Overview of High-Dynamic-Range Image Quality Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Subjective HDR Image Quality Assessment Databases
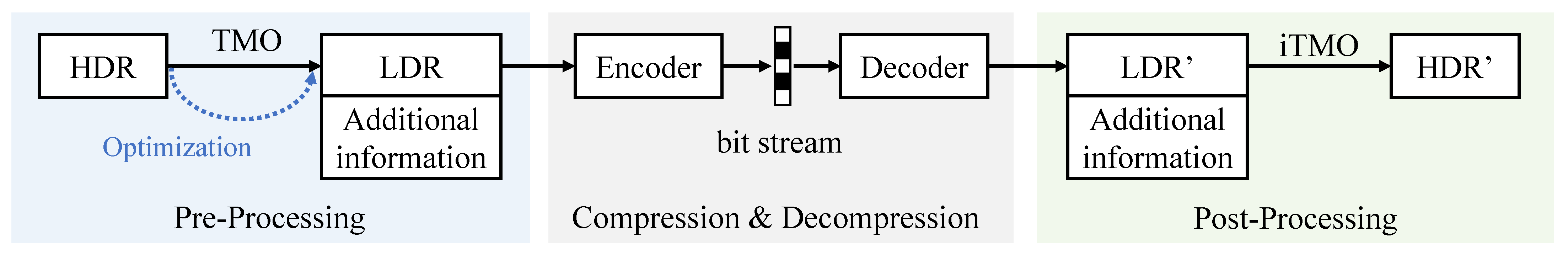
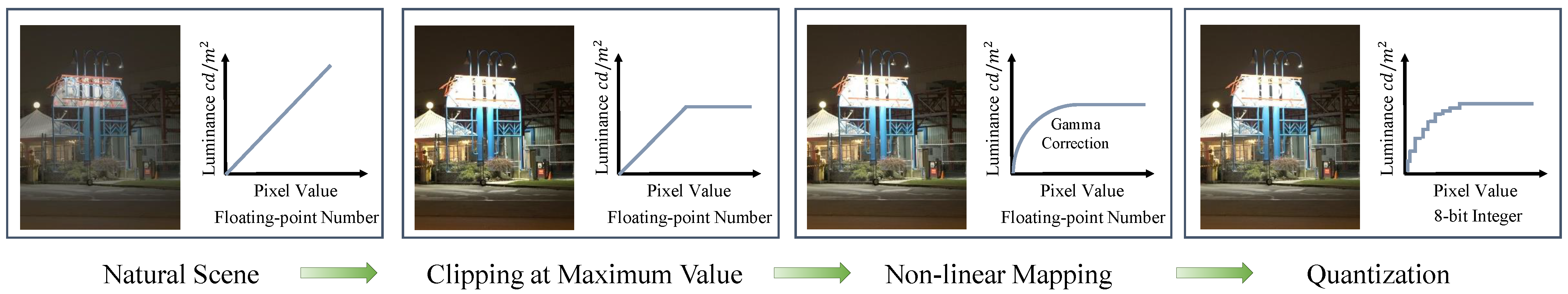
2.1. Existing HDR Image Compression Scheme
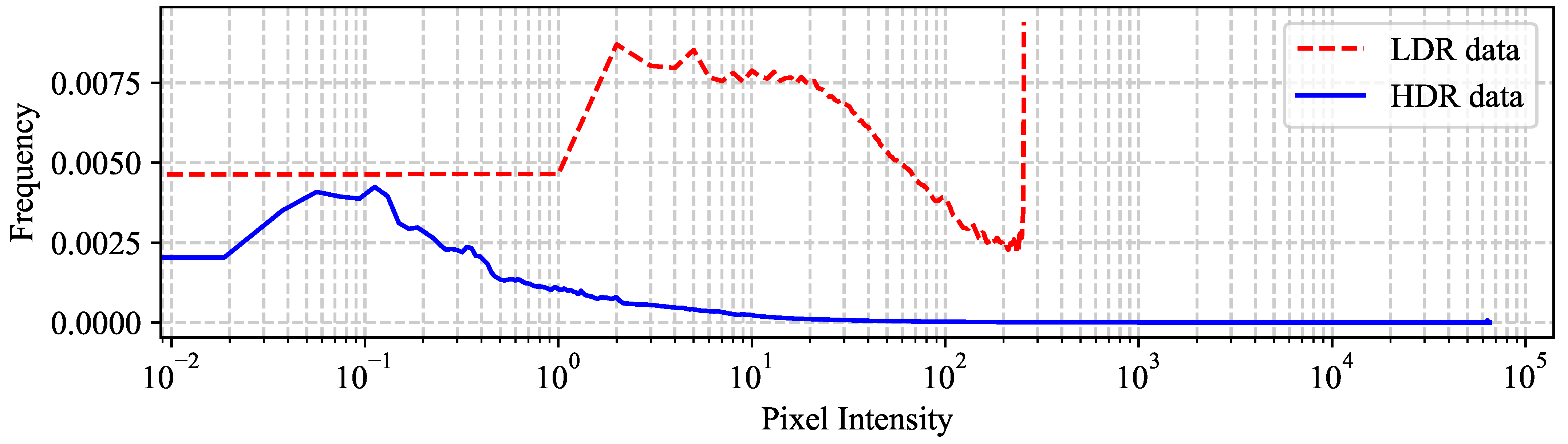
2.2. Existing HDR Databases for Quality Assessment
| Database | #Obs. | #Ref. | #Dis. | Dist. | TMO | Meth. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Narwaria2013 [5] | 27 | 10 | 140 | JPEG | iCAM06 | ACR-HR |
| Narwaria2014 [21] | 29 | 6 | 210 | JPEG2000 | AL, Dur RG, RL Log | ACR-HR |
| Korshunov2015 [6] | 24 | 20 | 240 | JPEG-XT | RG MT [32] | DSIS |
| Valenzise2014 [7] | 15 | 5 | 50 | JPEG JPEG2000 JPEG-XT | Mai | DSIS |
| Zerman2017 [22] | 15 | 5 | 50 | JPEG JPEG2000 | Mai, PQ | DSIS |
| UPIQ [24] (HDR part) | 20 | 30 | 380 | JPEG JPEG-XT | iCAM06 RG MT [32] | - |
| HDRC [26] | 20 | 80 | 400 | JPEG-XT VVC | RG PQ | DSIS |
3. Objective HDR Image Quality Assessment Methods
3.1. HVS-Modeling-Based HDR IQA Methods

3.2. PU-Encoding-Based HDR IQA Methods
| Method | Year | Classification | Major Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDR-VDP-1 [8] | 2005 | Full-Reference | HVS-modeling-based HDR IQA methods |
| DRIM [57] | 2008 | Full-Reference | HVS-modeling-based HDR IQA methods |
| HDR-VDP-2 [9] | 2011 | Full-Reference | HVS-modeling-based HDR IQA methods |
| HDR-VDP-2.2 [40] | 2015 | Full-Reference | HVS-modeling-based HDR IQA methods |
| HDR-VQM [11] | 2015 | Full-Reference | PU-encoding-based HDR IQA methods |
| Kottayil et al. [59] | 2017 | No-Reference | HVS-modeling-based HDR IQA methods |
| Jia et al. [62] | 2017 | No-Reference | PU-encoding-based HDR IQA methods |
| HDR-CQM [13] | 2018 | Full-Reference | Existing IQA metrics based HDR IQA methods |
| PU-PieAPP [24] | 2021 | Full-Reference | PU-encoding-based HDR IQA methods |
| HDR-VDP-3 [10] | 2023 | Full-Reference | HVS-modeling-based HDR IQA methods |
| LGFM [12] | 2023 | Full-Reference | PU-encoding-based HDR IQA methods |
| Cao et al. [14] | 2024 | Full-Reference | Existing IQA-metrics-based HDR IQA methods |
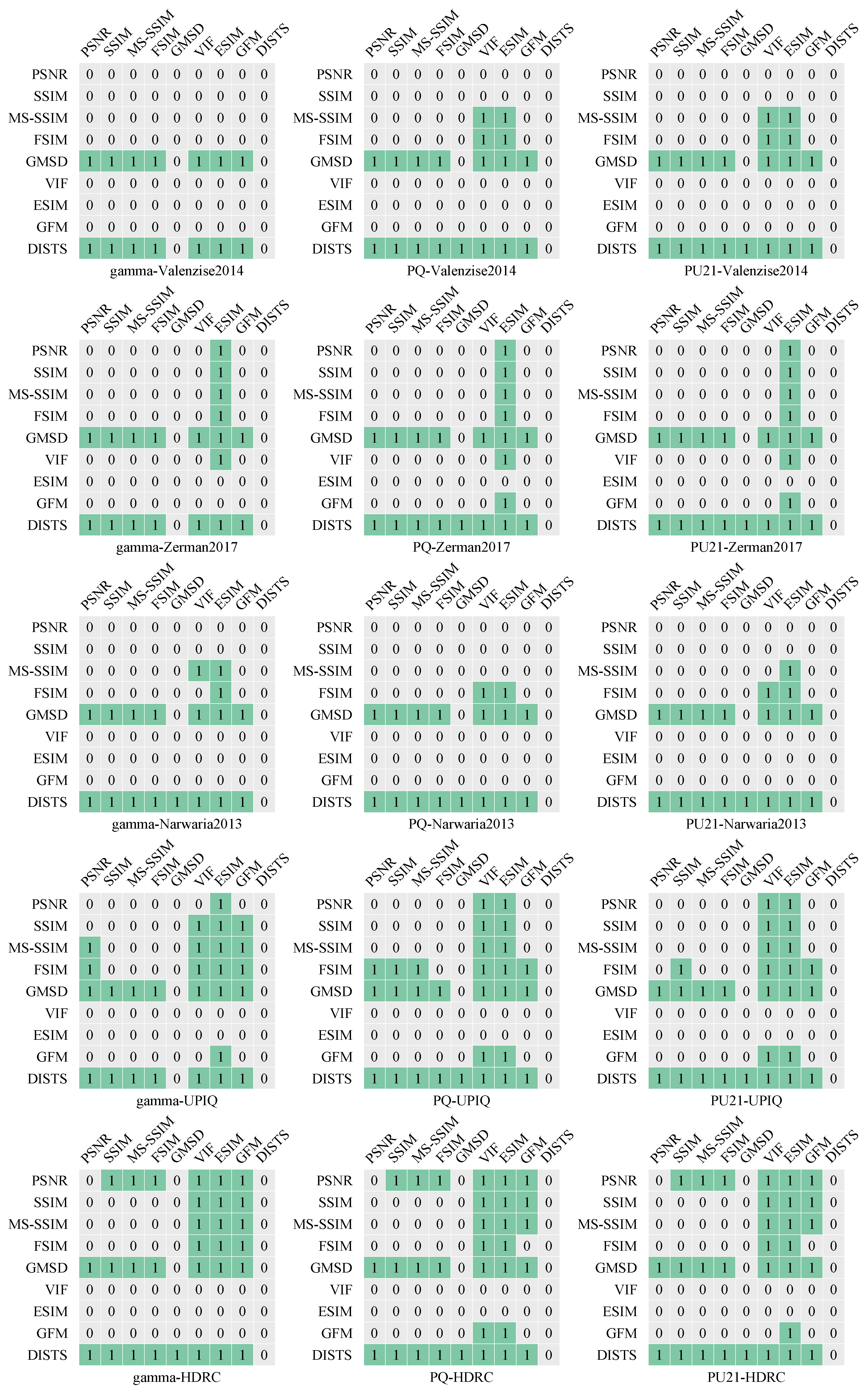
3.3. Existing IQA-Metrics-Based HDR IQA Methods
4. Discussion and Conclusions
4.1. Subjective HDR IQA Databases
4.2. Objective HDR IQA Metrics
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HDR | High Dynamic Range |
| LDR | Low Dynamic Range |
| HVS | Human Visual System |
| IQA | Image Quality Assessment |
| TMO | Tone-Mapping Operator |
| DSIS | Double-Stimulus Impairment Scale |
| ACR-HR | Absolute Category Rating with Hidden Reference |
| CSF | Contrast-Sensitive Function |
| PU | Perceptual Uniform |
| PQ | Perceptual Quantizer |
| HLG | Hybrid-Log-Gamma |
| MOS | Mean Opinion Score |
| VDP | Visual Difference Predictor |
| OTF | Optical Transfer Function |
| DNN | Deep Neural Network |
References
- Metzler, C.A.; Ikoma, H.; Peng, Y.; Wetzstein, G. Deep optics for single-shot high-dynamic-range imaging. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1375–1385. [Google Scholar]
