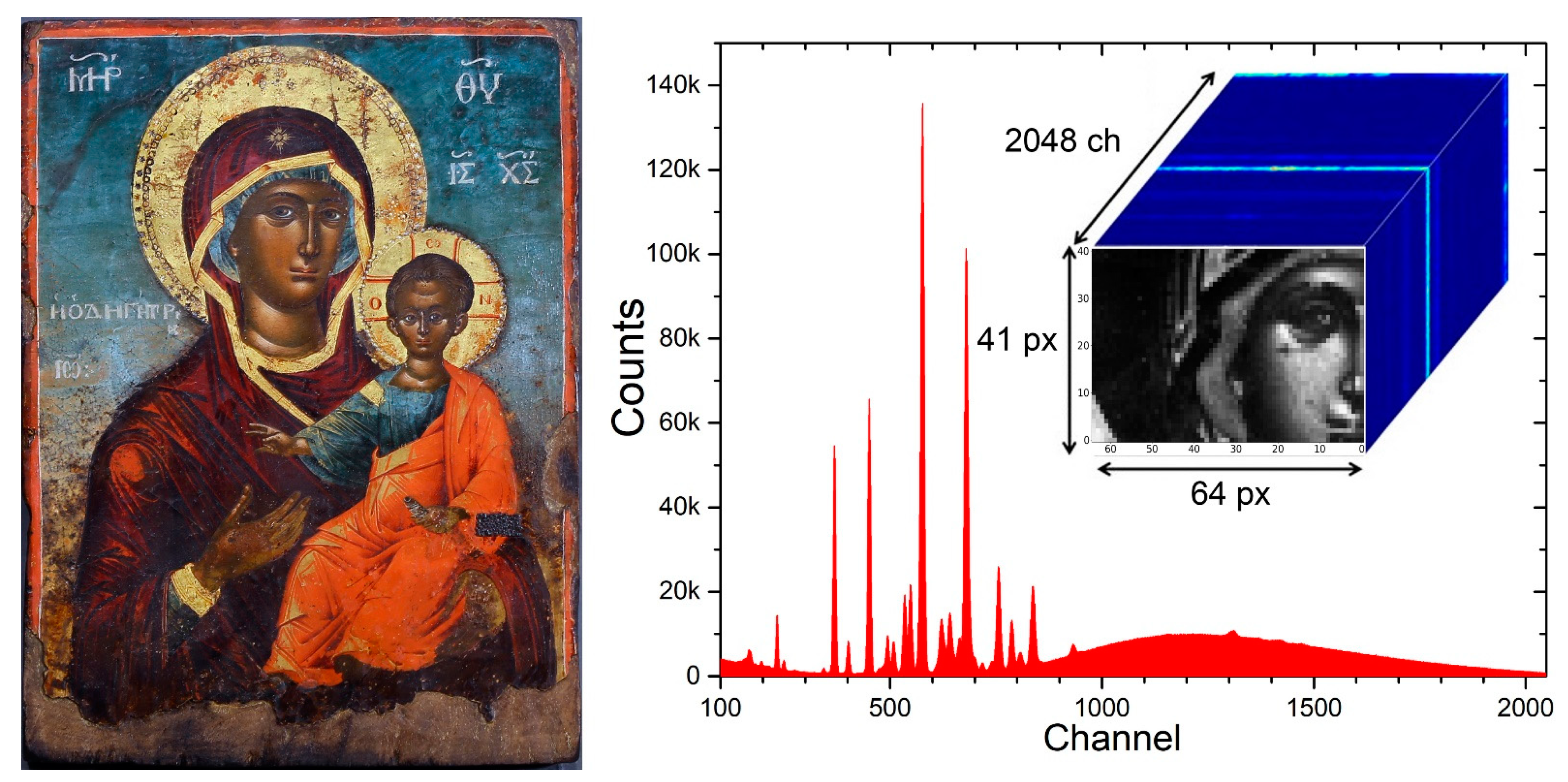
2.1. Experimental Setup
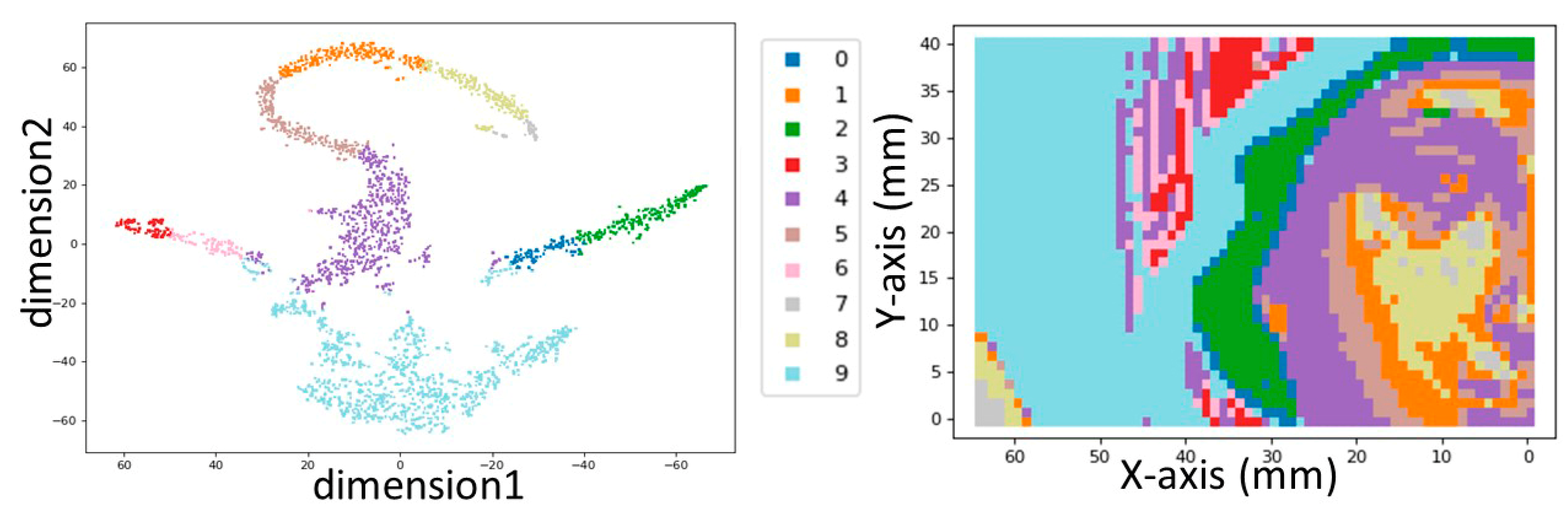
2.2. Clustering and Visualization
3. Results
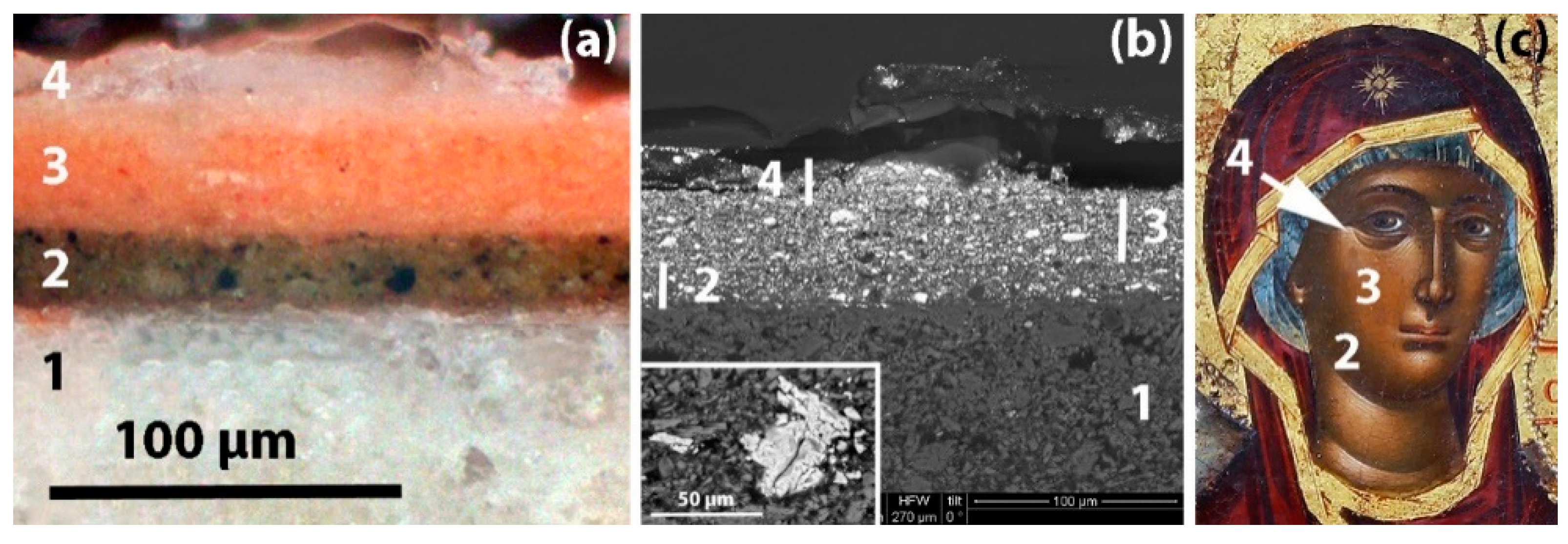
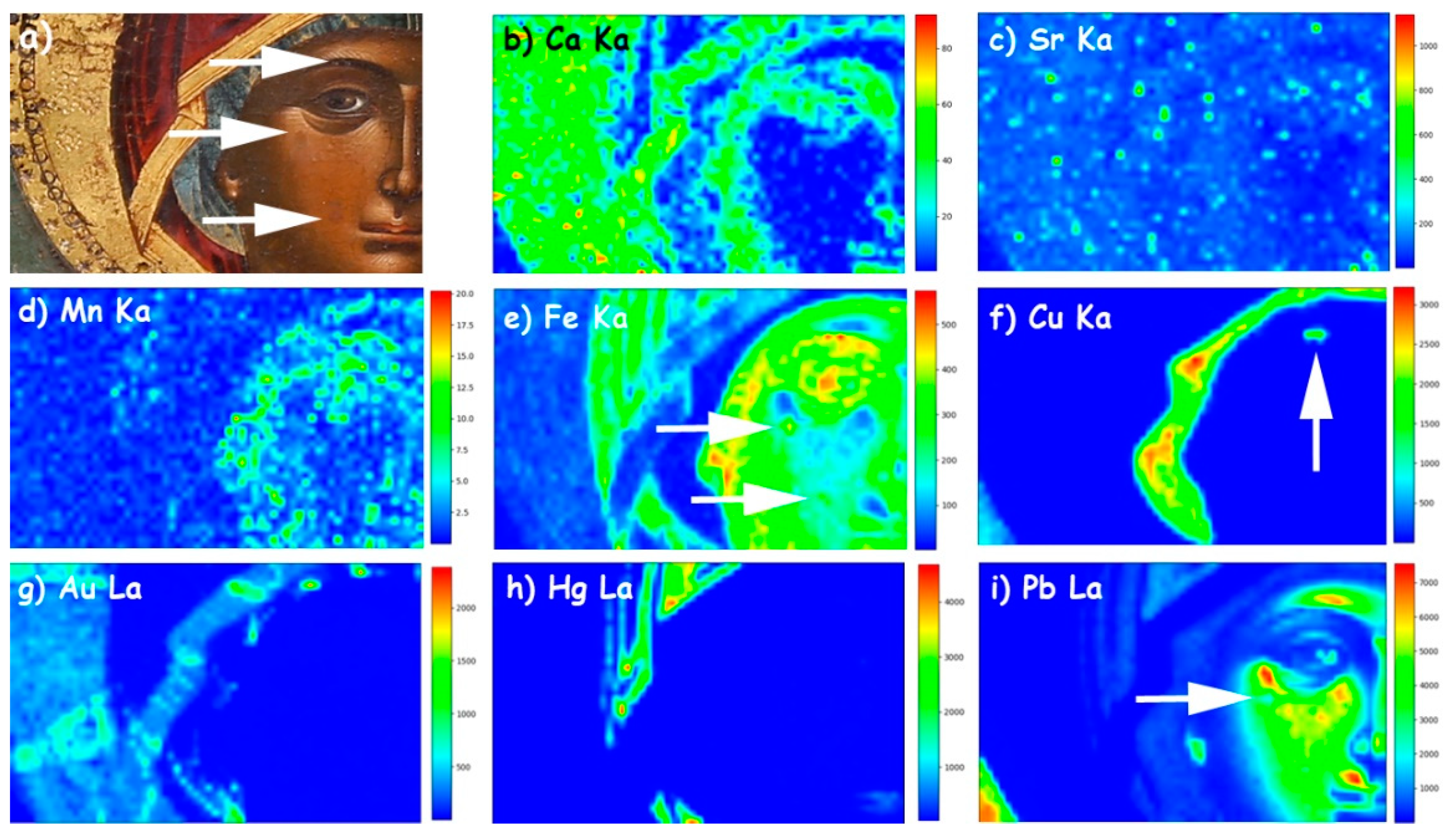
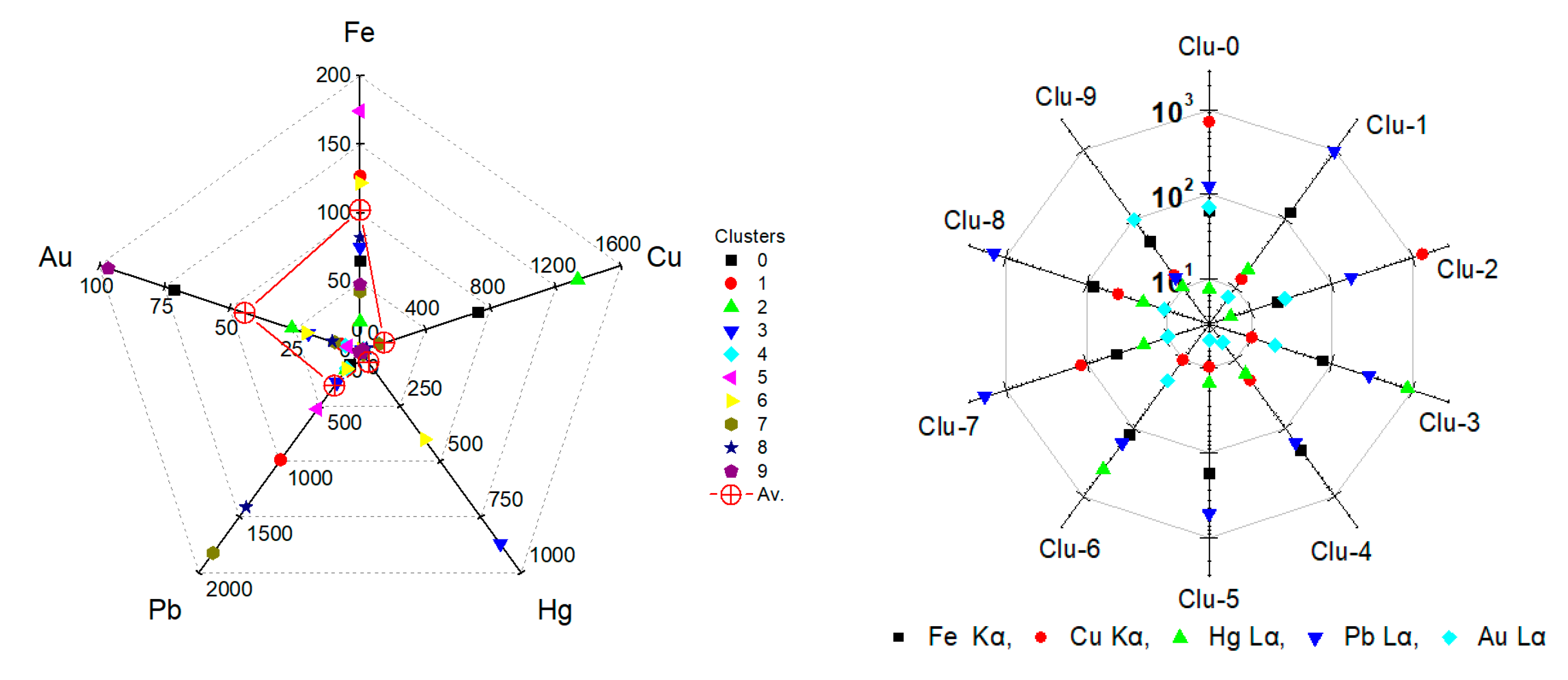
3.1. Data Analysis and Interpretation
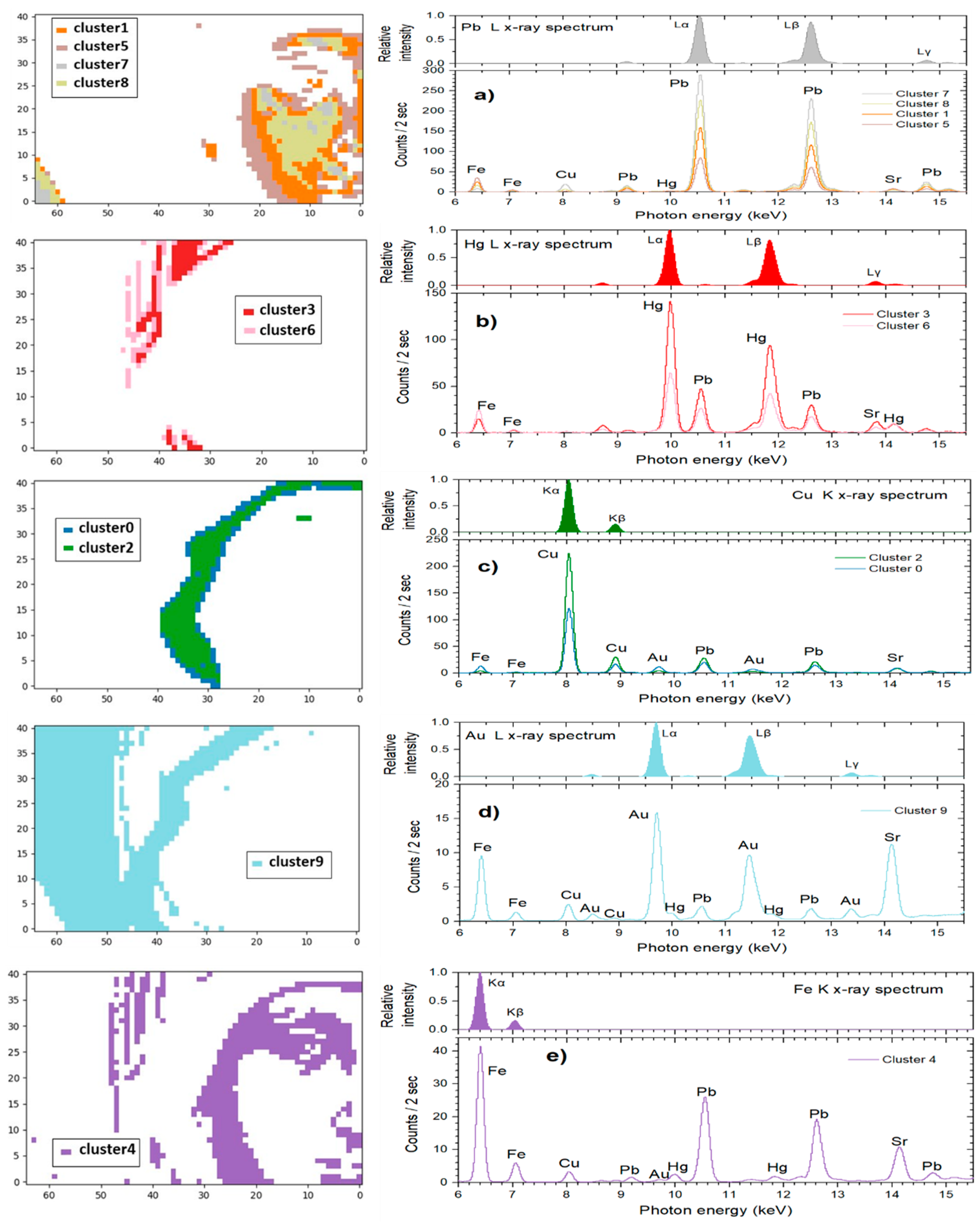
3.2. Spectroscopic Analysis
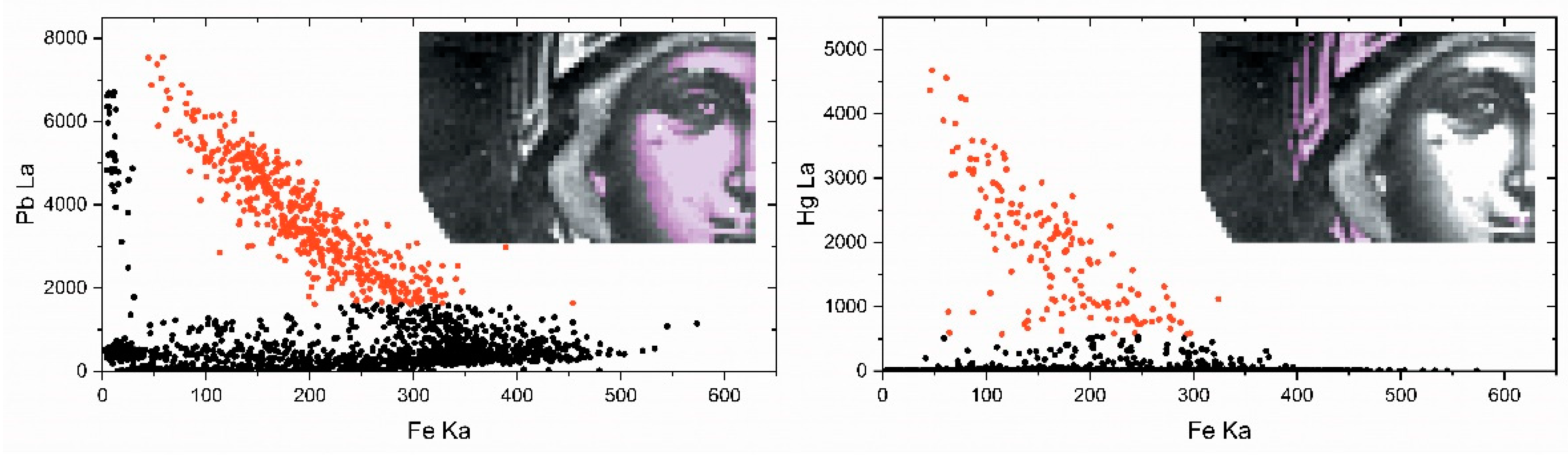
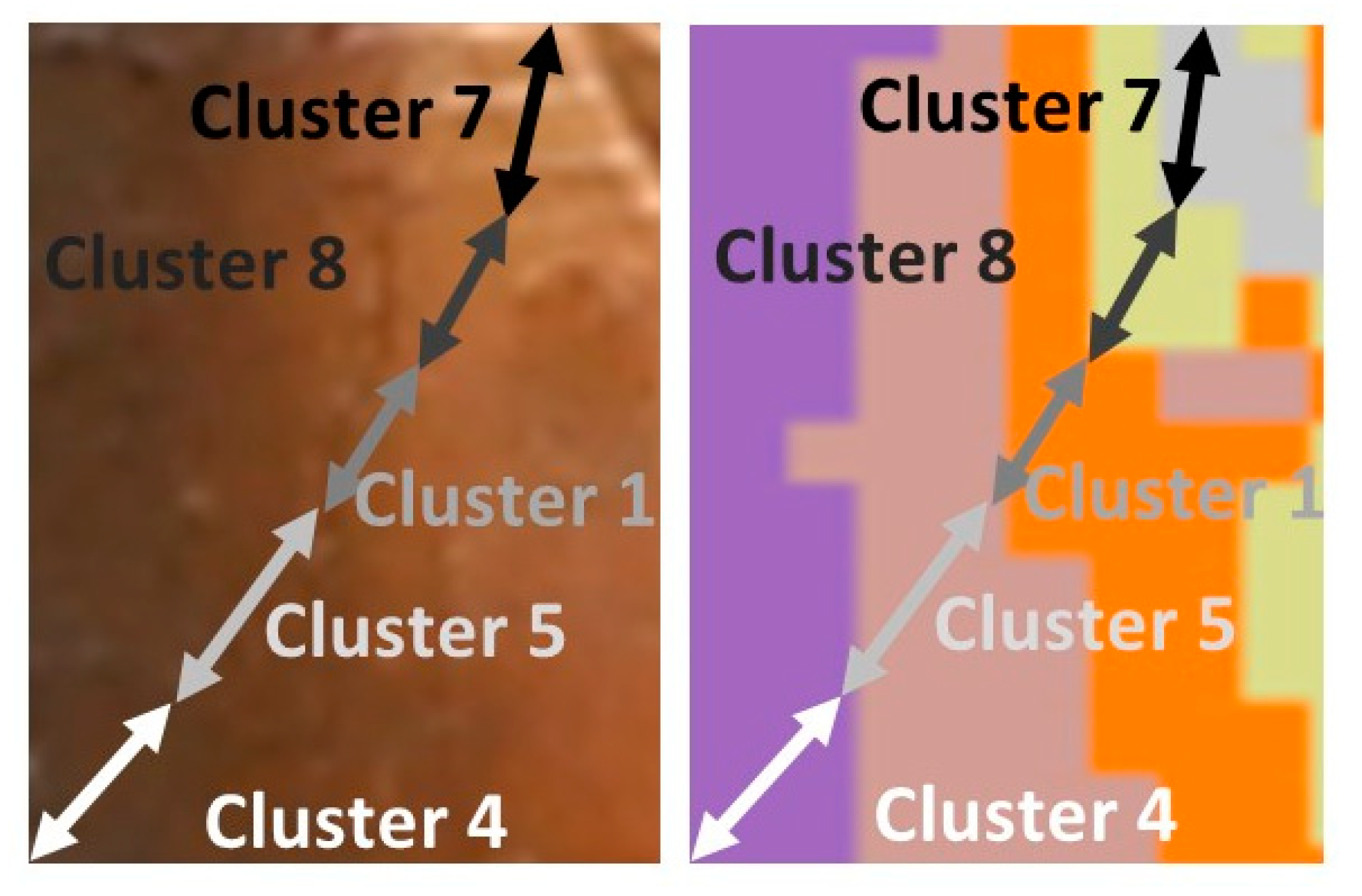
3.3. Cluster Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mantler, M.; Schreiner, M. X-ray fluorescence spectrometry in art and archaeology. X-ray Spectrom. 2000, 29, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, K.; Van der Snickt, G.; Vanmeert, F.; Legrand, S.; Nuyts, G.; Alfeld, M.; Monico, L.; Anaf, W.; De Nolf, W.; Vermeulen, M.; et al. Non-Invasive and Non-Destructive Examination of Artistic Pigments, Paints, and Paintings by Means of X-Ray Methods. Top. Curr. Chem. 2016, 374, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Romano, F.P.; Caliri, C.; Nicotra, P.; Di Martino, S.; Pappalardo, L.; Rizzo, F.; Santos, H.C. Real-time elemental imaging of large dimension paintings with a novel mobile macro X-ray fluorescence (MA-XRF) scanning technique. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2017, 32, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokiasmenou, E.; Caliri, C.; Kantarelou, V.; Karydas, A.G.; Romano, F.P.; Brecoulaki, H. Macroscopic XRF imaging in unravelling polychromy on Mycenaean wall-paintings from the Palace of Nestor at Pylos. