Intelligent Segmentation of Urban Building Roofs and Solar Energy Potential Estimation for Photovoltaic Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
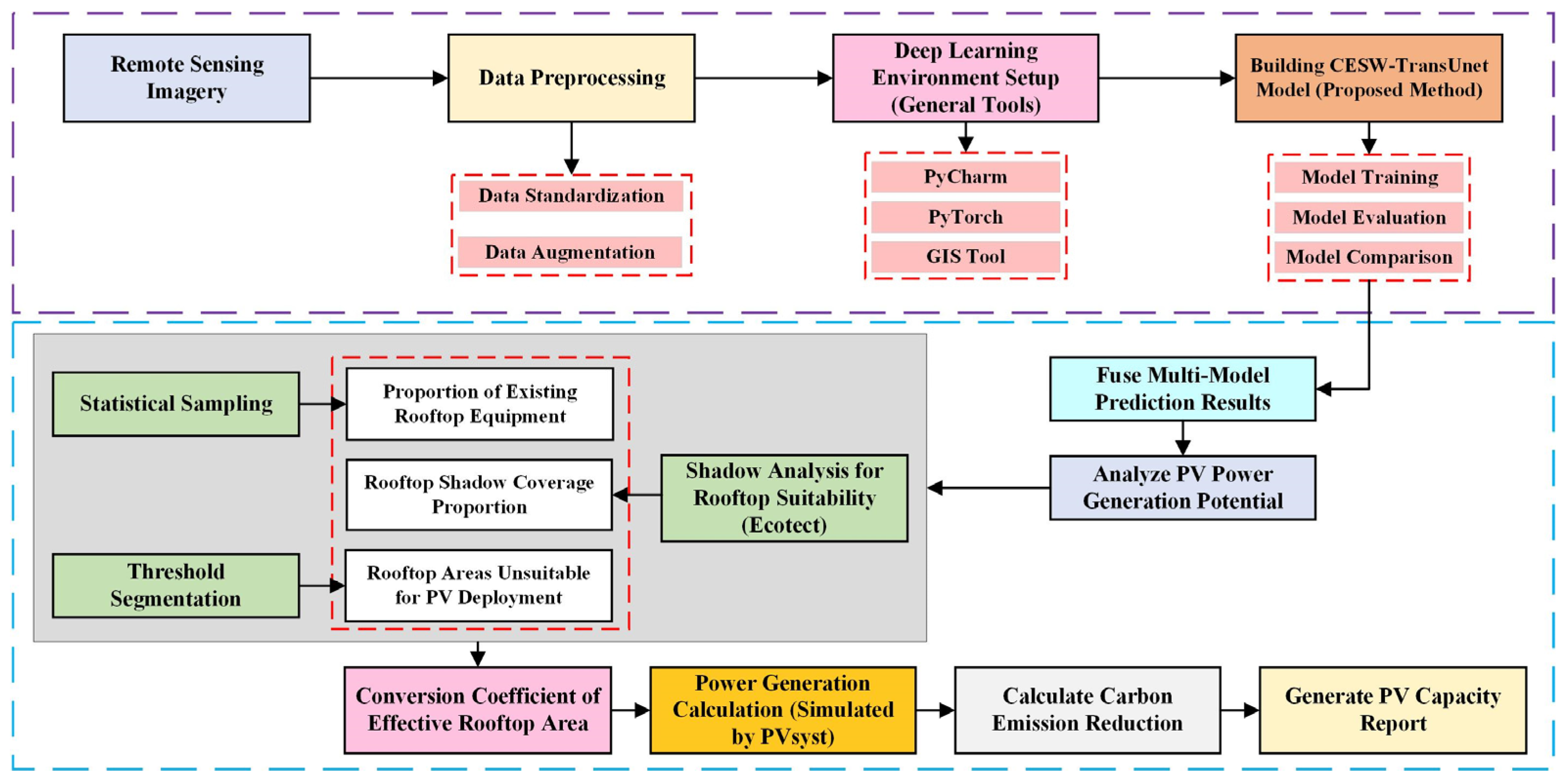
2.1. Technical Workflow for Rooftop PV Resource Potential Assessment
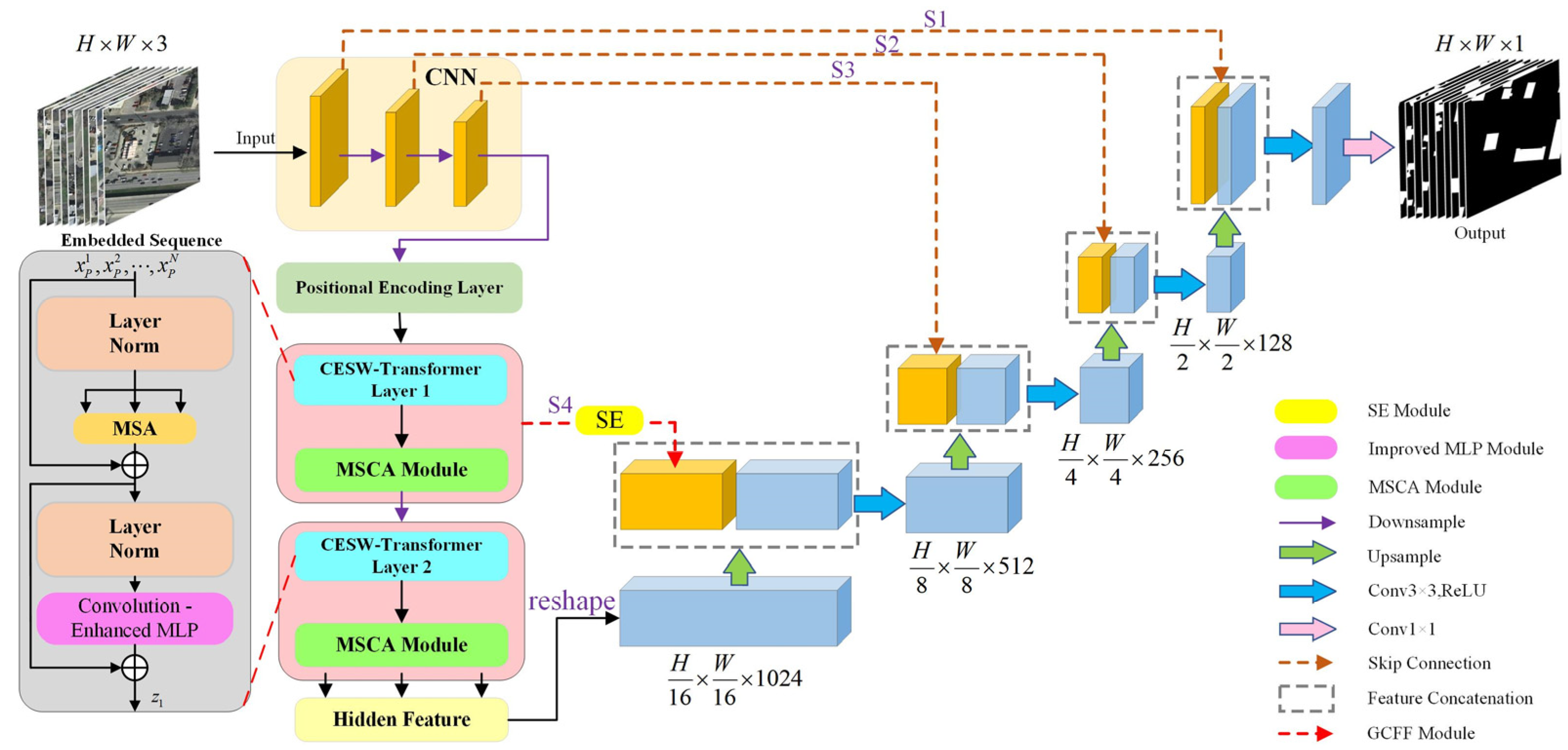
2.2. Construction of the Semantic Segmentation Network Model
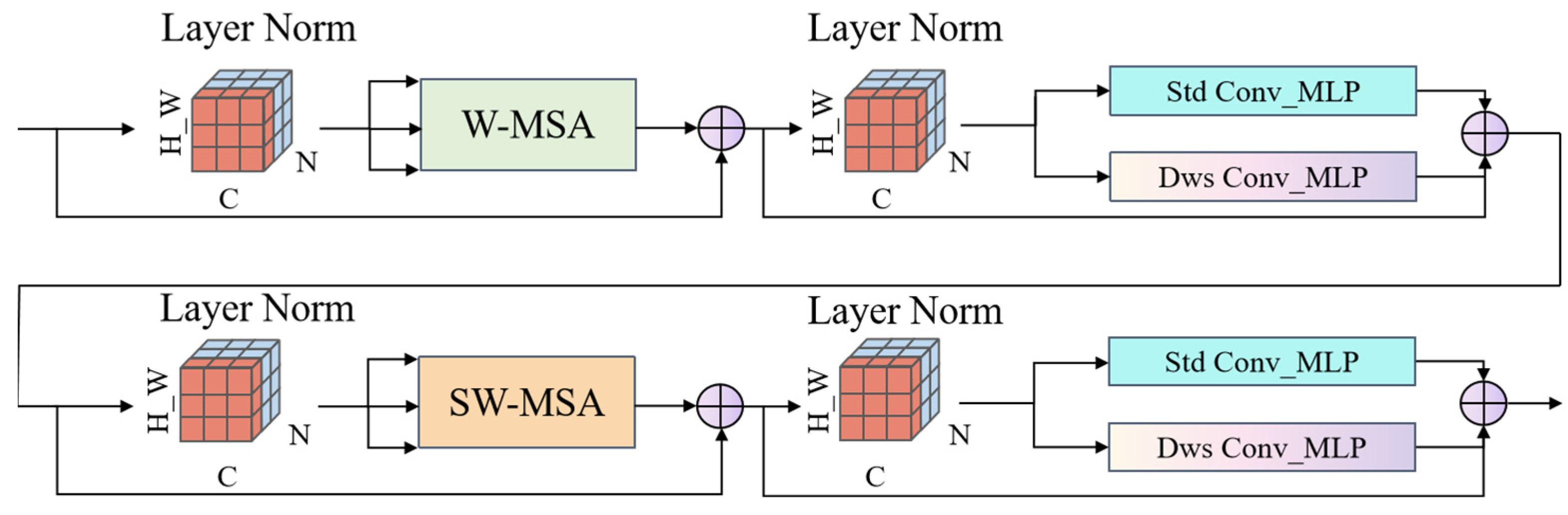
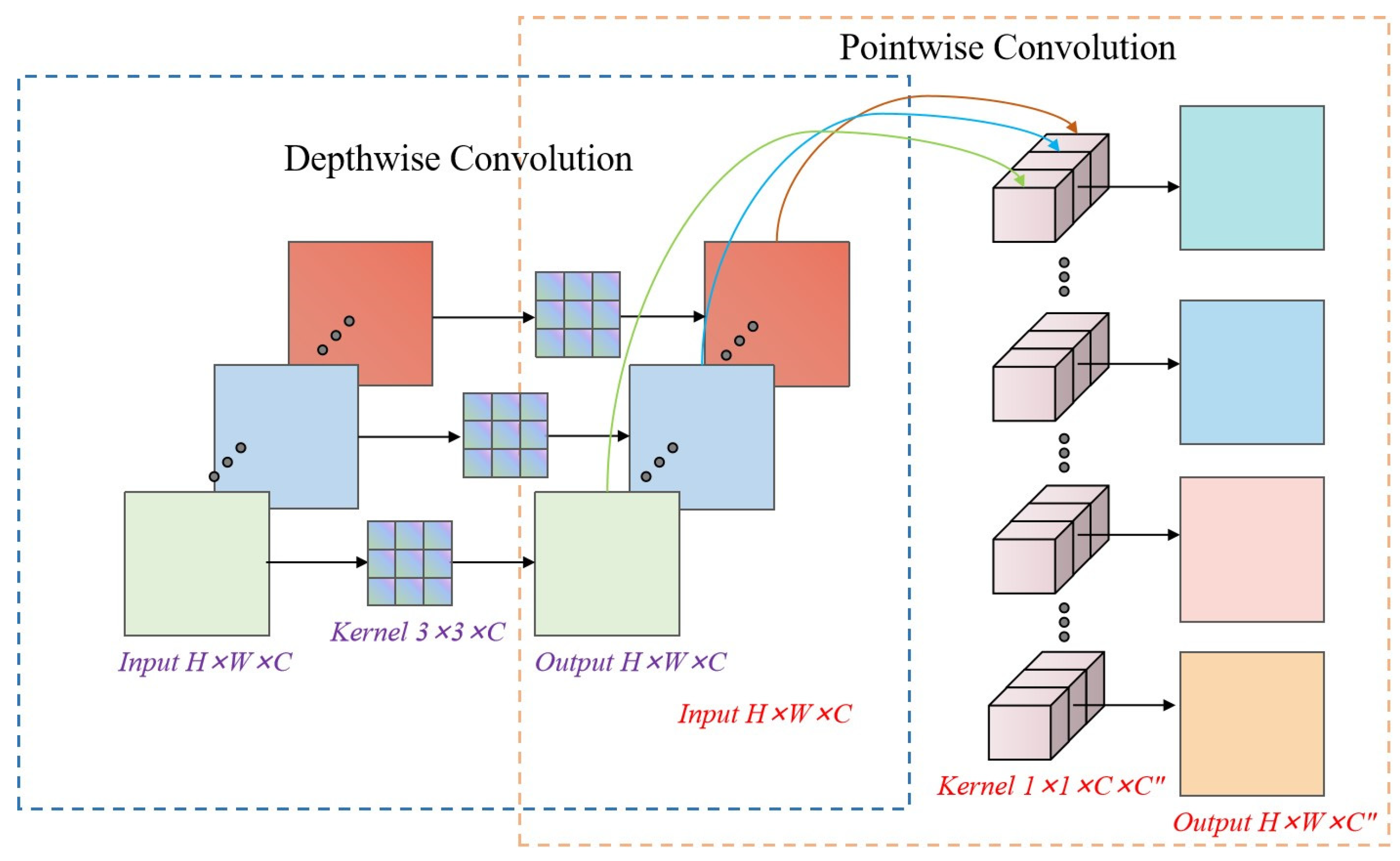
2.2.1. Convolution-Enhanced Swin Transformer Module
2.2.2. Multi-Scale Channel Attention Module (MSCA)
2.2.3. Global-Guided Cross-Level Feature Fusion (GCFF)
2.3. Evaluation Metrics
2.4. Rooftop Photovoltaic Resource Potential Assessment: Theoretical Framework
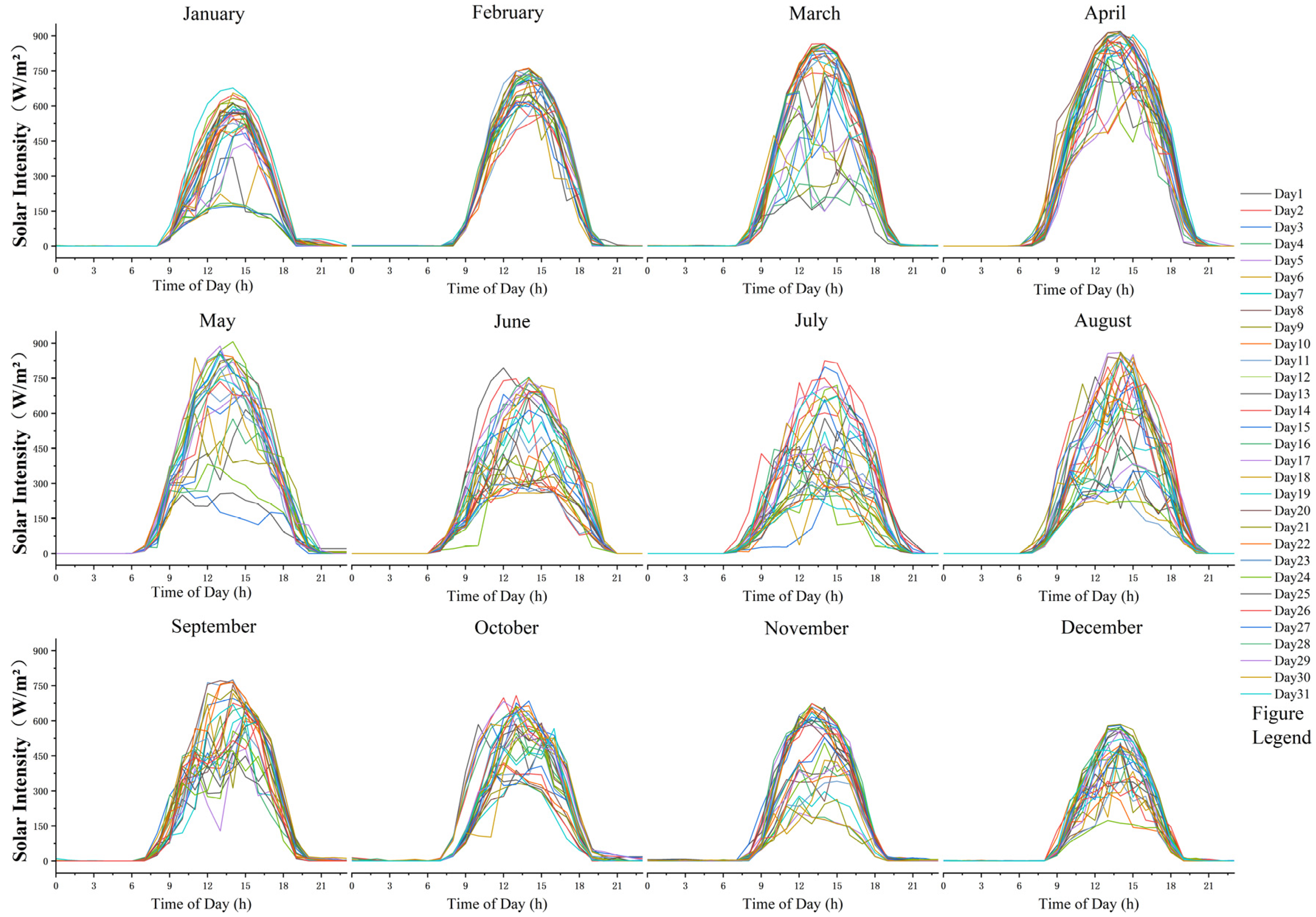
2.4.1. Fundamental Theory of Solar Radiation and Model Development
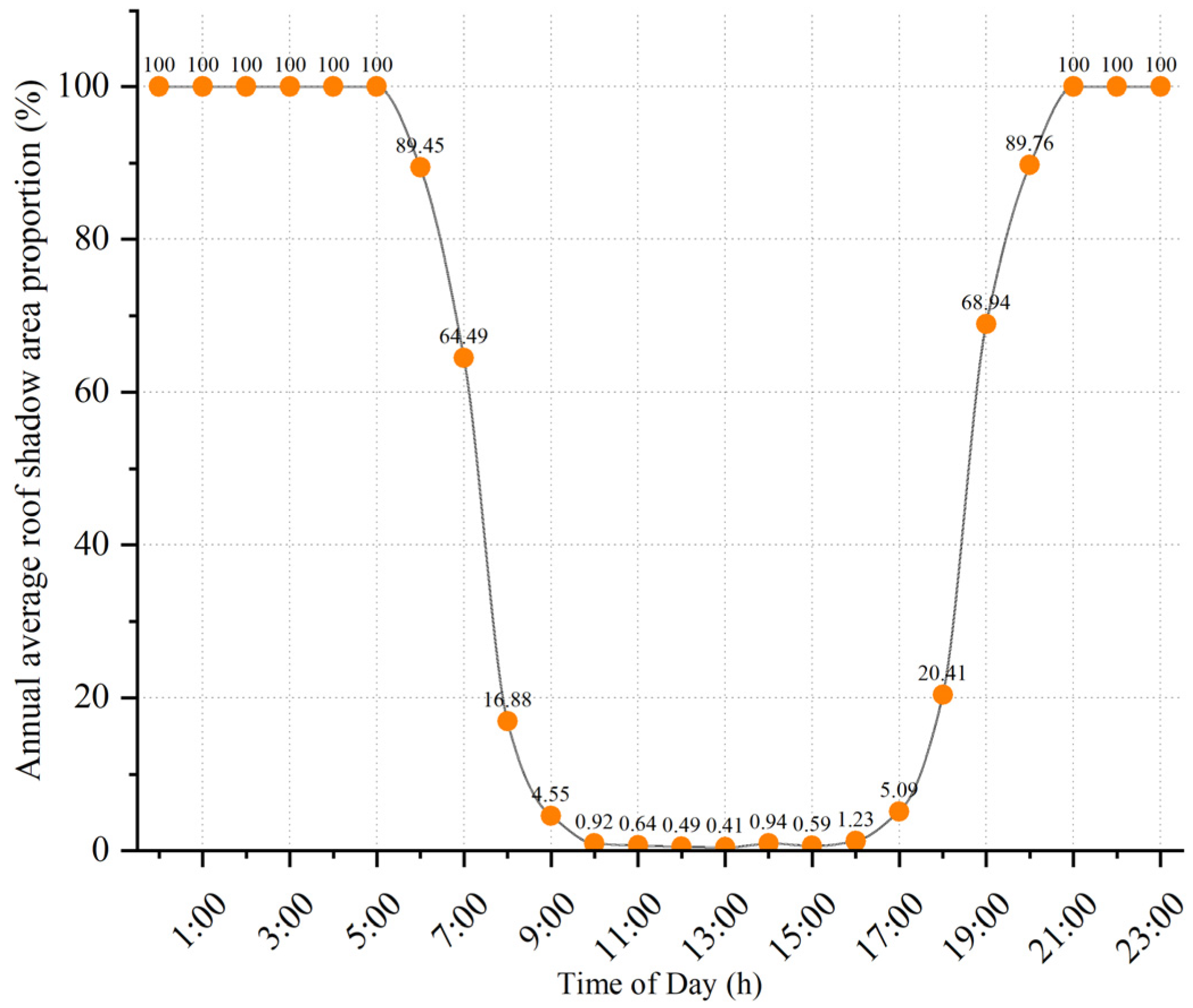
2.4.2. Calculation of Effective Rooftop Area
- (1)
- Basic Area Calculation
- (2)
- Correction of Effective Rooftop Area
2.4.3. Calculation Method for Rooftop Photovoltaic Power Generation
2.5. Post-Processing in Semantic Segmentation Tasks
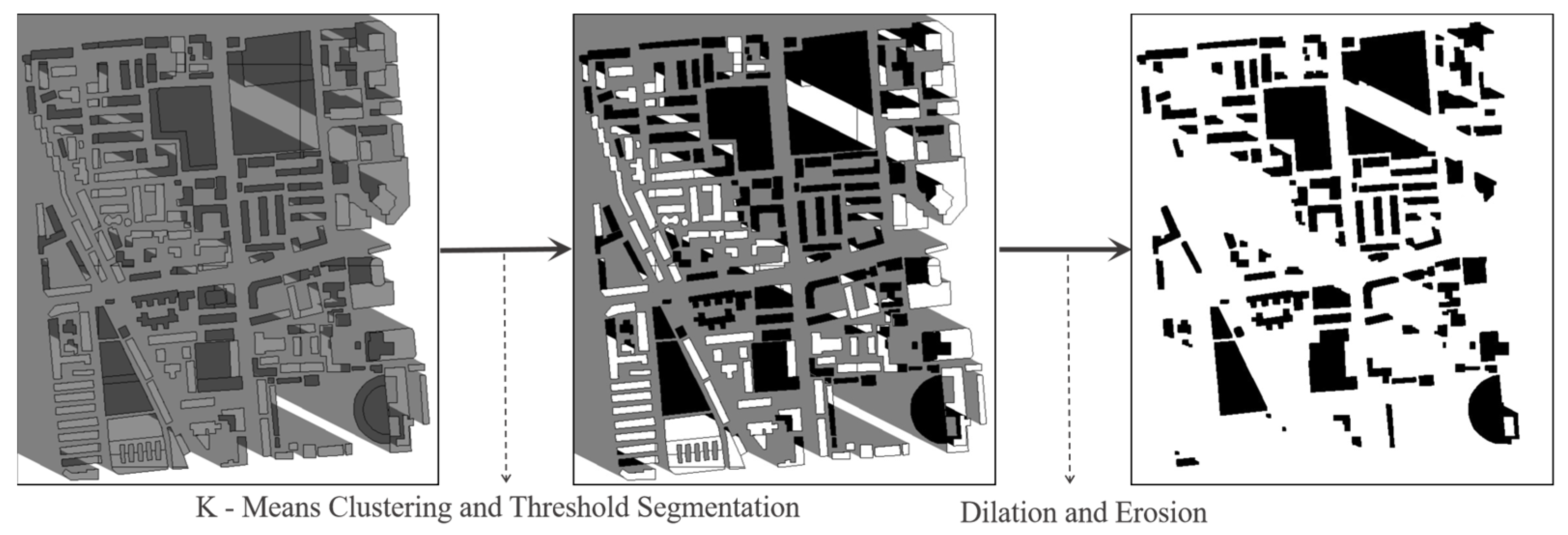
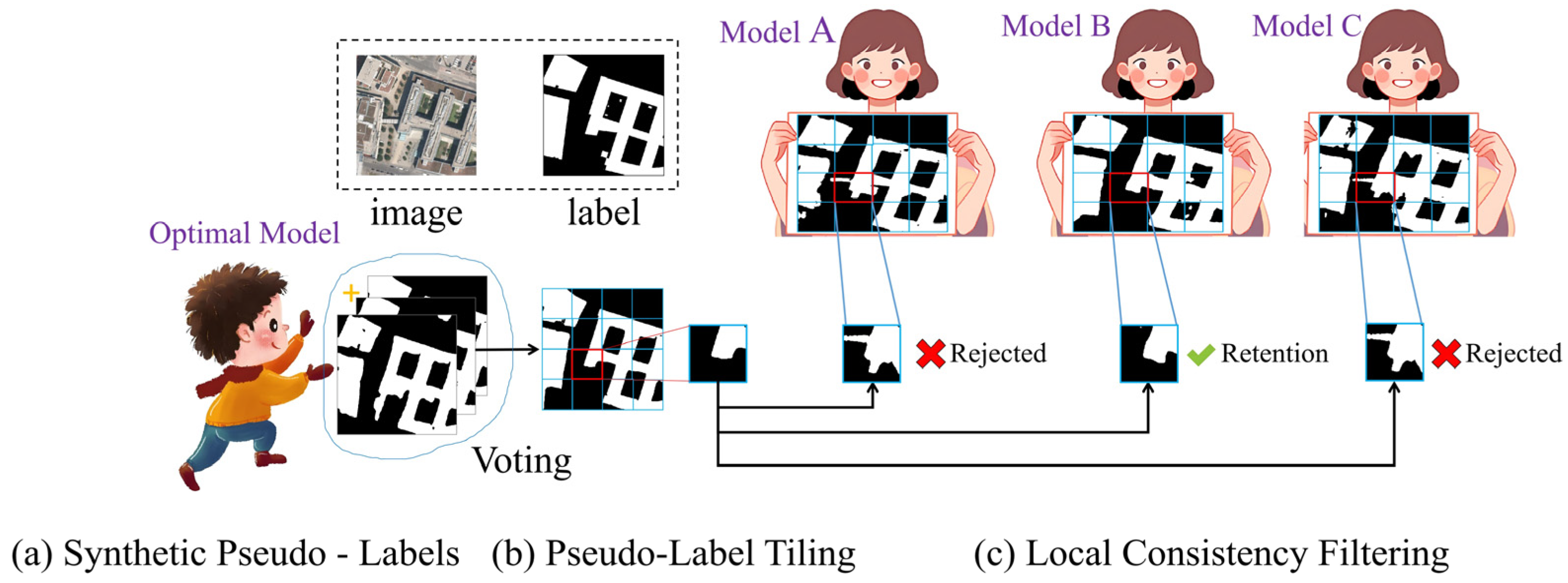
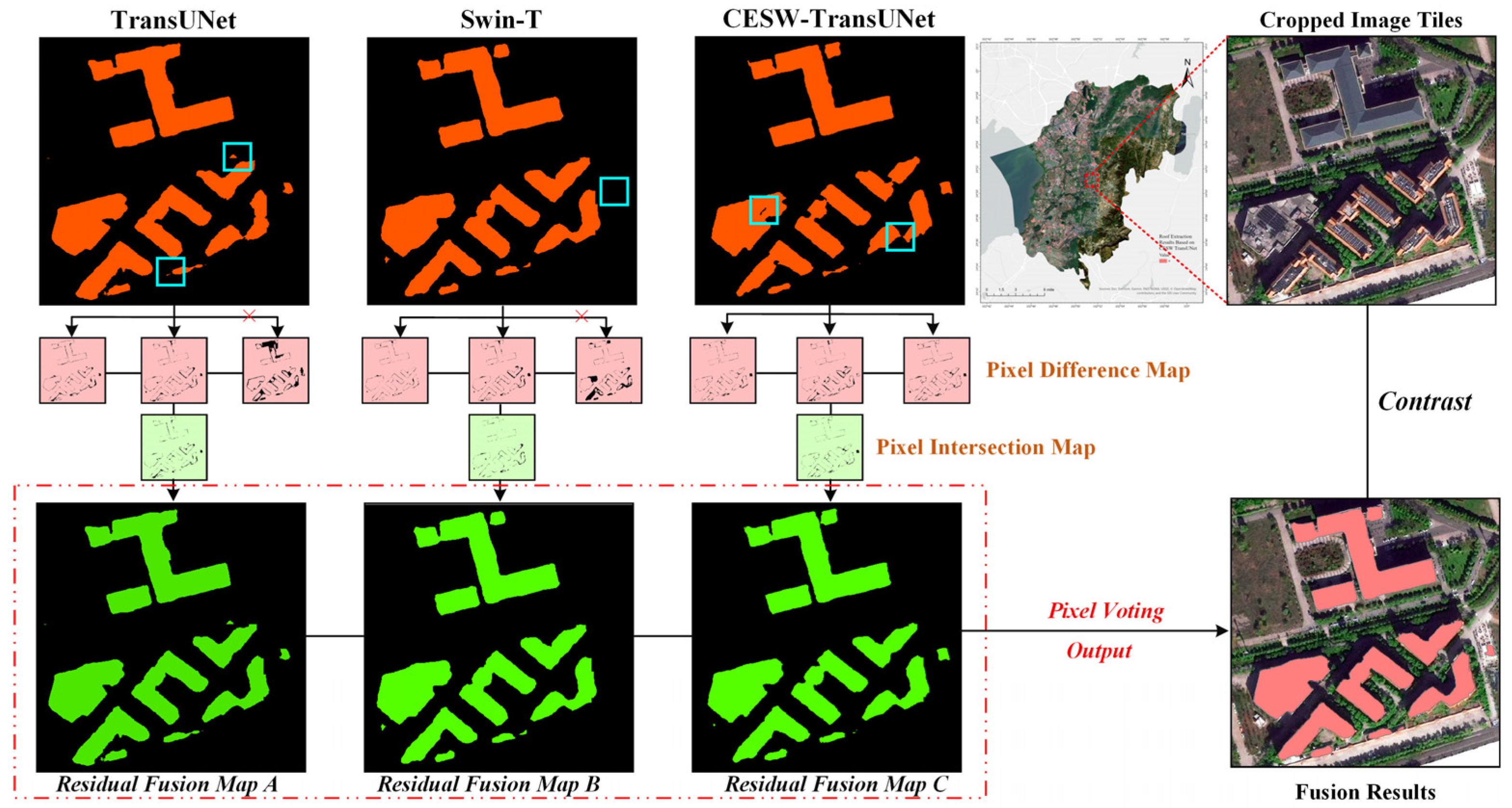
2.5.1. Overview of the Residual-Based Fusion Strategy
2.5.2. Fusion Procedure
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Environment Configuration
3.2. Dataset Processing and Training
3.3. Training Results
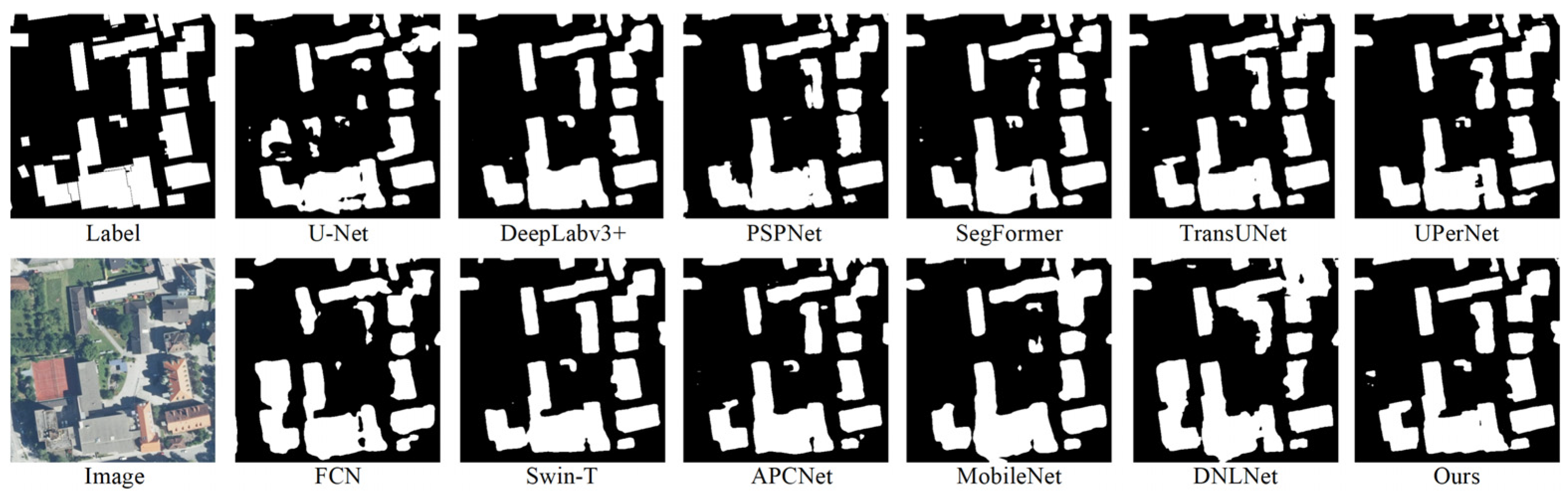
3.4. Analysis of Fusion Results
3.5. Application and Evaluation in the Study Area
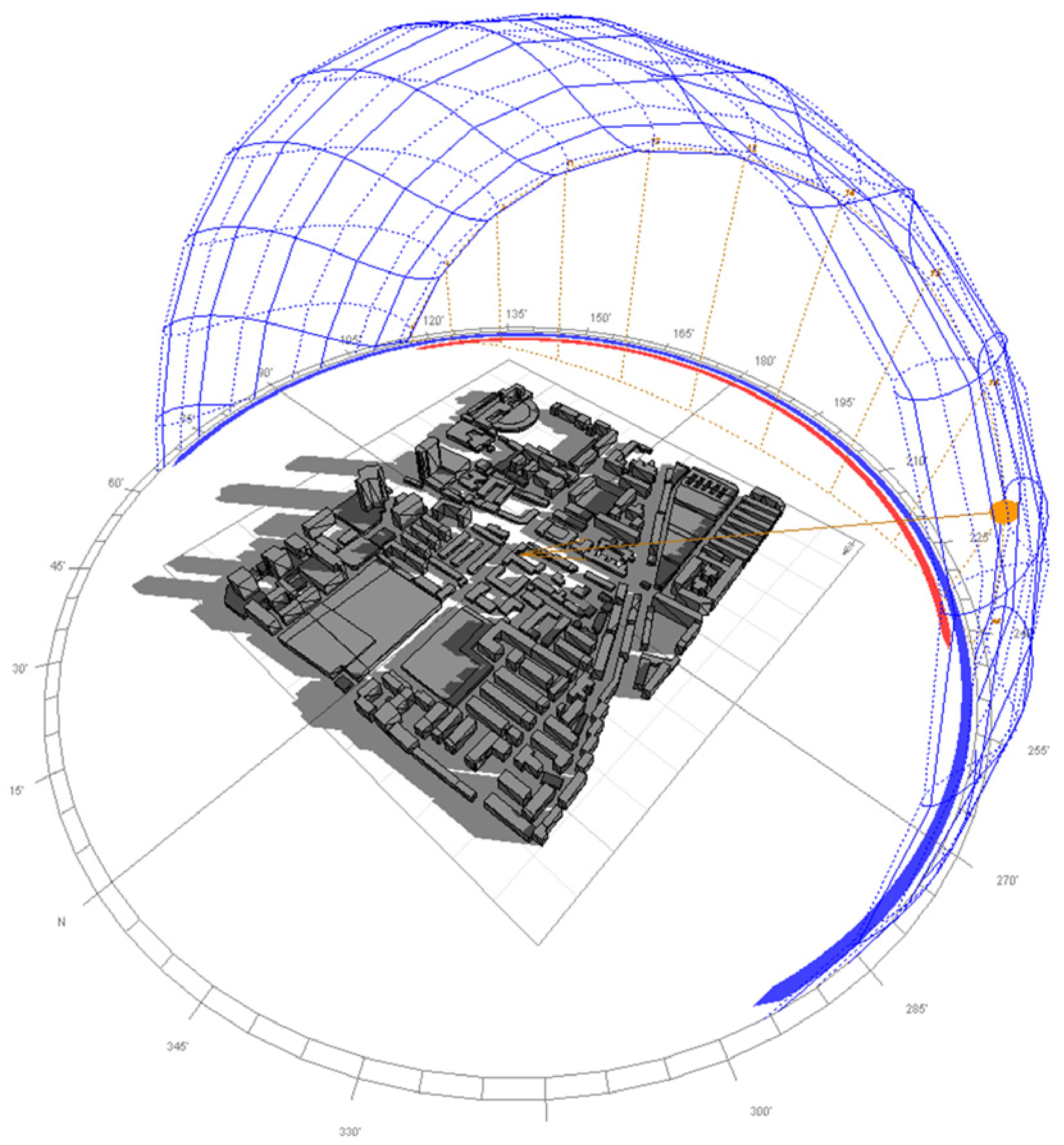
