Disease Recognition in X-ray Images with Doctor Consultation-Inspired Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
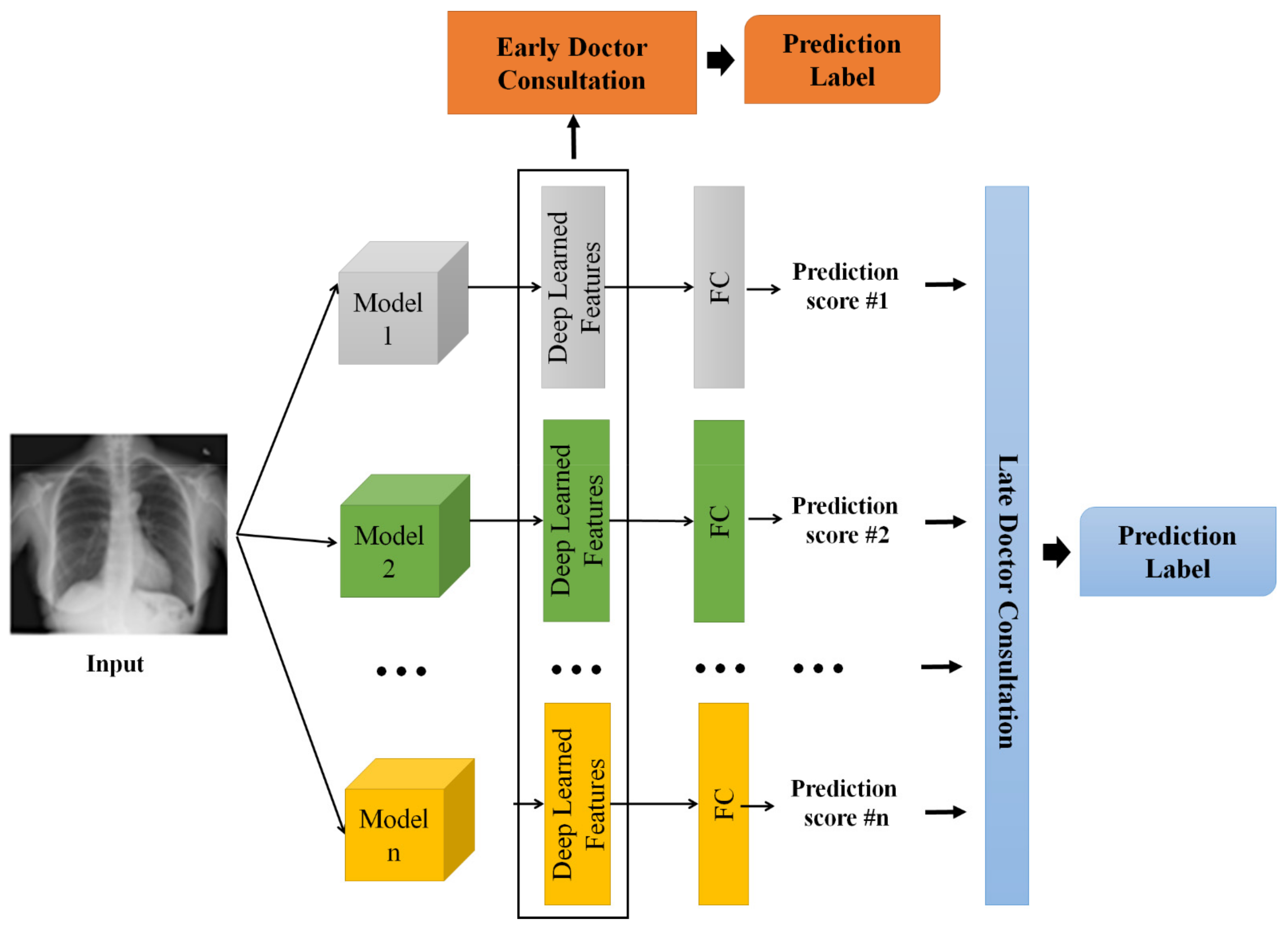
3. Proposed Framework
3.1. Individual Doctor Models
3.2. Doctor Consultation-Inspired Model
