CSANet: Context–Spatial Awareness Network for RGB-T Urban Scene Understanding
Abstract
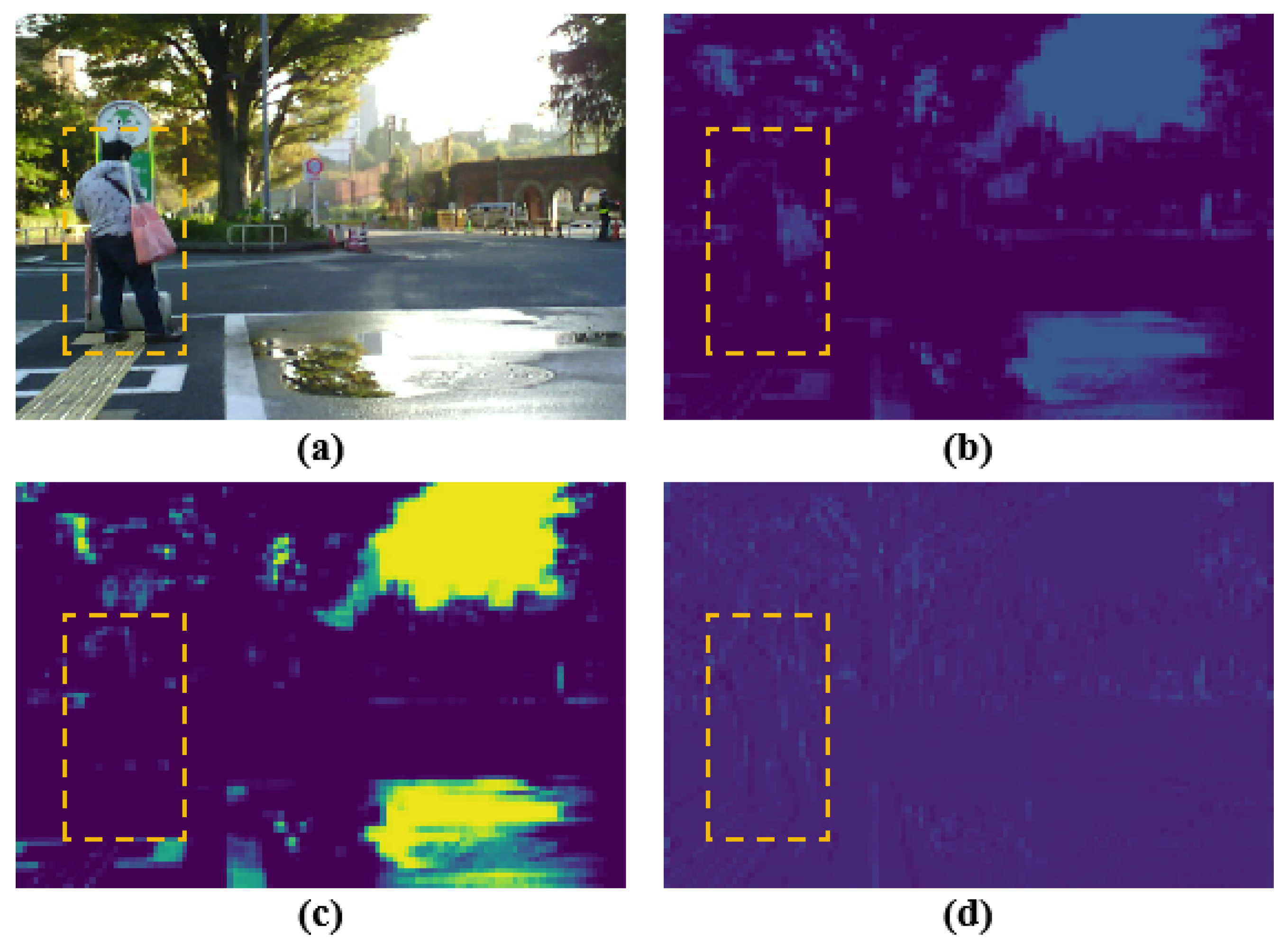
1. Introduction
- By fully exploring the feature differences between multi-modal data, we propose a novel Context Spatial Awareness Network (CSANet) for RGB-T semantic segmentation, achieving state-of-the-art performance on the MFNet and PST900 datasets.
- We design the CSCFM to extract shallow fine-grained local features from multi-modal data and the MHFM to capture and enhance deep semantic feature information. A cross-stage, multi-scale hierarchical framework is employed to efficiently fuse features across modalities.
- The SCAM is introduced into the encoder structure of CSANet to improve the localization accuracy of moving objects in complex scenes. Additionally, a lightweight decoder framework is used to restore multi-modal feature resolution while reducing computational complexity.
