CT Imaging Biomarkers in Rhinogenic Contact Point Headache: Quantitative Phenotyping and Diagnostic Correlations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethical Considerations
2.2. Study Population
- -
- Less than one year of consecutive clinical and diagnostic follow-up.
- -
- Presence of comorbid conditions including allergies, other sinonasal disorders, migraines, cluster headaches, ophthalmologic or vascular disorders, hypertension, pregnancy, or temporomandibular joint disorders.
- -
- A history of previous sinonasal surgeries.
2.3. Clinical Assessment
2.4. Imaging Protocol and Quantitative Analysis
2.4.1. Image Acquisition Protocol
2.4.2. Quantitative Parameters
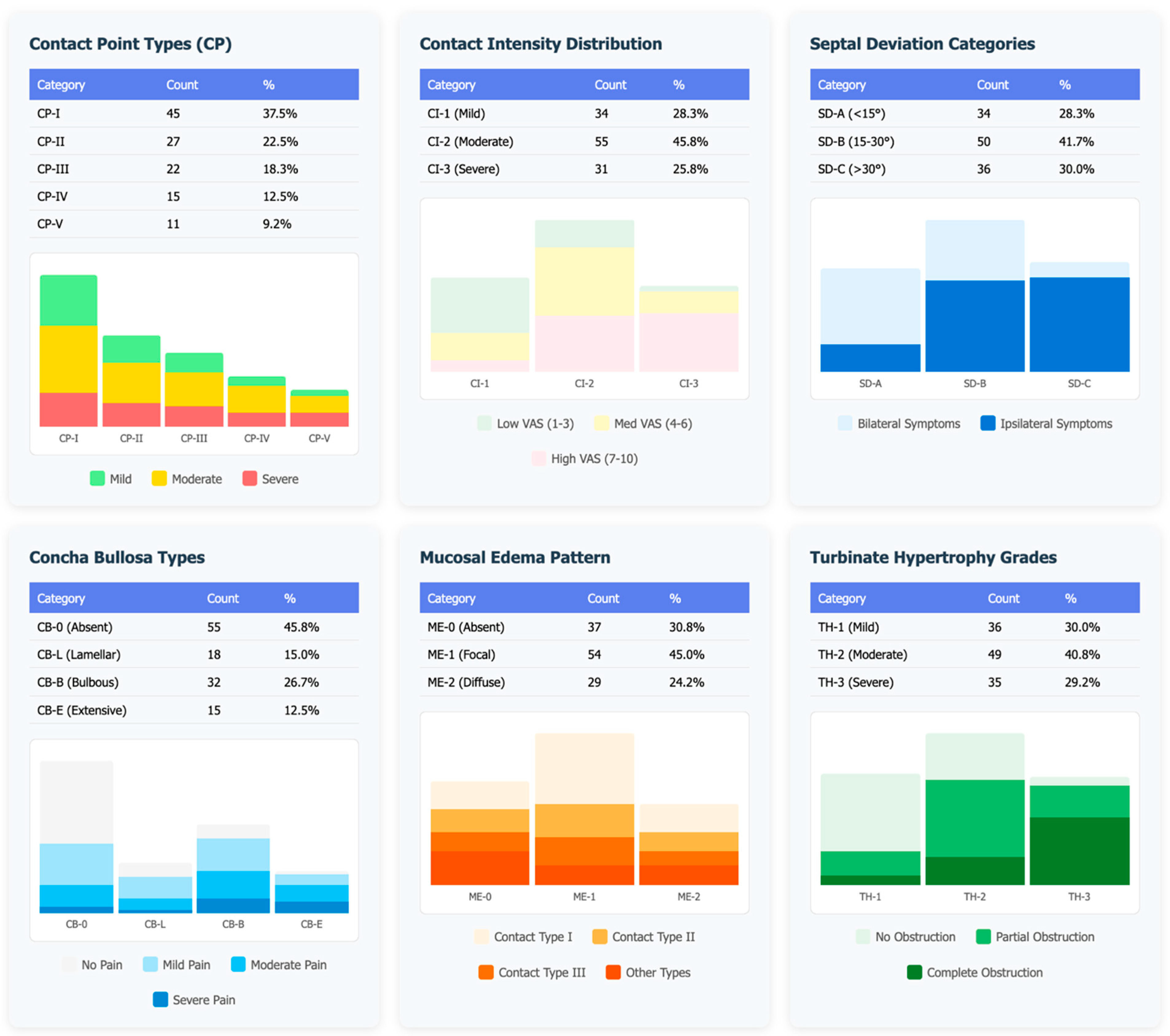
- Contact point type: Classified as CP-I (septum-middle turbinate), CP-II (septum-inferior turbinate), CP-III (septum-lateral wall), and CP-IV (other variants).
