Abstract
Alleviation of environmental waste is a significant challenge, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and wasting valuable resources. To address this issue sustainably, valorization techniques are being explored to convert environmental waste into valuable bio-based products. Additionally, the use of black soldier fly (Hermetia Illucens) larvae has emerged as a potential solution to degrade environmental waste and produce biomass. This study aimed to quantify the waste reduction index (WRI) of environmental waste through biodegradation by black soldier fly (BSF) larvae. A meta-analysis method was employed, involving a comprehensive search in the Scopus database for analysis. A total of 45 articles were analyzed and the results indicate that kitchen waste and fruit and vegetable wastes have a positive effect on WRI and other variables. The WRI of kitchen waste and fruit and vegetable wastes is 4.77 ± 2.98 g/day and 2.72 ± 2.14 g/day, respectively. Fecal waste results in a lower WRI than those of other waste categories, i.e., 2.22 ± 1.29 g/day. Overall, the BSF larvae effectively reduce organic environmental wastes and convert them into their body mass, which is rich in protein. This study contributes to a deeper understanding of the potential of BSF in waste management, offering insights into sustainable waste reduction strategies.
1. Introduction
Humans sometimes undertake environmentally detrimental actions to meet energy needs, such as emitting greenhouse gases that contribute to global warming or generating air pollution that damages air quality [1]. The population segment that produces household food waste is very high, with only 6.2% showing concern about food waste and the environment [2].
In 2019, food waste reached 931 million tons worldwide, with retailers and households being the largest contributors, at 61% and 13%, respectively, exacerbating economic, environmental, and societal issues by squandering valuable resources and money and emitting greenhouse gases [3]. The food system was responsible for emitting approximately 16 CO2eq per year in 2018, which accounted for around one-third of the total global anthropogenic emissions [4]. Households are the largest generators of food waste in industrialized nations. To support sustainable development, it is therefore crucial to reduce food loss [5].
Food waste valorization techniques contribute to sustainable economic growth and reduce the environmental impact of food waste by employing methods such as ultrasound-assisted extraction, microwave-assisted extraction, bioreactors, enzyme-immobilization-assisted extraction (including immobilized enzyme and bioconversion processes), and sub-zero-level decomposition to produce bio-based products like biofuel and bioplastics [6]. Food waste valorization can be achieved using various biological processes such as acidogenesis, fermentation, methanogenesis, solventogenesis, photosynthesis, oleaginous process, bio-electrogenesis, and others, which can yield a variety of bio-based products including biofuel, platform chemicals, bioelectricity, biomaterial, biofertilizer, animal feed, and more [7]. Utilizing food waste as a sustainable feedstock for microbial fermentation, extracting valuable bioactive compounds from food processing and agricultural wastes, producing biogas, biodiesel/biofuel, and biochar, and employing immobilized enzymatic bioconversion are some innovative approaches that have emerged to produce various high-value bioproducts from food waste [8].
BSFs can address the negative environmental impacts caused by food waste while simultaneously providing a sustainable protein source to meet the increasing global protein demand. They can digest food waste and convert it into biomass, offering opportunities for value-added products, including a new food source for humans [9]. Black soldier fly larvae (BSFL) can be effectively utilized in the bioconversion process of rice waste and chicken manure, with more than half of the raw materials estimated to be consumed by BSFL within 9 days of treatment [10].
The use of BSF larvae for food waste not only provides a solution for waste management but also produces insect biomass, organic fertilizer as a value-added byproduct [11], protein resources for animal feed such as ruminants [12] and alternative fish nutrition [13], as well as reducing methane emission [14]. A BSF larvae meal diet for quails can decrease the cholesterol content of their eggs [15].
Research is essential to integrate and quantify the WRI of BSFs for various environmental wastes. By conducting this research, we can understand the extent to which BSFs can contribute to effectively reducing environmental waste. The novelty of this study lies in its exploration of using BSFs as a waste reduction agent for different types of waste, aiming to integrate and quantify the WRI. This research contributes to a better understanding of how BSFs can effectively reduce environmental waste and offers new perspectives in addressing environmental waste challenges sustainably. This study aims to quantify the WRI of environmental waste through biodegradation by BSF larvae. This is essential as a foundation for implementing more targeted and effective waste management actions. Furthermore, it is important to understand the positive impacts of using BSFs to address waste problems on human life and the environment.
2. Results
The meta-database of this research was obtained from 45 articles comprising 520 experiments, as shown in Table 1. The substrate data in each article were categorized into three subgroups: kitchen waste, fruit and vegetable wastes, and fecal waste. From these data, information regarding the utilization of BSFs was gathered, including the conversion performance of BSF larvae, the growth of BSF larvae, and the composition of BSF larvae after the conversion process.

Table 1.
The articles used to investigate the utilization of BSFs.
Table 2 presents data on the conversion performance of BSF larvae obtained from 246 experiments. From the data, it can be observed that variables such as WRI, SRR, BR, and FCR are significantly influenced by the type of waste (p-value < 0.05). Overall and subgroup analyses of kitchen waste, fruit and vegetable wastes, and fecal waste significantly affect WRI, with p-values < 0.05. The overall and fecal waste subgroups significantly affect SRR, with p-values < 0.001. BR and FCR are also significantly influenced by the overall and fecal waste subgroups, with a p value < 0.001. However, variables such as WRR and MRR are not significantly affected by any type of waste. Nevertheless, there is significant heterogeneity between studies for WRI, with a Q value of 375.841 and an I2 value of 85.898, and the same applies to other variables, showing high Q and I2 values.

Table 2.
The variables related to the conversion performance.