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Settings
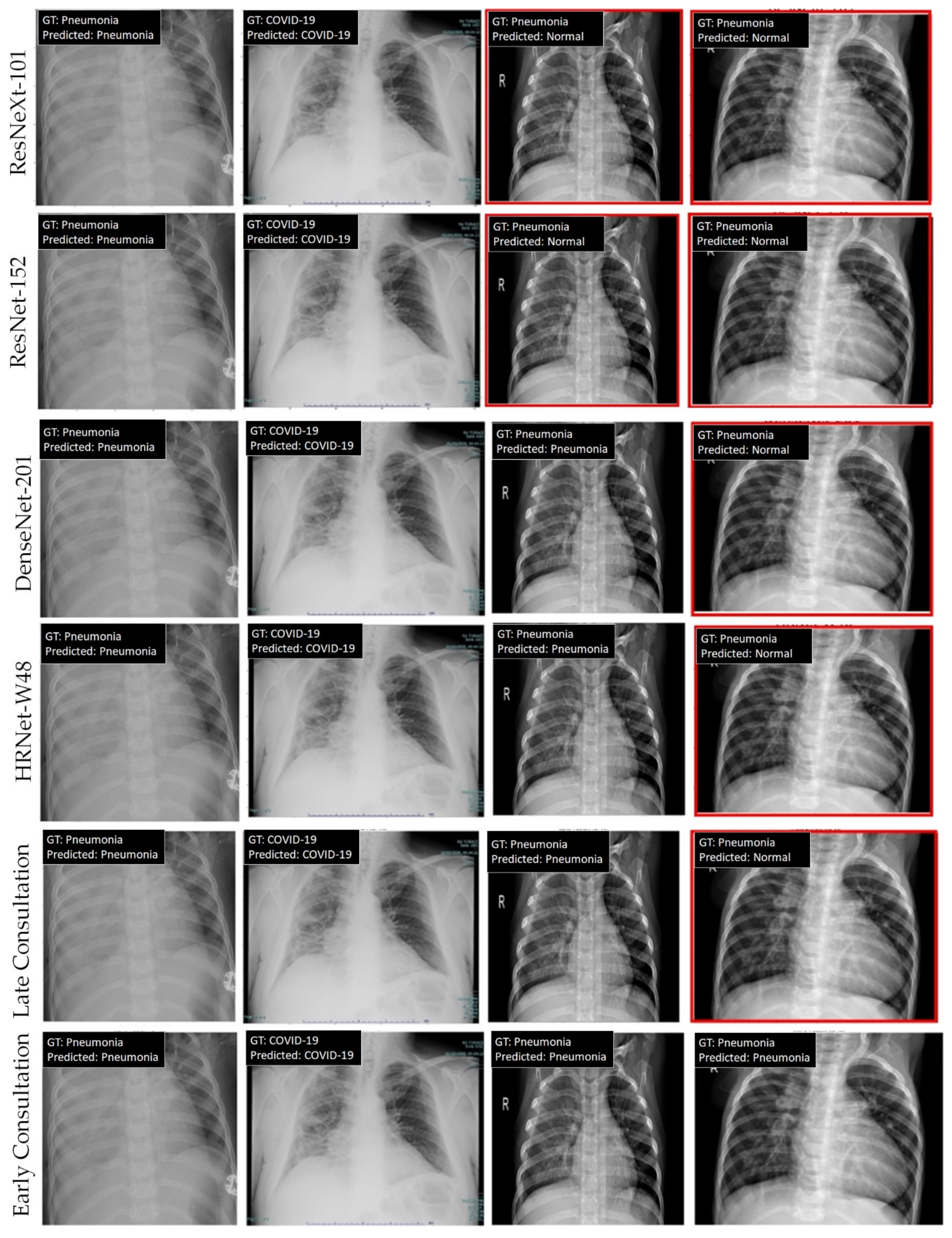
4.2. Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- COVID-19 Pandemic. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 (accessed on 20 August 2022).