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2020, 29, 102079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, M.; Tarsińska-Petruk, D.; Płotek, M.; Goryl, M.; Kruk, M.P. MA-XRF study of 15th–17th century icons from the collection of the National Museum in Krakow, Poland. X-ray Spectrom. 2019, 48, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé, V.A.; Papillon, E.; Cotte, M.; Walter, P.; Susini, J. A multiplatform code for the analysis of energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectra. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2007, 62, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfeld, M.; Janssens, K. Strategies for processing mega-pixel X-ray fluorescence hyperspectral data: A case study on a version of Caravaggio’s painting Supper at Emmaus. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2015, 30, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, A.; Caccia, M.; Alberti, R.; Bonizzoni, L.; Aresi, N.; Frizzi, T.; Bombelli, L.; Gironda, M.; Martini, M. Discovering the material palette of the artist: A p-XRF stratigraphic study of the Giotto panel ‘God the Father with Angels’. X-ray Spectrom. 2017, 46, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trentelman, K.; Janssens, K.; van der Snickt, G.; Szafran, Y.; Woollett, A.T.; Dik, J. Rembrandt’s An Old Man in Military Costume: The underlying image re-examined. Appl. Phys. A 2015, 121, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kogou, S.; Lee, L.; Shahtahmassebi, G.; Liang, H. A new approach to the interpretation of XRF spectral imaging data using neural networks. X-ray Spectrom. 