Bone Changes in Mandibular Condyle of Temporomandibular Dysfunction Patients Recognized on Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ey-Chmielewska, H.; Teul, I.; Lorkowskl, J. Functional disorders of the temporomandibular joints as a factor responsible for sleep apnoea. Ann. Acad. Med. Stetin. 2014, 60, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, G.; Pająk-Zielińska, B.; Ginszt, M. A meta-analysis of the global prevalence of temporomandibular disorders. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Progiante, P.S.; Pattussi, M.P.; Lawrence, H.P.; Goya, S.; Grossi, P.K.; Grossu, M.L. Prevalence of temporomandibular disorders in an adult Brazilian community population using the research diag nostic criteria (axes I and II) for temporomandibular disorders (the Maringá study). Int. J. Prosthodont. 2015, 28, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakkaphan, P.; Smith, J.G.; Chana, P.; Tan, H.L.; Ravindranath, P.T.; Lambru, G.; Renton, T. Temporomandibular disorders and fibromyalgia prevalence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Oral Facial Pain Headache 2023, 37, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouanounou, A.; Goldberg, M.; Haas, D.A. Pharmacotherapy in temporomandibular disorders: A review. J. Can. Dent. Assoc. 2017, 83, h7. [Google Scholar]
- Minervini, G.; Franco, R.; Marrapodi, M.M.; Fiorillo, L.; Cervino, G.; Cicciù, M. Prevalence of temporomandibular disorders in children and adolescents evaluated with diagnostic criteria for temporomandibular disorders: A systematic review with meta-analysis. J. Oral Rehabil. 2023, 50, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maixner, W.; Fillingim, R.B.; Williams, D.A.; Smith, S.B.; Slade, G.D. Overlapping chronic pain conditions: Implications for diagnosis and classification. J. Pain 2016, 17, T93–T107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lora, V.R.; Canales, G.L.; Goncalves, L.M.; Meloto, C.B.; Barbosa, C.M. Prevalence of temporomandibular disorders in postmenopausal women and relationship with pain and HRT. Braz. Oral Res. 2016, 30, e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, F.T.; Pacheco-Pereira, C.; Flores-Mir, C.; Le, L.H.; Jaremko, J.L.; Major, P.W. Diagnostic ultrasound assessment of temporomandibular joints: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2019, 48, 20180144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamon, N.M.; Casselman, J.W. Temporomandibular joint disorders: A pictorial review. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2020, 24, 591–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalladka, M.; Young, A.; Thomas, D.; Heir, G.M.; Quek, S.Y.P.; Khan, J. The relation of temporomandibular disorders and dental occlusion: A narrative review. Quintessence Int. 2022, 53, 450–459. [Google Scholar]