- Ai, T.; Yang, Z.; Hou, H.; Zhan, C.; Chen, C.; Lv, W.; Tao, Q.; Sun, Z.; Xia, L. Correlation of chest CT and RT-PCR testing in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: A report of 1014 cases. Radiology 2020, 296, E32–E40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Han, H.; Liu, F.; Lv, Z.; Wu, K.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhu, C. Positive rate of RT-PCR detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection in 4880 cases from one hospital in Wuhan, China, from Jan to Feb 2020. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 505, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radiation Risk from Medical Imaging. Available online: https://www.health.harvard.edu/cancer/radiation-risk-from-medical-imaging (accessed on 20 August 2022).
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, T.; Kalakota, R. The potential for artificial intelligence in healthcare. Future Healthc. J. 2019, 6, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phung, K.A.; Kirbas, C.; Dereci, L.; Nguyen, T.V. Pervasive Healthcare Internet of Things: A Survey. J. Inf. 2022, 13, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.H.; Beam, A.L.; Kohane, I.S. Artificial intelligence in healthcare. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 2, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguerol, T.M.; Paulano-Godino, F.; Martín-Valdivia, M.T.; Menias, C.O.; Luna, A. Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats analysis of artificial intelligence and machine learning applications in radiology. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2019, 16, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibly, K.H.; Dey, S.K.; Islam, M.T.U.; Rahman, M.M. COVID faster R–CNN: A novel framework to Diagnose Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) in X-Ray images. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2020, 20, 100405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Sethy, P.K.; Behera, S.K. Detection of Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Based on Deep Features. Preprints 2020, 2020030300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, B.; Nair, M.S. Computer-aided detection of COVID-19 from X-ray images using multi-CNN and Bayesnet classifier. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 40, 1436–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1251–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, X.; Lee, H.C.; Diao, K.Y.; Huang, M.; Lin, B.; Liu, C.; Xie, Z.; Ma, Y.; Robson, P.M.; Chung, M.; et al. Artificial intelligence–enabled rapid diagnosis of patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1224–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurt, B.; Kligerman, S.; Hsiao, A. Deep learning localization of pneumonia: 2019 coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak. J. Thorac. Imaging 2020, 35, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncer, T.; Dogan, S.; Ozyurt, F. An automated Residual Exemplar Local Binary Pattern and iterative ReliefF based COVID-19 detection method using chest X-ray image. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2020, 203, 104054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Pietikainen, M. Dynamic texture recognition using local binary patterns with an application to facial expressions. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2007, 29, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemdan, E.E.D.; Shouman, M.A.; Karar, M.E. Covidx-net: A framework of deep learning classifiers to diagnose COVID-19 in X-ray images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.11055. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Ardakani, A.A.; Kanafi, A.R.; Acharya, U.R.; Khadem, N.; Mohammadi, A. Application of deep learning technique to manage COVID-19 in routine clinical practice using CT images: Results of 10 convolutional neural networks. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 121, 103795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Girshick, R.; Dollár, P.; Tu, Z.; He, K. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1492–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Sun, K.; Cheng, T.; Jiang, B.; Deng, C.