2020, 50, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalić, I.B.; Fazinić, S.; Barac, M.; Karydas, A.G.; Migliori, A.; Doračić, D.; Desnica, V.; Mudronja, D.; Krstić, D. Multivariate analysis of PIXE + XRF and PIXE spectral images. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2021, 36, 654–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsilli, J.; Galli, A.; Bonizzoni, L.; Caccia, M. More than XRF Mapping: STEAM (Statistically Tailored Elemental Angle Mapper) a Pioneering Analysis Protocol for Pigment Studies. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacQueen, J. Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. Proc. Fifth Berkeley Symp. Math. Stat. Probab. 1967, 1, 281–296. [Google Scholar]
- Likas, A.; Vlassis, N.; Verbeek, J.J. The global k-means clustering algorithm. Pattern Recognit. 2003, 36, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rousseeuw, P.J. Silhouettes: A graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 1987, 20, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J. Principal component analysis. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2010, 2, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Maaten, L.J.P.; Hinton, G.E. Visualizing Data Using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Research. 2008, 9, 2579–2605. [Google Scholar]
- Ghojogh, B.; Samad, M.N.; Mashhadi, S.A.; Kapoor, T.; Ali, W.; Karray, F.; Crowley, M. Feature Selection and Feature Extraction in Pattern Analysis: A Literature Review. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1905.02845 (accessed on 16 February 2022).