- Herb, K.; Cho, S.; Stiles, M.A. Temporomandibular joint pain and dysfunction. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2006, 10, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm, P.E.; Stancampiano, F.F.; Rozen, T.D. Migraine headache: Updates and future developments. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2018, 93, 1648–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Reyes, M.; Bassiur, J.P. Temporomandibular disorders, bruxism and headaches. Neurol. Clin. 2024, 42, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredini, D.; Piccotti, F.; Ferronato, G.; Guarda-Nardini, L. Age peaks of different RDC/TMD diagnoses in a patient population. J. Dent. 2010, 38, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauer, R.L.; Semidey, M.J. Diagnosis and treatment of temporomandibular disorders. Am. Fam. Physician 2015, 91, 378–386. [Google Scholar]
- Miernik, M.; Więckiewicz, W. The basic conservative treatment of temporomandibular joint anterior disc displacement without reduction-Review. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 24, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L.; Huang, C.; Zhou, F.; Xia, F.; Xiong, G. Finite elements analysis of the temporomandibular joint disc in patients with intra-articular disorders. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osiewicz, M.A.; Lobbezoo, F.; Loster, B.W.; Loster, J.E.; Manfredini, D. Frequency of temporomandibular disorders diagnoses based on RDC/TMD in a Polish patient population. Cranio 2018, 36, 304–310. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.; Liu, L.; Zhai, X.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, H.; Jiang, H. Association between chewing side preference and MRI characteristics in patients with anterior disc displacement of the temporomandibular joint. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 124, 101484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, D.P.A.; Doblaré, M. An accurate simulation model of anteriorly displaced TMJ discs with and without reduction. Med. Eng. Phys. 2007, 29, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, I.M.; Coelho, P.R.; Picorelli Assis, N.M.; Pereira Leite, F.P.; Devito, K.L. Evaluation of the correlation between disc displacements and degenerative bone changes of the temporomandibular joint by means of magnetic resonance images. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 41, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, K.J.; List, T.; Petersson, A.; Rohlin, M. Relationship between clinical and magnetic resonance imaging diagnoses and findings in degenerative and inflammatory temporomandibular joint diseases: A systematic literature review. J. Orofac. Pain 2009, 23, 123–139. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.D.; Zhang, J.N.; Gan, Y.H.; Zhou, Y.H. Current understanding of pathogenesis and treatment of TMJ osteoarthritis. J. Dent. Res. 2015, 94, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Lu, L.; Yu, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, M. Initiation and progression of dental-stimulated temporomandibular joints osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2021, 29, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, K.; Natsumi, Y.; Urade, M. Correlation between MRI evidence of degenerative condylar surface changes, induction of articular disc displacement and pathological joint sounds in the temporomandibular joint. Gerodontology 2008, 25, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomas, X.; Pomes, J.; Berenguer, J.; Quinto, L.; Nicolau, C.; Mercader, J.M.; Castro, V. MR imaging of temporomandibular joint dysfunction: A pictorial review. Radiographics 2006, 26, 765–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styles, C.; Whyte, A. MRI in the assessment of internal derangement and pain within the temporomandibular joint: A pictorial essay. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2002, 40, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersson, A. What you can and cannot see in TMJ imaging -An overview related to the RDC/TMD diagnostic system. J. Oral Rehabil. 2010, 37, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotolo, R.P.; d’Apuzzo, F.; Femiano, F.; Nucci, L.; Minervini, G.; Grassia, V. Comparison between ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging of the temporomandibular joint in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: A systematic review. J. Oral Rehabil. 2023, 50, 1082–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willenbrock, D.; Lutz, R.; Wuest, W.; Heiss, R.; Uder, M.; Behrends, T.; Wurm, M.; Kesting, M.; Wiesmueller, M. Imaging temporomandibular disorders: Reliability of a novel MRI-based scoring system. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2022, 50, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshima, H.; Ogura, I. Characteristics of patients with temporomandibular joint osteoarthrosis on magnetic resonance imaging. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 64, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerele, C.; Avsenik, J.; Šurlan, P.K. MRI characteristics of the asymptomatic temporomandibular joint in patients with unilateral temporomandibular joint disorder. Oral Radiol. 2021, 37, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoliu, A.; Spinner, G.; Wyss, M.; Erni, S.; Ettlin, D.A.; Nanz, D.; Ulbrich, E.J.; Gallo, L.M.; Andreisek, G. Quantitative and qualitative comparison of MR imaging of the temporomandibular joint at 1.5 and 3.0 T using an optimized high-resolution protocol. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2016, 45, 20150240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertram, S.; Moriggl, A.; Rudisch, A.; Emshoff, R. Structural characteristics of bilateral temporomandibular joint disc displacement without reduction and osteoarthrosis are important determinants of horizontal mandibular and vertical ramus deficiency: A magnetic resonance imaging study. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 69, 1898–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badel, T.; Marotti, M.; Keros, J.; Kern, J.; Krolo, I. Magnetic resonance study on temporomandibular joint morphology. Coll. Antropol. 2009, 33, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kakimoto, N.; Wongratwanich, P.; Shimamoto, H.; Kitisubkanchana, J.; Tsujimoto, T.; Shimabukuro, K.; Verdonschot, R.G.; Hasegawa, Y.; Murakami, S. Comparison of T2 values of the displaced unilateral disc and retrodiscal tissue of temporomandibular joints and their implications. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, S.; Rudish, A.; Innerhofer, K.; Pümpel, E.; Grubwieser, G.; Emshoff, R. Diagnosing TMJ. internal derangement and osteoarthrosis with magnetic resonance imaging. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2001, 132, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, I.M.; Cordeiro, P.C.; Devito, K.L.; Tavares, M.L.; Leite, I.C.; Tesch, R.S. Evaluation of temporomandibular joint disc displacement as a risk factor for osteoarthrosis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuhashi, F.; Ogura, I.; Mizuhashi, R.; Watarai, Y.; Oohashi, M.; Suzuki, T.; Saegusa, H. Examination for the factors involving to joint effusion in patients with temporomandibular disorders using magnetic resonance imaging. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuhashi, F.; Ogura, I.; Mizuhashi, R.; Watarai, Y.; Oohashi, M.; Suzuki, T.; Kawana, M.; Nagata, K. Examination of joint effusion magnetic resonance imaging of patients with temporomandibular disorders with disc displacement. J. Imaging 2024, 10, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moncada, G.; Cortés, D.; Millas, R.; Marholz, C. Relationship between disk position and degenerative bone changes in temporomandibular joints of young subjects with TMD. An MRI study. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2014, 38, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L.; Tian, S.; Abdelrehem, A.; Feng, J.; Fu, G.; Chen, W.; Ding, C.; Luo, Y.; et al. Proteome analysis of temporomandibular joint with disc displacement. J. Dent. Res. 2022, 101, 1580–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalladka, M.; Quek, S.; Heir, G.; Eliav, E.; Mupparapu, M.; Viswanath, A. Temporomandibular joint osteoarthrosis: Diagnosis and long-term conservative management: A topic review. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2014, 14, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, A.; McNamara, D.; Rosenberg, I.; Whyte, A. Magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of temporomandibular joint disc displacement -A review of 144 cases. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 35, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, H.; Uehara, S.; Yokochi, M.; Nakatsuka, A.; Kobayashi, H.; Kurashina, K. A long-term follow-up study of radiographically evident degenerative changes in the temporomandibular joint with different conditions of disk displacement. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 35, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emshoff, R.; Brandlmaier, I.; Bertram, S.; Rudisch, A. Relative odds of temporomandibular joint pain as a function of magnetic resonance imaging findings of internal derangement, osteoarthrosis, effusion, and bone marrow edema. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2003, 95, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emshoff, R.; Brandlmaier, I.; Bertram, S.; Rudisch, A. Risk factors for temporomandibular joint pain in patients with disc displacement without reduction—A magnetic resonance imaging study. J. Oral Rehabil. 2003, 30, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilanova, L.; Goncalves, T.; Meirelles, L.; Garcia, R. Hormonal fluctuations intensify temporomandibular disorder pain without impairing masticatory function. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2015, 28, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harthy, M.; Ohrbach, R.; Michelotti, A.; List, T. The effect of culture on pain sensitivity. J. Oral Rehabil. 