- Shopovska, I.; Stojkovic, A.; Aelterman, J.; Van Hamme, D.; Philips, W. High-Dynamic-Range Tone Mapping in Intelligent Automotive Systems. Sensors 2023, 23, 5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, D.; Gómez, S.; Mauricio, J.; Freixas, L.; Sanuy, A.; Guixé, G.; López, A.; Manera, R.; Marín, J.; Pérez, J.M.; et al. HRFlexToT: A high dynamic range ASIC for time-of-flight positron emission tomography. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2021, 6, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, W.; Xing, J.; Zhang, X.; Tian, H.; Tang, H.; Bi, P.; Li, G.; Zhang, F. Extracting vegetation information from high dynamic range images with shadows: A comparison between deep learning and threshold methods. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 208, 107805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narwaria, M.; Da Silva, M.P.; Le Callet, P.; Pepion, R. Tone mapping-based high-dynamic-range image compression: Study of optimization criterion and perceptual quality. Opt. Eng. 2013, 52, 102008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korshunov, P.; Hanhart, P.; Richter, T.; Artusi, A.; Mantiuk, R.; Ebrahimi, T. Subjective quality assessment database of HDR images compressed with JPEG XT. In Proceedings of the 2015 Seventh International Workshop on Quality of Multimedia Experience (QoMEX), Costa Navarino, Greece, 26–29 May 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Valenzise, G.; De Simone, F.; Lauga, P.; Dufaux, F. Performance evaluation of objective quality metrics for HDR image compression. In Proceedings of the Applications of Digital Image Processing XXXVII, San Diego, CA, USA, 18–21 August 2014; Volume 9217, pp. 78–87. [Google Scholar]
- Mantiuk, R.; Daly, S.J.; Myszkowski, K.; Seidel, H.P. Predicting visible differences in high dynamic range images: Model and its calibration. In Proceedings of the Human Vision and Electronic Imaging X, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–20 January 2005; Volume 5666, pp. 204–214. [Google Scholar]
- Mantiuk, R.; Kim, K.J.; Rempel, A.G.; Heidrich, W. HDR-VDP-2: A calibrated visual metric for visibility and quality predictions in all luminance conditions. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2011, 30, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantiuk, R.K.; Hammou, D.; Hanji, P. HDR-VDP-3: A multi-metric for predicting image differences, quality and contrast distortions in high dynamic range and regular content. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.13625. [Google Scholar]
- Narwaria, M.; Da Silva, M.P.; Le Callet, P. HDR-VQM: An objective quality measure for high dynamic range video. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2015, 35, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ni, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Kwong, S. High dynamic range image quality assessment based on frequency disparity. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 4435–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.; Daly, S. HDR image quality assessment using machine-learning based combination of quality metrics. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP), Anaheim, CA, USA, 26–29 November 2018; pp. 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, P.; Mantiuk, R.K.; Ma, K. Perceptual Assessment and Optimization of HDR Image Rendering. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 22433–22443. [Google Scholar]
