Privacy-Preserving Face Recognition Method Based on Randomization and Local Feature Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We deeply study the learning of hidden human visual information in the end-to-end face image feature learning of deep neural networks and propose that preserving the light-and-dark relationship between facial image pixels and randomizing other information can eliminate human visual information while maintaining the recognizability of facial images. According to the results of our review, the proposed method is the most thorough method to eliminate human visual information in the current privacy-preserving face recognition methods. Using this technology can make a facial image have better privacy-protection ability.
- A deep neural network framework and RLLFPR method for face privacy protection are proposed. Different from traditional encryption and decryption methods, the proposed framework combines face privacy protection with face recognition optimization, which can jointly compute face privacy protection and recognition.
- The RLLFPR method produces privacy-preserved faces with fuzziness, revocability, and irreversibility for better privacy protection. All the information stored in the face recognition server, private face recognition model, private facial image, etc., cannot restore or deduce the original face, which improves the privacy protection of facial images in face recognition or authentication systems.
2. Related Work
2.1. Face Recognition
2.2. Face Privacy Protection
2.3. Privacy-Protected Face Recognition
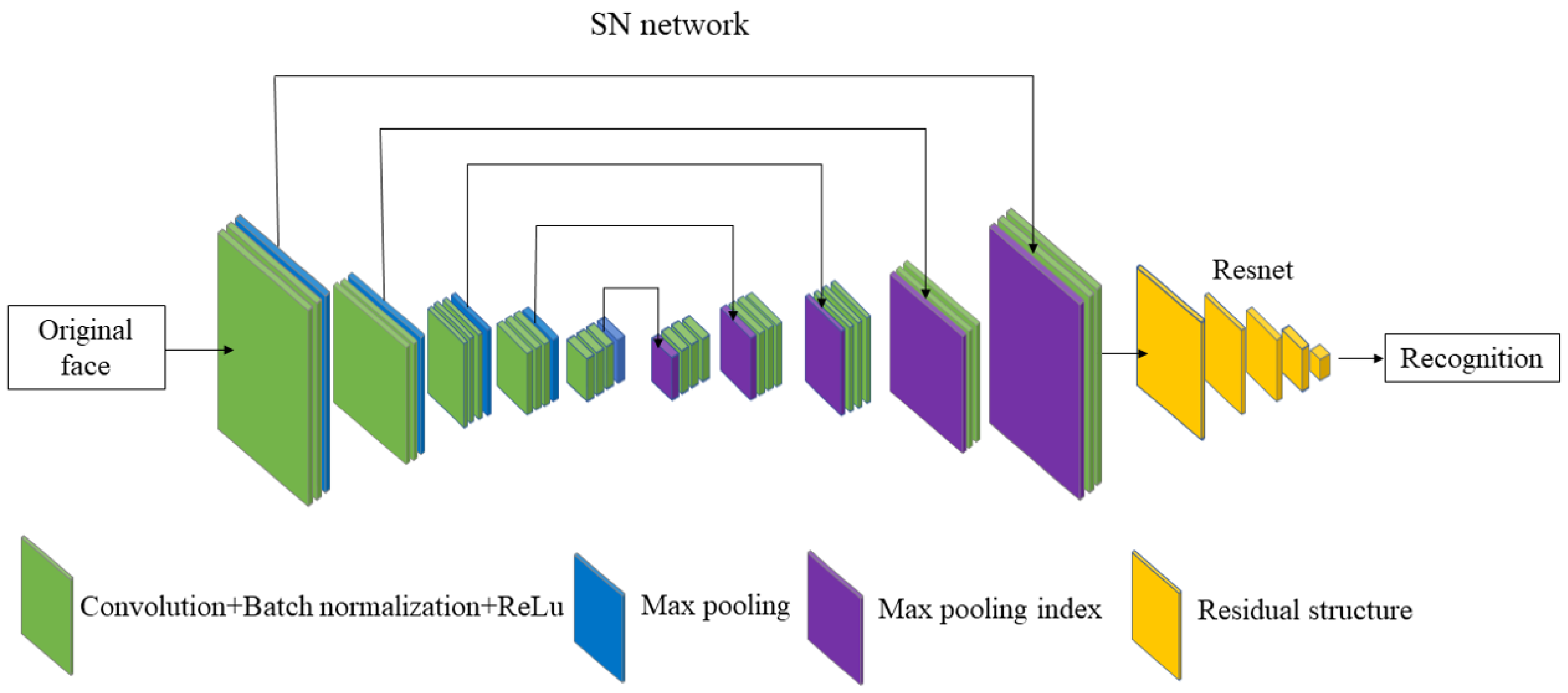
3. Privacy-Preserving Face Recognition Based on Randomization and Local Feature Learning (RLLFPR)
3.1. Privacy-Preserving Face Recognition Based on Randomization and Local Feature Learning (RLLFPR) Training Method
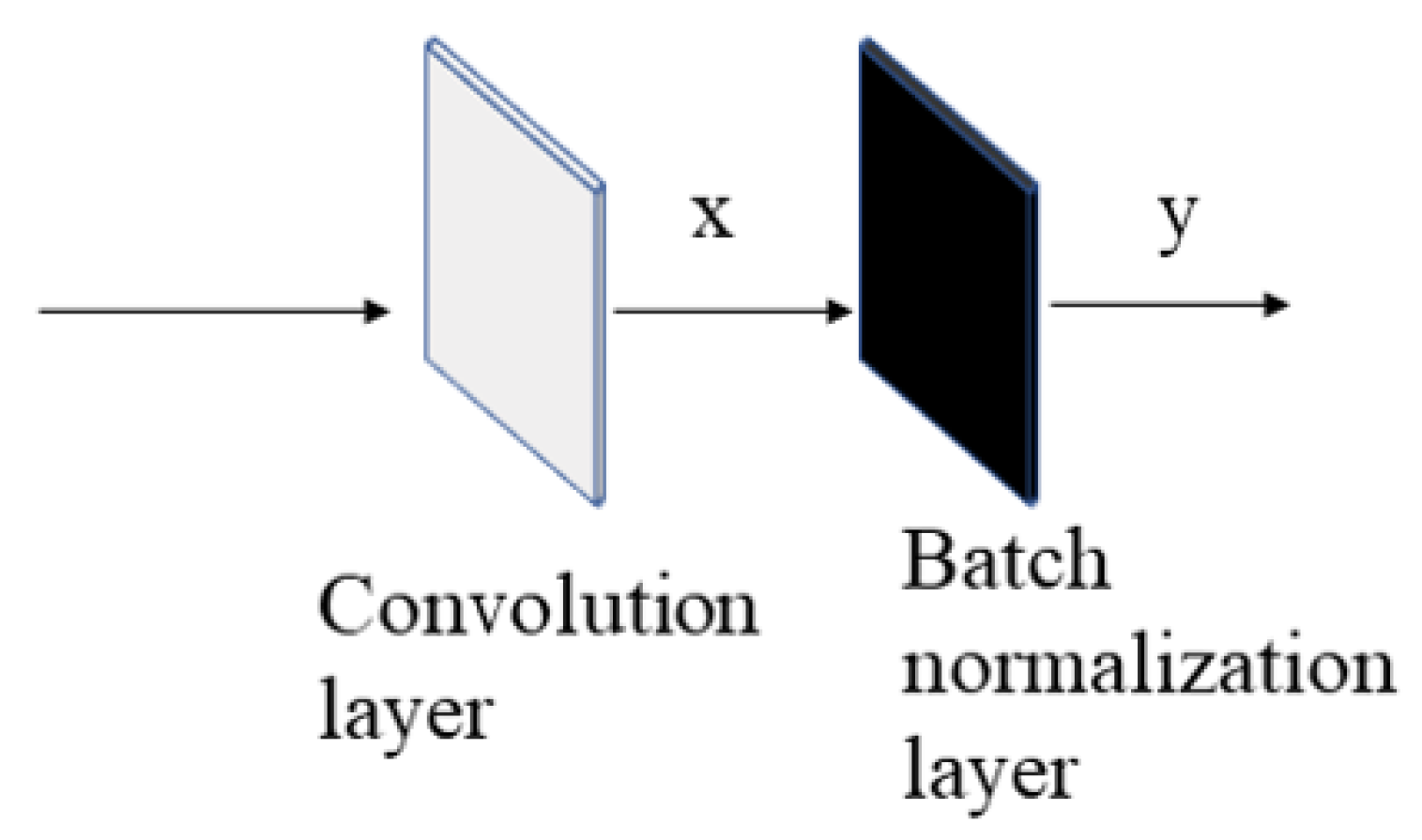
