High-Resolution Iodine-Enhanced Micro-Computed Tomography of Intact Human Hearts for Detailed Coronary Microvasculature Analyses
Abstract
1. Introduction
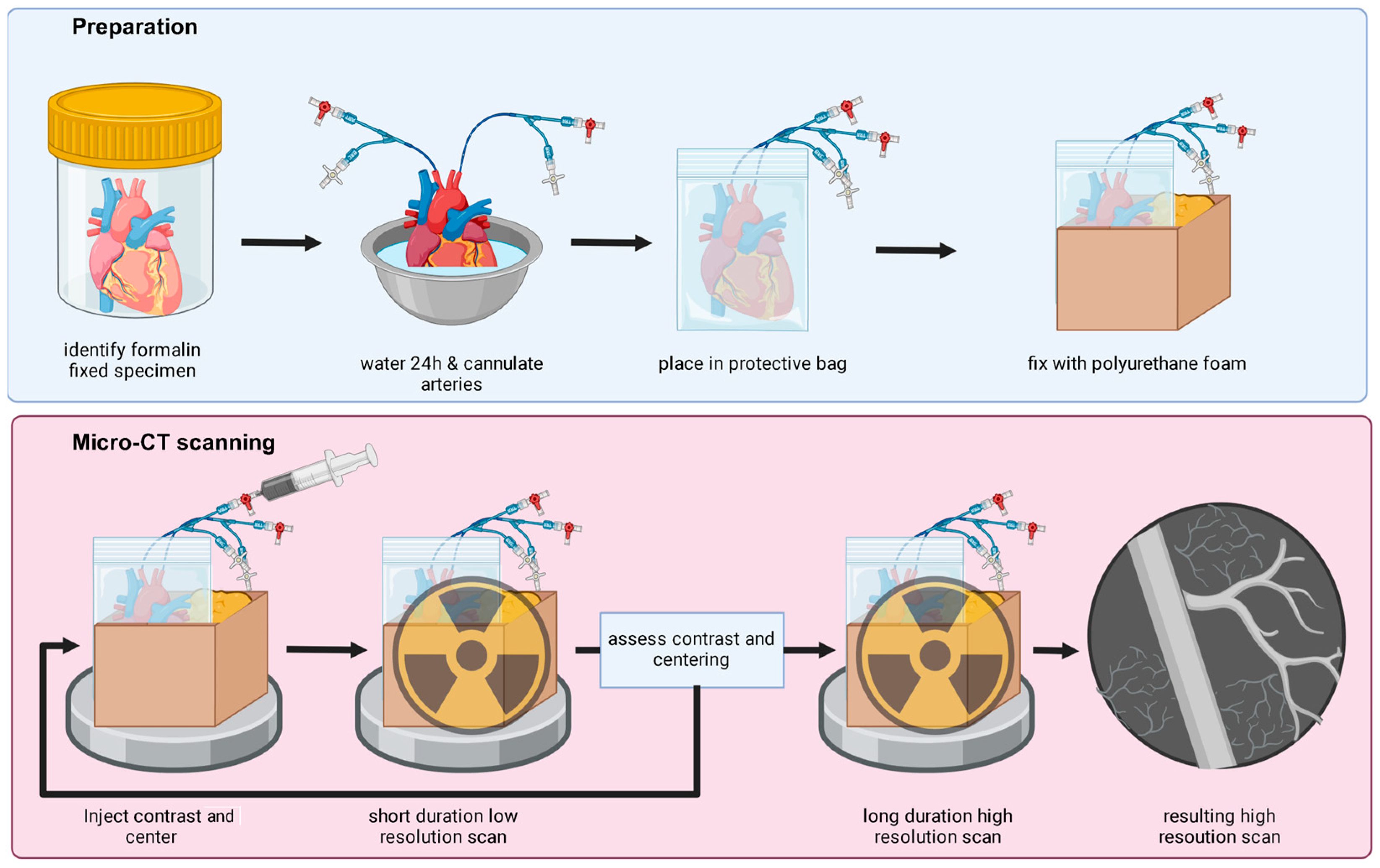
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Imaging Outcomes and Generated Models
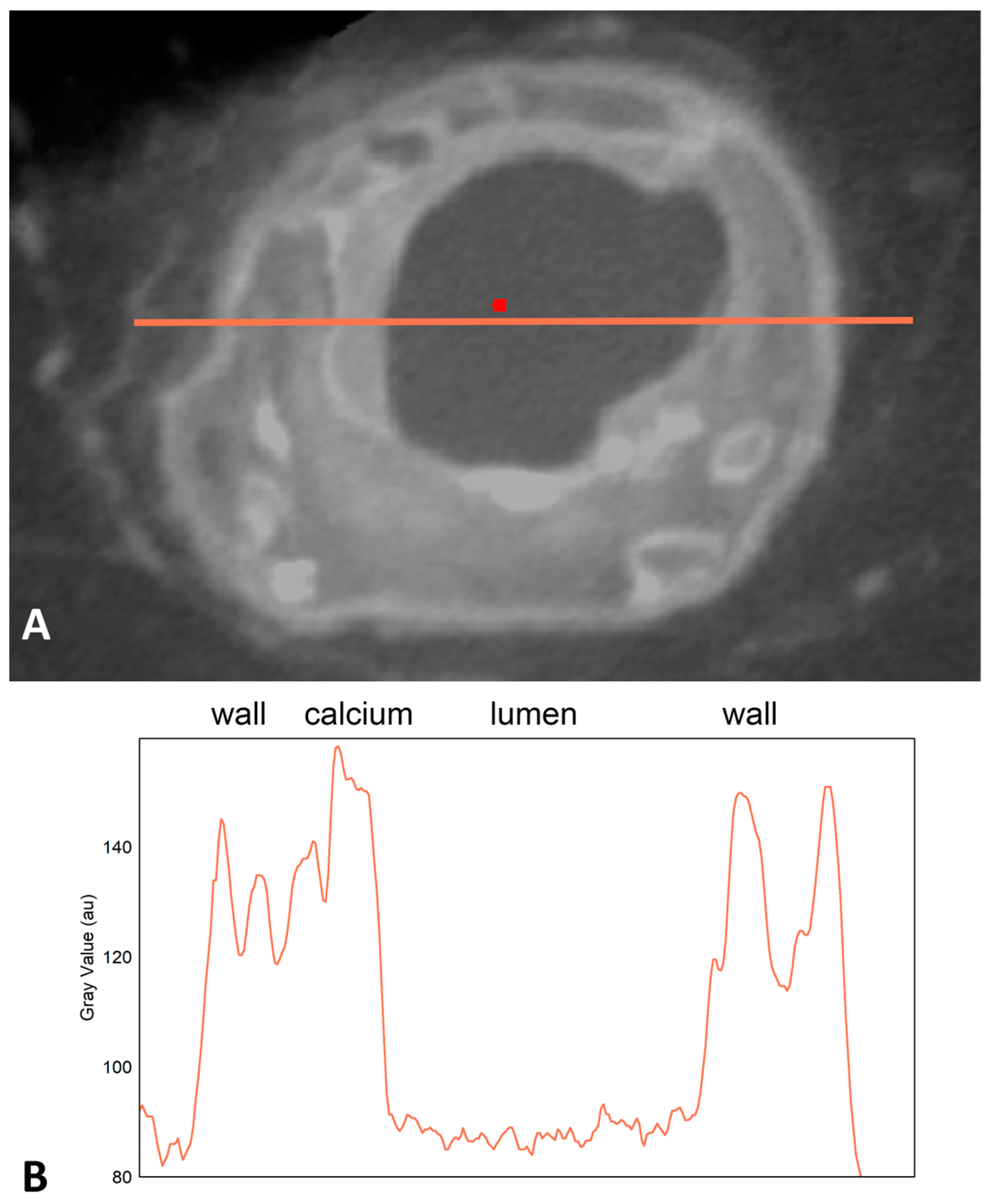
3.2. Individual Line Profiles
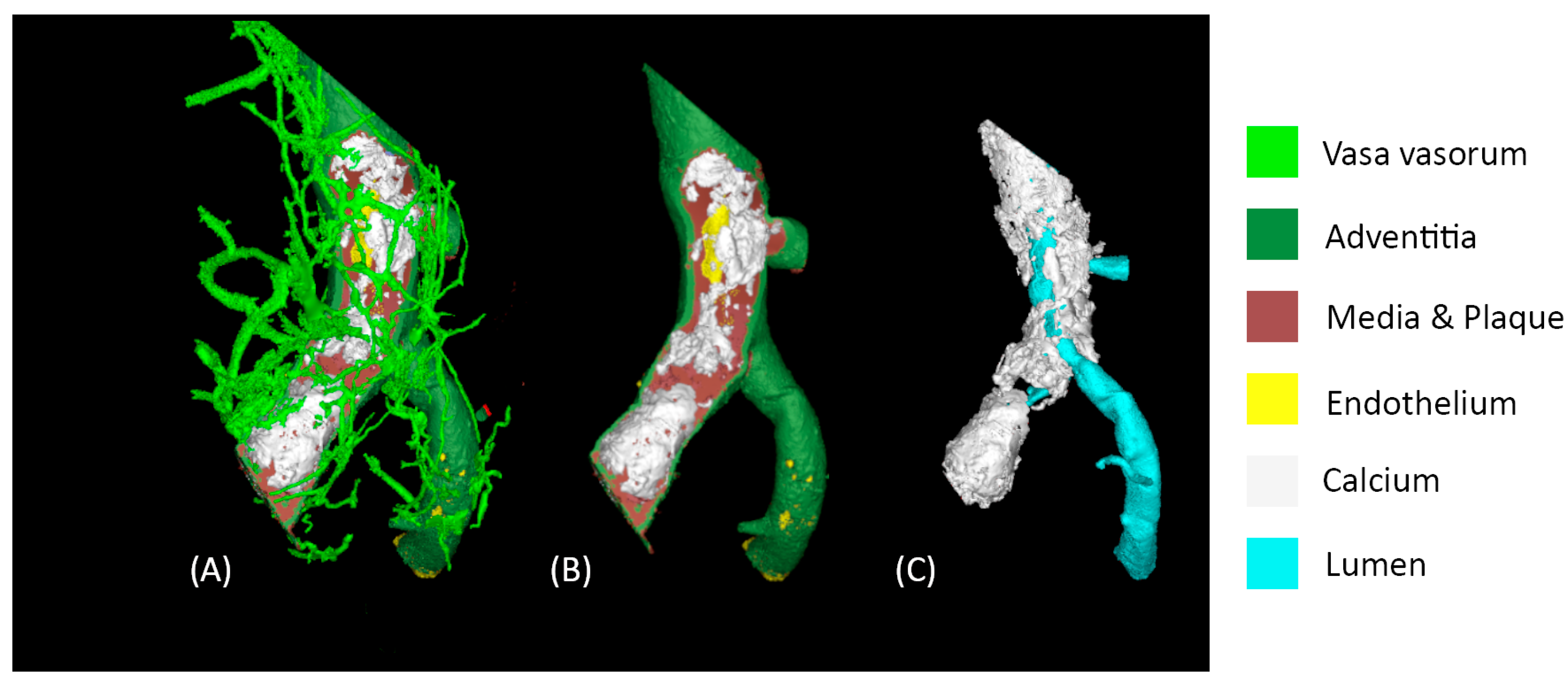
3.3. Vessel Segmentations
3.4. Specimen Assessments Post-Processing
4. Discussion
- (a)
- Enhancing our understanding of collateral coronary anatomy and potential recruitment in diseased or fully occluded coronary arteries. With the generated high-resolution 3D vasculature models, one can then employ computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analyses to simulate local hemodynamics and endothelial shear stresses [4,23,24].
- (b)
- Developing novel devices, based on three-dimensional tissue density patterns within occluded segments, to increase future successes of interventional procedures to treat chronic total occlusions [25].
- (c)
- (d)
- Enabling novel explorations of the presence or absence of continuous intralesional microchannels that may present in a heart with true chronic total occlusions, including their complex and highly variable three-dimensional paths. Previous work on these anatomies has been limited to cross-sectional pathology/HE slices or rabbit animal models of the femoral artery [5].