- Rousselot, M.; Le Meur, O.; Cozot, R.; Ducloux, X. Quality assessment of HDR/WCG images using HDR uniform color spaces. J. Imaging 2019, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, G.; Simmons, M. JPEG-HDR: A backwards-compatible, high dynamic range extension to JPEG. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2006 Courses; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 3–es. [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama, N.; Kaida, H.; Xue, X.; Jinno, T.; Adami, N.; Okuda, M. HDR image compression using optimized tone mapping model. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Taipei, Taiwan, 19–24 April 2009; pp. 1001–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Artusi, A.; Mantiuk, R.K.; Richter, T.; Hanhart, P.; Korshunov, P.; Agostinelli, M.; Ten, A.; Ebrahimi, T. Overview and evaluation of the JPEG XT HDR image compression standard. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2019, 16, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bross, B.; Wang, Y.K.; Ye, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, J.; Sullivan, G.J.; Ohm, J.R. Overview of the versatile video coding (VVC) standard and its applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 31, 3736–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, A.; Ye, Y.; Kim, S. Algorithm description for Versatile Video Coding and Test Model 16 (VTM 16). Jt. Video Expert. Team (JVET) ITu-T SG 2022, 16, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Narwaria, M.; Da Silva, M.P.; Le Callet, P.; Pépion, R. Impact of tone mapping in high dynamic range image compression. In Proceedings of the VPQM, Chandler, AZ, USA, 30–31 January 2014; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Zerman, E.; Valenzise, G.; Dufaux, F. An extensive performance evaluation of full-reference HDR image quality metrics. Qual. User Exp. 2017, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.; Nezamabadi, M.; Daly, S. Perceptual signal coding for more efficient usage of bit codes. SMPTE Motion Imaging J. 2013, 122, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailiuk, A.; Pérez-Ortiz, M.; Yue, D.; Suen, W.; Mantiuk, R.K. Consolidated dataset and metrics for high-dynamic-range image quality. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 24, 2125–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Ortiz, M.; Mikhailiuk, A.; Zerman, E.; Hulusic, V.; Valenzise, G.; Mantiuk, R.K. From pairwise comparisons and rating to a unified quality scale. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 29, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ni, Z.; Chen, P.; Wang, S.; Kwong, S. HDRC: A subjective quality assessment database for compressed high dynamic range image. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2024, 15, 4373–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, J.; Johnson, G.M.; Fairchild, M.D. iCAM06: A refined image appearance model for HDR image rendering. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2007, 18, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ITU. Video Quality Assessment Methods for Multimedia Applications. ITU-T Recommendation P.910. 2008. Available online: https://www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-P.910-202310-I/en (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- Available online: https://hdr.sim2.it/ (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- Narwaria, M.; Lin, W.; McLoughlin, I.V.; Emmanuel, S.; Chia, L.T. Fourier transform-based scalable image quality measure. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 21, 3364–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantiuk, R.; Myszkowski, K.; Seidel, H.P. A perceptual framework for contrast processing of high dynamic range images. ACM Trans. Appl. Percept. (TAP) 2006, 3, 286–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhard, E.; Stark, M.; Shirley, P.; Ferwerda, J. Photographic tone reproduction for digital images. ACM Trans. Graph. 2002, 21, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, F.; Dorsey, J. Fast bilateral filtering for the display of high-dynamic-range images. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, San Antonio, TX, USA, 23–26 July 2002; pp. 257–266. [Google Scholar]