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, D.; Mu, Y.; Tan, M.; Wang, X.; et al. Deep high-resolution representation learning for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 43, 3349–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, A.; Goyal, M.; Gupta, D.; Khanna, A.; Al-Turjman, F.; Pinheiro, P.R. Covidgan: Data augmentation using auxiliary classifier gan for improved COVID-19 detection. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 91916–91923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Park, S.; Ye, J.C. Deep learning COVID-19 features on CXR using limited training data sets. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 2688–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, L.O.; Pereira, R.M.; Bertolini, D.; Oliveira, L.S.; Nanni, L.; Cavalcanti, G.D.; Costa, Y.M. Impact of lung segmentation on the diagnosis and explanation of COVID-19 in chest X-ray images. Sensors 2021, 21, 7116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Munich, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Tartaglione, E.; Barbano, C.A.; Berzovini, C.; Calandri, M.; Grangetto, M. Unveiling COVID-19 from chest x-ray with deep learning: A hurdles race with small data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaha, H.M.; Balaha, M.H.; Ali, H.A. Hybrid COVID-19 segmentation and recognition framework (HMB-HCF) using deep learning and genetic algorithms. Artif. Intell. Med. 2021, 119, 102156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghdadi, N.A.; Malki, A.; Abdelaliem, S.F.; Balaha, H.M.; Badawy, M.; Elhosseini, M. An automated diagnosis and classification of COVID-19 from chest CT images using a transfer learning-based convolutional neural network. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 144, 105383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perumal, V.; Narayanan, V.; Rajasekar, S.J.S. Detection of COVID-19 using CXR and CT images using Transfer Learning and Haralick features. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porebski, A.; Vandenbroucke, N.; Macaire, L. Haralick feature extraction from LBP images for color texture classification. In Proceedings of the 2008 First Workshops on Image Processing Theory, Tools and Applications, Sousse, Tunisia, 23–26 November 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Hargreaves, C.A. A review study of the deep learning techniques used for the classification of chest radiological images for COVID-19 diagnosis. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 2022, 2, 100100. [Google Scholar]
- Clement, J.C.; Ponnusamy, V.; Sriharipriya, K.C.; Nandakumar, R. A survey on mathematical, machine learning and deep learning models for COVID-19 transmission and diagnosis. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 15, 325–340. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamad, Y.I.; Baraheem, S.S.; Nguyen, T.V. Olympic Games Event Recognition via Transfer Learning with Photobombing Guided Data Augmentation. J. Imaging 2021, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpathy, A.; Toderici, G.; Shetty, S.; Leung, T.; Sukthankar, R.; Fei-Fei, L. Large-scale video classification with convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1725–1732. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Lapedriza, A.; Khosla, A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Places: A 10 million image database for scene recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 1452–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID-19 Dataset. Available online: https://github.com/nguyenvd-uit/uit-together-dataset/blob/main/COVID-19.md (accessed on 20 August 2022).
- Chest X-ray Dataset. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/prashant268/chest-xray-covid19-pneumonia (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- MMClassification Toolbox. Available online: https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmclassification (accessed on 20 October 2022).

| Method | Year | Classification | Lung Segmentation | Refinement/Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shibly et al. [10] | 2020 | VGG-16 | No | No |
| Sethy et al. [12] | 2020 | ResNet-50, SVM | No | No |
| Abraham et al. [14] | 2020 | Xception, Bayes Net | No | No |
| Mei et al. [16] | 2020 | ResNet-18, MLP | No | No |
| Tuncer et al. [18] | 2020 | Local Binary Pattern, SVM | No | IRF-based feature selection |
| Hemdan et al. [20] | 2020 | DenseNet-201 | No | No |
| Ardakani et al. [22] | 2020 | ResNet-101 | No | No |
