Abstract
Multifunctional nanoparticles with superior imaging properties and therapeutic effects have been extensively developed for the nanomedicine. However, tumor-intrinsic barriers and tumor heterogeneity have resulted in low in vivo therapeutic efficacy. The poor in vivo targeting efficiency in passive and active targeting of nano-therapeutics along with the toxicity of nanoparticles has been a major problem in nanomedicine. Recently, image-guided nanomedicine, which can deliver nanoparticles locally using non-invasive imaging and interventional oncology techniques, has been paid attention as a new opportunity of nanomedicine. This short review will discuss the existing challenges in nanomedicine and describe the prospects for future image-guided nanomedicine.
1. Nanomedicine
Various nanomaterials, having special functions that have not been observed in bulk materials, can provide opportunities for innovative biomedical applications. Nanomedicine has been one of the key research areas among those various applications of nanotechnology for about 20 years. Cancer is the 2nd most common cause of death and cancer cases keep rising in every year [1]. Conventional therapies have not shown any significant progress or outcomes for treating cancers. Disruptive innovations are desperately needed to more effectively treat patients with cancer. Cancer nanomedicine using unique features of nanomaterials has been expected to provide new opportunities in early diagnosis, imaging and treatment of cancers. The small size, high surface area, aqueous solubility, and multi-functionality of nanoparticles have created new biomedical applications. Indeed, the novel properties of nanoparticles have demonstrated the ability to interact with complex cellular functions in new ways. This rapidly growing field as an inter-disciplinary research develops multifunctional nanostructures and approaches that can target, diagnose, and treat devastating cancers. With extensive efforts, liposomes and lipid-based nanoparticles have been FDA approved to deliver and enhance the bioavailability of doxorubicin and other drugs [2,3]. Micelles and nanocomplexes has also improved the pharmacokinetics (PK) and biodistribution of hydrophobic drug molecules [4]. In addition, carboxymethyldextran-coated iron oxide nanoparticles have been approved for iron supplements in drugs and are now being tested for MR contrast agents in clinics [5,6,7]. Approximately, 100 nanomedicine products have been commercialized and marketed [2]. Other various nanomaterials are on about 800 clinical trials [8].
In preclinical tests, numerous nanomaterials demonstrate very promising properties for cancer imaging and therapeutics. However, only a few nanomaterials composed of Fe, Si, Au, polysaccharides polymers or natural products have been considered for potential clinical applications. Representatively, iron oxide nanoparticles, which are one of the elements in blood, have been used for cellular hyperthermia and MR imaging contrast [9,10]. The superparamagnetic properties of nanoscale iron oxide particles have been using for those applications and beyond. The magnetic properties and functions for medicine are readily tailored for each purpose by changing the size and structure of the nanoparticles. Recently, anisotropic and high-complexity Au nanostructures such as hyper-branched or dendritic structures also have been observed to be advantageous, because they provide a larger number of available active sites and surface atoms per unit area compared to spherical nanoparticles [11]. Various shaped metallic nanoparticles having specific light absorption properties generate robust heating for the local ablation therapies. High-density metallic nanoparticles allow a CT imaging contrast effect [12]. Disk-shaped Au-coated magnetic particles with a magnetic spin vortex can directly kill cancer cells with magneto-mechanical stimulations modulated by an external magnetic field [13]. Temperature-sensitive polymeric micelles effectively deliver drug molecules at a specific temperature [14]. Magnetic clusters enhance the MR imaging properties and at the same time carry much of drug with the nanopores [15]. Further mesoporous silica nanoparticles have shown great potential for the drug carriers [16,17]. Upconversion nanoparticles have been developed for stable luminescent and multimodal imaging functions in pre-/intra-/post-operative imaging [18]. Those proposed nanomedicines using novel nanoparticles should be a desirable new approach to treat cancers.
