Abstract
The utilization of waste generated from industrial production is a burden to overcome for society to reach a circular economy. Usually, production waste is associated with low-quality materials compared to its natural counterparts. In some cases, high-purity materials are generated, while different hazardous substances such as heavy metals, radioactive elements, or organic chemical substances are pollutants that often limit the materials’ further application. One such material that has accumulated for decades is phosphogypsum (PG). The extraction of fertilizers from metamorphous rocks results in large quantities of PG. Until now, PG has been deposited in large stockpiles near the production plant, causing problems for the environment in the surrounding area. However, the chemical composition of PG places it as a high-purity artificial gypsum material, which means that it could be used as a substitution or supplementary material in gypsum-based material production. The concerns, with respect to both legislation and prevailing prejudices in society, about its impurities strongly limit its application. This manuscript reviews current research practices for the effective use of PG and analyzes the importance of the circular economy. A life cycle assessment of current state-of-the-art technologies regarding PG application is proposed.
1. Practice of Circular Economy in the Gypsum Industry
According to the Waste and Resources Action Programme, the circular economy is a concept of transition from the linear “take–make–dispose” model to the optimization of resource utilization by prolonging operational life [1]. The objective is to extract the maximum value from resources through extensive use, fostering a systematic approach that mitigates the adverse environmental effects associated with resource depletion and waste disposal. Circular economy principles are gaining momentum within the communities of practitioners and scholars, exerting influence on extractive industries to transition from a linear economic model to a more circular one. The inherent challenges in the mining sector make this shift particularly demanding. Circular economy approaches in mining primarily emphasize a reduction in natural resource extraction and residual waste, with a notable emphasis on managing waste and byproducts, including mine tailings [2,3]. In contemporary times, policies and business strategies place a strong emphasis on sustainable development, with a particular focus on the principles of the circular economy. This approach extends to addressing the challenges associated with waste and secondary materials, e.g., phosphogypsum (PG) in civil engineering. Gypsum is a traditional building material with vast applications and acceptance in the building industry. The European gypsum industry boasts a substantial financial turnover, estimated at approximately EUR 7.7 billion. This industry’s operations span 154 quarries and 160 plants, directly employing 28,000 individuals while indirectly fostering employment for an additional 300,000 individuals [4]. According to the Study on the Critical Raw Materials for EU 2023, gypsum is extracted in 11 European countries. The largest volumes were extracted in Spain (45%), Germany (19%), and France (11%), while a notable amount was also extracted in Latvia (1%) [5].
Natural gypsum is an infinitely recyclable material due to its simple chemical formulation and low treatment temperature requirement for obtaining binder material. Gypsum is a vastly available material with relatively low production costs; thus, there is a high amount of waste gypsum at the end of the life cycle. As gypsum consumption in civil engineering is high, the gypsum sector contributes approximately 1% to the overall volume of construction and demolition waste (CDW). To represent trends in the EU, in Portugal, it has been approximated that, on average, each standalone house covering 186 m2 contains roughly 1021 kg of gypsum drywall, which has the potential to be classified as CDW after demolition [6]. Because gypsum is a widespread naturally deposited mineral material around the world, the recycling of gypsum has not been a critical concern until now. However, the disposal of gypsum CDW in landfills results in the production of hydrogen sulfide gas through the anaerobic breakdown of gypsum residues, giving rise to environmental concerns [7]. Thus, the recycling of gypsum CDW is imperative for society to address. The European Union’s target for recycling gypsum within CDW, as established by its 27 member states, stands at 70% [8].
Until now, it has been possible to segregate and gather plasterboard CDW at a construction site, and, upon processing, approximately 20 to 30% of recycled gypsum can be incorporated into the manufacture of new plasterboards. In 2019, as much as 600,000 metric tons of recycled gypsum was employed in the production of plasterboard [9]. This approach allows gypsum CDW to serve as a secondary raw material, replacing more than 30% of natural gypsum in plasterboard production [10]. Suárez and colleagues found that processing recycled gypsum requires 65% less energy compared to natural gypsum [11]. An environmental impact assessment reveals that the use of recycled gypsum offers advantages even when compared to FGD gypsum from coal-fired power plants and natural gypsum. However, the study also highlights that the specific transportation distance significantly influences the results. Haneklaus et al. investigated the historical EU gypsum market and forecast potential demand for 2030 [12]. They underlined that “undisputed is the fact that there will be a gypsum gap in the EU”. Following the good practice of CDW gypsum recycling, the opportunity has opened for other gypsum waste stream materials. One of the most concerning materials that requires effective recycling and circularity is PG.
2. Burdens of Phosphogypsum in the Circular Economy
PG is a byproduct of the phosphate fertilizer industry and is generated as a result of the sulfuric acid treatment of phosphate rock. When natural phosphate raw material (apatite or phosphorite) is treated with sulfuric acid, a reaction takes place [13]:
Ca5(PO4)3F + 5H2SO4 + 5nH2O = 5CaSO4∙nH2O + HF + 3H3PO4,
The production of phosphoric acid involves two processes: the dissolution of the phosphate raw material in a mixture of sulfuric and phosphoric acids (which is formed during the process) and the crystallization of calcium sulfate. This means that, to obtain 1 kg of P2O5, about 4.5–5 kg of PG is produced [14]. Depending on the process conditions, i.e., depending on the concentration, temperature, and composition of raw phosphate materials and impurities, the solid phase of calcium sulfate could come in three forms:
- Dihydrate gypsum, CaSO4∙2H2O;
- Hemihydrate gypsum, CaSO4∙0.5H2O;
- Anhydrous gypsum (anhydrite), CaSO4;
Approximately 300 million metric tons of PG is generated annually [15]. The current cumulative global PG generation is about 6 billion tons. It is assumed that, by 2045, the total amount of PG will be twice as high [16]. In Lithuania alone, PG has been transported to landfills for many years, and now, about 45 million tons has accumulated. The other possible “utilization” of PG described in the literature for end-of-life PG scenarios is to dump it into the sea [17]. Both of these options cause many negative impacts on the environment. This poses important challenges and highlights the need to find effective solutions for the management of this byproduct (see Figure 1). Finding innovative uses for it, such as in construction materials, in soil amendments, or even as a raw material for other processes, could contribute to a more sustainable and circular approach by closing the loop and minimizing waste.