3.2. Randomized Convolution and Batch Normalization Learning for RLLFPR
4. Experiment
4.1. Setting
4.2. The Recognition Performance of Privacy-Preserving Face Recognition Based on Randomization and Local Feature Learning (RLLFPR)
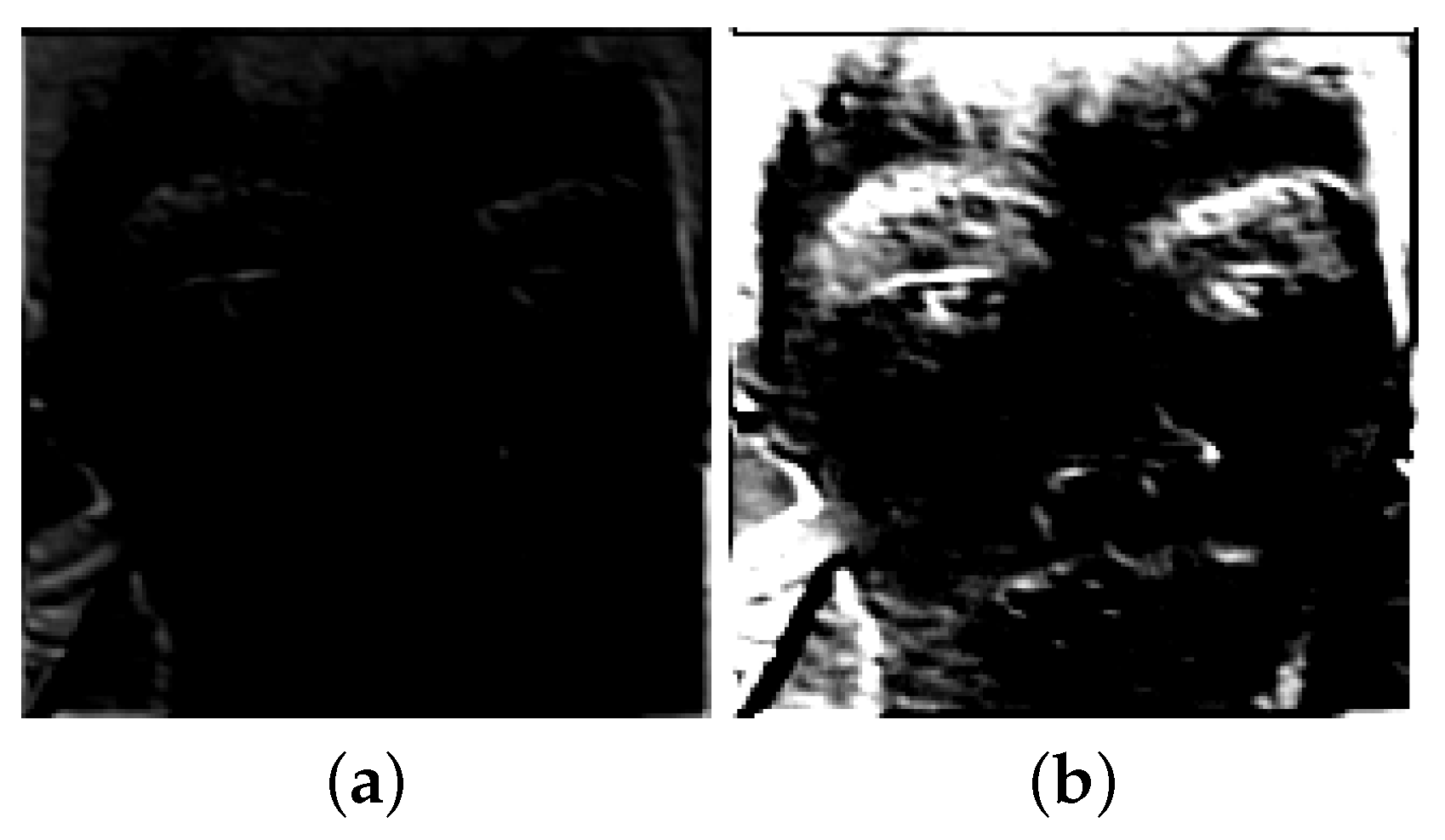
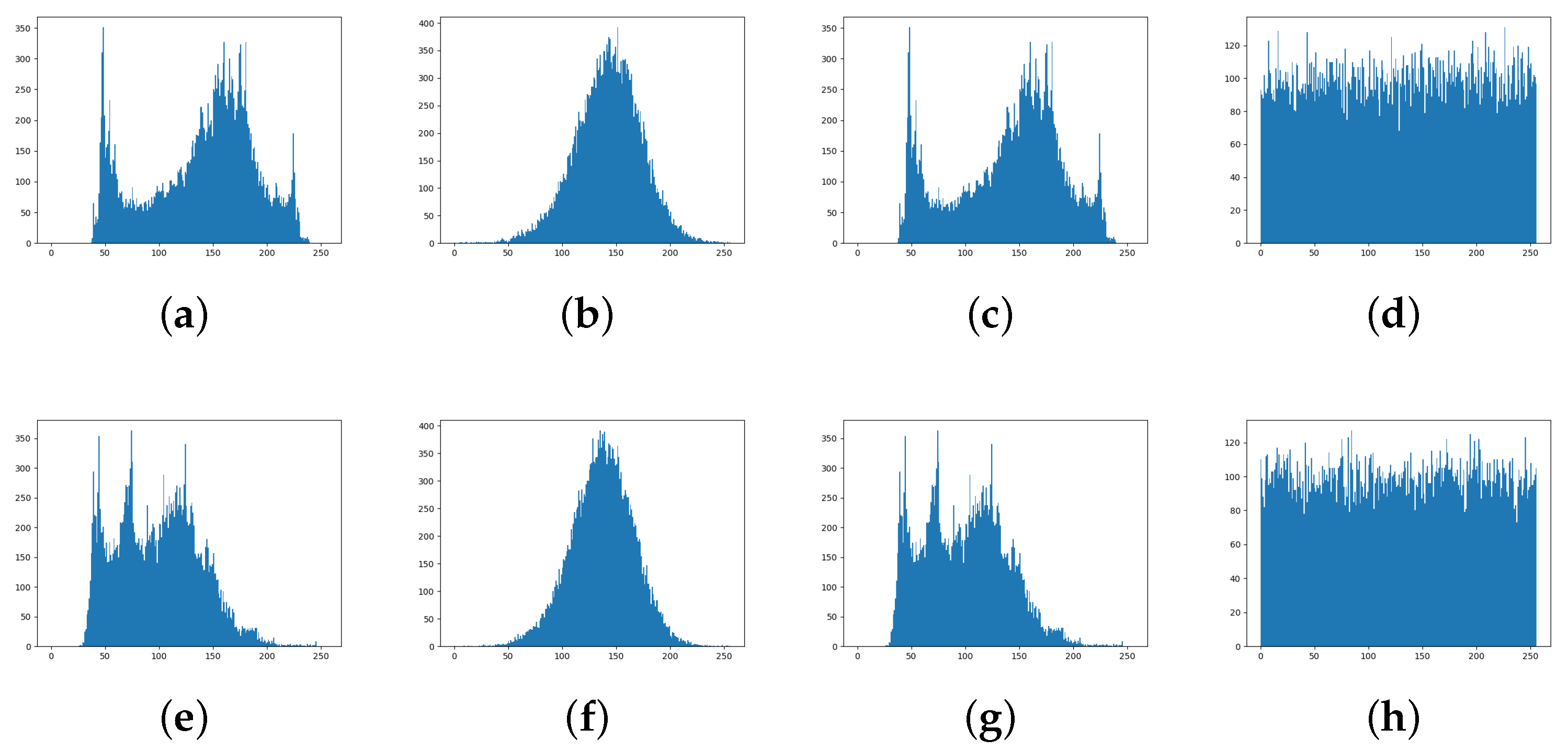
4.3. RLLFPR Fuzzing Performance Test
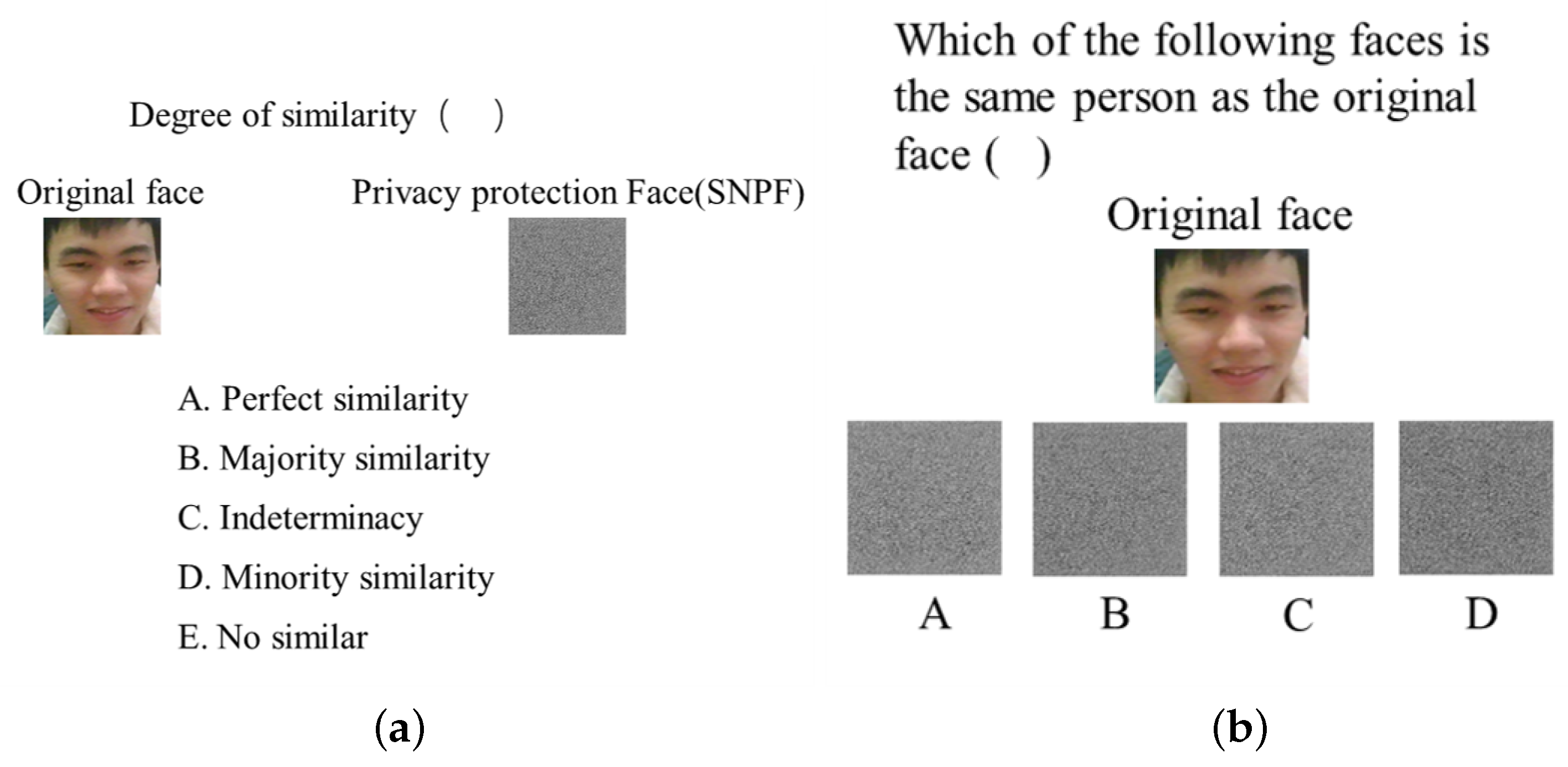
4.3.1. Fuzziness Test Method
4.3.2. Fuzzy Performance of Privacy-Preserving Face Recognition Based on Randomization and Local Feature Learning (RLLFPR)
4.4. Network Structure Ablation Experiment of RLLFPR Method
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boddeti, V.N. Secure face matching using fully homomorphic encryption. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 9th International Conference on Biometrics Theory, Applications and Systems (BTAS), Redondo Beach, CA, USA, 22–25 October 2018; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Shen, W.; Wu, Z. Recognition of face privacy protection using convolutional neural networks. J. Image Graph. 2019, 24, 0744–0752. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, F.; Xu, Y.; Ling, H. Privacy-protective-GAN for privacy preserving face de-identification. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2019, 34, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Li, T.; Li, J.; Shen, C. GMM and CNN hybrid method for short utterance speaker recognition. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 3244–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroff, F.; Kalenichenko, D.; Philbin, J. Facenet: A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 815–823. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Q.; Shen, L.; Xie, W.; Parkhi, O.M.; Zisserman, A. Vggface2: A dataset for recognising faces across pose and age. In Proceedings of the 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), Xi’an, China, 15–19 May 2018; pp. 