2. Current Limitations of Nanomedicine
However, big challenges of those nanoparticles for nanomedicine applications has been issued during recent in vivo and clinical translations [19]. In 2016, Wilhelm et al. [20] reviewed the literature from the past 10 years on nanoparticles-based nanomedicine; they reported that only 0.7% [median] of the administered nanoparticle dose was delivered to a solid tumor. The enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect and active targeting using tumor specific molecules are regarded as promising approaches for the tumor targeting, but RES sequestration, tumor-intrinsic barriers and tumor heterogeneity resulted in extremely low tumor targeting and tumor uptake efficiency [20,21,22]. This low targeting efficiency negatively affects the translation of nanomedicine to clinical applications. Hence, current future cancer nanomedicine strongly requires more localized and personalized approaches considering the tumor heterogeneity. More efforts for in-depth understanding of nanoparticles and tumor interactions are needed [2]. Eventually, nanomedicine approaches should be tailored and personalized based on medical diagnosis and imaging. Medical image-guided interventional oncology approaches should be one of the promising solutions for current nanomedicine.
3. Image Guided Cancer Nanomedicine: A New Opportunity
Interventional oncology is a subspecialty field of interventional radiology that performs the diagnosis and treatment of cancer using targeted minimally invasive procedures performed under image guidance. It employs X-ray, ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to help guide miniaturized instruments (e.g., intravascular catheter, biopsy needles, ablation electrodes) to allow targeted and precise treatment of solid tumors located in various organs of the human body. Advances in medical imaging and image guidance for the detection, characterization, targeting and therapy of cancers now allow for minimally invasive image-guided treatment of many solid tumors without the toxicity of chemotherapy and radiation. The image-guided procedures have been shown to result in fewer complications, faster recoveries, and reduced costs [23,24,25]. The most widely practiced procedures are transcatheter-directed therapies with intra-tumoral or intra-arterial delivery and percutaneous or endoscopic ablative therapies. Transcatheter-directed therapies such as transcatheter arterial embolization (TAE) and chemoembolization (TACE) are catheter-based intra-arterially delivered tumor treatments. Ablative therapies such as radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and cryo-ablation generally involve the destruction of the lesion via a percutaneously placed needle. Medical imaging plays key roles in those image-guided therapies and interventional procedures. Those roles are (a) preprocedure planning (identifying tumor volume); (b) intraprocedural targeting (guiding catheter delivery); (c) intraprocedural monitoring (monitoring tumor tissue changes caused by the treatment during the procedure); (d) intraprocedural control (making adjustments); and (e) postprocedure assessment (measuring effectiveness and for further intervention). Contrast agents are often required to highlight a target site that is not visualized well on unenhanced scans in pre-, intra- and post-procedural therapies.