2016, 43, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, C.H.; Pereira, D.D.; Pattussi, M.P.; Grossi, P.K.; Grossi, M.L. Gender differences in temporomandibular disorders in adult populational studies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Oral Rehabil. 2018, 45, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlo, C.A.; Patcas, R.; Kau, T.; Watzal, H.; Signorelli, L.; Müller, L.; Ullrich, O.; Luder, H.U.; Kellenberger, C.J. MRI of the temporo-mandibular joint: Which sequence is best suited to assess the cortical bone of the mandibular condyle? A cadaveric study using micro-CT as the standard of reference. Eur. Radiol. 2012, 22, 1579–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larheim, T.A.; Abrahamsson, A.K.; Kristensen, M.; Arvidsson, L.Z. Temporomandibular joint diagnostics using CBCT. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2015, 44, 20140235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almashraqi, A.A.; Ahmed, E.A.; Mohamed, N.S.; Halboub, E.S. An MRI evaluation of the effects of qat chewing habit on the temporomandibular joint. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2018, 126, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgenberg-Sydney, P.B.; Bonotto, D.V.; Stechman-Neto, J.; Zwir, L.F.; Pachêco-Pereira, C.; Canto, G.L.; Porporatti, A.L. Diagnostic validity of CT to assess degenerative temporomandibular joint disease: A systematic review. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2018, 47, 20170389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, O.; Cattrysse, E.; Scafoglieri, A.; Luypaert, R.; Clarys, J.P.; de Mey, J. Accuracy of peripheral quantitative computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in assessing cortical bone cross-sectional area: A cadaver study. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2010, 34, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehling, C.; Vieth, V.; Bachmann, R.; Nassenstein, I.; Kugel, H.; Kooijman, H.; Heindel, W.; Fischbach, R. High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging of the temporomandibular joint: Image quality at 1.5 and 3.0 Tesla in volunteers. Investig. Radiol. 2007, 42, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
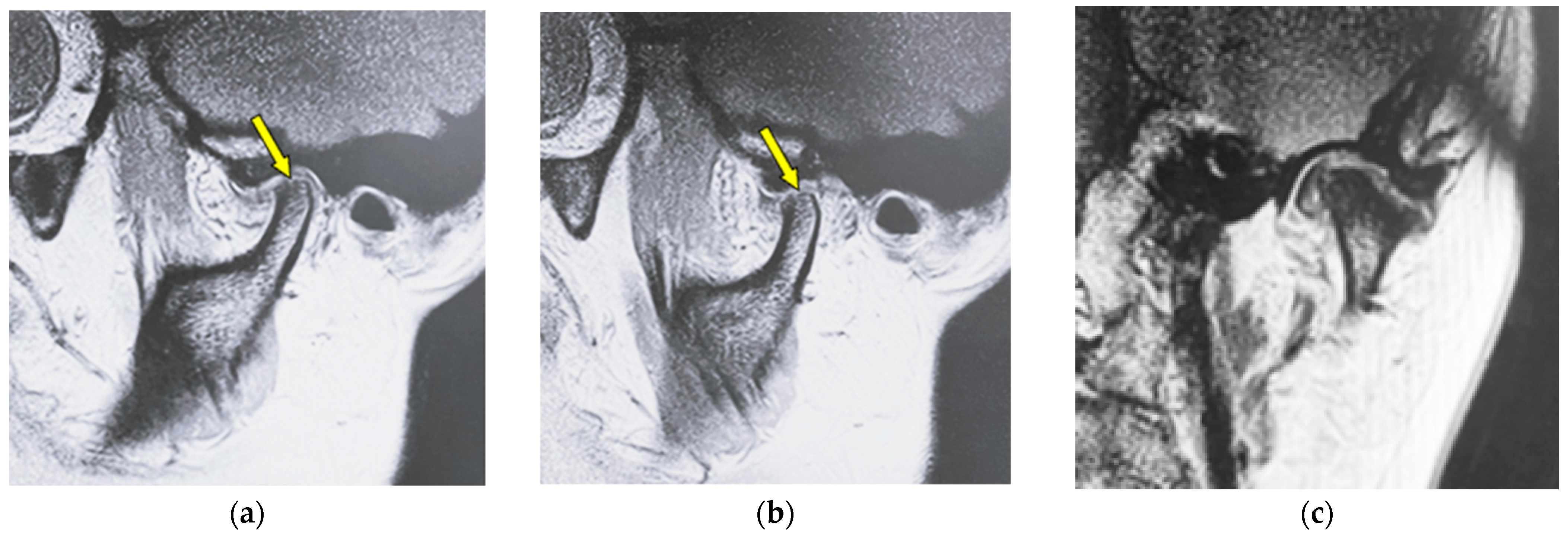
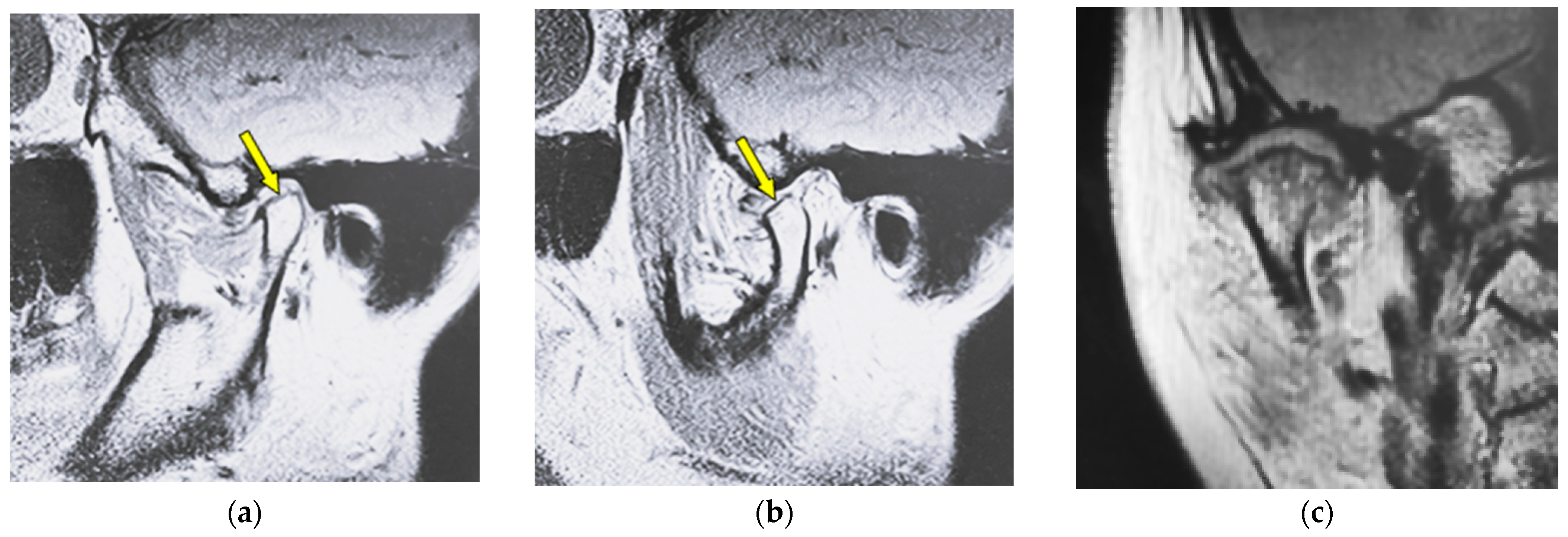
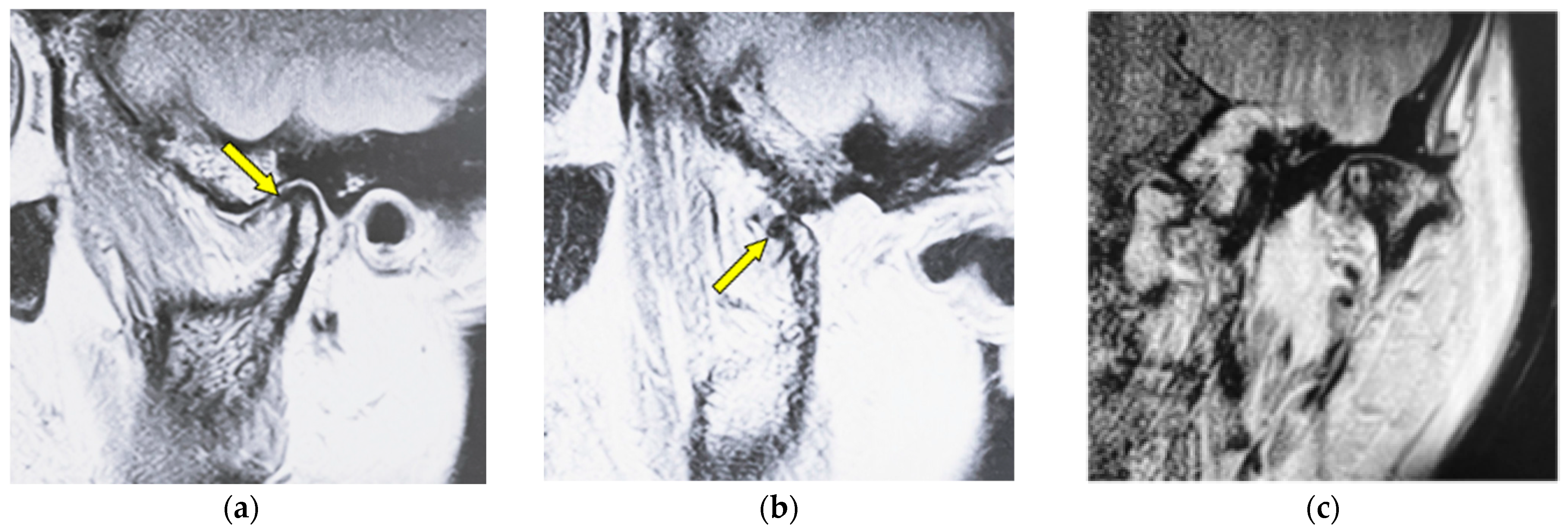
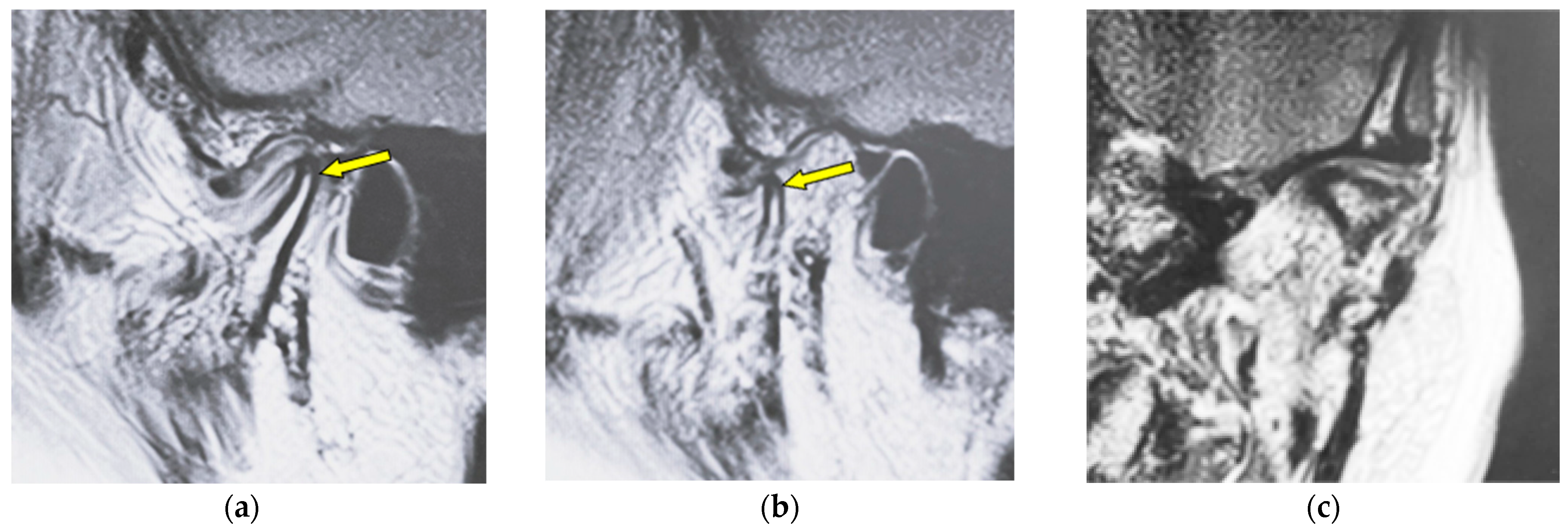
| Type of Bone Changes | Conditions |
|---|---|
| Erosion | Local area of rarefaction in compact bone with a lack of cortical bone continuously |
| Flattening | Loss of convexity of the condylar head outline and keeping the cortical bone continuously |