3.5.1. Overview of the Study Area
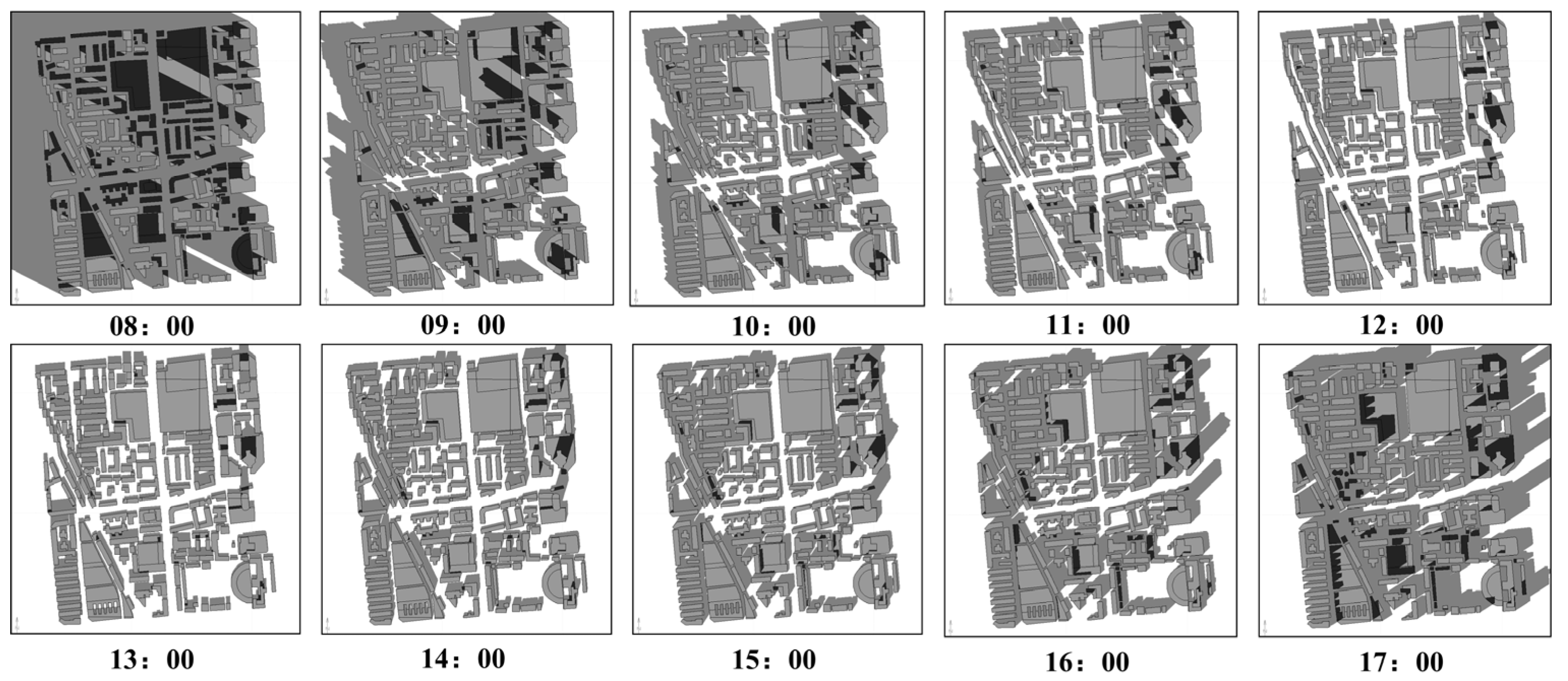
3.5.2. Visualization Analysis of Residual Fusion
3.5.3. Comprehensive Assessment of Photovoltaic Potential in the Study Area
4. Discussion
4.1. Methodological Advantages and Comparative Analysis
4.2. Significance of the Findings
4.3. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gielen, D.; Boshell, F.; Saygin, D.; Bazilian, M.D.; Wagner, N.; Gorini, R. The role of renewable energy in the global energy transformation. Energy Strategy Rev. 2019, 24, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomo, P.; Frontini, F.; Loonen, R.; Reinders, A. Comprehensive review and state of play in the use of photovoltaics in buildings. Energy Build. 2024, 323, 114737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Ghasemi, R.; Khalkhali, M.; Mo, W. Dynamics of large-scale solar PV adoption feedback effects: A technical, economic, and environmental assessment. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 205, 107571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Lau, W.S.; You, L.; Yan, J.; Ratti, C.; Chen, M.; Wong, M.S.; Qin, Z. Multi-sourced data modelling of spatially heterogenous life-cycle carbon mitigation from installed rooftop photovoltaics: A case study in Singapore. Appl. Energy 2024, 362, 122957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Miao, D.; Hou, X.; Jia, M. Just Transition for China’s Coal Regions Towards Carbon Neutrality Targets. Soc. Incl. 2024, 12, 7494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Rooftop, P.V. Development Suitability and Carbon Benefits: An Anhui Province Case Study. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Yao, L.; Lu, N.; Qin, J.; Liu, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, C. Geospatial assessment of rooftop solar photovoltaic potential using multi-source remote sensing data. Energy AI 2022, 10, 100185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, R. Integrating artificial intelligence in energy transition: A comprehensive review. Energy Strategy Rev. 2025, 57, 101600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Sharieff, R.; Olawale, M.; Khan, M.I. Unlocking the potential of unregulated rooftops for solar PV on residential buildings: Identifying and addressing key challenges. Energy Nexus 2025, 18, 100447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Huang, Y.; Bai, J.; Wang, C. AI-Based Rooftop PV Resource Assessment Method and Its Application. Prog. New Energy 2023, 11, 280–288. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jenila, V.M.; Varalakshmi, P. Extraction of Building Footprint Using MASK-RCNN for High Resolution Aerial Imagery; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, C.; Qi, L.; Luo, Y.; Qi, J. Object-Oriented and Deep-Learning-Based Extraction of Mine-Area Ground Objects. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2021, 33, 9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H. Recognition of Building Roofs and Assessment of Solar Energy Potential Based on High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images; Wuhan University: Wuhan, China, 2019. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Q.; Zhao, J.; Tan, Z.; Tao, K.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Y. Development assessment of regional rooftop photovoltaics based on remote sensing and deep learning. Appl. Energy 2024, 375, 124172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Hu, J.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Y.; Yang, J.; Tan, Z.; Bai, J. Photovoltaic resource assessment through roof usable area extraction based on image segmentation. Sol. Energy 2025, 297, 113646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Luo, X.; Adeli, E.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yuille, A.L.; Zhou, Y. TransUNet: Transformers Make Strong Encoders for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.04306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.H.; Lu, C.Z.; Hou, Q.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, M.M.; Hu, S.M. Segnext: Rethinking convolutional attention design for semantic segmentation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 1140–1156. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.Z.; Zhang, W.M. Relationship between scattered solar radiation, global solar radiation and extraterrestrial solar radiation in mainland China. Acta Energiae Solaris Sin. 1994, 3, 201–208. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tian, X.; Wang, L.; Ding, Q. A review of deep learning-based image semantic segmentation methods. J. Softw. 2019, 30, 440–468. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Tang, X.; Ruan, C.; Fu, C.; Tao, Z.; Yang, Y. A Survey on Real-Time Semantic Segmentation Based on Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Big Data and Security, Washington, DC, USA, 15–18 December 2024; Springer: Singapore, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Carunta, C.; Carunta, A.; Popa, C.A. Heavy and Lightweight Deep Learning Models for Semantic Segmentation: A Survey. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 17745–17765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid Scene Parsing Network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 39, 640–651. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, J. Unified Perceptual Parsing for Scene Understanding; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.-C.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; et al. Searching for MobileNetV3. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, M.; Yao, Z.; Cao, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Hu, H. Disentangled Non-Local Neural Networks. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Deng, Z.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, Y. Adaptive Pyramid Context Network for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, E.; Wang, W.; Yu, Z.; Anandkumar, A.; Alvarez, J.M.; Luo, P. SegFormer: Simple and Efficient Design for Semantic Segmentation with Transformers. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 12077–12090. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Yuan, H. A Rooftop PV Potential Assessment Method Based on Improved U-Net. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Wavelet Analysis and Pattern Recognition (ICWAPR), Miyazaki, Japan, 20–23 September 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q. Rooftop PV Potential Assessment Based on Airborne LiDAR Data; Hubei Normal University: Huangshi, China, 2025. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]






| Metric | Formula |
|---|---|
| Accuracy | |
| Intersection over Union (IoU) | |
| Precision | |
| Recall | |
| F1 Score/F1 |
| Parameter | Value/Description |
|---|---|
| Batch size | 4 |
| Number of iterations | 40,000 |
| Learning rate (lr) | 0.01/dynamically adjusted |
| Optimizer | SGD |
| Momentum | 0.9 |
| Activation function | ReLU, GELU |
| Weight decay | 1 × 10−5 |
| Model | Pa (%) | IoU (%) | Pr (%) | Re (%) | F1 (%) | Parameters (M) | FLOPS (G) | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net [24] | 93.71 | 72.12 | 85.40 | 82.27 | 83.80 | 15.17 | 130.71 | 30.86 |
| DeepLabv3+ [25] | 94.38 | 75.48 | 86.28 | 83.88 | 85.18 | 42.40 | 46.81 | 31.06 |
| PSPNet [26] | 94.42 | 75.73 | 84.28 | 86.40 | 85.34 | 57.10 | 53.59 | 40.16 |
| FCN [27] | 93.69 | 70.91 | 88.88 | 77.81 | 82.98 | 28.15 | 27.64 | 88.50 |
| UPerNet [28] | 94.51 | 75.17 | 87.75 | 83.98 | 85.82 | 40.75 | 115.43 | 27.93 |
| MobileNet [29] | 93.38 | 71.63 | 82.45 | 84.52 | 83.47 | 11.60 | 61.85 | 69.93 |
| DNLNet [30] | 93.83 | 72.31 | 83.93 | 86.52 | 85.21 | 14.27 | 79.14 | 18.55 |
| APCNet [31] | 94.01 | 72.27 | 89.49 | 78.97 | 83.90 | 218.84 | 69.97 | 30.67 |
| SegFormer [32] | 94.50 | 74.89 | 88.49 | 82.98 | 85.64 | 32.13 | 51.78 | 93.46 |
