Boundary-Guided Differential Attention: Enhancing Camouflaged Object Detection Accuracy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Motivation and Contributions
- Inspired by how the human eye perceives camouflaged objects, we propose a differential attention mechanism, which leverages the difference between GAP and GMP under the guidance of boundary knowledge to highlight camouflaged objects.
- We introduce a method for boundary prior extraction, which first fuses multi-scale features of the input image and then applies channel attention mechanism to emphasize boundary features.
- Building on these insights, we developed BDA-Net for COD. Guided by boundary priors, the network applies differential attention to the multi-scale features of the input image, achieving superior performance.
3. Method
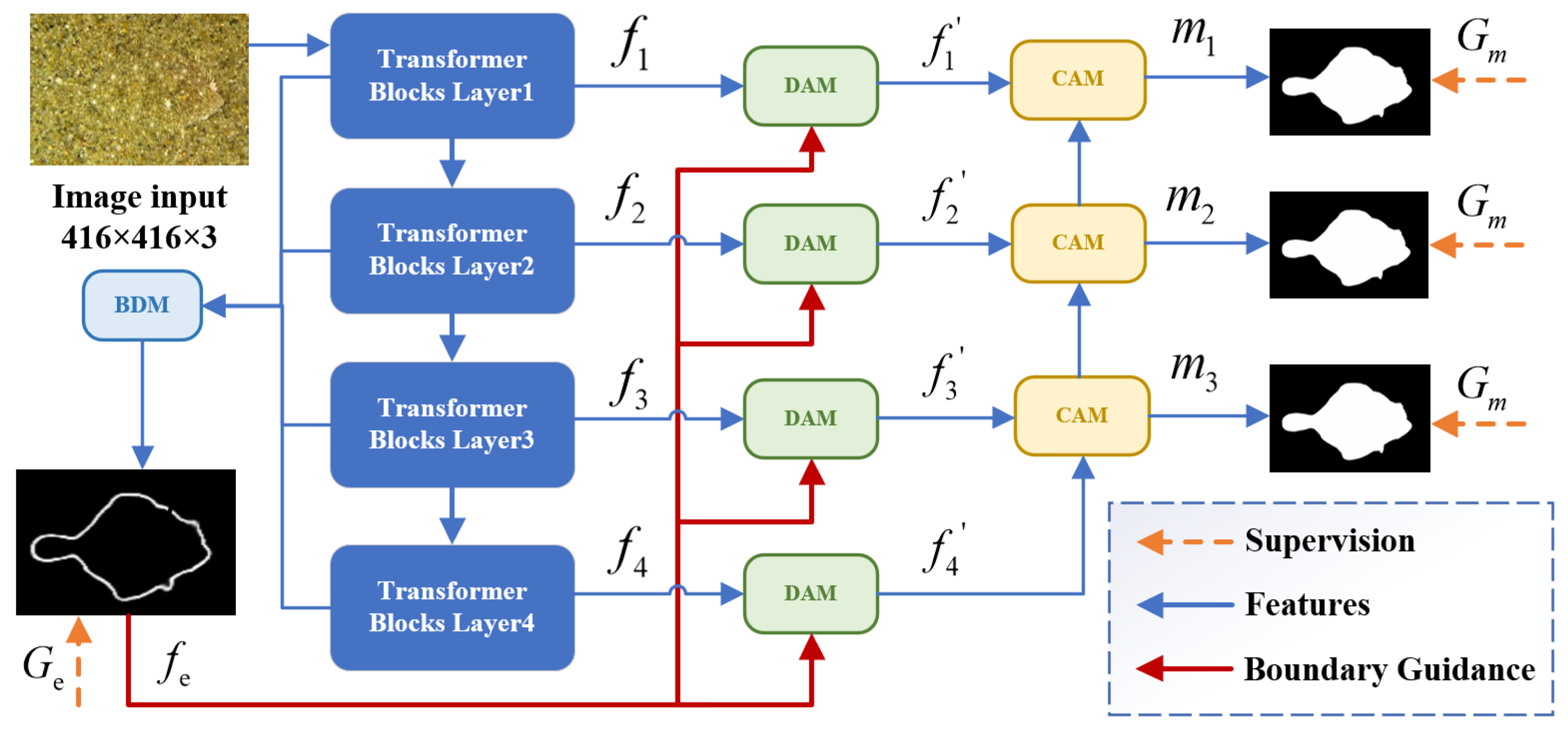
3.1. Overall Architecture
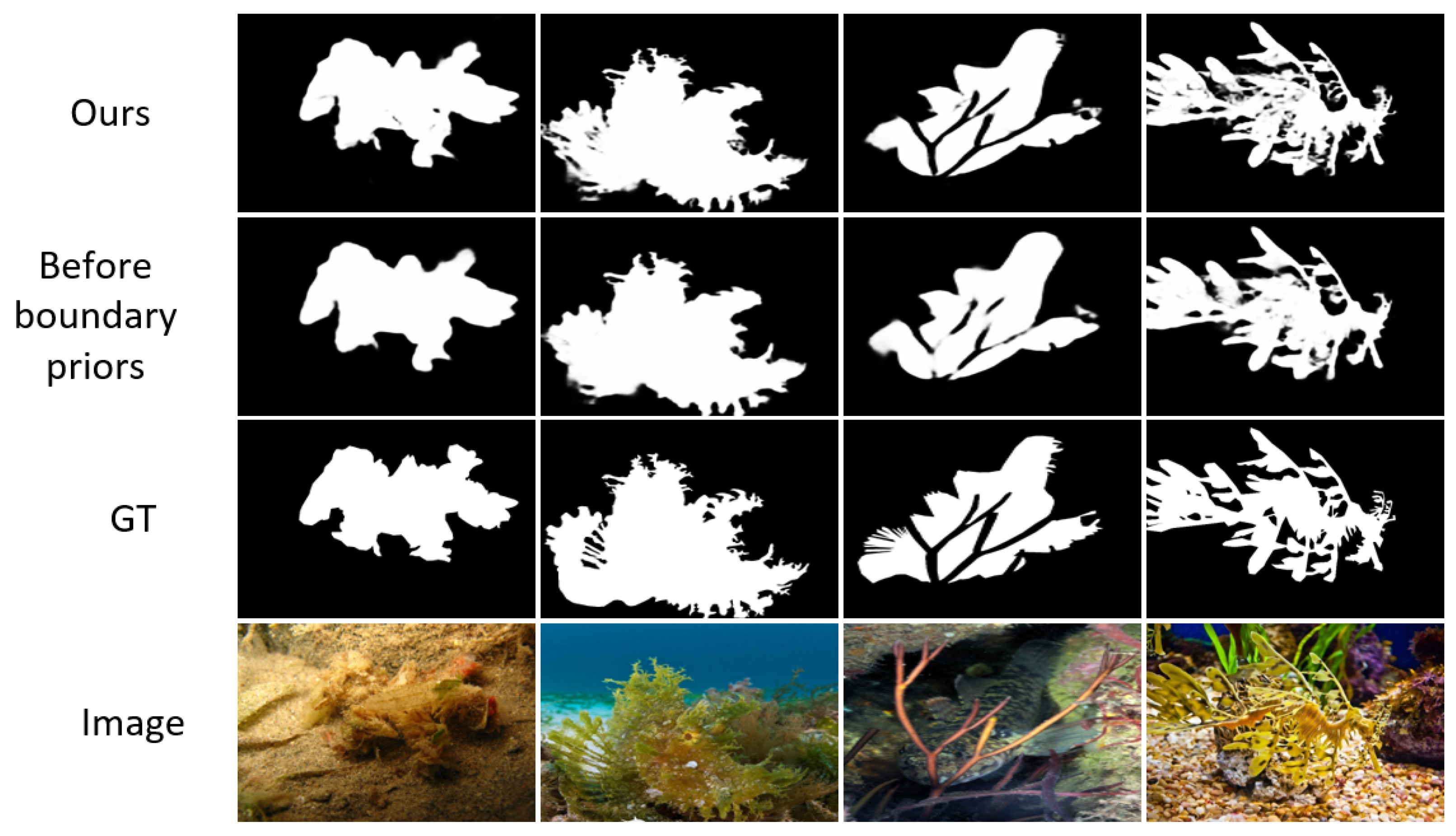
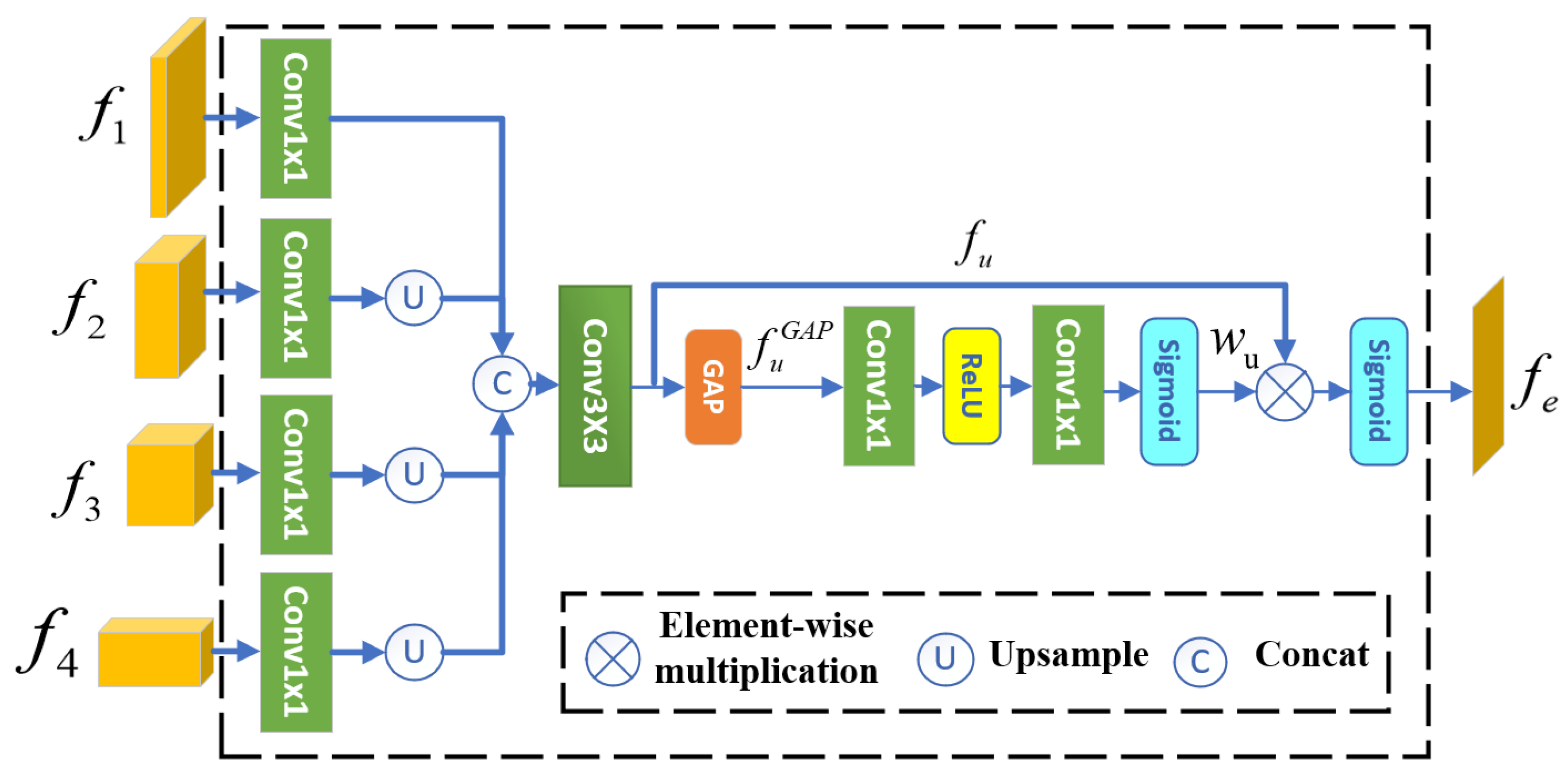
3.2. Boundary Detection Module
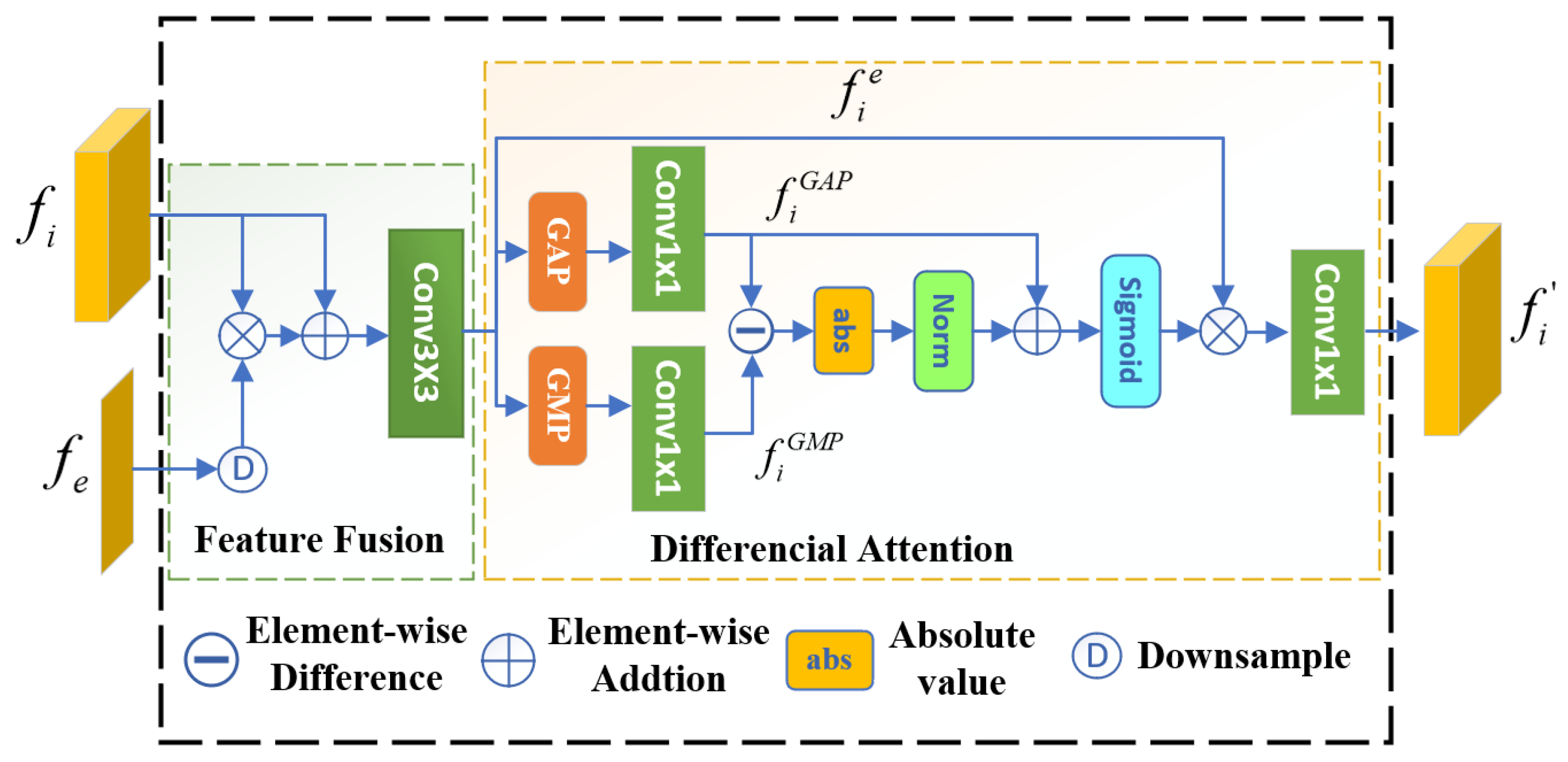
3.3. Differential Attention Module
3.3.1. Boundary Prior Fusion
3.3.2. Differential Attention Mechanism
3.4. Context Aggregation Module
3.5. Loss Function
4. Experiments
4.1. Implementation Details
4.2. Datasets
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
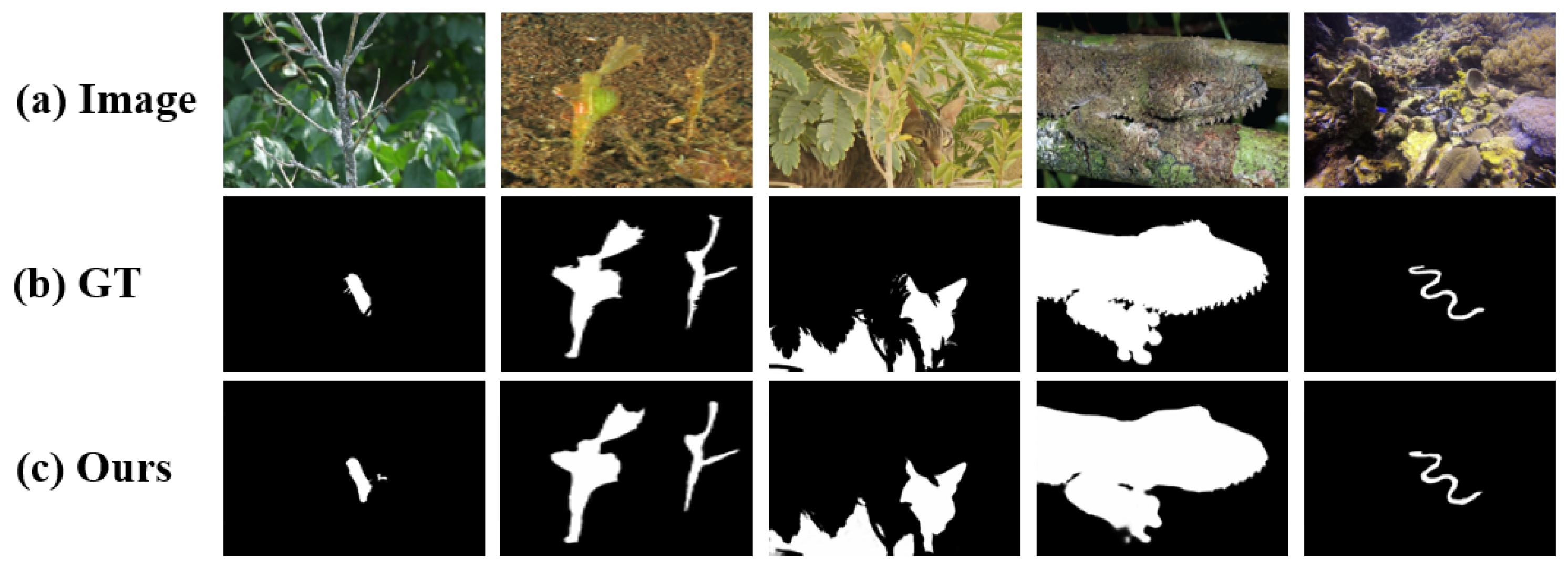
4.4. Comparison with SOTA Methods
4.4.1. Quantitative Comparison
4.4.2. Evaluation Curves of COD Methods
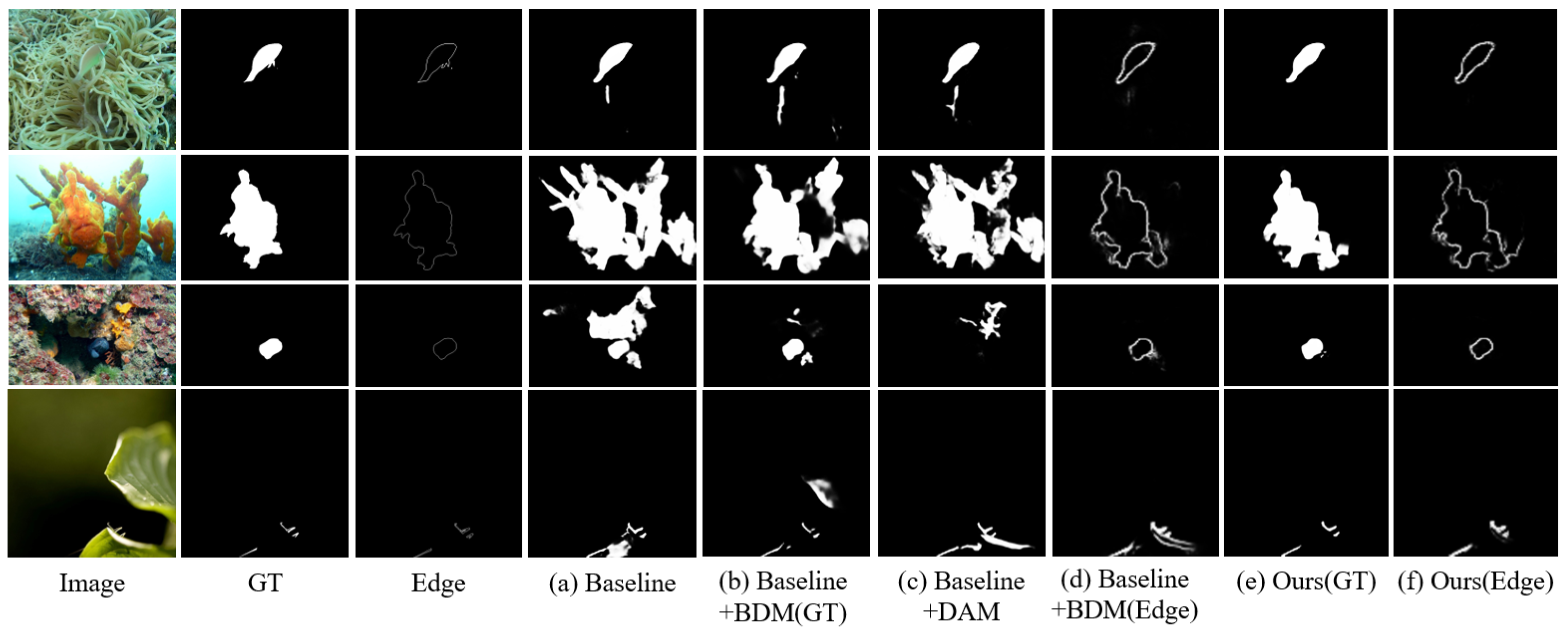
4.5. Ablation Analysis
4.5.1. Key Modules
4.5.2. Differential Attention Analysis
4.6. Analysis of the Effects of Different Hyparameters
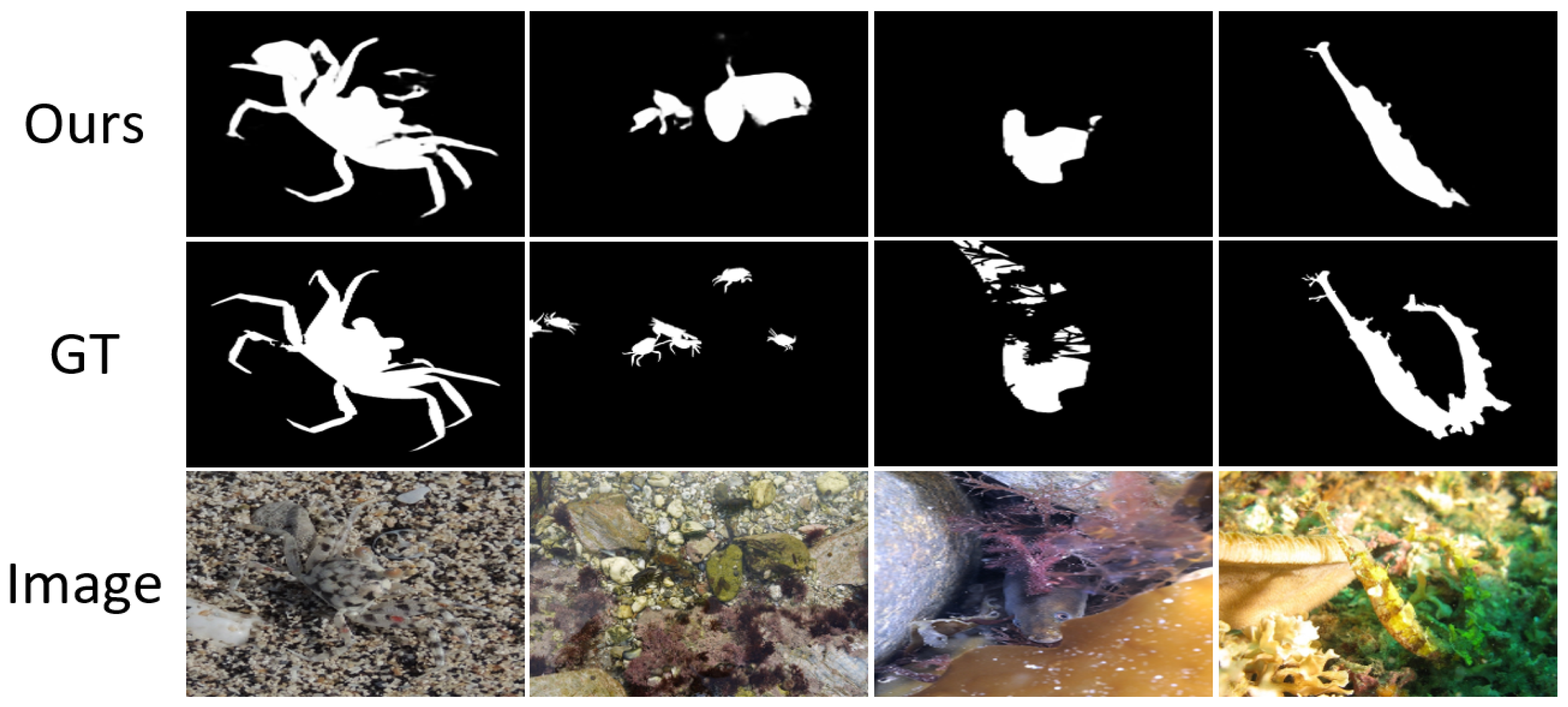
4.7. Failure Cases