Table 3 presents the growth rates of BSF larvae obtained from 183 experiments. From the data, it can be observed that all variables such as GR, LW, SR, and TD are significantly influenced by the type of waste (p-value < 0.05). GR is significantly influenced by the overall and fruit and vegetable wastes subgroups, with a p-value of 0.012 and 0.002. LW is significantly affected by the overall, fecal waste, and kitchen waste subgroups, with a p-value of <0.001, <0.001, and 0.006. LW, SR, and TD are also significantly influenced by the overall and fecal waste subgroups, with a p-value of 0.08. SR is significantly influenced by the overall and fecal waste subgroups, with a p-value of 0.08 and <0.001. Meanwhile, TD is also significantly affected by the overall and fecal waste subgroups, with a p-value of 0.017 and <0.001. Regarding heterogeneity, all variables also exhibit heterogeneity between studies, with high I2 values.

Table 3.
Variables related to the growth of BSF larvae.
Table 4 displays the composition of BSF larvae after the conversion process, synthesized from 42 experiments. From the data, it can be observed that the variable of protein is significantly influenced by the overall waste, with a p-value of 0.009. Dry matter is not significantly influenced by all types of waste. Regarding heterogeneity, all variables also exhibit heterogeneity between studies, with high I2 values.

Table 4.
Variables of BSF composition.
Table 5 presents the descriptive statistical data of WRI. The overall average WRI value from the experiments is 3.03 g/day, with a standard deviation of 2.34. The WRI values range from 0.18 g/day to 10.6 g/day. For the fecal waste subgroup, the average WRI value is 2.22 g/day, with a standard deviation of 1.29. The WRI values for the fecal waste subgroup range from 0.18 g/day to 5.4 g/day. Meanwhile, for the kitchen waste subgroup, the average WRI value is 4.47 g/day, with a standard deviation of 2.98. The WRI values for the kitchen waste subgroup range from 1.92 g/day to 10.6 g/day.

Table 5.
Descriptive statistics of WRI.
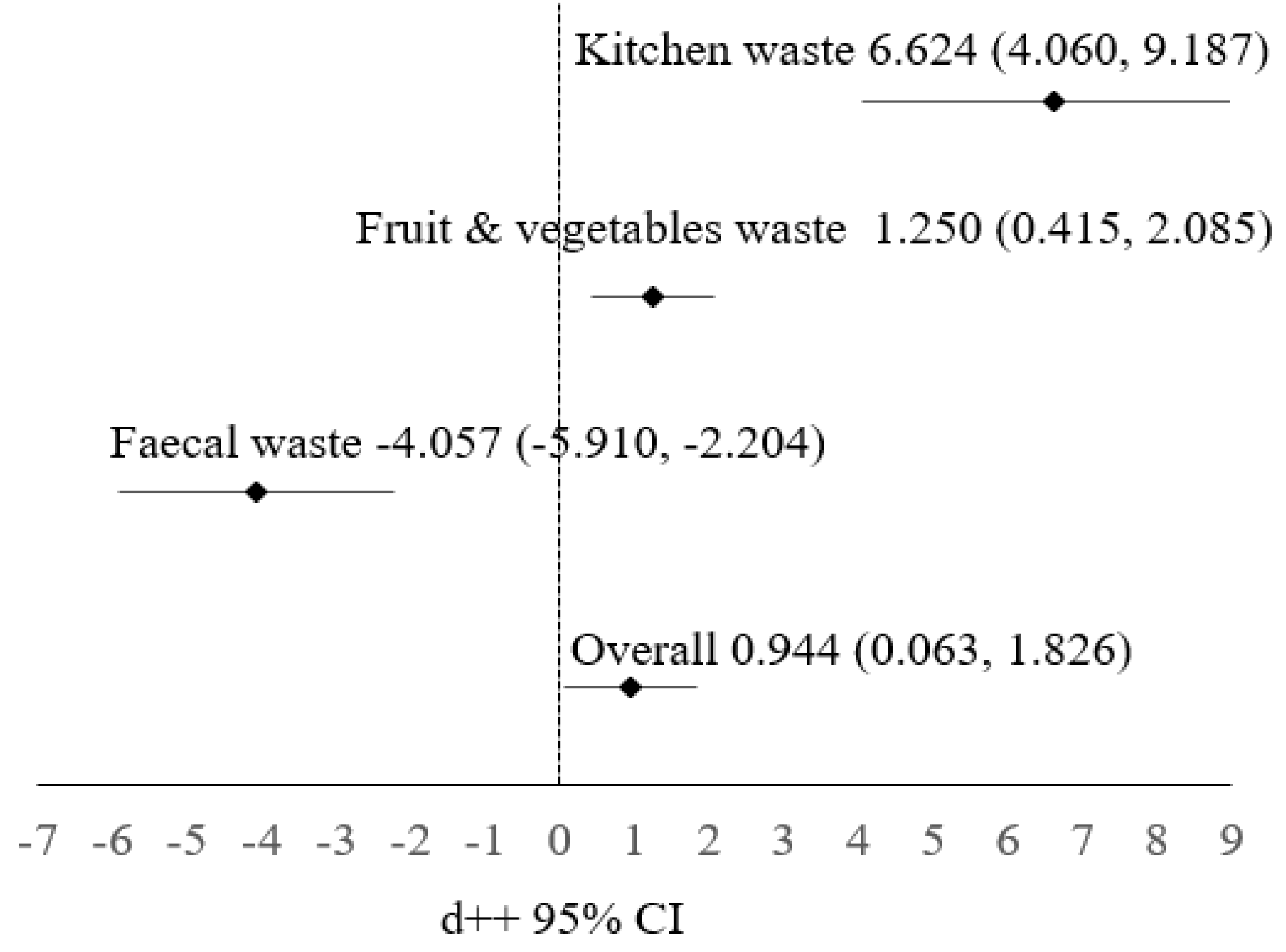
Figure 1 presents a forest plot of the WRI variables with a 95% confidence interval (CI). The plot indicates that the kitchen waste and fruit and vegetable wastes subgroups have a positive effect on the control group, while the fecal waste subgroup has a negative effect. Overall, the experimental application of waste also shows a positive effect.
