An Efficient Forest Smoke Detection Approach Using Convolutional Neural Networks and Attention Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Overview of Forest Fire Detection Model
2.2. Motivation and Our Approach
3. Proposed Model
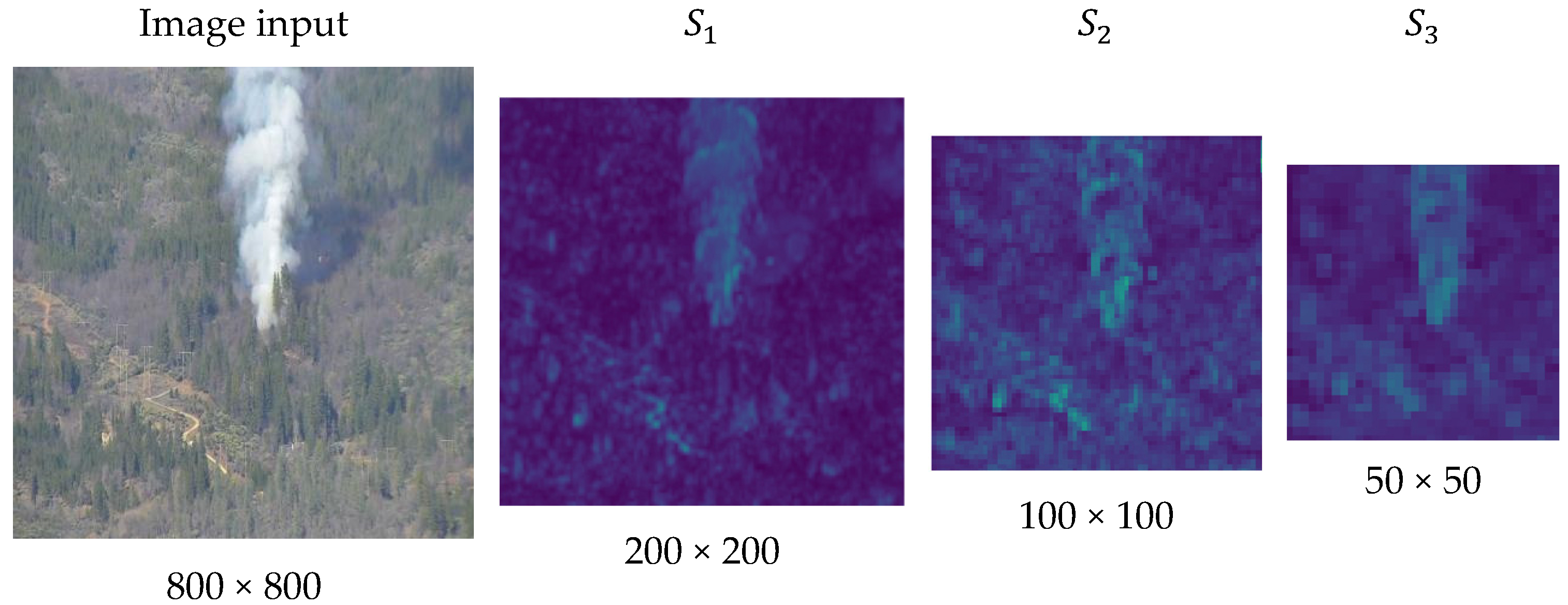
3.1. Backbone
3.1.1. Stem Block
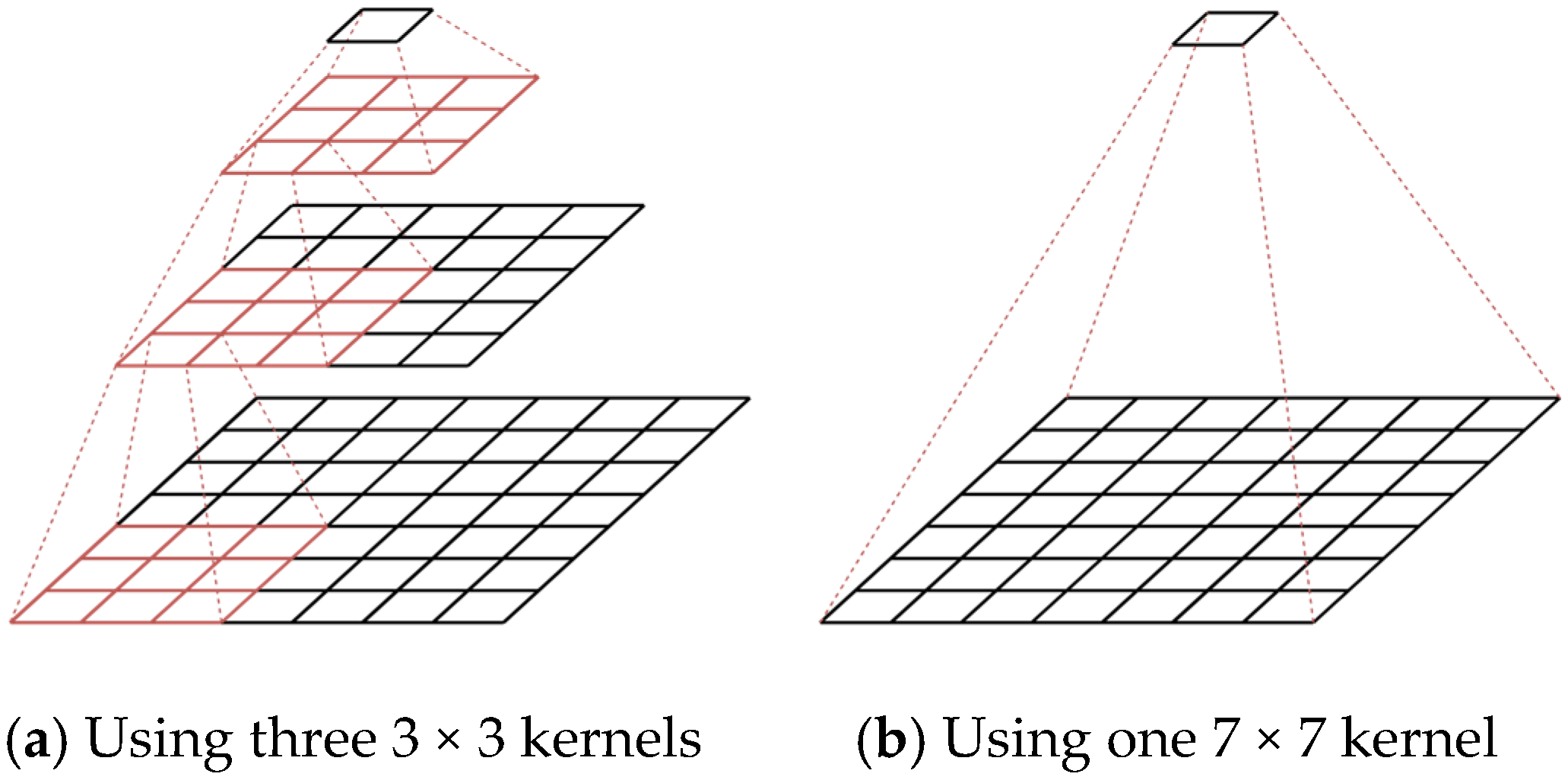