2. Related Works
2.1. RGB Semantic Segmentation
2.2. RGB-T Semantic Segmentation
3. Methodology
| Algorithm 1 CSANet: RGB-T Semantic Segmentation |
| Require: RGB image , TIR image . |
Ensure: Segmentation map .
|
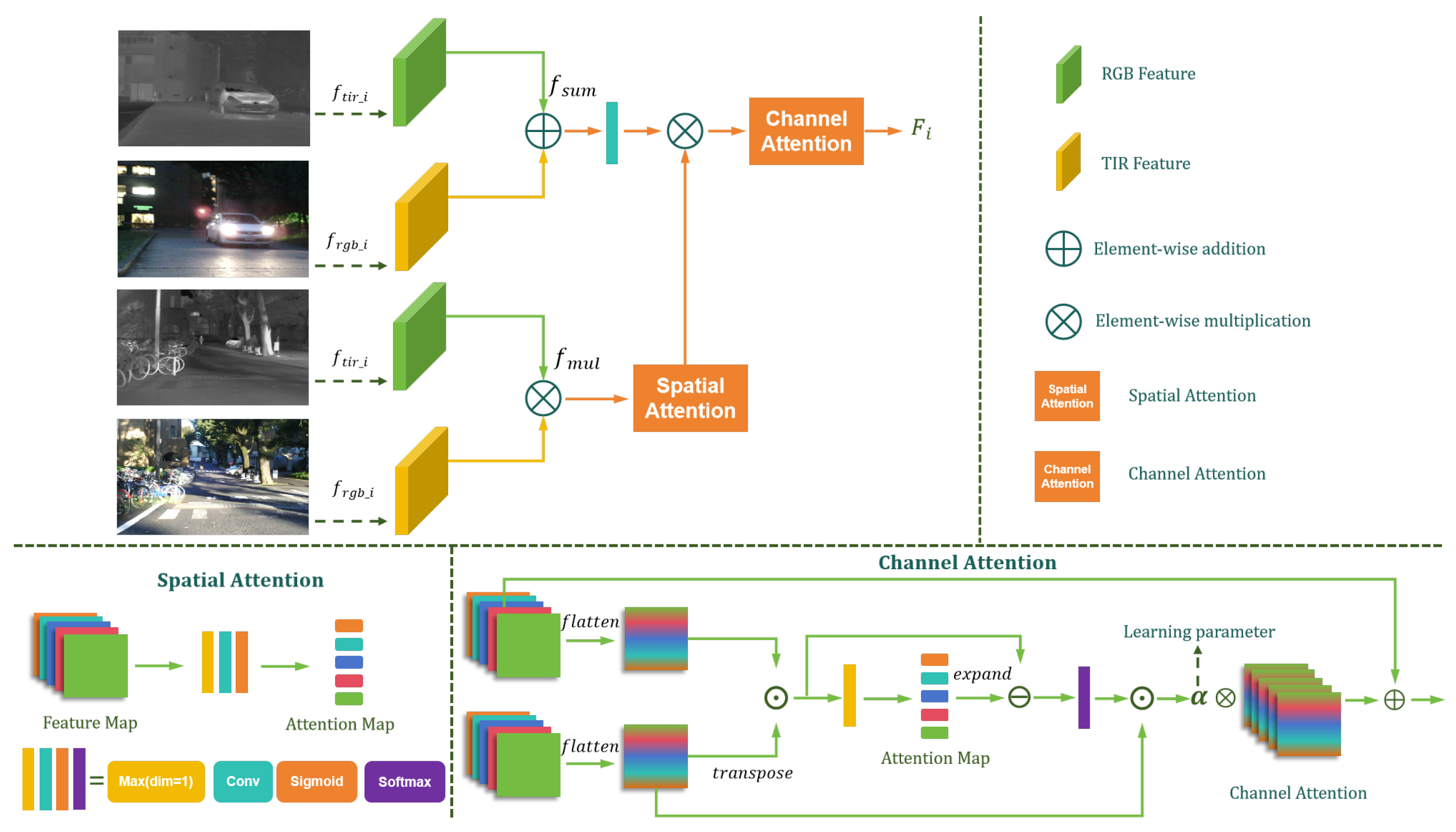
3.1. Channel–Spatial Cross-Fusion Module
3.2. Multi-Head Fusion Module
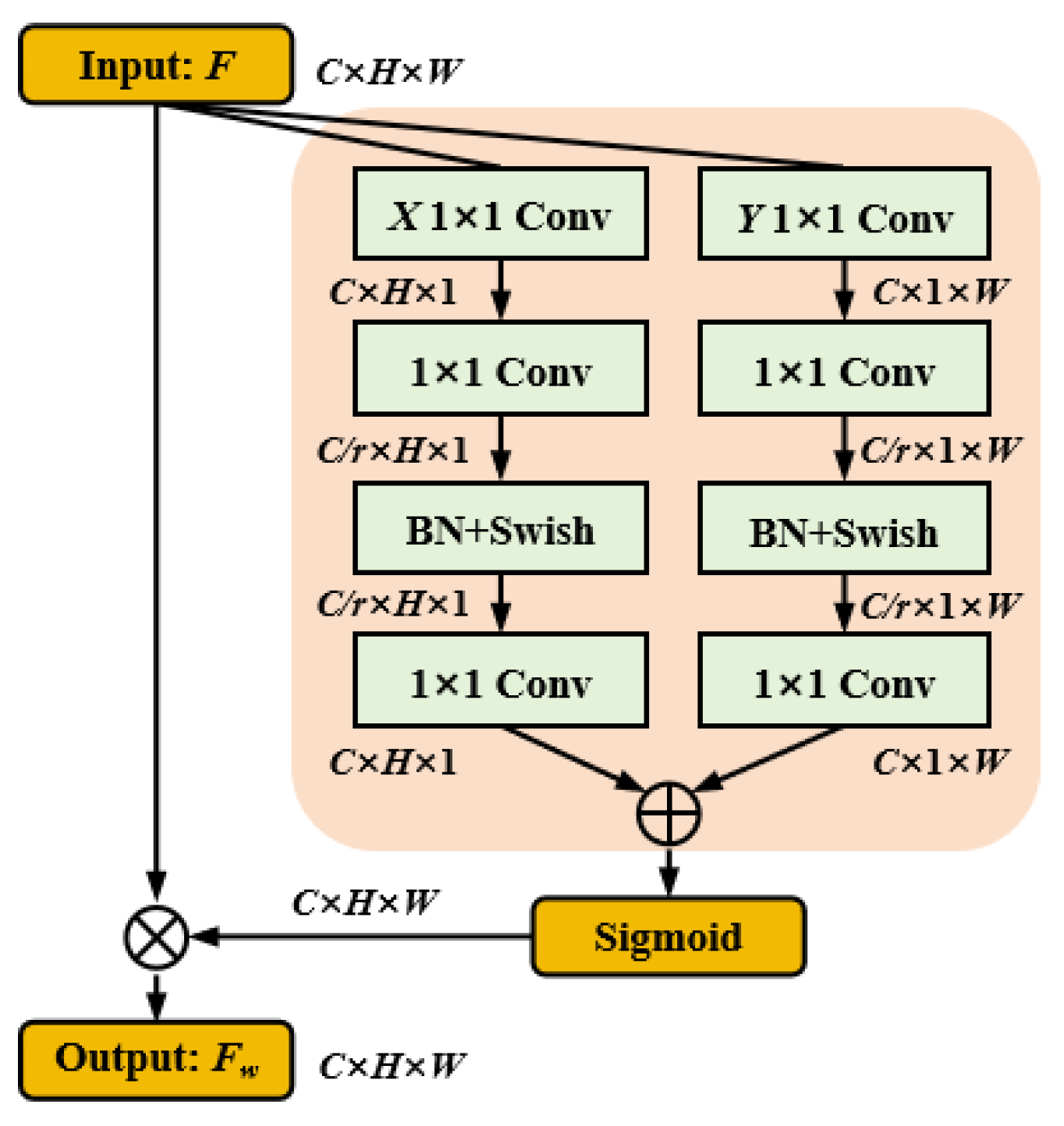
3.3. Spatial Coordinate Attention Mechanism
3.4. Decoder and Optimization Function
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Experimental Protocol
4.1.1. Dataset
4.1.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.1.3. Implementation Details
4.2. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
4.2.1. Evaluation on the MFNet Dataset
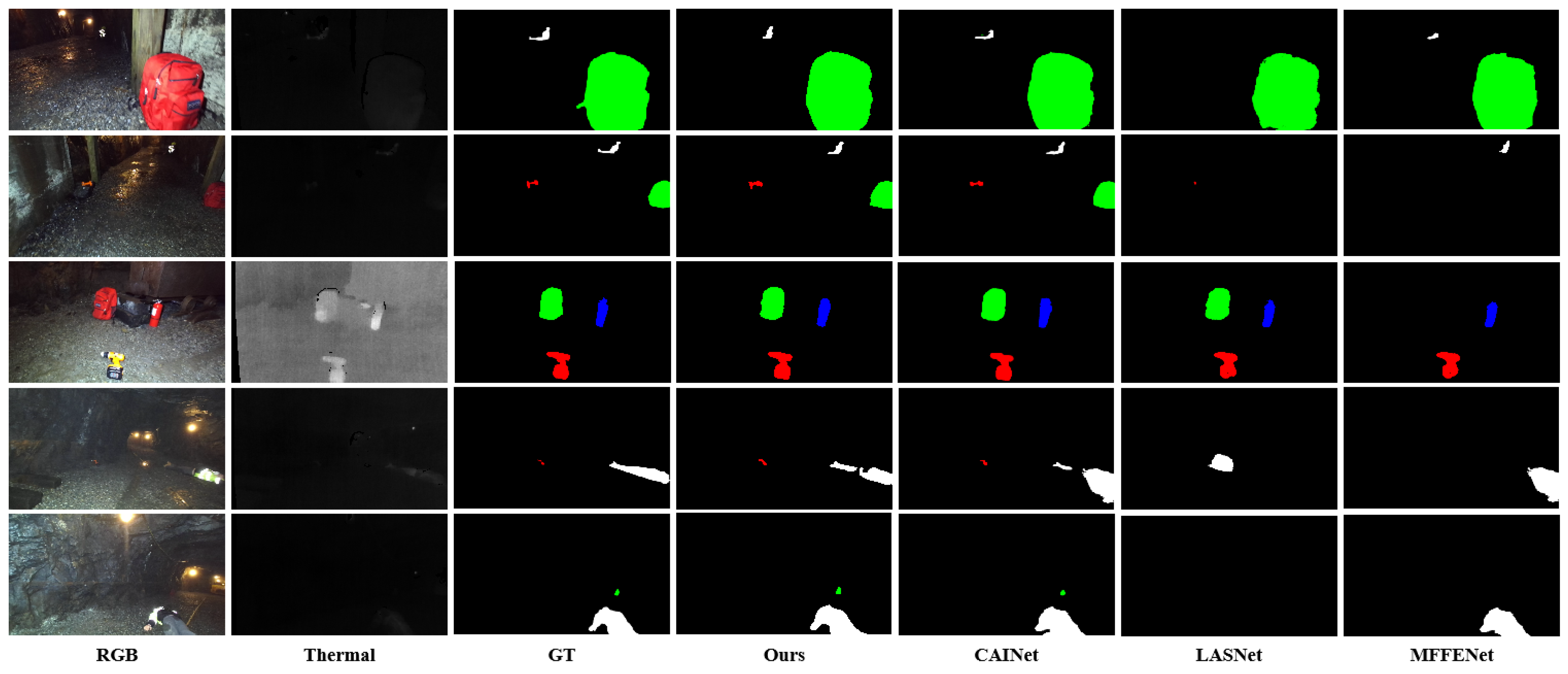
4.2.2. Evaluation on PST900 Dataset
4.2.3. Computational Complexity
4.3. Ablation Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Noh, H.; Hong, S.; Han, B. Learning deconvolution network for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1520–1528. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, J. Learning hybrid semantic affinity for point cloud segmentation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 32, 4599–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Haase-Schütz, C.; Rosenbaum, L.; Hertlein, H.; Glaeser, C.; Timm, F.; Wiesbeck, W.; Dietmayer, K. Deep multi-modal object detection and semantic segmentation for autonomous driving: Datasets, methods, and challenges. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 22, 1341–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, B.; Horanont, T.; Aryal, J. Deep learning-based semantic segmentation of urban features in satellite images: A review and meta-analysis. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cai, J.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, H. Joint semantic-instance segmentation method for intelligent transportation system. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 24, 15540–15547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampffmeyer, M.; Salberg, A.B.; Jenssen, R. Semantic segmentation of small objects and modeling of uncertainty in urban remote sensing images using deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, R.; Pan, X.; Li, F. DenseU-net-based semantic segmentation of small objects in urban remote sensing images. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 65347–65356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, A.; Wang, J.; Zhong, Y.; Zheng, Z. FactSeg: Foreground activation-driven small object semantic segmentation in large-scale remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5606216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeuffer, A.; Dietmayer, K. Robust semantic segmentation in adverse weather conditions by means of sensor data fusion. In Proceedings of the 2019 22th International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2–5 July 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Valada, A.; Vertens, J.; Dhall, A.; Burgard, W. Adapnet: Adaptive semantic segmentation in adverse environmental conditions. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 4644–4651. [Google Scholar]