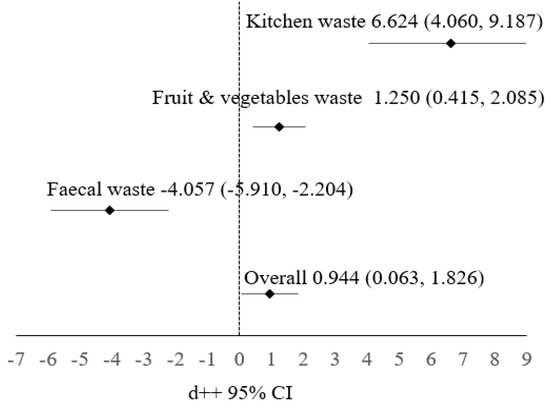
Figure 1.
Forest plot of the cumulative effect of WRI with 95% confidence interval.
3. Discussion
3.1. The Impact of Environmental Waste on the Conversion Performance of BSF Larvae
In this study, all types of waste have significant effects on WRI. The overall WRI estimation is roughly 0.944. The 95% confidence interval represents a range of values within which we can be 95% confident that the actual WRI value falls. In this instance, the interval spans from 0.063 to 1.826. An approximate standard error of 0.450 signifies a reasonably strong degree of precision for the estimated WRI. The fruit and vegetable and kitchen waste subgroups have positive effects on WRI. This suggests that BSF larvae have demonstrated effective decomposition capabilities for both types of waste. More specifically, they excel in breaking down kitchen waste compared to fruit and vegetable wastes. This promising outcome raises expectations regarding the potential of BSF larvae to efficiently manage kitchen-waste-related challenges. On the other hand, the negative estimation value associated with fecal waste implies that BSF larvae may not be as proficient in decomposing fecal waste.
According to a previous study, managing food waste (kitchen waste) using BSF larvae achieved high levels of waste reduction [60]. In another study, restaurant waste (kitchen waste) had the highest WRI [61]. This is also consistent with another study stating that food waste (kitchen waste) has the best WRI [62,63,64].
This is consistent with previous research, which found that organic waste, including fruit and vegetable wastes, resulted in better WRI [65]. In another study, vegetable wastes were more effectively managed using BSF larvae [66]. Meanwhile, fruit waste feeding had the highest WRI [64].
This study highlights that overall waste has a significant effect on WRI. WRI is an important metric that quantifies the effectiveness of BSF larvae in converting waste into biomass. The fact that overall waste has a substantial impact implies that the quantity and composition of waste fed to the larvae directly influence their growth and performance. This study also highlights the positive impact of the kitchen waste and fruit and vegetable wastes subgroups on other performance variables of BSF larvae. Feeding larvae with kitchen waste leads to higher waste reduction, faster waste conversion, and improved overall performance. Utilizing BSF larvae for the management of kitchen waste and fruit and vegetable wastes could be a promising and sustainable solution to address waste reduction challenges and contribute to a more circular and eco-friendly approach to waste management. Further research and implementation of such waste management systems could have significant environmental and economic benefits in the long term.
3.2. The Impact of Environmental Waste on the Growth Performance of BSF Larvae
In this study, all types of waste significantly affect the variables of GR, LW, and SR in a positive way. This means that providing all types of waste has a positive impact on the growth of BSF larvae. The subgroup of kitchen waste has a significant positive impact on LW. This is consistent with previous research, which stated that feeding food waste (kitchen waste) to BSF larvae resulted in a continuous increasing trend in LW [64,65,67]. Among the various waste types tested, kitchen waste showed the most significant daily reduction rate and resulted in the heaviest BSFs [68]. The increase in protein and carbohydrate content positively correlated with larval growth, resulting in greater larval weight gain as the composition of food waste (kitchen waste) in the substrate increased [63]. The fruit and vegetable wastes subgroup has a positive impact on GR. This is consistent with a previous study in which larvae raised on an apple-based diet had a fat content that was 50% higher than those that were fed a combination of fruit and spent grain [69].
The findings of this study highlight the positive impact of providing kitchen waste and fruit and vegetable wastes on the growth and performance of BSF larvae. Feeding larvae with kitchen waste and fruit and vegetable wastes leads to increased larval weight. This suggests that utilizing kitchen waste and fruit and vegetable wastes as feed sources for BSF larvae could be a viable and sustainable approach to improve waste reduction.
3.3. The Impact of Environmental Waste on the Composition of BSF Larvae
Overall, the provision of waste has a significant effect on the composition of BSF larvae after the conversion process, especially the protein variable, with a p-value of 0.009. The subgroup kitchen waste has a positive influence on the dry matter variable. In a previous study, the dry matter composition in BSFs fed on food waste and tofu (kitchen waste) was better than that of another waste type; 40.99 ± 1.56% and 42.94 ± 1.48%, respectively [69].
This study demonstrates that feeding BSF larvae with kitchen waste significantly impacts the composition of the larvae after the conversion process, especially dry matter, which shows significant changes, suggesting that these waste sources have notable effects on the nutrient profile of the larvae. Understanding these compositional changes can help in developing efficient waste management strategies and utilizing BSF larvae as a sustainable solution for waste conversion and biomass production. Further research in this area can contribute to maximizing the potential of BSF larvae in waste reduction and resource recovery efforts.
