Online Calibration of a Linear Micro Tomosynthesis Scanner
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Adaptation of Linear Tomosynthesis to Microscopy of Pathology Samples
1.2. What Is New about the Present Calibration Method
2. Materials and Methods
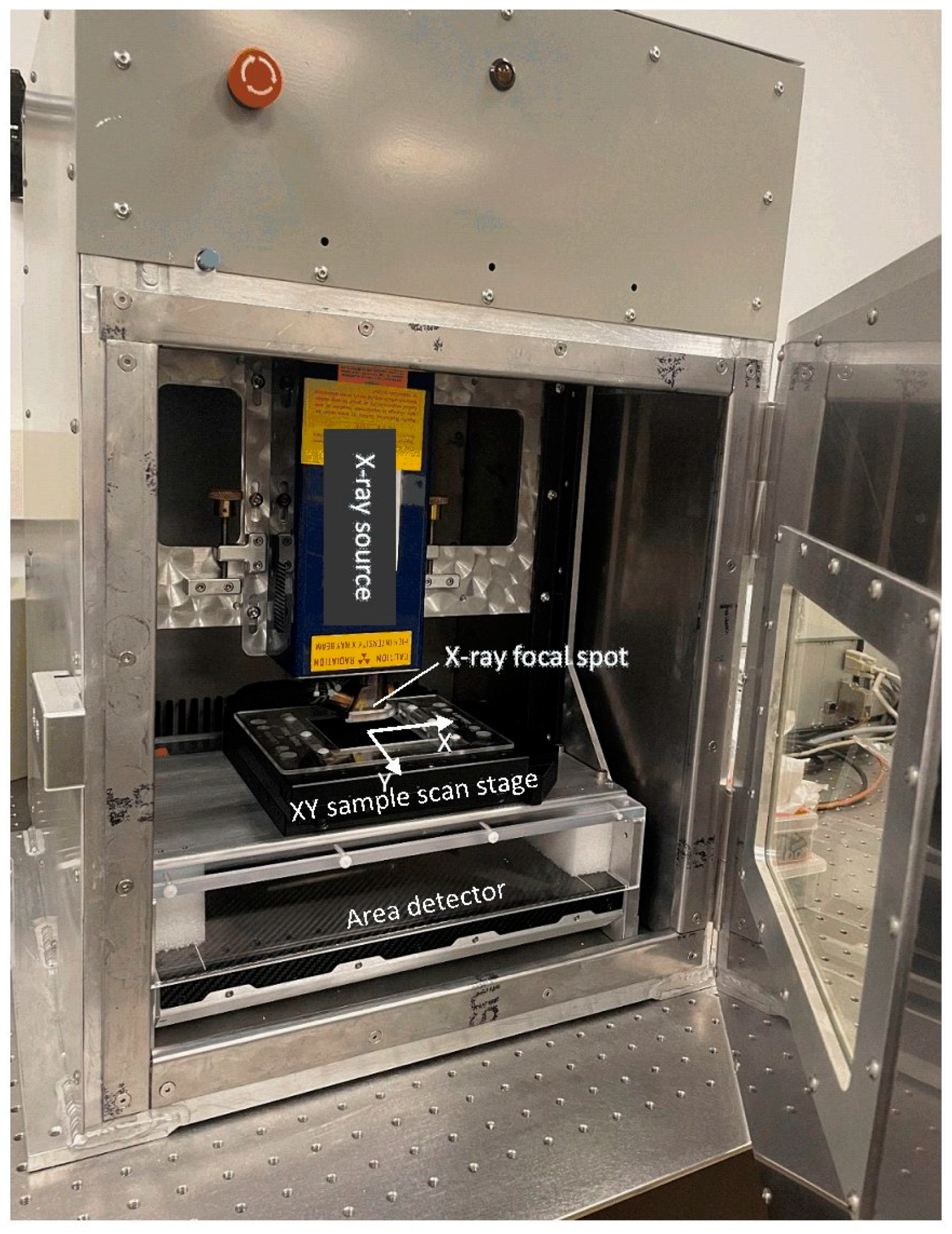
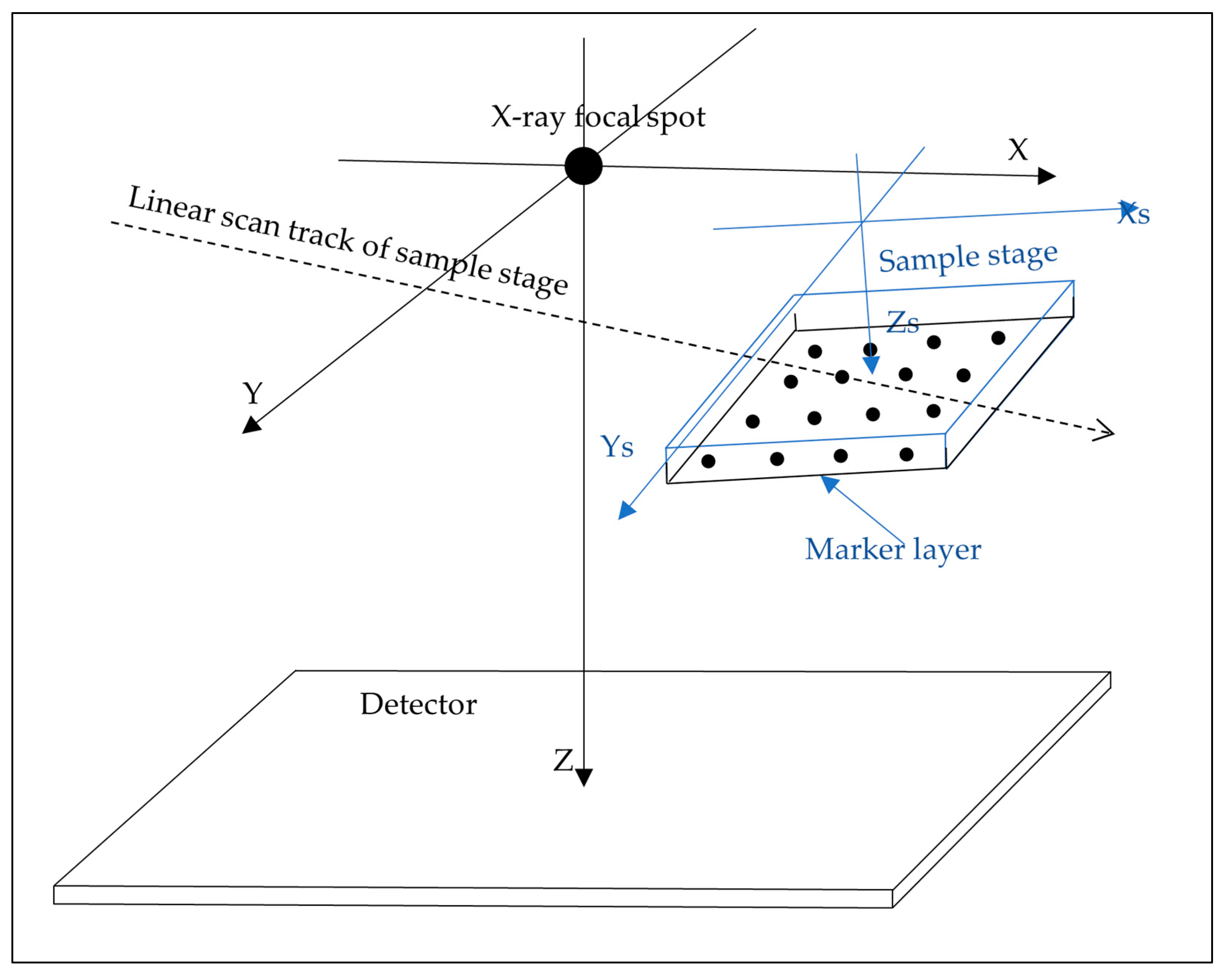
2.1. Scanner Hardware Geometry and Scan Procedure
2.2. Theoretical Basis of the Calibration Method
2.3. Fabrication of a Layer of Dispersed Markers
2.4. Measurement of the Geometric Parameters
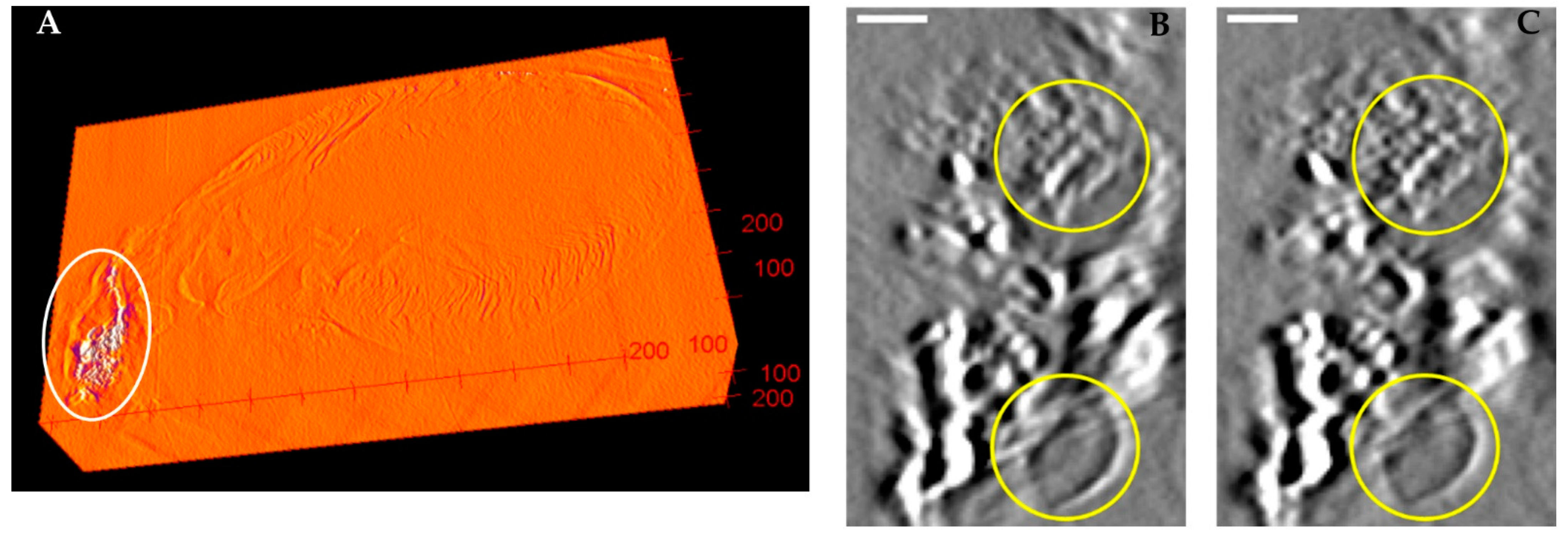
2.5. Assessing the Effect of Calibration by the Misalignment of Back-Projected Images
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dobbins, J.T.; Godfrey, D.J. Digital X-ray Tomosynthesis: Current State of the Art and Clinical Potential. Phys. Med. Biol. 2003, 48, R65–R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vedantham, S.; Karellas, A.; Vijayaraghavan, G.R.; Kopans, D.B. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: State of the Art. Radiology 2015, 277, 663–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, A.; Weinstein, S.P.; McDonald, E.S.; Conant, E.F. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Concepts and Clinical Practice. Radiology 2019, 292, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomi, T.; Nakajima, M.; Fujiwara, H.; Takeda, T.; Saito, K.; Umeda, T.; Sakaguchi, K. Comparison between Chest Digital Tomosynthesis and CT as a Screening Method to Detect Artificial Pulmonary Nodules: A Phantom Study. Br. J. Radiol. 2012, 85, e622–e629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, A.; Noël, A.; Regent, D.; Villani, N.; Gillet, R.; Gondim Teixeira, P. Tomosynthesis in Musculoskeletal Pathology. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2018, 99, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machida, H.; Yuhara, T.; Tamura, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Tate, E.; Ueno, E.; Nye, K.; Sabol, J.M. Whole-Body Clinical Applications of Digital Tomosynthesis. RadioGraphics 2016, 36, 735–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Maisl, M.; Reiter, H.; Arnold, W. Computed Laminography for Materials Testing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 68, 3500–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondrom, S.; Zhou, J.; Maisl, M.; Reiter, H.; Kröning, M.; Arnold, W. X-ray Computed Laminography: An Approach of Computed Tomography for Applications with Limited Access. Nucl. Eng. Des. 1999, 190, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Xing, Y.; Xue, H.; Cheng, J. Straight-Line-Trajectory-Based X-ray Tomographic Imaging for Security Inspections: System Design, Image Reconstruction and Preliminary Results. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2013, 60, 3955–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, N.S.; Boardman, R.P.; Sinclair, I.; Blumensath, T. Recent Advances in X-ray Cone-Beam Computed Laminography. J. X-ray Sci. Technol. 2016, 24, 691–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howes, W.E. Planigraphy—Its Application to Thoracic Diagnosis. Radiology 1939, 32, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Martinez, A.M.; Miao, H.X.; Larsen, T.C.; Nguyen, C.P.; Bennett, E.E.; Moorse, K.P.; Yu, Z.X.; Remaley, A.T.; Boehm, M.; et al. Correlative Detection of Isolated Single and Multi-Cellular Calcifications in the Internal Elastic Lamina of Human Coronary Artery Samples. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.T.; Larsen, T.C.; Wang, M.; Knutsen, R.H.; Yang, Z.; Bennett, E.E.; Mazilu, D.; Yu, Z.-X.; Tao, X.; Donahue, D.R.; et al. X-ray Microtomosynthesis of Unstained Pathology Tissue Samples. J. Microsc. 2021, 283, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Mainprize, J.G.; Kempston, M.P.; Mawdsley, G.E.; Yaffe, M.J. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Geometry Calibration. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2007: Physics of Medical Imaging, SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA, 17 March 2007; Volume 6510, pp. 1118–1128. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Liu, B. A Generic Geometric Calibration Method for Tomographic Imaging Systems with Flat-Panel Detectors—A Detailed Implementation Guide. Med. Phys. 2010, 37, 3844–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Wu, X.; Zhao, H.; Liu, H. A Phantom-Based Calibration Method for Digital x-Ray Tomosynthesis. J. X-ray Sci. Technol. 2012, 20, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, N.; Gao, J.; Hu, Z. Geometric Calibration of a Stationary Digital Breast Tomosynthesis System Based on Distributed Carbon Nanotube X-ray Source Arrays. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.J.; Vent, T.L.; Acciavatti, R.J.; Maidment, A.D.A. Geometric Calibration for a Next-Generation Digital Breast Tomosynthesis System Using Virtual Line Segments. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2018: Physics of Medical Imaging, SPIE, Houston, TX, USA, 9 March 2018; Volume 10573, pp. 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.-H.; Ni, Y.-C.; Huang, S.-Y.; Hsieh, H.-H.; Tseng, S.-P.; Tseng, F.-P. A Geometric Calibration Method for the Digital Chest Tomosynthesis with Dual-Axis Scanning Geometry. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullberg, G.T.; Tsui, B.M.W.; Crawford, C.R.; Ballard, J.G.; Hagius, J.T. Estimation of Geometrical Parameters and Collimator Evaluation for Cone Beam Tomography. Med. Phys. 1990, 17, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, S.G.; Schneberk, D.J.; Fitch, J.P.; Martz, H.E. Calculation of the Rotational Centers in Computed Tomography Sinograms. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 1990, 37, 1525–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noo, F.; Clackdoyle, R.; Mennessier, C.; White, T.A.; Roney, T.J. Analytic Method Based on Identification of Ellipse Parameters for Scanner Calibration in Cone-Beam Tomography. Phys. Med. Biol. 2000, 45, 3489–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, G.M.; Saunders, R.; Pelc, N.J. Alignment of a Volumetric Tomography System. Med. Phys. 2001, 28, 1472–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beque, D.; Nuyts, J.; Bormans, G.; Suetens, P.; Dupont, P. Characterization of Pinhole SPECT Acquisition Geometry. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2003, 22, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Smekal, L.; Kachelriess, M.; Stepina, E.; Kalender, W.A. Geometric Misalignment and Calibration in Cone-Beam Tomography. Med. Phys. 2004, 31, 3242–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.; Moseley, D.J.; Siewerdsen, J.H.; Jaffray, D.A. Accurate Technique for Complete Geometric Calibration of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Systems. Med. Phys. 2005, 32, 968–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Kwan, A.L.C.; Miller, D.F.; Boone, J.M. A Geometric Calibration Method for Cone Beam CT Systems. Med. Phys. 2006, 33, 1695–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, S.; Noo, F.; Dennerlein, F.; Lauritsch, G.; Hornegger, J. Geometric Calibration of the Circle-plus-Arc Trajectory. Phys. Med. Biol. 2007, 52, 6943–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panetta, D.; Belcari, N.; Guerra, A.D.; Moehrs, S. An