| Waheed et al. [25] | 2020 | CNN | No | GAN-based data augmentation |
| Tartaglione et al. [29] | 2020 | ResNet-18 | Yes | Segmented lung |
| Perumal et al. [32] | 2021 | CNN | No | Transfer learning with Haralick features, CT scan |
| Teixeira et al. [27] | 2021 | InceptionV3 | Yes | Segmented lung |
| Balaha et al. [30] | 2021 | CNN | Yes | Geometric transformation-based data augmentation, segmented lung, genetic algorithm |
| Baghdadi et al. [31] | 2022 | CNN | No | Sparrow search algorithm, CT scan |
| Ours | 2022 | CNN, SVM | No | Doctor consultation-inspired fusion |
| Abbreviation | Meaning |
|---|---|
| CXR | Chest X-ray |
| CT scan | Computed tomography scan |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| RT-PCR | Real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction |
| ARDS | Acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| ResNet | Residual neural network |
| HRNet | High-resolution network |
| DenseNet | Dense convolutional network |
| SVM | Support vector machine |
| Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|
| The number of models (doctors) | |
| The prediction score of model | |
| The number of classes, such as COVID, pneumonia, and normal | |
| Concatenation operation | |
| The classification function for late fusion | |
| The deep-learned features extracted from model | |
| The classification function for early fusion | |
| norm | The square root of the inner product of a vector with itself |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet-18 | 89.39 | 89.70 | 89.39 | 89.34 |
| ResNet-50 | 90.15 | 90.18 | 90.15 | 90.09 |
| ResNet-101 | 90.91 | 90.87 | 90.91 | 90.87 |
| ResNet-152 | 90.53 | 90.64 | 90.53 | 90.46 |
| ResNeXt-101 | 90.53 | 90.60 | 90.53 | 90.46 |
| DenseNet-169 | 90.53 | 92.05 | 92.05 | 92.03 |
| DenseNet-201 | 91.67 | 91.82 | 91.67 | 91.64 |
| HRNet-W48 | 91.29 | 91.29 | 91.29 | 91.26 |
| Late Consultation | 92.42 | 92.42 | 92.42 | 92.42 |
| Early Consultation | 94.70 | 94.70 | 94.70 | 94.70 |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet-18 | 89.75 | 90.42 | 89.75 | 89.93 |
| ResNet-50 | 92.47 | 92.49 | 92.47 | 92.42 |
| ResNet-101 | 90.53 | 90.49 | 90.53 | 90.37 |
| ResNet-152 | 89.52 | 89.45 | 89.52 | 89.37 |
| ResNeXt-101 | 92.55 | 92.54 | 92.55 | 92.49 |
| DenseNet-169 | 92.00 | 91.95 | 92.00 | 91.95 |
| DenseNet-201 | 93.17 | 93.16 | 93.17 | 93.12 |
| HRNet-W48 | 92.62 | 92.60 | 90.62 | 92.56 |
| Late Consultation | 93.94 | 93.92 | 93.94 | 93.93 |
| Early Consultation | 95.03 | 95.03 | 95.03 | 95.03 |
| Method | UIT COVID-19 Dataset | Chest X-ray Dataset | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Precision | Recall | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | |
| Shibly et al. [17] | 90.24 | 90.24 | 90.24 | 90.68 | 90.60 | 90.68 |
| Sethy et al. [18] | 90.15 | 90.18 | 90.15 | 92.47 | 92.49 | 92.47 |
| Abraham et al. [38] | 88.24 | 89.28 | 88.24 | 92.00 | 91.99 | 92.00 |
| Mei et al. [39] | 89.39 | 89.70 | 89.39 | 89.75 | 90.42 | 89.75 |
| Hemdan et al. [32] | 91.67 | 91.82 | 91.67 | 93.17 | 93.16 | 93.17 |
| Ardakani et al. [22] | 90.91 | 90.87 | 90.91 | 90.53 | 90.49 | 90.53 |
| Late Consultation | 92.42 | 92.42 | 92.42 | 93.94 | 93.92 | 93.94 |
| Early Consultation | 94.70 | 94.70 | 94.70 | 95.03 | 95.03 | 95.03 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Phung, K.A.; Nguyen, T.T.; Wangad, N.; Baraheem, S.; Vo, N.D.; Nguyen, K. Disease Recognition in X-ray Images with Doctor Consultation-Inspired Model. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging8120323
Phung KA, Nguyen TT, Wangad N, Baraheem S, Vo ND, Nguyen K. Disease Recognition in X-ray Images with Doctor Consultation-Inspired Model. Journal of Imaging. 2022; 8(12):323. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging8120323
Chicago/Turabian StylePhung, Kim Anh, Thuan Trong Nguyen, Nileshkumar Wangad, Samah Baraheem, Nguyen D. Vo, and Khang Nguyen. 2022. "Disease Recognition in X-ray Images with Doctor Consultation-Inspired Model" Journal of Imaging 8, no. 12: 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging8120323
APA StylePhung, K. A., Nguyen, T. T., Wangad, N., Baraheem, S., Vo, N. D., & Nguyen, K. (2022). Disease Recognition in X-ray Images with Doctor Consultation-Inspired Model. Journal of Imaging, 8(12), 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging8120323