- Konstantios, D. An Approach to the Work of Painters from Kapesovo in Epirus; Greek Ministry of Culture: Athens, Greece, 2001. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Nanou, M. The Virgin Mary Galaktotrophousa the “Spelaiotissa” in works of the Kapesovites painters. Delt. Christ. Archaeol. Soc. 2012, 33, 213–228. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Sotiropoulou, S.; Daniilia, S. Material aspects of icons. A review on physicochemical studies of Greek icons. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapanagiotis, I.; Lampakis, D.; Konstanta, A.; Farmakalidis, H. Identification of colourants in icons of the Cretan School of iconography using Raman spectroscopy and liquid chromatography. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazidou, D.; Lampakis, D.; Karapanagiotis, I.; Panayiotou, C. Investigation of the cross-section stratifications of icons using micro-Raman and micro-Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy. Appl. Specroscopy 2018, 72, 1258–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malletzidou, L.; Zorba, T.T.; Ganitis, V.; Kyriakou, N.; Pavlidou, E.; Paraskevopoulos, K.M. Folk ecclesiastical art in Northern Greece: Characterization of a 17 th century portable icon. In AIP Conference Proceedings 2075, Proceedings of the 10th Jubilee International Conference of the Balkan Physical Union, Sofia, Bulgaria, 26–30 August 2019; American Institute of Physics: College Park, MD, USA, 2019; p. 200003. [Google Scholar]