Optimization-Based Method for Geometrical Calibration in Cone-Beam CT without Dedicated Phantoms. Phys. Med. Biol. 2008, 53, 3841–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakou, Y.; Lapp, R.M.; Hillebrand, L.; Ertel, D.; Kalender, W.A. Simultaneous Misalignment Correction for Approximate Circular Cone-Beam Computed Tomography. Phys. Med. Biol. 2008, 53, 6267–6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.; Chityala, R.N.; Hoffmann, K.R.; Ionita, C.N.; Bednarek, D.R.; Rudin, S. Self-Calibration of a Cone-Beam Micro-CT System. Med. Phys. 2009, 36, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingston, A.; Sakellariou, A.; Varslot, T.; Myers, G.; Sheppard, A. Reliable Automatic Alignment of Tomographic Projection Data by Passive Auto-Focus. Med. Phys. 2011, 38, 4934–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Liu, B. Sensitivity Analysis of a Geometric Calibration Method Using Projection Matrices for Digital Tomosynthesis Systems. Med. Phys. 2011, 38, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Xing, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xiao, Y. Geometric Calibration of Cone-Beam CT with a Flat-Panel Detector. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record, Valencia, Spain, 23–29 October 2011; pp. 2952–2955. [Google Scholar]
- Sawall, S.; Knaup, M.; Kachelrieß, M. A Robust Geometry Estimation Method for Spiral, Sequential and Circular Cone-Beam Micro-CT. Med. Phys. 2012, 39, 5384–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, D.; Heil, U.; Schulze, R.; Schoemer, E.; Schwanecke, U. Auto Calibration of a Cone-Beam-CT. Med. Phys. 2012, 39, 5959–5970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicklein, J.; Kunze, H.; Kalender, W.A.; Kyriakou, Y. Image Features for Misalignment Correction in Medical Flat-Detector CT. Med. Phys. 2012, 39, 4918–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladikos, A.; Wein, W. Geometric Calibration Using Bundle Adjustment for Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Devices. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2012: Physics of Medical Imaging, SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA, 3 March 2012; Volume 8313, pp. 814–819. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.; Gong, H.; Yang, X. Online Geometric Calibration of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography for Arbitrary Imaging Objects. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2013, 32, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Tekaya, I.; Kaftandjian, V.; Buyens, F.; Sevestre, S.; Legoupil, S. Registration-Based Geometric Calibration of Industrial X-ray Tomography System. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2013, 60, 3937–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Li, D. Direct Determination of Cone-Beam Geometric Parameters Using the Helical Phantom. Phys. Med. Biol. 2014, 59, 5667–5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zechner, A.; Stock, M.; Kellner, D.; Ziegler, I.; Keuschnigg, P.; Huber, P.; Mayer, U.; Sedlmayer, F.; Deutschmann, H.; Steininger, P. Development and First Use of a Novel Cylindrical Ball Bearing Phantom for 9-DOF Geometric Calibrations of Flat Panel Imaging Devices Used in Image-Guided Ion Beam Therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, N592–N605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Huang, Y.; Meng, X.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Yang, K.; Ren, Q. A New Method for Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Geometric Parameters Estimation. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2016, 40, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M.W.; Ketcha, M.D.; Capostagno, S.; Martin, A.; Uneri, A.; Goerres, J.; Silva, T.D.; Reaungamornrat, S.; Han, R.; Manbachi, A.; et al. A Line Fiducial Method for Geometric Calibration of Cone-Beam CT Systems with Diverse Scan Trajectories. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 025030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Luo, S.; You, C.; Getzin, M.; Zheng, L.; Wang, G.; Gu, N. A Novel Calibration Method Incorporating Nonlinear Optimization and Ball-Bearing Markers for Cone-Beam CT with a Parameterized Trajectory. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.; Sanctorum, J.G.; Van Wassenbergh, S.; Dirckx, J.J.J.; Sijbers, J.; De Beenhouwer, J. Geometry Calibration of a Modular Stereo Cone-Beam X-ray CT System. J. Imaging 2021, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graetz, J. Auto-Calibration of Cone Beam Geometries from Arbitrary Rotating Markers Using a Vector Geometry Formulation of Projection Matrices. Phys. Med. Biol. 2021, 66, 075013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, S.; Choi, S.; Jang, H.; Shin, M.; Roh, Y.; Baek, J. Geometry Calibration and Image Reconstruction for Carbon-Nanotube-Based Multisource and Multidetector CT. Phys. Med. Biol. 2021, 66, 165005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Cai, J.; Ling, Q.; Huang, Y.; Qi, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, L.; Xu, Y. Knowledge-Based Self-Calibration Method of Calibration Phantom by and for Accurate Robot-Based CT Imaging Systems. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2021, 229, 107343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Typical Scan Speed and Range | Half Scan Speed and Range | Double Scan Speed and Range | Typical Scan Setting #2 Trial | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δy (radians) | 1.76 × 10−3 | 3.98 × 10−3 | 1.58 × 10−3 | 1.92 × 10−3 |
| δz (radians) | −1.04 × 10−3 | −1.25 × 10−3 | −1.71 × 10−3 | −1.66 × 10−3 |
| ωx (radians/mm) | −6.88 × 10−6 | 3.18 × 10−5 | −2.28 × 10−6 | −5.17 × 10−6 |
| ωy (radians/mm) | −1.18 × 10−5 | −1.23 × 10−5 | −4.14 × 10−5 | −3.57 × 10−5 |
| ωz (radians/mm) | −6.94 × 10−7 | 1.68 × 10−6 | −2.30 × 10−7 | −6.69 × 10−7 |
| RMS of the deviation angles (radians) | 1.83 × 10−3 | 2.80 × 10−3 | 1.66 × 10−3 | 1.98 × 10−3 |
| RMS of the residual deviation angles after subtracting model fit (radians) | 6.66 × 10−5 | 1.71 × 10−4 | 1.18 × 10−4 | 1.35 × 10−4 |
| RMS of the range of misalignment of back-projected marker positions without calibration (µm) | 45.75 | 35.01 | 83.18 | 50.04 |
| RMS of the range of misalignment of back-projected marker positions with calibration (µm) | 1.66 | 2.14 | 5.92 | 3.40 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bahar, P.; Nguyen, D.; Wang, M.; Mazilu, D.; Bennett, E.E.; Wen, H. Online Calibration of a Linear Micro Tomosynthesis Scanner. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging8100292
Bahar P, Nguyen D, Wang M, Mazilu D, Bennett EE, Wen H. Online Calibration of a Linear Micro Tomosynthesis Scanner. Journal of Imaging. 2022; 8(10):292. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging8100292
Chicago/Turabian StyleBahar, Piroz, David Nguyen, Muyang Wang, Dumitru Mazilu, Eric E. Bennett, and Han Wen. 2022. "Online Calibration of a Linear Micro Tomosynthesis Scanner" Journal of Imaging 8, no. 10: 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging8100292
APA StyleBahar, P., Nguyen, D., Wang, M., Mazilu, D., Bennett, E. E., & Wen, H. (2022). Online Calibration of a Linear Micro Tomosynthesis Scanner. Journal of Imaging, 8(10), 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging8100292