| TransUNet [16] | 95.33 | 76.23 | 87.92 | 84.84 | 86.35 | 123.84 | 85.67 | 26.18 |
| Swin-T [17] | 95.38 | 77.92 | 88.53 | 88.14 | 88.33 | 33.22 | 65.15 | 23.04 |
| Ours | 95.47 | 78.50 | 88.60 | 88.12 | 88.36 | 90.89 | 67.69 | 32.69 |
| Configuration | SW-Block | CESW-Block | MSCA | GCFF | Pa (%) | IoU (%) | Pr (%) | Re (%) | F1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | × | × | × | × | 93.85 | 76.32 | 86.40 | 86.75 | 86.07 |
| + SW-Block | √ | × | × | × | 94.38 | 77.09 | 87.14 | 87.01 | 87.08 |
| + CESW-Block | × | √ | × | × | 95.20 | 78.25 | 88.35 | 87.90 | 87.83 |
| + MSCA | × | × | √ | × | 94.35 | 77.18 | 87.05 | 87.30 | 87.12 |
| + GCFF | × | × | × | √ | 94.62 | 77.41 | 87.51 | 87.29 | 87.40 |
| Full Model | √ | √ | √ | √ | 95.47 | 78.50 | 88.60 | 88.12 | 88.36 |
| Method | Pa (%) | IoU (%) | Pr (%) | Re (%) | F1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TransUNet [16] | 95.33 | 76.23 | 87.92 | 84.84 | 86.35 |
| Swin-T [17] | 95.38 | 77.92 | 88.53 | 88.14 | 88.33 |
| CESW-TransUNet | 95.47 | 78.50 | 88.60 | 88.12 | 88.36 |
| Full-range majority voting fusion [12,13] | 95.36 ± 0.15 | 77.56 ± 0.82 | 88.37 ± 0.40 | 87.29 ± 0.65 | 87.83 ± 0.47 |
| Residual fusion | 95.81 ± 0.09 | 79.85 ± 0.18 | 89.42 ± 0.15 | 89.15 ± 0.20 | 89.28 ± 0.12 |
| University | Effective Rooftop Area (km2) | Grid-Connected Electricity (MWh) | Carbon Emission Reduction (tCO2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yunnan University (YNU) | 0.2995 | 79,596 | 50,136 |
| Kunming University of Science and Technology (KUST) | 0.2426 | 64,541 | 40,652 |
| Yunnan Normal University (YNU) | 0.2894 | 77,414 | 48,761 |