- (e)
Potential Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Camici, P.G.; d’Amati, G.; Rimoldi, O. Coronary microvascular dysfunction: Mechanisms and functional assessment. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2015, 12, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gössl, M.; Versari, D.; Lerman, L.O.; Chade, A.R.; Beighley, P.E.; Erbel, R.; Ritman, E.L. Low vasa vasorum densities correlate with inflammation and subintimal thickening: Potential role in location—Determination of atherogenesis. Atherosclerosis 2009, 206, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boerhout, C.K.M.; de Waard, G.A.; Lee, J.M.; Mejía-Rentería, H.; Lee, S.H.; Jung, J.-H.; Hoshino, M.; Echavarria-Pinto, M.; Meuwissen, M.; Matsuo, H.; et al. Prognostic value of structural and functional coronary microvascular dysfunction in patients with non-obstructive coronary artery disease; from the multicentre international ILIAS registry. EuroIntervention 2022, 18, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEntegart, M.B.; Badar, A.A.; Ahmad, F.A.; Shaukat, A.; MacPherson, M.; Irving, J.; Strange, J.; Bagnall, A.J.; Hanratty, C.G.; Walsh, S.J. The collateral circulation of coronary chronic total occlusions. EuroIntervention 2016, 11, e1596–e1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munce, N.R.; Strauss, B.H.; Qi, X.; Weisbrod, M.J.; Anderson, K.J.; Leung, G.; Sparkes, J.D.; Lockwood, J.; Jaffe, R.; Butany, J.; et al. Intravascular and Extravascular Microvessel Formation in Chronic Total Occlusions. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2010, 3, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantella, L.E.; Liblik, K.; Johri, A.M. Vascular imaging of atherosclerosis: Strengths and weaknesses. Atherosclerosis 2021, 319, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gössl, M.; Rosol, M.; Malyar, N.M.; Fitzpatrick, L.A.; Beighley, P.E.; Zamir, M.; Ritman, E.L. Functional anatomy and hemodynamic characteristics of vasa vasorum in the walls of porcine coronary arteries. Anat. Record. Part A Discov. Mol. Cell. Evol. Biol. 2003, 272, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Self, T.S.; Ginn-Hedman, A.-M.; Newell-Fugate, A.E.; Weeks, B.R.; Heaps, C.L. Iodine-based contrast staining improves micro-computed tomography of atherosclerotic coronary arteries. MethodsX 2021, 8, 101297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Self, T.S.; Ginn-Hedman, A.M.; Kaulfus, C.N.; Newell-Fugate, A.E.; Weeks, B.R.; Heaps, C.L. Iodine-enhanced micro-computed tomography of atherosclerotic plaque morphology complements conventional histology. Atherosclerosis 2020, 313, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barger, A.C.; Beeuwkes, R.; Lainey, L.L.; Silverman, K.J. Hypothesis: Vasa Vasorum and Neovascularization of Human Coronary Arteries. N. Engl. J. Med. 1984, 310, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salg, G.A.; Steinle, V.; Labode, J.; Wagner, W.; Studier-Fischer, A.; Reiser, J.; Farjallah, E.; Guettlein, M.; Albers, J.; Hilgenfeld, T.; et al. Multiscale and multimodal imaging for three-dimensional vascular and histomorphological organ structure analysis of the pancreas. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keklikoglou, K.; Arvanitidis, C.; Chatzigeorgiou, G.; Chatzinikolaou, E.; Karagiannidis, E.; Koletsa, T.; Magoulas, A.; Makris, K.; Mavrothalassitis, G.; Papanagnou, E.-D.; et al. Micro-CT for Biological and Biomedical Studies: A Comparison of Imaging Techniques. J. Imaging 2021, 7, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginn-Hedman, A.-M.; Self, T.S.; Jessen, S.L.; Heaps, C.L.; Weeks, B.R.; Clubb, F.J. Diffusible contrast-enhanced micro-CT improves visualization of stented vessels. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2022, 60, 107428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- du Plessis, A.; Broeckhoven, C.; Guelpa, A.; le Roux, S.G. Laboratory X-ray micro-computed tomography: A user guideline for biological samples. GigaScience 2017, 6, gix027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metscher, B.D. MicroCT for comparative morphology: Simple staining methods allow high-contrast 3D imaging of diverse non-mineralized animal tissues. BMC Physiol. 2009, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quill, J.L.; Hill, A.J.; Laske, T.G.; Alfieri, O.; Iaizzo, P.A. Mitral leaflet anatomy revisited. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2009, 137, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.H.; Herman, A.M.; Stephenson, J.M.; Wu, T.; Bahadur, A.N.; Burns, A.R.; Marrelli, S.P.; Wythe, J.D. Development of barium-based low viscosity contrast agents for micro CT vascular casting: Application to 3D visualization of the adult mouse cerebrovasculature. J. Neurosci. Res. 2020, 98, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottardi, W. Iodine and disinfection: Theoretical study on mode of action, efficiency, stability, and analytical aspects in the aqueous system. Arch. Pharm. 