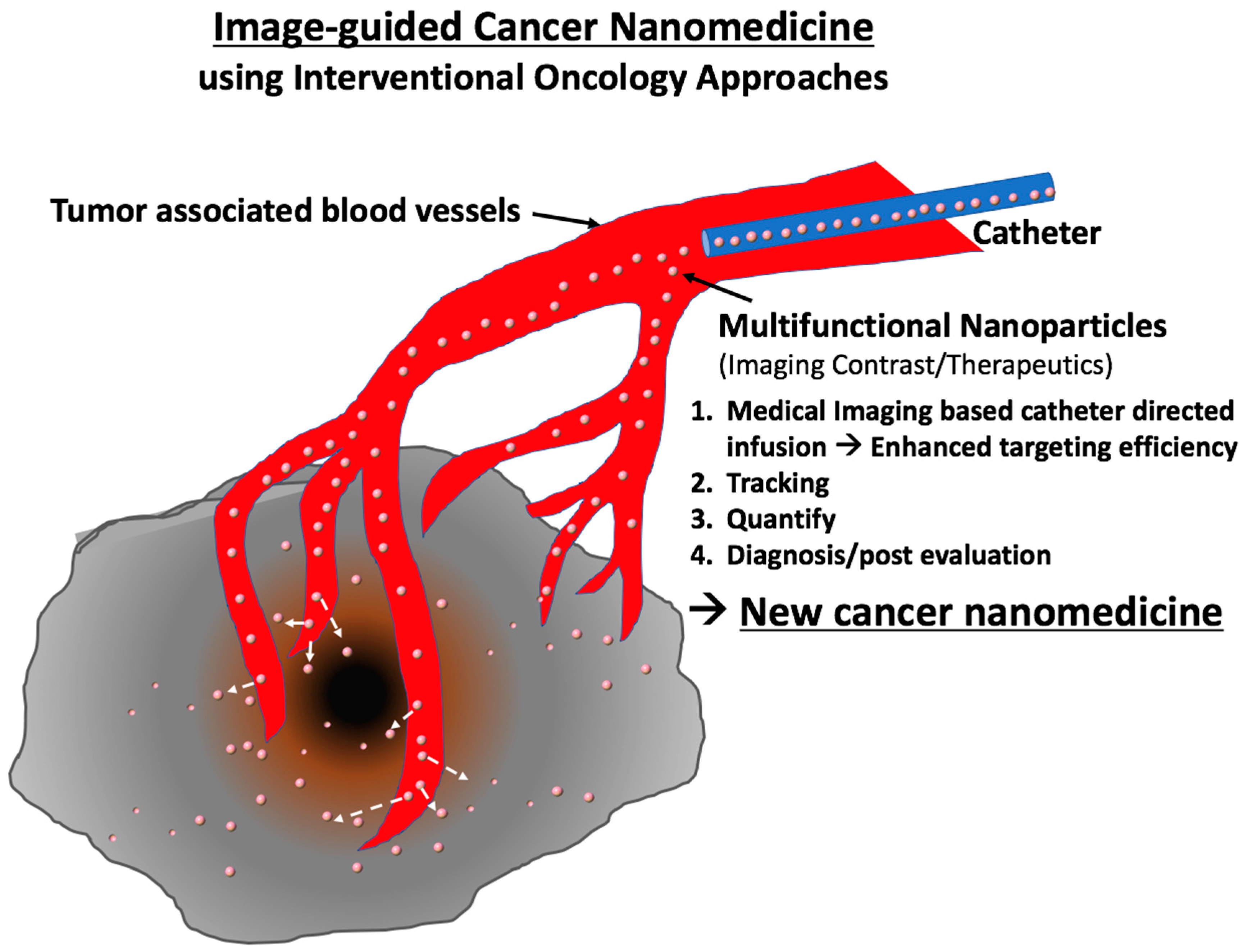
Although those interventional approaches mainly have been used for traditional local therapies such as radiofrequency/cryo/chemical tumor ablation, focal laser ablation, tumor (chemo-) embolization, local drug infusion and so on, those conventional interventional therapeutics are conveniently combined with multifunctional nanoparticle-based nanomedicine. Recently, various image-guided cancer nanomedicine approaches have been tested and have shown promising results in preclinical settings (Table 1). Advanced functions of nanoparticles provide high imaging contrast effects during image-guided therapeutic procedures and more tumor-specific triggered therapeutics at the same time. These features also suggest a new opportunity of nanomedicine that has been stagnant with low tumor targeting and toxicity issues for clinical translation. Now, emerging next-generation nanomedicine—“image-guided cancer nanomedicine”—combined with interventional oncology approaches fulfills minimal systemic distribution, homogeneous distribution at targeted sites and high local delivery of nanomedicine resulting in enhancing the efficacy of cutting-edge nanomedicines (Figure 1). Furthermore, the image-guided delivery of nanomedicine will be important in future clinical practice (Figure 1). First, an effective dosage of nanomedicine can be highly localized in tumor regions with minimized systemic toxicity; second, it is possible to monitor and confirm whether the nanoparticles-based nanomedicine is properly delivered to the disease site after injection (local infusion and tracking); third, an amount of the injected nanoparticles can be quantitatively analyzed to determine the amount of the post infusion (non-invasive quantification); finally, distribution of the injected nanoparticles in the body can be monitored for a long-term period (diagnosis and post evaluation). The proposed new image-guided cancer nanomedicine approaches should eventually permit patient-specific dosimetry and tumor-specific treatment of cancers for the superior therapeutic effect in a personalized manner [18,26,27,28]. At the same time, it is expected that the use of nanomedicine techniques in interventional oncology will open a new chapter for exceptional therapeutic efficacies [15,29]. It is worth noting that image-guided cancer nanomedicine incorporates new medical imaging techniques, nanoparticles, molecular entities and novel classes of therapeutic agents (siRNA, mRNA, gene editing, immune checkpoint inhibitors) as well as existing drugs/therapeutics. Strong collaborative multidisciplinary teams including clinicians, basic scientists and nano-scientists are essential for advancing the image-guided cancer nanomedicine for clinical translation.

