Lung Nodule Detection in CT Images Using Statistical and Shape-Based Features
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- In most existing CAD-based nodule detectors, the lungs are manually marked by the radiologist, which is a tedious and time-consuming task. In the proposed algorithm, the lungs are automatically segmented from the CT images without any user intervention;
- Nodules can have different regular and irregular shapes and sizes. Some existing techniques use a few shape templates to detect the nodules, however the proposed algorithm is independent of the nodule shape and size;
- The proposed system uses basic image processing techniques, e.g., histogram processing, morphological operators, connected components analysis, etc., which makes it implementable on simple computers, making it an efficient and cost effective solution;
- In an experimental evaluation carried out on a standard LIDC dataset, the proposed system achieved high sensitivity and accuracy, outperforming the existing similar techniques.
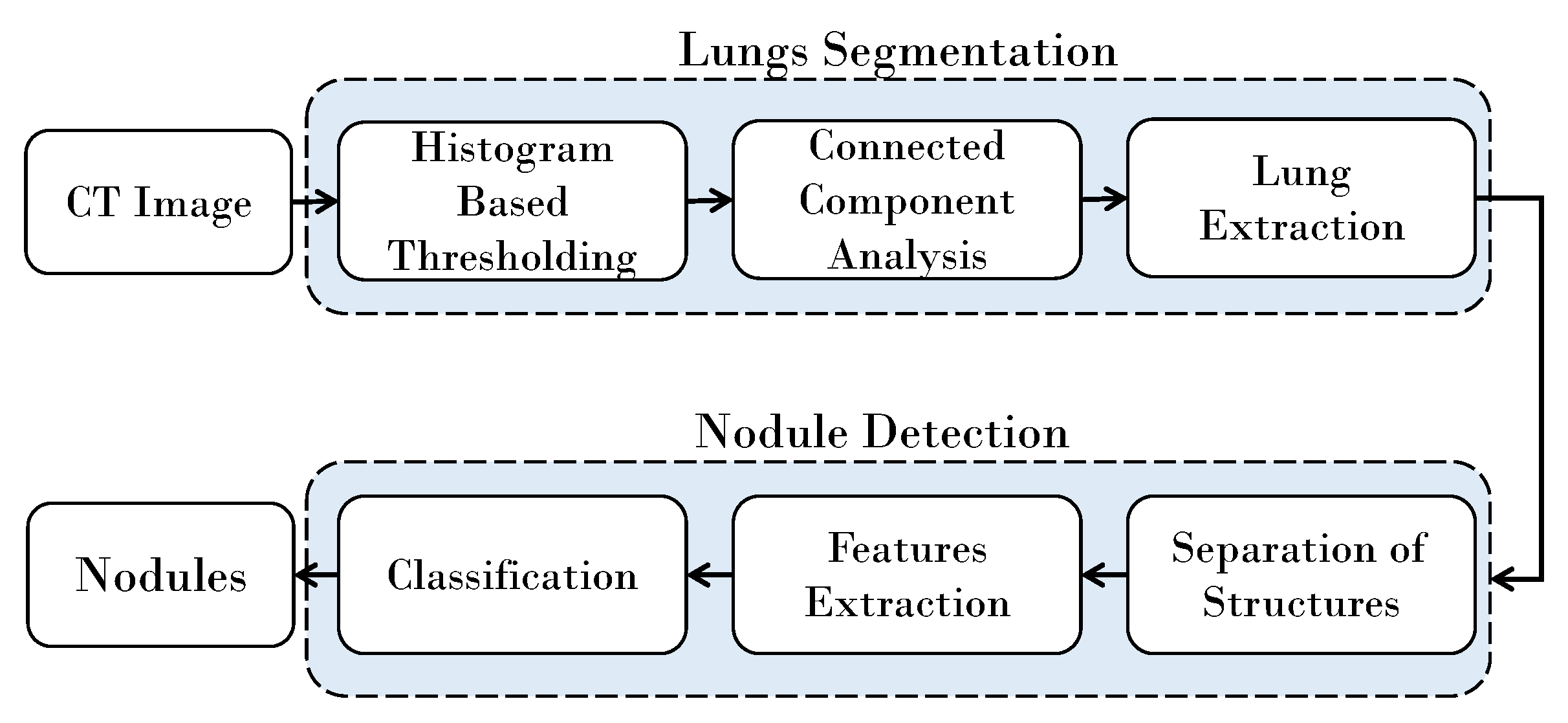
2. Materials and Methods
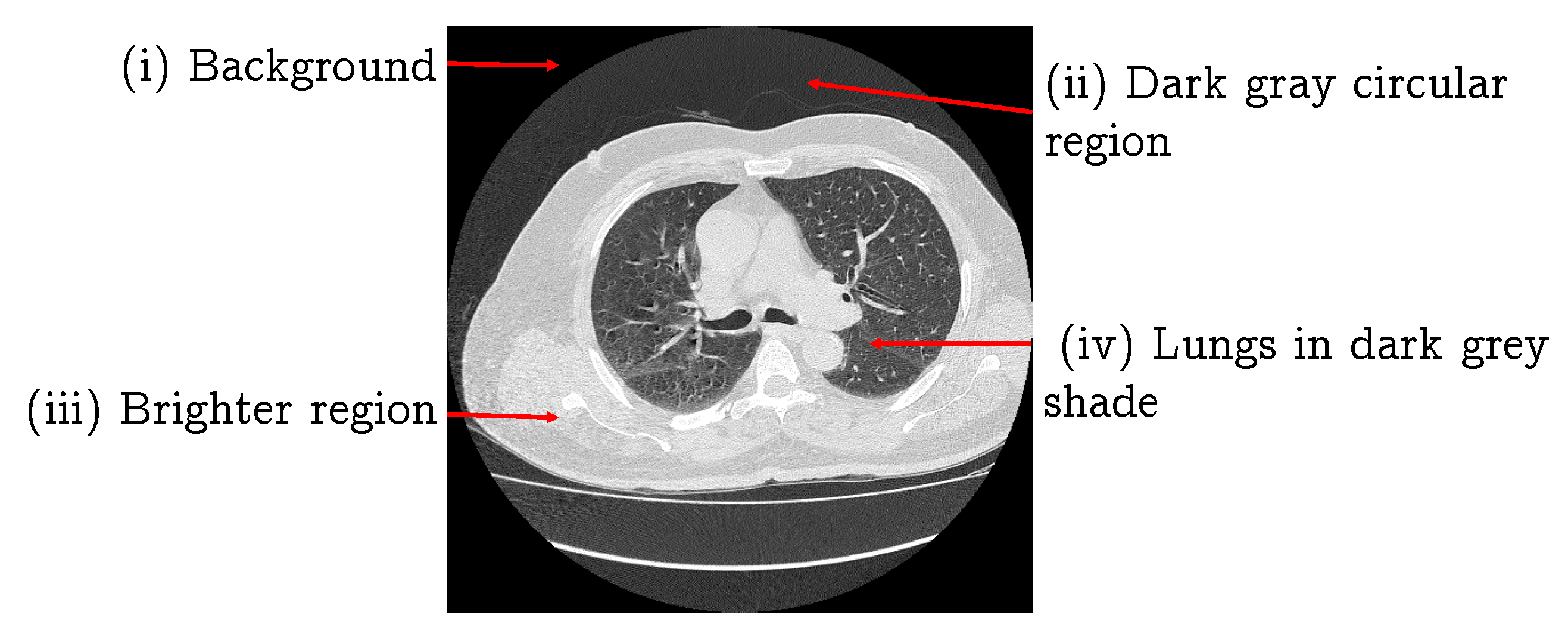
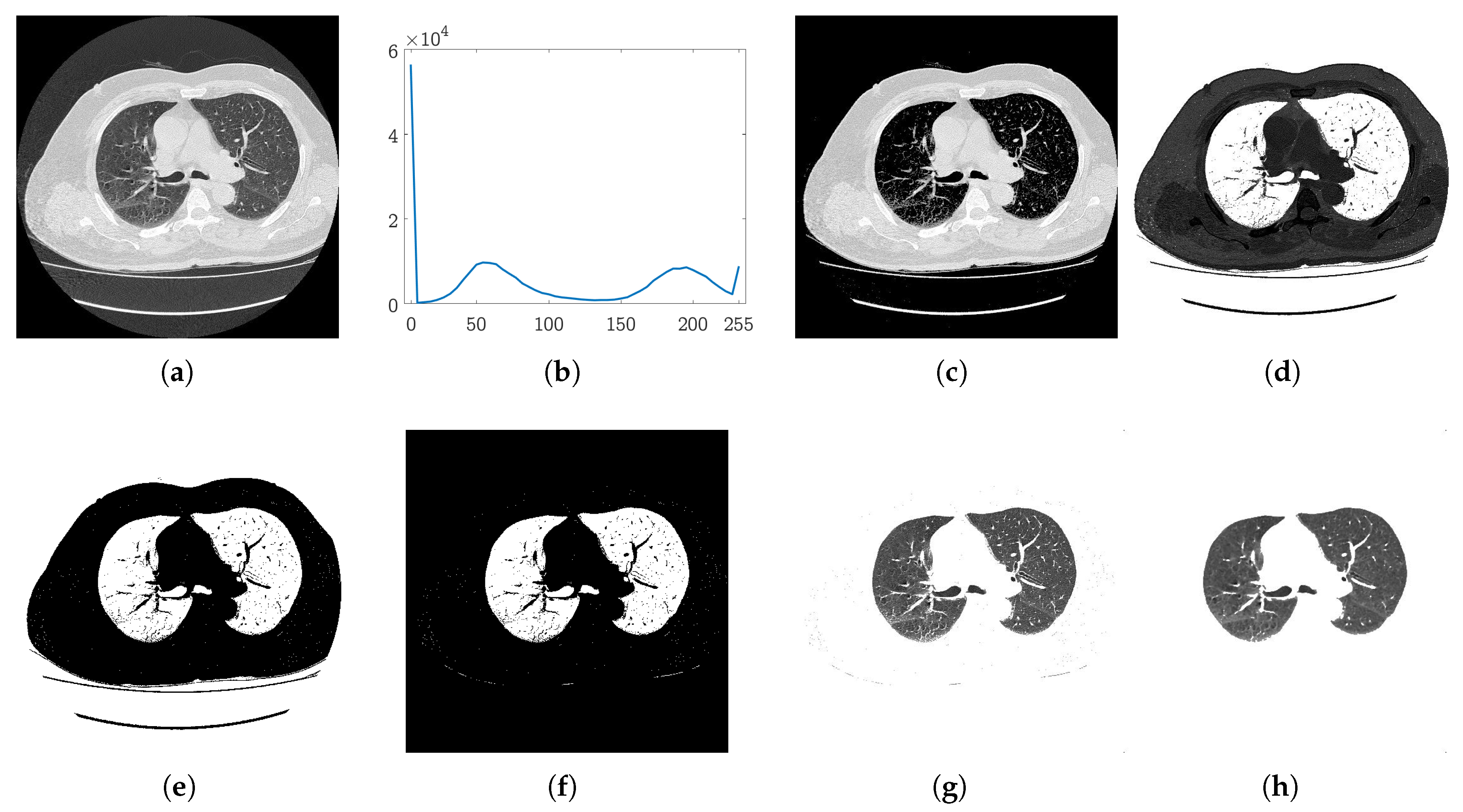
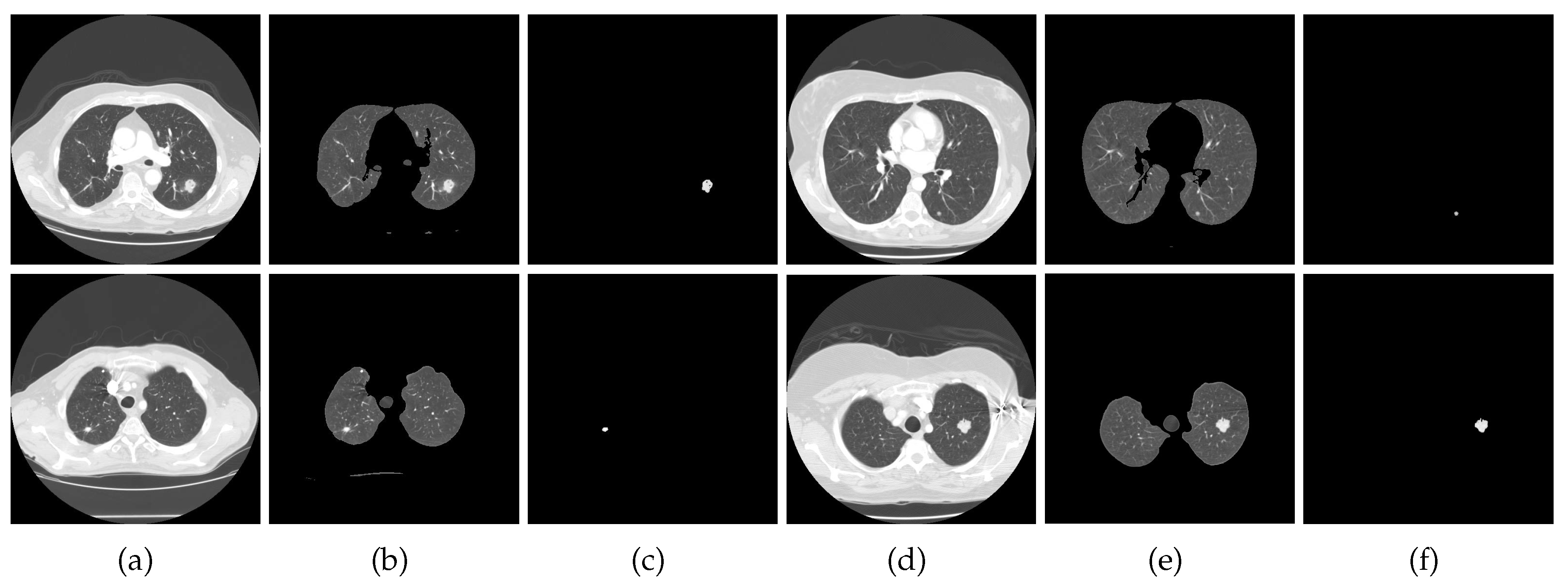
2.1. Lung Segmentation
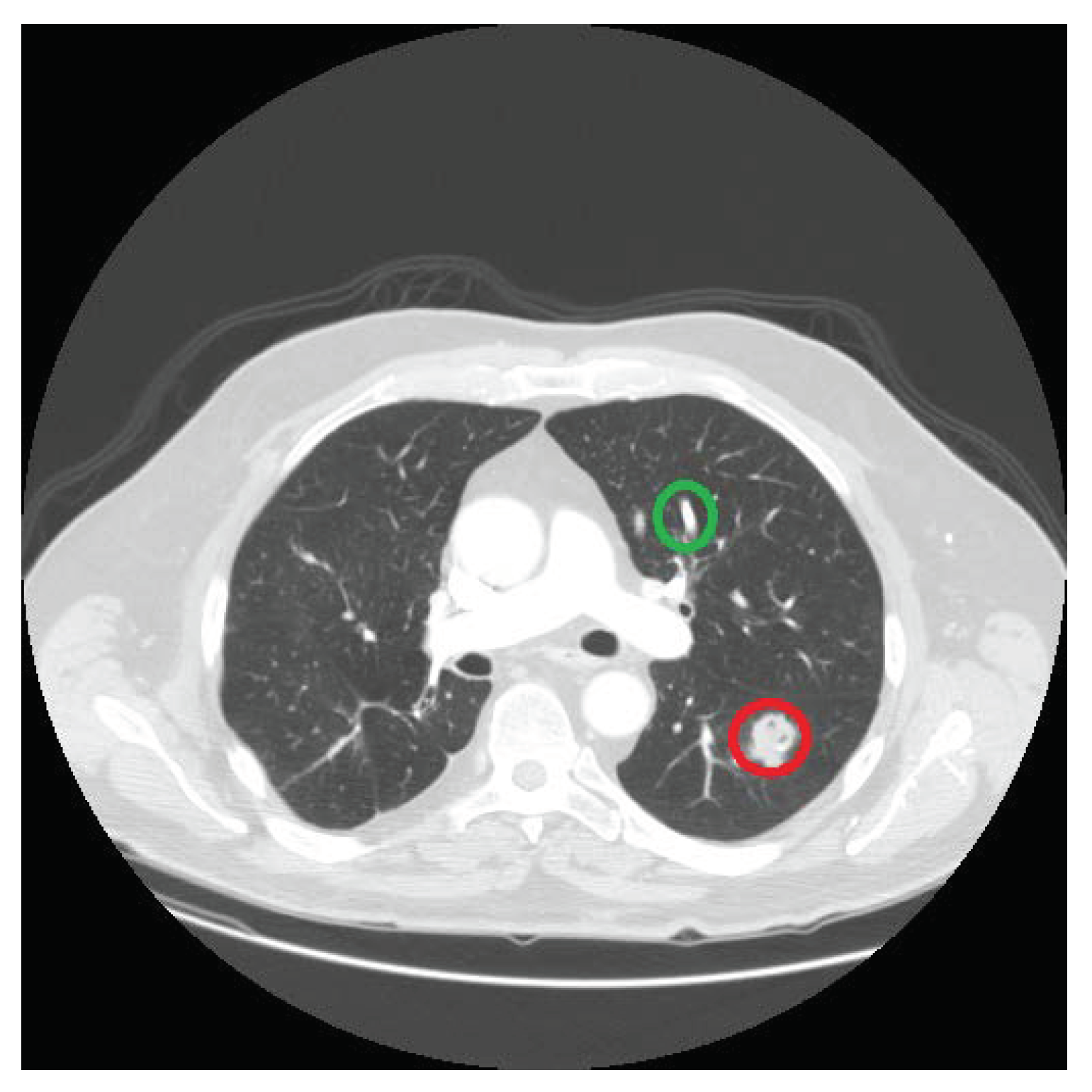
2.2. Nodules Detection
- Mean () represents the average value of the region :
- Median () is the mid-point of when arranged in non-decreasing order;
- Mode () is the most repetitive element of the data in ;
- Variance () represents to what extent the data varies from the mean value. For region , is:where and represent the size and mean of the region , respectively;
- Standard deviation is the square root of variance:
- Consistency feature: one more important feature is based on the shape of the lesion and its appearance in the colocated slices of the CT scan. That is, if a nodule exists in one slice, it must also appear in the preceding slices or in the succeeding slices of a CT scan. On the other hand, the vessels and bronchi transform further into new shapes, so if they are detected in one slice there are high chances that they will not be present in the exact location in the next slice of the series. This property is an important feature of nodules. Therefore, the center points detected in slice are traced in a window of size in adjacent slices. That is, the center points detected in