1999, 332, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeppel, D.R.; Boehm, I.B. Shortage of iodinated contrast media: Status and possible chances—A systematic review. Eur. J. Radiol. 2023, 164, 110853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gignac, P.M.; Kley, N.J.; Clarke, J.A.; Colbert, M.W.; Morhardt, A.C.; Cerio, D.; Cost, I.N.; Cox, P.G.; Daza, J.D.; Early, C.M.; et al. Diffusible iodine-based contrast-enhanced computed tomography (diceCT): An emerging tool for rapid, high-resolution, 3-D imaging of metazoan soft tissues. J. Anat. 2016, 228, 889–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedby, Ö. Viscosity of Some Contemporary Contrast Media before and after Mixing with Whole Blood. Acta Radiol. 1992, 33, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kestin, J.; Sokolov, M.; Wakeham, W.A. Viscosity of liquid water in the range −8 °C to 150 °C. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1978, 7, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, D.; Pinilla-Echeverri, N.; Coskun, A.U.; Pu, Z.; Kajander, O.A.; Rupert, D.; Maynard, C.; Cefalo, N.; Siasos, G.; Papafaklis, M.I.; et al. The role of endothelial shear stress, shear stress gradient, and plaque topography in plaque erosion. Atherosclerosis 2023, 376, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, G.S.; Jandt, E.; Krack, A.; Schwarz, G.; Mutschke, O.; Kuethe, F.; Ferrari, M.; Figulla, H.R. Growth Factors in the Collateral Circulation of Chronic Total Coronary Occlusions. Circulation 2004, 110, 1940–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Xing, H.; Wang, R.; Tian, J.; Ju, Z.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; Song, X. A Novel Classification for Predicting Chronic Total Occlusion Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 762351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, H.; Wakatsuki, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Fukuda, D.; Kawabata, Y.; Matsuura, T.; Kusunose, K.; Ise, T.; Tobiume, T.; Yagi, S.; et al. Atherosclerotic Coronary Plaque Is Associated With Adventitial Vasa Vasorum and Local Inflammation in Adjacent Epicardial Adipose Tissue in Fresh Cadavers. Circ. J. 2020, 84, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwakar, M.; Kumar, M. A review on CT image noise and its denoising. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2018, 42, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadkarni, R.; Clark, D.P.; Allphin, A.J.; Badea, C.T. A Deep Learning Approach for Rapid and Generalizable Denoising of Photon-Counting Micro-CT Images. Tomography 2023, 9, 1286–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, C.L.; Tafforeau, P.; Wagner, W.L.; Jafree, D.J.; Bellier, A.; Werlein, C.; Kühnel, M.P.; Boller, E.; Walker-Samuel, S.; Robertus, J.L.; et al. Imaging intact human organs with local resolution of cellular structures using hierarchical phase-contrast tomography. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 1532–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng-Zhuang, M.; Jing-Wen, F.; Cheng-Wen, Y.; Yu, S. A method for metal artifacts reduction using virtual dual-energy CT images generated from single energy CT scans. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Optical Instruments and Technology: Optical Systems and Modern Optoelectronic Instruments, Beijing, China, 26–28 October 2019; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA; Volume 11434. [Google Scholar]


| Micro-CT Technique | |
|---|---|
| Voltage (kV) | 60 |
| Current (micro-amperes) | 900 |
| Focal spot (microns) | 54 |
| Effective pixel pitch (mm) | 0.01989 |
| Resolution (microns) | 19.83 |
| Tube to detector (mm) | 1323.609 |
| Tube to object (mm) | 207.34 |
| Calculated ug (mm) | 0.209 |
| Frame rate (fps) | 1 |
| Projections | 3600 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reifart, J.; Iaizzo, P. High-Resolution Iodine-Enhanced Micro-Computed Tomography of Intact Human Hearts for Detailed Coronary Microvasculature Analyses. J. Imaging 2024, 10, 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10070173
Reifart J, Iaizzo P. High-Resolution Iodine-Enhanced Micro-Computed Tomography of Intact Human Hearts for Detailed Coronary Microvasculature Analyses. Journal of Imaging. 2024; 10(7):173. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10070173
Chicago/Turabian StyleReifart, Joerg, and Paul Iaizzo. 2024. "High-Resolution Iodine-Enhanced Micro-Computed Tomography of Intact Human Hearts for Detailed Coronary Microvasculature Analyses" Journal of Imaging 10, no. 7: 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10070173
APA StyleReifart, J., & Iaizzo, P. (2024). High-Resolution Iodine-Enhanced Micro-Computed Tomography of Intact Human Hearts for Detailed Coronary Microvasculature Analyses. Journal of Imaging, 10(7), 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10070173