- Contact intensity: Categorized as mild, moderate, or severe based on the degree of mucosal compression.
- Septal deviation: Measured at the point of maximum deviation and classified as SD-A (<15°) or SD-B/SD-C (>15°).
- CB morphology: Categorized as absent, bulbous, lamellar, or extensive types.
- Mucosal edema: Assessed as ME-1 (focal edema) or ME-2 (diffuse edema) at CP.
- TH: Classified as absent, mild, moderate, or severe.
- Associated anatomical variants: Including paradoxical middle turbinate, Haller cells, pneumatized uncinate process, etc.
- -
- Surface area of mucosal contact (mm2), calculated using multiplanar reconstruction.
- -
- Turbinate pneumatization volume (mm3) when applicable.
- -
- Laterality index, defined as unilateral vs. bilateral involvement.
2.4.3. Inter-Observer Agreement
2.5. Treatment and Follow-Up
2.6. Statistical Analysis
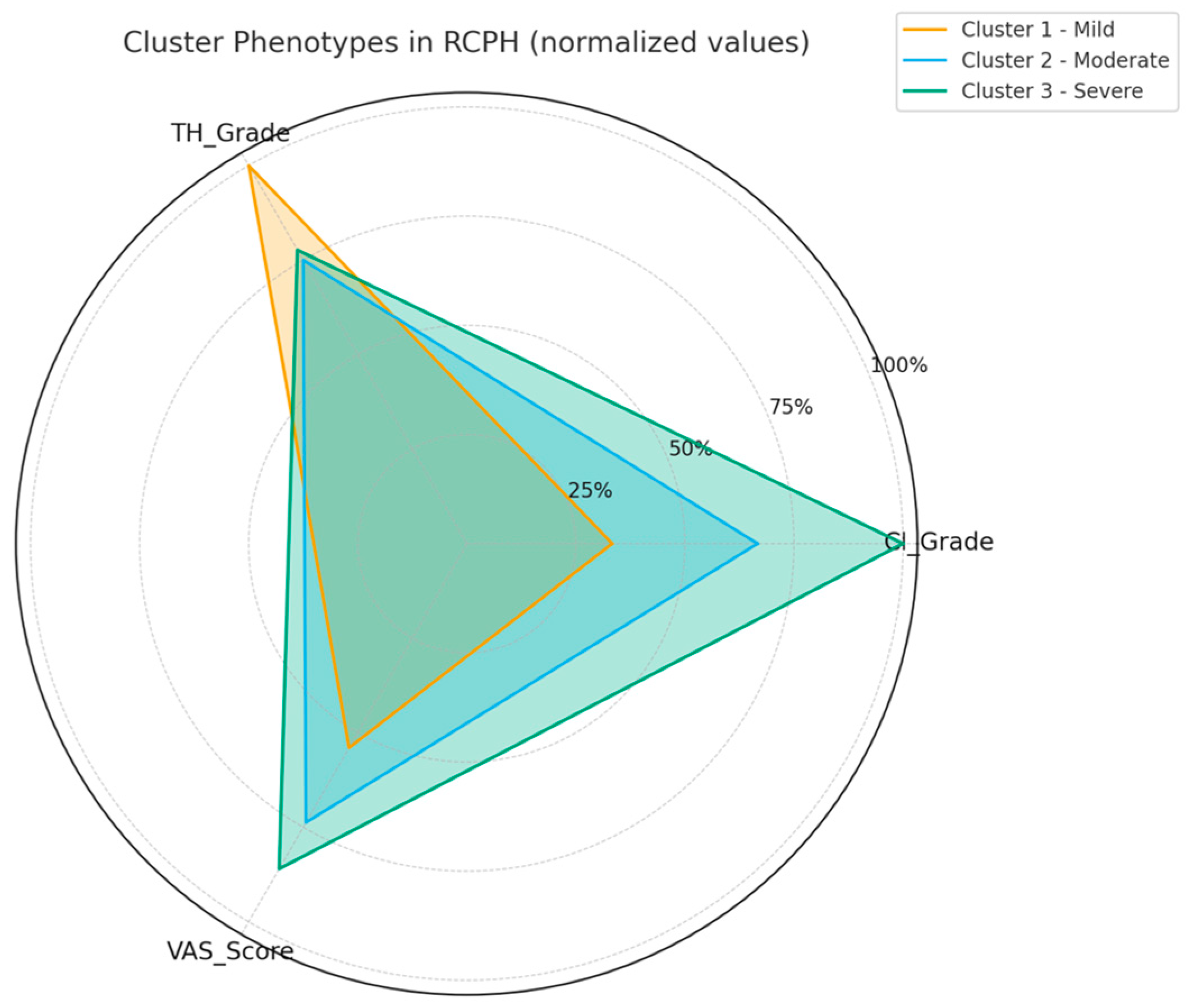
- Cluster 1 (mild): Patients with light mucosal contact and minimal structural deviation, reporting the lowest pain scores.
- Cluster 2 (moderate): Patients with moderate CI and ME-1, showing intermediate pain levels.
- Cluster 3 (severe): Patients with strong mucosal compression and ME-2, experiencing the highest pain severity.
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics and Clinical Characteristics
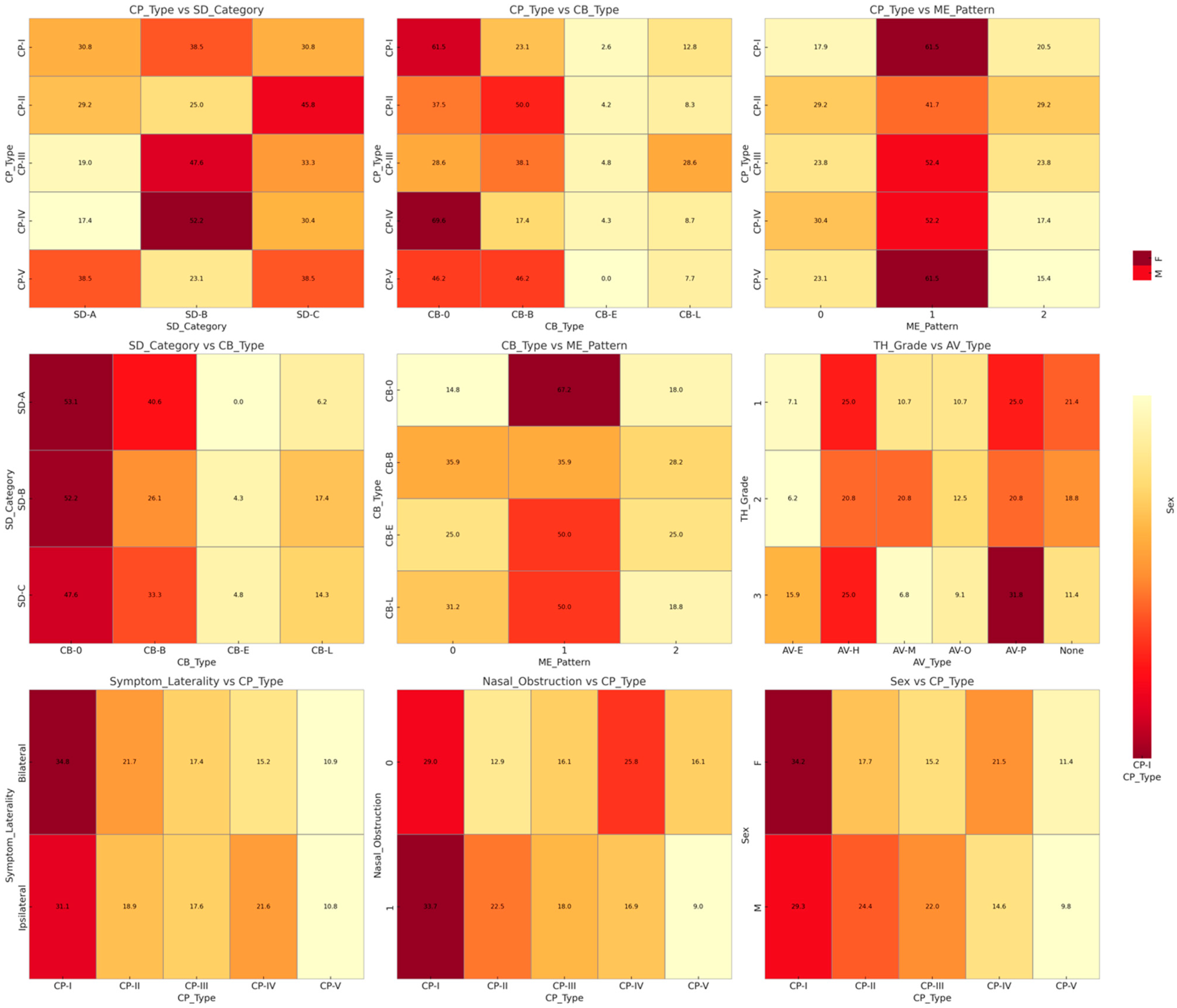
3.2. Radiological Phenotype Distribution
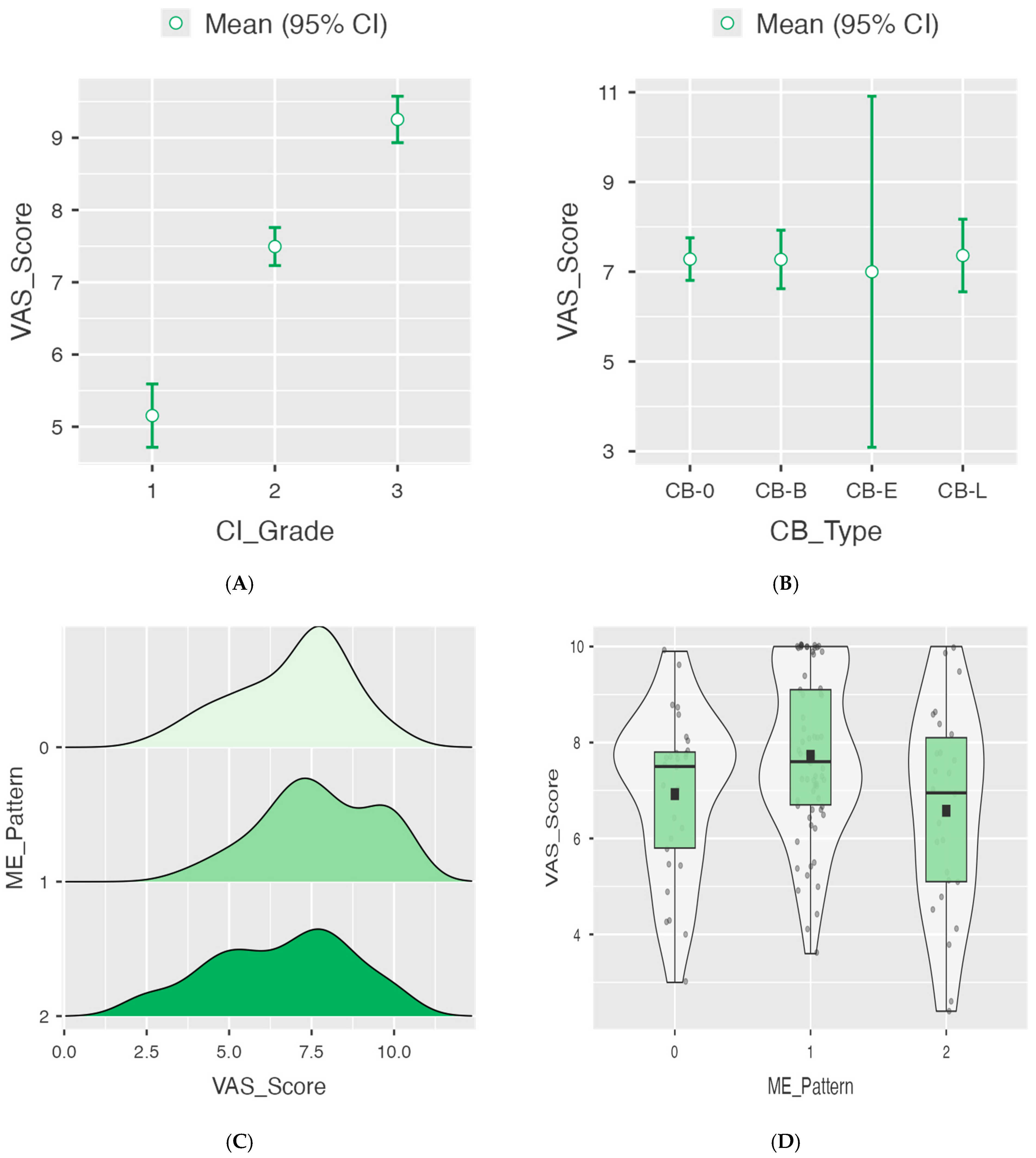
3.3. Correlation Between Imaging Biomarkers and Pain Severity
3.4. Multivariate Predictors of Clinical Severity