3.4. Quantifying the WRI for Environmental Waste
Overall, waste has a positive impact on WRI. The subgroups of kitchen waste and fruit and vegetable wastes show a positive effect on WRI, while the faecal waste subgroup has a negative effect. For kitchen waste, the average WRI value is 4.77 ± 2.98 g/day. The WRI values for the kitchen waste subgroup range from 1.92 g/day to 10.60 g/day. This range of WRI values for restaurant waste (kitchen waste) similar with previous study [59,64].
Meanwhile, for the fruit and vegetable wastes subgroup, the average WRI value is 2.72 ± 2.14 g/day. The WRI values for the fruit and vegetable wastes subgroup range from 0.33 g/day to 9.53 g/day. This WRI for fruit and vegetable wastes is similar with previous study [64,70].
Overall, this study demonstrates the diversity of studies conducted on the utilization of BSFs in waste management. Further research is needed to obtain more robust results. Nevertheless, this study provides a deeper understanding of the performance of BSFs in processing environmental waste. It offers comprehensive and relevant insights into utilizing BSFs as an effective and sustainable solution for waste management.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Database Development
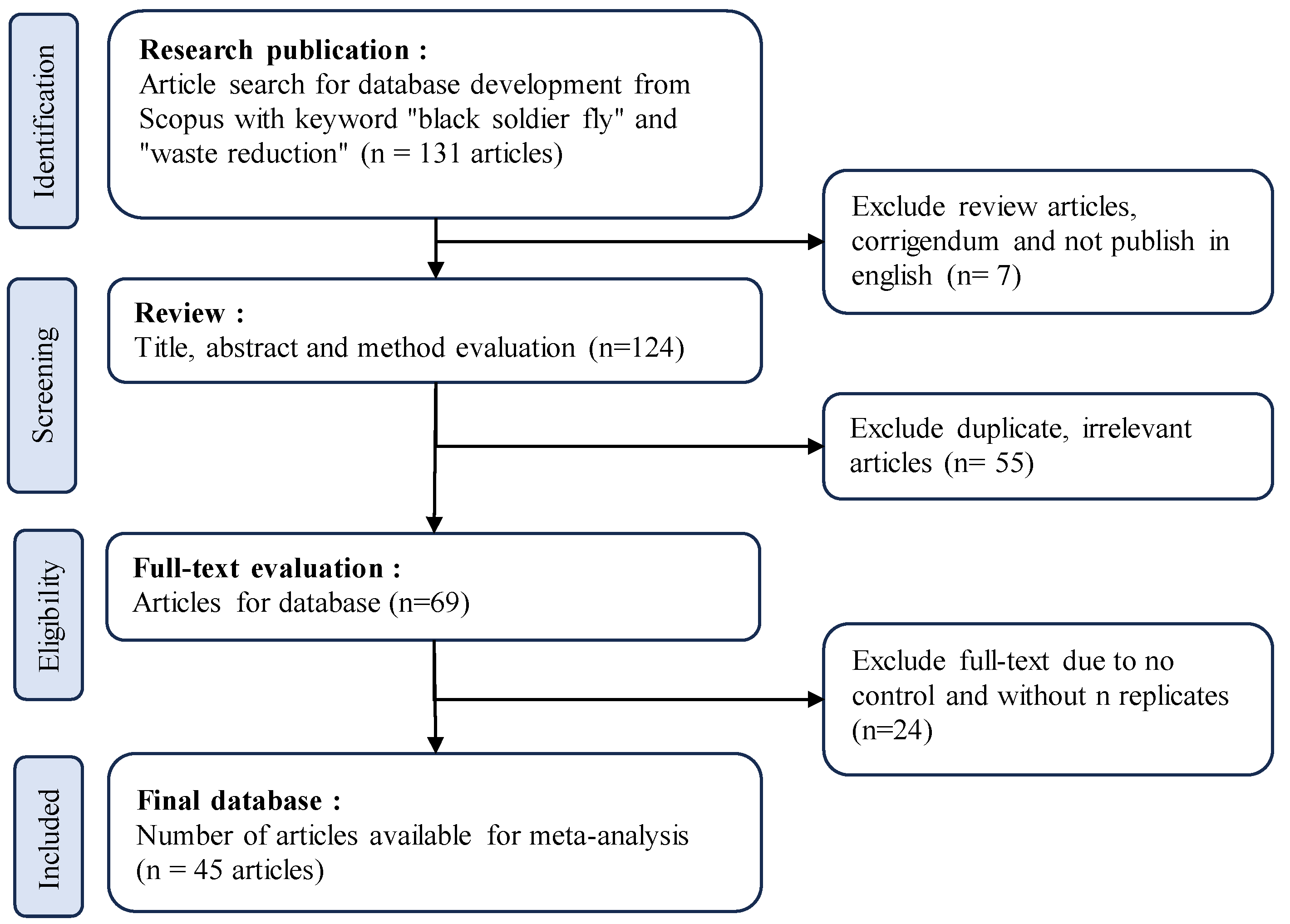
This study utilized a meta-analysis method involving several sequential steps. Figure 2 illustrates the process of article selection for analysis. In the first step, relevant research publications were identified by conducting a comprehensive search in the Scopus database using the keywords “black soldier fly” and “waste reduction” or “bioconversion” or “waste management”, resulting in 131 articles. Seven articles were excluded as they were review articles, correction journals, or articles not published in English. The second step involved screening the remaining 124 articles based on title, abstract, and method evaluation. A total of 45 duplicate and irrelevant articles were excluded, resulting in a smaller set of 69 articles. Subsequently, in the third step, a thorough evaluation of the full-text articles was conducted. Articles lacking control groups and replication were excluded, leaving 45 eligible articles for further analysis. These 45 articles formed the basis of the final database for the meta-analysis.