- Ravishankar, H.; Venkataramani, R.; Thiruvenkadam, S.; Sudhakar, P.; Vaidya, V. Learning and incorporating shape models for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 11–13 September 2017; pp. 203–211. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, D. RGB-T semantic segmentation with location, activation, and sharpening. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 33, 1223–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, U.; Lee, K.; Kweon, I.S.; Oh, J. Complementary random masking for rgb-thermal semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Yokohama, Japan, 13–17 May 2024; pp. 11110–11117. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, R.; Shi, H.; Yang, K.; Reiß, S.; Peng, K.; Fu, H.; Wang, K.; Stiefelhagen, R. Delivering arbitrary-modal semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 1136–1147. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, S.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, D.; Huang, N.; Han, J. ABMDRNet: Adaptive-weighted bi-directional modality difference reduction network for RGB-T semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 2633–2642. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Dong, S.; Lei, J.; Yu, L. MTANet: Multitask-aware network with hierarchical multimodal fusion for RGB-T urban scene understanding. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2022, 8, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zuo, W.; Liu, M. RTFNet: RGB-thermal fusion network for semantic segmentation of urban scenes. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 2576–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Li, X.; Xu, Q.; Sun, Z. Robust semantic segmentation based on RGB-thermal in variable lighting scenes. Measurement 2021, 186, 110176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Feng, H.; Liang, M.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, J.; Guo, X.; Lam, T.L. FEANet: Feature-enhanced attention network for RGB-thermal real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Prague, Czech Republic, 27 September–1 October 2021; pp. 4467–4473. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Yang, K.; Hu, X.; Liu, R.; Stiefelhagen, R. CMX: Cross-modal fusion for RGB-X semantic segmentation with transformers. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 14679–14694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, H. CGFNet: Cross-guided fusion network for RGB-thermal semantic segmentation. Vis. Comput. 2022, 38, 3243–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, W.; Cui, Y.; Yu, L.; Luo, T. GCNet: Grid-like context-aware network for RGB-thermal semantic segmentation. Neurocomputing 2022, 506, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Fan, D.P.; Ji, G.P.; Zhao, Q.; Shen, J.; Zhu, C. Siamese network for RGB-D salient object detection and beyond. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 5541–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Fan, D.P.; Ji, G.P.; Zhao, Q. JL-DCF: Joint learning and densely-cooperative fusion framework for RGB-D salient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 3052–3062. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, H.T.; Yang, J.; Zareapoor, M. Multi-scale convolutional neural network for multi-focus image fusion. Image Vis. Comput. 2019, 85, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Peng, C.; Xue, X.; Sun, J. Exfuse: Enhancing feature fusion for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 269–284. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Li, Y. Multi-feature fusion network for road scene semantic segmentation. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 92, 107155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, H.; Han, L.; Tong, Y.; Tan, S.; Yang, K. Gated fully fusion for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 11418–11425. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Z.; Zhong, G.; Yu, H. A review on the attention mechanism of deep learning. Neurocomputing 2021, 452, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets and fully connected crfs. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.7062. [Google Scholar]