- Mastrotheodoros, G.P.; Theodosis, M.; Filippaki, E.; Beltsios, K.G. By the hand of Angelos? Analytical investigation of a remarkable 15th century Cretan icon. Heritage 2020, 4, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrotheodoros, G.P.; Beltsios, K.G.; Bassiakos, Y. On the blue and green pigments of post-byzantine Greek icons. Archaeometry 2020, 62, 774–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armetta, F.; Chirco, G.; Celso, F.L.; Ciaramitaro, V.; Caponetti, E.; Midiri, M.; Re, G.L.; Gaishun, V.; Kovalenko, D.; Semchenko, A.; et al. Sicilian Byzantine Icons through the Use of Non-Invasive Imaging Techniques and Optical Spectroscopy: The Case of the Madonna dell’Elemosina. Molecules 2021, 26, 7595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrotheodoros, G.P.; Beltsios, K.G.; Bassiakos, Y. On the red and yellow pigments of post-byzantine Greek icons. Archaeometry 2021, 63, 753–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzidakis, Μ. Έλληνες ζωγράφοι μετά την Άλωση (1450–1830) [Greek Painters after the Fall of Constantinople (1450–1830)]; Center for Neo-Hellenic Studies: Athens, Greece, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Vokotopoulos, P. Βυζαντινές εικόνες [Byzantine Icons]; Series “Greek Art”; Ekdotike Athenon: Athens, Greece, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Mastrotheodoros, G.P.; Beltsios, K.G.; Bassiakos, Y.; Papadopoulou, V. On the Grounds of Post-Byzantine Greek Icons. Archaeometry 2016, 58, 830–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrotheodoros, G.P.; Beltsios, K.G. Sound practice and practical conservation recipes as described in Greek post-Byzantine painters’ manuals. Stud. Conserv. 