- Ashikhmin, M. A tone mapping algorithm for high contrast images. In Proceedings of the 13th Eurographics workshop on Rendering, Pisa, Italy, 26–28 June 2002; pp. 145–156. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, T. On the standardization of the JPEG XT image compression. In Proceedings of the 2013 Picture Coding Symposium (PCS), San Jose, CA, USA, 8–11 December 2013; pp. 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- ITU. Methodology for the Subjective Assessment of the Quality of Television Pictures. ITU-R Recommendation BT.500. 2002. Available online: https://www.itu.int/rec/R-REC-BT.500-15-202305-I/en (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- Mai, Z.; Mansour, H.; Mantiuk, R.; Nasiopoulos, P.; Ward, R.; Heidrich, W. Optimizing a Tone Curve for Backward-Compatible High Dynamic Range Image and Video Compression. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 1558–1571. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aydın, T.O.; Mantiuk, R.; Seidel, H.P. Extending quality metrics to full luminance range images. In Proceedings of the Human Vision and Electronic Imaging Xiii, San Jose, CA, USA, 28–31 January 2008; Volume 6806, pp. 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Narwaria, M.; Mantiuk, R.K.; Da Silva, M.P.; Le Callet, P. HDR-VDP-2.2: A calibrated method for objective quality prediction of high-dynamic range and standard images. J. Electron. Imaging 2015, 24, 010501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurstone, L.L. A law of comparative judgment. In Scaling; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Z.; Yuan, F.; Lei, J.; Fang, Y.; Shao, X.; Kwong, S. VCRNet: Visual compensation restoration network for no-reference image quality assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 1613–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, K.; Ma, K.; Wang, S.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: Unifying structure and texture similarity. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 2567–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, B.; Kwong, S. Causal Representation Learning for GAN-Generated Face Image Quality Assessment. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 7589–7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ding, K.; Yang, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, S. Opinion-Unaware Blind Image Quality Assessment using Multi-Scale Deep Feature Statistics. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024. early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, L.; Wang, S.; Kwong, S. Deep Feature Statistics Mapping for Generalized Screen Content Image Quality Assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2024, 33, 3227–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, B.; Chen, B.; Wang, M.; Wang, S.; Lin, W. Perceptual quality assessment of face video compression: A benchmark and an effective method. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 8596–8608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wu, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, B.; Zhu, L.; Fang, Y.; Zhai, G.; Lin, W.; Wang, S. Adaptive Image Quality Assessment via Teaching Large Multimodal Model to Compare. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.19298. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Chen, B.; Wang, S.; Kwong, S. Towards Thousands to One Reference: Can We Trust the Reference Image for Quality Assessment? IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 26, 3278–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Li, D.; Pan, Z.; Sun, Z.; Kwong, S.; Hou, C. Fast intra prediction based on content property analysis for low complexity HEVC-based screen content coding. IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 2016, 63, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Kwong, S.; Chang, Y.; Ren, Q. Consensus unsupervised feature ranking from multiple views. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2008, 29, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanji, P.; Mantiuk, R.; Eilertsen, G.; Hajisharif, S.; Unger, J. Comparison of single image HDR reconstruction methods—the caveats of quality assessment. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 Conference Proceedings, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–11 August 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Daly, S.J. Visible differences predictor: An algorithm for the assessment of image fidelity. In Proceedings of the Human Vision, Visual Processing, and Digital Display III, San Jose, CA, USA, 10–13 February 1992; Volume 1666, pp. 2–15. [Google Scholar]
- Deeley, R.J.; Drasdo, N.; Charman, W.N. A simple parametric model of the human ocular modulation transfer function. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 1991, 11, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockman, A.; Sharpe, L.T. The spectral sensitivities of the middle-and long-wavelength-sensitive cones derived from measurements in observers of known genotype. Vis. Res. 2000, 40, 1711–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikh, H.R.; Sabir, M.F.; Bovik, A.C. A statistical evaluation of recent full reference image quality assessment algorithms. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2006, 15, 3440–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, T.O.; Mantiuk, R.; Myszkowski, K.; Seidel, H.P. Dynamic range independent image quality assessment. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2008, 27, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, A. The cortex transform- Rapid computation of simulated neural images. Comput. Vision Graph. Image Process. 1987, 39, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottayil, N.K.; Valenzise, G.; Dufaux, F.; Cheng, I. Blind quality estimation by disentangling perceptual and noisy features in high dynamic range images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 27, 1512–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinson, M.H.; Wolf, S. An objective method for combining multiple subjective data sets. In Proceedings of the Visual Communications and Image Processing 2003, Lugano, Switzerland, 8–11 July 2003; Volume 5150, pp. 583–592. [Google Scholar]