- Yurtkulu, S.C.; Şahin, Y.H.; Unal, G. Semantic segmentation with extended DeepLabv3 architecture. In Proceedings of the 2019 27th Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), Sivas, Turkey, 24–26 April 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Xu, Z.; Xu, B. Research on improved DeepLabv3+ image Semantic Segmentation algorithm. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Control Engineering and Artificial Intelligence, Sanya, China, 28–30 January 2023; pp. 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Chai, Z. Image semantic segmentation based on improved DeepLabv3+ network and superpixel edge optimization. J. Electron. Imaging 2022, 31, 013011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015, Proceedings, Part III 18; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Alom, M.Z.; Yakopcic, C.; Hasan, M.; Taha, T.M.; Asari, V.K. Recurrent residual U-Net for medical image segmentation. J. Med. Imaging 2019, 6, 014006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Rahman Siddiquee, M.M.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. Unet++: A nested u-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support: 4th International Workshop, DLMIA 2018, and 8th International Workshop, ML-CDS 2018, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2018, Granada, Spain, 20 September 2018, Proceedings 4; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A. Attention is all you need. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.03762. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Strudel, R.; Garcia, R.; Laptev, I.; Schmid, C. Segmenter: Transformer for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 7262–7272. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, Q.; Watanabe, K.; Karasawa, T.; Ushiku, Y.; Harada, T. MFNet: Towards real-time semantic segmentation for autonomous vehicles with multi-spectral scenes. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 5108–5115. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zuo, W.; Yun, P.; Wang, H.; Liu, M. FuseSeg: Semantic segmentation of urban scenes based on RGB and thermal data fusion. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2020, 18, 1000–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivakumar, S.S.; Rodrigues, N.; Zhou, A.; Miller, I.D.; Kumar, V.; Taylor, C.J. Pst900: Rgb-thermal calibration, dataset and segmentation network. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 9441–9447. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Sun, Y. IGFNet: Illumination-Guided Fusion Network for Semantic Scene Understanding using RGB-Thermal Images. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Koh Samui, Thailand, 4–9 December 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, E.; Wang, W.; Yu, Z.; Anandkumar, A.; Alvarez, J.M.; Luo, P. SegFormer: Simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 12077–12090. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Xie, E.; Li, X.; Fan, D.P.; Song, K.; Liang, D.; Lu, T.; Luo, P.; Shao, L. Pyramid vision transformer: A versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 568–578. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Xie, E.; Li, X.; Fan, D.P.; Song, K.; Liang, D.; Lu, T.; Luo, P.; Shao, L. Pvt v2: Improved baselines with pyramid vision transformer. Comput. Vis. Media 2022, 8, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13713–13722. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, T.H.; Yamamoto, K. Resolving class imbalance in object detection with weighted cross entropy losses. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.01413. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Lin, X.; Lei, J.; Yu, L.; Hwang, J.N. MFFENet: Multiscale feature fusion and enhancement network for RGB–thermal urban road scene parsing. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 24, 2526–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Liu, J.; Lei, J.; Yu, L.; Hwang, J.N. GMNet: Graded-feature multilabel-learning network for RGB-thermal urban scene semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 7790–7802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Gu, X.; Gu, X. MMNet: Multi-modal multi-stage network for RGB-T image semantic segmentation. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 5817–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Dong, S.; Xu, C.; Qian, Y. Edge-aware guidance fusion network for rgb–thermal scene parsing. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual, 22 February–1 March 2022; Volume 36, pp. 3571–3579. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Chu, T.; Liu, Q. Complementarity-aware cross-modal feature fusion network for RGB-T semantic segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 131, 108881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Yuan, X. CCAFFMNet: Dual-spectral semantic segmentation network with channel-coordinate attention feature fusion module. Neurocomputing 2022, 482, 236–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Li, Q.; Jiang, X.; Yu, D.; Zhou, Y. Dual-space graph-based interaction network for RGB-thermal semantic segmentation in electric power scene. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 33, 1577–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Q. A feature divide-and-conquer network for RGB-T semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 33, 2892–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Lv, Y.; Lei, J.; Yu, L. Embedded control gate fusion and attention residual learning for RGB–thermal urban scene parsing. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 4794–4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhang, H.; Yan, W.; Lin, W. MMSMCNet: Modal memory sharing and morphological complementary networks for RGB-T urban scene semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 7096–7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wang, M.; Liu, T.; Zhao, L.; Yue, Y. SFAF-MA: Spatial feature aggregation and fusion with modality adaptation for RGB-thermal semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 5012810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Gong, T.; Lei, J.; Yu, L. DBCNet: Dynamic bilateral cross-fusion network for RGB-T urban scene understanding in intelligent vehicles. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2023, 53, 7631–7641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, G. Context-aware interaction network for rgb-t semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 6348–6360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, Y. U-kan makes strong backbone for medical image segmentation and generation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 25 February–4 March 2025; Volume 39, pp. 4652–4660. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Li, F.; Wang, B. U-mamba: Enhancing long-range dependency for biomedical image segmentation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.04722. [Google Scholar]