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Qiao, Y. A discriminative feature learning approach for deep face recognition. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Proceedings, Part VII 14. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 499–515. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Wen, Y.; Yu, Z.; Li, M.; Raj, B.; Song, L. Sphereface: Deep hypersphere embedding for face recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 212–220. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Ji, X.; Gong, D.; Zhou, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, W. Cosface: Large margin cosine loss for deep face recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 5265–5274. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Guo, J.; Xue, N.; Zafeiriou, S. Arcface: Additive angular margin loss for deep face recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 4690–4699. [Google Scholar]
- Meden, B.; Rot, P.; Terhörst, P.; Damer, N.; Kuijper, A.; Scheirer, W.J.; Ross, A.; Peer, P.; Štruc, V. Privacy–enhancing face biometrics: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2021, 16, 4147–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljeraisy, A.; Barati, M.; Rana, O.; Perera, C. Privacy laws and privacy by design schemes for the internet of things: A developer’s perspective. ACM Comput. Surv. (Csur) 2021, 54, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Z.; Li, S.; Qian, Z.; Zhang, X. Reversible privacy-preserving recognition. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Shenzhen, China, 5–9 July 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial networks. Commun. ACM 2020, 63, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korshunova, I.; Shi, W.; Dambre, J.; Theis, L. Fast face-swap using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 3677–3685. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Shi, M.; Chen, K.; Zhang, W. Invertible mask network for face privacy preservation. Inf. Sci. 2023, 629, 566–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, V.; Raschka, S.; Ross, A. PrivacyNet: Semi-adversarial networks for multi-attribute face privacy. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 9400–9412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Li, P.; Min, G.; Li, H. Enhanced Embedded AutoEncoders: An Attribute-Preserving Face De-identification Framework. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 9438–9452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanitha, C.; Malathy, S.; Anitha, K.; Suwathika, S. Enhanced Security using Advanced Encryption Standards in Face Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2021 2nd International Conference on Communication, Computing and Industry 4.0 (C2I4), Bangalore, India, 16–17 December 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Erkin, Z.; Franz, M.; Guajardo, J.; Katzenbeisser, S.; Lagendijk, I.; Toft, T. Privacy-preserving face recognition. In Proceedings of the Privacy Enhancing Technologies: 9th International Symposium, PETS 2009, Seattle, WA, USA, 5–7 August 2009; Proceedings 9. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 235–253. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Zhang, X.; Song, X.; Shao, H.; Wang, Q.; Cui, S.; Russello, G. CryptoMask: Privacy-preserving Face Recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information and Communications Security, Tianjin, China, 18–20 November 2023; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 333–350. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, J.; Ren, K. Lightweight privacy-preserving ensemble classification for face recognition. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 5778–5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boragule, A.; Yow, K.C.; Jeon, M. On-device Face Authentication System for ATMs and Privacy Preservation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 6–8 January 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Im, J.H.; Jeon, S.Y.; Lee, M.K. Practical privacy-preserving face authentication for smartphones secure against malicious clients. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2020, 15, 2386–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Yang, L.X.; Xiang, Y.; Zhong, S. Secure and efficient outsourcing of PCA-based face recognition. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2019, 15, 1683–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Pei, Q.; Wang, Y.; Sun, W.; Liu, X. PRIVFACE: Fast privacy-preserving face authentication with revocable and reusable biometric credentials. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2021, 19, 3101–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, G.; Cao, K.; Lan, X.; Yuen, P.C. Secureface: Face template protection. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2020, 16, 262–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walia, G.S.; Jain, G.; Bansal, N.; Singh, K. Adaptive weighted graph approach to generate multimodal cancelable biometric templates. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2019, 15, 1945–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, A.; Fierrez, J.; Vera-Rodriguez, R.; Tolosana, R. SensitiveNets: Learning agnostic representations with application to face images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 43, 2158–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhao, R.; Wen, W.; Zhu, Y. RAPP: Reversible Privacy Preservation for Various Face Attributes. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2023, 18, 3074–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Kang, J.; Jiang, Q. Semantic key generation based on natural language. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2022, 37, 4041–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Lv, Z.; Kang, J.; Ding, W.; Zhang, J. Fingerprint bio-key generation based on a deep neural network. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2022, 37, 4329–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamikara, M.A.P.; Bertok, P.; Khalil, I.; Liu, D.; Camtepe, S. Privacy preserving face recognition utilizing differential privacy. Comput. Secur. 2020, 97, 101951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ji, J.; Liu, H.; Xu, X.; Ding, S.; Zhou, S. Duetface: Collaborative privacy-preserving face recognition via channel splitting in the frequency domain. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisboa, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 6755–6764. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ji, J.; Zhao, M.; Wu, J.; Xu, X.; Ding, S.; Zhou, S. Privacy-Preserving Face Recognition Using Random Frequency Components. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–3 October 2023; pp. 19673–19684. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.B.; Mattar, M.; Berg, T.; Learned-Miller, E. Labeled faces in the wild: A database forstudying face recognition in unconstrained environments. In Workshop on Faces in ‘Real-Life’ Images: Detection, Alignment, and Recognition; HAL: Lyon, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Qiao, Y. Joint face detection and alignment using multitask cascaded convolutional networks. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 1499–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, M.; Pentland, A. Eigenfaces for recognition. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 1991, 3, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]