3.5. Cluster-Based Patient Stratification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RCPH | Rhinogenic contact point headache |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| VAS | Visual Analog Scale |
| CP | Contact point |
| CI | Contact intensity |
| CB | Concha bullosa |
| ME | Mucosal edema |
| TH | Turbinate hypertrophy |
| AV | Accessory variant |
| ICHD-3 | International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition |
| STROBE | Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology |
| ICC | Intraclass correlation coefficient |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| ISI | Imaging Severity Index |
| MIDAS | Migraine Disability Assessment Scale |
References
- La Mantia, I.; Grillo, C.; Andaloro, C. Rhinogenic Contact Point Headache: Surgical Treatment Versus Medical Treatment. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2018, 29, e228–e230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavalle, S.; Pace, A.; Magliulo, G.; Lentini, M.; Lechien, J.R.; Calvo-Henriquez, C.; Parisi, F.M.; Iannella, G.; Maniaci, A.; Messineo, D. Impact of Nasal Anatomical Variation Subtype on Surgical Outcomes for Rhinogenic Contact Point Headache. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swain, S.K.; Dubey, D. Anatomical Variations of Nose Causing Rhinogenic Contact Point Headache-A Study at a Tertiary Care Hospital. Pol. Ann. Med. 2018, 25, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.K.; Mohanty, S.; Sahu, M.C. Rhinogenic Contact Point Headache in Pediatric Age Group. Int. J. Contemp. Pediatr. 2022, 9, 1234–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernichi, J.V. Rhinogenic and Sinus Headache-Literature Review. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2015, 35, 345–352. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, Z.M.; Kennedy, D.W.; Setzen, M.; Poetker, D.M.; DelGaudio, J.M. “Sinus Headache”: Rhinogenic Headache or Migraine? An Evidence-Based Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2013, 3, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniaci, A.; Merlino, F.; Cocuzza, S.; Iannella, G.; Vicini, C.; Cammaroto, G.; Lechien, J.R.; Calvo-Henriquez, C.; La Mantia, I. Endoscopic Surgical Treatment for Rhinogenic Contact Point Headache: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 278, 1743–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; STROBE Initiative. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for Reporting Observational Studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welge-Luessen, A.; Hauser, R.; Schmid, N.; Kappos, L.; Probst, R. Endonasal Surgery for Contact Point Headaches: A 10-Year Longitudinal Study. Laryngoscope 2003, 113, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clerico, D.M. Pneumatized Superior Turbinate as a Cause of Referred Migraine Headache. Laryngoscope 1996, 106, 874–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Periƒá, A.; Baletiƒá, N.; Sotiroviƒá, J. Surgical Treatment of Rhinogenic Contact Point Headache: An Experience from a Tertiary Care Hospital. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2016, 36, 386–392. [Google Scholar]
- Behrbohm, H.; Tardy, M.E. Contact Point Headaches: Clinical Manifestations and Therapeutic Results. HNO 1991, 39, 183–187. [Google Scholar]