| Methods | Years | Car | Person | Bike | Curve | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acc | IoU | Acc | IoU | Acc | IoU | Acc | IoU | ||
| MFNet | 2017 | 77.2 | 65.9 | 67.0 | 58.9 | 53.9 | 42.9 | 36.2 | 29.9 |
| RTFNet | 2019 | 91.3 | 86.3 | 78.2 | 67.8 | 71.5 | 58.2 | 69.8 | 43.7 |
| PSTNet | 2020 | - | 76.8 | - | 52.6 | - | 55.3 | - | 29.6 |
| MLFNet | 2021 | - | 82.3 | - | 68.1 | - | 67.3 | - | 27.3 |
| FuseSeg | 2021 | 93.1 | 87.9 | 81.4 | 71.7 | 78.5 | 64.6 | 68.4 | 44.8 |
| ABMDRNet | 2021 | 94.3 | 84.8 | 90.0 | 69.6 | 75.7 | 60.3 | 64.0 | 45.1 |
| FEANet | 2021 | 93.3 | 87.8 | 82.7 | 71.1 | 76.7 | 61.1 | 65.5 | 46.5 |
| MFFENet | 2021 | 93.1 | 88.2 | 83.2 | 74.1 | 77.1 | 62.9 | 67.2 | 46.2 |
| GMNet | 2021 | 94.1 | 86.5 | 83.0 | 73.1 | 76.9 | 61.7 | 59.7 | 44.0 |
| MMNet | 2022 | - | 83.9 | - | 69.3 | - | 59.0 | - | 43.2 |
| EGFNet | 2022 | 95.8 | 87.6 | 89.0 | 69.8 | 80.6 | 58.8 | 71.5 | 42.8 |
| MTANet | 2022 | 95.8 | 88.1 | 90.9 | 71.5 | 80.3 | 60.7 | 75.3 | 40.9 |
| CCFFNet | 2022 | 94.5 | 89.6 | 83.6 | 74.2 | 73.2 | 63.1 | 67.2 | 50.5 |
| CCAFFMNet | 2022 | 95.2 | 89.1 | 85.9 | 72.5 | 82.3 | 67.5 | 71.8 | 46.3 |
| DSGBINet | 2022 | 95.2 | 87.4 | 89.2 | 69.5 | 85.2 | 64.7 | 66.0 | 46.3 |
| CMXSegF | 2022 | - | 89.4 | - | 74.8 | - | 64.7 | - | 47.3 |
| FDCNet | 2022 | 94.1 | 87.5 | 91.4 | 72.4 | 78.1 | 61.7 | 70.1 | 43.8 |
| ECGFNet | 2023 | 89.4 | 83.5 | 85.2 | 72.1 | 72.9 | 61.6 | 62.8 | 40.5 |
| MMSMCNet | 2023 | 96.2 | 89.2 | 93.2 | 69.1 | 83.4 | 63.5 | 74.4 | 46.4 |
| LASNet | 2023 | 94.9 | 84.2 | 81.7 | 67.1 | 82.1 | 56.9 | 70.7 | 41.1 |
| SFAF-MA | 2023 | 94.3 | 87.8 | 83.9 | 72.4 | 72.0 | 59.5 | 64.4 | 46.0 |
| DBCNet | 2024 | 93.0 | 87.4 | 82.7 | 73.6 | 70.3 | 61.8 | 71.2 | 47.1 |
| CAINet | 2024 | 93.0 | 88.5 | 74.6 | 66.3 | 85.2 | 68.7 | 65.9 | 55.4 |
| U-Mamba | 2024 | 82.7 | 74.3 | 77.9 | 65.5 | 59.9 | 48.8 | 52.4 | 36.2 |
| U-KAN | 2025 | 81.2 | 72.4 | 76.4 | 64.1 | 58.3 | 47.2 | 51.7 | 35.0 |
| CSANet (Ours) | - | 95.3 ± 0.2 | 85.6 ± 0.2 | 91.0 ± 0.2 | 65.7 ± 0.3 | 86.0 ± 0.2 | 71.7 ± 0.3 | 49.5 ± 0.3 | 37.2 ± 0.3 |
| Methods | Years | Car Stop | Guardrail | Color Cone | Bump | mAcc | mIoU | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acc | IoU | Acc | IoU | Acc | IoU | Acc | IoU | ||||
| MFNet | 2017 | 19.1 | 9.9 | 0.1 | 8.5 | 30.3 | 25.2 | 30.0 | 27.7 | 45.1 | 39.7 |
| RTFNet | 2019 | 32.1 | 24.3 | 13.4 | 3.6 | 40.4 | 26.0 | 73.5 | 57.2 | 62.2 | 51.7 |
| PSTNet | 2020 | - | 25.1 | - | 15.1 | - | 39.4 | - | 45.0 | - | 48.4 |
| MLFNet | 2021 | - | 30.4 | - | 15.7 | - | 55.6 | - | 40.1 | - | 53.8 |
| FuseSeg | 2021 | 29.1 | 22.7 | 63.7 | 6.4 | 55.8 | 46.9 | 66.4 | 47.9 | 70.6 | 54.5 |
| ABMDRNet | 2021 | 44.1 | 33.1 | 31.0 | 5.1 | 61.7 | 47.4 | 66.2 | 50.0 | 69.5 | 54.8 |
| FEANet | 2021 | 26.6 | 22.1 | 70.8 | 6.6 | 66.6 | 55.3 | 77.3 | 48.9 | 73.2 | 55.3 |
| MFFENet | 2021 | 52.3 | 37.1 | 65.0 | 7.6 | 58.5 | 52.4 | 73.4 | 47.4 | 74.3 | 57.1 |
| GMNet | 2021 | 55.0 | 42.3 | 71.2 | 14.5 | 54.7 | 48.7 | 73.1 | 47.4 | 74.1 | 57.3 |
| MMNet | 2022 | - | 24.7 | - | 4.6 | - | 42.2 | - | 50.7 | 62.7 | 52.8 |