slice will be compared with the center points identified in k previous and k next slices,and we assign a center point 1 if it exists in any of those slices, and 0 if it does not exist in any of them. This consistency feature for candidate in the current slice is represented as . In this paper, we use a window of size 3, (), to determine the the value of feature for each location in a given slice.
3. Experiments and Results
3.1. Evaluation Dataset
3.2. Performance Evaluation
3.3. Performance Comparison
3.4. Computational Complexity Analysis
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Shin, H.; Bray, F.; Forman, D.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2893–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA-Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capocaccia, R.; Gatta, G.; Dal Maso, L. Life expectancy of colon, breast, and testicular cancer patients: An analysis of US-SEER population-based data. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, J.; Zhao, H.; Lan, L.; Sun, P.; Feng, Y. A Computer-Aided Detection System for the Detection of Lung Nodules Based on 3D-ResNet. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saleem, M.; Farid, M.S.; Saleem, S.; Khan, M.H. X-ray image analysis for automated knee osteoarthritis detection. Signal Image Video Process. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, J.; O’Neill, T.; Felson, D.; Cootes, T. Automated shape and texture analysis for detection of osteoarthritis from radiographs of the knee. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Das, D.; Mukherjee, R.; Chakarborty, C. Computational microscopic imaging for malaria parasite detection: A systematic review. J. Microsc. 2015, 260, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, T.; Farid, M.S. Automatic detection of Plasmodium parasites from microscopic blood images. J. Parasit. Dis. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehanian, C.; Jaiswal, M.; Delahunt, C.; Thompson, C.; Horning, M.; Hu, L.; Ostbye, T.; McGuire, S.; Mehanian, M.; Champlin, C.; et al. Computer-Automated Malaria Diagnosis and Quantitation Using Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nasrullah, N.; Sang, J.; Alam, M.S.; Mateen, M.; Cai, B.; Hu, H. Automated Lung Nodule Detection and Classification Using Deep Learning Combined with Multiple Strategies. Sensors 2019, 19, 3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saien, S.; Moghaddam, H.A.; Fathian, M. A unified methodology based on sparse field level sets and boosting algorithms for false positives reduction in lung nodules detection. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2018, 13, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, D.M.; Luo, S.; Abdelgader, A.M.S. Auto Diagnostics of Lung Nodules Using Minimal Characteristics Extraction Technique. Diagnostics 2016, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, Y.; Pandit, S.; Saraee, E.; Nordahl, T.; Ellis, T.; Betke, M. Home-Based Physical Therapy with an Interactive Computer Vision System. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.H.; Helsper, J.; Farid, M.S.; Grzegorzek, M. A computer vision-based system for monitoring Vojta therapy. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2018, 113, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.H.; Schneider, M.; Farid, M.S.; Grzegorzek, M. Detection of Infantile Movement Disorders in Video Data Using Deformable Part-Based Model. Sensors 2018, 18, 3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Narayanan, B.N.; Hardie, R.C.; Kebede, T. M Performance analysis of a computer-aided detection system for lung nodules in CT at different slice thicknesses. J. Med. Imaging 2018, 5, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nishio, M.; Nishizawa, M.; Sugiyama, O.; Kojima, R.; Yakami, M.; Kuroda, T.; Togashi, K. Computer-aided diagnosis of lung nodule using gradient tree boosting and Bayesian optimization. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Yang, Z.; Gong, L.; Jiang, S.; Wang, L.; Cao, X.; Wei, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z. An Appraisal of Nodule Diagnosis for Lung Cancer in CT Images. J. Med. Syst. 2019, 43, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Regaily, S.A.; Salem, M.A.; Abdel Aziz, M.H.; Roushdy, M.I. Survey of Computer Aided Detection Systems for Lung Cancer in Computed Tomography. Curr. Med. Imaging Rev. 2018, 14, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, J.R.; Chelvan, A.C.; Duela, J.S. Multi-Class Neural Networks to Predict Lung Cancer. J. Med. Syst. 2019, 43, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netto, S.M.B.; Silva, A.C.; Nunes, R.A.; Gattass, M. Automatic segmentation of lung nodules with growing neural gas and support vector machine. Comput. Biol. Med. 2012, 42, 1110–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.L.A.; Kouzani, A.Z.; Hu, E.J. Automated identification of lung nodules. In Proceedings of the 10th Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing (MMSP), Cairns, Australia, 8–10 October 2008; pp. 497–502. [Google Scholar]