- Bektas, D.; Alioglu, Z.; Akyol, N.; Ural, A.; Bahadir, O.; Caylan, R. Surgical Outcomes for Rhinogenic Contact Point Headaches. Med. Princ. Pract. 2011, 20, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniaci, A.; Lechien, J.R.; Calvo-Henriquez, C.; Iannella, G.; Leigh, S.; Ingrassia, A.; Merlino, F.; Bannò, V.; Cocuzza, S.; La Mantia, I. Long-Term Stability of Outcomes of Endoscopic Surgery for Rhinogenic Contact Point Headache (Sluder’s Neuralgia). Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2022, 43, 103368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eross, E.J.; Dodick, D.W.; Eross, M.D. The Sinus, Allergy and Migraine Study (SAMS). Headache 2007, 47, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farmer, R.L.; Garg, R.K.; Afifi, A.M. Can Functional Nasal Surgery Treat Chronic Headaches? A Systematic Review. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 142, 1583–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Category | N (%) | Mean VAS ± SD | Range | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | – | – | 42.3 ± 8.2 | 29–56 | – |
| Sex | Female | 79 (65.8) | – | – | – |
| Male | 41 (34.2) | – | – | – | |
| Contact intensity (CI) | |||||
| Grade 1 (mild) | 5.15 ± 1.28 | 5.2 | 2.4–7.3 | <0.001 * | |
| Grade 2 (moderate) | 7.49 ± 0.95 | 7.6 | 5.1–9.9 | <0.001 * | |
| Grade 3 (severe) | 9.25 ± 0.89 | 9.9 | 7.4–10.0 | Ref | |
| Concha bullosa (CB) | |||||
| Absent (CB-0) | 7.28 ± 1.85 | 7.3 | 2.4–10.0 | 0.993 | |
| Bulbous (CB-B) | 7.27 ± 2.01 | 7.5 | 2.6–10.0 | ||
| Extensive (CB-E) | 7.00 ± 2.46 | 6.8 | 4.5–9.9 | ||