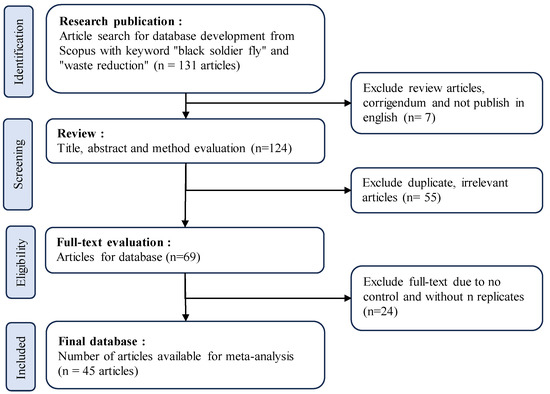
Figure 2.
The literature selection process of the articles using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) protocol.
The next step involved data extraction from each article, including information about the types of waste used. The waste type data from all articles were categorized into kitchen waste, fruit and vegetable wastes, and fecal waste. The data from the 45 articles were synthesized to obtain data on waste management using BSFs. The collected data included performance parameters of BSF larvae conversion, such as BSF larvae conversion rate, BSF larvae growth performance, and post-bioconversion composition of BSF larvae. Performance parameters related to waste conversion included WRI, waste reduction rate (WRR), material reduction rate (MRR), substrate reduction rate (SRR), bioconversion rate (BR), and feed conversion rate (FCR). BSF growth parameters included growth rate (GR), larval weight (LW), survival rate (SR), and time development (TD). Parameters related to the composition of residual waste after conversion included dry matter and protein.
WRR was calculated based on substrate dry weight, while WRI factored in both material reduction and the time required by larvae to achieve waste reduction, with higher WRI values signifying greater efficiency in reduction [16]. The formulae of WRR, WRI, SR, and BR are as follows [39]:
The formulae of TD and FCR are as follows [32]:
The formulae of GR and SRR are as follows [23]:
4.2. Data Analysis
The data were analyzed using a random effects meta-analysis method [71]. The calculation of effect size (d) was based on the standardized mean difference using Hedges’ d [72,73] as follows:
where is the mean of the experimental group,
is the mean of the control group, and S is the standard deviation. The value of S can be described as follows:
J is a correction factor for small sample size, and it can be described as follows:
where NE is the sample size of the experimental group, NC is the sample size of the control group, SE is the standard deviation of the experimental group, and SC is the standard deviation of the control group. A one-way random effects model is used in the data analysis with the following formula:
where the effect size value (in Hedges’ d) for the i-th observation is represented by yi, the overall common effect size parameter is θ, the variation of the actual effect sizes is vi, and the error of the i-th observation is εi. The estimated variation between studies (τ2) is measured using the DerSimonian and Laird method [74] with the following formula:
where Q is the weighted sum of squares, degrees of freedom is df, and CI is the value of the confidence interval. The meta-analysis software used in this study is the OpenMEE version 2015 platform (http://www.cebm.brown.edu/openmee/ accessed on 1 September 2023) for cumulative meta-analysis and subgroup meta-analysis.
5. Conclusions
Kitchen waste and fruit and vegetable wastes play a significant role in maximizing the utilization of BSFs, benefiting conversion performance, larval growth, and nutritional content after the conversion process. Quantifying the WRI is crucial for environmental waste reduction efforts. This presents a valuable opportunity for employing BSFs in managing organic waste, especially kitchen waste and fruit and vegetable wastes, which is currently a global challenge in waste management. Moreover, considering the nutritional content of BSF larvae, they can be effectively utilized for various agricultural products, including animal feed and organic fertilizers. By considering the distinct characteristics of various environmental waste, more efficient and sustainable strategies for waste management can be developed. To ensure the successful implementation of BSF utilization for waste management, further research is necessary to explore sustainability aspects, encompassing economic, social, and environmental factors. Understanding and addressing these aspects will pave the way for a more comprehensive and holistic approach towards organic waste management, contributing to a greener and more sustainable future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.Z. and A.J.; methodology, A.J., B.P. and M.R.F.; software, S.Z.; validation, A.J. and M.R.; formal analysis, S.Z.; investigation, S.Z.; resources, S.Z.; data curation, M.R.; writing—original draft preparation, S.Z.; writing—review and editing, A.J.; visualization, S.Z.; supervision, M.R.; project administration, S.Z.; funding acquisition, S.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Awasthi, S.K.; Joshi, R.; Dhar, H.; Verma, S.; Awasthi, M.K.; Varjani, S.; Sarsaiya, S.; Zhang, Z.; Kumar, S. Improving methane yield and quality via co-digestion of cow dung mixed with food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 251, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delley, M.; Brunner, T.A. Foodwaste within Swiss households: A segmentation of the population and suggestions for preventive measures. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 122, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; van Herpen, E.; Van Loo, E.J.; Pandelaere, M.; Geuens, M. Save near-expired food: Does a message to avoid food waste affect food purchase and household waste prevention behaviors? J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubiello, F.N.; Rosenzweig, C.; Conchedda, G.; Karl, K.; Gütschow, J.; Xueyao, P.; Obli-Laryea, G.; Wanner, N.; Qiu, S.Y.; De Barros, J.; et al. Greenhouse gas emissions from food systems: Building the evidence base. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 065007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribbers, D.; Geuens, M.; Pandelaere, M.; van Herpen, E. Development and validation of the motivation to avoid food waste scale. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2023, 78, 102626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Gaur, V.K.; Sirohi, R.; Varjani, S.; Kim, S.H.; Wong, J.W. Sustainable processing of food waste for production of bio-based products for circular bioeconomy. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 325, 124684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhu, R.; Gnansounou, E.; Rebello, S.; Binod, P.; Varjani, S.; Thakur, I.S.; Nair, R.B.; Pandey, A. Conversion of food and kitchen waste to value-added products. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 241, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, H.S.; Kee, P.E.; Yim, H.S.; Chen, P.-T.; Wei, Y.-H.; Lan, J.C.-W. Recent advances on the sustainable approaches for conversion and reutilization of food wastes to valuable bioproducts. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 302, 122889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, I.; Newman, L.P.; Gill, H.; Danaher, J. The Influence of Food Waste Rearing Substrates on Black Soldier Fly Larvae Protein Composition: A Systematic Review. Insects 2021, 12, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruwita, I.; Prasetya, A.; Purnomo, C.W. The effects of feedstock on the bioconversion of organic solid waste with black soldier fly larvae. AIP Conf. Proc. 2022, 2578, 020003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.-F.; Wang, D.-H.; Xie, Z.; Zou, H.; Zheng, Y. Producing insect protein from food waste digestate via black soldier fly larvae cultivation: A promising choice for digestate disposal. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 830, 154654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayanegara, A.; Novandri, B.; Yantina, N.; Ridla, M. Use of black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) to substitute soybean meal in ruminant diet: An in vitro rumen fermentation study. Vet. World 2017, 10, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmi, M.R.; Nurjanah, N. The Nutrient Content of Nile Tilapia Fed with Black Soldier Fly (BSF) Larvae Mikrobiologi Hasil Perikanan View Project Bioconversion View Project. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/355218195 (accessed on 4 September 2023).
- Jayanegara, A.; Haryati, R.P.; Nafisah, A.; Suptijah, P.; Ridla, M.; Laconi, E.B. Derivatization of Chitin and Chitosan from Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) and Their Use as Feed Additives: An In vitro Study. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2020, 8, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suparman, S.; Purwanti, S.; Nahariah, N. The effect of fish meal protein substitution with Black Soldier Fly (BSF) larva meal protein in quail feed on the chemical quality of eggs. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 788, 012071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalander, C.; Diener, S.; Magri, M.E.; Zurbrügg, C.; Lindström, A.; Vinnerås, B. Faecal sludge management with the larvae of the black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens)—From a hygiene aspect. Sci. Total. Environ. 2013, 458–460, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Zheng, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J. Developmental and Waste Reduction Plasticity of Three Black Soldier Fly Strains (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Raised on Different Livestock Manures. J. Med Èntomol. 2013, 50, 1224–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, I.J.; Gibson, W.T.; Cameron, M.M. Growth rates of black soldier fly larvae fed on fresh human faeces and their implication for improving sanitation. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2014, 19, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyakeri, E.; Ogola, H.; Ayieko, M.; Amimo, F. Valorisation of organic waste material: Growth performance of wild black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) reared on different organic wastes. J. Insects Food Feed. 2017, 3, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ur Rehman, K.; Cai, M.; Xiao, X.; Zheng, L.; Wang, H.; Soomro, A.A.; Zhou, Y.; Li, W.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J. Cellulose decomposition and larval biomass production from the co-digestion of dairy manure and chicken manure by mini-livestock (Hermetia illucens L.). J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 196, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, K.U.; Rehman, A.; Cai, M.; Zheng, L.; Xiao, X.; Somroo, A.A.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J. Conversion of mixtures of dairy manure and soybean curd residue by black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens L.). J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 154, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Minor, M.; Morel, P.C.H.; Najar-Rodriguez, A.J. Bioconversion of Three Organic Wastes by Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larvae. Environ. Èntomol. 2018, 47, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meneguz, M.; Schiavone, A.; Gai, F.; Dama, A.; Lussiana, C.; Renna, M.; Gasco, L. Effect of rearing substrate on growth performance, waste reduction efficiency and chemical composition of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 5776–5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Mazza, L.; Yu, Y.; Cai, M.; Zheng, L.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Yu, J.; van Huis, A.; Yu, Z.; Fasulo, S.; et al. Efficient co-conversion process of chicken manure into protein feed and organic fertilizer by Hermetia illucens L. (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larvae and functional bacteria. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 217, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, M.; Zhang, K.; Zhong, W.; Liu, N.; Wu, X.; Li, W.; Zheng, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J. Bioconversion-Composting of Golden Needle Mushroom (Flammulina velutipes) Root Waste by Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens, Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larvae, to Obtain Added-Value Biomass and Fertilizer. Waste Biomass Valorization 2019, 10, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappellozza, S.; Leonardi, M.G.; Savoldelli, S.; Carminati, D.; Rizzolo, A.; Cortellino, G.; Terova, G.; Moretto, E.; Badaile, A.; Concheri, G.; et al. A first attempt to produce proteins from insects by means of a circular economy. Animals 2019, 9, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermolaev, E.; Lalander, C.; Vinnerås, B. Greenhouse gas emissions from small-scale fly larvae composting with Hermetia illucens. Waste Manag. 2019, 96, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganda, H.; Zannou-Boukari, E.; Kenis, M.; Chrysostome, C.; Mensah, G. Potentials of animal, crop and agri-food wastes for the production of fly larvae. J. Insects Food Feed. 2019, 5, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, C.D.; Cammack, J.A.; Tomberlin, J.K. Life-History Traits of the Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens (L.) (Diptera: Stratiomyidae), Reared on Three Manure Types. Animals 2019, 9, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyakeri, E.; Ayieko, M.; Amimo, F.; Salum, H.; Ogola, H. An optimal feeding strategy for black soldier fly larvae biomass production and faecal sludge reduction. J. Insects Food Feed. 2019, 5, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ur Rehman, K.; Ur Rehman, R.; Somroo, A.A.; Cai, M.; Zheng, L.; Xiao, X.; Ur Rehman, A.; Rehman, A.