- Cascio, D.; Magro, R.; Fauci, F.; Iacomi, M.; Raso, G. Automatic detection of lung nodules in CT datasets based on stable 3D mass–spring models. Comput. Biol. Med. 2012, 42, 1098–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akram, S.; Javed, M.Y.; Akram, M.U.; Qamar, U.; Hassan, A. Pulmonary Nodules Detection and Classification Using Hybrid Features from Computerized Tomographic Images. J. Med. Imaging Health Inform. 2016, 6, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshani, M.; Azimifar, Z.; Tajeripour, F.; Boostani, R. Lung nodule segmentation and recognition using SVM classifier and active contour modeling: A complete intelligent system. Comput. Biol. Med. 2013, 43, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, C.C.; Saravanan, V.; Devi, M.R.V. Lung Nodule Diagnosis from CT Images Using Fuzzy Logic. In Proceedings of the ICCIMA, Sivakasi, India, 13–15 December 2007; Volume 3, pp. 159–163. [Google Scholar]
- Özekes, S. Rule-Based Lung Region Segmentation and Nodule Detection via Genetic Algorithm Trained Template Matching. İstanbul Ticaret Üniversitesi Fen Bilim. Derg. 2007, 6, 17–30. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, J.; Zheng, B.; Leader, J.; Wang, X.; Gur, D. An automated CT based lung nodule detection scheme using geometric analysis of signed distance field. Med. Phys. 2008, 35, 3453–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messay, T.; Hardie, R.C.; Rogers, S.K. A new computationally efficient CAD system for pulmonary nodule detection in CT imagery. Med. Image Anal. 2010, 14, 390–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Deklerck, R.; Jansen, B.; Bister, M.; Cornelis, J. A novel computer-aided lung nodule detection system for CT images. Med. Phys. 2011, 38, 5630–5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golosio, B.; Masala, G.L.; Piccioli, A.; Oliva, P.; Carpinelli, M.; Cataldo, R.; Cerello, P.; De Carlo, F.; Falaschi, F.; Fantacci, M.E.; et al. A novel multithreshold method for nodule detection in lung CT. Med. Phys. 2009, 36, 3607–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Ma, J.; Zhao, M.