Table 1.
Recent Image-guided Cancer Nanomedicine Approaches
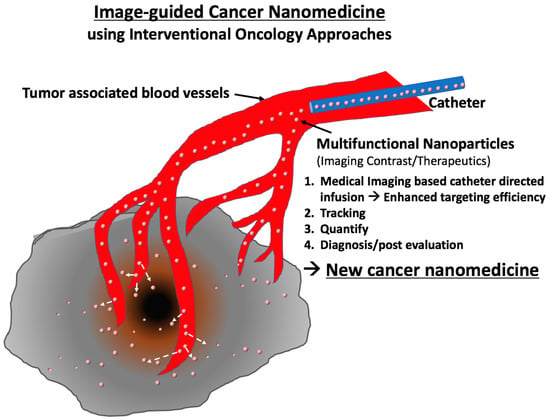
Figure 1.
Image-guided Cancer Nanomedicine. Image-guided infusion of nanomedicine using interventional procedures allows personalized therapeutics with highly localized nano-therapeutics.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants of R21CA173491, R21CA185274 and R21EB017986 from the National Cancer Institute and National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, G.; Xie, J.; Chen, X. Rethinking cancer nanotheranostics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Kantoff, P.W.; Wooster, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Cancer nanomedicine: Progress, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.Y.; Rutka, J.T.; Chan, W.C. Nanomedicine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2434–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thu, M.S.; Bryant, L.H.; Coppola, T.; Jordan, E.K.; Budde, M.D.; Lewis, B.K.; Chaudhry, A.; Ren, J.; Varma, N.R.; Arbab, A.S.; et al. Self-assembling nanocomplexes by combining ferumoxytol, heparin and protamine for cell tracking by magnetic resonance imaging. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissleder, R.; Nahrendorf, M.; Pittet, M.J. Imaging macrophages with nanoparticles. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, A.; Nejadnik, H.; Gawande, R.; Lin, G.T.; Lee, S.; Messing, S.; Castaneda, R.; Derugin, N.; Pisani, L.; Lue, T.F.; et al. Intravenous Ferumoxytol Allows Noninvasive MR Imaging Monitoring of Macrophage Migration into Stem Cell Transplants. Radiology 2012, 264, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobo, D.; Robinson, K.J.; Islam, J.; Thurecht, K.J.; Corrie, S.R. Nanoparticle-Based Medicines: A Review of FDA-Approved Materials and Clinical Trials to Date. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 2373–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Nikles, D.E.; Johnson, D.T.; Brazel, C.S. Heat generation of aqueously dispersed CoFe2O4 nanoparticles as heating agents for magnetically activated drug delivery and hyperthermia. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 2390–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Nikles, D.E.; Brazel, C.S. Synthesis and Characterization of Multifunctional Chitosan-MnFe2O4 Nanoparticles for Magnetic Hyperthermia and Drug Delivery. Materials 2010, 3, 4051–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, F.; Nehl, C.L.; Hafner, J.H.; Nordlander, P. Plasmon resonances of a gold nanostar. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 729–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.; Cho, S.; Huang, X.; Larson, A.C.; Kim, D.H. Branched Gold Nanoparticle Coating of Clostridium novyi-NT Spores for CT-Guided Intratumoral Injection. Small 2017, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Rozhkova, E.A.; Ulasov, I.V.; Bader, S.D.; Rajh, T.; Lesniak, M.S.; Novosad, V. Biofunctionalized magnetic-vortex microdiscs for targeted cancer-cell destruction. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Vitol, E.A.; Liu, J.; Balasubramanian, S.; Gosztola, D.J.; Cohen, E.E.; Novosad, V.; Rozhkova, E.A. Stimuli-Responsive Magnetic Nanomicelles as Multifunctional Heat and Cargo Delivery Vehicles. Langmuir 2013, 29, 7425–7432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, M.J.; Gordon, A.C.; Larson, A.C.; Chung, J.W.; Kim, Y.I.; Kim, D.H. Transcatheter intra-arterial infusion of doxorubicin loaded porous magnetic nano-clusters with iodinated oil for the treatment of liver cancer. Biomaterials 2016, 88, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Procissi, D.; Nicolai, J.; Omary, R.A.; Larson, A.C. Temperature-sensitive magnetic drug carriers for concurrent gemcitabine chemohyperthermia. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 714–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Kim, D.H.; Guo, Y.; Teng, Z.G.; Li, Y.J.; Zheng, L.F.; Zhang, Z.L.; Larson, A.C.; Lu, G.M. A c(RGDfE) conjugated multi-functional nanomedicine delivery system for targeted pancreatic cancer therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Gordon, A.C.; Kim, H.; Park, W.; Cho, S.; Lee, B.; Larson, A.C.; Rozhkova, E.A.; Kim, D.H. Targeted multimodal nano-reporters for pre-procedural MRI and intra-operative image-guidance. Biomaterials 2016, 109, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanotechnology Fact Sheet. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/ScienceResearch/SpecialTopics/Nanotechnology/ucm402230.htm (accessed on 10 January 2018).
- Wilhelm, S.; Tavares, A.J.; Dai, Q.; Ohta, S.; Audet, J.; Dvorak, H.F.; Chan, W.C.W. Analysis of nanoparticle delivery to tumours. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, S.E. Evaluation of nanomedicines: Stick to the basics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, S.; Tavares, A.J.; Chan, W.C.W. Reply to “Evaluation of nanomedicines: Stick to the basics”. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, S.G.; Deuson, T.E.; Kane, N.; Adams, D.F.; Seltzer, S.E.; Phillips, M.D.; Khorasani, R.; Zinner, M.J.; Holman, B.L. Percutaneous abdominal biopsy: Cost-identification analysis. Radiology 1998, 206, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Link, R.E.; Permpongkosol, S.; Gupta, A.; Jarrett, T.W.; Solomon, S.B.; Kavoussi, L.R. Cost analysis of open, laparoscopic, and percutaneous treatment options for nephron-sparing surgery. J. Endourol. 2006, 20, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, S.B.; Silverman, S.G. Imaging in interventional oncology. Radiology 2010, 257, 624–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Chen, J.; Omary, R.A.; Larson, A.C. MRI visible drug eluting magnetic microspheres for transcatheter intra-arterial delivery to liver tumors. Theranostics 2015, 5, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Choy, T.; Huang, S.; Green, R.M.; Omary, R.A.; Larson, A.C. Microfluidic fabrication of 6-methoxyethylamino numonafide-eluting magnetic microspheres. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.; Cho, S.; Han, J.; Shin, H.; Na, K.; Lee, B.; Kim, D.H. Advanced smart-photosensitizers for more effective cancer treatment. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; White, S.B.; Harris, K.R.; Li, W.; Yap, J.W.; Kim, D.H.; Lewandowski, R.J.; Shea, L.D.; Larson, A.C. Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres for MRI-monitored delivery of sorafenib in a rabbit VX2 model. Biomaterials 2015, 61, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomitaka, A.; Arami, H.; Raymond, A.; Yndart, A.; Kaushik, A.; Jayant, R.D.; Takemura, Y.; Cai, Y.; Toborek, M.; Nair, M. Development of magneto-plasmonic nanoparticles for multimodal image-guided therapy to the brain. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.; Park, W.; Kim, D.H. Silica-Coated Metal Chelating-Melanin Nanoparticles as a Dual-Modal Contrast Enhancement Imaging and Therapeutic Agent. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detappe, A.; Thomas, E.; Tibbitt, M.W.; Kunjachan, S.; Zavidij, O.; Parnandi, N.; Reznichenko, E.; Lux, F.; Tillement, O.; Berbeco, R. Ultrasmall Silica-Based Bismuth Gadolinium Nanoparticles for Dual Magnetic Resonance-Computed Tomography Image Guided Radiation Therapy. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 1733–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, N.; Bozeman, E.N.; Qian, W.; Wang, L.; Chen, H.; Lipowska, M.; Staley, C.A.; Wang, Y.A.; Mao, H.; Yang, L. Tumor Penetrating Theranostic Nanoparticles for Enhancement of Targeted and Image-guided Drug Delivery into Peritoneal Tumors following Intraperitoneal Delivery. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1689–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Qian, W.; Uckun, F.M.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.A.; Chen, H.; Kooby, D.; Yu, Q.; Lipowska, M.; Staley, C.A.; et al. IGF1 Receptor Targeted Theranostic Nanoparticles for Targeted and Image-Guided Therapy of Pancreatic Cancer. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7976–7991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-H.; Li, W.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Green, R.M.; Huang, S.; Larson, A. Multimodal Imaging of Nanocomposite Microspheres for Transcatheter Intra-Arterial Drug Delivery to Liver Tumors. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.; Chen, J.; Cho, S.; Park, S.J.; Larson, A.C.; Na, K.; Kim, D.H. Acidic pH-Triggered Drug-Eluting Nanocomposites for Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Monitored Intra-arterial Drug Delivery to Hepatocellular Carcinoma. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 12711–12719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Chi, C.; Liu, M.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, C.; Ye, J.; Wang, J.; Tian, J.; Yang, W.; et al. Nanoparticle-mediated radiopharmaceutical-excited fluorescence molecular imaging allows precise image-guided tumor-removal surgery. Nanomedicine 2017, 13, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lin, T.Y.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, W.; Guo, W.; Lac, D.; Zhang, H.; Feng, C.; Wachsmann-Hogiu, S.; et al. A smart and versatile theranostic nanomedicine platform based on nanoporphyrin. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Larson, A.C. Deoxycholate bile acid directed synthesis of branched Au nanostructures for near infrared photothermal ablation. Biomaterials 2015, 56, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Cho, S.; Procissi, D.; Larson, A.C.; Kim, D.H. Non-invasive monitoring of branched Au nanoparticle-mediated photothermal ablation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2017, 105, 2352–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, S.B.; Kim, D.H.; Guo, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; Gogineni, V.R.; Larson, A.C. Biofunctionalized Hybrid Magnetic Gold Nanoparticles as Catalysts for Photothermal Ablation of Colorectal Liver Metastases. Radiology 2017, 285, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.; Gordon, A.C.; Cho, S.; Huang, X.; Harris, K.R.; Larson, A.C.; Kim, D.H. Immunomodulatory Magnetic Microspheres for Augmenting Tumor-Specific Infiltration of Natural Killer (NK) Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 13819–13824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).