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiao, F.; Hu, S.; Shen, Y.; Fang, C.; Huang, J.; He, C.; Tang, L.; Yang, Z.; Li, X. A survey of camouflaged object detection and beyond. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.14562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Ji, G.; Sun, G.; Cheng, M.; Shen, J.; Shao, L. Camouflaged object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 2777–2787. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Hu, X.; Zhu, L.; Xu, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, W.; Deng, Z.; Heng, P. Deep texture-aware features for camouflaged object detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 33, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.; Ji, G.; Wei, Z.; Yang, X.; Wei, X.; Fan, D. Camouflaged object segmentation with distraction mining. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 8772–8781. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xiang, T.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H. Zoom in and out: A mixed-scale triplet network for camouflaged object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 2160–2170. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, C.; Xiang, T. Boundary-guided camouflaged object detection. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.00794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Chen, T.; Hu, X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, S. Boundary-guided context-aware network for camouflaged object detection. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 15075–15093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhai, Q.; Li, X.; Huang, R.; Luo, A.; Cheng, H.; Fan, D. Uncertainty-guided transformer reasoning for camouflaged object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 4146–4155. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Shi, Y. EPANet: Edge-assisted Position Aware Attention Network for Camouflaged Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2023 8th International Conference on Intelligent Informatics and Biomedical Sciences (ICIIBMS), Okinawa, Japan, 23–25 November 2023; pp. 376–382. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Jiang, P.; Lin, L.; Deng, X. Edge attention learning for efficient camouflaged object detection. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2024—2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 14–19 April 2024; pp. 5230–5234. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Li, P.; Xie, H.; Yan, X.; Liang, D.; Chen, D.; Wei, M.; Qin, J. I can find you! boundary-guided separated attention network for camouflaged object detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Pomona, CA, USA, 24–28 October 2022; pp. 3608–3616. [Google Scholar]
- Bayraktar, I.; Bakirci, M. Attention-Augmented YOLO11 for High-Precision Aircraft Detection in Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery. In Proceedings of the 2025 27th International Conference on Digital Signal Processing and Its Applications (DSPA), Moscow, Russia, 26–28 March 2025; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, B.; Cong, K.; Zou, W. Dual Attention and Edge Refinement Network for Camouflaged Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2023 8th International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC), Dalian, China, 27–29 July 2023; pp. 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, J.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, S.; Qin, Y. Double-branch fusion network with a parallel attention selection mechanism for camouflaged object detection. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2023, 66, 162403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Yao, C.; Kong, Y.; Yang, Y. BANet: Camouflaged Object Detection Based on Boundary Guidance and Multiple Attention Mechanisms. In Proceedings of the 2023 9th Annual International Conference on Network and Information Systems for Computers (ICNISC), Wuhan, China, 27–29 October 2023; pp. 464–469. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.; Wu, J.; Wu, Y.; Mu, X.; Xu, J. FINet: Frequency injection network for lightweight camouflaged object detection. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2024, 31, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qi, L.; Song, Y.; Wen, Q. Depth awakens: A depth-perceptual attention fusion network for RGB-D camouflaged object detection. Image Vis. Comput. 2024, 143, 104924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Fang, X.; Zhu, T.; Qian, W. SDRNet: Camouflaged object detection with independent reconstruction of structure and detail. Knowl. Based Syst. 2024, 299, 112051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Bi, H.; Mo, D.; Sun, W.; Tong, J.; Jin, W.; Sun, Y. CCNet: Collaborative Camouflaged Object Detection via decoder-induced information interaction and supervision refinement network. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 133, 108328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, M.; Ma, J.; Wang, X. EPFDNet: Camouflaged object detection with edge perception in frequency domain. Image Vis. Comput. 2025, 154, 105358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11534–11542. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Wang, S.; Huang, Q. F3Net: Fusion, feedback and focus for salient object detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 12321–12328. [Google Scholar]
- Le, T.; Nguyen, T.; Nie, Z.; Tran, M.; Sugimoto, A. Anabranch network for camouflaged object segmentation. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2019, 184, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Zhang, J.; Dai, Y.; Li, A.; Liu, B.; Barnes, N.; Fan, D. Simultaneously localize, segment and rank the camouflaged objects. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 11591–11601. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.; Cheng, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Borji, A. Structure-measure: A new way to evaluate foreground maps. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4548–4557. [Google Scholar]