| Database | LFW | Celeba | HDU | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methods |
Privacy Protection | Accuracy | Misidentification | F1 | Accuracy | Misidentification | F1 | Accuracy | Misidentification | F1 |
| Original face | No | 99.98 | 0.10 | 99.83 | 99.69 | 0.08 | 99.73 | 99.97 | 0.10 | 99.75 |
| AES | Yes | 0 | ∖ | ∖ | 0 | ∖ | ∖ | 0 | ∖ | ∖ |
| Eigenface [40] | No | 98.93 | 0.45 | 98.88 | 98.41 | 0.52 | 98.41 | 80.39 | 18.90 | 79.61 |
| Arnold [2] | Yes | 99.82 | 0.10 | 99.66 | 98.33 | 0.15 | 98.13 | 90.57 | 9.06 | 89.74 |
| Differential | Yes | 83.73 | 8.77 | 83.61 | 81.68 | 9.31 | 81.98 | <50 | >50 | <50 |
| privacy [33] | ||||||||||
| PartialFace [35] | Yes | 99.80 | 0.15 | 99.67 | 98.73 | 0.24 | 97.91 | 99.34 | 0.78 | 98.94 |
| RLLFPR | Yes | 99.93 | 0.13 | 99.67 | 98.77 | 0.11 | 98.67 | 99.58 | 0.59 | 99.23 |
| Method | Horizontal | Vertical | Diagonal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Original face | 0.9923 | 0.9916 | 0.9829 |
| Arnold | 0.8608 | 0.7548 | 0.9279 |
| AES | −0.0039 | −0.0032 | −0.0007 |
| RLLFPR | −0.0929 | 0.0326 | −0.0795 |
| Method | PSNR | UACI |
|---|---|---|
| Noise | 14.16 | 36.24 |
| Arnold | 11.53 | 53.93 |
| AES | 8.77 | 75.27 |
| RLLFPR | 11.80 | 50.61 |
| Purpose of the Question | Types of Design Problems (Two Groups) | Experimental Group | Control Group (AES) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fuzziness test | Group 1 dissimilarity | 3.51 | 3.55 |
| (0–4, 0 clear, 4 no similarity) | |||
| Group 2 match | 20.90% | 25.35% | |
| (choose 1 from 4, measure accuracy) |