| Lamellar (CB-L) | 7.36 ± 1.52 | 7.6 | 4.3–10.0 | ||
| Mucosal edema (ME) | |||||
| ME-0 (absent) | 6.92 ± 1.72 | 7.5 | 3.0–9.9 | 0.566 | |
| ME-1 (focal) | 7.72 ± 1.71 | 7.6 | 3.6–10.0 | Ref | |
| ME-2 (diffuse) | 6.58 ± 2.12 | 6.95 | –2.4–10.0 | ||
| Accessory variants (AVs) | – | – | – | ||
| Agger nasi (AV-E) | 12 (10.0) | ||||
| Haller cells (AV-H) | 28 (23.3) | – | – | – | |
| Onodi cells (AV-O) | 13 (10.8) | – | – | – | |
| Paradoxical MT (AV-P) | 31 (25.8) | – | – | – | |
| Miscellaneous (AV-M) | 16 (13.3) | – | – | – | |
| None | 20 (16.7) | – | – | – |
| ANOVA results for VAS according to CI Grade. | ||
| Comparison | Mean difference | p-value |
| Mild vs. moderate | −2.34 | <0.001 |
| Mild vs. severe | −4.1 | <0.001 |
| Moderate vs. severe | −1.76 | <0.001 |
| ANOVA for VAS according to CB type. | ||
| Comparison | Mean difference | p-value |
| CB-0 vs. CB-B | 0.00761 | - |
| CB-0 vs. CB-E | 0.282 | 0.991 |
| CB-0 vs. CB-L | −0.0805 | 0.999 |
| CB-B vs. CB-E | 0.274 | 0.993 |
| CB-B vs. CB-L | −0.0881 | 0.999 |
| CB-E vs. CB-L | −0.3625 | 0.986 |
| Predictor | Estimate | SE | 95% CI Lower | 95% CI Upper | t | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 7.422 | 0.299 | 6.83 | 8.014 | 24.825 | <0.001 |
| ME pattern | −0.145 | 0.252 | −0.644 | 0.354 | −0.575 | 0.566 |
| Variable | CI_Grade | SD_Angle | ME_Pattern | TH_Grade | VAS_Score | Imaging_Severity_Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CI_Grade | — | |||||
| SD_Angle | −0.077 (p = 0.406) | — | ||||
| ME_Pattern | −0.052 (p = 0.572) | 0.121 (p = 0.189) | — | |||
| TH_Grade | 0.121 (p = 0.188) | −0.078 (p = 0.396) | −0.154 (p = 0.093) | — | ||