- Perazzi, F.; Krähenbühl, P.; Pritch, Y.; Hornung, A. Saliency filters: Contrast based filtering for salient region detection. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 733–740. [Google Scholar]
- Achanta, R.; Hemami, S.; Estrada, F.; Susstrunk, S. Frequency-tuned salient region detection. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 1597–1604. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.; Gong, C.; Cao, Y.; Ren, B.; Cheng, M.; Borji, A. Enhanced-alignment measure for binary foreground map evaluation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.10421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Ji, G.; Cheng, M.; Shao, L. Concealed object detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 6024–6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Q.; Yao, S.; Liu, Y.; Fan, X.; Liu, R.; Luo, Z. Segment, magnify and reiterate: Detecting camouflaged objects the hard way. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 4713–4722. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, C.; Bi, H. Tprnet: Camouflaged object detection via transformer-induced progressive refinement network. Vis. Comput. 2023, 39, 4593–4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, Y.; Wu, W. Boosting camouflaged object detection with dual-task interactive transformer. In Proceedings of the 2022 26th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Montreal, QC, Canada, 21–25 August 2022; pp. 140–146. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, J. Polarization-based camouflaged object detection. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2023, 174, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Cheng, J.; Chen, X. MSCAF-Net: A general framework for camouflaged object detection via learning multi-scale context-aware features. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 4934–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y.; Wei, X.; Tang, H.; Zhang, W. Go closer to see better: Camouflaged object detection via object area amplification and figure-ground conversion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 5444–5457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Li, X. Camouflaged object detection with feature decomposition and edge reconstruction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 22046–22055. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Dai, H.; Xiang, T.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Qin, J.; Xiong, H. Feature shrinkage pyramid for camouflaged object detection with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 5557–5566. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.; Wu, J.; Mu, X.; Hao, F.; Du, J.; Xu, J.; Li, P. Weighted dense semantic aggregation and explicit boundary modeling for camouflaged object detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 21108–21122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, C.; Fu, Q. Efficient camouflaged object detection via progressive refinement network. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2023, 31, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, K.; Ding, H.; Lin, X. Camouflaged object detection via dual-branch fusion and dual self-similarity constraints. Pattern Recognit. 2025, 157, 110895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Method | Year | COD10K | CAMO | NC4K | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE ↓ | MAE ↓ | MAE ↓ | |||||||||||
| PFNet [4] | 2021 | 0.800 | 0.040 | 0.660 | 0.877 | 0.782 | 0.085 | 0.695 | 0.855 | 0.829 | 0.053 | 0.745 | 0.887 |
| SINetV2 [29] | 2022 | 0.815 | 0.037 | 0.680 | 0.887 | 0.820 | 0.070 | 0.743 | 0.882 | 0.847 | 0.048 | 0.770 | 0.903 |