Figure 1.
Phosphogypsum end-of-life scenarios.
According to the information provided by Wang et. al, only about 15% of PG is recycled, and the rest (85%) is mostly disposed of in landfills [16]. It has been pointed out that the number of tons accumulated in PG landfills can have dangerous consequences for the environment. Potential problems include the leaching of chemicals into soil or water, which can have negative effects on the ecosystem, plants, animals, and human health.
According to the content of the main substance—calcium sulfate—PG corresponds to the raw material of the highest type of natural gypsum (91–95%) [18,19]. In addition to the main calcium sulfate component, PG contains various impurities. Many scientists have found that most PG impurities consist of phosphates that are mostly soluble in water, i.e., free orthophosphoric acid H3PO4 and calcium tetrahydrogen phosphate CaHPO4∙2H2O. They are usually expressed as the amount of P2O5 that is soluble in water. Water-soluble fluorine exists in the form of hydrofluoric acids HF and H2SiF6. There are also unreacted phosphate raw materials such as Ca(H2PO4)2∙H2O, H2SO4, NaF, CaF2, iron, aluminum, and rare-earth element salts [20,21,22]. In addition, wet processing causes the selective separation of natural radium (Ra), uranium (U), and thorium (Th). About 80% of 226Ra is concentrated in PG, and almost 86% of U and 70% of Th enter phosphoric acid [23]. The amounts of impurities depend on the degree of leaching of PG on the carousel vacuum filter. The impurities are known to coat calcium sulfate crystals and slow down their dissolution rate. Some impurities are embedded in the framework of calcium sulfate crystals [24,25]. Therefore, due to health and safety concerns, for now, the utilization rate of PG is low [16].
Despite the known limitations and possible concerns, research on PG has gained significant attention due to environmental and economic considerations. Some of the current research directions and areas of interest in relation to PG are associated with environmental impact mitigation. One of the primary research areas focuses on finding sustainable and environmentally friendly ways to manage and utilize PG. Utilization and recycling using various applications for PG to reduce waste and environmental concerns include using PG in construction materials, as a soil conditioner, or as a source of calcium for various industrial processes. Radioactivity management is often considered the top concern in PG applications. PG is a naturally occurring radioactive material (NORM) and can contain radionuclides, necessitating research on the safe handling, transportation, and disposal of this byproduct while managing its radioactivity effectively [23]. Different approaches have been adapted with respect to safely using PG in the production of building materials. Chemical and physical properties have been determined to understand the properties of PG, which are essential for its effective utilization. Research is ongoing to characterize these properties and assess how they impact their suitability for different applications. Innovations in processing techniques are being explored to improve the quality of PG and reduce impurities. This may involve methods for recovering valuable components or altering their composition to render them more suitable for specific applications.
There are several main research topics relating to the utilization of PG. PG could be a raw material for cement and gypsum binders, but the quality of PG deteriorates the properties of the binders due to the relatively large amounts of acid-soluble impurities, which limits its use. Soluble phosphates prolong the hydration of gypsum and reduce the compressive strength of gypsum specimens [26]. Impurities change the morphology of CaSO4∙2H2O crystals, resulting in irregular crystal shapes that adversely affect strength [27]. On the other hand, phosphate impurities affect the solidification/hardening and mechanical properties of gypsum-based materials. In particular, lattice-bound phosphorus (CaHPO4·2H2O) is the most difficult to remove [24,25]. Acidic impurities are also the main cause of long setting times and the low early strength of cement [28]. Both globally and in Lithuania, where large PG stockpiles are produced and stored, substantial research has been carried out with respect to solving the problem of neutralizing these harmful impurities. The following methods are most often used to remove or decontaminate impurities in PG:
- Washing PG with water [29,30];
- Washing PG with water while neutralizing impurities in an aqueous suspension [13,30,31,32];
- Thermal treatment [14,21,33,34];
- Use of various neutralizing, mineralizing, and crystallization-regulating additives [26,35,36].
Legislation and regulation are important for the legal and regulatory aspects of PG management. These include investigating and recommending guidelines for safe handling, storage, and disposal, as well as limiting radioactivity. Research on the health and safety aspects of working with PG and potential exposure to its constituents is important to ensure the wellbeing of workers and nearby communities. Research into the economic feasibility of using PG in various industries and applications is also a crucial area of interest. Understanding the costs and benefits of its use compared to alternative materials is essential.