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, M.; He, L.; Suzuki, K. Many is better than one: An integration of multiple simple strategies for accurate lung segmentation in CT Images. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1480423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozekes, S.; Osman, O.; Ucan, O.N. Nodule detection in a lung region that’s segmented with using genetic cellular neural networks and 3D template matching with fuzzy rule based thresholding. Korean J. Radiol. 2008, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jo, H.H.; Hong, H.; Goo, J.M. Pulmonary nodule registration in serial CT scans using global rib matching and nodule template matching. Comput. Biol. Med. 2014, 45, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Baz, A.; Elnakib, A.; Abou El-Ghar, M.; Gimel’farb, G.; Falk, R.; Farag, A. Automatic detection of 2D and 3D lung nodules in chest spiral CT scans. Int. J. Biomed. Imaging 2013, 2013, 517632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolejsi, M.; Kybic, J.; Polovincak, M.; Tuma, S. The Lung TIME: Annotated lung nodule dataset and nodule detection framework. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2009: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, Lake Buena Vista (Orlando Area), FL, USA, 7–12 February 2009; p. 72601U. [Google Scholar]
- Opfer, R.; Wiemker, R. Performance analysis for computer-aided lung nodule detection on LIDC data. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2007: Image Perception, Observer Performance, and Technology Assessment, San Diego, CA, USA, 17–22 February 2007; Volume 6515, p. 65151C. [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan, B.N.; Hardie, R.C.; Kebede, T.M.; Sprague, M.J. Optimized Feature Selection-Based Clustering Approach for Computer-Aided Detection of Lung Nodules in Different Modalities. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2019, 22, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Guo, H.; Dai, J. Computerized Detection of Lung Nodules in CT Images by Use of Multiscale Filters and Geometrical Constraint Region Growing. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Chengdu, China, 18–20 June 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Soliman, A.; Khalifa, F.; Elnakib, A.; Abou El-Ghar, M.; Dunlap, N.; Wang, B.; Gimel’farb, G.; Keynton, R.; El-Baz, A. Accurate Lungs Segmentation on CT Chest Images by Adaptive Appearance-Guided Shape Modeling. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Sousa, J.R.F.; Silva, A.C.; de Paiva, A.C.; Nunes, R.A. Methodology for automatic detection of lung nodules in computerized tomography images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2010, 98, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negahdar, M.; Beymer, D.; Syeda-Mahmood, T. Automated volumetric lung segmentation of thoracic CT images using fully convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2018: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, Houston, TX, USA, 10–15 February 2018; Petrick, N., Mori, K., Eds.; Volume 10575, pp. 356–361. [Google Scholar]
- Gruetzemacher, R.; Gupta, A.; Paradice, D. 3D deep learning for detecting pulmonary nodules in CT scans. J. Am. Med. Inf. Assoc. 2018, 25, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Ma, H.; Qian, W.; Gao, M.; Li, Y. An Automatic Detection System of Lung Nodule Based on Multigroup Patch-Based Deep Learning Network. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2018, 22, 1227–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Jiang, S.; Yang, Z.; Gong, L.; Ma, X.; Zhou, Z.; Bao, C.; Liu, Q. Automatic nodule detection for lung cancer in CT images: A review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 103, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaukat, F.; Raja, G.; Frangi, A.F. Computer-aided detection of lung nodules: A review. J. Med. Imaging 2019, 6, 020901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehrson, L.M.; Nielsen, M.B.; Ammitzbøl Lauridsen, C. Automatic Pulmonary Nodule Detection Applying Deep Learning or Machine Learning Algorithms to the LIDC-IDRI Database: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otsu, N. A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samet, H.; Tamminen, M. Efficient component labeling of images of arbitrary dimension represented by linear bintrees. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1988, 10, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atherton, T.; Kerbyson, D. Size invariant circle detection. Image Vis. Comput. 1999, 17, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.; Bischof, L. Seeded region growing. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1994, 16, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, R.E.; Chang, K.W.; Hsieh, C.J.; Wang, X.R.; Lin, C.J. LIBLINEAR: A library for large linear classification. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 1871–1874. [Google Scholar]