- Field, D.J. Relations between the statistics of natural images and the response properties of cortical cells. JOSA A 1987, 4, 2379–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, S.; Zhang, Y.; Agrafiotis, D.; Bull, D. Blind high dynamic range image quality assessment using deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Beijing, China, 17–20 September 2017; pp. 765–769. [Google Scholar]
- Prashnani, E.; Cai, H.; Mostofi, Y.; Sen, P. Pieapp: Perceptual image-error assessment through pairwise preference. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 1808–1817. [Google Scholar]
- Mantiuk, R.K.; Azimi, M. PU21: A novel perceptually uniform encoding for adapting existing quality metrics for HDR. In Proceedings of the 2021 Picture Coding Symposium (PCS), Bristol, UK, 29 June–2 July 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Mantiuk, R.K.; Kim, M.; Ashraf, M.; Xu, Q.; Luo, M.R.; Martinovic, J.; Wuerger, S. Practical Color Contrast Sensitivity Functions for Luminance Levels up to 10000 cd/m2. In Proceedings of the Color and Imaging Conference. Society for Imaging Science & Technology, Online, 4–19 November 2020; Volume 28, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Borer, T.; Cotton, A. A display-independent high dynamic range television system. SMPTE Motion Imaging J. 2016, 125, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q. Hdr-nerf: High dynamic range neural radiance fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 18398–18408. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Dong, C. Hdrunet: Single image hdr reconstruction with denoising and dequantization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 354–363. [Google Scholar]
- Catley-Chandar, S.; Tanay, T.; Vandroux, L.; Leonardis, A.; Slabaugh, G.; Pérez-Pellitero, E. Flexhdr: Modeling alignment and exposure uncertainties for flexible hdr imaging. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 5923–5935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, S.S. On the psychophysical law. Psychol. Rev. 1957, 64, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.S.; Tsang, R.; Khademi Kalantari, N. Single Image HDR Reconstruction Using a CNN with Masked Features and Perceptual Loss. ACM Trans. Graph. 2020, 39, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, Z.; Chan, T.N.; Li, H.; Hou, J.; Chau, L.P. Attention-guided progressive neural texture fusion for high dynamic range image restoration. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 2661–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanhart, P.; Bernardo, M.V.; Pereira, M.; Pinheiro, A.M.G.; Ebrahimi, T. Benchmarking of objective quality metrics for HDR image quality assessment. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2015, 2015, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudil, P.; Novovičová, J.; Kittler, J. Floating search methods in feature selection. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 1994, 15, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.; Mantiuk, R.K.; Chapiro, A.; Wuerger, S. castleCSF—A contrast sensitivity function of color, area, spatiotemporal frequency, luminance and eccentricity. J. Vis. 2024, 24, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, W.; Zhang, L.; Mou, X.; Bovik, A.C. Gradient magnitude similarity deviation: A highly efficient perceptual image quality index. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 23, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Simoncelli, E.P.; Bovik, A.C. Multiscale structural similarity for image quality assessment. In Proceedings of the Thrity-Seventh Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems & Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 9–12 November 2003; Volume 2, pp. 1398–1402. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Mou, X.; Zhang, D. FSIM: A feature similarity index for image quality assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 2378–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, H.R.; Bovik, A.C.; De Veciana, G. An information fidelity criterion for image quality assessment using natural scene statistics. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2005, 14, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Ma, L.; Zeng, H.; Chen, J.; Cai, C.; Ma, K.K. ESIM: Edge similarity for screen content image quality assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 4818–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Zeng, H.; Ma, L.; Hou, J.; Chen, J.; Ma, K.K. A Gabor feature-based quality assessment model for the screen content images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 4516–4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.U.; Nizami, I.F.; Majid, M.; Ullah, F.; Hussain, I.; Chong, K.T. CN-BSRIQA: Cascaded network-blind super-resolution image quality assessment. Alex. Eng. J. 2024, 91, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerdvibulvech, C.; Li, Q. Empowering Zero-Shot Object Detection: A Human-in-the-Loop Strategy for Unveiling Unseen Realms in Visual Data. In Proceedings of the Digital Human Modeling and Applications in Health, Safety, Ergonomics and Risk Management; Duffy, V.G., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 235–244. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, W.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Ma, S.; Gao, W. Fine-grained quality assessment for compressed images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 28, 1163–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaswani, A. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Alexey, D. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, F.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, Z. An effective CNN and Transformer complementary network for medical image segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 136, 109228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, C.; Deng, Y.; Xie, B.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.F. TransIFC: Invariant cues-aware feature concentration learning for efficient fine-grained bird image classification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023. early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Kwong, S. Overview of High-Dynamic-Range Image Quality Assessment. J. Imaging 2024, 10, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10100243
Liu Y, Tian Y, Wang S, Zhang X, Kwong S. Overview of High-Dynamic-Range Image Quality Assessment. Journal of Imaging. 2024; 10(10):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10100243
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yue, Yu Tian, Shiqi Wang, Xinfeng Zhang, and Sam Kwong. 2024. "Overview of High-Dynamic-Range Image Quality Assessment" Journal of Imaging 10, no. 10: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10100243
APA StyleLiu, Y., Tian, Y., Wang, S., Zhang, X., & Kwong, S. (2024). Overview of High-Dynamic-Range Image Quality Assessment. Journal of Imaging, 10(10), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10100243