| EGFNet | 2022 | 48.7 | 33.8 | 33.6 | 7.0 | 65.3 | 48.3 | 71.1 | 47.1 | 72.7 | 54.8 |
| MTANet | 2022 | 62.8 | 38.9 | 38.7 | 13.7 | 63.8 | 45.9 | 70.8 | 47.2 | 75.2 | 56.1 |
| CCFFNet | 2022 | 38.7 | 31.9 | 30.6 | 4.8 | 55.2 | 49.7 | 72.9 | 56.3 | 68.3 | 57.6 |
| CCAFFMNet | 2022 | 32.5 | 25.2 | 56.8 | 17.3 | 58.3 | 50.6 | 76.6 | 58.3 | 72.9 | 58.2 |
| DSGBINet | 2022 | 56.7 | 43.4 | 7.8 | 3.3 | 82.0 | 61.7 | 72.8 | 48.9 | 72.6 | 58.1 |
| CMXSegF | 2022 | - | 30.1 | - | 8.1 | - | 52.4 | - | 59.4 | - | 58.2 |
| FDCNet | 2022 | 34.4 | 27.2 | 61.5 | 7.3 | 64.0 | 52.0 | 74.5 | 56.6 | 74.1 | 56.3 |
| ECGFNet | 2023 | 44.8 | 30.8 | 45.2 | 11.1 | 57.2 | 49.7 | 65.1 | 50.9 | 69.1 | 55.3 |
| MMSMCNet | 2023 | 56.6 | 41.9 | 26.9 | 8.8 | 70.2 | 48.8 | 77.5 | 57.6 | 75.2 | 58.1 |
| LASNet | 2023 | 56.8 | 39.6 | 59.5 | 18.9 | 58.1 | 48.8 | 77.2 | 40.1 | 75.4 | 54.9 |
| SFAF-MA | 2023 | 34.0 | 24.7 | 35.6 | 4.3 | 55.8 | 39.1 | 67.9 | 52.6 | 67.5 | 53.8 |
| DBCNet | 2024 | 46.2 | 33.8 | 78.2 | 62.9 | 57.7 | 50.9 | 74.6 | 45.4 | 74.8 | 56.2 |
| CAINet | 2024 | 34.7 | 31.5 | 65.6 | 9.0 | 55.6 | 48.9 | 85.0 | 60.7 | 73.2 | 58.6 |
| U-Mamba | 2024 | 29.5 | 18.1 | 41.6 | 24.3 | 62.7 | 42.8 | 48.8 | 38.3 | 63.5 | 48.2 |
| U-KAN | 2025 | 28.2 | 16.6 | 40.1 | 22.7 | 61.4 | 41.2 | 47.6 | 37.0 | 62.1 | 46.7 |
| CSANet (Ours) | - | 64.7 ± 0.4 | 48.5 ± 0.3 | 78.2 ± 0.3 | 44.2 ± 0.3 | 87.0 ± 0.2 | 58.9 ± 0.3 | 62.1 ± 0.2 | 53.5 ± 0.2 | 79.1 ± 0.15 | 62.5 ± 0.13 |
| Methods | Daytime | Nighttime | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAcc | mIoU | mAcc | mIoU | |
| DSGBINet | 62.8 | 47.2 | 65.3 | 48.9 |
| FEANet | 64.7 | 52.3 | 61.5 | 44.2 |
| CAINet | 66.4 | 53.9 | 60.2 | 41.3 |
| GMNet | 65.1 | 52.7 | 63.4 | 46.5 |
| FDCNet | 63.6 | 49.2 | 61.7 | 44.9 |
| MFFENet | 66.5 | 52.3 | 64.9 | 47.6 |
| DBCNet | 67.2 | 54.5 | 62.3 | 45.1 |
| MTANet | 65.8 | 53.4 | 61.2 | 43.9 |
| MMSMCNet | 66.9 | 54.7 | 62.0 | 44.6 |
| LASNet | 68.9 | 56.3 | 69.2 | 55.1 |
| CSANet (Ours) | 76.2 | 61.1 | 71.9 | 58.3 |
| Methods | Years | Background | Hand-Drill | Backpack | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acc | IoU | Acc | IoU | Acc | IoU | ||
| MFNet | 2017 | - | 98.63 | - | 41.13 | - | 64.27 |
| PSTNet | 2020 | - | 98.85 | - | 53.60 | - | 69.20 |
| MFFENet | 2021 | - | 99.40 | - | 72.50 | - | 81.02 |
| GMNet | 2021 | 99.81 | 99.44 | 90.29 | 85.17 | 89.01 | 83.82 |
| EGFNet | 2022 | 99.48 | 99.26 | 97.99 | 64.67 | 94.17 | 83.05 |
| MTANet | 2022 | - | 99.33 | - | 62.05 | - | 87.50 |
| CCFFNet | 2022 | 99.9 | 99.4 | 89.7 | 82.8 | 77.5 | 75.8 |
| DSGBINet | 2022 | 99.73 | 99.39 | 94.53 | 74.99 | 88.65 | 85.11 |
| FDCNet | 2022 | 99.72 | 99.15 | 82.52 | 70.36 | 77.45 | 72.17 |
| MMSMCNet | 2023 | 99.55 | 99.39 | 97.96 | 62.36 | 96.94 | 89.22 |
| LASNet | 2023 | 99.77 | 99.46 | 91.81 | 82.80 | 90.80 | 86.48 |
| DBCNet | 2024 | - | 99.40 | - | 77.19 | - | 82.67 |
| CAINet | 2024 | 99.66 | 99.50 | 95.87 | 80.30 | 96.09 | 88.02 |
| CSANet (Ours) | - | 99.73 | 99.55 | 95.65 | 83.76 | 97.90 | 89.88 |
| Methods | Years | Fire-Extinguisher | Survivor | mAcc | mIoU | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acc | IoU | Acc | IoU | ||||
| MFNet | 2017 | - | 60.35 | - | 20.70 | - | 57.02 |
| PSTNet | 2020 | - | 70.12 | - | 50.03 | - | 68.36 |
| MFFENet | 2021 | - | 66.38 | - | 75.60 | - | 78.98 |
| GMNet | 2021 | 88.28 | 73.79 | 80.86 | 78.36 | 89.61 | 84.12 |
| EGFNet | 2022 | 95.17 | 71.29 | 83.30 | 74.30 | 94.02 | 78.51 |