- Froz, B.R.; de Carvalho Filho, A.O.; Silva, A.C.; de Paiva, A.C.; Nunes, R.A.; Gattass, M. Lung nodule classification using artificial crawlers, directional texture and support vector machine. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 69, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, A.; Fujita, H. Fast lung nodule detection in chest CT images using cylindrical nodule-enhancement filter. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2013, 8, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Xia, K.; Yu, H. Correlation coefficient based supervised locally linear embedding for pulmonary nodule recognition. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2016, 136, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergtholdt, M.; Wiemker, R.; Klinder, T. Pulmonary nodule detection using a cascaded SVM classifier. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2016: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, San Diego, CA, USA, 27 February–3 March 2016; Volume 9785, pp. 268–278. [Google Scholar]
- Armato, S.G., III; McLennan, G.; McNitt-Gray, M.F.; Meyer, C.R.; Yankelevitz, D.; Aberle, D.R.; Henschke, C.I.; Hoffman, E.A.; Kazerooni, E.A.; MacMahon, H.; et al. Lung Image Database Consortium: Developing a Resource for the Medical Imaging Research Community. Radiology 2004, 232, 739–748. [Google Scholar]
- Farid, M.S.; Lucenteforte, M.; Grangetto, M. DOST: A distributed object segmentation tool. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 20839–20862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasaki, Y. The truth of the F-measure. Teach Tutor Mater. 2007, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chinchor, N. The Statistical Significance of the MUC-4 Results. In Proceedings of the 4th Conference on Message Understanding, MUC4 ’92; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 1992; pp. 30–50. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, B. Comparison of the predicted and observed secondary structure of T4 phage lysozyme. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Protein Struct. 