3. Current State of the Art in Phosphogypsum Research
In a thorough literature review comprising 153 articles, Bourgane et al. examined various aspects of PG recycling and valorization technologies [37]. The review covered different treatment and purification methods, as well as techno-economic, life cycle, and environmental assessments associated with PG recycling. Furthermore, the review delved into recent technologies focused on extracting rare-earth elements from PG. Different authors mostly focus on the physical and chemical characteristics of PG and its combination with other materials. For example, Oumnih et al. investigated the effects of raw bentonite, PG waste, and lime on the properties of cementitious materials through various tests [38]. Bituh et al. summarized the availability of PG recycling and assessed opportunities for using PG in Croatia [39]. Gabsi et al. conducted a study in Tunisia that focused on assessing the application of PG in various crops over two consecutive years in degraded soil areas [40]. The research outcomes revealed that incorporating organic manure amendments and PG positively influenced the germination rates of different crops under investigation. Notably, the highest crop yield was observed when the maximum dose of PG was applied. Similarly, Outbakat et al. investigated soil physical properties in Morocco and found that “PG application improved soil structure by promoting flocculant action provided by calcium” [41]. The study conducted by Majdoubi et al. suggests that geopolymer–PG composites have the potential to serve as effective and sustainable alternatives to traditional building materials [42]. The findings propose that these composites could be applied not only in construction but also in various industrial contexts, showcasing their versatility. Bilal et al. studied the results of 67 industrial storage facilities around the world and concluded that newly produced PG should not be considered as waste but can and should be recycled, thus remaining a part of the circular economy [43]. Simultaneously, large amounts of stored PG can be recycled to significantly reduce the extraction of raw materials, thus closing the loop and returning resources. According to Tsioka and Voudrias, utilizing life cycle assessment (LCA) proves to be a valuable approach for evaluating and comparing different PG waste valorization methods within the circular economy framework [44]. They compared alternative management methods for PG waste and found that utilizing PG waste as a substitute for sand and clay in brick production results in greater environmental impact compared to the traditional brick production method. Consequently, this approach is not recommended due to its higher environmental footprint.
3.1. Application of Phosphogypsum as a Hemihydrate Gypsum Binder
The dihydrate PG is often proposed as a substitution for traditional gypsum binders. XRD analyses have been used to describe its mineralogical composition and its transformation during heat treatment between 100 and 180 °C [45]. Technological properties such as fineness, consistency (water–binder (W/B) ratio), set time, and strength are usually described. This is a traditional gypsum production range that is typically researched in the scientific literature. The presence of water plays a pivotal role in various aspects of binder performance, influencing factors such as workability in fresh paste, the hydration process, porosity, mechanical strength, and material durability. A comprehensive overview of the relationship between the W/B ratio in gypsum-based binders and the properties of the resulting hardened gypsum binder, delineating the boundaries of properties affected by the W/B ratio, was carried out by the authors. The W/B ratios can range from 0.3 to 1.15 [46]. To reduce the negative effects of impurities and compensate for the fineness of PG, additives and chemical admixtures such as slaked lime or plasticizers are used. The findings reveal that higher heat-treatment temperatures for PG reduce the time required for the conversion of PG into hemihydrate, and they slightly extend the initial setting time of the resulting binder. The addition of plasticizer results in a reduction in the water–PG ratio from 0.80 to 0.43. As the water content changes, the bulk density of PG binders ranges from 726 to 1600 kg/m3, with total porosity varying from 35% to 71%. The early-age (2 h) strength of the binder ranged from 0.1 to 15 MPa, and, after 14 days of hardening, it reached 2.5 to 29 MPa. These results are promising considering the potential utilization of PG as a secondary raw material for binder production. Another novel research direction with respect to PG binders advises the inclusion of a pore-forming agent, which allows for the creation of ultra-porous gypsum materials, resulting in bulk densities spanning from 213 to 726 kg/m3, total porosities from 67.9% to 90.6%, and strength values from 0.1 to 0.8 MPa. Such materials provide high-added-value products, such as insulation and fire-proofing materials.
3.2. Pressed Phosphogypsum Building Blocks
The utilization of PG in building products can improve the properties of the final product when novel processing methods are applied during manufacturing. Some of the main methods are further reviewed. The press-forming processing of PG specimens has been explored by various authors. The main advantage of this method is that it results in more compact and strong PG products. However, there is an important disadvantage: press forming permits a lower proportion of mixing water than that usually employed in the specimens produced via simple casting. If the PG mixture contains too much water, press-forming pressure would cause it to “escape” the mixture, thus damaging the microstructure and mechanical properties of specimens. However, when a lower amount of water is included, the resulting specimens are poorly hydrated. In several studies by Zhou et al., the team was able to successfully address this water shortage issue by adopting various strategies. In an initial study, a so-called “hydration–recrystallization” process was applied [46]. This process consisted of creating some initial “green bricks” through press forming, which were hot-dried at 180 °C to convert the di-hydrate gypsum into a hemihydrate phase. Subsequently, these bricks were immersed in water for a brief period, resulting in the secondary hydration (recrystallization) of calcium sulfate and improving the hydration degree and mechanical properties of the cured specimens. In this manner, the optimal recipe was found to be 75 wt.% PG, 19.5 wt.% river sand, 4.0 wt.% OPC, and 1.2 wt.% hydrated lime, and the compressive and flexural strengths were found to be 21.87 MPa and 5.2 MPa, respectively.
Another study investigated an alternative PG specimen press-forming method and called it “the two-step hydration process” [47]. The process consisted of creating specimens through press forming and, after 1 d of curing, immersing them in water for 0.5 h (for secondary hydration); then, they were naturally cured for a determined time period. In this case, the optimal mixture was found to be 25 wt.% PG, 23.47 wt.% river sand, and 1.53 wt.% hydrated lime, with a 7-day compressive strength of 29 MPa, which is a remarkably high value that is comparable to concrete. It should be noted that no OPC was included in the mixture; thus, this solution is ecologically friendly.
Fornes et al. thoroughly investigated the previously mentioned “two-step hydration process” in subsequent publications by studying the dependence of the compressive strength of PG specimens on various processing parameters: mixing-water content; press-forming pressure; and the application (or not) of the immersion procedure with respect to the content of zeolite additives, specimen size, and the type of PG [48]. Hence, a deeper understanding of the applicability of these processing methods was achieved.
Press-forming processing is not only suitable for producing PG bricks or blocks. Other types of products, such as plasterboards, can also be manufactured. Zhou et al. created paper-free and fiber-free plasterboards by applying intermittent press forming in immersion conditions [49]. In this manner, the achieved flexural strength of the manufactured PG boards was 14.7 MPa. Hence, it can be concluded that the application of press forming, which improves the mechanical properties of PG products, may be encouraged in building products.