| MTANet | 2022 | - | 64.95 | - | 79.14 | - | 78.60 |
| CCFFNet | 2022 | 87.6 | 79.9 | 79.7 | 72.7 | 86.9 | 82.1 |
| DSGBINet | 2022 | 94.78 | 79.31 | 81.37 | 75.56 | 91.81 | 82.87 |
| FDCNet | 2022 | 91.77 | 71.52 | 78.36 | 72.36 | 85.96 | 77.11 |
| MMSMCNet | 2023 | 97.36 | 73.29 | 84.28 | 74.70 | 95.20 | 79.80 |
| LASNet | 2023 | 92.36 | 77.75 | 83.43 | 75.49 | 91.63 | 84.40 |
| DBCNet | 2024 | - | 72.95 | - | 76.68 | - | 81.78 |
| CAINet | 2024 | 88.38 | 77.21 | 91.35 | 78.69 | 94.27 | 84.73 |
| CSANet (Ours) | - | 98.41 | 86.35 | 86.18 | 76.51 | 95.57 | 86.01 |
| Methods | Input Size | FLOPs/G ↓ | Params/M ↓ | mAcc | mIoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RTFNet | 640 × 480 | 245.71 | 185.24 | 62.2 | 51.7 |
| PSTNet | 640 × 480 | 337.04 | 254.51 | - | 48.4 |
| FuseSeg | 640 × 480 | 129.37 | 20.38 | 70.6 | 54.6 |
| ABMDRNet | 640 × 480 | 194.33 | 64.60 | 69.5 | 54.8 |
| EGFNet | 640 × 480 | 201.29 | 62.82 | 72.7 | 54.8 |
| MTANet | 640 × 480 | 264.69 | 121.58 | 75.2 | 56.1 |
| FDCNet | 640 × 480 | 159.05 | 52.91 | 74.1 | 56.3 |
| MMSMCNet | 640 × 480 | 181.82 | 98.58 | 75.2 | 58.1 |
| LASNet | 640 × 480 | 233.81 | 93.58 | 75.4 | 54.9 |
| DBCNet | 640 × 480 | 67.49 | 47.87 | 74.8 | 56.2 |
| CAINet | 640 × 480 | 123.62 | 12.16 | 73.2 | 58.6 |
| CSANet (Ours) | 640 × 480 | 84.32 | 38.36 | 79.1 | 62.5 |
| Variants | mAcc | mIoU | Car | Person | Bike | Guardrail | Car Stop | Pole |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 64.8 | 53.2 | 85.1 | 88.2 | 59.3 | 32.7 | 25.6 | 28.2 |
| Baseline + w/o CSCFM | 76.9 | 58.7 | 86.8 | 90.1 | 62.5 | 36.4 | 31.7 | 34.8 |
| Baseline + w/o MHFM | 69.5 | 57.3 | 86.0 | 89.4 | 61.7 | 35.8 | 30.2 | 33.5 |
| Baseline + w/o SCAM | 75.3 | 56.8 | 86.4 | 89.8 | 62.1 | 35.9 | 29.7 | 31.2 |
| CSANet (Ours) | 79.1 | 62.5 | 87.6 | 91.0 | 65.7 | 37.2 | 44.2 | 39.6 |
| Variants | mAcc | mIoU | Car | Person | Bike | Guardrail | Car Stop | Pole |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSANet (RGB only) | 72.4 | 56.7 | 82.1 | 85.9 | 61.2 | 33.5 | 35.8 | 32.1 |
| CSANet (TIR only) | 69.8 | 54.2 | 80.4 | 83.6 | 59.4 | 31.2 | 33.6 | 30.8 |
| CSANet (RGB+TIR) | 79.1 | 62.5 | 87.6 | 91.0 | 65.7 | 37.2 | 44.2 | 39.6 |
| Variants | mAcc | mIoU | Car | Person | Bike | Guardrail | Car Stop | Pole |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSANet w/CoordConv | 76.8 | 59.3 | 81.2 | 88.3 | 62.1 | 38.5 | 38.7 | 35.8 |
| CSANet w/CoordAtt | 77.5 | 60.1 | 82.3 | 89.1 | 63.0 | 39.6 | 39.8 | 36.5 |
| CSANet w/SCAM | 79.1 | 62.5 | 87.6 | 91.0 | 65.7 | 37.2 | 44.2 | 39.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, R.; Wang, Z.; Guo, J.; Zhang, C. CSANet: Context–Spatial Awareness Network for RGB-T Urban Scene Understanding. J. Imaging 2025, 11, 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11060188
Li R, Wang Z, Guo J, Zhang C. CSANet: Context–Spatial Awareness Network for RGB-T Urban Scene Understanding. Journal of Imaging. 2025; 11(6):188. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11060188
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ruixiang, Zhen Wang, Jianxin Guo, and Chuanlei Zhang. 2025. "CSANet: Context–Spatial Awareness Network for RGB-T Urban Scene Understanding" Journal of Imaging 11, no. 6: 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11060188
APA StyleLi, R., Wang, Z., Guo, J., & Zhang, C. (2025). CSANet: Context–Spatial Awareness Network for RGB-T Urban Scene Understanding. Journal of Imaging, 11(6), 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11060188