1975, 405, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicco, D.; Jurman, G. Machine learning can predict survival of patients with heart failure from serum creatinine and ejection fraction alone. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2020, 20, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Division | Sensitivity | Specificity | Precision | Accuracy | F Score | MCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40:60 | 0.8611 | 0.8824 | 0.8378 | 0.8736 | 1.0276 | 0.3491 |
| 50:50 | 0.8621 | 0.8864 | 0.8333 | 0.8767 | 1.0274 | 0.3908 |
| 60:40 | 0.9200 | 0.8889 | 0.8519 | 0.9016 | 1.0866 | 0.5838 |
| 70:30 | 0.9375 | 0.9118 | 0.8333 | 0.9200 | 1.0976 | 0.8385 |
| Method | Year | Database | Size | Sensitivity | FPI | FPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dolejsi [36] | 2009 | TIME-LIDC-ANODE | 38 | 89.60 | 12.03 | - |
| Golosio [31] | 2009 | LIDC | 484 | 71.00 | - | 4 |
| Messay [29] | 2010 | LIDC | 84 | 82.66 | - | 3 |
| Tan [30] | 2011 | LIDC | 399 | 87.50 | - | 4 |
| Stelmo [21] | 2012 | LIDC | 29 | 85.93 | 0.001 | 0.14 |
| Teramoto [54] | 2013 | LIDC | 84 | 80.00 | - | 4.2 |
| Bergtholdt [56] | 2016 | LIDC-IDRI | 243 | 85.90 | - | 2.5 |
| Wu [55] | 2017 | LIDC-IDRI | 60 | 79.23 | - | - |
| Froz [53] | 2017 | LIDC-IDRI | 833 | 91.86 | - | - |
| Saien [11] | 2018 | LIDC/LIDC-IDRI | 70 | 83.98 | 0.02 | - |
| Ours | 2019 | LIDC | 75 | 93.75 | 0.13 | 0.22 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khehrah, N.; Farid, M.S.; Bilal, S.; Khan, M.H. Lung Nodule Detection in CT Images Using Statistical and Shape-Based Features. J. Imaging 2020, 6, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging6020006
Khehrah N, Farid MS, Bilal S, Khan MH. Lung Nodule Detection in CT Images Using Statistical and Shape-Based Features. Journal of Imaging. 2020; 6(2):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging6020006
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhehrah, Noor, Muhammad Shahid Farid, Saira Bilal, and Muhammad Hassan Khan. 2020. "Lung Nodule Detection in CT Images Using Statistical and Shape-Based Features" Journal of Imaging 6, no. 2: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging6020006
APA StyleKhehrah, N., Farid, M. S., Bilal, S., & Khan, M. H. (2020). Lung Nodule Detection in CT Images Using Statistical and Shape-Based Features. Journal of Imaging, 6(2), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging6020006