| VAS_Score | 0.844 (p < 0.001) | −0.133 (p = 0.147) | −0.036 (p = 0.697) | 0.040 (p = 0.664) | — | |
| Imaging_Severity_Index | 0.450 (p < 0.001) | 0.630 (p < 0.001) | 0.567 (p < 0.001) | −0.081 (p = 0.380) | 0.352 (p < 0.001) | — |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lavalle, S.; Ferlito, S.; Lechien, J.R.; Lentini, M.; Romeo, P.; Saibene, A.M.; Fadda, G.L.; Maniaci, A. CT Imaging Biomarkers in Rhinogenic Contact Point Headache: Quantitative Phenotyping and Diagnostic Correlations. J. Imaging 2025, 11, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11100362
Lavalle S, Ferlito S, Lechien JR, Lentini M, Romeo P, Saibene AM, Fadda GL, Maniaci A. CT Imaging Biomarkers in Rhinogenic Contact Point Headache: Quantitative Phenotyping and Diagnostic Correlations. Journal of Imaging. 2025; 11(10):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11100362
Chicago/Turabian StyleLavalle, Salvatore, Salvatore Ferlito, Jerome Rene Lechien, Mario Lentini, Placido Romeo, Alberto Maria Saibene, Gian Luca Fadda, and Antonino Maniaci. 2025. "CT Imaging Biomarkers in Rhinogenic Contact Point Headache: Quantitative Phenotyping and Diagnostic Correlations" Journal of Imaging 11, no. 10: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11100362
APA StyleLavalle, S., Ferlito, S., Lechien, J. R., Lentini, M., Romeo, P., Saibene, A. M., Fadda, G. L., & Maniaci, A. (2025). CT Imaging Biomarkers in Rhinogenic Contact Point Headache: Quantitative Phenotyping and Diagnostic Correlations. Journal of Imaging, 11(10), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11100362