| Method | Privacy Protection | Identification after Protection | Fuzziness2 | Fuzziness3 | Key | Reversibility | Revocability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arnold | Yes | Yes | 0.40–0.70 | 0.996 | No | Reversible | Revocable |
| AES | Yes | No | 0.60–0.90 | 0.999 | Yes | Reversible | Revocable |
| Noise | Yes | Yes | 0.20–0.40 | 0.992 | No | Irreversible | Irrevocable |
| Original face | No | ∖ | 0 | 0 | No | ∖ | Irrevocable |
| RLLFPR | Yes | Yes | 0.80–0.95 | 0.997 | No | Irreversible | Revocable |
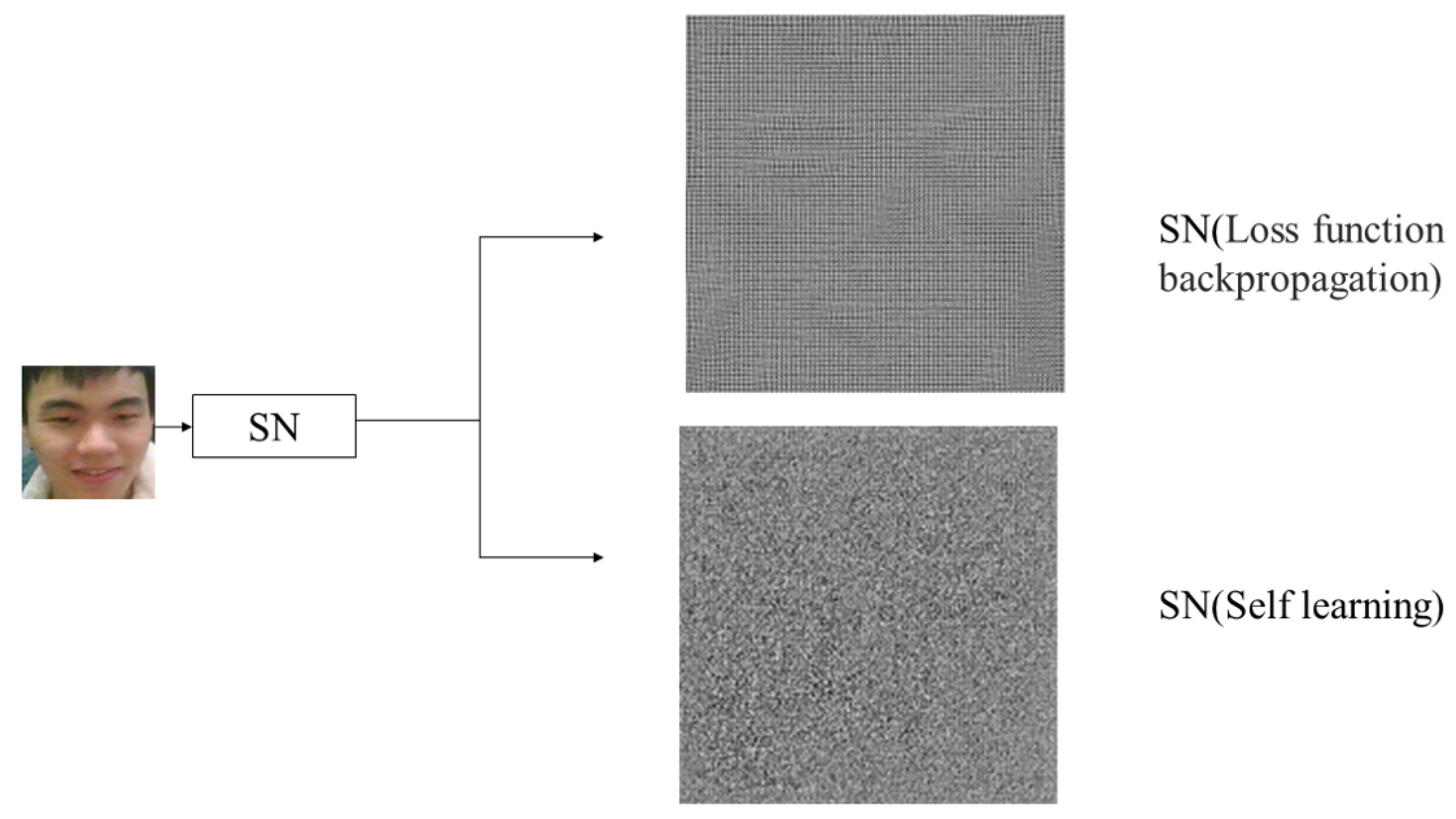
| Fuzziness1 | Fuzziness2 | Fuzziness3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SN (loss function backpropagation) | 2.11 | 0.75–0.95 | 0.983 |
| SN (self-learning) | 3.51 | 0.80–0.95 | 0.997 |
| Accuracy | Misidentification Rate | F1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet50 | 99.93 | 0.13 | 99.67 |
| DenseNet121 | 99.91 | 0.07 | 99.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Chen, J.; Xiang, H. Privacy-Preserving Face Recognition Method Based on Randomization and Local Feature Learning. J. Imaging 2024, 10, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10030059
Huang Y, Wu Z, Chen J, Xiang H. Privacy-Preserving Face Recognition Method Based on Randomization and Local Feature Learning. Journal of Imaging. 2024; 10(3):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10030059
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yanhua, Zhendong Wu, Juan Chen, and Hui Xiang. 2024. "Privacy-Preserving Face Recognition Method Based on Randomization and Local Feature Learning" Journal of Imaging 10, no. 3: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10030059
APA StyleHuang, Y., Wu, Z., Chen, J., & Xiang, H. (2024). Privacy-Preserving Face Recognition Method Based on Randomization and Local Feature Learning. Journal of Imaging, 10(3), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10030059