| Yunnan Minzu University (YMU) | 0.2993 | 79,635 | 50,160 |
| Yunnan Jiaotong University (YJTU) | 0.0732 | 19,559 | 12,320 |
| Yunnan Open University (YOU) | 0.0864 | 23,081 | 14,538 |
| Kunming Medical University (KMU) | 0.1466 | 38,963 | 24,542 |
| Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine (YUNCM) | 0.0947 | 25,302 | 15,937 |
| Yunnan Arts University (YAU) | 0.0828 | 22,141 | 13,946 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, J.; Yang, M.; Tang, X.; Guan, X.; Ma, T. Intelligent Segmentation of Urban Building Roofs and Solar Energy Potential Estimation for Photovoltaic Applications. J. Imaging 2025, 11, 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11100334
Zeng J, Yang M, Tang X, Guan X, Ma T. Intelligent Segmentation of Urban Building Roofs and Solar Energy Potential Estimation for Photovoltaic Applications. Journal of Imaging. 2025; 11(10):334. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11100334
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Junsen, Minglong Yang, Xiujuan Tang, Xiaotong Guan, and Tingting Ma. 2025. "Intelligent Segmentation of Urban Building Roofs and Solar Energy Potential Estimation for Photovoltaic Applications" Journal of Imaging 11, no. 10: 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11100334
APA StyleZeng, J., Yang, M., Tang, X., Guan, X., & Ma, T. (2025). Intelligent Segmentation of Urban Building Roofs and Solar Energy Potential Estimation for Photovoltaic Applications. Journal of Imaging, 11(10), 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11100334