3.3. Phosphogypsum-Based Biocomposites
3.3.1. Phosphogypsum-Based Hempcrete
In response to the sustainability challenges faced by the construction industry, an innovative composite material has been developed to address these concerns. This new material boasts significantly lower embodied energy and carbon footprint when compared to traditional construction materials. It is formulated using a low-emission gypsum binder, which includes industrial byproducts such as PG, along with agricultural waste hemp shives. The development of bio-based construction materials using a combination of hemp shives and gypsum resulted in low-density materials (from 200 to 400 kg/m3), employing a straightforward and robust production method [50]. The resulting building material exhibited a negative net carbon dioxide (CO2) impact, with up to 92 kg CO2 equivalent entrapped per cubic meter. The study encompassed an examination of both physical and mechanical properties. The weight ratio of the biofiller to binder in compositions ranged from 0.83 to 2.50 (volume ratio from 0.04 to 0.12). Increasing the gypsum content in these mixtures resulted in enhancements in mechanical properties and an increase in the thermal conductivity coefficient. Thermal conductivity ranged from 0.058 to 0.101 W/(m·K), and compressive strength varied from 0.10 to 0.57 MPa. Biodeterioration testing revealed that the biocomposites, with a pH in the range of 5.60 to 6.55, facilitated the rapid growth of mold. Mold growth was somewhat reduced in composites with higher gypsum content, while PG promoted even faster mold growth (Figure 2). Notably, Cladosporium, Rhizopus, Chaetomium, and other molds were observed on samples, even in early testing stages, raising concerns about the limited suitability of such gypsum-based biocomposites in dry conditions. To enhance water and mold resistance, treatment with waterproof or fungicidal substances, or pH adjustment using lime or another mineral binder with a high pH value, is essential.

Figure 2.
PG-based bio-aggregate composites with different gypsum contents. Gypsum binder is partially (a) or completely (b) covered by individual hemp shives.
The same mixture formulations were evaluated with respect to fire performance. Significantly, the research utilized a cone calorimeter to evaluate the fire performance of commercially available gypsum-based and PG-based composites for the first time [51]. The findings indicate that the gypsum content plays a pivotal role in determining fire resistance. With elevated gypsum content, a char layer was formed, contributing to a reduction in the peak heat release rate by limiting mass and thermal transfer. Increasing the gypsum content led to a delayed ignition time, extending it from 14 to 19 s, and a substantial 57% reduction in the peak heat release rate. Interestingly, the use of PG as a binder, when compared to commercial gypsum, demonstrated a slight improvement in fire resistance. This improvement may be attributed to the presence of impurities with high water-attracting properties within the PG structure.
3.3.2. Phosphogypsum and Wood Fiber Waste Composites
One way to reuse PG could be the development of environmentally friendly composite materials made from PG and fibers. Guna et al. investigated gypsum samples reinforced with wool and coir fibers [52]. This reinforcement of gypsum made with wool and coir fibers improved the mechanical properties (up to 90%) of the composite and increased its resistance to moisture. Fantilli et al. used sheep wool fibers and hemp fibers in the gypsum matrix [53]. They highlighted the better mechanical properties of biocomposites with wool fibers compared with hemp fibers as reinforcements. This could be explained by the better adhesion of wool fibers (more rough fiber surfaces) with gypsum matrixes. Kaya et al. stated that the increase in wood particles increased the water absorption values by about 28.5% and 2.1% thickness swelling values, respectively [54]. In the study by de Oliveira et al., recycled cellulose fibers with expanded polystyrene were used for the reinforcement of gypsum composites [55]. These additives (with the highest amounts of expanded polystyrene) improved the thermal conductivity of the obtained composites, and even the lowest values reached 0.18 W/mK. According to Álvarez et al., the mechanical properties of a gypsum-based material with the fibers of glass, basalt, polypropylene, and wood significantly increased compared with the samples without fibers [56]. The main properties (size, surface finishing, and length) of the fibers affected the strength values of composite materials, as stated by Suárez et al. [57]. In some studies, the thermal and sound insulation properties of gypsum samples were improved by incorporating fibers based on biomaterials. In the study, a gypsum building material was designed with the incorporation of two different fiber types: cork and paper [58]. The incorporation of cork led to improvements with respect to insulation capacity, and the paper fiber resulted in the improved acoustic insulation of gypsum-based composite materials. It was observed that gypsum composite materials with natural fibers have a positive influence on sound and thermal values [59]. The gypsum-based composite was made from gypsum as a binder, and wood shavings or sawdust used as reinforcements could result in sound and thermal property improvements [60]. Cherki et al. investigated the composites based on granular cork and gypsum plaster [61]. This composite material was three times more insulating and two times lighter than gypsum.
Fornes et al. evaluated the impact of waste wood fiber on the thermal and acoustic insulation properties of PG samples [62]. Wood fiber waste (WFW) was obtained from used chipboards. An inverse linear correlation was found between the amount of incorporated WWF in the composite samples based on PG and the thermal conductivity coefficient λ. At the highest amount of WFW (5%), the samples had the lowest value λ = 0.33 W/mK, i.e., 26% lower than control samples (without WFW). However, this option was not recommended due to the low strength of the samples (<10 MPa). For this reason, a compromise between strength and thermal insulation properties was recommended. A reduction in coefficient λ, together with satisfactory strength values, confers PG products with better parameters for use as bricks or composite blocks.