| SegMar [30] | 2022 | 0.833 | 0.034 | 0.724 | 0.899 | 0.815 | 0.071 | 0.753 | 0.874 | 0.841 | 0.046 | 0.781 | 0.896 |
| ZoomNet [5] | 2022 | 0.838 | 0.029 | 0.729 | 0.888 | 0.820 | 0.066 | 0.752 | 0.877 | 0.853 | 0.043 | 0.784 | 0.896 |
| DTINet [32] | 2022 | 0.824 | 0.034 | 0.695 | 0.896 | 0.856 | 0.050 | 0.796 | 0.916 | 0.863 | 0.041 | 0.792 | 0.917 |
| PolarNet [33] | 2023 | 0.820 | 0.034 | 0.735 | 0.896 | 0.816 | 0.073 | 0.785 | 0.874 | 0.849 | 0.046 | 0.810 | 0.905 |
| FEDER [36] | 2023 | 0.822 | 0.032 | 0.716 | 0.900 | 0.802 | 0.071 | 0.738 | 0.867 | 0.847 | 0.044 | 0.789 | 0.907 |
| BCNet [7] | 2023 | 0.827 | 0.033 | 0.704 | 0.894 | 0.829 | 0.068 | 0.761 | 0.889 | 0.857 | 0.043 | 0.788 | 0.910 |
| FSPNet [37] | 2023 | 0.851 | 0.026 | 0.735 | 0.895 | 0.856 | 0.071 | 0.799 | 0.899 | 0.879 | 0.035 | 0.816 | 0.915 |
| MSCAF-Net [34] | 2023 | 0.865 | 0.024 | 0.775 | 0.927 | 0.873 | 0.046 | 0.828 | 0.929 | 0.887 | 0.032 | 0.838 | 0.934 |
| SARNet [35] | 2023 | 0.864 | 0.024 | 0.777 | 0.931 | 0.868 | 0.047 | 0.828 | 0.927 | 0.886 | 0.032 | 0.842 | 0.937 |
| EANet [10] | 2024 | 0.825 | 0.029 | 0.709 | 0.910 | 0.841 | 0.051 | 0.793 | 0.919 | 0.825 | 0.039 | 0.798 | 0.922 |
| SAE-Net [38] | 2024 | 0.837 | 0.064 | 0.770 | 0.891 | 0.837 | 0.064 | 0.770 | 0.891 | 0.862 | 0.042 | 0.796 | 0.912 |
| PRNet [39] | 2024 | 0.821 | 0.035 | 0.742 | 0.895 | 0.816 | 0.072 | 0.791 | 0.875 | 0.844 | 0.047 | 0.813 | 0.903 |
| DSNet [40] | 2025 | 0.809 | 0.038 | 0.657 | 0.878 | 0.817 | 0.073 | 0.726 | 0.870 | 0.843 | 0.050 | 0.753 | 0.894 |
| BDA-Net (Ours) | - | 0.877 | 0.021 | 0.805 | 0.938 | 0.879 | 0.043 | 0.847 | 0.931 | 0.891 | 0.030 | 0.853 | 0.939 |
| Model | COD10K | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE ↓ | ||||
| Baseline | 0.869 | 0.023 | 0.784 | 0.928 |
| +BDM | 0.874 | 0.023 | 0.796 | 0.928 |
| +DAM | 0.874 | 0.022 | 0.796 | 0.926 |