2019, 64, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, M. The Art of All Colours. Mediaeval Recipe Books for Painters and Illuminators; Archetype: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, D.T.; Dimov, S.S.; Nguyen, C.D. Selection of K in K-means clustering. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2005, 219, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anowar, F.; Sadaoui, S.; Selim, B. Conceptual and empirical comparison of dimensionality reduction algorithms (PCA, KPCA, LDA, MDS, SVD, LLE, ISOMAP, LE, ICA, t-SNE). Comput. Sci. Rev. 2021, 40, 100378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoglou, P.H. Έκφρασις [Ekphrasis], 4th ed.; Papademetriou Editions: Athens, Greece, 1993; Volume A. [Google Scholar]
- Egerton, R.F. Physical Principles of Electron Microscopy: An Introduction to TEM, SEM, and AEM; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gettens, R.J.; Kühn, H.; Chase, W. T Lead white. In Artist’s Pigments: A Handbook of Their History and Characteristics; Roy, A., Ed.; National Gallery of Art: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; Volume 2, pp. 67–82. [Google Scholar]
- Mastrotheodoros, G.P.; Beltsios, K.G. Fe-based pigments: Red, yellow and brown ochres. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2022, 14, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrotheodoros, G.P.; Beltsios, K.G.; Bassiakos, Y.; Papadopoulou, V. On the Metal-Leaf Decorations of Post-Byzantine Greek Icons. Archaeometry 2018, 60, 269–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouspensky, L. Theology of the Icon; St. Vladimir’s Seminary Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, D.V. Τα υλικά και οι τεχνικές της μεσαιωνικής ζωγραφικής [The Materials and Techniques of Medieval Painting]; Armos: Athens, Greece, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Franceschi, E.; Locardi, F. Strontium, a new marker of the origin of gypsum in cultural heritage? J. Cult. Herit. 2014, 15, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoonjans, T.; Solé, V.A.; Vincze, L.; Sanchez del Rio, M.; Appel, K.; Ferrero, C. A general Monte Carlo simulation of energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometers—Part 6. Quantification through iterative simulations. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2013, 82, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessanha, S.; Manso, M.; Antunes, V.; Carvalho, M.L.; Sampaio, J.M. Monte Carlo simulation of portable X-ray fluorescence setup: Non-invasive determination of gold leaf thickness in indo-Portuguese panel paintings. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2019, 156, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesareo, R.; De Assis, J.T.; Roldán, C.; Bustamante, A.D.; Brunetti, A.; Schiavon, N. Multilayered samples reconstructed by measuring Kα/K β or Lα/Lβ X-ray intensity ratios by EDXRF. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2013, 312, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gerodimos, T.; Asvestas, A.; Mastrotheodoros, G.P.; Chantas, G.; Liougos, I.; Likas, A.; Anagnostopoulos, D.F. Scanning X-ray Fluorescence Data Analysis for the Identification of Byzantine Icons’ Materials, Techniques, and State of Preservation: A Case Study. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging8050147
Gerodimos T, Asvestas A, Mastrotheodoros GP, Chantas G, Liougos I, Likas A, Anagnostopoulos DF. Scanning X-ray Fluorescence Data Analysis for the Identification of Byzantine Icons’ Materials, Techniques, and State of Preservation: A Case Study. Journal of Imaging. 2022; 8(5):147. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging8050147
Chicago/Turabian StyleGerodimos, Theofanis, Anastasios Asvestas, Georgios P. Mastrotheodoros, Giannis Chantas, Ioannis Liougos, Aristidis Likas, and Dimitrios F. Anagnostopoulos. 2022. "Scanning X-ray Fluorescence Data Analysis for the Identification of Byzantine Icons’ Materials, Techniques, and State of Preservation: A Case Study" Journal of Imaging 8, no. 5: 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging8050147
APA StyleGerodimos, T., Asvestas, A., Mastrotheodoros, G. P., Chantas, G., Liougos, I., Likas, A., & Anagnostopoulos, D. F. (2022). Scanning X-ray Fluorescence Data Analysis for the Identification of Byzantine Icons’ Materials, Techniques, and State of Preservation: A Case Study. Journal of Imaging, 8(5), 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging8050147