3.4. Ternary System Binders with Phosphogypsum
There have been efforts to develop sustainable and high-performance construction materials through the utilization of a green hydraulic ternary system binder based on waste PG. A high-strength ternary system binder was developed, containing a major part of gypsum, metakaolin, and Portland cement (PC) [63]. Valorization options for waste PG and metakaolin were offered by incorporating these materials in high-performance cementitious composites and producing highly porous lightweight foam materials. The proposed binder has technological properties that are similar to traditional cementitious binders based on PC. The mixture’s composition with a low W/B ratio of 0.34 was developed with the addition of a superplasticizer. An impressive compressive strength value of up to 88 MPa was reached. The binder proved to be suitable for producing mortar with a strength of up to 50 MPa (Figure 3a). Foamed ternary system binder materials with density values within the range from 368 to 697 kg/m3 were obtained, with compressive strength values from 0.33 to 3.5 MPa and thermal conductivity values between 0.086 and 0.153 W/mK (Figure 3b). In addition to technological properties, long-term properties, such as durability and shrinkage/swelling, should be evaluated, as gypsum with cement can form hazardous compounds, such as ettringite, which could lead to a loss of integrity of the material. The utilization of PG up to 50% by weight in the binder composition was reported. Water tightness, represented by the softening coefficient of such foamed materials, falls within the range of 0.5 to 0.64. This approach represents a practical and sustainable solution for decreasing the environmental impact associated with waste disposal.

Figure 3.
(a) Prototypes of the high-strength ternary system binder’s mortar. (b) Foamed and highly porous ternary system binder.
4. Life Cycle Assessment
CO2 emissions stemming from the production of PC are recognized as the highest among those from all construction materials, accounting for approximately 8% of the world’s total CO2 emissions. On average, the production of PC clinker, which involves the calcination process, generates 0.81 kg of carbon dioxide for every kilogram of cement produced. Therefore, there is a pressing need for innovative approaches that can mitigate the adverse environmental effects associated with cement production and facilitate the development of more advanced methods. One potential avenue for reducing environmental risks is the adoption of materials with lower energy consumption in production that can partially substitute PC in cement binders. This has resulted in the exploration of alternative binders as one of the most promising solutions. Current research delves into the environmental impact of the construction industry when an alternative to PC binders is employed.
At first glance, replacing PC with supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) appears to be an effective and immediate solution for reducing the environmental impact of PC-based materials. However, results have shown that the total energy consumption and CO2 emissions during the production of cement-based materials do not decrease proportionally to the reduction in PC usage. In some cases, this substitution may even lead to additional environmental harm. Three reviewed scenarios were compared regarding CO2 emissions using LCA—all materials used in the scenarios are calculated for 1 kg of material (Table 1). In the first scenario, a commercial gypsum binder (CG), PG, and lime binder were used to produce hempcrete with a bulk density of 400 kg/m3 [51]. The second scenario was associated with ternary hydraulic binder production from PG, PC, and SCM. The material was compared to traditional PC CEM I 42.5 N from the Ecoinvent database. Both binders had a compressive strength of 50 MPa at the age of 28 days [63]. The third scenario compared pressed blocks produced from 100% PG. In total, a mass of water equal to 16% of the mixture’s weight was added to the mixture and then pressed with 15 or 20 MPa pressure to attain a specimen density value from 1882 to 1914 kg/m3 and compressive strength value from 48 to 58 MPa [64]. Blocks were compared to commercial concrete blocks with a density of 1840 kg/m3 and a compressive strength of 13.1 MPa. Data for comparison were taken from the results of Dahmen et al. [65].

Table 1.
The mixture compositions used for LCA with various PG applications and reference compositions.
Data with respect to PG are not available in the Ecoinvent database; thus, a process was developed to avoid the dumping of PG in stockpiles, and the PG stockpile was transported to the production site [44]. However, no CO2 emissions were reduced from PG stockpiles; thus, the main climate change benefit is from the transformation of PG as a waste product, meaning that there are no added impacts due to the material’s production.
When PG is transformed into products with market value instead of being sent to landfill, CO2 can be captured during this process. Within this study, the capture of CO2 was achieved by replacing traditionally used materials in different composites with PG [67]. Figure 4 indicates that using PG instead of lime results in a CO2 reduction of 0.61 kg CO2 eq/1 kg instead of CG 0.55 kg CO2 eq/1 kg. Considering that all three biocomposites contain hemp shives in their composition, there is potential for these materials to yield a net-negative CO2 value, thereby benefiting the environment through CO2 capture via hemp shives. However, this outcome hinges on the proportions of hemp shives and other materials in the composition. Among these biocomposites, two demonstrate a capacity to capture more CO2 than they produce, while lime biocomposites generate more CO2 than they capture despite containing the same amount of hemp shives as the others. Both PG and CG ternary binders exhibit comparable results, whereas the CEM I binder leads to a more than twofold increase in CO2 emissions at 0.89 kg CO2 eq/1 kg. Given their equivalent strength, it can be inferred that both PG and CG ternary binders offer viable options for realizing similar outcomes in addressing climate change. Regarding blocks, while all exhibit similar densities, there are substantial variations in the strength of pressed concrete blocks. Nonetheless, this discrepancy bears minimal significance considering that both CG and concrete pressed blocks yield nearly identical impacts on climate change.
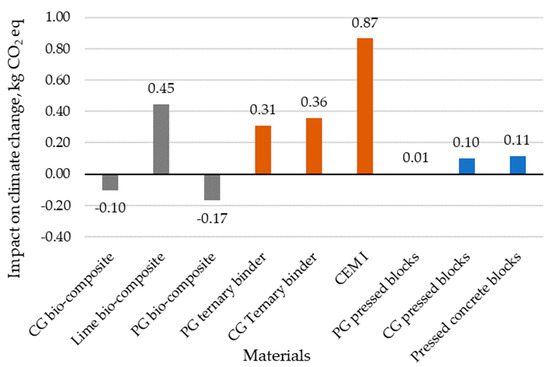
Figure 4.