| +DAM +BDM (Ours) | 0.877 | 0.021 | 0.805 | 0.938 |
| Model | COD10K | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE ↓ | ||||
| N1 | 0.874 | 0.022 | 0.802 | 0.936 |
| N2 | 0.873 | 0.022 | 0.802 | 0.934 |
| N3 | 0.876 | 0.021 | 0.803 | 0.938 |
| N4 (Ours) | 0.877 | 0.021 | 0.805 | 0.938 |
| Attention | Combinations | COD10K | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ⊖ | ⊕ | ||||||
| GMP | GAP | GAP | MAE ↓ | ||||
| A1 | ✓ | 0.873 | 0.022 | 0.794 | 0.933 | ||
| A2 | ✓ | ✓ | 0.876 | 0.022 | 0.799 | 0.936 | |
| A3 | ✓ | 0.875 | 0.021 | 0.800 | 0.938 | ||
| A4 | ✓ | ✓ | 0.876 | 0.021 | 0.799 | 0.937 | |
| A5 | ✓ | ✓ | 0.874 | 0.022 | 0.796 | 0.936 | |
| A6 (Ours) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 0.877 | 0.021 | 0.805 | 0.938 |
| Model | COD10K | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE ↓ | ||||
| 0.874 | 0.023 | 0.799 | 0.933 | |
| 0.875 | 0.023 | 0.801 | 0.936 | |
| (Ours) | 0.877 | 0.021 | 0.805 | 0.938 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Xu, B.; Jiang, S. Boundary-Guided Differential Attention: Enhancing Camouflaged Object Detection Accuracy. J. Imaging 2025, 11, 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11110412
Zhang H, Xu B, Jiang S. Boundary-Guided Differential Attention: Enhancing Camouflaged Object Detection Accuracy. Journal of Imaging. 2025; 11(11):412. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11110412
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hongliang, Bolin Xu, and Sanxin Jiang. 2025. "Boundary-Guided Differential Attention: Enhancing Camouflaged Object Detection Accuracy" Journal of Imaging 11, no. 11: 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11110412
APA StyleZhang, H., Xu, B., & Jiang, S. (2025). Boundary-Guided Differential Attention: Enhancing Camouflaged Object Detection Accuracy. Journal of Imaging, 11(11), 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11110412