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Yu, Z.; et al. Enhanced bioconversion of dairy and chicken manure by the interaction of exogenous bacteria and black soldier fly larvae. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 237, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somroo, A.A.; Rehman, K.U.; Zheng, L.; Cai, M.; Xiao, X.; Hu, S.; Mathys, A.; Gold, M.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J. Influence of Lactobacillus buchneri on soybean curd residue co-conversion by black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) for food and feedstock production. Waste Manag. 2019, 86, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, M.; Cassar, C.M.; Zurbrügg, C.; Kreuzer, M.; Boulos, S.; Diener, S.; Mathys, A. Biowaste treatment with black soldier fly larvae: Increasing performance through the formulation of biowastes based on protein and carbohydrates. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalander, C.; Ermolaev, E.; Wiklicky, V.; Vinnerås, B. Process efficiency and ventilation requirement in black soldier fly larvae composting of substrates with high water content. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 729, 138968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, I.G.; Lalander, C.; Vidotti, R.M.; Vinnerås, B. Reduction of Bacteria in Relation to Feeding Regimes When Treating Aquaculture Waste in Fly Larvae Composting. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazza, L.; Xiao, X.; Rehman, K.U.; Cai, M.; Zhang, D.; Fasulo, S.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Zheng, L.; Soomro, A.A.; Yu, Z.; et al. Management of chicken manure using black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larvae assisted by companion bacteria. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.Y.; Aris, M.N.M.; Daud, H.; Lam, M.K.; Yong, C.S.; Abu Hasan, H.; Chong, S.; Show, P.L.; Hajoeningtijas, O.D.; Ho, Y.C.; et al. In-Situ Yeast Fermentation to Enhance Bioconversion of Coconut Endosperm Waste into Larval Biomass of Hermetia illucens: Statistical Augmentation of Larval Lipid Content. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broeckx, L.; Frooninckx, L.; Slegers, L.; Berrens, S.; Noyens, I.; Goossens, S.; Verheyen, G.; Wuyts, A.; Van Miert, S. Growth of Black Soldier Fly Larvae Reared on Organic Side-Streams. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzepe, D.; Nana, P.; Kuietche, H.M.; Kimpara, J.M.; Magatsing, O.; Tchuinkam, T.; Djouaka, R. Feeding strategies for small-scale rearing black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) as organic waste recycler. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, M.; Fowles, T.; Fernandez-Bayo, J.; Miner, L.P.; Zurbrügg, C.; Nansen, C.; Bischel, H.; Mathys, A. Effects of rearing system and microbial inoculation on black soldier fly larvae growth and microbiota when reared on agri-food by-products. J. Insects Food Feed. 2022, 8, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klammsteiner, T.; Walter, A.; Bogataj, T.; Heussler, C.D.; Stres, B.; Steiner, F.M.; Schlick-Steiner, B.C.; Insam, H. Impact of Processed Food (Canteen and Oil Wastes) on the Development of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae and Their Gut Microbiome Functions. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 619112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalander, C.; Diener, S.; Zurbrügg, C.; Vinnerås, B. Effects of feedstock on larval development and process efficiency in waste treatment with black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens). J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 208, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliantiangtam, N.; Chundang, P.; Kovitvadhi, A. Growth Performance, Waste Reduction Efficiency and Nutritional Composition of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae and Prepupae Reared on Coconut Endosperm and Soybean Curd Residue with or without Supplementation. Insects 2021, 12, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, N.; Fischer, H.; Kumar, V.; Francis, S.A.; Sinha, A.K. Productivity, conversion ability, and biochemical composition of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae fed with sweet potato, spent coffee or dough. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2022, 42, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Srikanth, B.H.; Kumari, K. Determining the Black Soldier fly larvae performance for plant-based food waste reduction and the effect on Biomass yield. Corrigendum to Waste Manag. 2021, 130, 147–154. Waste Manag. 2022, 144, 122–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taufek, N.; Lim, J.; Abu Bakar, N. Comparative evaluation of Hermetia illucens larvae reared on different substrates for red tilapia diet: Effect on growth and body composition. J. Insects Food Feed. 2021, 7, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldkamp, T.; van Rozen, K.; Elissen, H.; van Wikselaar, P.; van der Weide, R. Bioconversion of Digestate, Pig Manure and Vegetal Residue-Based Waste Operated by Black Soldier Fly Larvae, Hermetia illucens L. (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Animals 2021, 11, 3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.Y.; Kiatkittipong, K.; Kiatkittipong, W.; Ntwampe, S.K.O.; Lam, M.K.; Goh, P.S.; Cheng, C.K.; Bashir, M.J.K.; Lim, J.W. Black Soldier Fly Larval Valorization Benefitting from Ex-Situ Fungal Fermentation in Reducing Coconut Endosperm Waste. Processes 2021, 9, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabzadeh, G.; Delisle-Houde, M.; Tweddell, R.J.; Deschamps, M.-H.; Dorais, M.; Lebeuf, Y.; Derome, N.; Vandenberg, G. Diet Composition Influences Growth Performance, Bioconversion of Black Soldier Fly Larvae: Agronomic Value and In Vitro Biofungicidal Activity of Derived Frass. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm, K.; Hatley, G.A.; Robinson, B.H.; Gutiérrez-Ginés, M.J. Black Soldier Fly-based bioconversion of biosolids creates high-value products with low heavy metal concentrations. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 180, 106149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.; Scieuzo, C.; Salvia, R.; Mancini, I.M.; Caniani, D.; Masi, S.; Falabella, P. A mobile black soldier fly farm for on-site disposal of animal dairy manure. Bull Insectology 2022, 75, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Holeh, G.M.; Opiyo, M.A.; Brown, C.L.; Sumbule, E.; Gatagwu, J.; Oje, E.O.; Munyi, F. Effect of Different Waste Substrates on the Growth, Development and Proximate Composition Of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae. Available online: www.lrrd.org/lrrd34/7/3457hole.html (accessed on 4 September 2023).