CO2 emissions of various construction materials and their reduction with respect to the application of PG.
In order to understand the reduced CO2 emission correlations when replacing traditionally used materials with a certain amount of PG, an indicator was developed, where the difference in impact between PG and traditional materials is determined based on the amount of PG (kg) in the material (see Table 2). The total CO2 reduction kg/CO2 eq was calculated per 1 kg of material and divided by the sPG content in the material. The higher the reduction coefficient, the more effective the substitution of traditional construction materials. It is also noteworthy that the highest CO2 capture was observed with respect to biocomposites, and the most effective use of PG in the production of construction materials is in the ternary binder. This can also be concluded from two factors. First, PC has higher CO2 release values during production compared to the lime binder; the other factor is that the higher amount of PG in biocomposites produces a good reduction value, while it does not reach the efficiency of PC substitution as the density of the produced material is lower. Furthermore, when comparing PG materials to those with the greatest impact, it is crucial to acknowledge that CO2 reduction is not dependent on PG alone but also on other materials within the composition, such as metakaolin. This distinction is vital, as the compositions are not identical.

Table 2.
The CO2 reduction efficiency of PG in proposed applications.
5. Closing the Loop of Phosphogypsum—Conclusions
PG, a byproduct of the phosphate fertilizer industry, presents both environmental challenges and opportunities for recycling and utilization. Due to its association with naturally occurring radioactive elements, such as radium, uranium, and thorium, the proper management of PG is essential in order to minimize radiation exposure and environmental contamination. Regulatory guidelines and PG practices should be followed to ensure the safe handling, storage, and disposal of PG. The effective recycling and utilization of PG offer significant environmental, economic, and social benefits, including reduced waste generation, resource conservation, and sustainable development. By implementing innovative technologies and practices, as well as fostering collaboration among stakeholders, the full potential of PG can be realized, contributing to a more circular and resilient economy. Recycling and utilizing PG contributes to waste reduction and resource conservation by repurposing a byproduct of industrial processes. This supports circular economy principles by minimizing waste generation and maximizing the value of secondary resources.
PG offers a sustainable alternative to natural gypsum in various applications; its abundance, cost-effectiveness, nutrient content, and waste utilization potential can be leveraged. However, proper management and regulatory oversight are necessary to address environmental and health considerations associated with its utilization.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.B. and D.V.; methodology, G.B., D.V. and D.B.; software, M.S. and L.P.; validation, D.N., I.V.F. and D.B.; formal analysis, G.B., D.V., T.T. and L.P.; investigation, G.B., D.V., T.T., L.P. and I.V.F.; resources, D.V., M.S. and D.B.; data curation, G.B., D.V. and L.P.; writing—original draft preparation, G.B., D.V., T.T. and L.P.; writing—review and editing, M.S., D.N. and I.V.F.; visualization, G.B. and L.P.; supervision, G.B., D.V., M.S. and D.B.; project administration, D.V. and D.V.; funding acquisition, D.V., M.S. and D.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is funded by the FLPP (Fundamental and Applied Research Projects) program in Latvia under the research project lzp-2022/1-0585 “Development and characterization of sustain-able gypsum-cement-pozzolanic ternary compositions for 3D printing”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request due to restrictions of the project privacy.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the COST Action CircularB “Implementation of Circular Economy in the Built Environment” CA21103.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- WRAP and the Circular Economy | WRAP. Available online: https://wrap.org.uk/taking-action/climate-change/circular-economy (accessed on 9 February 2024).
- Upadhyay, A.; Laing, T.; Kumar, V.; Dora, M. Exploring Barriers and Drivers to the Implementation of Circular Economy Practices in the Mining Industry. Resour. Policy 2021, 72, 102037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda-Pereira, I.; Campos-Medina, F. International Trends in Mining Tailings Publications: A Descriptive Bibliometric Study. Resour. Policy 2021, 74, 102272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Gypsum Industry—Eurogypsum. Available online: https://eurogypsum.org/about-eurogypsum/the-european-gypsum-industry/ (accessed on 9 February 2024).
- European Commission; Directorate-General for Internal Market, Industry, Entrepreneurship; SMEs. Study on the Critical Raw Materials for the EU 2023—Final Report; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco-Torgal, F. Introduction to the Recycling of Construction and Demolition Waste (CDW). In Handbook of Recycled Concrete and Demolition Waste; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 1–6. ISBN 9780857096906. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Xu, Q.; Townsend, T.G.; Chadik, P.; Bitton, G.; Booth, M. Hydrogen Sulfide Generation in Simulated Construction and Demolition Debris Landfills: Impact of Waste Composition. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2006, 56, 1130–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission LIFE 3.0—LIFE Project Public Page. Available online: https://webgate.ec.europa.eu/life/publicWebsite/index.cfm?fuseaction=search.dspPage&n_proj_id=4191 (accessed on 4 April 2022).
- Jiménez-Rivero, A.; García-Navarro, J. Best Practices for the Management of End-of-Life Gypsum in a Circular Economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 167, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gypsum Recycling International Profile. Available online: https://www.environmental-expert.com/companies/gypsum-recycling-international-29016 (accessed on 16 February 2021).