3.1.2. Transition Block
3.1.3. Residual Block
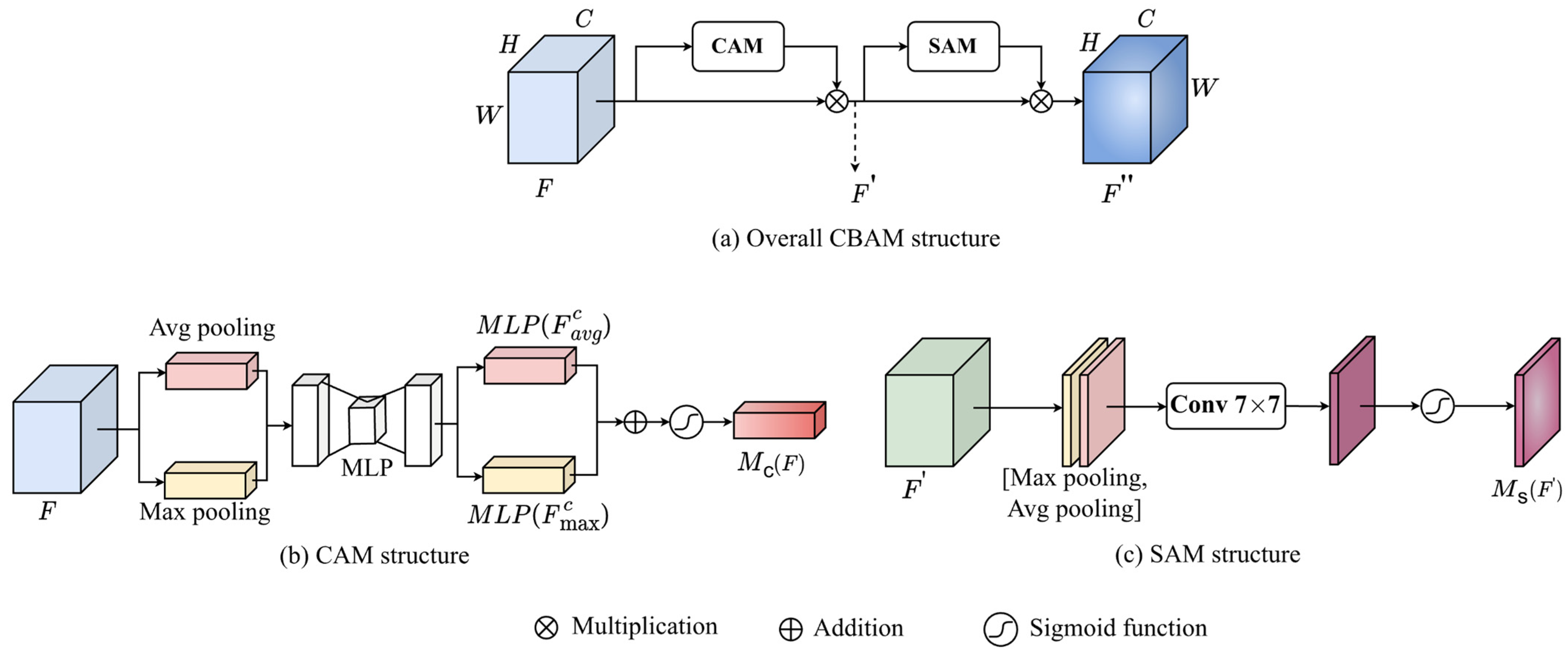
3.1.4. Attention Block
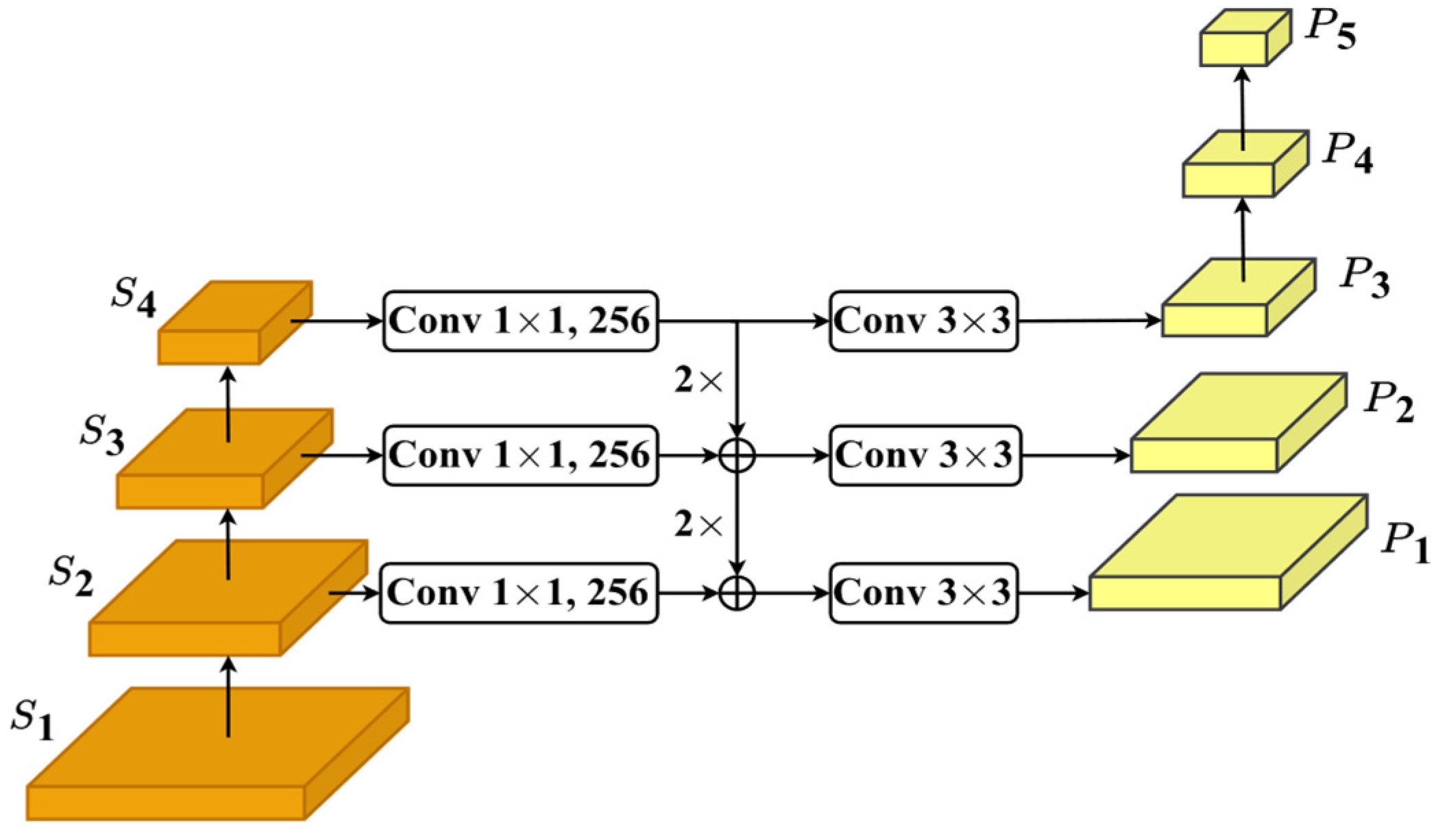
3.2. Neck and Head
3.3. Loss Function
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Experimental Setup
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
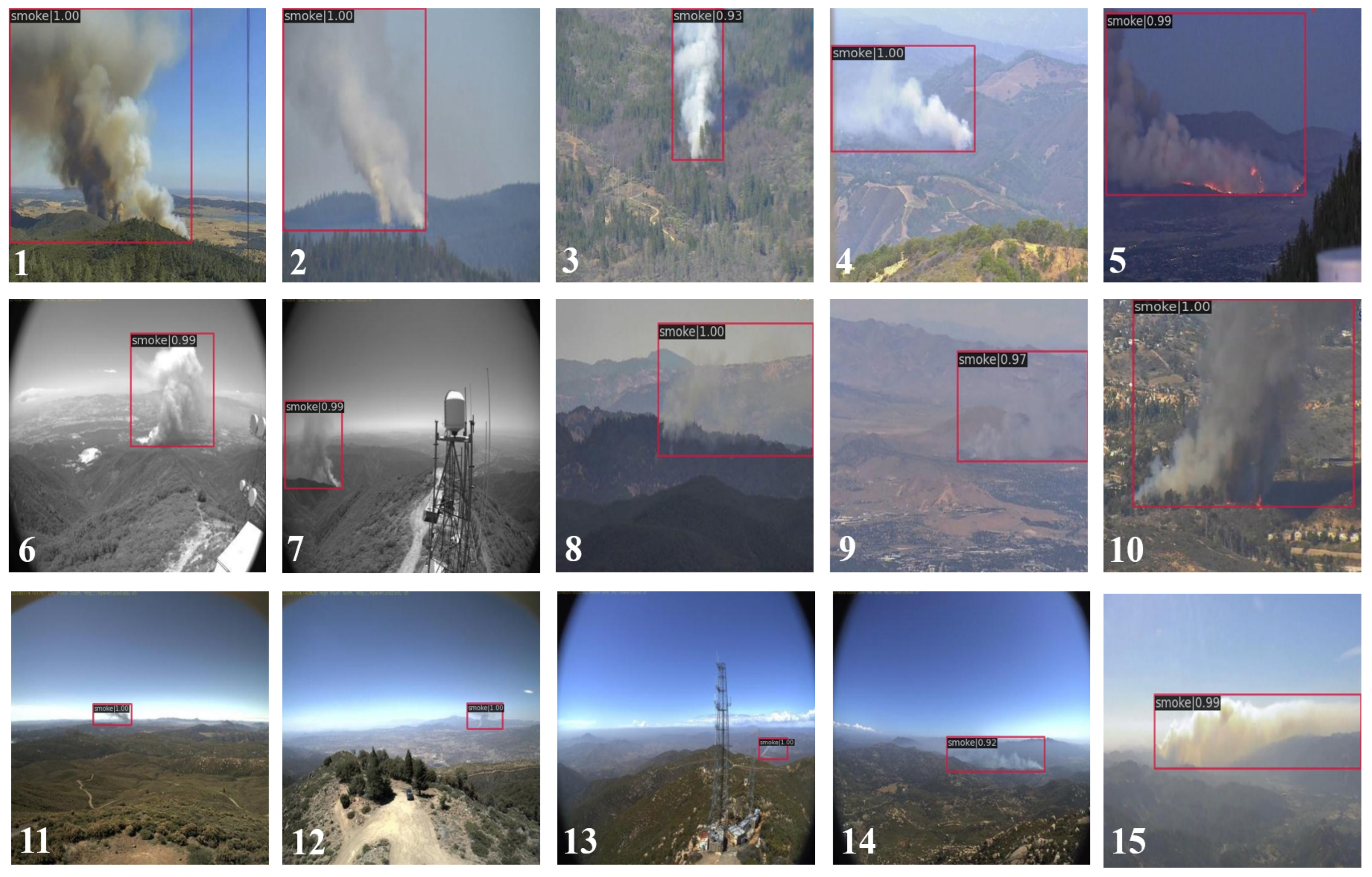
4.4. Experimental Results
4.5. Ablation Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Facts + Statistics: Wildfires. Available online: https://www.iii.org/fact-statistic/facts-statistics-wildfires (accessed on 1 April 2023).
- Chowdary, V.; Gupta, M.K. Automatic forest fire detection and monitoring techniques: A survey. In Intelligent Communication, Control and Devices: Proceedings of ICICCD 2017; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2018; pp. 1111–1117. [Google Scholar]
- Alkhatib, A.A.A. A review on forest fire detection techniques. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2014, 10, 597368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmpoutis, P.; Papaioannou, P.; Dimitropoulos, K.; Grammalidis, N. A review on early forest fire detection systems using optical remote sensing. Sensor 2022, 20, 6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- History of the Osborne Firefinder. Available online: https://www.fs.usda.gov/t-d/pubs/pdf/hi_res/03511311hi.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2023).