- Khaekratoke, K.; Laksanawimol, P.; Thancharoen, A. Use of fermented spent coffee grounds as a substrate supplement for rearing black soldier fly larvae, Hermetia illucens (L), (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). PeerJ 2022, 10, e14340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, L.; Ermolaev, E.; Vinnerås, B.; Lalander, C. Process efficiency and greenhouse gas emissions in black soldier fly larvae composting of fruit and vegetable waste with and without pre-treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 338, 130552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Zhang, J.; Hou, D.; Li, X.; Jiang, H.; Chen, H.; Yu, Z.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Q. Effects of biochar amendment on bioconversion of soybean dregs by black soldier fly. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 829, 154605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasdi FL, M.; Ishak, A.R.; Hua, P.W.; Shaifuddin SN, M.; Dom, N.C.; Shafie, F.A.; Abdullah, A.M.; Kari, Z.A.; Atan, E.H. Article History Growth and Development of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens (L.), Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larvae Grown on Carbohydrate, Protein, and Fruit-Based Waste Substrates. Malays. Appl. Biol. 2022, 51, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scieuzo, C.; Franco, A.; Salvia, R.; Triunfo, M.; Addeo, N.F.; Vozzo, S.; Piccolo, G.; Bovera, F.; Ritieni, A.; Di Francia, A.; et al. Enhancement of fruit byproducts through bioconversion by Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Insect Sci. 2022, 30, 991–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.C.; Hasan, H.A. Effect of Feeding Rate on Growth Performance and Waste Reduction Efficiency of Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Trop. Life Sci. Res. 2022, 33, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muin, H.; Alias, Z.; Nor, A.M.; Taufek, N.M. Bioconversion of Desiccated Coconut and Soybean Curd Residues for Enhanced Black Soldier Fly Larvae Biomass as a Circular Bioeconomy Approach. Waste Biomass-Valorization 2023, 14, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalová, M.; Borkovcová, M. Voracious larvae Hermetia illucens and treatment of selected types of biodegradable waste. Acta Univ. Agric. et Silvic. Mendel. Brun. 2013, 61, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuwono, A.S.; Permana, I.G.; Nurulalia, L.; Mentari, P.D. Decomposition Characteristics of Selected Solid Organic Wastes by Black Soldier Fly (BSF) Larvae as Affected by Temperature Regimes. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 4343–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitriana, E.L.; Laconi, E.B.; Jayanegara, A. Influence of various organic wastes on growth performance and nutrient composition of black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens): A meta-analysis. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 788, 012051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadhillah, N.; Bagastyo, A.Y. Utilization of Hermetia illucens Larvae as A Bioconversion Agent to Reduce Organic Waste. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 506, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julita, U.; Fatimah, S.; Suryani, Y.; Kinasih, I.; Fitri, L.; Permana, A. Bioconversion of Food Waste by Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens larvae (Diptera: Stratiomyidae L.) for Alternative Animal Feed Stock. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Islam, Science and Technology, ICONISTECH 2019, Bandung, Indonesia, 11–12 July 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyambada, I.B.; Sumiyati, S.; Puspita, A.S.; A Wirawan, R. Optimization of organic waste processing using Black Soldier Fly larvae Case study: Diponegoro university. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 896, 012017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Zhu, J.; Wang, G.; Xu, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, P.; Yuan, Q. Effects of three major nutrient contents, compost thickness and treatment time on larval weight, process performance and residue component in black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) composting. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 307, 114610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo, H.A.; Kemabonta, K.A.; Ogbogu, S.S.; Elechi, M.C.; Obe, M.T. Comparative assessment of developmental parameters, proximate analysis and mineral compositions of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) prepupae reared on organic waste substrates. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2021, 41, 1953–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Vanlaerhoven, S. Ability of Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larvae to Recycle Food Waste. Environ. Èntomol. 2015, 44, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scala, A.; Cammack, J.A.; Salvia, R.; Scieuzo, C.; Franco, A.; Bufo, S.A.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Falabella, P. Rearing substrate impacts growth and macronutrient composition of Hermetia illucens (L.) (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larvae produced at an industrial scale. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, K.; Liyanage, C.; Jinadasa, H.; Gedara, P.K.; Karunaratne, W. Resource-efficient and eco-friendly model for fruit processing industry waste valorisation using black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae under tropical conditions. J. Insects Food Feed. 2021, 8, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.V.; Olkin, I. Statistiacl Methods for Meta-Analysis; Harcourt Brace Jovanovich Publisher: Orlando, FL, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Palupi, E.; Jayanegara, A.; Ploeger, A.; Kahl, J. Comparison of nutritional quality between conventional and organic dairy products: A meta-analysis. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 2774–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmadani, M.; Susanto, I.; Prasetya, R.D.D.; Kondo, M.; Nahrowi, N.; Jayanegara, A. Modification of dietary rumen degradable starch content by chemical processing of feed ingredients: A meta-analysis. Anim. Sci. J. 2023, 94, e13834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dersimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-Analysis in Clinical Trials. Control. Clin. Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).