- Suárez, S.; Roca, X.; Gasso, S. Product-Specific Life Cycle Assessment of Recycled Gypsum as a Replacement for Natural Gypsum in Ordinary Portland Cement: Application to the Spanish Context. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 117, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haneklaus, N.; Barbossa, S.; Basallote, M.D.; Bertau, M.; Bilal, E.; Chajduk, E.; Chernysh, Y.; Chubur, V.; Cruz, J.; Dziarczykowski, K.; et al. Closing the Upcoming EU Gypsum Gap with Phosphogypsum. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 182, 106328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, L.; Xue, M.; Duan, X.; Feng, C.; Zhu, J. Efficient Precipitation of Soluble Phosphorus Impurities in the Recycling of Phosphogypsum to Produce Hemihydrate Gypsum. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 396, 136455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ouyang, J.; Ren, J. Mechanism of Calcination Modification of Phosphogypsum and Its Effect on the Hydration Properties of Phosphogypsum-Based Supersulfated Cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 243, 118226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Cao, Y.; Guan, H.; Hu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; Hu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, R. Resource Utilization and Development of Phosphogypsum-Based Materials in Civil Engineering. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 387, 135858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yuan, X.; Dong, W.; Fu, Q.; Ao, X.; Chen, Q. Gradient Removal of Si and P Impurities from Phosphogypsum and Preparation of Anhydrous Calcium Sulfate. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akfas, F.; Elghali, A.; Aboulaich, A.; Munoz, M.; Benzaazoua, M.; Bodinier, J.L. Exploring the Potential Reuse of Phosphogypsum: A Waste or a Resource? Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roszczynialski, W.; Gawlicki, M.; Nocuń-Wczelik, W. Production and Use of By-Product Gypsum in the Construction Industry. Waste Mater. Used Concr. Manuf. 1996, 53–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhadi, M.; Abdelhadi, N.; El-Hasan, T.; Hadi, N.A. Optimization of Phosphogypsum By-Production Using Orthophosphoric Acid as Leaching Solvent with DifferentTemperatures and Leaching Time Periods. Earth Sci. Res. 2018, 7, p28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, L.; Liao, S.; Zhao, Z. Effects of Particle Shaping on the Performance of Phosphorus Building Gypsum. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Yu, B. Effect of Modified Phosphogypsum on the Hydration Properties of the Phosphogypsum-Based Supersulfated Cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 214, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Liu, S.; Qu, G.; Chen, B.; Zhao, C.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Ren, Y. Highly Targeted Solidification Behavior of Hazardous Components in Phosphogypsum. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 9, 100227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayibi, H.; Choura, M.; López, F.A.; Alguacil, F.J.; López-Delgado, A. Environmental Impact and Management of Phosphogypsum. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2377–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Gao, J.; Zhao, Y. Investigation on the Hydration of Hemihydrate Phosphogypsum after Post Treatment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 229, 116864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Wang, Q.; Luo, T. Reuse of Phosphogypsum as Hemihydrate Gypsum: The Negative Effect and Content Control of H3PO4. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 174, 105830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizevičienė, D.; Vaičiukynienė, D.; Michalik, B.; Bonczyk, M.; Vaitkevičius, V.; Jusas, V. The Treatment of Phosphogypsum with Zeolite to Use It in Binding Material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 180, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M. Role of Phosphogypsum Impurities on Strength and Microstructure of Selenite Plaster. Constr. Build. Mater. 2005, 19, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M. Treating Waste Phosphogypsum for Cement and Plaster Manufacture. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Garg, M.; Verma, C.L.; Handa, S.K.; Kumar, R. An Improved Process for the Purification of Phosphogypsum. Constr. Build. Mater. 1996, 10, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Zhao, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Quan, S. On Pretreatment Experimental Study of Yunnan Phosphorus Building Gypsum. Adv. Mat. Res. 2014, 1025–1026, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Fang, P.; Ren, J.; Li, S. Application of Lime Neutralised Phosphogypsum in Supersulfated Cement. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaziliunas, A.; Leskeviciene, V.; Vektaris, B.; Valancius, Z. The Study of Neutralization of the Dihydrate Phosphogypsum Impurities. Ceram. Silik. 2006, 50, 178–184. [Google Scholar]
- Ölmez, H.; Erdem, E. The Effects of Phosphogypsum on the Setting and Mechanical Properties of Portland Cement and Trass Cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 1989, 19, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.S.; Wang, C.Q.; Mei, X.D.; Zhang, C. An Effective Treatment Method for Phosphogypsum. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 30533–30539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Gao, J.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Y. Effect of Neutralization on the Setting and Hardening Characters of Hemihydrate Phosphogypsum Plaster. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 190, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizevičienė, D.; Vaičiukynienė, D.; Vaitkevičius, V.; Rudžionis, Z. Effects of Waste Fluid Catalytic Cracking on the Properties of Semi-Hydrate Phosphogypsum. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 137, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouargane, B.; Laaboubi, K.; Biyoune, M.G.; Bakiz, B.; Atbir, A. Effective and Innovative Procedures to Use Phosphogypsum Waste in Different Application Domains: Review of the Environmental, Economic Challenges and Life Cycle Assessment. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2023, 25, 1288–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oumnih, S.; Bekkouch, N.; Gharibi, E.K.; Fagel, N.; Elhamouti, K.; El Ouahabi, M. Phosphogypsum Waste as Additives to Lime Stabilization of Bentonite. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2019, 29, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bituh, T.; Petrinec, B.; Skoko, B.; Babic, D.; Raseta, D. Phosphogypsum and Its Potential Use in Croatia: Challenges and Opportunities Fosfogips i Njegovo Potencijalno Koristenje u Republici Hrvatskoj Izazovi i Prilike. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2021, 72, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabsi, H.; Tallou, A.; Aziz, F.; Boukchina, R.; Karbout, N.; Caceres, L.A.; García-Tenorio, R.; Boudabbous, K.; Moussa, M. Application of Phosphogypsum and Organic Amendment for Bioremediation of Degraded Soil in Tunisia Oasis: Targeting Circular Economy. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outbakat, M.B.; El Mejahed, K.; El Gharous, M.; El Omari, K.; Beniaich, A. Effect of Phosphogypsum on Soil Physical Properties in Moroccan Salt-Affected Soils. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdoubi, H.; Makhlouf, R.; Haddaji, Y.; Nadi, M.; Mansouri, S.; Semllal, N.; Oumam, M.; Manoun, B.; Alami, J.; Hannache, H.; et al. Valorization of Phosphogypsum Waste through Acid Geopolymer Technology: Synthesis, Characterization, and Environmental Assessment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 371, 130710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, E.; Bellefqih, H.; Bourgier, V.; Mazouz, H.; Dumitraş, D.G.; Bard, F.; Laborde, M.; Caspar, J.P.; Guilhot, B.; Iatan, E.L.; et al. Phosphogypsum Circular Economy Considerations: A Critical Review from More than 65 Storage Sites Worldwide. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 414, 137561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsioka, M.; Voudrias, E.A. Comparison of Alternative Management Methods for Phosphogypsum Waste Using Life Cycle Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 266, 121386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumanis, G.; Zorica, J.; Bajare, D.; Korjakins, A. Technological Properties of Phosphogypsum Binder Obtained from Fertilizer Production Waste. Energy Procedia 2018, 147, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Gao, H.; Shu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yan, C. Utilization of Waste Phosphogypsum to Prepare Non-Fired Bricks by a Novel Hydration-Recrystallization Process. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 34, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yu, D.; Shu, Z.; Li, T.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y. A Novel Two-Step Hydration Process of Preparing Cement-Free Non-Fired Bricks from Waste Phosphogypsum. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 73, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalón Fornés, I.; Doroševas, V.; Vaičiukynienė, D.; Nizevičienė, D. The Investigation of Phosphogypsum Specimens Processed by Press-Forming Method. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 1539–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Shu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, X. Preparation of Paper-Free and Fiber-Free Plasterboard with High Strength Using Phosphogypsum. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 243, 118091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumanis, G.; Irbe, I.; Sinka, M.; Bajare, D. Biodeterioration of Sustainable Hemp Shive Biocomposite Based on Gypsum and Phosphogypsum. J. Nat. Fibers 2021, 19, 10550–10563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumanis, G.; Andzs, M.; Sinka, M.; Bajare, D. Fire Resistance of Phosphogypsum- and Hemp-Based Bio-Aggregate Composite with Variable Amount of Binder. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guna, V.; Yadav, C.; Maithri, B.R.; Ilangovan, M.; Touchaleaume, F.; Saulnier, B.; Grohens, Y.; Reddy, N. Wool and Coir Fiber Reinforced Gypsum Ceiling Tiles with Enhanced Stability and Acoustic and Thermal Resistance. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 41, 102433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantilli, A.P.; Jóźwiak-Niedźwiedzka, D.; Denis, P. Bio-Fibres as a Reinforcement of Gypsum Composites. Materials 2021, 14, 4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, A.İ.; Yalcin, Ö.Ü.; Turker, Y. Physical, Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Red Pine Wood-Gypsum Particleboard. Bilge Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2021, 5, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, K.A.; Oliveira, C.A.B.; Molina, J.C. Lightweight Recycled Gypsum with Residues of Expanded Polystyrene and Cellulose Fiber to Improve Thermal Properties of Gypsum. Mater. Constr. 2021, 71, e242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, M.; Ferrández, D.; Morón, C.; Atanes-sánchez, E. Characterization of a New Lightened Gypsum-Based Material Reinforced with Fibers. Materials 2021, 14, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, F.; Felipe-Sesé, L.; Díaz, F.A.; Gálvez, J.C.; Alberti, M.G. On the Fracture Behaviour of Fibre-Reinforced Gypsum Using Micro and Macro Polymer Fibres. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 244, 118347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sair, S.; Mandili, B.; Taqi, M.; El Bouari, A. Development of a New Eco-Friendly Composite Material Based on Gypsum Reinforced with a Mixture of Cork Fibre and Cardboard Waste for Building Thermal Insulation. Compos. Commun. 2019, 16, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Wang, Q.; Feng, P. A Comprehensive Overview of Fibre-Reinforced Gypsum-Based Composites (FRGCs) in the Construction Field. Compos. B Eng. 2021, 205, 108540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedreño-Rojas, M.A.; Morales-Conde, M.J.; Pérez-Gálvez, F.; Rodríguez-Liñán, C. Eco-Efficient Acoustic and Thermal Conditioning Using False Ceiling Plates Made from Plaster and Wood Waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 166, 690–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherki, A.B.; Remy, B.; Khabbazi, A.; Jannot, Y.; Baillis, D. Experimental Thermal Properties Characterization of Insulating Cork–Gypsum Composite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 54, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalón Fornés, I.; Vaičiukynienė, D.; Nizevičienė, D.; Tamošaitis, G.; Pupeikis, D. The Improvement of the Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Properties of Phosphogypsum Specimens by Adding Waste Wood Fibre. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 331, 127341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumanis, G.; Zorica, J.; Bajare, D. Properties of Foamed Lightweight High-Performance Phosphogypsum-Based Ternary System Binder. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalón Fornés, I.; Vaičiukynienė, D.; Nizevičienė, D.; Doroševas, V.; Dvořák, K. A Method to Prepare a High-Strength Building Material from Press-Formed Phosphogypsum Purified with Waste Zeolite. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 34, 101919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmen, J.; Kim, J.; Ouellet-Plamondon, C.M. Life Cycle Assessment of Emergent Masonry Blocks. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 1622–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinka, M.; Spurina, E.; Korjakins, A.; Bajare, D. Hempcrete—CO2 Neutral Wall Solutions for 3D Printing. Environ. Clim. Technol. 2022, 26, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez-Castro, L.; Bejarano-Nieto, A.C.; Mendoza-Serna, R.; Pavón-Duarte, A.; Morales-Flórez, V.; Esquivias, L. Capture of CO2 through Phosphogypsum and Lye Residues from the Olive Industry. J. CO2 Util. 2023, 72, 102504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).