- Bouabdellah, K.; Noureddine, H.; Larbi, S. Using wireless sensor networks for reliable forest fires detection. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2013, 19, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, A.; Singh, A.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, A.; Kapoor, K. Video flame and smoke based fire detection algorithms: A literature review. Fire Technol. 2020, 56, 1943–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.H.; Wu, P.H.; Chiou, Y.C. An early fire-detection method based on image processing. In Proceedings of the 2004 International Conference on Image Processing, ICIP’04, Singapore, 24–27 October 2004; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 3, pp. 1707–1710. [Google Scholar]
- Vipin, V. Image processing based forest fire detection. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2012, 2, 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. UAV-based forest fire detection and tracking using image processing techniques. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Denver, CO, USA, 9–12 June 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 639–643. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, D.; Qu, C.; Ke, Y.; Cai, B. Contour based forest fire detection using FFT and wavelet. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering, Wuhan, China, 12–14 December 2008; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; Volume 1, pp. 760–763. [Google Scholar]
- Foggia, P.; Saggese, A.; Vento, M. Real-time fire detection for video-surveillance applications using a combination of experts based on color, shape, and motion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2015, 25, 1545–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.A.; Ren, H. Forest fire detection using a rule-based image processing algorithm and temporal variation. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 2018, 7612487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, T.; Lv, X.; Zhao, J.; Zou, X.; Zhao, X.; Xiao, M.; Wei, H. Forest fire detection based on lightweight Yolo. In Proceedings of the 2021 33rd Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Kunming, China, 22–24 May 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1560–1565. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.C.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; et al. Searching for mobilenetv3. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xin, J.; Mu, L.; Yi, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, D. A deep learning based forest fire detection approach using UAV and YOLOv3. In Proceedings of the 2019 1st International Conference on Industrial Artificial Intelligence (IAI), Shenyang, China, 23–27 July 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.X.; Lin, G.H.; Zhang, Y.M.; Xu, G.; Wang, J.T. Wildland forest fire smoke detection based on faster R-CNN using synthetic smoke images. Procedia Eng. 2018, 211, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.014972015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vani, K. Deep learning based forest fire classification and detection in satellite images. In Proceedings of the 2019 11th International Conference on Advanced Computing (ICoAC), Chennai, India, 18–20 December 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Meena, U.; Munjal, G.; Sachdeva, S.; Garg, P.; Dagar, D.; Gangal, A. RCNN Architecture for Forest Fire Detection. In Proceedings of the 2023 13th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science & Engineering (Confluence), Noida, India, 19–20 January 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 699–704. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Glenn, J. Yolov8. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/tree/main (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Wang, C.Y.; Yeh, I.H.; Liao, H.Y.M. Yolov9: Learning what you want to learn using programmable gradient information. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.13616. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J.; Ding, G. YOLOv10: Real-Time End-to-End Object Detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.14458. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Proceedings, Part I 14. Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- High Performance Wireless Research and Education Network. Available online: http://hpwren.ucsd.edu/index.html (accessed on 1 April 2023).