| Osteophyte | Local forward outgrowth of the condyle bone with an acute angle from the top of the head of the mandible |
| Atrophy | Reduction in anteroposterior widths in the mandibular condyle without a round form |
| Characteristics | No Changes | Erosion | Flattening | Osteophyte | Atrophy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 81 | 6 | 13 | 8 | 9 |
| Gender | |||||
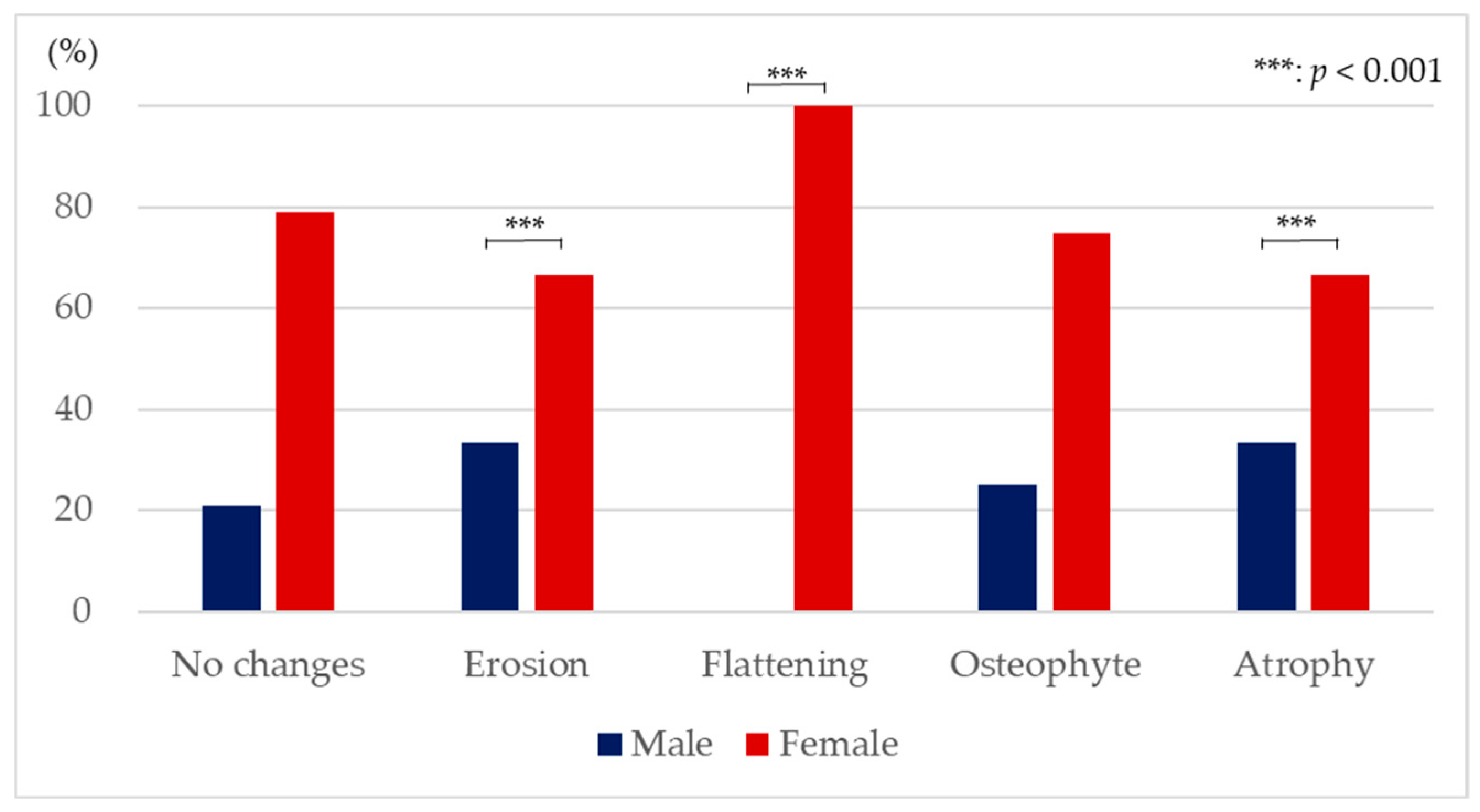
| Male | 17 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 3 |
| Female | 64 | 4 | 13 | 6 | 6 |
| Age | |||||
| Mean ± S.D. | 41.8 ± 18.4 | 59.3 ± 9.7 | 51.7 ± 16.5 | 41.0 ± 19.1 | 41.9 ± 16.7 |
| Min | 13 | 47 | 29 | 15 | 18 |
| Max | 79 | 78 | 79 | 64 | 71 |
| Type of Bone Changes | No Changes | Erosion | Flattening | Osteophyte | Atrophy | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Joint effusion (%) | 64.2 | 33.3 | 69.2 | 62.5 | 100.0 | <0.001 |
| TMJ pain (%) | 39.5 | 33.3 | 46.2 | 62.5 | 44.4 | 0.027 |
| Opening dysfunction (%) | 59.3 | 66.7 | 76.9 | 87.5 | 44.4 | 0.002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Mizuhashi, F.; Ogura, I.; Mizuhashi, R.; Watarai, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Kawana, M.; Nagata, K.; Niitsuma, T.; Oohashi, M. Bone Changes in Mandibular Condyle of Temporomandibular Dysfunction Patients Recognized on Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Imaging 2026, 12, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging12010005
Mizuhashi F, Ogura I, Mizuhashi R, Watarai Y, Suzuki T, Kawana M, Nagata K, Niitsuma T, Oohashi M. Bone Changes in Mandibular Condyle of Temporomandibular Dysfunction Patients Recognized on Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Journal of Imaging. 2026; 12(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging12010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleMizuhashi, Fumi, Ichiro Ogura, Ryo Mizuhashi, Yuko Watarai, Tatsuhiro Suzuki, Momoka Kawana, Kotono Nagata, Tomonori Niitsuma, and Makoto Oohashi. 2026. "Bone Changes in Mandibular Condyle of Temporomandibular Dysfunction Patients Recognized on Magnetic Resonance Imaging" Journal of Imaging 12, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging12010005
APA StyleMizuhashi, F., Ogura, I., Mizuhashi, R., Watarai, Y., Suzuki, T., Kawana, M., Nagata, K., Niitsuma, T., & Oohashi, M. (2026). Bone Changes in Mandibular Condyle of Temporomandibular Dysfunction Patients Recognized on Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Journal of Imaging, 12(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging12010005