- Roboflow. Available online: https://roboflow.com/ (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Mao, H.; Wu, C.Y.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Darrell, T.; Xie, S. A convnet for the 2020s. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 11976–11986. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Proceedings, Part V 13. Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Padilla, R.; Netto, S.L.; Silva, E.A.D. A survey on performance metrics for object-detection algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Systems, Signals and Image Processing (IWSSIP), Niteroi, Brazil, 1–3 July 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 237–242. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]





| γ | α | β | AP | AP50 | AP75 | APS | APM | APL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.75 | 1 | 48.3 | 79.7 | 46.2 | 22.6 | 44.6 | 80.4 |
| 0.1 | 0.75 | 1 | 49.4 | 82.8 | 50.2 | 25.3 | 45.4 | 80.5 |
| 0.2 | 0.75 | 1 | 50.6 | 84.2 | 47.0 | 25.0 | 47.9 | 84.2 |
| 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 50.2 | 82.9 | 48.0 | 25.8 | 45.3 | 83.8 |
| 1 | 0.25 | 1 | 51.6 | 85.6 | 49.8 | 26.7 | 48.8 | 83.8 |
| 2 | 0.25 | 1 | 52.9 | 85.7 | 53.3 | 27.8 | 50.2 | 85.8 |
| 5 | 0.25 | 1 | 52.3 | 82.8 | 50.4 | 26.6 | 50.3 | 85.0 |
| Model | AP | AP50 | AP75 | APS | APM | APL | #Params (Millions) | GFLOPs | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Our model | 52.9 | 85.7 | 53.3 | 27.8 | 50.2 | 85.8 | 18.6 | 120.6 | 21.5 |
| RetinaNet [25] | 50.8 | 82.1 | 49.3 | 24.3 | 46.6 | 85.6 | 36.1 | 127.8 | 20.4 |
| YOLOv8s [26] | 49.7 | 77.0 | 51.1 | 14.4 | 45.9 | 77.0 | 11.2 | 28.6 | 102.0 |
| YOLOv8m [26] | 48.8 | 76.5 | 49.2 | 13.4 | 43.9 | 76.4 | 25.9 | 78.9 | 39.8 |
| YOLOv9s [27] | 49.1 | 76.1 | 50.6 | 14.0 | 43.1 | 76.6 | 7.1 | 26.4 | 79.5 |
| YOLOv9m [27] | 49.5 | 77.2 | 51.2 | 14.3 | 44.2 | 77.0 | 20.1 | 76.3 | 37.9 |
| YOLOv10s [28] | 48.2 | 75.4 | 48.5 | 15.8 | 40.7 | 75.9 | 7.2 | 21.6 | 88.5 |
| YOLOv10m [28] | 47.6 | 74.3 | 47.4 | 13.3 | 38.4 | 76.5 | 15.4 | 59.1 | 40.3 |
| Faster-RCNN [20] | 48.3 | 79.5 | 46.7 | 27.5 | 45.3 | 78.3 | 41.1 | 134.4 | 17.7 |
| SSD [29] | 43.0 | 77.8 | 42.4 | 21.6 | 47.1 | 70.8 | 24.4 | 214.2 | 17.4 |
| Backbone | AP | AP50 | AP75 | APS | APM | APL | #Params (Millions) | GFLOPs | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Our model | 52.9 | 85.7 | 53.3 | 27.8 | 50.2 | 85.8 | 18.61 | 120.63 | 21.5 |
| VGG16 [36] | 49.7 | 83.7 | 48.8 | 25.6 | 45.5 | 82.6 | 142.93 | 331.82 | 12.2 |
| Convnext [37] | 48.0 | 81.0 | 46.3 | 19.7 | 45.6 | 78.9 | 19.61 | 90.11 | 22.0 |
| EfficientNet [38] | 44.0 | 70.9 | 42.0 | 17.2 | 40.7 | 73.1 | 14.58 | 25.75 | 26.1 |
| Inceptionv1 [39] | 41.2 | 69.4 | 40.4 | 9.6 | 33.8 | 82.1 | 16.13 | 52.25 | 23.8 |
| Inceptionv4 [40] | 41.0 | 66.4 | 40.3 | 7.5 | 39.2 | 82.0 | 52.92 | 120.43 | 21.0 |
| Basic | Splitting | DW-Coord | CBAM | AP | #Params (Million) | GFLOPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| √ | 49.9 | 28.21 | 140.49 | |||
| √ | √ | 50.7 | 20.93 | 125.55 | ||
| √ | √ | √ | 52.6 | 18.52 | 120.62 | |
| √ | √ | √ | √ | 52.9 | 18.61 | 120.63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoang, Q.-Q.; Hoang, Q.-L.; Oh, H. An Efficient Forest Smoke Detection Approach Using Convolutional Neural Networks and Attention Mechanisms. J. Imaging 2025, 11, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11020067
Hoang Q-Q, Hoang Q-L, Oh H. An Efficient Forest Smoke Detection Approach Using Convolutional Neural Networks and Attention Mechanisms. Journal of Imaging. 2025; 11(2):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11020067
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoang, Quy-Quyen, Quy-Lam Hoang, and Hoon Oh. 2025. "An Efficient Forest Smoke Detection Approach Using Convolutional Neural Networks and Attention Mechanisms" Journal of Imaging 11, no. 2: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11020067
APA StyleHoang, Q.-Q., Hoang, Q.-L., & Oh, H. (2025). An Efficient Forest Smoke Detection Approach Using Convolutional Neural Networks and Attention Mechanisms. Journal of Imaging, 11(2), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11020067






